Chapter 5: Energy, Protein, Water
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Nutrition balances
1) Energy balance
Energy flows (measurements)
Energy value vs requirements
2) Nitrogen balance
Nitrogen flows (measurements)
Protein value vs requirements
3) Water balance
Urine production
Essential vs metabolic water
Energy balance
Energy intake (food) = energy consumption (heat, work) + energy stored
in equilibrium when energy content of food = total amount energy used by the body
Energy intake > energy consumption → excess energy is stored
Energy intake < energy consumption for a long period → undernutrition
Energy balance: requirement of energy
ingesta = egesta
ingesta = food, water, air
egesta =
breading
urine, faeces, gasses
sweat, hair, nails
milk, growth, pregnancy
Balance technique
shortage, equilibrium, excess
Balance technique (different types of energy)
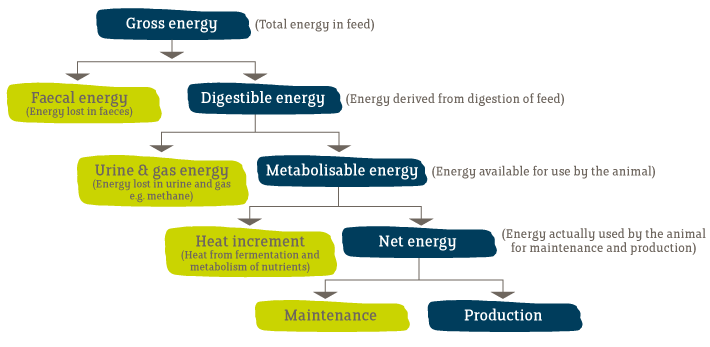
Gross energy (GE) = heat released during complete combustion of a food to CO2 and H2O
Digestible energy (DE) = ingested GE that is not completely retained in the feces and the gasses
Metabolisable energy (ME) = ingested DE that is not retained in intestinal gasses, and in excreted hair, skin, respired air and urine
Net energy (NE) = ingested ME that is not removed as heat
In short time-intervals (e.g. hours), energy-intake does not correspond to energy consumption
Intake of energy is not continuous → storage of energy
1) Free glucose
2) Glycogen
3) Proteins
4) Adipose tissue
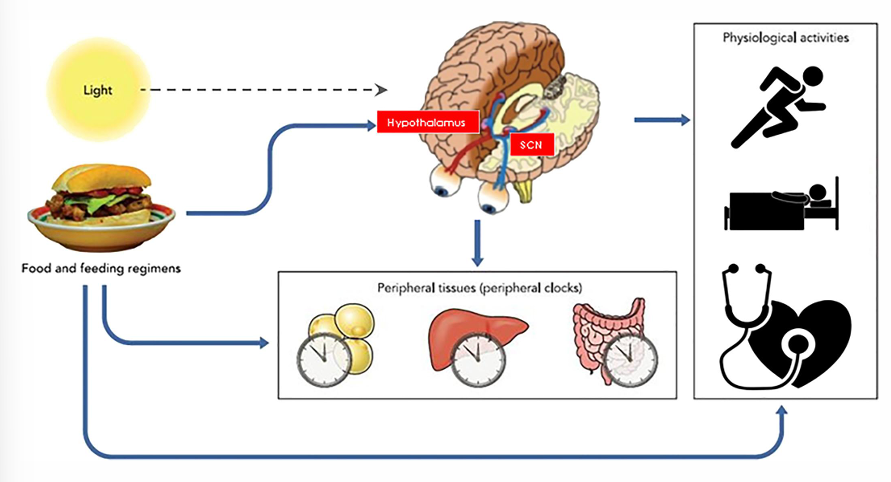
Circadian rythm
= biological rythms
Hypothalamus: SCN: sensitive to light/dark cycles crossing the eyes
periodic synchronizers that
involve schedule of ingestion and fasting, activity and rest
influence other clocks in organs and tissues like adipose tissue, liver and gut
Chronodisruption (chronic extension, how to lose weight, how obesity is formed)
related to chronic diseases (e.g. metabolic syndrome and CVD)
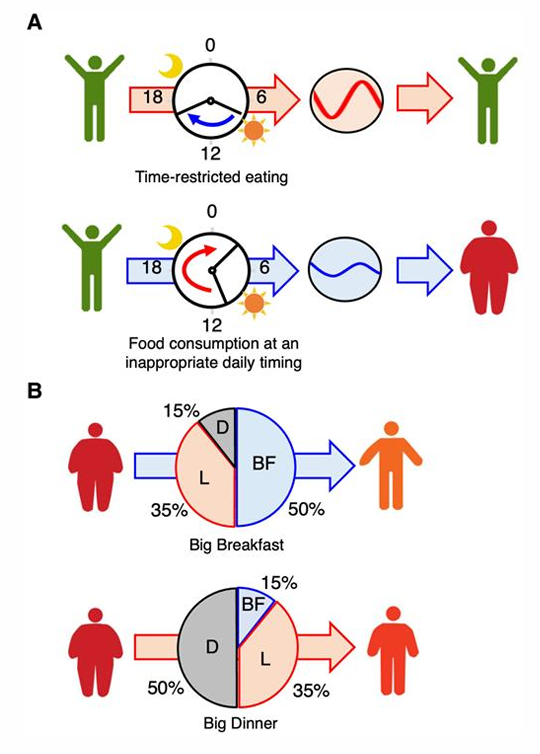
Chronic extension of appropriate meal (e.g. late night eating)
cause metabolic dysregulation due to circadian disruption
How to benefit weight loss?
TRE = time restricted eating = control of meal time
decrease in calorie intake
keeping energy intake constant (large breakfast vs small dinner)
meal composition
Example: night shifts, jet lags
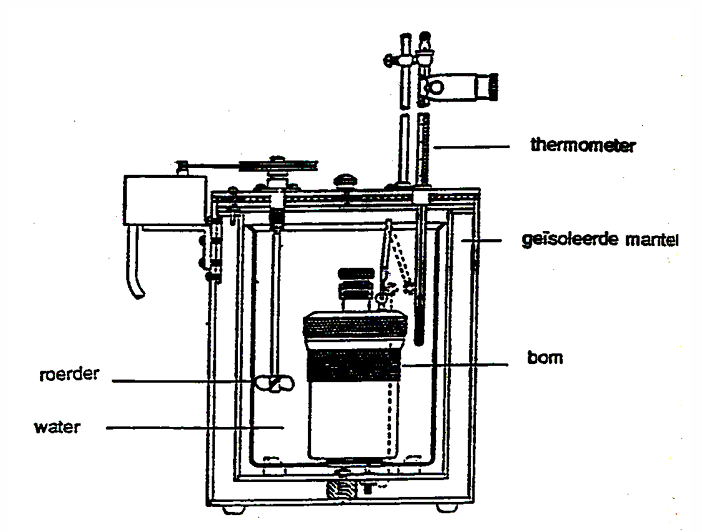
Determination of energy value: caloric bomb and tables
Energy value
determined from chemical composition of food + atwater factors
is variable
energy value phospholipids < energy value fat
chain length for carbohydrates
contribution of alcohol
overestimation for vegetable products
Influenced by turnover
Caloric bomb
= closed recipient container heated up in water container
measures GE
measures energy available in the body for ATP-formation
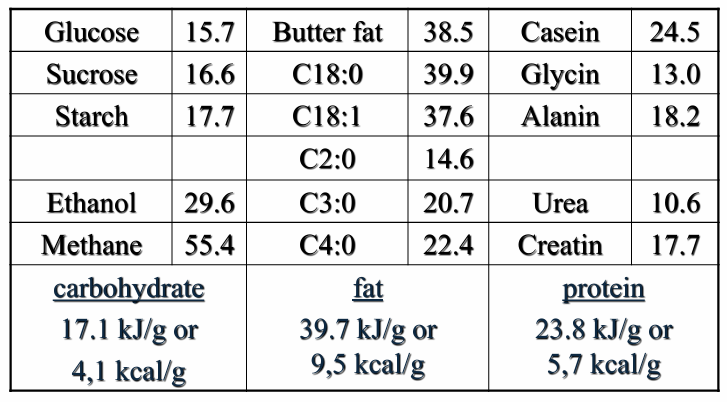
combustion value of N corrected for excretion of N as urea in urine
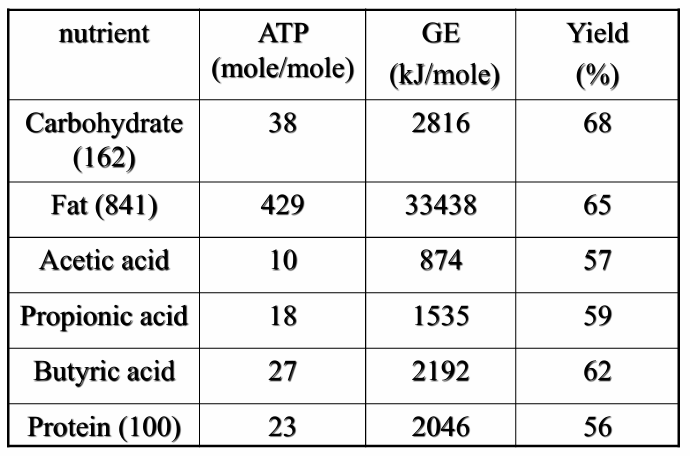
Carbohydrate and fat show ATP yield higher than that of volatile FA and protein
Determination of energy value: Weende analysis
Water vs DM
Ash vs OM
Crude fat: Soxhlet
Crude protein: Kjeldahl
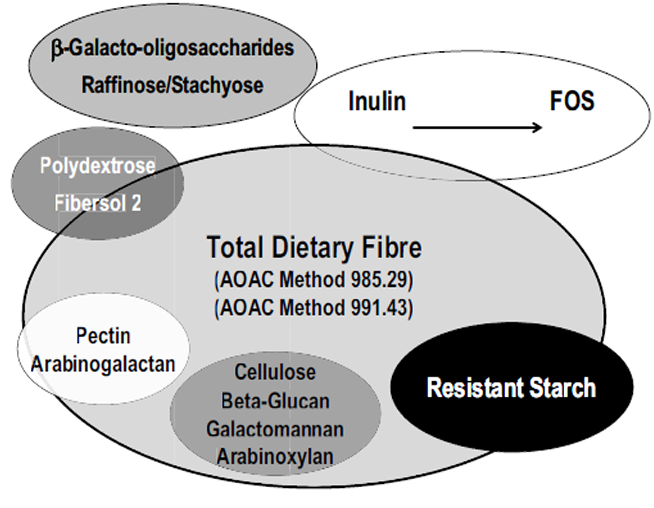
Total Dietary Fibre
Remaining carbohydrates = 100 -%H2O - %ASH - %fibre - %CP - %CF
Determination of energy value: Total dietary fibre
= edible carbohydrate polymers with 3 or more monomeric units, which are not digested or absorbed in the small intestine of humans
determination by the Prosky method
alfa-amylase, protease, amyloglucosidase
EtOH (precipitation TDF)
Correction protein and ash
Additional separation by
Insoluble in water (e.g. cellulose)
Soluble in water (e.g. pectin, beta-glucan)
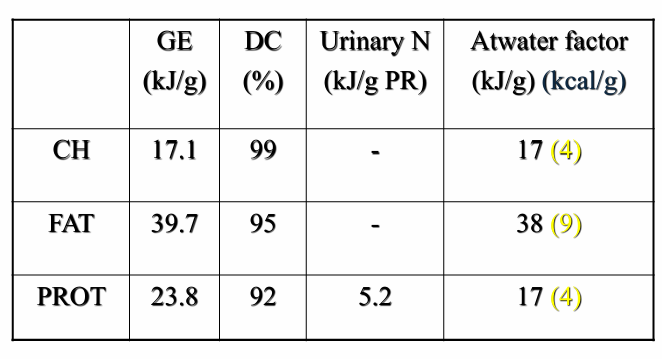
Determination of energy value: Atwater coefficients
= a set of values that estimate the metabolizable energy provided per gram of carbohydrate, protein, fat, and alcohol in the human diet.
Energy consumption: Flow of energy - BMR
What
= Basal Metabolic Rate
minimum heat production at
rest (lying)
post-absorptive
fastened
thermoneutrality
Problems to measure in animals → resting metabolism or fasting metabolism
Formula
BMR\left(\frac{kJ}{d}\right)=293\cdot G^{\left(\frac34\right)} (with G in kg)
Energy consumption: Flow of energy - DIT
= Diet-Induced thermogenesis
When a person at BMR receives food → heat production increases ( mechanical work for chewing…)
Determined by composition of food
Thermal effect for protein is higher than for carbohydrate and fat
Energy consumption: Flow of energy - Thermal effect of physical exercise
caused by use of skeletal muscle for any type of physical movement
Energy consumption: Flow of energy - thermogenesis by stimulans
energy cost for growth
adaptive thermogenesis during exposure to reduced or increased T
thermogenesis can be increased by nicotin, caffein and spicy peppers
Energy consumption: Flow of energy - energy requirement at maintenance (MR)
MR = BM + heat production for maintenance
Measurement of energy flow
Direct calorimetry | Indirect calorimetry |
measurement heat production and heat of evaporation of water | determination O2 and CO2 by oxidation of fat, protein, carbohydrate |
Expensive equipment and difficult to handle | Correction for methane production and urea excretion
|
Short measuring period | fixed period of time |
Respiration coefficient
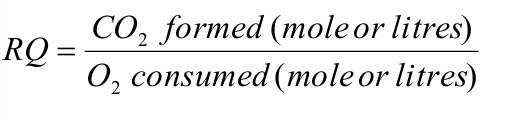
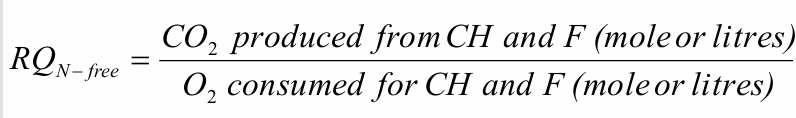
Method measuring CO2-production
Place
1) Respiration room
2) ventilated hood
3) mouthpiece
Method
DLW method = Double Labelled Water method
1) Organism ingests water with stable isotopes (2H and 18O)
2) 2H is removed by water loss and 18O is removed by water loss or CO2-production
Disadvantage
you need mass spectroscopy meter
Energy requirements
MR (= maintenance requirements) + extra amount of ME (= metabolic energy) necessary for production
ME = NE for production from composition of final product *kp (= yield factor for energy utilisation)
Pregnancy
NE = combustion value of gestation products (fetus, placenta, weight increase of the mother due to fat deposition
kp = NE/ME = 20 to 30% = low = high cost for protein synthesis and turnover
Growth
Composition tissues changes with age
18% protein (lower yield) vs 16% fat (higher yield)
kp = NE/ME = 50%
TEE + energy deposit of growing tissues
Lactation
kp = NE/ME = 60 to 80%
physical activity
Derived from indirect calorimetry
Expressed as multiple of BMR
Use of metabolic coefficients
Maintenance: 1 - 4
Light activity: 1-3
Heavy activity: 3-6
Low yield
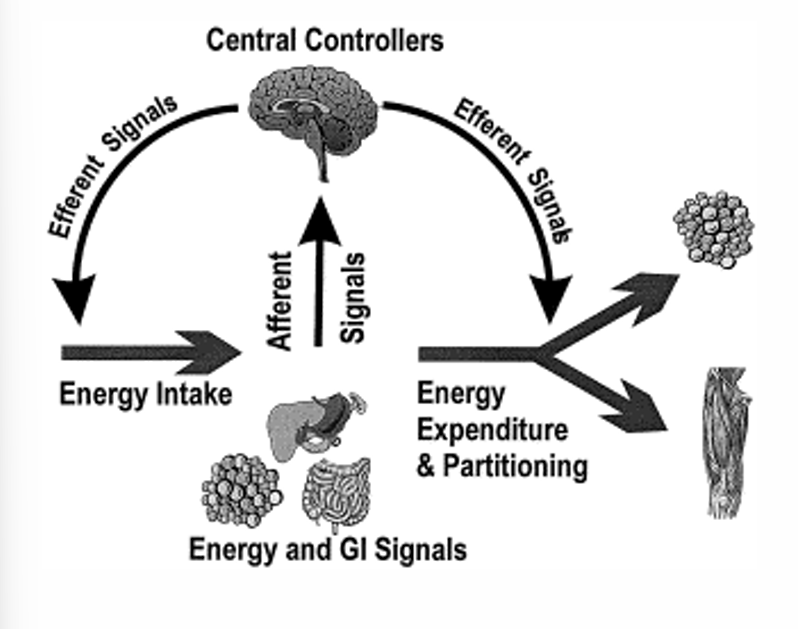
Regulation energy balance
1) Signals sent to central nervous system
afferent signals: periferic signals from energy reserves (adipose tissue, muscles, liver)
hormonal and gastro-intestinal signals: gastro-intestinal system, pancreas
2) Central nervous system gets information from signals about
internal conditions: eg. nutritional status
external conditions: eg. sensorial perception of food
3) Signals are translated into efferent signals → lead to changes in energy intake, energy consumption and distribution of energy throughout the body
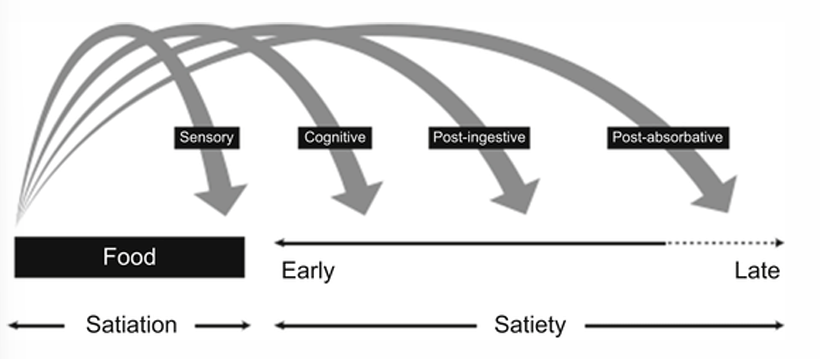
Regulation energy balance: Satiation
= processes that bring the meal to an end
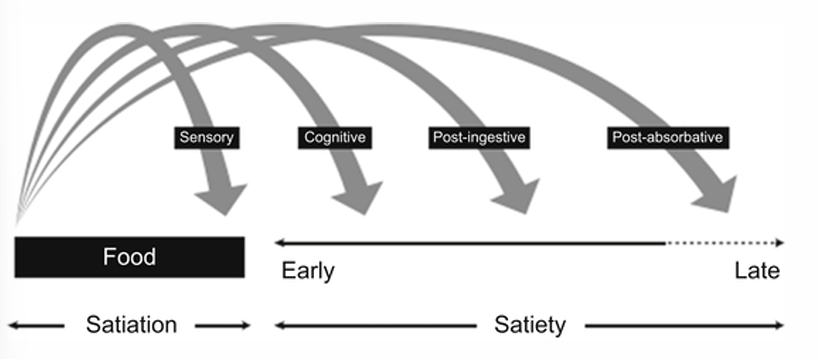
Regulation energy balance: Satiety
= cognitive, post-ingestive and post-absorptive processes that occur after a meal to inhibit further eating
= suppression of hunger and a feeling of fullness during the intermeal period
Regulation energy balance: brain
LHA
= Lateral Hypothalamus
Central hunger zone in the brain
When stimulated: start hunger feeling
VMH
= Ventral Medium Hypothalamus
Central satiety or satiation zone
When stimulated: stop eating food
Other parts of CZS
NTS (= nucleus tractus solitarius) in DVC (= dorsal vagal complex)
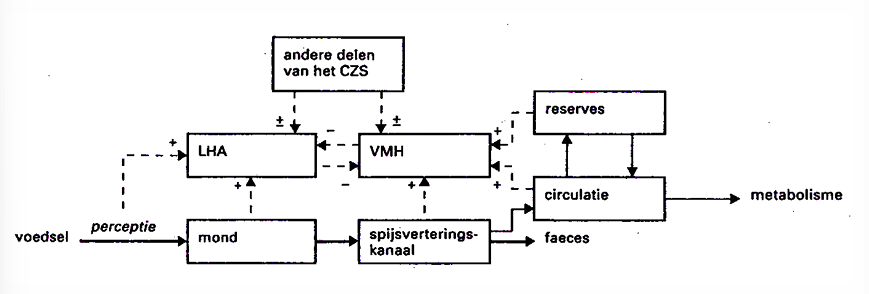
External signals of food (appearance, smell…) → secretion of hormones, saliva and gastric juice → stimulation of food uptake → internal signals of food (digestion, metabolism) → peptides originate in digestive tract
cholecystokinin
CKK
ghrelin
GIP
insulin (pancreas)
leptin (fat tissue)
→ reach hypothalamus via blood stream → inhibition of food intake
Regulation energy balance: role endogenous peptides
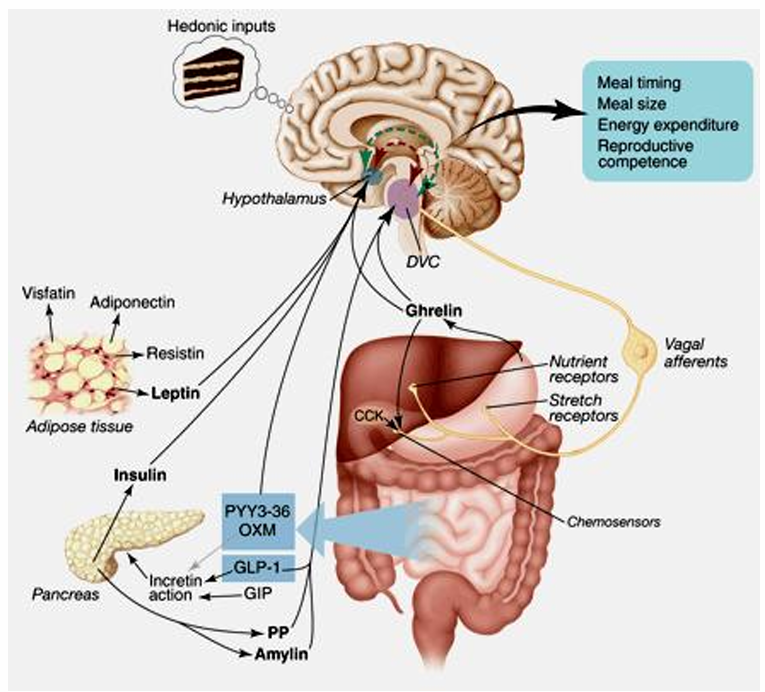
GLP-1 = Glucagon Like Peptide-1
°GI-system
incretin activity → pancreas produces insulin → insulin binds to insulin receptor in the brain → reduce feeling of hunger
satiating peptide
Active via: GLP-1 receptor in the brains (DVC)
OXM = OxynthoModuline
°GI-system
incretin activity → pancreas produces insulin → insulin binds to insulin receptor in the brain → reduce feeling of hunger
satiating peptides
Active via: GLP-1 receptor in the brains (hypothalamus)
GIP = Gastric Inhibitory Peptide
° GI-system
incretin activity → pancreas produces insulin → insulin binds to insulin receptor in the brain → reduce feeling of hunger
CCK = Cholecystokinin
Reduces food intake by slowing down stomach emptying
Active via: CCK1 receptor in the pancreas, pyloris sfyncter, hypothalamus and NTS
NPY = Neuropeptide Y
stimulates appetite
being activated by ghrelin produced in the stomach
neuropeptide
PP = Pancreatic Polypeptide
lowers appetite and food intake without influencing stomach emptying
neuropeptide
PYY = Peptide YY
°ileum and colon
stimulates ileal break
neuropeptide
Leptin
°adipose tissue
formed after increase in adipose tissue by stimulation of obesity-gen
reduction of appetite and energy intake
increase of sympathic activity and fat combustion
endogenous peptide
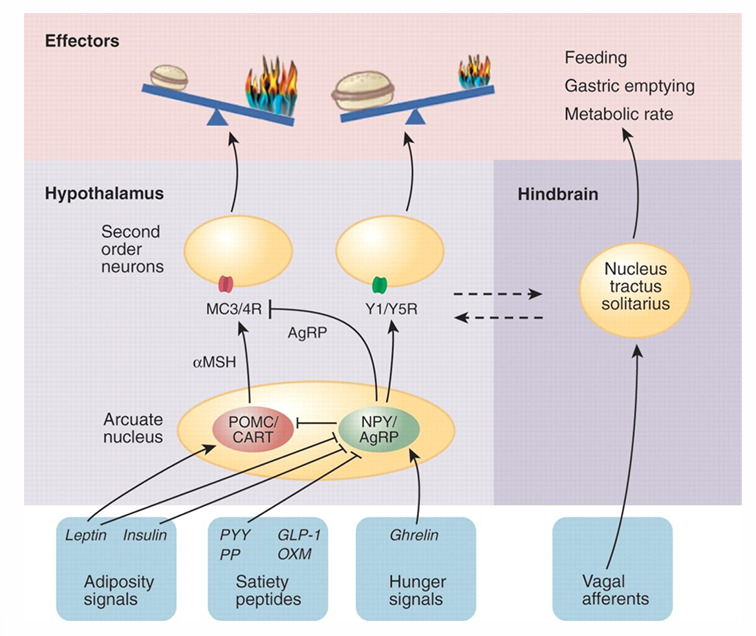
obese people (environment vs genes)
“leptin resistance”
Relationship between risk-alleles and BMI, but life style and environmental conditions will determine the seriousness of his disease
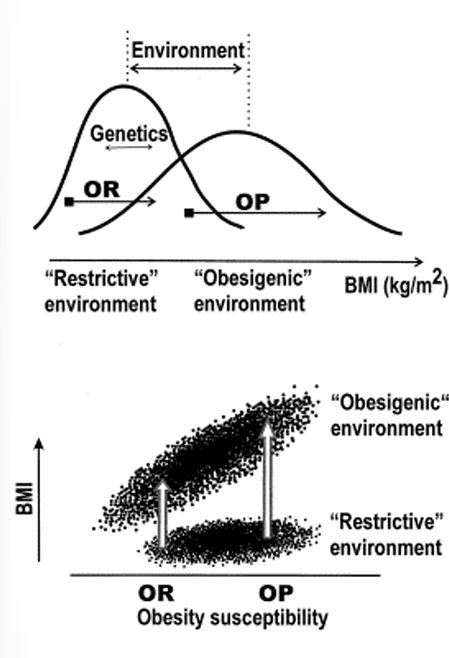
Obese resistant + Restrictive environment: small BMI
Obese resistant + Obesigenic environment (nutrition, physical activity): slightly higher BMI
Obese prone + Restrictive environment: small BMI
Obese prone + Obesigenic environment (nutrition, physical activity): way higher
Obesigenic environment
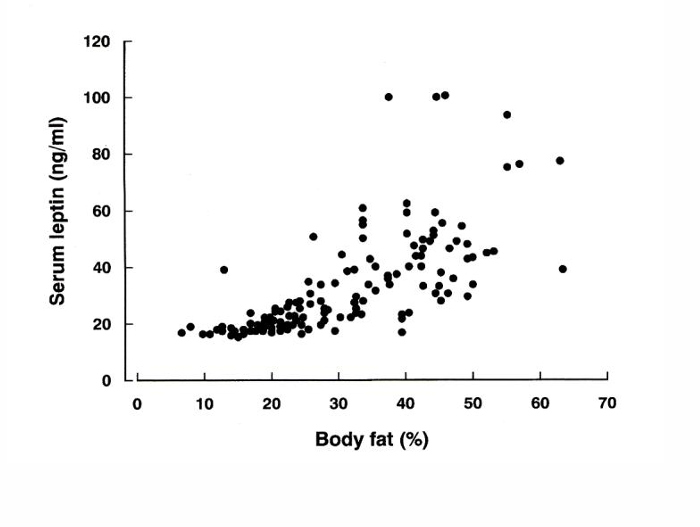
Regulation energy balance: leptin deficiency
If percentage of fat increase normally the leptin concentration would decrease, but in this graph it is the other way around
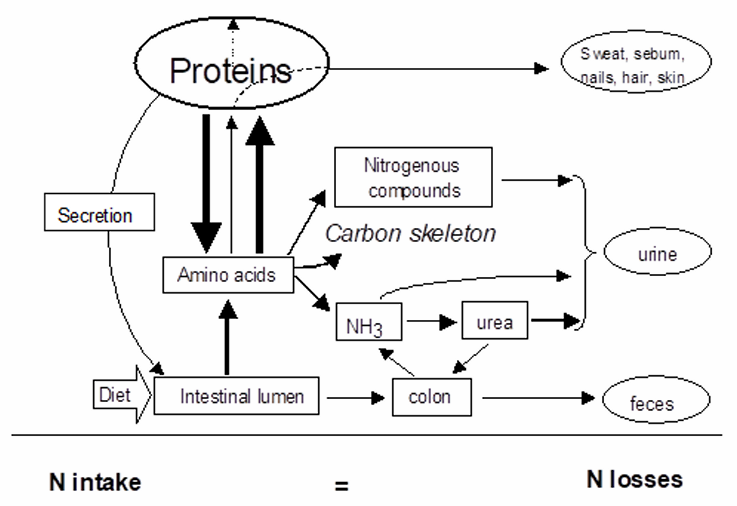
Nitrogen (protein) balance
Measure for synthesis of
Protein
Bile acids (taurine, glycine)
Creatine, glutathion
Porfyrines, choline, nucleic acids
Nitrogen balance
N_{balance}=N_{^{"ingesta"}}-N_{egesta}
N_ingesta = nitrogen content of food consumed
N_egesta = nitrogen losses via urinary nitrogen, fecal nitrogen and remaining losses
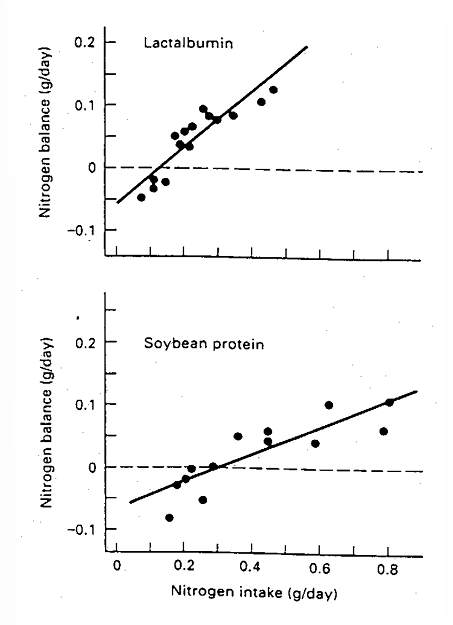
Nitrogen (protein) balance: requirements
deduced from the N intake necessary to obtain a N balance = 0
Inclination = quality of protein → more steeper curve, higher quality, less intake needed
Nitrogen (protein) balance: limitations
miscellanous N-losses not know
Small differences between large values for N intake and N losses
Difficult determination of
N gas
Urea losses by the skin, ammonia by breath
Nitrate in food and urine not measured by Kjeldahl
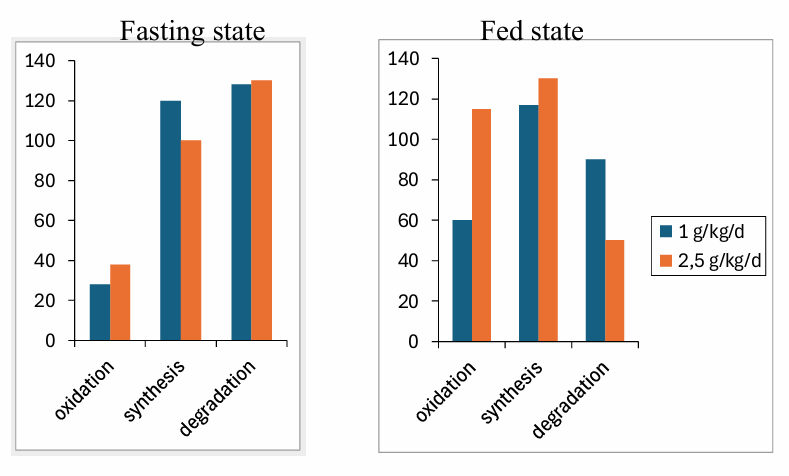
Nitrogen (protein) balance: Leucine kinetics in function of protein intake
Nitrogen (protein) balance: nitrogen and protein requirements
essential AA
infants up to 6 months: lowest intake of AA from breastmilk
older infants and shildren: factorial approach based on maintenance and growth → validated for total branched-chain AA requirements by the IAAO method using stable isotopes
Adults: 13C-balance study
total nitrogen (protein) = requirements neccessary for synthesis of non-essential and conditionally indispensible (semi-essential) AA + N-containing compounds
Infants, children, adolescents → same factorial approach based on N balance at maintenance
Adults → factorial method based on N balance at maintenance which is taken as estimate for the population average N requirement
extra corrections for pregnancy and lactation
Average requirement of N intake goes down when you get older
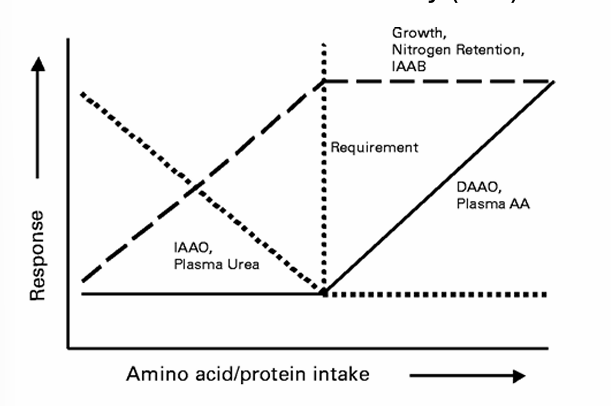
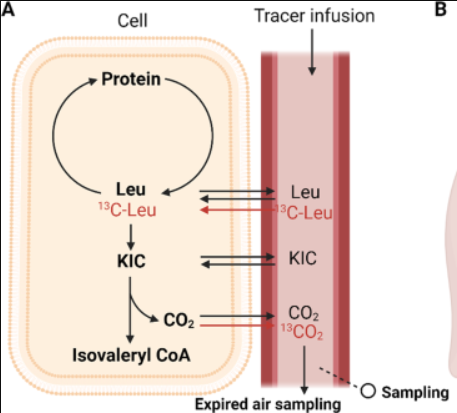
Nitrogen (protein) balance: 13C-balance study
General
Amino acids that are not used for protein synthesis kan be oxidised
When requirement is reached → no protein synthesis anymore, but oxidation
DAAO = Direct Amino Acid Oxidation
= measure oxidation of AA that is added
labelled (13C) + non-labelled (12C)
Oxidation measured by
13CO2 + 12CO2 in breathing air
indirect precursor = KIC → determine which part of 12CO2 is from non-labelled AA
C-balans = intake - oxidation
Under requirement
AA is fully used
low oxidation → low respons
Above requirement
extra AA can not be builded in → linear increase of oxidation
IAAO = indicator amino acid oxidation
= measure oxidation of indicator-AA (eg. Trp)
labelled (13C) + non-labelled (12C)
Under requirement
Leucine is limiting → protein synthesis is low
indicator-AA is oxidised
At requirement
Leucine is no longer limiting
Tryptophane does not get longer used or oxidised
respons = constant
Nitrogen (protein) balance: Protein digestibility
NPU = Net Protein Utilization = nutritional value of protein
digestibility
biological value = cellular bioavailability of absorbed AA in relation to their demand
apparent fecal nitrogen digestibility | apparent ileal nitrogen digestibility | true ileal nitrogen digestibility |
VC_{fecal}=\frac{\left(N_{^{"ingesta"}}-N_{"feces"}\right)}{N_{"ingesta"}} | VC_{ileal}=\frac{\left(N_{^{"ingesta"}}-N_{"ileum"}\right)}{N_{"ingesta"}} | VC_{ileal}=\frac{\left(N_{^{"ingesta"}}-\left(N_{"ileum"}-EAAL\right)\right)}{N_{"ingesta"}} |
not accurate because:
| influence of microbial flora is assumed to be minimal or negligible | EAAL:
|
Nitrogen (protein) balance: PDCAAS-score
= Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score
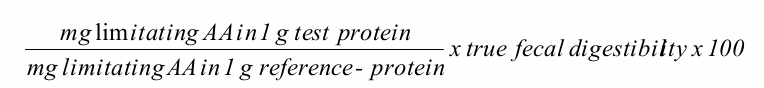
points of discussion
uncertainty about reference protein
use of true fecal instead of ileal DC
Adjusting values above 100%
Nitrogen (protein) balance: Protein quality
related to amount of essential AA (EAA) in a protein
limiting AA: EAA giving the lowest proportion → when 1 or more EAA are lacking, the use of all other EAA decreases in the same proportion
Nitrogen (protein) balance: DIAAS-score
= Digestible Indispensable (= essential) Amino Acid Score
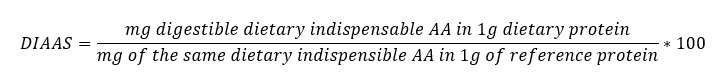
Developped to better reflect the digestibility of individual dietary indispensable AA
AA pattern for reference protein is taken from
breastmilk
pattern for 0,5 year old infants
pattern for 3 to 10 year old children
Devided in 3 categories
Not to be used as single protein source
good quality
excellent quality
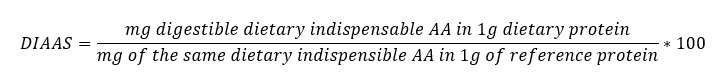
Water homeostasis: The water balance
50 - 70% of body weight is water
60 % intracellular water
40% extracellular water: blood, interstitial fluid
Importance for supply and excretion
Homeokinesis = dynamic equilibrium
determined by movement of water and electrolytes
dependent of 4 processes
filtration
diffusion
osmosis → most dominant regulating system
active transport
Minimal intake (ml/d) = minimal secretion (ml/d)
Metabolic water
1 g carbohydrate = 0,6 g H2O
1 g protein = 0,41 g H2O
1 g fat = 1,07 g H2O
Essential water
needed to remove endproducts from the metabolism (urea, sulphates, phosphates)
Water homeostasis: The water balance: osmole, osmolarity, osmolality
osmole = 1 mole/n (n = number of particles in 1 mole)
Eg. 1 mole NaCl => 2 osmoles
Eg. 1 mole CaCl2 => 3 osmoles
osmolarity = osmole/l solution
osmolality = osmole/l solvent
Water homeostasis: The water balance: electrolyte composition
K+ mostly intracellular
Na+ mostly extracellular
Water homeostasis: Regulation of thirst and urine production
Thirst → hypothalamus is stimulated
Urine production = control of water balance → nephron (kidney)
formation and composition of urine is based on
1) glomerular filtration
2) tubular secretion of the nephrons: H+ and K+
3) tubular reabsorption: Na+
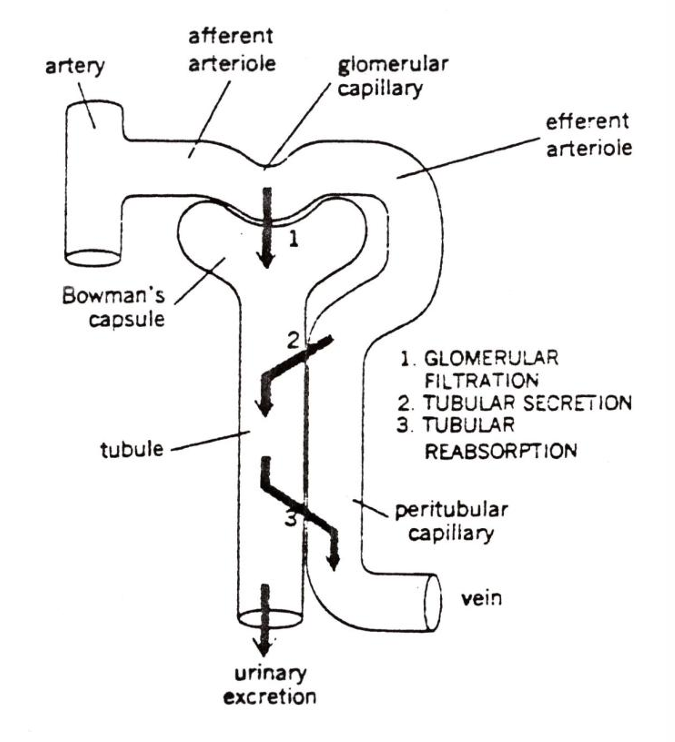
GFR = glomerular filtration rate = 180 l/d
net filtration pressure = blood pressure - pressure in the capsule of Bowman - colloid osmotic pressure of blood plasma
Water homeostasis: Regulation of water and Na balance
Based on active Na-reabsorption preceeding a passive water reabsorption
Examples:
Lack of water | blood volume ↓ → osmotic pressure ↑ → secretion of ADH (= anti-diuretic hormone = vasopressine) by hypothalamus → reabsorption of water ↑ |
Excess of water | reverse mechanism of lack of water |
Lack of Na+ | osmotic blood pressure ↓ → GFR ↓ → Na+ excretion↓→ renin ↑ + aldosteron ↑→ reabsorption Na+ ↑ |
Excess of Na+ | osmotic blood pressure ↑ → reverse mechanism → Na+ loss in urine + large water loss Water loss without Na loss is possible Na loss without water loss is not possible (drinking seawater) |
Water homeostasis: Regulation of water and Na balance: tubular reabsorption
reabsorption by diffusion: water, PO4(3-), glucose, Na+ and K+
reabsorption by active transport: eg. sugar
Steps
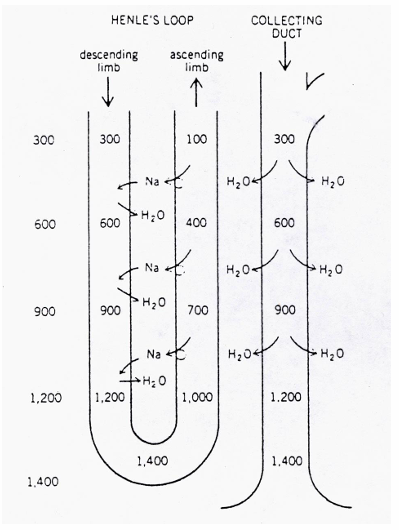
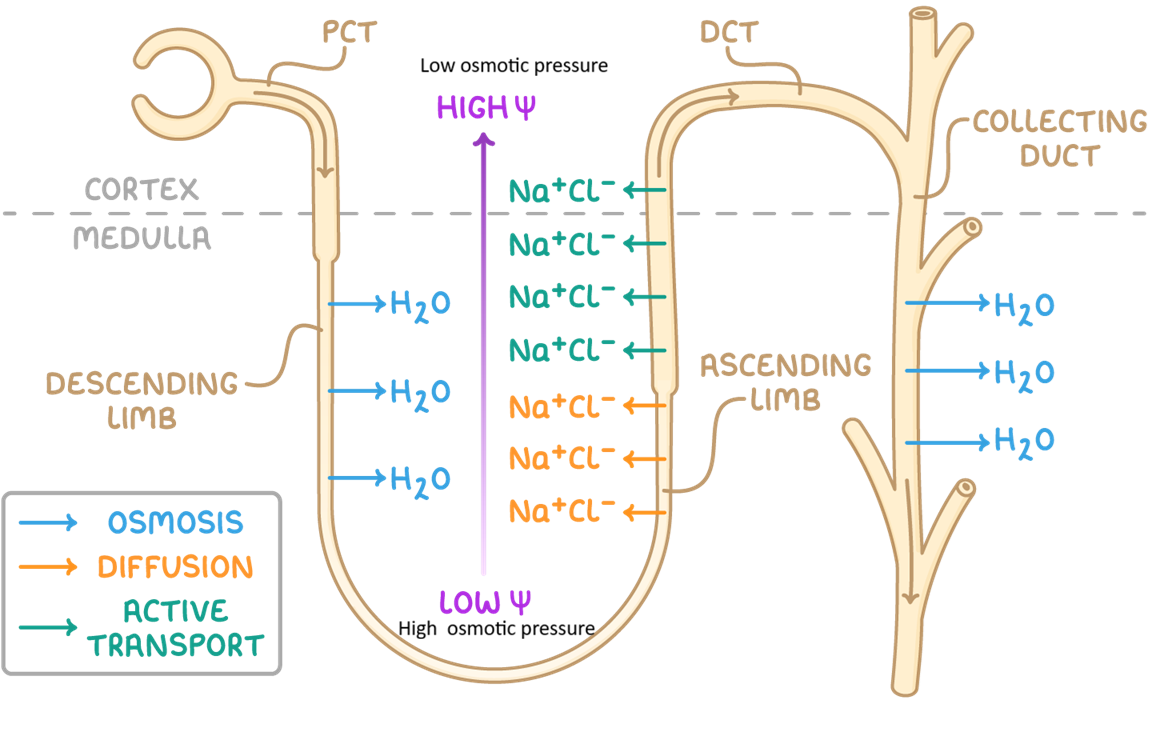
1) Loop of Henle
Descending limb: Na+ comes in → limb is permeable to water and water is lost by osmosis → filtrate gets concentrated (up to 1400 mosmol/l)
Ascending limb: impermeable to water but actively pumps Na+ out → filtrate gets diluted→ creates high osmolality → hyptertonic environment (= higher osmotic pressure)
2) Collecting duct
water is drawn out by osmosis → concentrates the urine to match the omsolality of the deep medulla, allowing the body to conserve water
dependant of ADH (no ADH = water is removed out of CD; ADH = water stays in CD)