Antiarrhythmic Agents NAULI... PART 2/2
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
what are the major causes of arrhythmias?
(1) Electrolyte imbalance
(2) Enhanced automaticity
(3) Triggered automaticity
(4) Re-entry
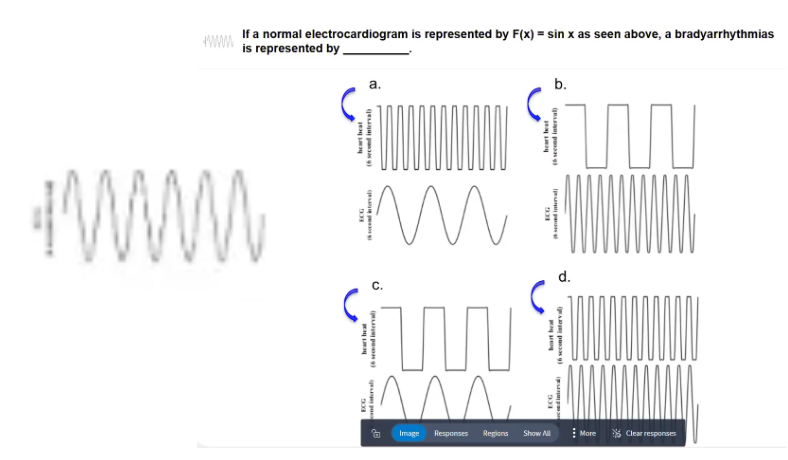
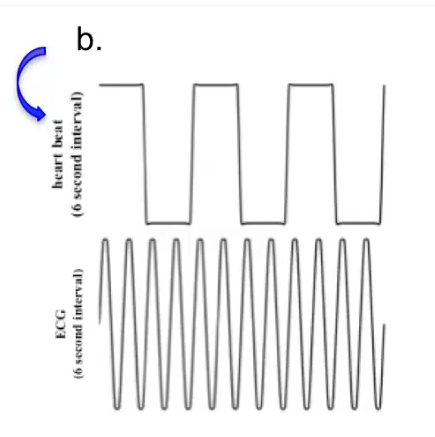
POLLEV: If an normal electrocardiogram is represented by F(x) = sin x as seen above, a bradyarrhythmia is represented by _____.
Graph B: Bradyarrhythmia
Heart beat > (faster than) SA node firing (ECG)

Graph A = tachyarrhythmia
Graph C = bradycardia
Graph D = tachycardia
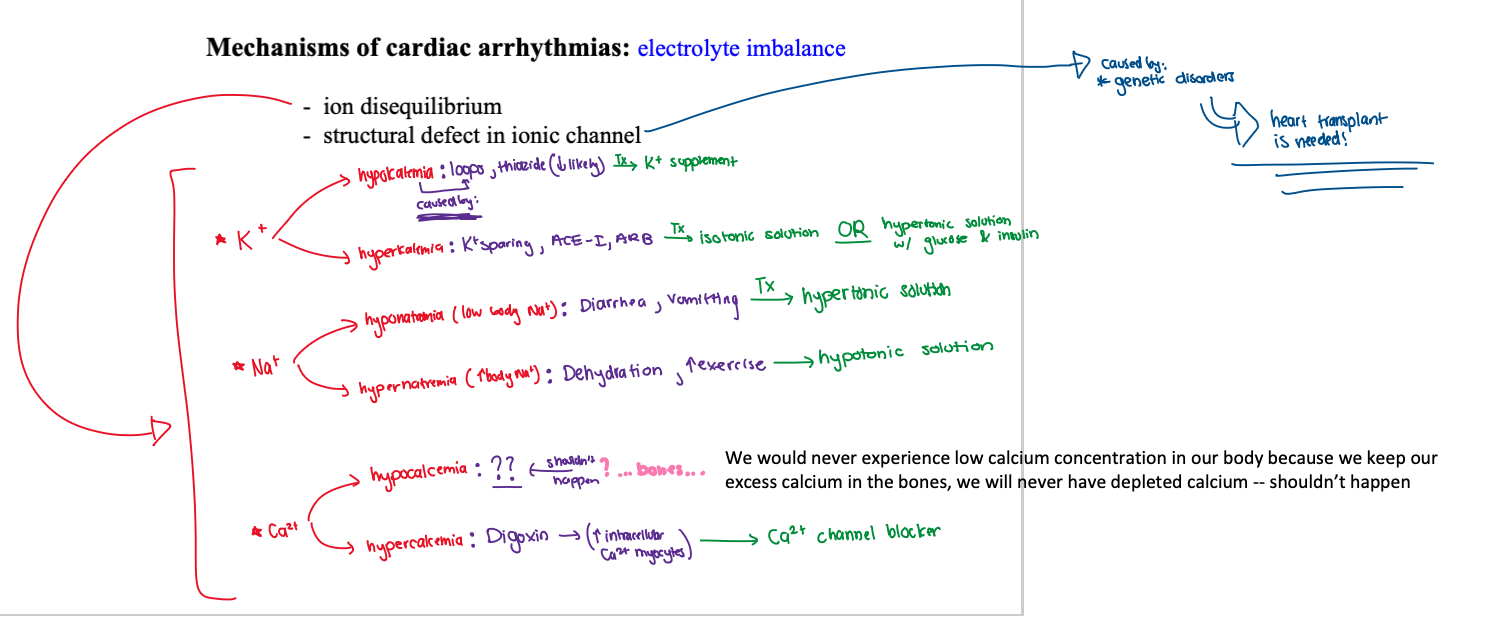
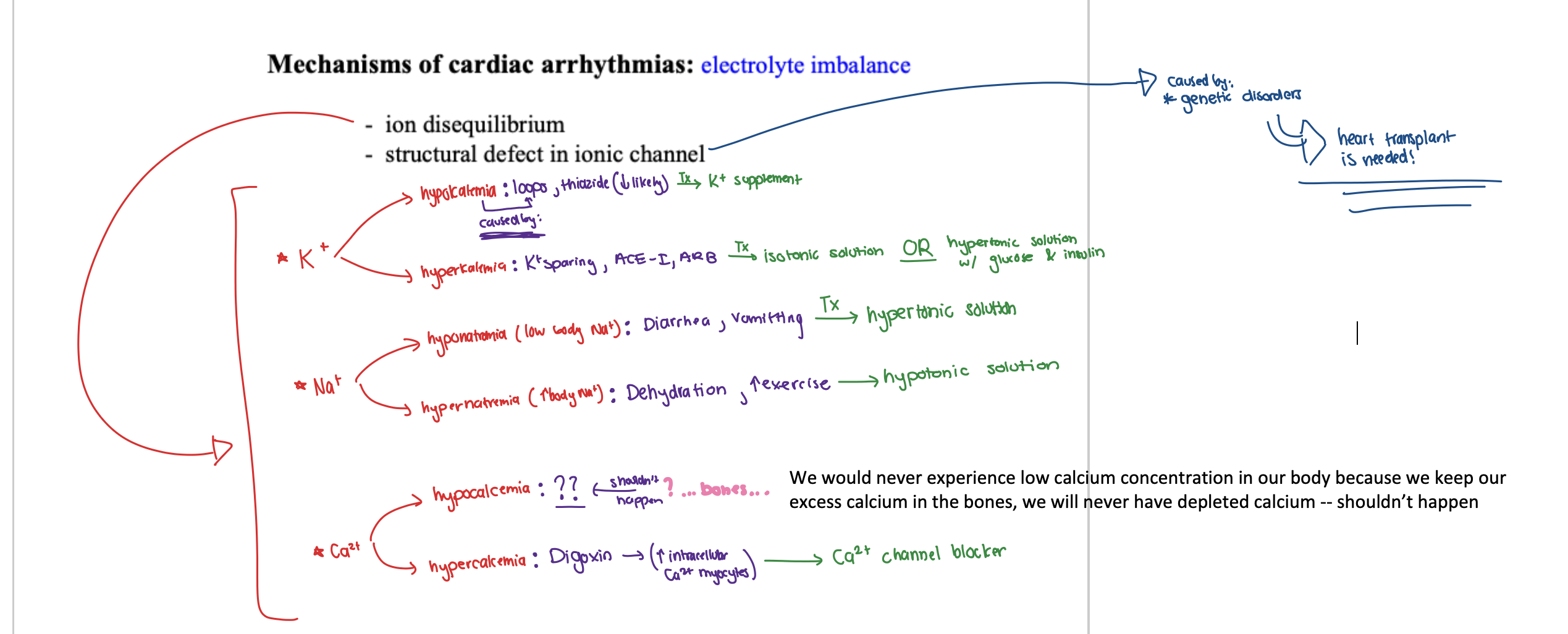
what occurs in electrolyte imbalance in cardiac arrhythmias?
(1) ion disequilibrium
(2) structural defect in ionic channel

which ions are affected in ion disequilibrium of electrolyte imbalance in cardiac arrhythmia? what do they result in?
(1) K+
⚫️ hypokalemia
⚫️ hyperkalemia
(2) Na+
⚫️ hyponatremia
⚫️ hypernatremia
(3) Ca2+
⚫️ hypocalcemia
⚫️ hypercalcemia
in regards to ion disequilibrium in arrhythmia, what is hypokalemia caused by?
(1) loops
(2) thiazides (LESS likely)
in regards to ion disequilibrium in arrhythmia, what is hyperkalemia caused by?
(1) K+ sparing
(2) ACE-I
(3) ARB
in regards to ion disequilibrium in arrhythmia, what is hyponatremia (low body Na+) caused by?
(1) Diarrhea
(2) Vomitting
in regards to ion disequilibrium in arrhythmia, what is hypernatremia caused by?
(1) Dehydration
(2) Increased exercise
in regards to ion disequilibrium in arrhythmia, what is hypocalcemia caused by?
We should NEVER experience low calcium concentration in our body because we keep our excess calcium in the bones, so calcium levels will never be depleted…
in regards to ion disequilibrium in arrhythmia, what is hypercalcemia caused by?
Digoxin ==> INCREASED intracellular Ca2+ myocytes
in regards to ion disequilibrium in arrhythmia, what is the treatment for hypokalemia?
K+ supplement
in regards to ion disequilibrium in arrhythmia, what is the treatment for hyperkalemia?
(1) isotonic solution
OR
(2) hypertonic solution WITH glucose & insulin
in regards to ion disequilibrium in arrhythmia, what is the treatment for hypnatremia?
hypertonic solution
in regards to ion disequilibrium in arrhythmia, what is the treatment for hypernatremia?
hypotonic solution
in regards to ion disequilibrium in arrhythmia, what is the treatment for hypocalcemia?
We should NEVER experience low calcium concentration in our body because we keep our excess calcium in the bones, so calcium levels will never be depleted… ==> NO TX needed!
in regards to ion disequilibrium in arrhythmia, what is the treatment for hypercalcemia?
Ca2+ channel blocker
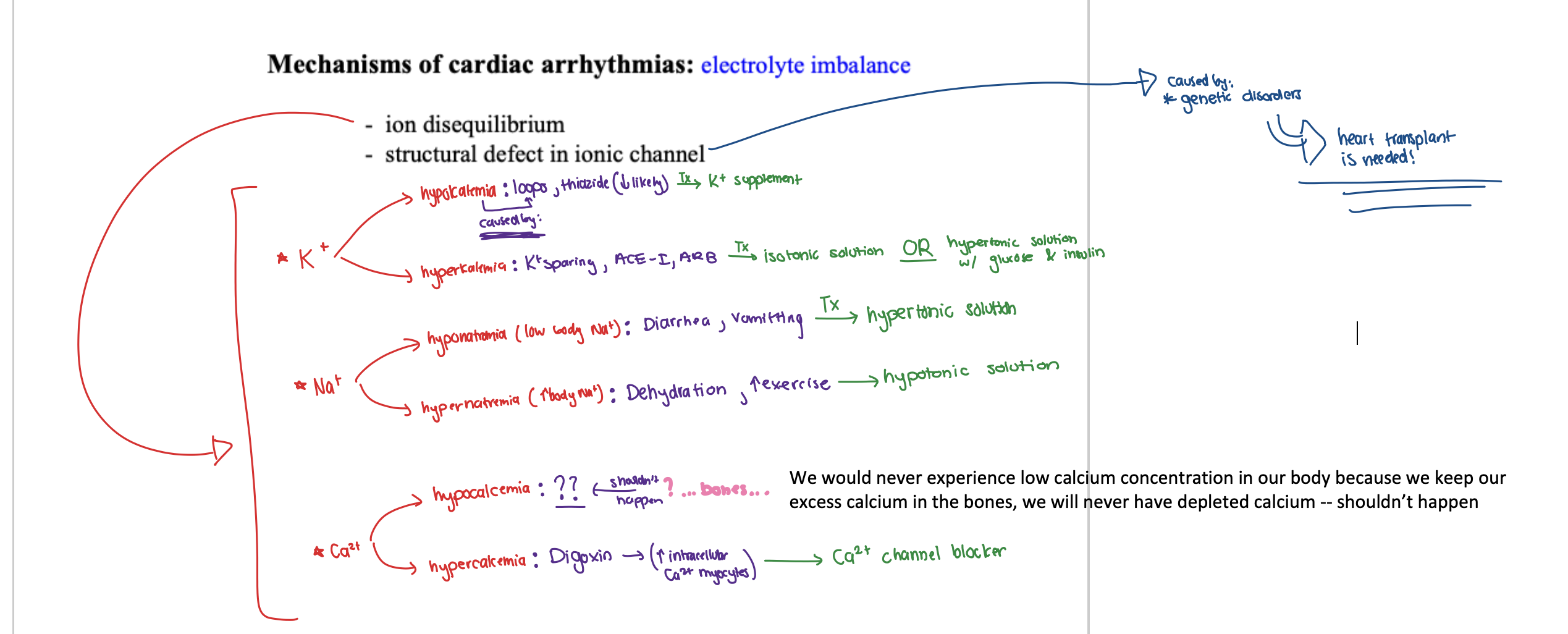
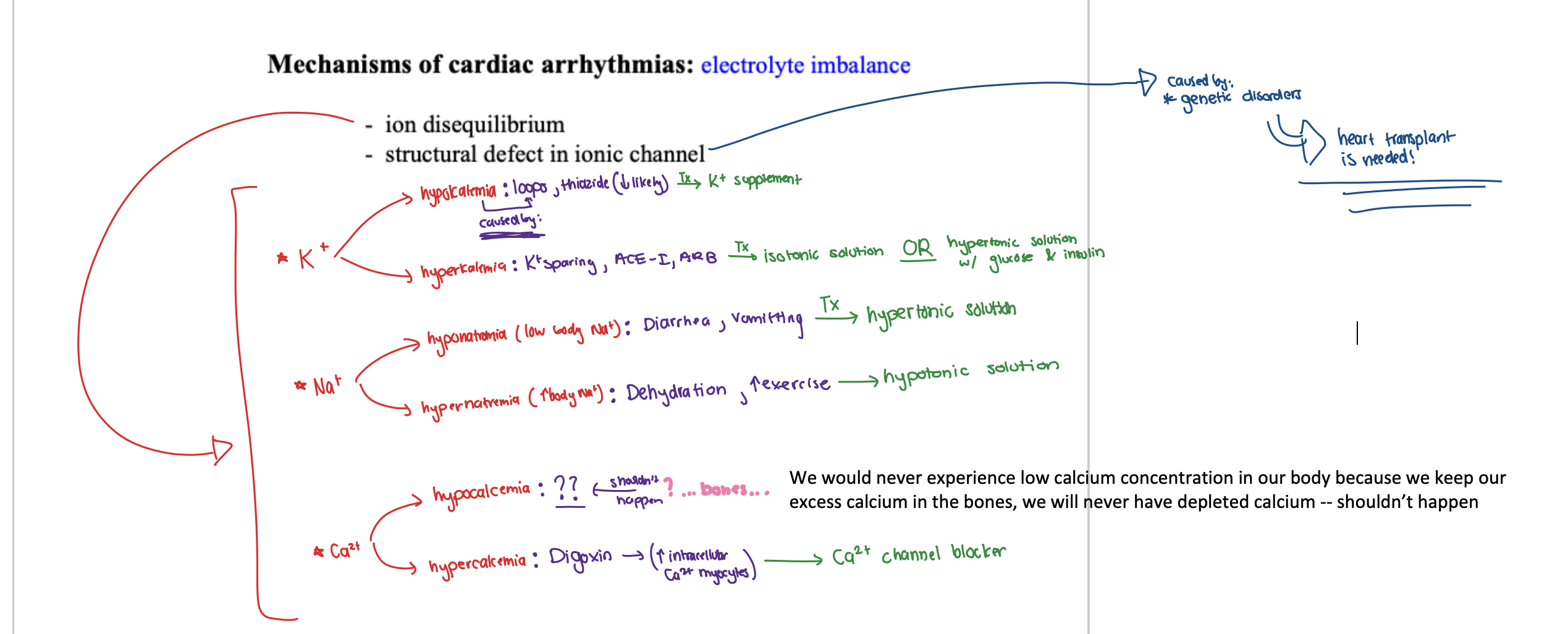
SUMMARY:
Mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmias: electrolyte imbalance
⭐️ ion disequilibrium
REFER TO IMAGE:
(1) K+
⚫️ hypokalemia: loops, thiazide (↓ likely) ==> K+ supplement
⚫️ hyperkalemia: K+ sparing, ACE-I, ARB ==> isotonic solution OR hypertonic solution w/ glucose & insulin
(2) Na+
⚫️ hyponatremia: diarrhea, vomitting ==> hypertonic solution
⚫️ hypernatremia: dehydration, ↑ exercise ==> hypotonic solution
(3) Ca2+
⚫️ hypocalcemia = n/a
⚫️ hypercalcemia: Digoxin → ↑ intracellular Ca2+ myocytes ==> Ca2+ blocker
in regards to electrolyte imbalance in cardiac arrhythmia, what are structural defects in ionic channel caused by? what does this mean?
caused by genetic disorders ==> heart transplant is needed

POLLEV: The following pharmacological agents can induce arrhythmia, except _____.
|
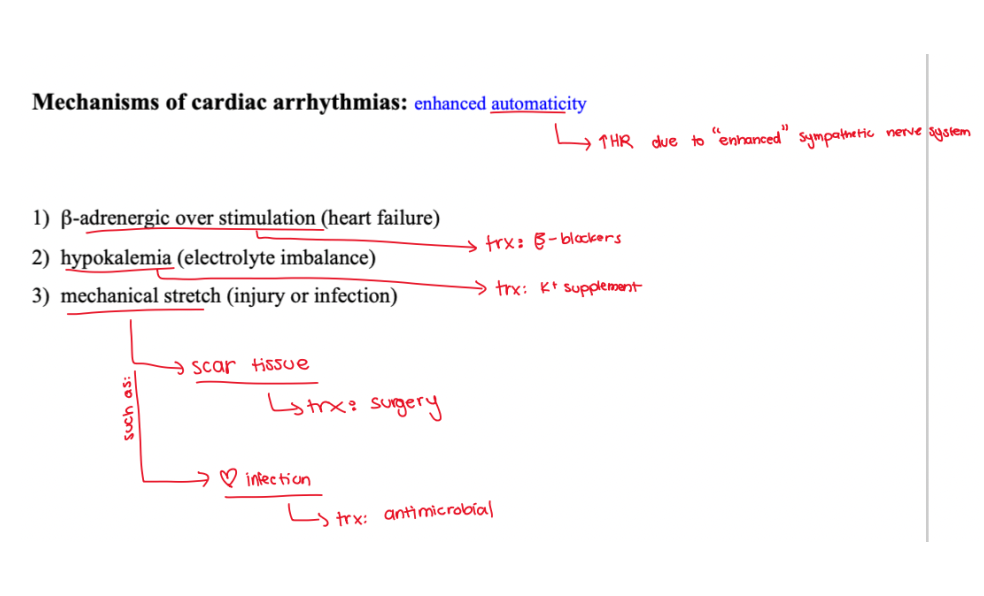
in regards to the mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmias, what is enhanced automaticity?
↑HR due to “enhanced” sympathetic nerve system
in regards to the mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmias, what is enhanced automaticity? what are the main effects caused by this?
↑HR due to “enhanced” sympathetic nerve system
(1) beta-adrenergic over stimulation
(2) hypokalemia
(3) mechanical stretch
what can beta-adrenergic over stimulation due to enhanced automaticity cause?
heart failure
what can hypokalemia due to enhanced automaticity cause?
electrolyte imbalance
what can mechanical stretch due to enhanced automaticity cause?
(1) injury
(2) infection
what is the treatment of beta-adrenergic overstimulation caused by enhanced automaticity?
beta-blockers
what is the treatment of hypokalemia caused by enhanced automaticity?
K+ supplement
what is the treatment of mechanical stretch caused by enhanced automaticity?
(1) scar tissue ==> TX: surgery
(2) heart infection ==> TX: antimicrobial
SUMMARY:
Enhanced automaticity

POLLEV: Arrythmia can be caused by the following, except _____.
Calcium loss due to osteoporosis
what is triggered automaticity in cardiac arrhythmias?
Two major forms of trigger rhythms are recognized
(1) DAD (delayed afterdepolarization)
(2) EAD (early afterdepolarization)
what does DAD stand for?
delayed afterdepolarization (DAD)
what does EAD stand for?
early afterdepolarization (EAD)
what is DAD caused by?
(1) intracellular Ca2+ overload
(2) Na+ channel (delayed or partially open)
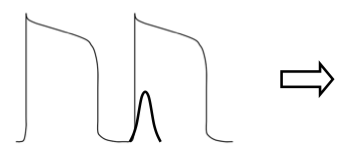
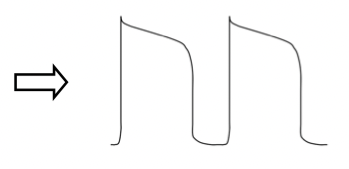
what does this initial action potential represent and what would the outcome be?
This is a normal action potential
calcium current is occurring immediately after depolarization phase 0
This will result in a normal action potential
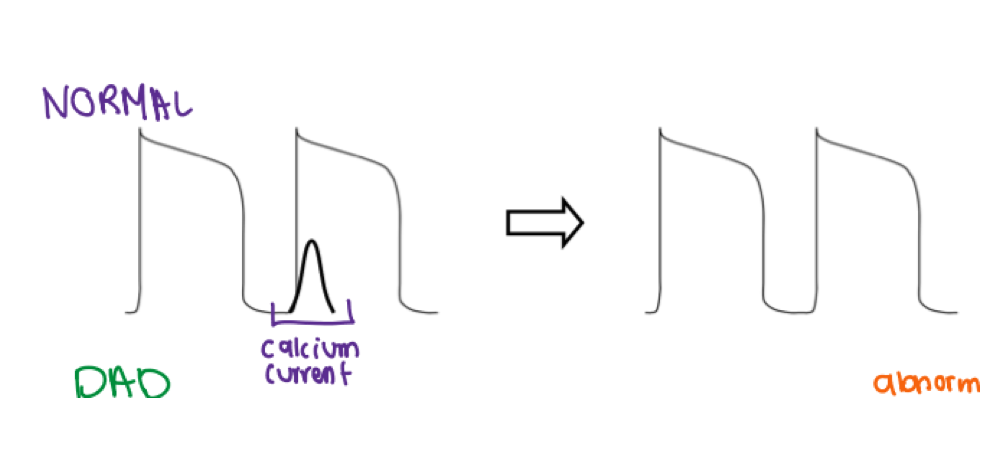
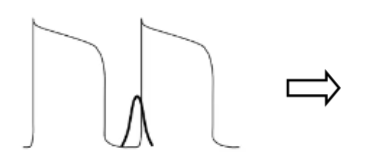
what does this initial action potential represent and what would the outcome be?
This is an abnormal action potential
calcium current is occurring too early
leading to intracellular calcium overload
This will result in DAD
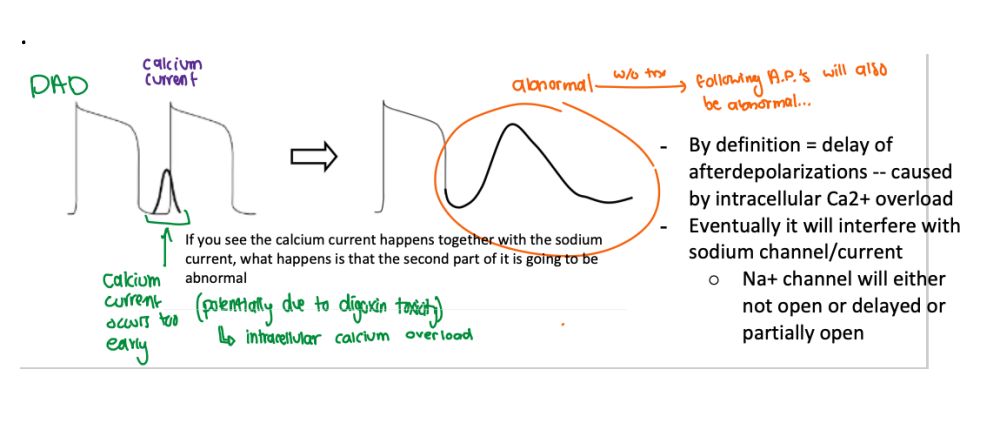
what occurs if DAD is not treated?
the following action potential will also be abnormal
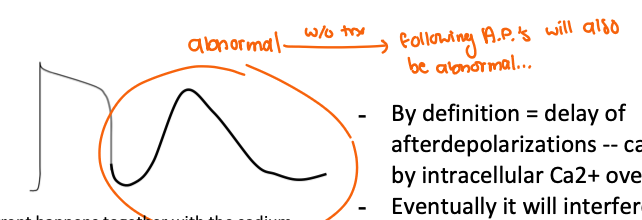
describe how DAD affects Na+ channel?
By definition = delay of afterdepolarizations -- caused by intracellular Ca2+ overload
Eventually it will interfere with sodium channel/current
Na+ channel will either not open or delayed or partially open
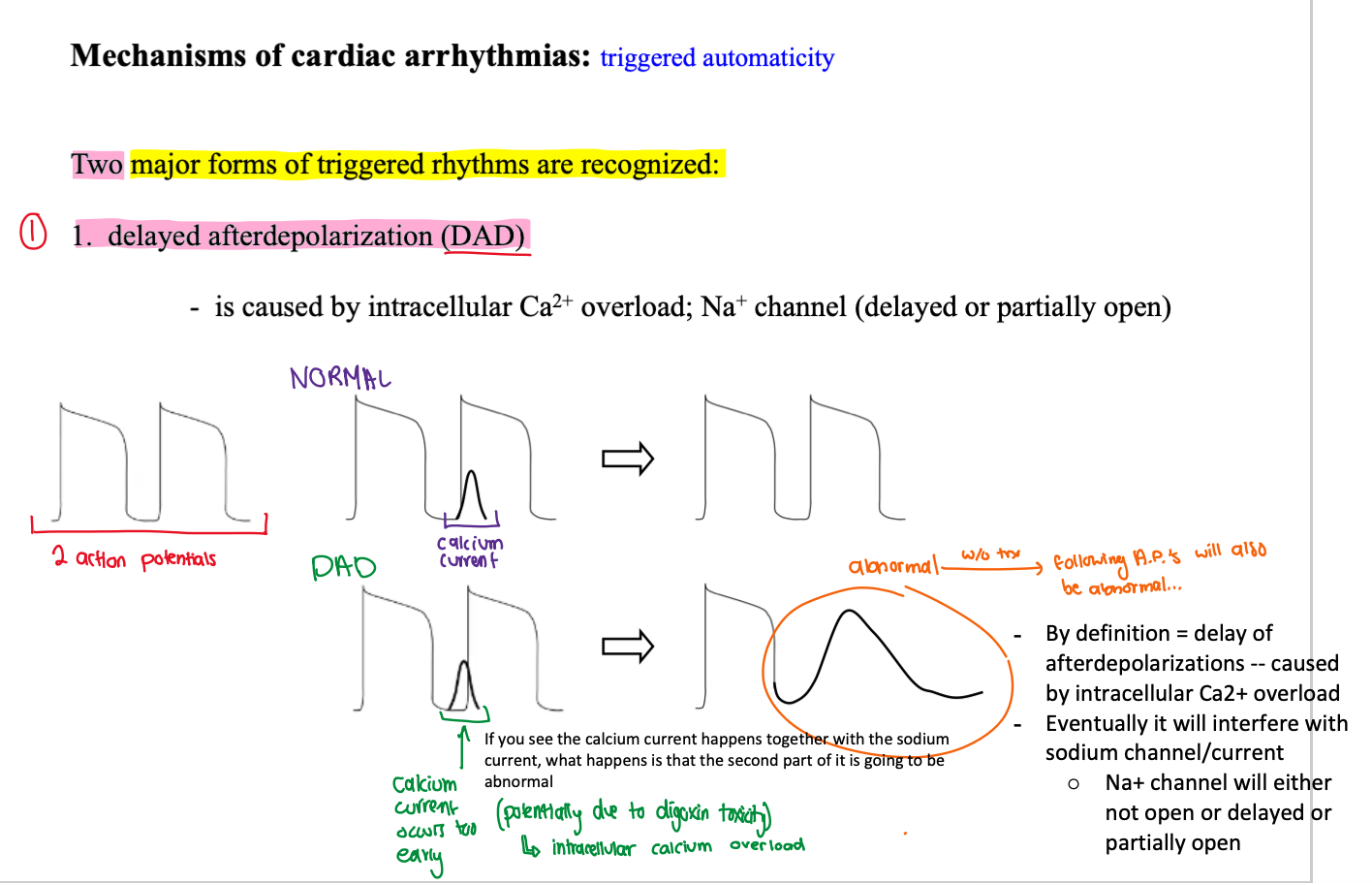
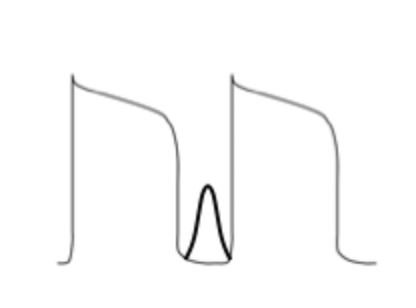
what is the current in black?
calcium current
we usually don’t see it as its only for contractions
as it does not affect depolarization or repolarization
it’s drawn in to demonstrate the early calcium current ==> DAD
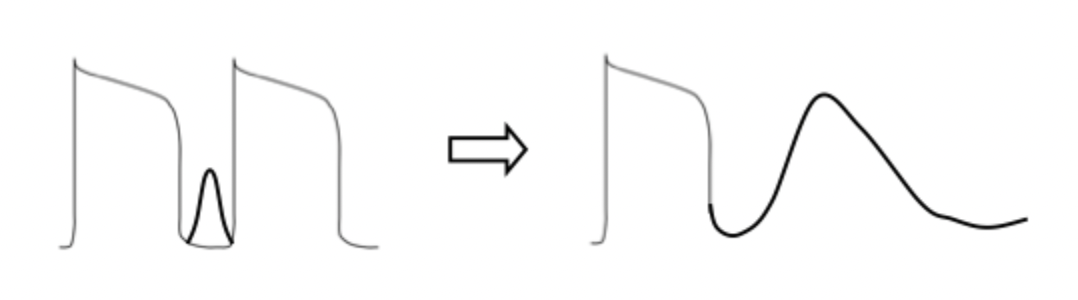
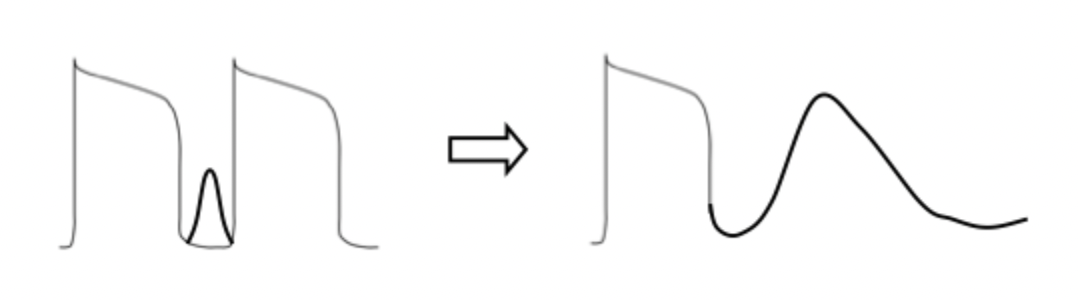
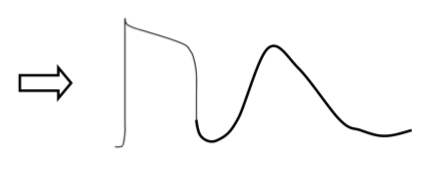
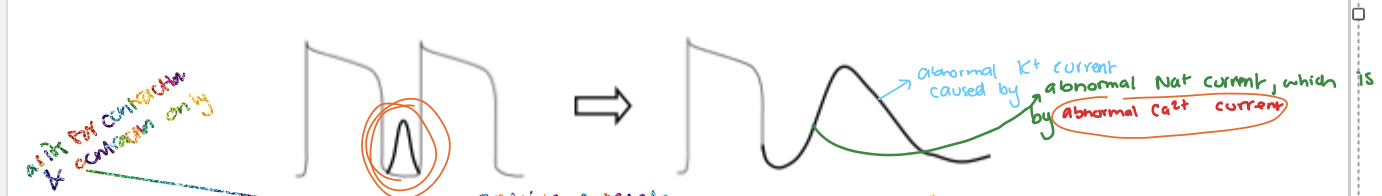
describe what is occurring in this diagram? focus on the currents
DAD — Abnormal 2nd action potential:
Abnormal (early) Ca2+ current ==> Abnormal Na+ current ==> Abnormal K+ current
what are the main treatments for DAD?
(1) Ca2+ blocker
(2) Na+ blocker

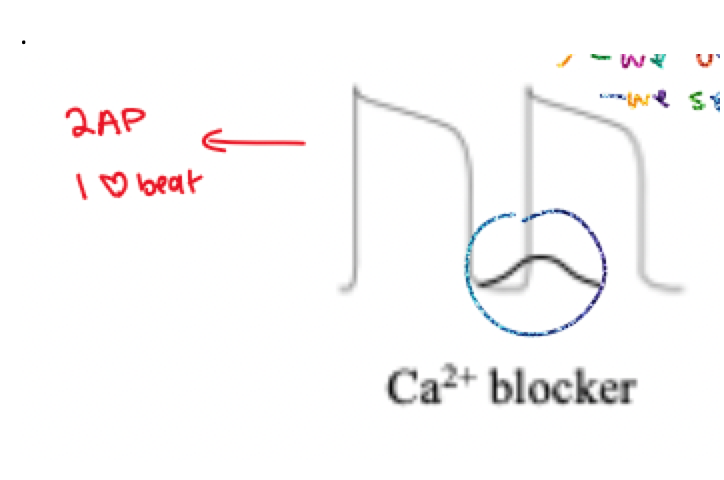
(1) what does this diagram represent?
(2) how many action potential are present?
(3) how many heart beats are present?
(1) DAD treatment using a Ca2+ blocker
(2) 2 AP
(3) 1 beat.
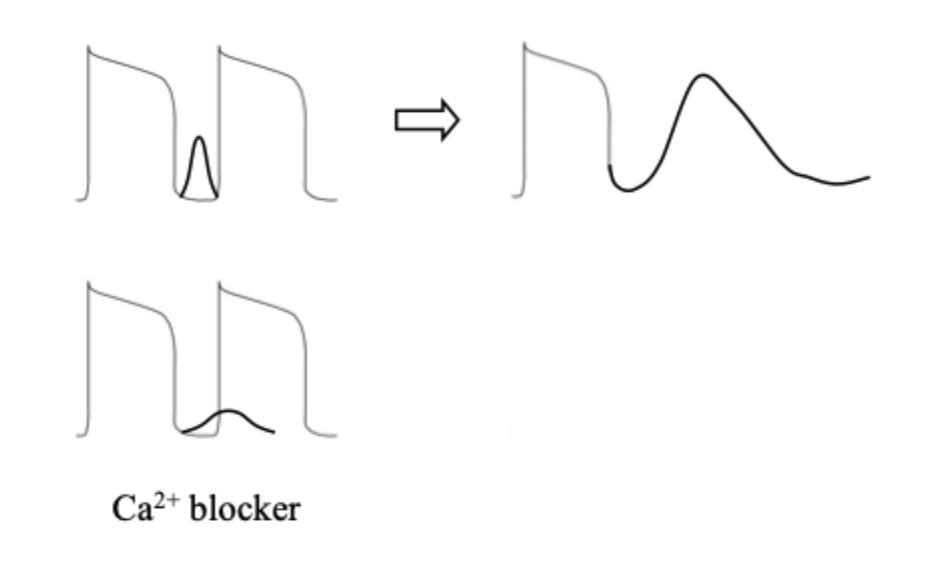
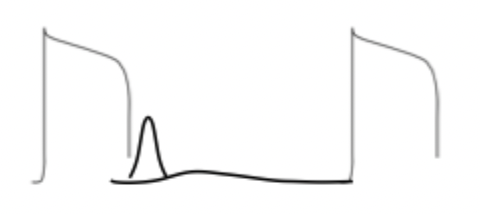
(1) what does this diagram represent?
(2) how many action potential are present?
(3) how many heart beats are present?
(1) DAD treatment using a Na+ blocker
(2) 2 AP
(3) 3 beats.
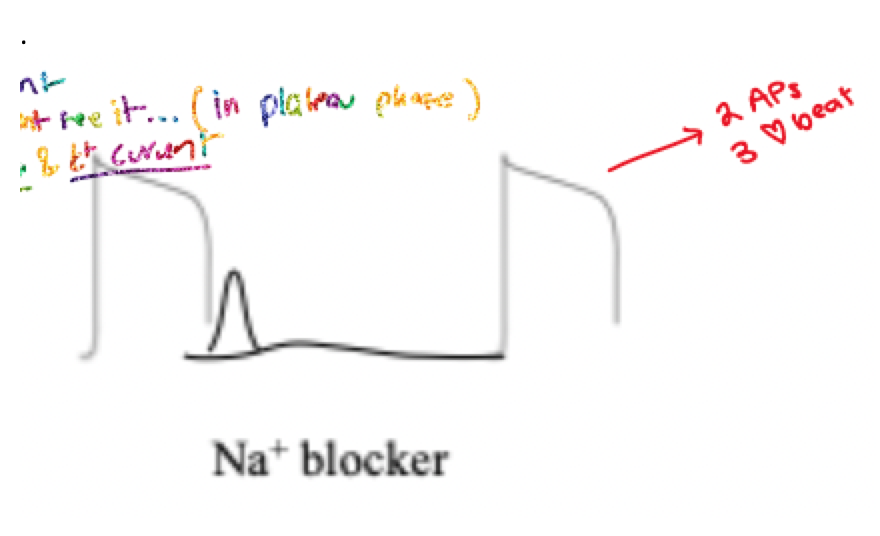
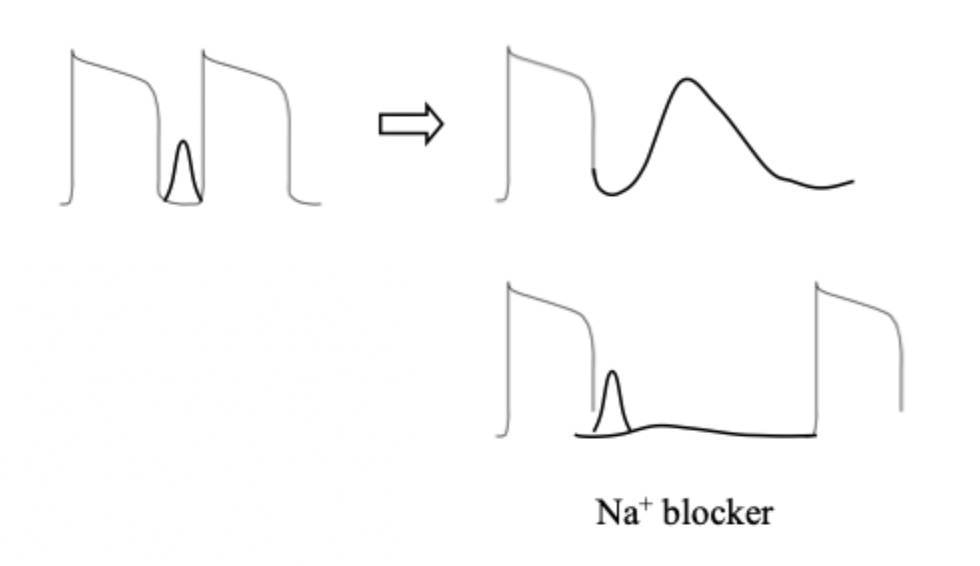
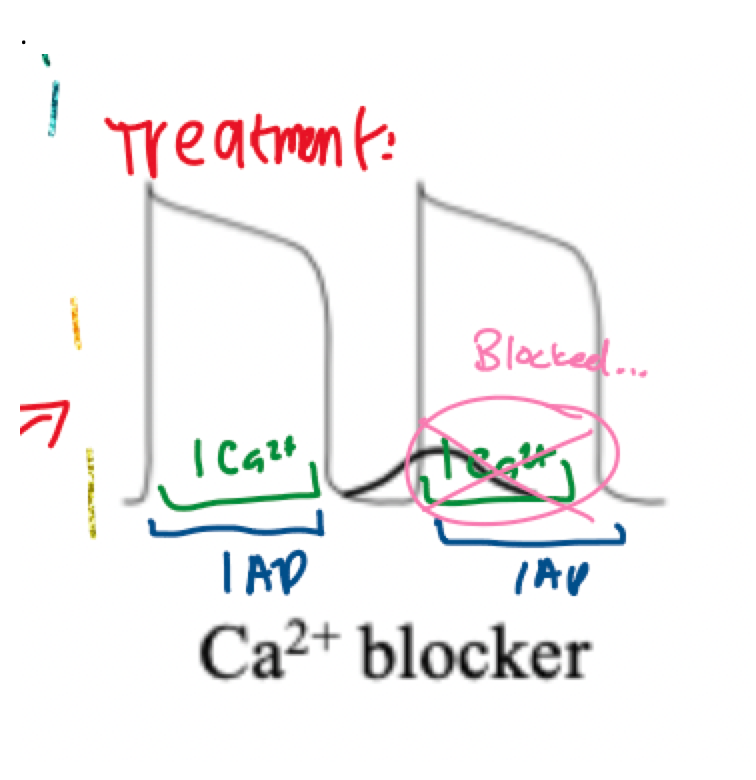
describe the function of a Ca2+ blocker on DAD
Ca2+ blocker would depress/block the Ca2+ current ==> block heart beat ==> skip in next incoming action potential ==> action potential returns normal
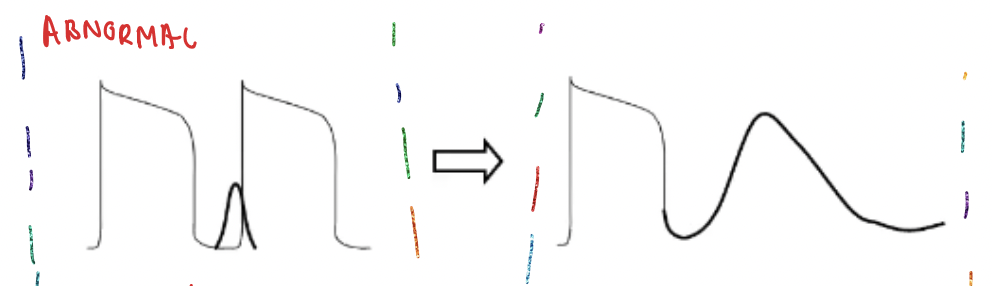
describe the function of a Na+ blocker on DAD
Na⁺ blocker delays sodium channel opening after an action potential → prevents immediate depolarization → does not interfere with calcium currents → reduces the chance of a second triggered action potential → may result in skipping one action potential → helps suppress DAD-related arrhythmias..

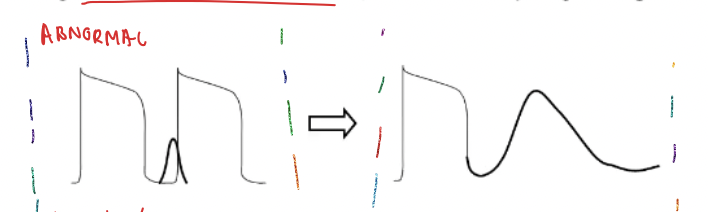
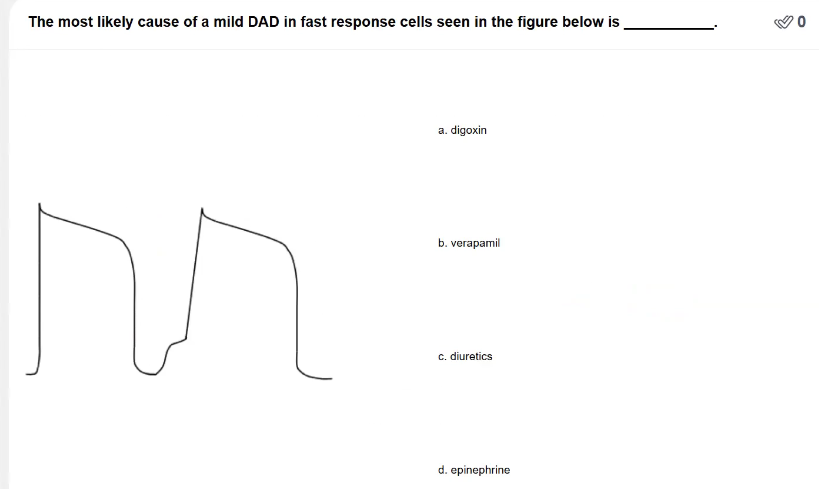
POLLEV: The most likely cause of a mild DAD in fast response cells seen in the figure below is _____.
Digoxin
DAD is caused by intracellular Ca2+ overload
Digoxin causes increased intracellular Ca2+ myocytes
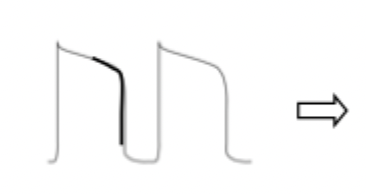
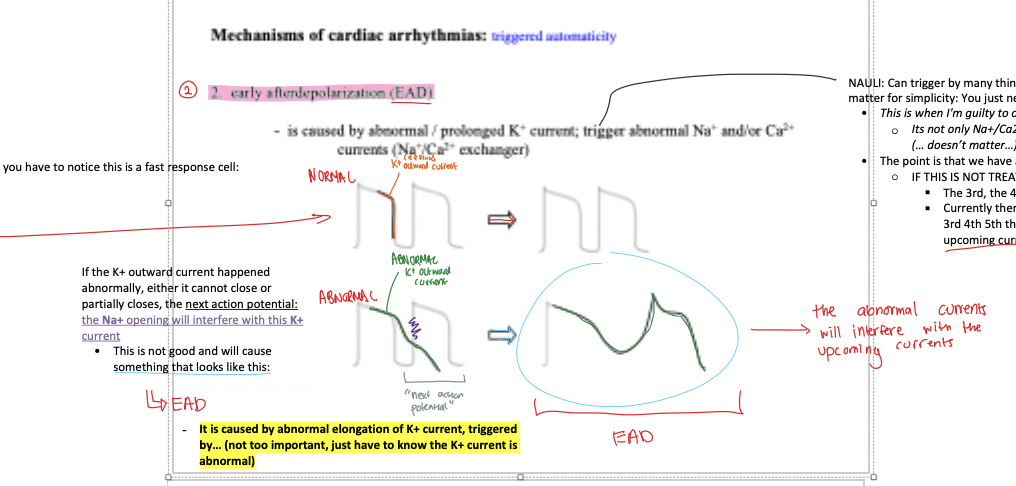
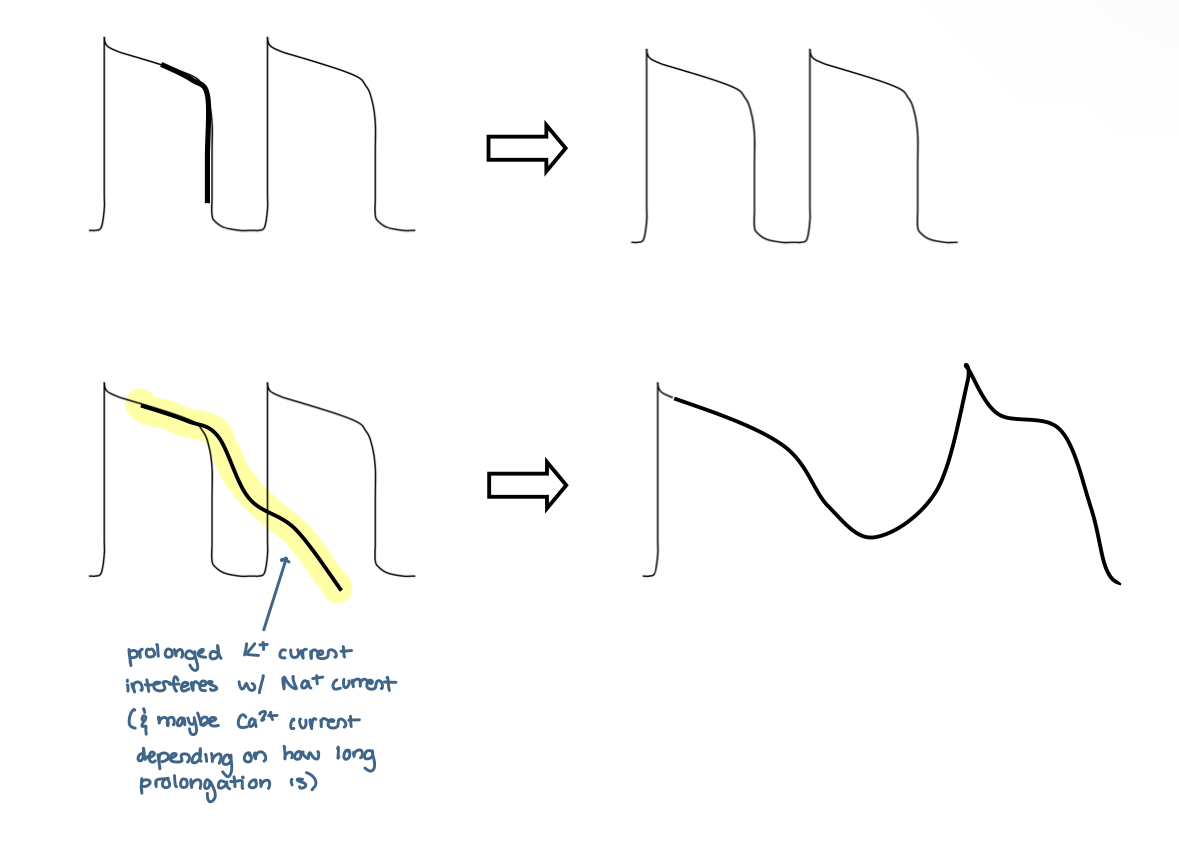
what does the bold line in this diagram represent? and what is the result?
normal K+ outward current ==> normal action potential
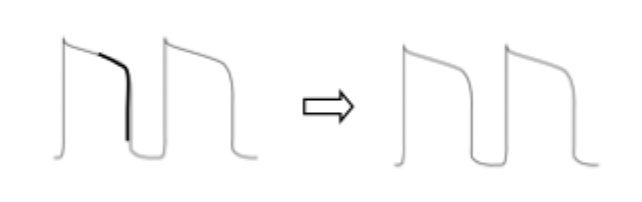
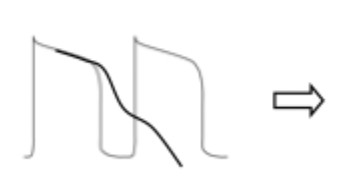
would this diagram lead to a normal or abnormal action potential?
ABNORMAL
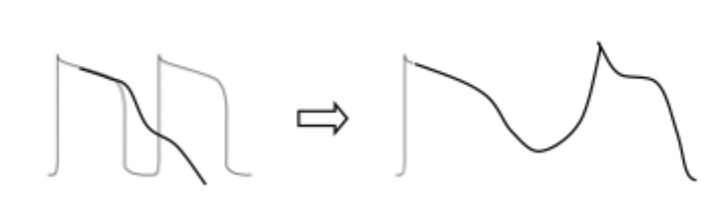
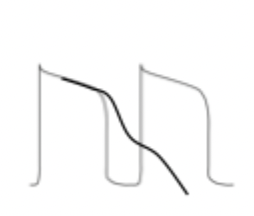
what type of arrhythmia does this action potential result in?
EAD
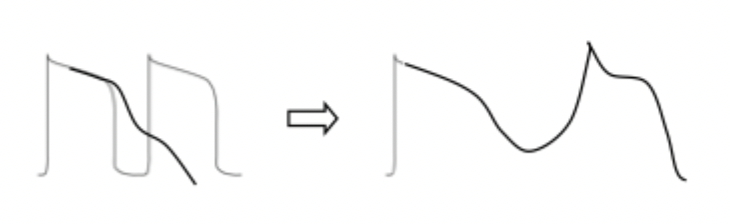
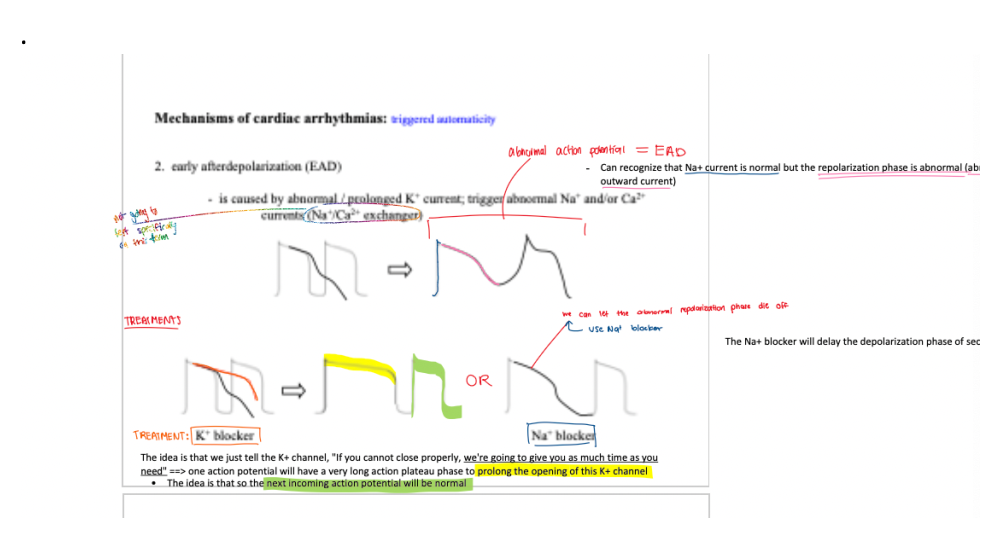
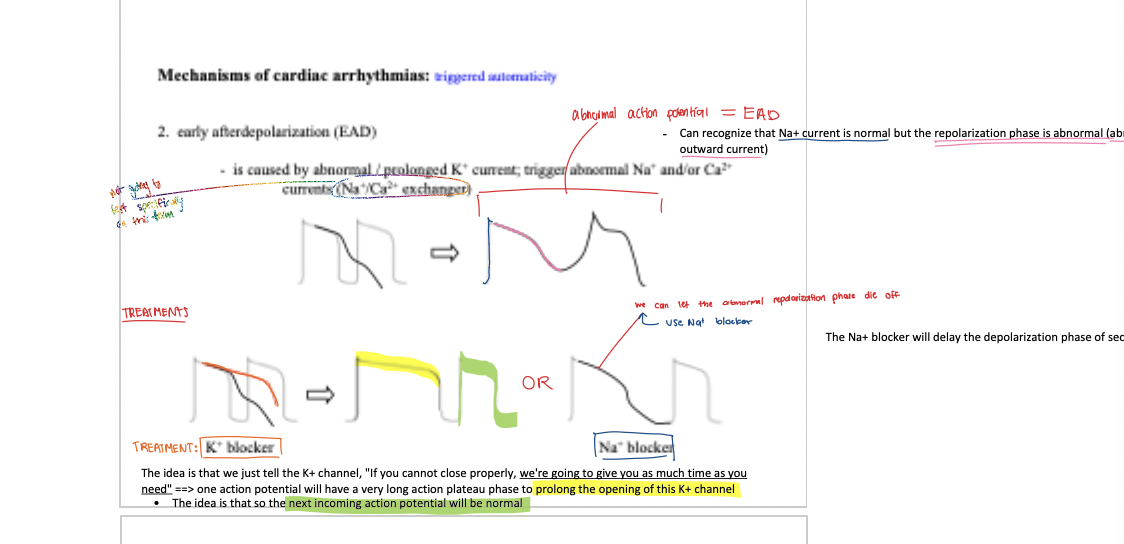
what is EAD caused by? what does it result in?
caused by abnormal/prolonged K+ current ==> triggers abnormal Na+ AND / OR Ca2+ currents
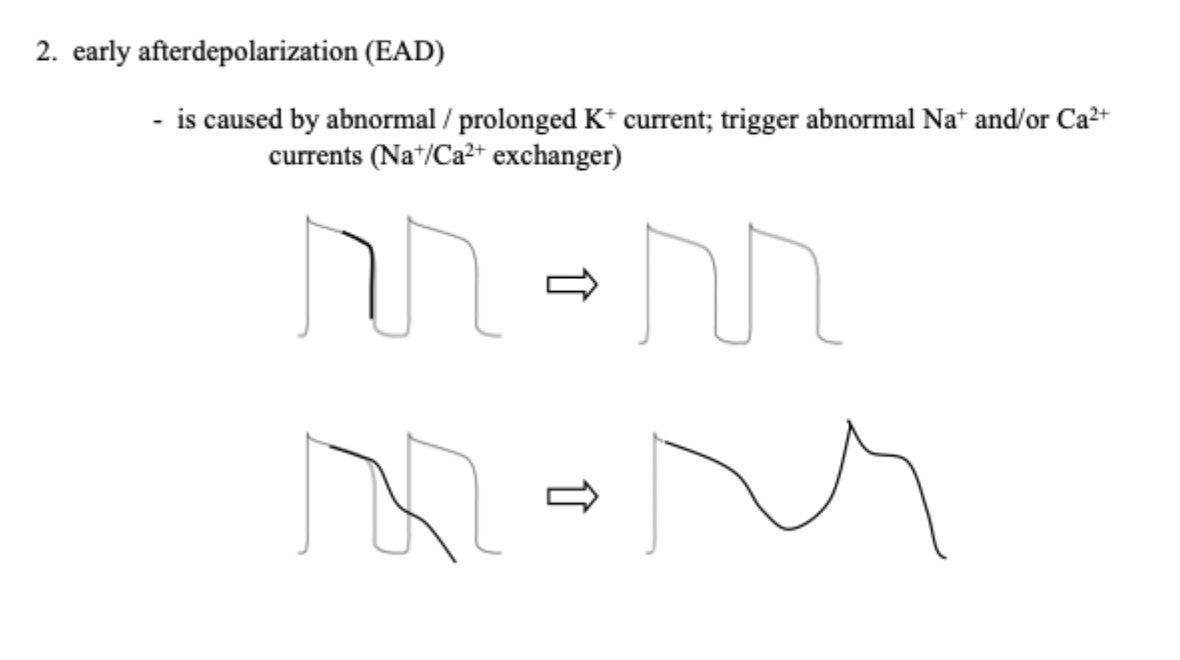
describe EAD
If the K+ outward current happened abnormally, either it cannot close or partially closes, the next action potential: the Na+ opening will interfere with this K+ current

==> will result in abnormal AP = EAD
// just have to know the K+ current is abnormal

what currents are normal in EAD? how about abnormal?.
COME BACK TO THIS .
OVERALL = ABNORAL AP
but…
normal:
(1) Na+ current
(2)
COME BACK TO THIS .
early after depolarization (EAD)
caused by abnormal/prolonged K+ current; trigger abnormal Na+ and/ or Ca2+ currents (Na+/Ca2+ exchanger)
treatment for EAD
K+ blocker, Na+ blocker, B-blocker
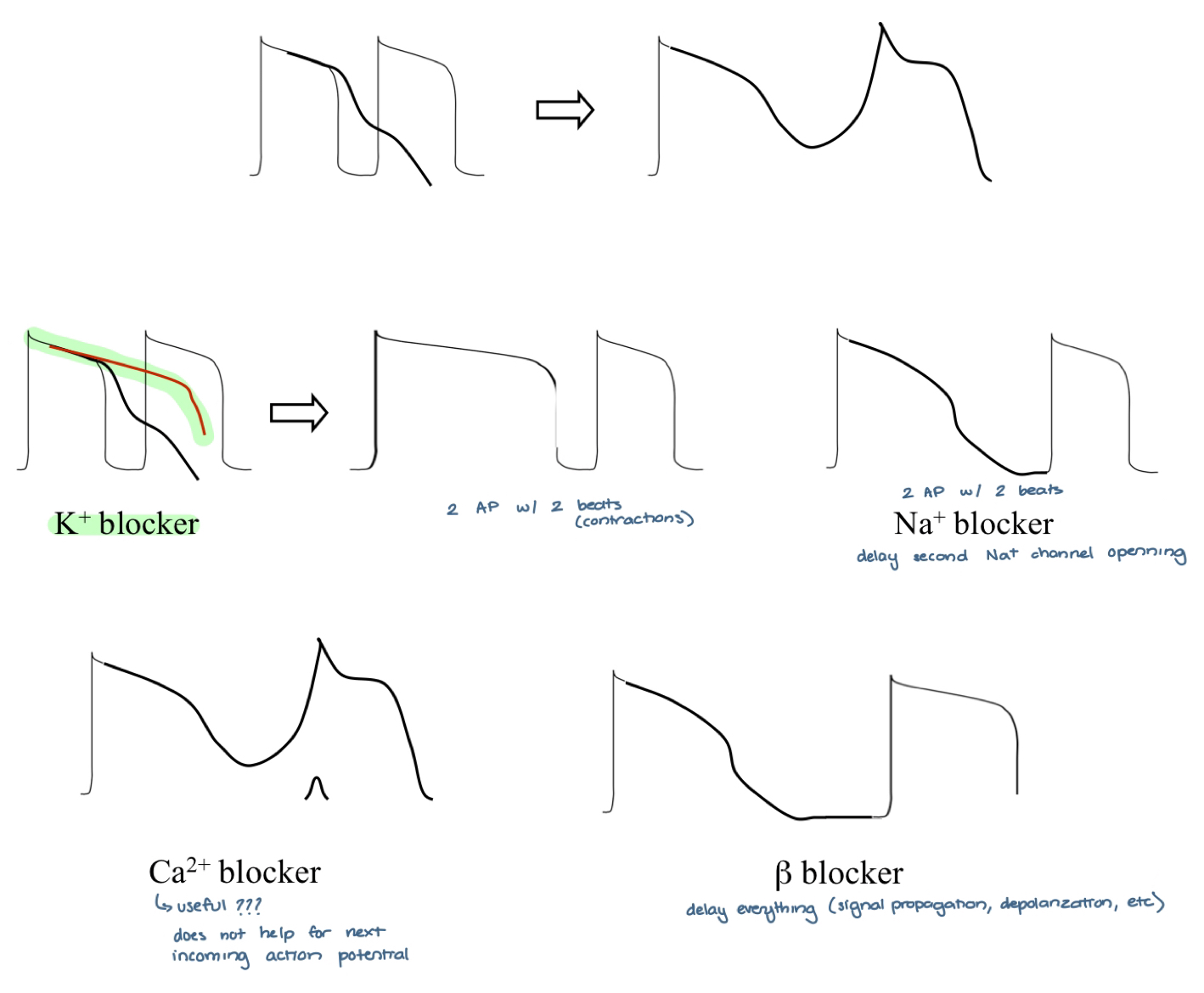
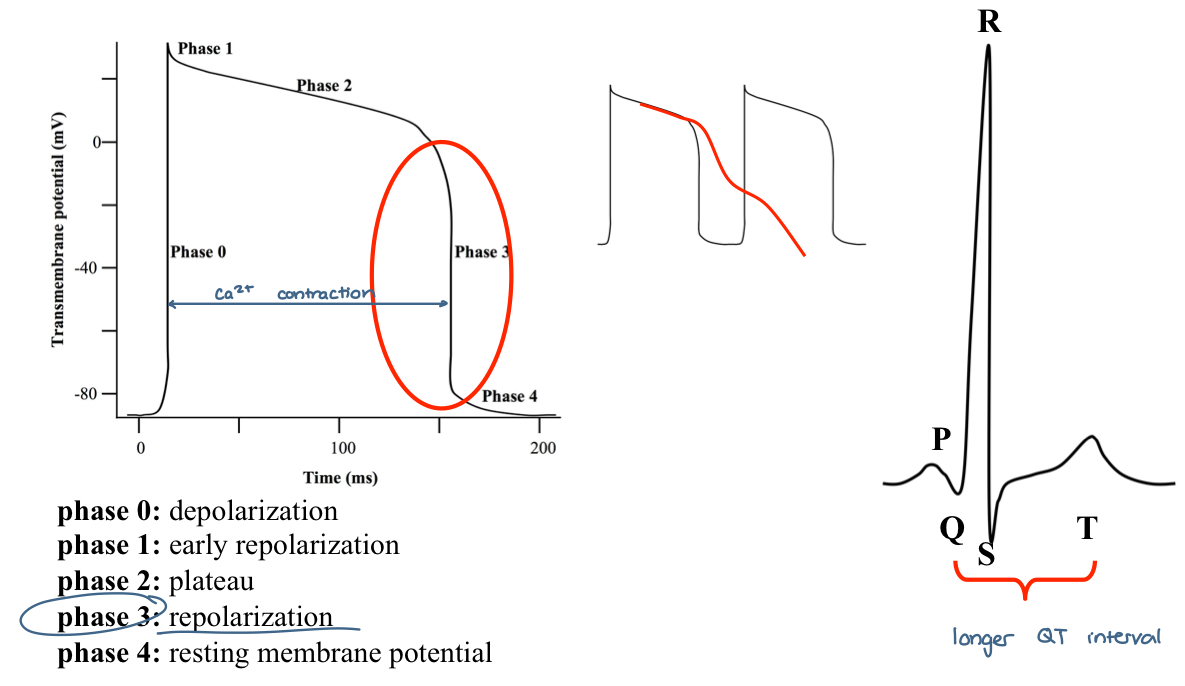
early after depolarization (EAD) — side effect
when phase 3 repolarization is prolonged, polymorphic ventricular tachycardia with a long QT interval may ocur
this is known as the tornadoes de pointes syndrome
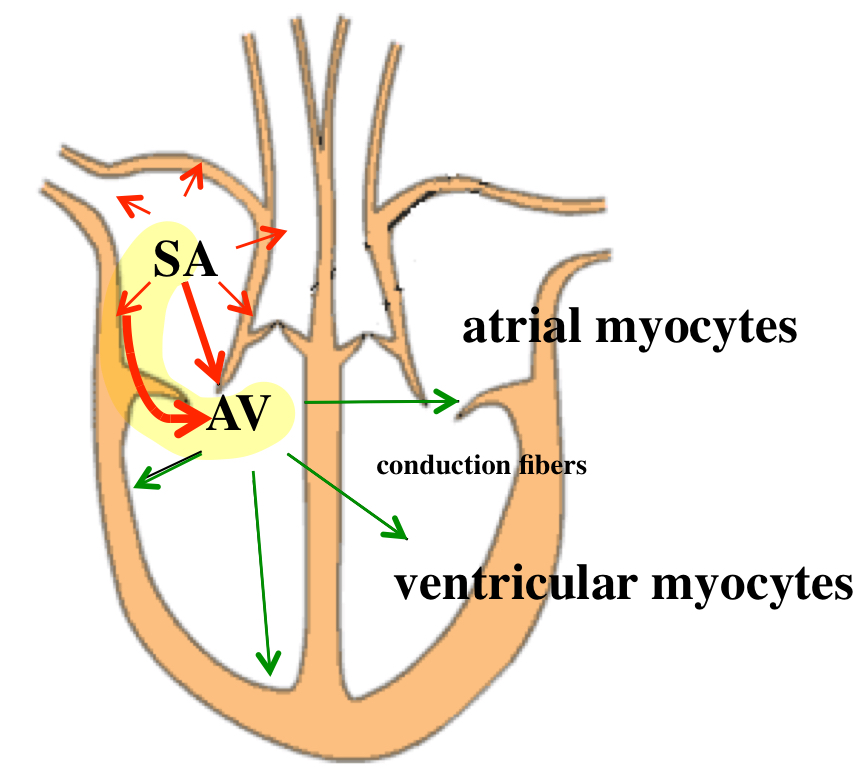
anatomically defined re-entry
≥ 2 addition pathways (more than one pathway)
anatomically defined re-entry — Wolff-Parkinson-White
additional pathway to AV node —> send 2 pulses instead of 1 to the rest of the heart
the normal AV node pathway, consist of slow-response tissue
the accessory pathway, consist of fast-response tissue
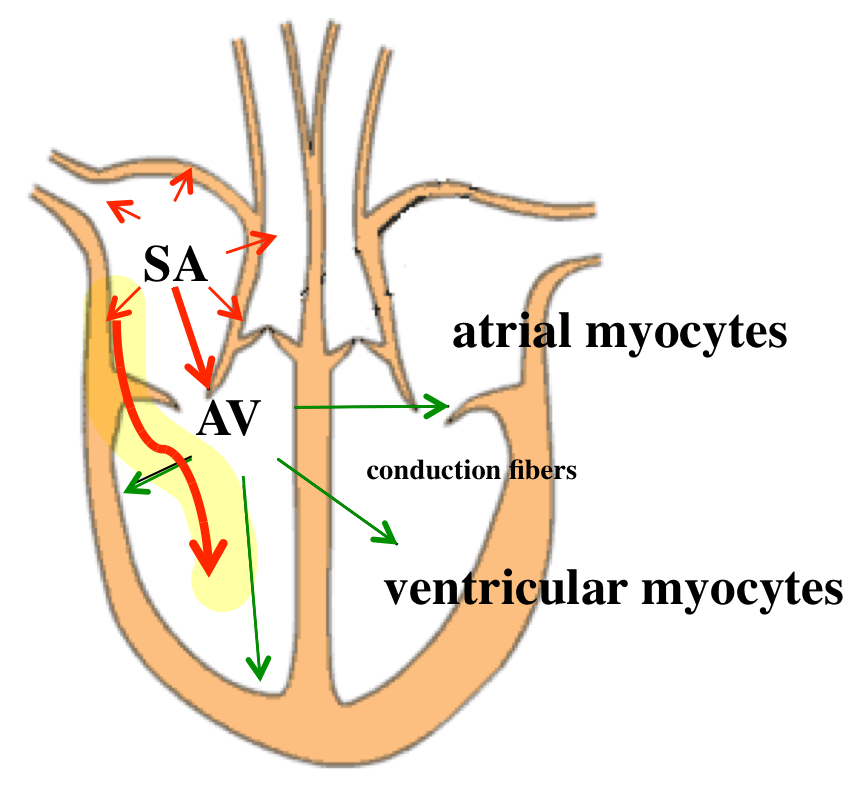
anatomically defined re-entry — premature atrial beat
addition pathway arrives in the atrium
anatomically defined re-entry — premature ventricular beat
addition pathway arrives in the ventricle
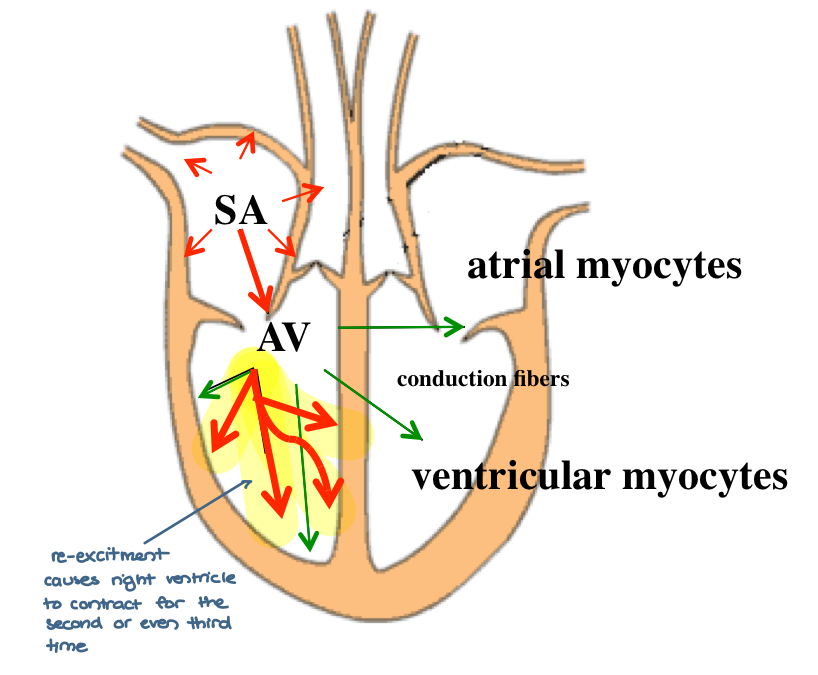
functionally defined re-entry
occurs with the same impulse (re-excites)
post infarction scarring
low conductance
What is a key risk associated with all antiarrhythmic drugs?
They can cause arrhythmias, especially during long-term therapy
Why should the frequency and reproducibility of arrhythmias be established before starting therapy?
To avoid confusing natural variability with drug effects
Should all arrhythmias be treated with antiarrhythmic drugs?
No, not all arrhythmias should be treated
What are the two main goals of antiarrhythmic drug therapy?
(1) Termination of an ongoing arrhythmia (2) Prevention of an arrhythmia