Blood Gases and Acid-Base Balance
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
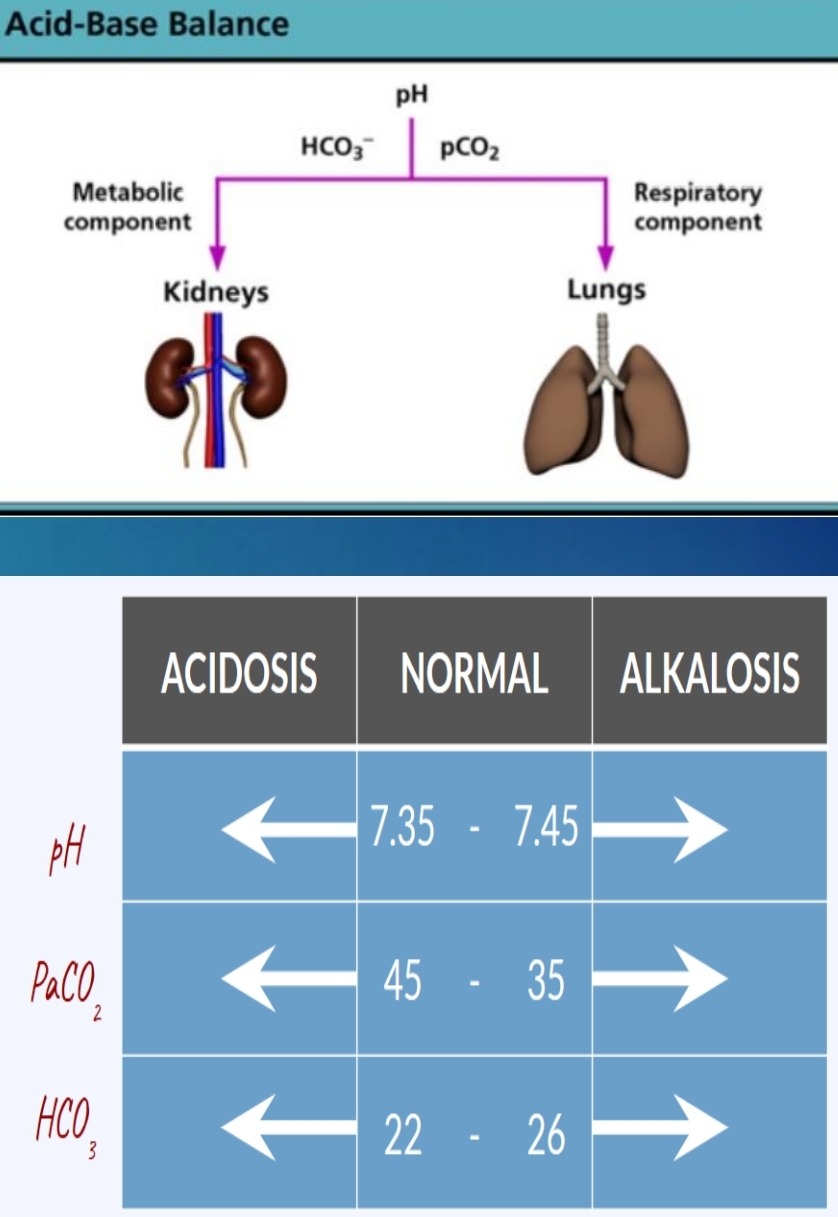
The pH of plasma is function of two independent variables:
Partial pressure of Carbon dioxide (pCO2) - regulated by lungs
Concentration of Bicarbonate (HCO3-) - regulated by kidneys
Blood Gas Analysis - Specimens
In most institutions, the respiratory department is responsible for collection and analysis, but some clinical laboratories still perform blood gas analysis
Arterial puncture - evaluate pH, oxygen content, and CO2 content of blood
Capillary specimens - infants
Order of Draw: BSEON
Arterial Blood Gas
method of determination could be done through: (2)
Gasometer (Van Slyke or Natelson)
Electrodes

Arterial Blood Gas
Electrode for:
→pH:
→pCO2
→pO2:
→pH: Silver- Silver Chloride Electrode or Calomel Electrode
→pCO2: Severinghaus Electrode
→pO2: Clarke Electrode
Sample Collection and Handling
Anticoagulant:
Must use _ collection for pH and blood gases
Sodium heparin
Anaerobic collection
Sample Collection and Handling
If blood is exposed to air (bubbles in syringe; uncapped tube):
→CO2 and PCO2
→pH
→PO2
→CO2 and PCO2: DECREASED
→pH: INCREASED
→PO2: INCREASED
Sample Collection and Handling
If testing is prolonged (>15 minutes), blood should be kept in cracked ice to prevent hemolysis
Hemolysis leads to:
→pCO2 and CO2:
→pH:
→pO2:
→pCO2 and CO2: INCREASED
→pH: DECREASED
→pO2: DECREASED
ABG Values
pH:
pCO2:
HCO3-:
pO2:
pH: 7.35 to 7.45
pCO2: 35 to 45 mmHg
HCO3-: 22 to 26 mmol/L
pO2: 80 to 110 mmHg
3-Step Interpretation of ABG Results
Identify it is alakalosis or acidosis
Identify if it is respiratory or metabolic
Identify if it is compensated or uncomepensated
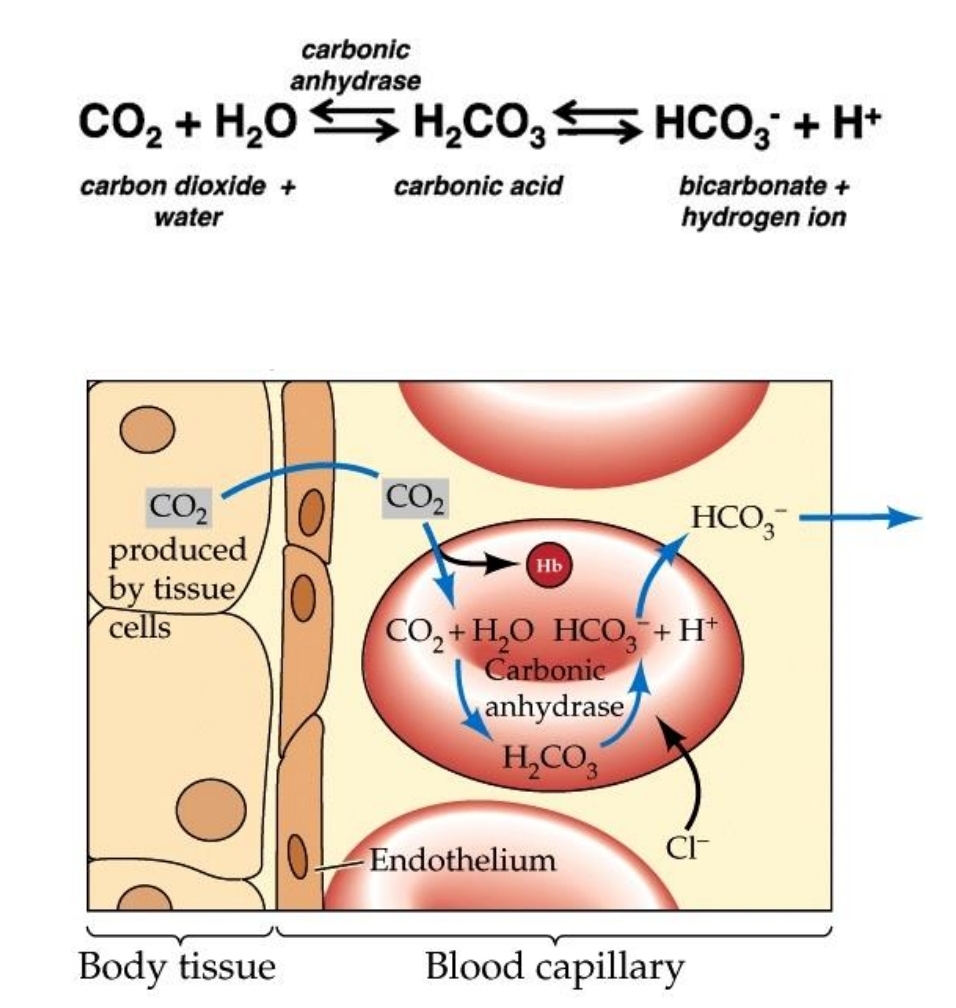
Most CO2 combines with H2O to form H2CO3 (carbonic acid) which immediately dissociates into H+ and HCO3 (bicarbonate)
This reaction is accelerated by _
The dissociation of H2CO3 increases HCO3 in RBC causing it diffuse into plasma
To maintain electroneutrality, _ diffuse into the cell as an exchange to moving out HCO3
carbonic anhydrase
chloride
Action of the Lungs
The H+ that was carried on the reduced hemoglobin in venous blood is released to recombine with HCO3 - to form H2CO3 (carbonic acid) which dissociates into H2O and CO2
The CO2 diffuses into the alveoli and is eliminated through ventilation
Slow or non-removal of CO2 results to increased H+ concentration
Rapid or fast elimination of CO2 results to decrease of H+ ion concentration
-------------
Action of the Kidneys
Excrete considerable amounts of acid-base for acid-base balance
The main role is to reclaim _ from the glomerular filtrate and add it to blood
The H+ combine with HCO3, forming carbonic acid, and later converted to H2O and CO2 by carbonic anhydrase
CO2 diffuses into the tubule an reacts with H2O, reform carbonic acid and then go back to bicarbonate
bicarbonate
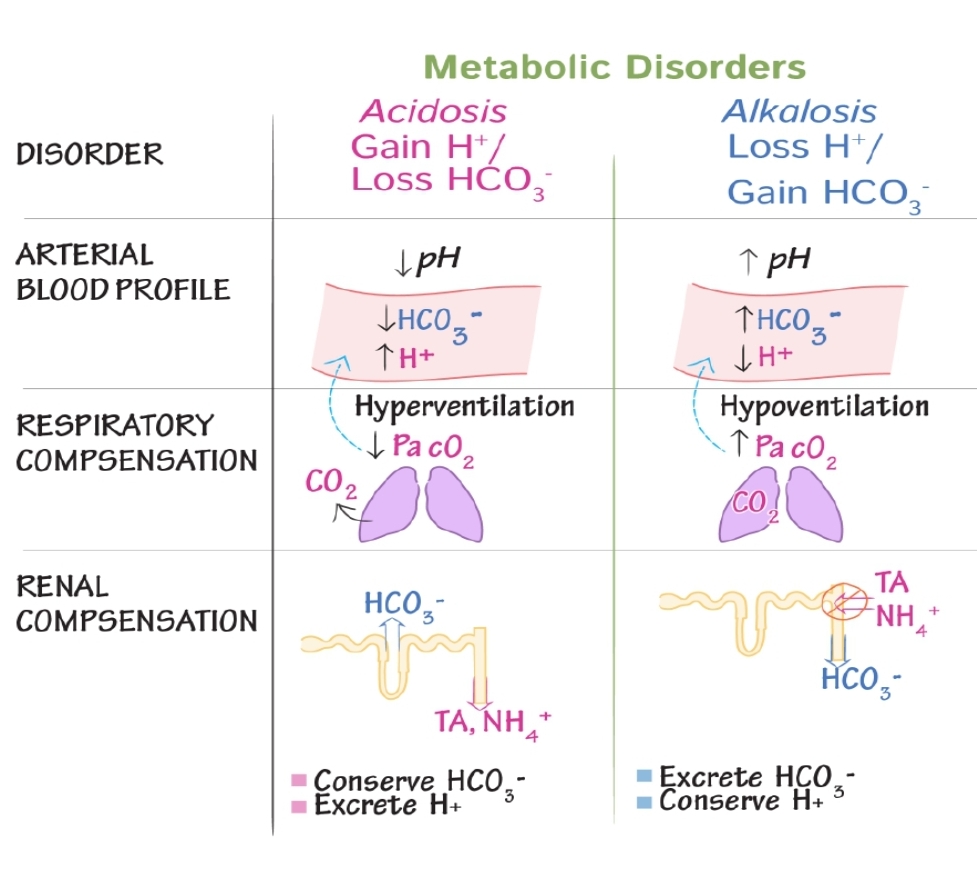
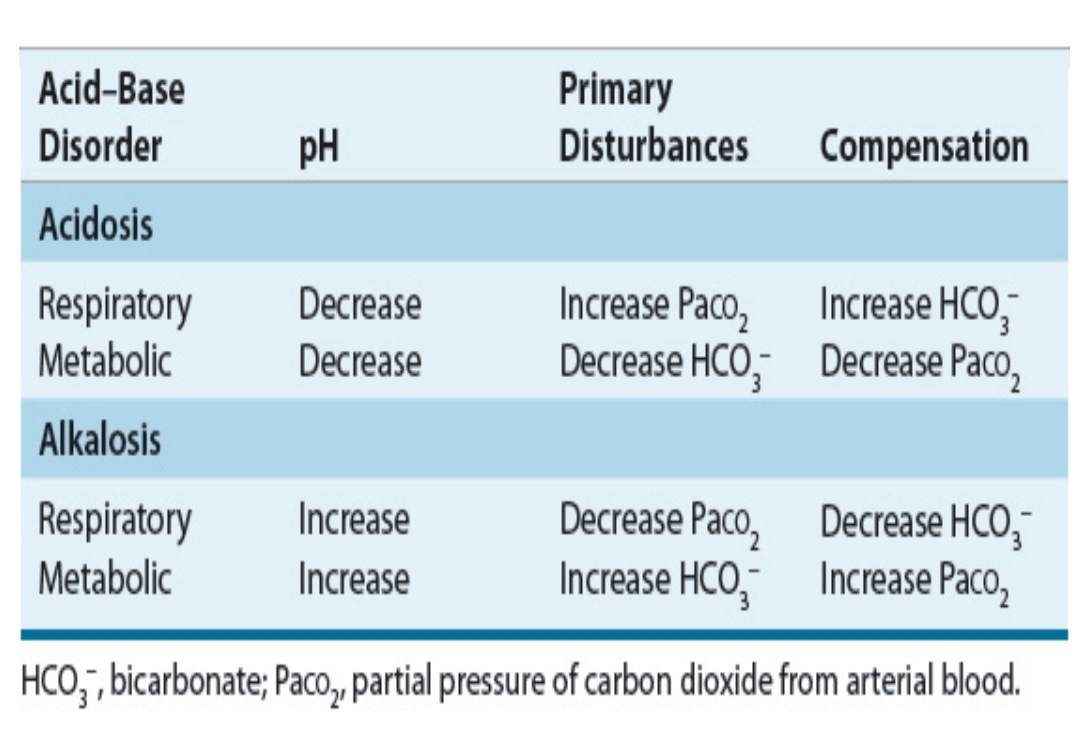
Metablic acidosis
low pH with bicarbonate deficiency
production of increased amount of acid (3)
Lab findings:
→pH:
→HCO3:
→pCO2:
low pH with bicarbonate deficiency
production of increased amount of acid:
→Diabetic ketoacidosis
→Lactic acidosis
→Renal failure
Lab findings:
→pH:DECREASED
→HCO3: DECREASED
→pCO2: NORMAl
Metaboli Acidosis - Compensation
Hyprventilation
Metablolic Alkalosis
Bicarbonate excess
May be due to excess ingestion of base, decreased elimination of base or loss of acididc fluis
Caused by:_
Lab Findings:
pH: INCREASED
pCO2: NORMAL
HCO3-: INCREASED
Caused by:
→Intestinal obstruction
→Vomiting
→Glucocorticoid excess - Cishing's Syndrome
→Mineralocorticoid excess - Hyperaldosteronism
Lab Findings:
pH: INCREASED
pCO2:
HCO3-:
Metabolic Alkalosis - Compensation
Hypoventilation - CO2 is converted to H2CO3 (carbonic acid) which lowers blood pH
Respiratory Acidosis
Excessive amount of pCO2
May be due to inability to exhale CO2
Caused by: _
Lab Findings:
pH:
pCO2:
HCO3-:
Caused by:
→Chronic bronchitis
→Emphysema
→Ingestion of narcotics and barbiturates
→Meningitis
Lab Findings:
pH: DECREASED
pCO2: INCREASED
HCO3-: NORMAL
Respiratory Acidosis - Compensation
Increased bicarbonate retention/reabsorption
Respiratory Alkalosis
Decreased amount pCO2
May be due to excessive exhalation pCO2
Caused by: _
Lab Findings:
pH:
pCO2:
HCO3-:
Caused by:
→Hypoxia
→Anxiety, Nervousness, Excessive crying
→Pulmonary embolism
→Pneumonia
→Congestive heart failure
→Salicylate overdose
Lab Findings:
pH: INCREASED
pCO2: DECREASED
HCO3-: NORMAL
Respiratory Alkalosis - Compensation
Increased excretion of bicarbonate
When the kidney and lungs are working properly, a _ ratio of bicarbonate to carbonic acid will be maintained
The body's cellular and metabolic actibities are pH-dependent, thus the body tries to return pH toward normal whenever imbalance occur
The lungs compensate immediately but the response is _ and incomplete
The kidneys are slow but response is _ and complete
20:1
short-term
long-term