2024 - 2025 CP Bio Midterm Study Guide
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of vocabulary flashcards based on the key concepts from the Biology midterm study guide.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Homeostasis
Homeostasis es la capacidad de un organismo para mantener un ambiente interno estable.
Cell
Smallest unit of life, encompassing both structure and function.
Levels of Organization
Order from simplest to most complex: atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism.
Scientific Method
A systematic process used for experimentation that includes observation, question, hypothesis, experiment, results analysis, conclusion, and communication.
Independent Variable
The variable intentionally manipulated by the experimenter. (EX: Fertilizer, because the experimenter can change the amount or type of fertlizer )
Dependent Variable
The responding variable that results from changes in the independent variable. (Ex: Plant’s growth, because the growth depends of the fertilizer)
Constants
Factores que siguen siendo los mismos a lo largo de un experimento, para que los resultados sean únicamente dependientes de la independent variable. (Ex: cantidad de agua, luz solar, tipo de suelo, tamaño de la maceta). Son importantes, porque si no se mantienen constantes no sabrías si el crecimiento de la planta fue por alguno de esos factores o por el uso del fertilizante.
Control
El control es la variante de un experimento que no recibe el tratamiento o cambio que se quiere estudiar, y se usa como referencia para comparar resultados. (Ex: planta sin fertilizante, pero preserva las mismas constantes)
Universal Solvent
Water, known for its ability to dissolve many substances.
What is an acidic solution?
Solución donde predominan los iones H⁺; tiene pH menor que 7.
Ex: Limón, vinagre, café.
What is a basic solution?
Solución donde predominan los iones OH- tiene pH mayor que 7.
Ex: Jabón, limpiador de horno.
Organic Compounds
Son sustancias químicas que contienen carbono y normalmente hidrógeno, formando la base de las moléculas de los seres vivos (como azúcares, grasas y proteínas).
Monomer
Molécula pequeña que es una “pieza” repetida; se une con otras para formar un polymer (ex: polysaccharides)
Carbohydrate's monomer
Monomer: Monossacharide (single sugar)
Carbs examples
Monossacharides: Glucose, fructose, galactose
Dissacharides: Sucrose, lactose, maltose
Polysscharides: Starch, glycogen, cellulose
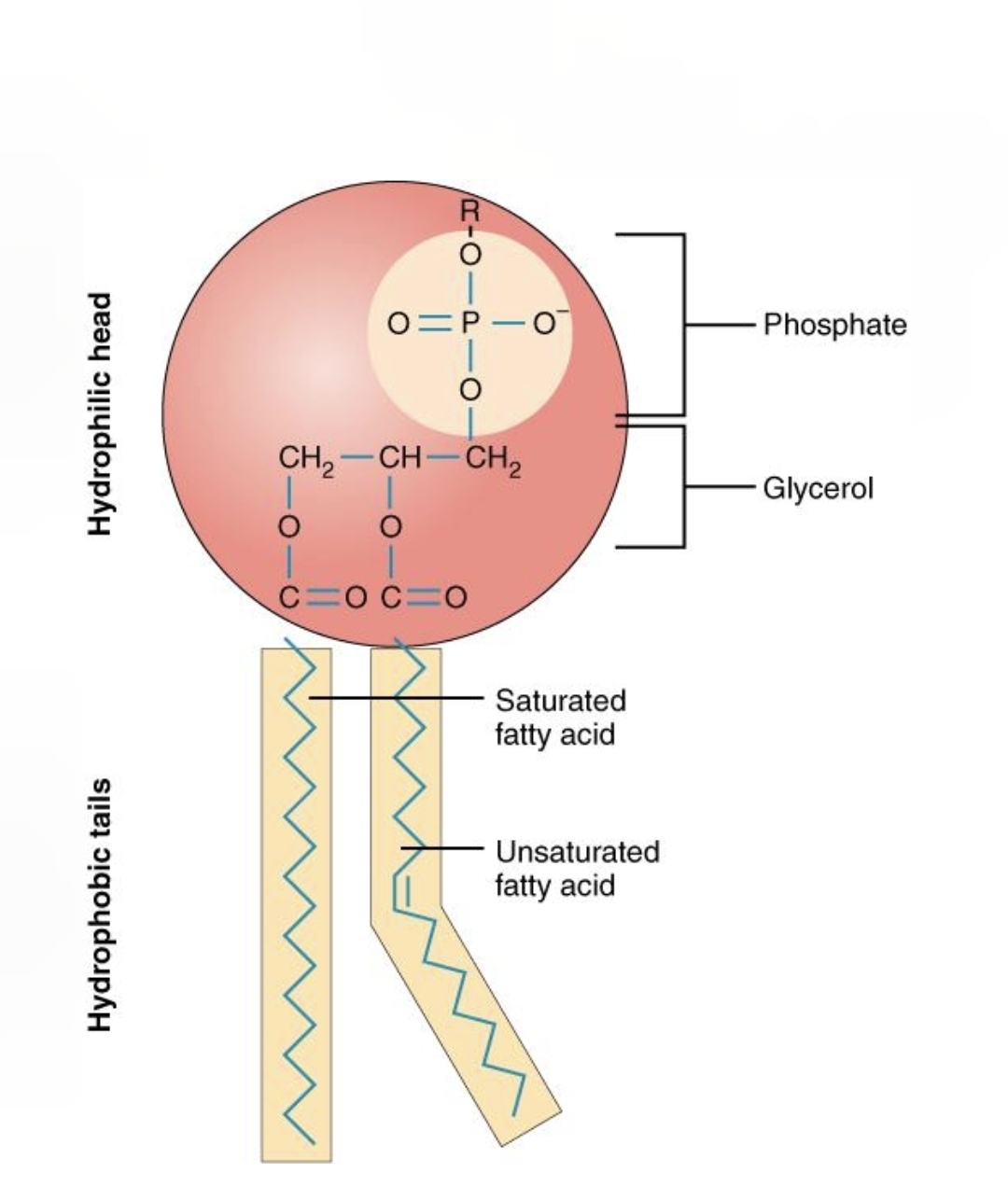
Lipid, fats, and oils monomers
glycerol = head, and fatty acid = tail
Lipids, fats, and oils’ functions and dietary sources
Functions: insulation, protection from physical injury, prevent dehydration, cell membrane
Dietary sources: oils, fish, avocadoes, nuts/seeds, olives = good = unsaturated fats
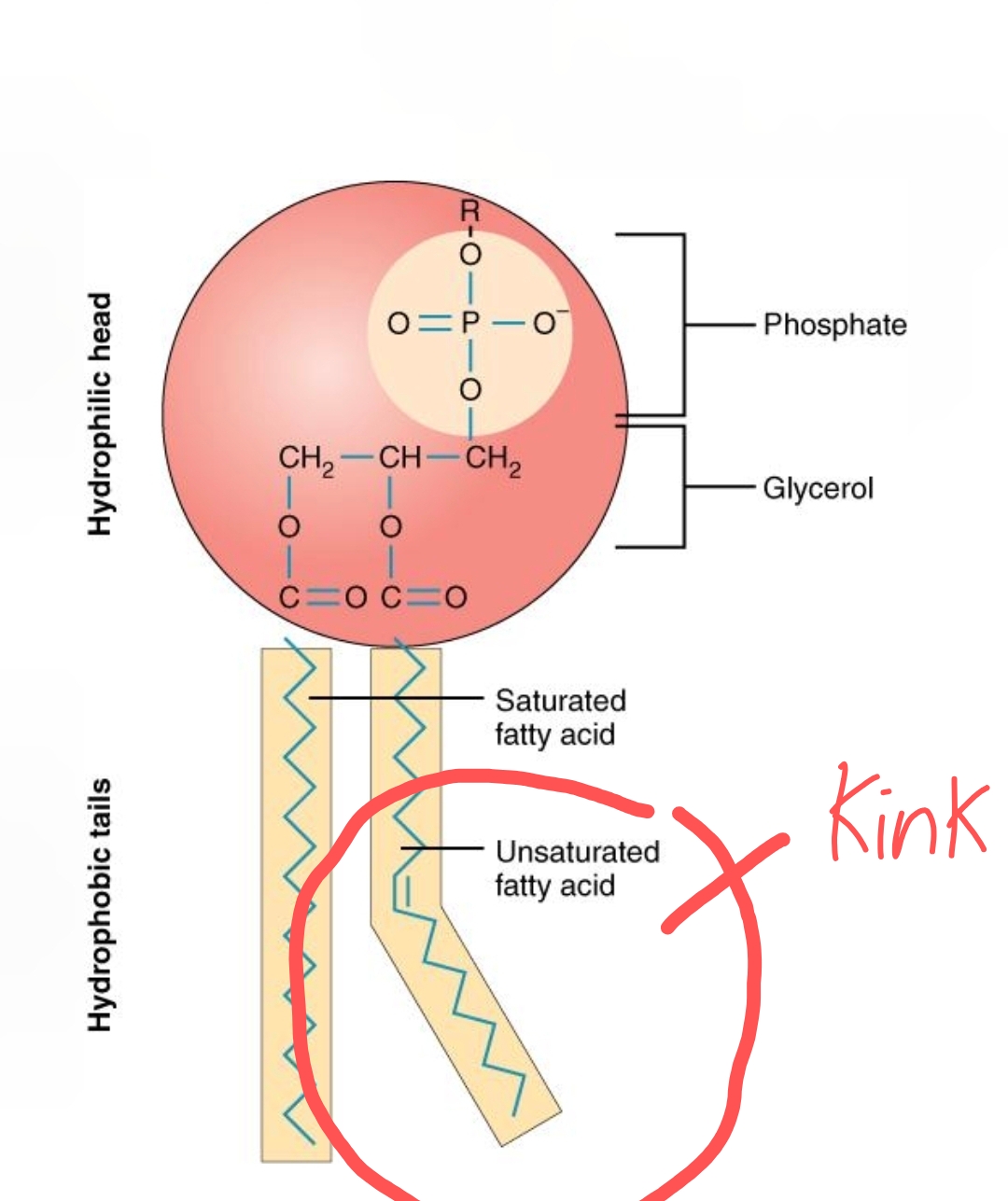
Why do lipids have a ‘kink’ in the tail?
They have a kink in the tail because the cis double bond (c = c) between the Carbon atoms is rigid and bends the fatty acid chain.
Protein Functions
Include storage, transport, and structural roles in organisms.
Phospholipid
A molecule with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails, essential for cell membrane structure.
Prokaryotic Cell
Simple, unicellular organisms without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotic Cell
Complex cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, can be unicellular or multicellular.
Mitochondria
The powerhouse of the cell where energy (ATP) is produced.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The cell's packaging department, modifying and sending lipids and proteins.
Ribosomes
Locations in the cell where proteins are created.
Golgi Apparatus
The organelle that modifies proteins and lipids for export from the cell.
Plasma Membrane
A selectively permeable barrier protecting the cell and maintaining homeostasis.
Diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Active Transport
The movement of molecules against the concentration gradient, requiring ATP (energy because it is active yk)
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, composed of nucleotides that store genetic information.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, involved in the synthesis of proteins.
Complementary Base Pairing (DNA and RNA)
Adenine pairs with Thymine, and Cytosine pairs with Guanine in DNA.
In RNA Adenine pairs with Uracil, and the other ones stay the same.
Transcribe DNA to RNA:
ATCG
TACG
AACTG
TRANSCRIPTION follows COMPLEMENTARY PAIRING:
UAGC
AUGC
UUGAC
DNA Replication
The process of copying DNA before cells splits in two. So that when a cell divides, each new cell gets a complete copy of the genetic instructions it needs to live and function.
OSMOSIS
Movimiento del agua a través de una semipermeable cell desde la zona con más concentración de agua hasta la zona de menor concentración de agua, con el objetivo de equilibrar la concentración en ambas partes.
Semipermeable Cell
Es una celula que permite al agua pasar a través de ella, pero no permite large solutes (such as salt, sugar) pasar a través de ella.
EX of semipermeable cell: Cell membrane
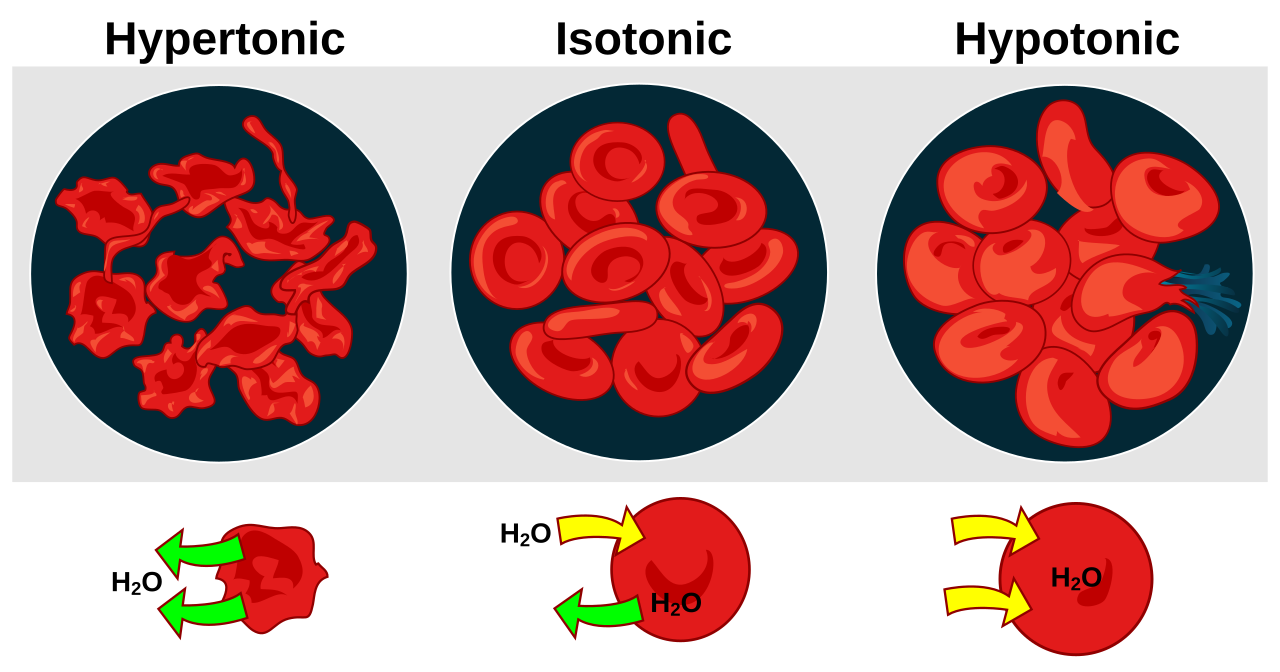
Hypotonic solution
Pocos solutes fuera de la celula
Más agua fuera de la celula. Por lo que el agua ingresa a la celula, haciendo que se hinche.
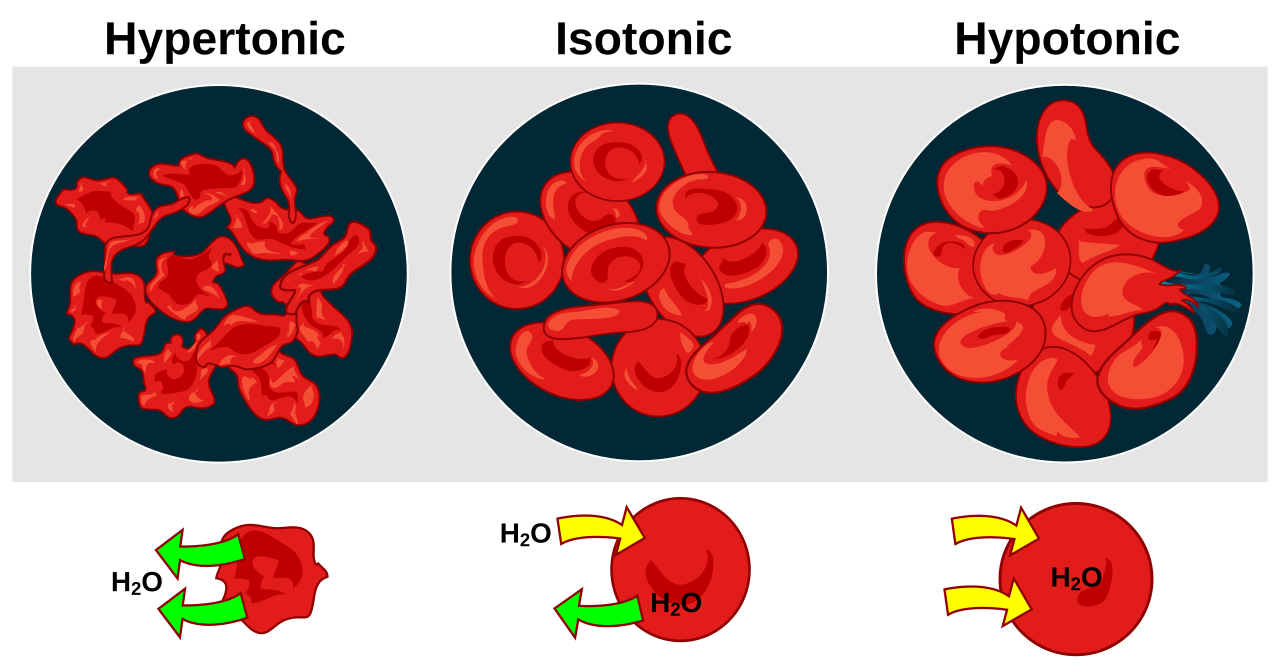
Isotonic solution
Igual cantidad de solutes dentro y fuera. El agua entra y sale en igual cantidad, por lo que la cell permanece igual.
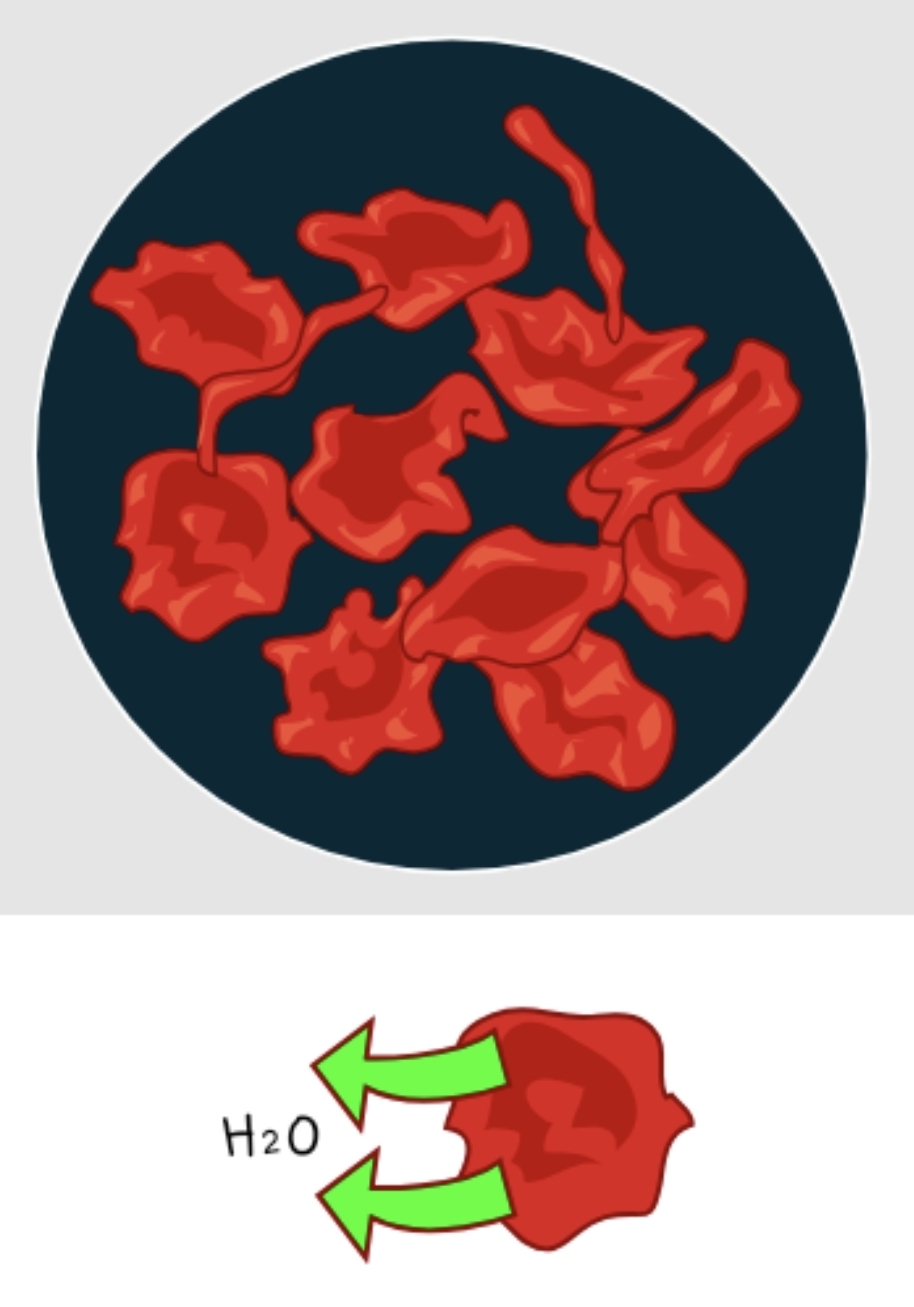
Hypertonic solution
Más solutes FUERA de la celula, menos agua FUERA de la celula. El agua sale de la celula haciendo que se encoja