Prokaryotes (Topic 2)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1
New cards
3\.5 bya
Prokaryotes first appeared
2
New cards
Prebiotic Soup & Iron Sulfur
Hypotheses of origin of life
3
New cards
Nucleoid
Where do prokaryotes put their DNA?
4
New cards
Bacteria & Archaea
Which 2 domains (of the 3 main domains) are prokaryotes?
5
New cards
Basic characteristics of prokaryotes
* ribosomes
* nucleoid: single haploid chromosome
* cytosol
* cell membrane & cell wall
* many have: enzymes for respiration & photosynthesis
* many have: plasmids (extra DNA) \**do not confuse plasmids with plastids*\*
* nucleoid: single haploid chromosome
* cytosol
* cell membrane & cell wall
* many have: enzymes for respiration & photosynthesis
* many have: plasmids (extra DNA) \**do not confuse plasmids with plastids*\*
6
New cards
Cell wall functions
* protection
* maintains cell shape
* prevents bursting in hypotonic solution (hypotonic = less solute outside)
* maintains cell shape
* prevents bursting in hypotonic solution (hypotonic = less solute outside)
7
New cards
Peptidoglycan
Which protein sugar is in the cell water for *bacteria only*?
8
New cards
Gram staining
ONLY in bacteria
2 step process stain wash to identify bacteria: tells whether there is a lot of __peptidoglycan__ or not in bacteria
* 1st: add crystal violet dye (purple; retained in cell with thick peptidoglycan layer) + iodine
* 2nd: rinse with alcohol (removes crystal violet from thin peptidoglycan layers)
* 3rd: add safranin dye (pink)
*color & shape of the cells help identify which bacteria are present*
2 step process stain wash to identify bacteria: tells whether there is a lot of __peptidoglycan__ or not in bacteria
* 1st: add crystal violet dye (purple; retained in cell with thick peptidoglycan layer) + iodine
* 2nd: rinse with alcohol (removes crystal violet from thin peptidoglycan layers)
* 3rd: add safranin dye (pink)
*color & shape of the cells help identify which bacteria are present*
9
New cards
Gram POSITIVE
Purple > pink
* thick peptidoglycan cell walls
* holds violet stain
* lots of peptidoglycan
* safranin is present but not expressed
* thick peptidoglycan cell walls
* holds violet stain
* lots of peptidoglycan
* safranin is present but not expressed
10
New cards
Gram NEGATIVE
Pink > purple
* thin peptidoglycan cell walls
* Does not hold violet
* little peptidoglycan = outer membrane of lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
* safranin is present & expressed
* thin peptidoglycan cell walls
* Does not hold violet
* little peptidoglycan = outer membrane of lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
* safranin is present & expressed
11
New cards
Motile
* capable of motion
* some prokaryotes are ___ b/c of flagella
* some prokaryotes are ___ b/c of flagella
12
New cards
Taxis
movement (+ vs -)
13
New cards
Flagella
* Found in __all__ domains but analogous
* Smaller in prokaryotes
* no plasma membrane
* H+ and ETC
* H+ pump across PM by ETC
* forms gradient
* H+ diffuses through motor
* E-s from diffusion turns motor
* proton motive force
* Bacterial ________ have
* motor
* hook
* filament
* Smaller in prokaryotes
* no plasma membrane
* H+ and ETC
* H+ pump across PM by ETC
* forms gradient
* H+ diffuses through motor
* E-s from diffusion turns motor
* proton motive force
* Bacterial ________ have
* motor
* hook
* filament
14
New cards
* rapid reproduction & mutation (errors in a gene)
* genetic recombination
* genetic recombination
If binary fission makes identical copies, where does the diversity come from? What gave rise to high levels of genetic diversity?
15
New cards
Vertical gene transfer
parent → offspring
16
New cards
Horizontal gene transfer
NOT from parent → offspring
* transformation
* transduction
* conjugation
* mutation
* transformation
* transduction
* conjugation
* mutation
17
New cards
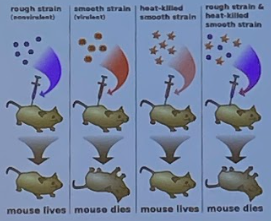
Transformation
* DNA from surroundings/environment
* incorporate foreign DNA as __plasmids__ or into the bacterial genome
* types of species: don’t have to be the same
* horizontal
* Griffith’s experiment
* not specific
* # of bacteria: 1
\
1) donor bacterium dies, leaves behind DNA fragments
2) recipient cell takes up donor DNA
3) recipient cell integrates same donor DNA into genome
* incorporate foreign DNA as __plasmids__ or into the bacterial genome
* types of species: don’t have to be the same
* horizontal
* Griffith’s experiment
* not specific
* # of bacteria: 1
\
1) donor bacterium dies, leaves behind DNA fragments
2) recipient cell takes up donor DNA
3) recipient cell integrates same donor DNA into genome
18
New cards
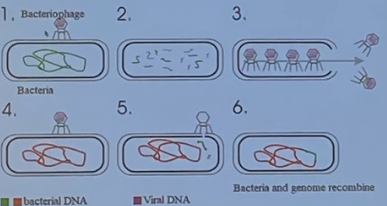
Transduction
* bacterio**phages** transfer bacterial DNA/prokaryotic genes from one host to another
* bacteria is now using the virus to transmit bacterial DNA
* types of species: generally the same
* horizontal
* specific
* # of bacteria: 2 (1 donor, 1 recipient)
\
1) phages in lytic cycle, bacterial DNA is fragmented
2) breaks down bacterial genome in the host
3) some bacterial DNA (region A+) is incorporated into a replicated phage
4) this phage infects a new cell (recipient)
5) region A+ is incorporated into the new cell
* bacteria is now using the virus to transmit bacterial DNA
* types of species: generally the same
* horizontal
* specific
* # of bacteria: 2 (1 donor, 1 recipient)
\
1) phages in lytic cycle, bacterial DNA is fragmented
2) breaks down bacterial genome in the host
3) some bacterial DNA (region A+) is incorporated into a replicated phage
4) this phage infects a new cell (recipient)
5) region A+ is incorporated into the new cell
19
New cards
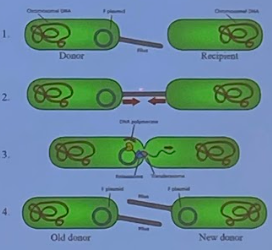
Conjugation
* one-way DNA transfer b/w 2 cells of same spp
* DNA shared b/w 2 individuals
* F (Fertility) Factor F+ = allele to grow **pilus**: thin, tubelike structure that donor uses to contact recipient
* horizontal
* types of species: same
* not specific
* # of bacteria: 2 (1 donor, 1 recipient)
\
1) F+ bacterium grows a pilus
2) transfers DNA plasmid (including F+ allele) to another bacteria
3) now both can grow pili!
* DNA shared b/w 2 individuals
* F (Fertility) Factor F+ = allele to grow **pilus**: thin, tubelike structure that donor uses to contact recipient
* horizontal
* types of species: same
* not specific
* # of bacteria: 2 (1 donor, 1 recipient)
\
1) F+ bacterium grows a pilus
2) transfers DNA plasmid (including F+ allele) to another bacteria
3) now both can grow pili!
20
New cards
Photoautotrophs
Cyanobacteria are…
(E from sun/C from CO2)
(E from sun/C from CO2)
21
New cards
Chemoheterotroph
*Clostridium botulinum* are…
(E from chemical rxns/C from glucose)
(E from chemical rxns/C from glucose)
22
New cards
Phototroph
Uses light as E
23
New cards
Chemotroph
Obtains E from chemical rxns
24
New cards
Autotroph
Uses CO2 for C
25
New cards
Heterotroph
Obtains C from environment
26
New cards
Obligate aerobe
Needs oxygen to survive
27
New cards
Obligate anaerobe
Oxygen will kill, __must__ have no oxygen
28
New cards
Facultative anaerobe
No oxygen, but its presence can’t kill it
Can live with or without oxygen
Can live with or without oxygen
29
New cards
Proteobacteria, Cyanobacteria
Groups of bacteria
30
New cards
Halophiles, thermophiles, methanogens
Groups of Archaea
31
New cards
Proteobacteria
* gram negative (thin peptidoglycan layer, outer membrane of lipopolysaccharides)
* include mitochondria & other mutualistic bacteria
* include mitochondria & other mutualistic bacteria
32
New cards
Cyanobacteria
* most gram negative phytoplankton
* ancestors of chloroplasts
* representative organisms: *prochlorococcus*
* believed to be the most abundant photosynthetic organism on Earth
* responsible for generating 1/2 world’s O
* Eukaryotic chloroplasts believed to be derived from bacteria in this group
* ancestors of chloroplasts
* representative organisms: *prochlorococcus*
* believed to be the most abundant photosynthetic organism on Earth
* responsible for generating 1/2 world’s O
* Eukaryotic chloroplasts believed to be derived from bacteria in this group
33
New cards
Archaea characteristics
* Prokaryotes
* Extremophiles
* Cells walls but no peptidoglycan
* Extremophiles
* Cells walls but no peptidoglycan
34
New cards
Halophiles
Group of Archaea in high salt environments
35
New cards
Thermophiles
Group of Archaea in v hot environments
36
New cards
Methanogens
* Group of Archaea that release methane as a by-product metabolism
* Strict anaerobes (poisoned by O2)
* Strict anaerobes (poisoned by O2)