Exam 3 – Immunology I
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is innate immunity?
aka genetic immunity, aka nonspecific
encompasses innate defenses covered last time
species immunity – all members of species “born with” (part of innate immunity)
ex. humans do not get infected with canine distemper
What are the two parts of the adaptive (specific) section of the immune system?
cellular components – cell mediated
humoral components – antibodies
What is an antigen?
something the body recognizes as foreign and mounts an immune response to
usually a protein
sometimes polysaccharides (sugar)
often on surface of microoganisms and cells
What is an epitope?
area on antigen where antibodies bind
What is an antibody?
a protein produced in response to an antigen
What is acquired immunity
immunity obtained in some other way than heredity
naturally or artificially acquired
active or passive
active – production of antibodies (you make them)
can be natural or artificial
passive – ready-made antibodies introduced (pre-formed antibodies from somewhere else are put into someone)
can be natural or artificial
SPECIFIC
ANYTIME ANTIBODIES INVOLVED
Name all the various types of immunity
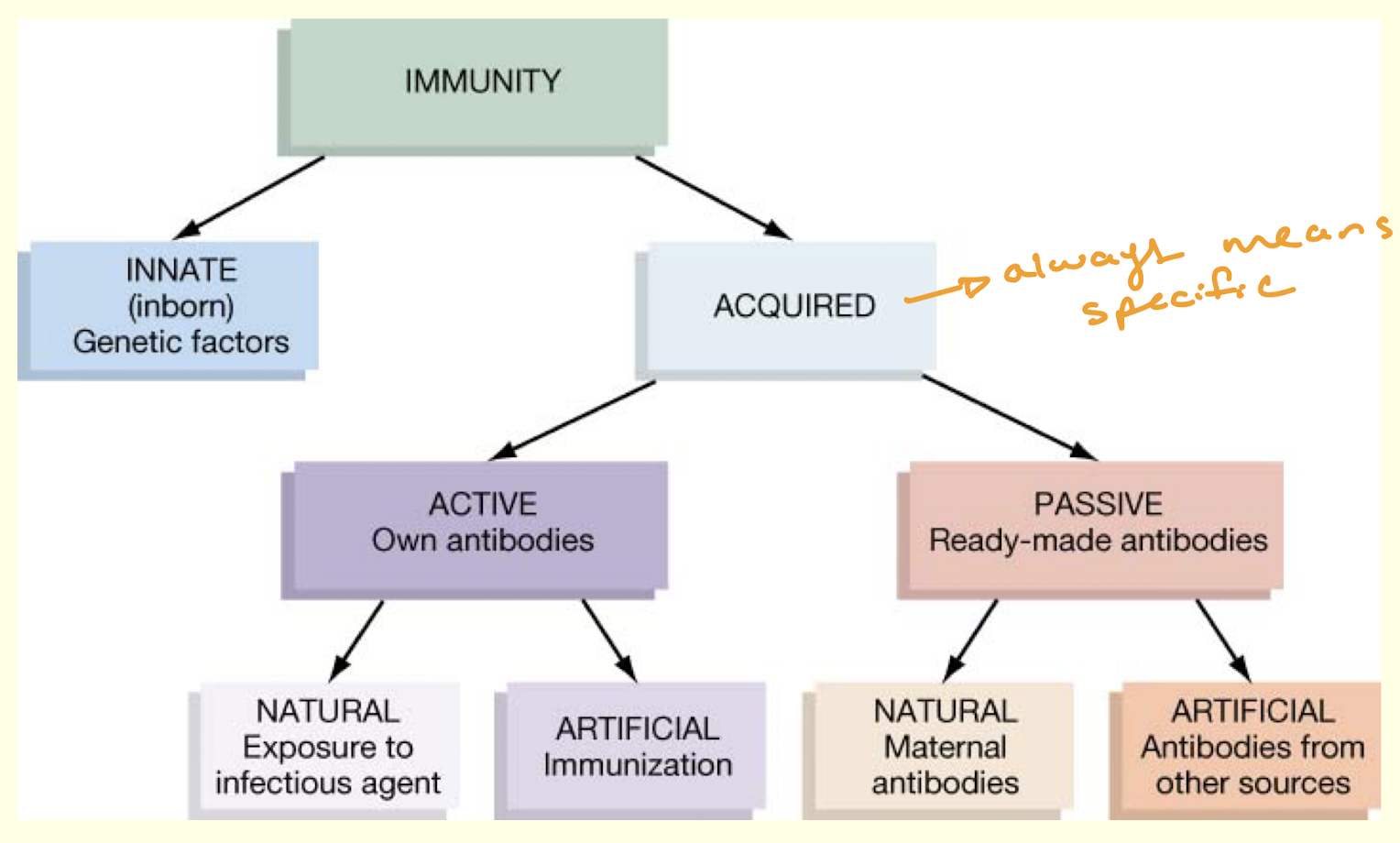
What are the four types of acquired immunity?
naturally acquired active immunity (sickness)
artificially acquired active immunity (vaccine)
naturally acquired passive immunity (fetus from mother in womb)
artificially acquired passive immunity (someone else’s antibodies given in a serum like a drug)
Overview of whole immune system?
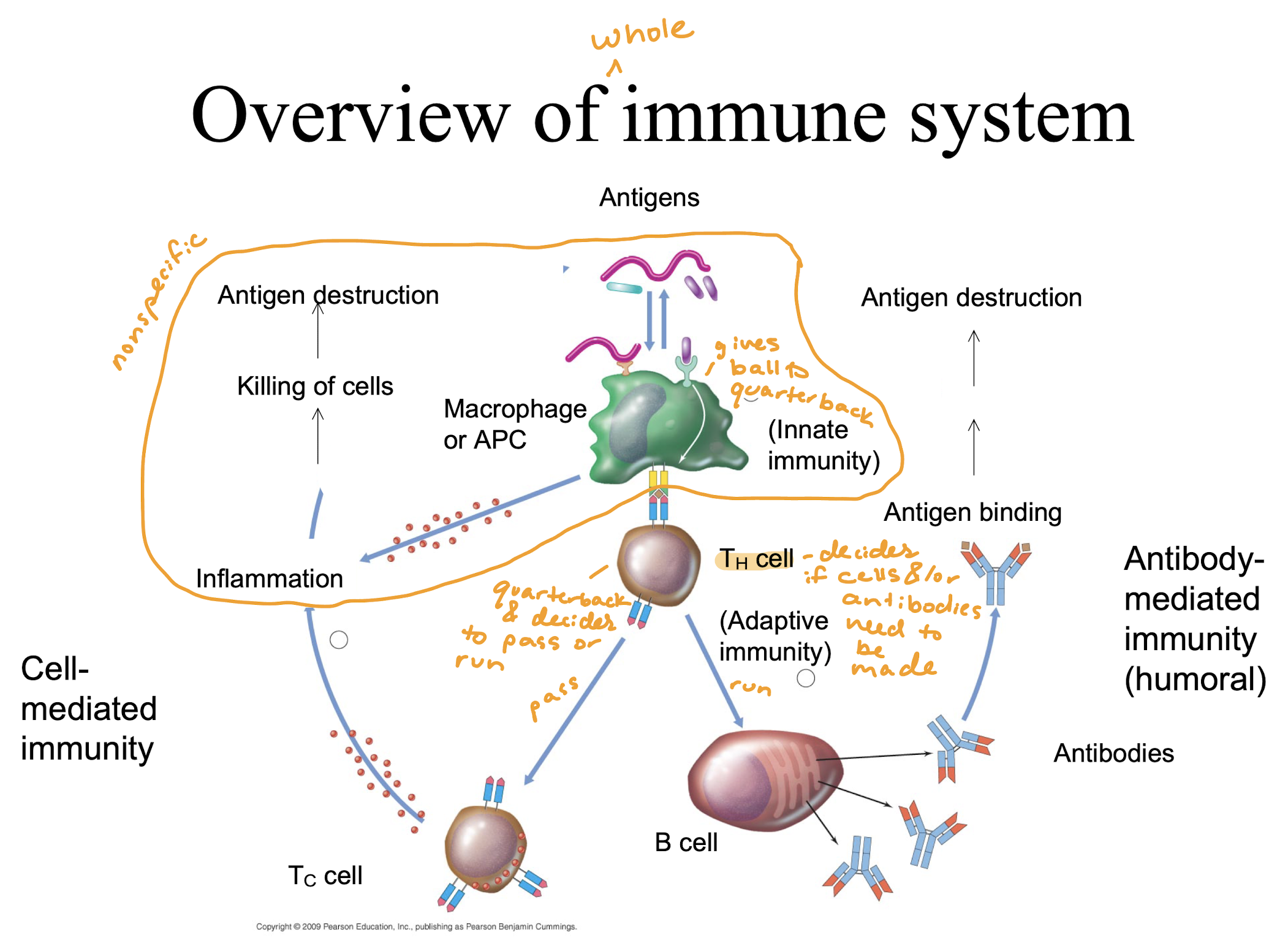
What are the cells and tissues of the immune system?
Lymphocytes – WBCs that carry out immune responses
B cells – make specific antibodies
humoral immunity – antibodies in the blood
T cells
T c are cytotoxic (cell killers – recognize our own cells that are infected and kills them – very specific)
T h are “helpers” to specific responses
help cell mediated immunity
help humoral immunity
B cells
antibody production
bone marrow and bursa (of poultry?)
humoral immunity
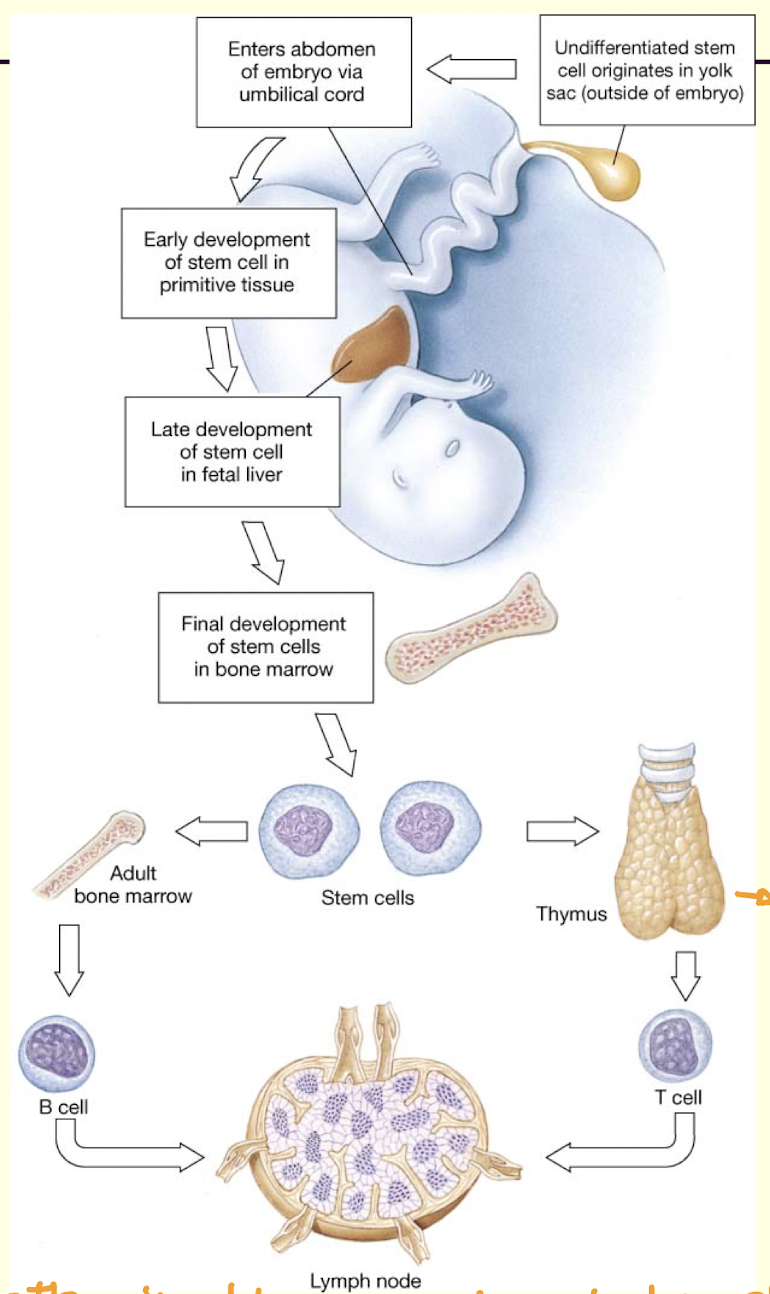
T cells
cell mediated immunity (thymus)
also involved in humoral response
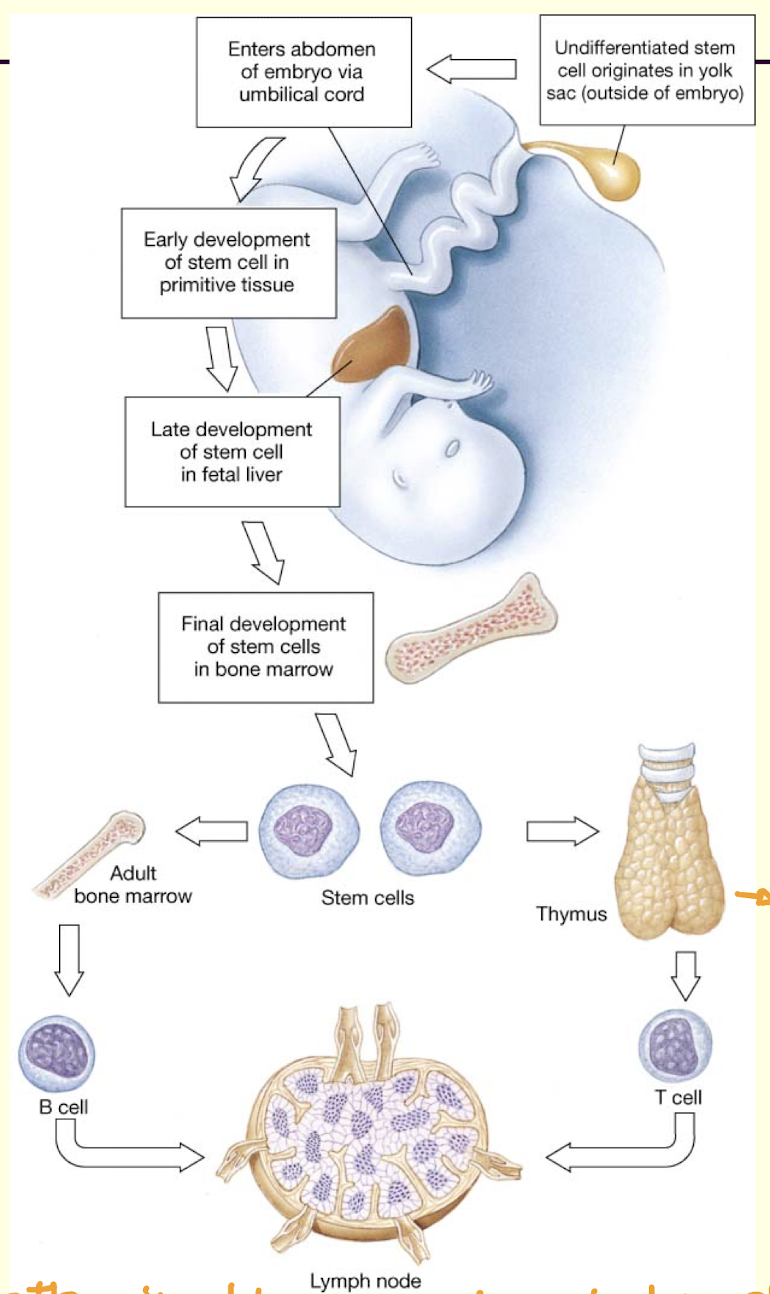
What is a lymph and a lymph node
lymph – like blood but no RBCs
lymph nodes – high concentration of WBCs
interactions with microbes and antigens
What are lymphatic organs?
lymph nodes – filter foreign materials out of lymph
thymus – maturation of T-cells (lymphocytes)
spleen – largest lymphatic organ and contains phagocytes
tonsils – aggregation of lymphocytes
for all
swelling is a sign of infection
all involved in immunity
cite of fighting between our immune system and antigens
What are the properties of adaptive immunity?
specificity
memory
self versus non-self recognition
tolerance
What is clonal selection theory?
explains specificity and memory
the immune system can recognize billions of antigens
each T cell and B cell is specific for one antigen
the immune system has “memory”
similar for T cells and B cells
each T and B cell only recognizes one antigen, but it needs times to build response to antigen it recognizes
memory cells are available after first infection to fight second infection
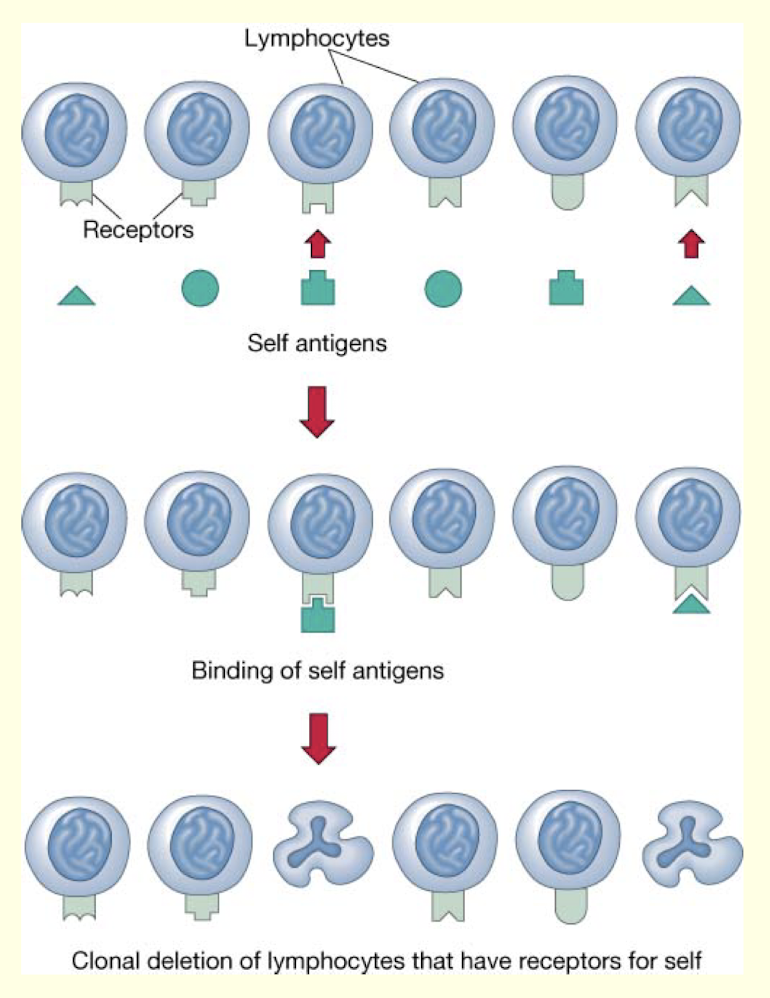
What is the clonal deletion theory?
it explains tolerance
during development, T and B cells that recognize “self” antigens are deleted
this results in tolerance for “self”
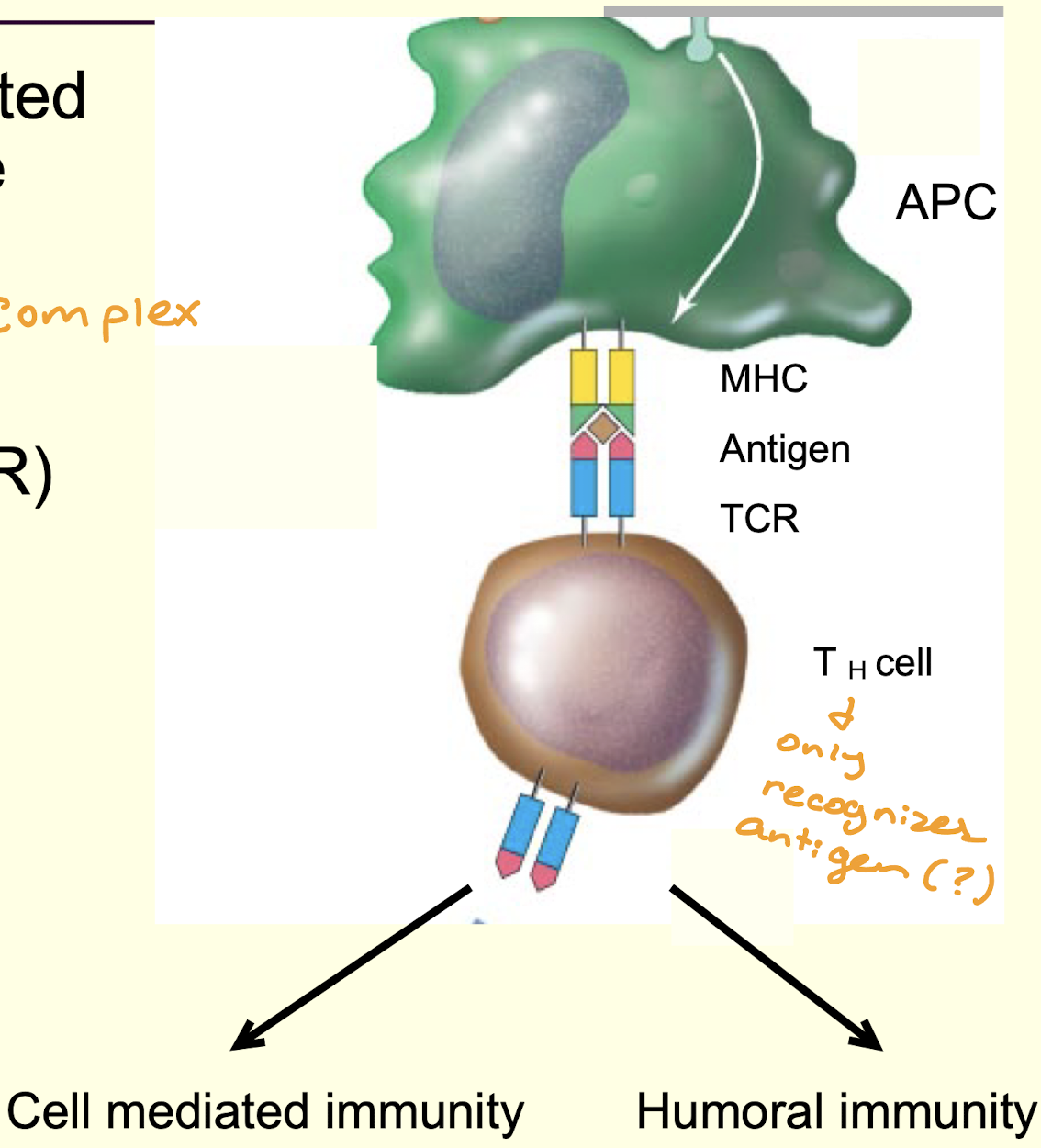
What is the antigen presenting cell (APC)?
usually macrophages
ingest pathogen
lyse pathogen
process antigens
What is antigen presentation?
antigens are presented on the surface of the APC using major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins
T cell receptors (TCR) recognize specific antigens and MHC
T helper (T h) cell is activated
simulated cell mediated and/or humoral response
What is humoral (liquid) immunity?
antibodies (made by B cells) in the blood and fluids
effective before invaders enter cells
small pathogens destroyed
What is cell-mediated immunity?
carried out by T cells
antigens embedded or within cells
entire cell is destroyed
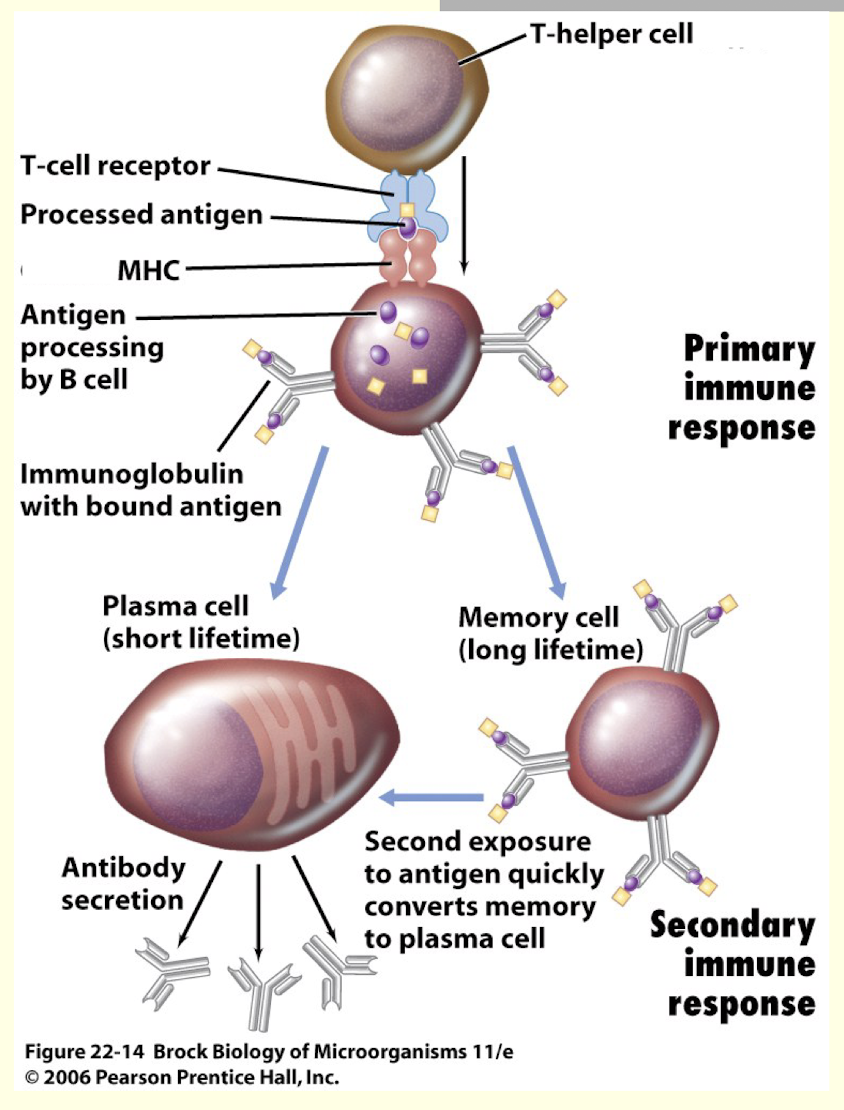
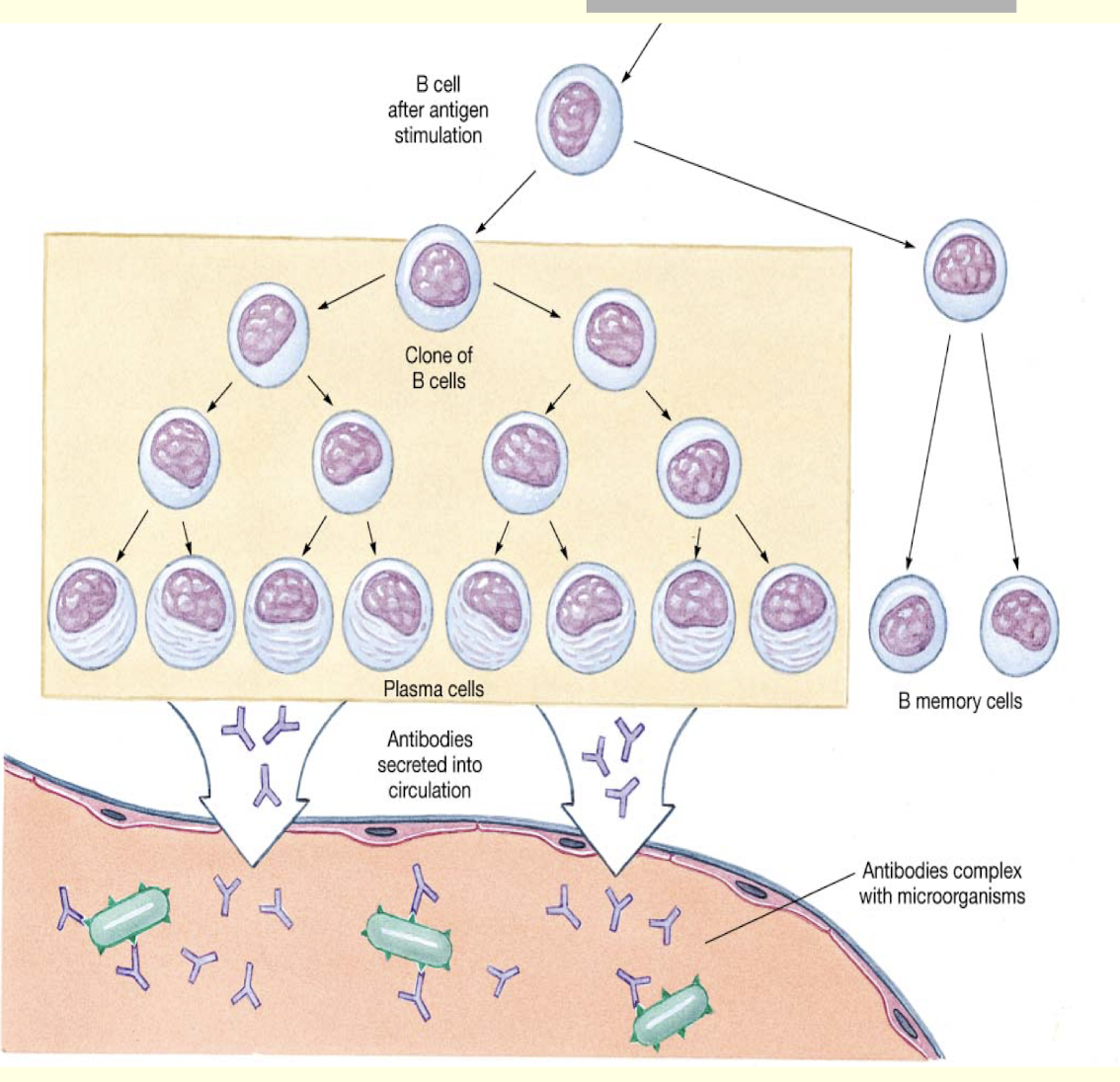
What happens during humoral immunity (AKA antibody mediated immunity)?
B cells express antibodies on their surface
Bind specific antigen then divide
some offspring are plasma cells that pump out antibody
some offspring are memory cells
What are antibodies?
immunoglobulins (Ig)
soluble proteins
found in serum (plasma) and some other body fluids (milk, gastric secretions, mucus)
antiserum
5 classes
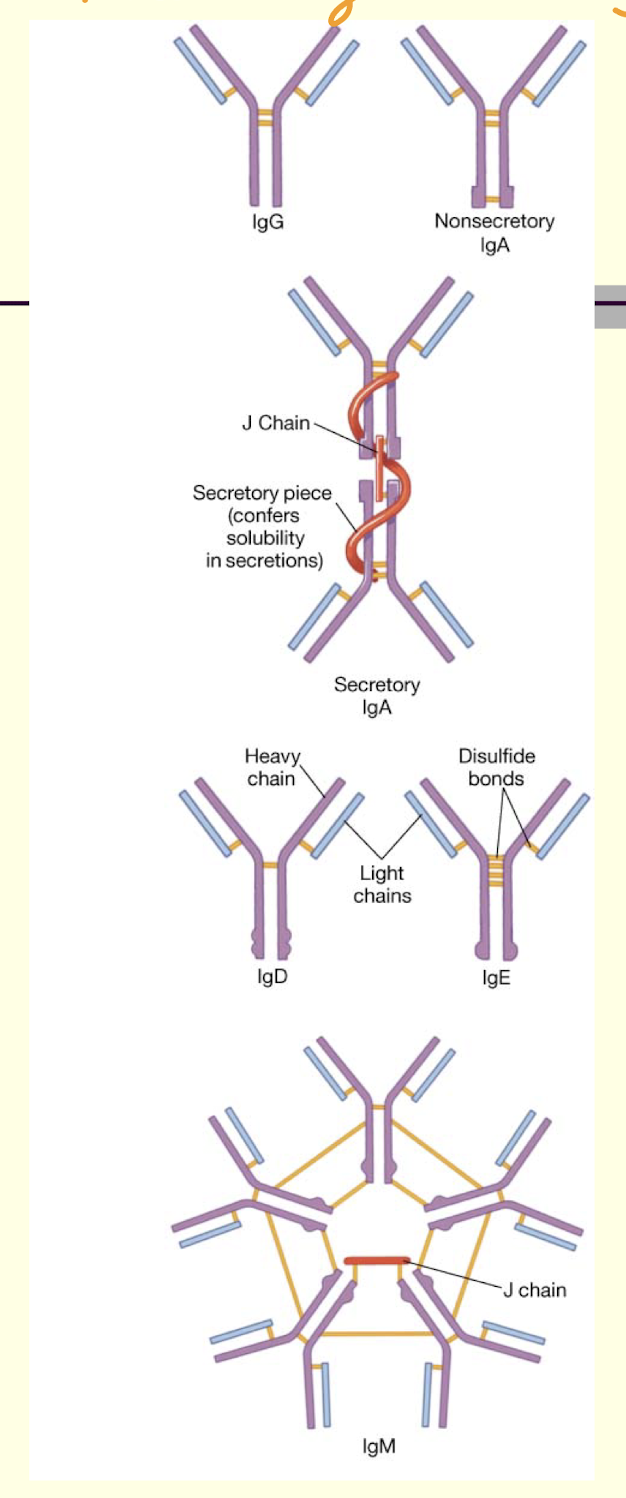
What are the five classes of Ig?
IgG (~80% of total, 2º [2nd] response)
IgM (largest, 1º [1st] response)
IgA (secretions)
IgD
IgE (allergies)
What is primary response?
when a B cell first finds its antigen with the help of T helper cell
produce plasma cells and IgM antibodies (big, multipurpose [?], less potent)
![<ul><li><p>when a B cell first finds its antigen with the help of T helper cell</p><ul><li><p>produce plasma cells and IgM antibodies (big, multipurpose [?], less potent)</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c602f2d6-76ad-4d4c-b659-157c26b4cdfc.png)
What is secondary response?
memory cells quickly respond to antigen without the help of T helper cell
produce plasma cells and IgG antibodies (very potent)
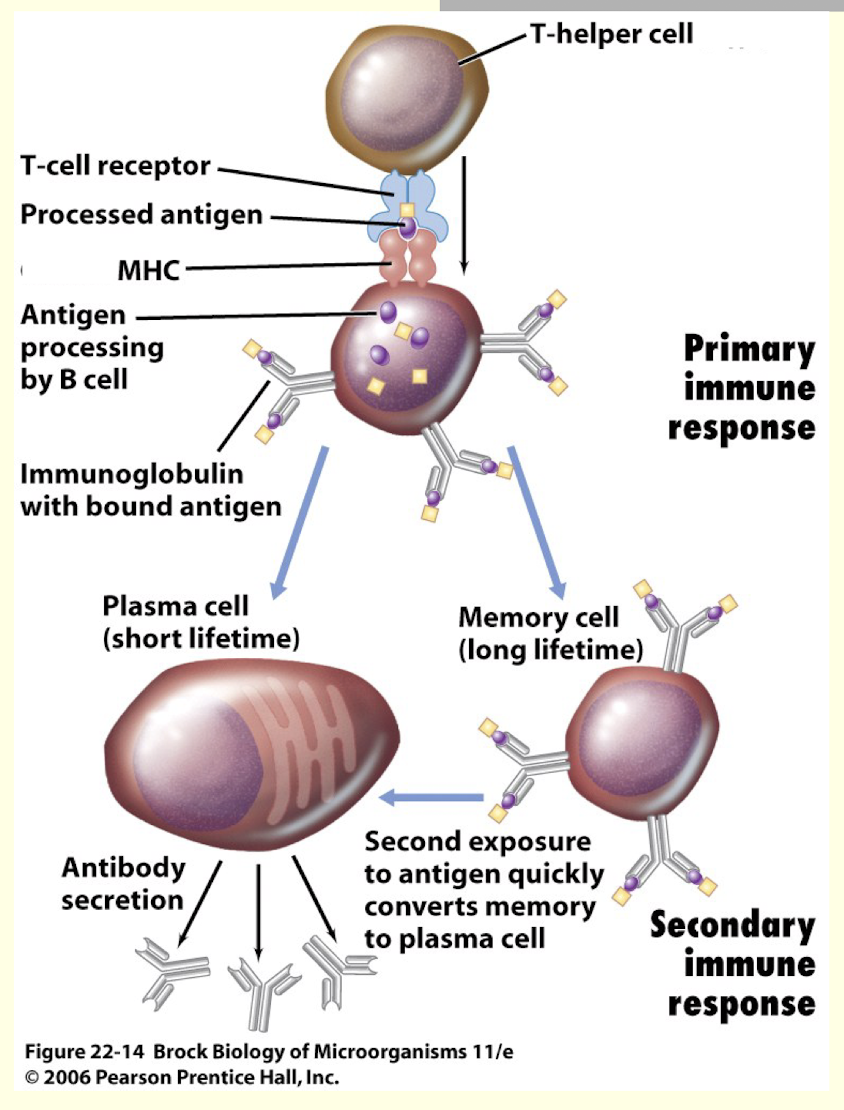
What do the primary and secondary responses look like when graphed?