CHEM - Kinetics
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Kinetics tells us
how fast a reaction occurs
Rate of reaction is the
change in the amount of reactant/product per unit of time
oxygens oxidation number is usually
-2
equation for finding the rate
Rate=Δ[A]/Δt
Finding the rate of a product will be
positive
Finding the rate of a reactant will be
negative
List five factors that affect reaction rates
chemical nature, physical states, temperature, concentration, and catalysts
Physical states increase the reaction rate as you go from
solid to liquid to gas - because you are increasing surface area
As you increase temperature, you increase rate because
there more kinetic energy and therefore more collisions
What is a catalyst?
A substance that increase a reaction rate but it is not consumed
The rate constant K is influenced by
temperature
The rate constant k is NOT influenced by
concentrations
Zero order units
M/s
First order units
1/s
Second order units
1/(M s)
Third order units
M-2 s-1
How much faster will the rate be if the concentration of OH- (aq) is quadrupled?
4 times faster
What would happen if you increased the temperature of this reaction by 100K?
Rate increases
Use the integrated rate law when:
when given concentration vs. time data.
to calculate concentrations at a specific time.
to determine half-life or how long it takes for something to decay or react.
Use rate law when:
when working with initial rates.
to find the order of the reaction
find the rate constant (k) from how rate changes, not time.
First order plot slope
negative (-K)
First order plot
ln[A] and time
![<p>ln[A] and time</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4e5b7b38-054b-4792-b603-8f9d03164c83.png)
Second order plot
1/[A] and time
![<p>1/[A] and time</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/11c3d4eb-b690-46ba-bb8c-baae78b69c07.png)
Second order slope
positive (K)
Zero order plot
[A] and time
![<p>[A] and time</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1e8bfa8f-4831-43ef-8249-045fde23021f.png)
Zero order slope
negative (-K)
All graphs must be
linear (a super straight line)
Slope = -K
K = -slope
Zero order rate law looks like:
rate = k
Collision theory 3 main points:
Rate of reaction is proportional to the rate of reactant collisions
Collisions need to be in the correct orientation
Collisions need enough energy to react
If you increase temperature
kinetic energy increases as well
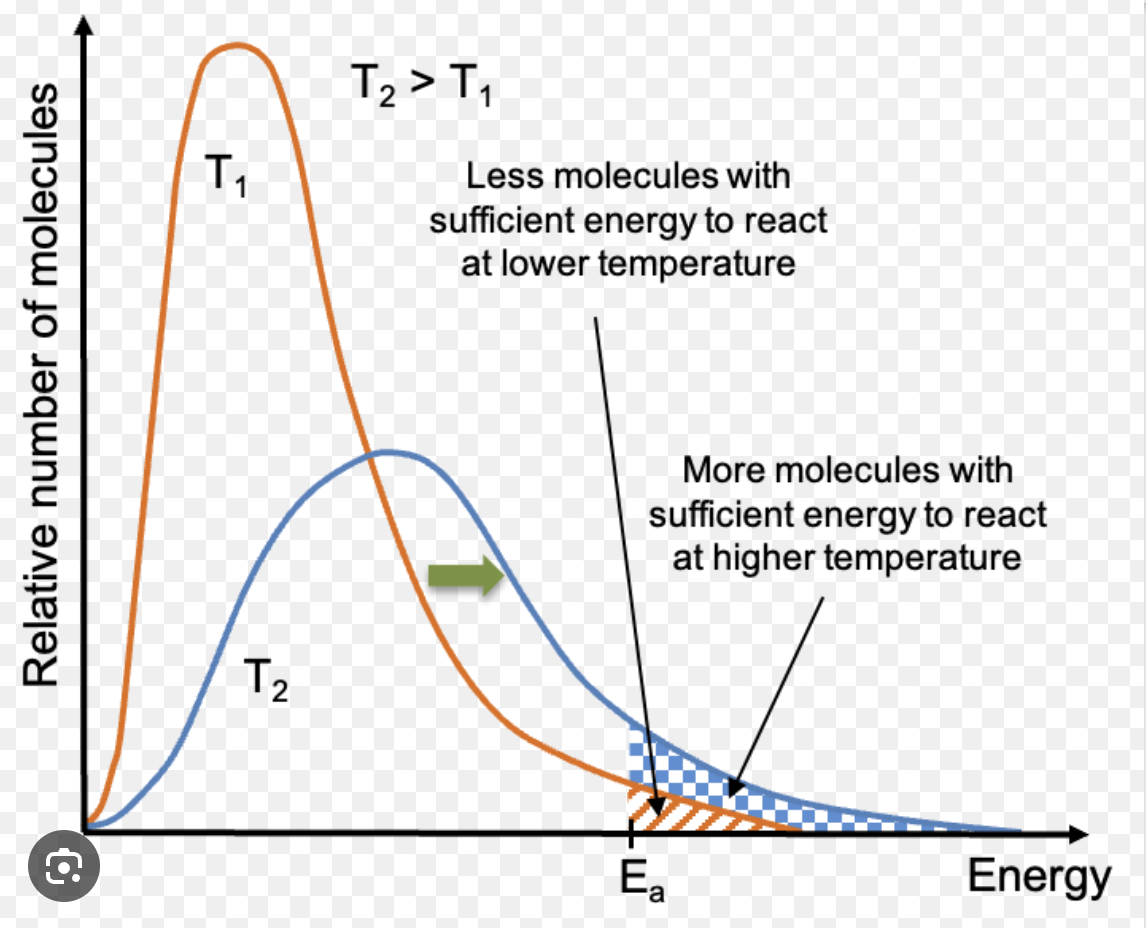
A is the frequency factor, does it change with temperature?
no it doesn’t change, and units match k
y = mx + b m = what? b = what?
m = slope = -Ea/R b = ln A
Whats the Arrhenius equation?
k = Ae-(Ea/RT)
What should the units for Ea be?
J/mol
Activation energy ________ impacts rate
greatly
Intermediates are
chemical species produced in one step of a reaction mechanism and then used in another
Transition states are different than intermediates because:
non-isoluble
never part of rate law
energy high
Intermediates are different from transition states because:
Isolute
In elementary steps of rate laws
energy lows
Bimolecular
involves two molecules colliding and reacting to form products
unimolecular
involves one molecule reacting to form products
Termolecular
involves three molecules colliding and reacting to form products (very rare)
The ______ step controls the overall rate
slow
Which steps are always reversible?
fast steps