L16: Recreational Drug Use
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
What is the reward pathway of the brain?
- aka the limbic/mesolimbic system (emotional center)- processes rewards & guides behaviors that enhance survival & well being
- main fx: makes individuals repeat survival habits by releasing dopamine, which creates pleasure and reinforces behavior associated with rewards
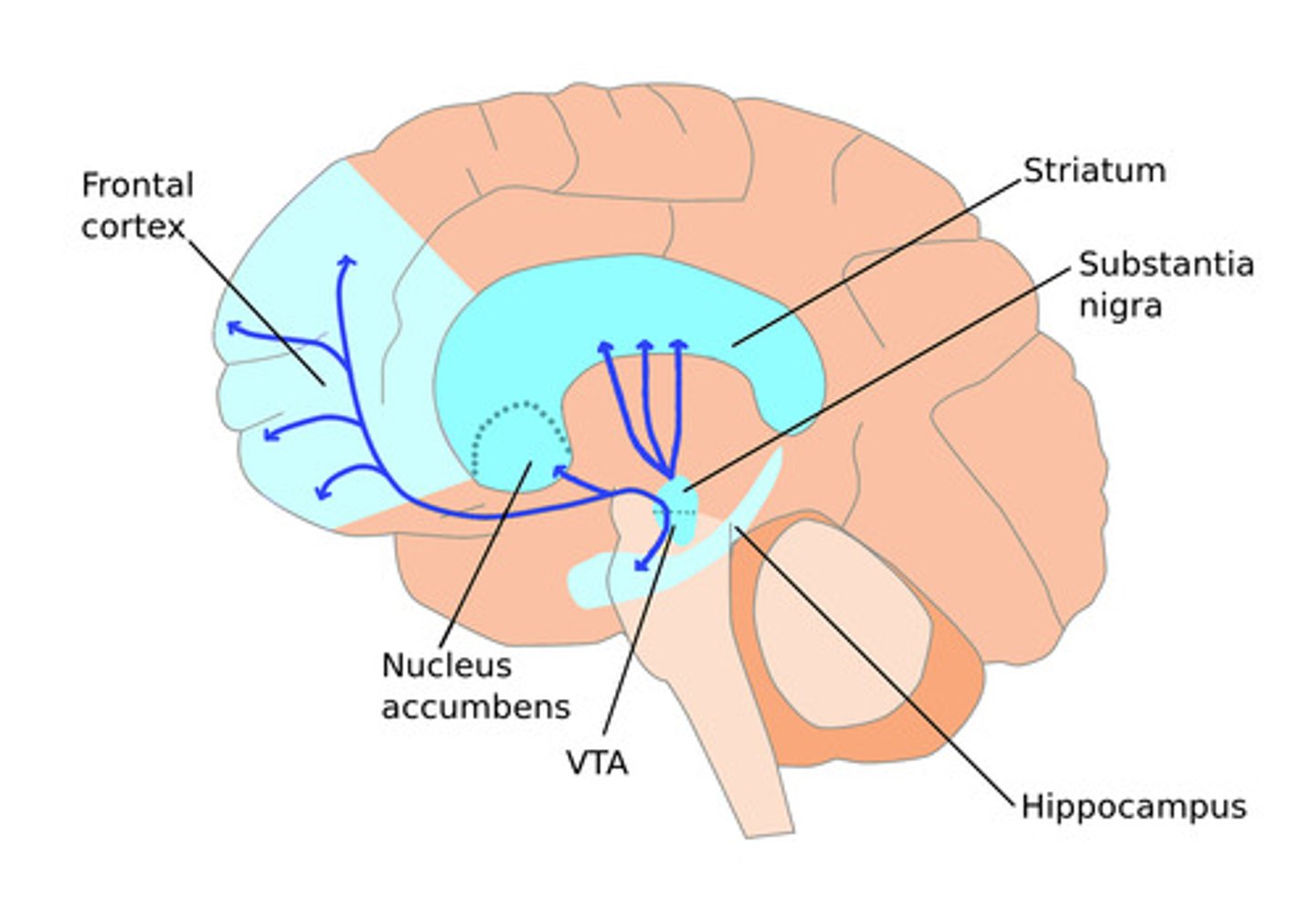
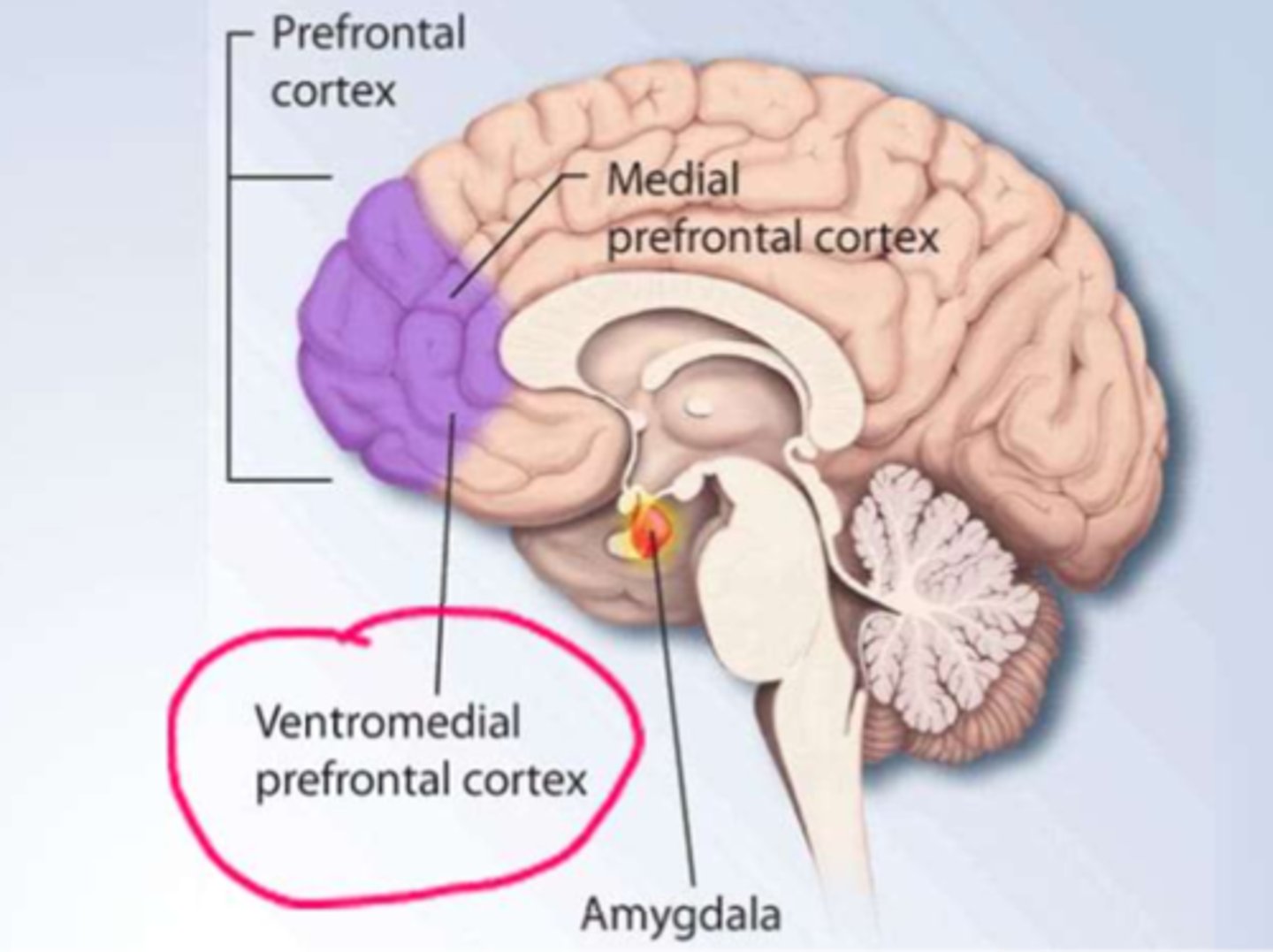
What happens to the reward centre in psychological dependence of drugs (addiction)
- addictive substances increase Dopamine => stimulating the Reward pathway (and therefor addictive behaviour)
- 'addictive personalities' have: decreased activity in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex => leading to decreased impulse control (giving into the addiction over & over)
*! addiction is a disease (must be aware of this, however we cannot deny tx d/t it.
What are the ABCDE's of overdose
Airway - patency!!!
Breathing - oxygenation & ventilation
Circulation - organ perfusion (CO, BP)
Disability - assess for dysfunction & treat as needed (eg. CNS, bradypnea, arrhythmias)
Exposure: identify the drug/substance; initiate tx

How would we tx certain disability that is OD induced
- seizures - Diazepam
- hypertension - Nipride
- bradypnea - intubate
How would we tx exposure to a drug causing OD
Tx: ADME, algorithms, toxidromes & labs (serum, urine)
- supportive tx until the cause/substance is known
- how may we eliminate it? (ADME => activated charcoal?)

What drugs are considered 'downers'
- Opioids
- Ketamine, PCP, mushrooms
- Benzodiazepines (eg. Xanax, Valium)
- sedatory, decrease excitatory NTs in the CNS
What drugs are considered 'mixed'
- Alcohol
- Cannabinoids
- Nicotine

What drugs are considered 'uppers'
- Cocaine
- Amphetamines
- LSD
- Ecstasy

What is the fx of 'downer' drugs (opioids, ketamine, PCP, mushroom, benzodiazepines)
- Relaxation (euphoria) "chill zone"
- Altered mood
- Uninhibited behavior

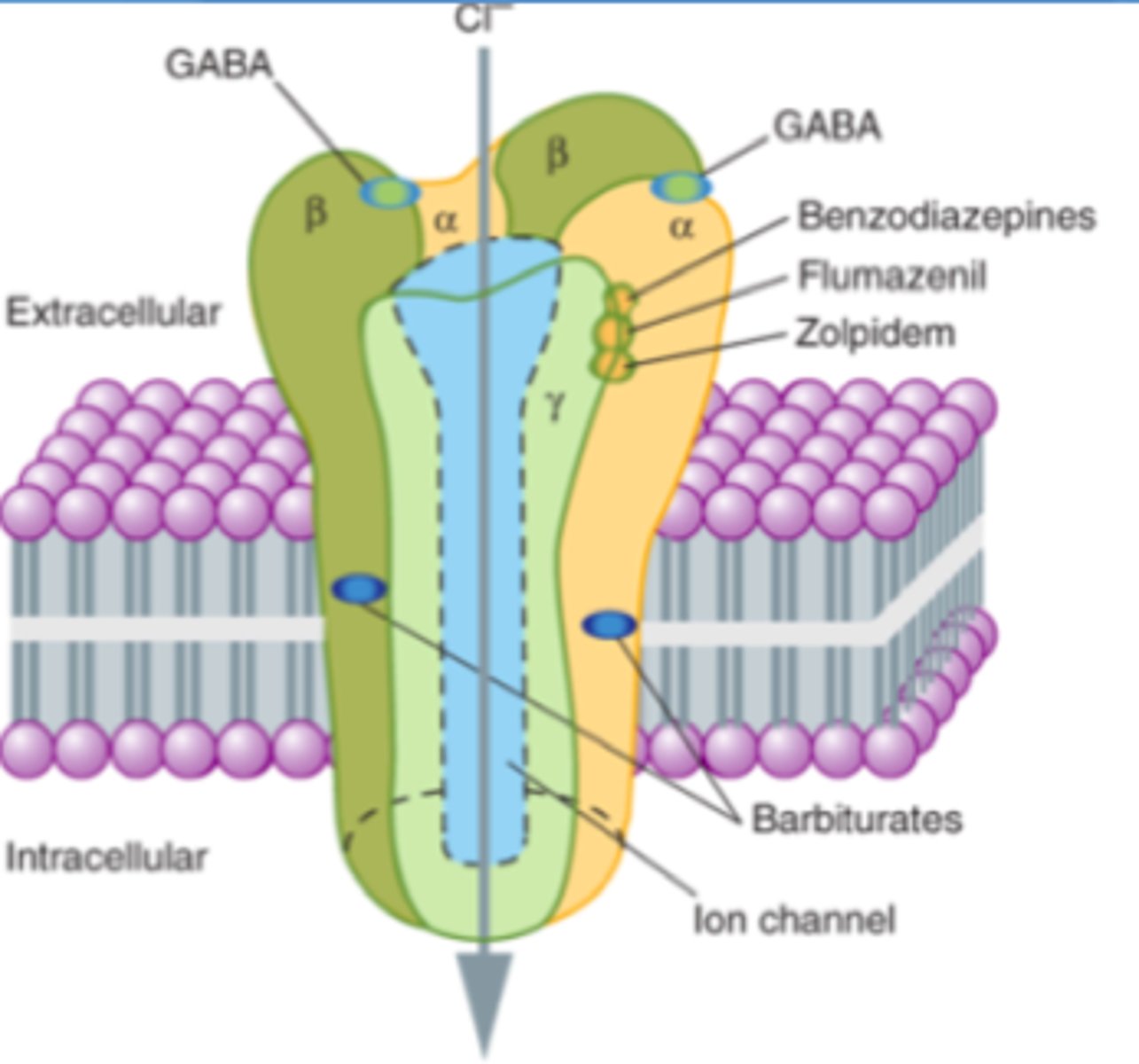
What are the overall pharmacodynamics of 'downer' drugs
- inhibit excitatory NTs such as glutamate & substance P
- agonize inhibitory NTs like: GABA
- stimulate mood via: Serotonin & Dopamine (reward pathway) release
What can high doses of 'downers' lead to
with increasing dose: depressed LOC & VS

What is the therapeutic use of opioids?
substance P inhibition = analgesia

What are the most common opioid drugs to be abused?
- Fentanyl, Morphine, Oxycodone, Codeine
- Heroin, Opium
- Buprenorphine (partial agonist)
What are the recreational use dangers of opioids?
- addiction
- toxicity: potency, affinity to opioid receptors (drug dependant), dosage
- neuromodulation: lasting alterations in emotional & cognitive processes

What is meant by neuromodulation in rec drug use
- altering normal fx & judgement
- behaviour change & increased dependency only for drug

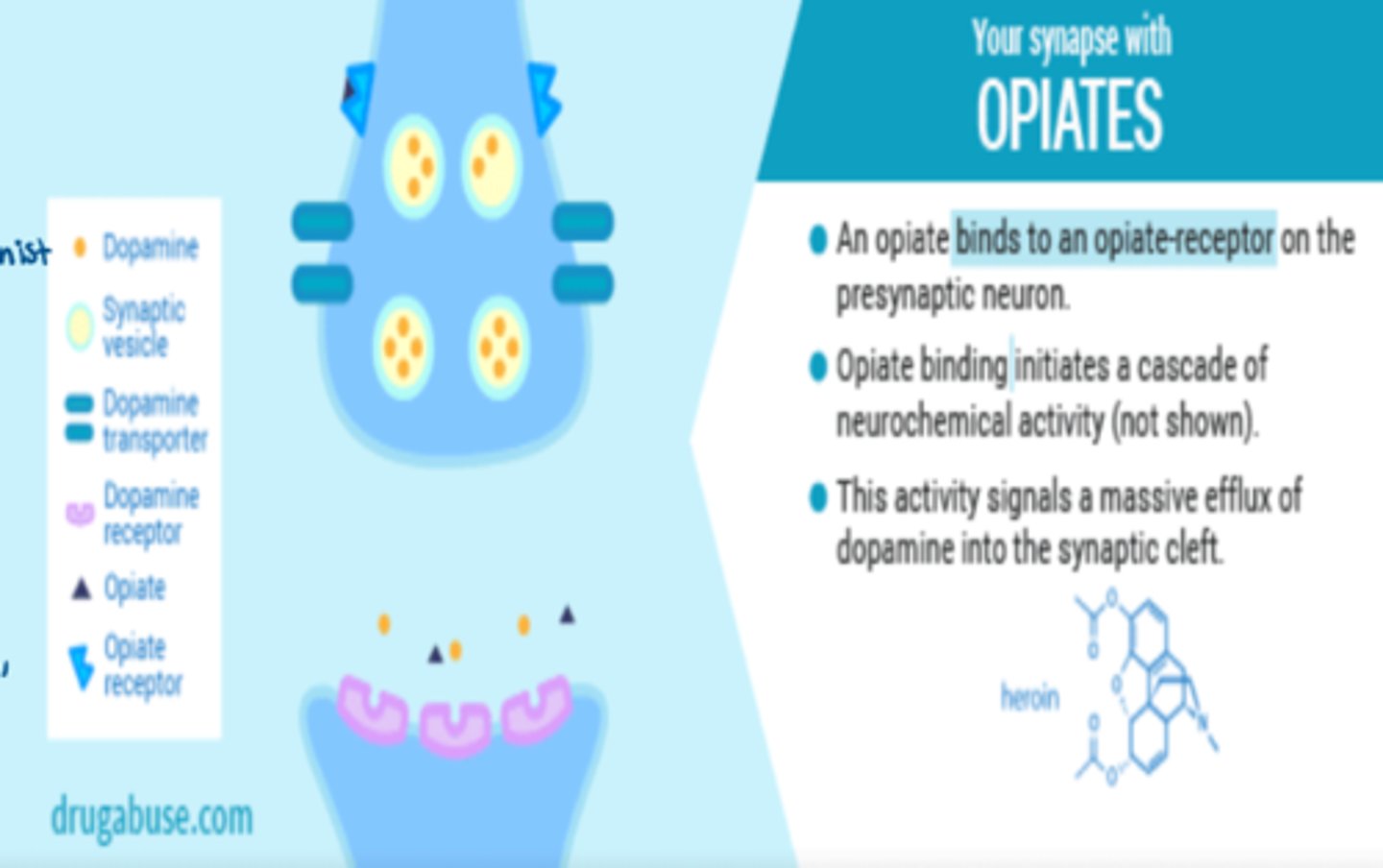
What is the synaptic function of opioid binding
- opioid binds to opioid receptors at presynaptic neuron
- opioid binding initiates cascade of neurochemical activity
- this activity signals a massive efflux of dopamine into the synaptic cleft
What is 'lean'
- opioid downer
- combo: Codeine + soda/hard candy

What are the morphine vs fentanyl dosage IV levels (for potency reference)
- morphine IV: 2-10 milligrams/dose
- fentanyl IV: 25-50 MICROGRAMS/dose (about 1000x more potent than morphine!)

What is fentanyl
- opioid downer
- extremely high potency !!! (more potent than any other drug)
- kills more people than any other opioid, d/t easy OD => 1 salt crystal = OD (measured to the millionth of a gram)
- risk of death or vegetative state of even a laced drug has it
- laced into other drugs (cheap!) (may be laced into both downers or uppers)
- routes: PO, snorted, IV, SL (blotter paper), patch
Why is there fear due to affinity with fentanyl
- fear is that it may be more potent & higher affinity than narcan
- risk of lack of reversal via narcan, may require continuous IV of narcan w/ multiple doses to prevent this.
What is heroin
- opioid downer
- highly lipophilic & potent, crosses BBB rapidly
- routes: IV (usually injected), inhaled, snorted, smoked
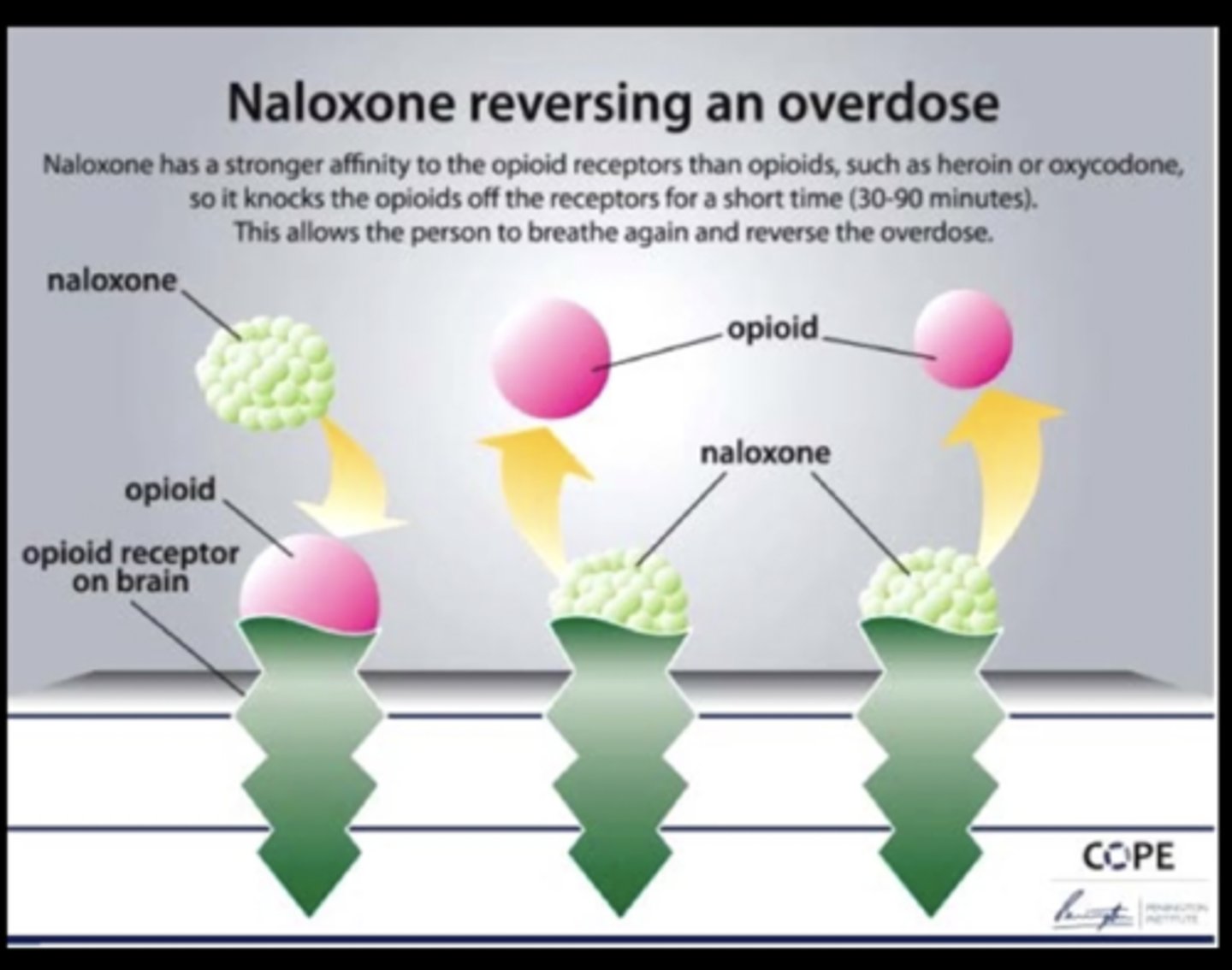
How do we treat opioid ODs via pharmacological tx
1) Narcan - gold standard
2) Suboxone => combo: narcan + buponephrine (wean & reversal at the same time)
How do we treat opioid addiction via pharmacological tx
*Weaning protocol
- Buprenorphine (Partial agonist)
- Methadone (weaker opioid used for titration)
How do we treat opioid addiction via supportive tx
- Counselling, CBT
- Support group meetings
- Rehabilitation centers (may use withdrawal symptom management (eg. benzodiazepines)) => lots of addicts are scared of withdrawal symptoms and end up trying to smuggle drugs in
Which PKPD information is pertinent with Narcan tx of opioid OD
- Narcan's t1/2 is shorter than opioid usually
- may require continuous IV infusion of Narcan to match dose until all of it is out of the system
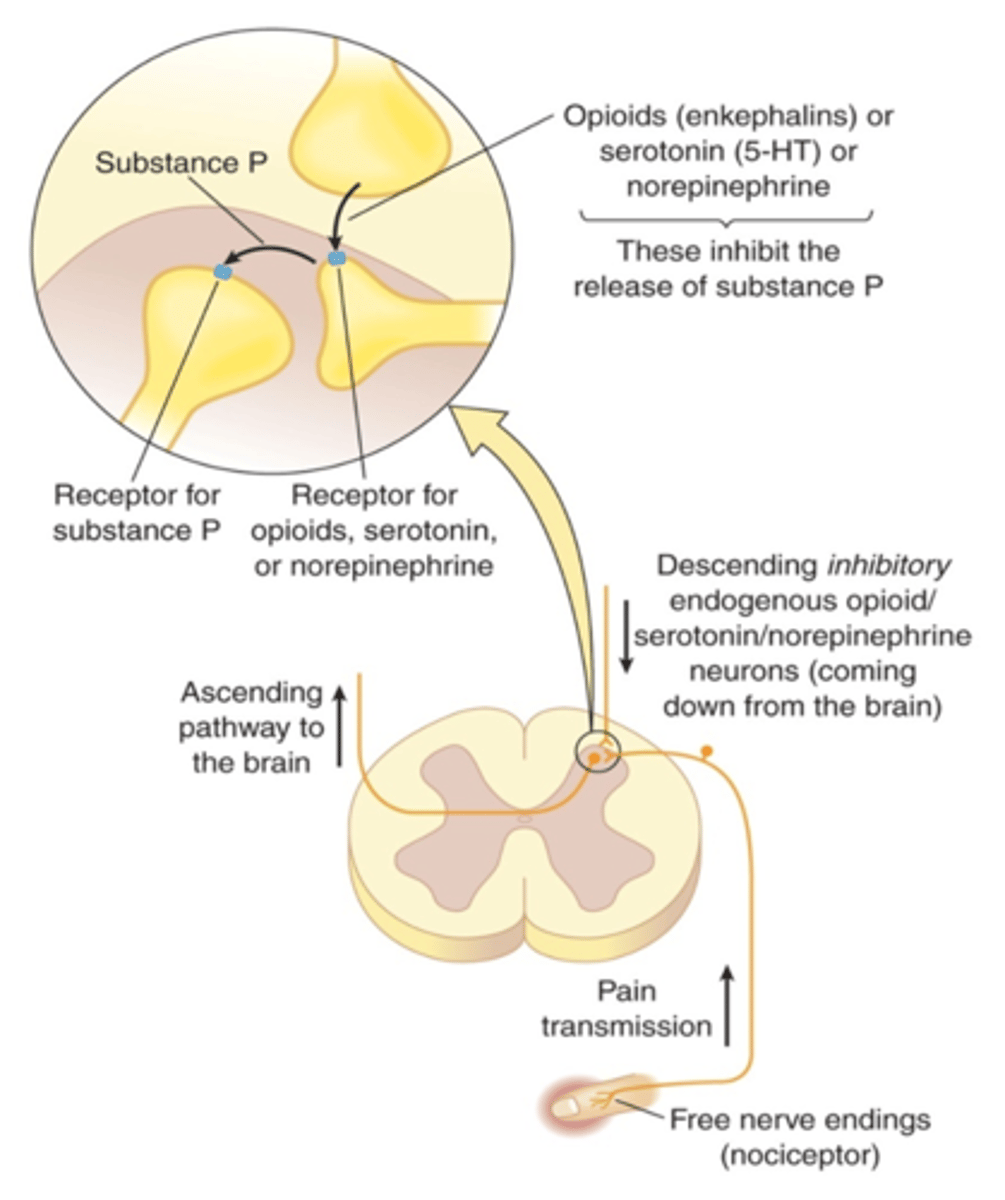
What are the dynamics of opioids
- dynamics: opioid (mu, kappa, delta) receptor agonist
- inhibiting substance P
- release more drug = more receptors bound
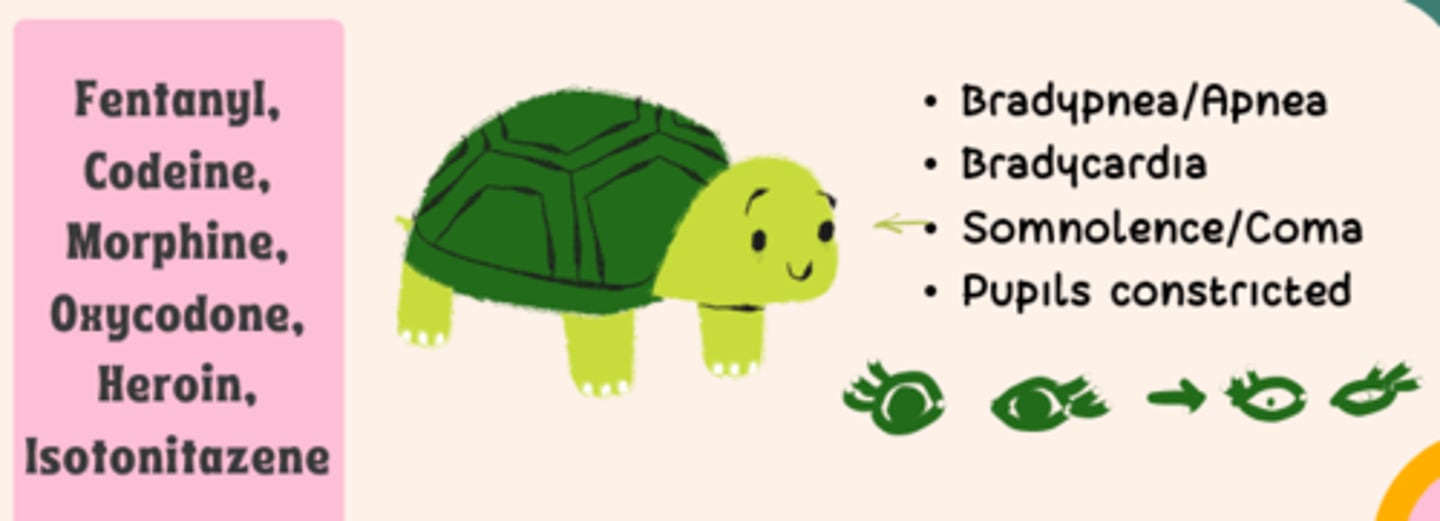
What are the side effects of opioids ("Toni the Turtle Can't Tinkle)
- CNS - decreased LOC
- bradypnea/apnea
- hypotension (peripheral vasodilation)
- pruritus
- nausea (d/t substance P binding in CTZ)
- constipation
- urinary retention (d/t mu receptor agonism)
- pregnancy category D
Why does constipation occur with opioid use & what do we do about it
- d/t mu receptor - decreased peristalsis
=> tx: Laxatives
note: may cause a bowel obstruction or perforation which could even result in a colostomy bag

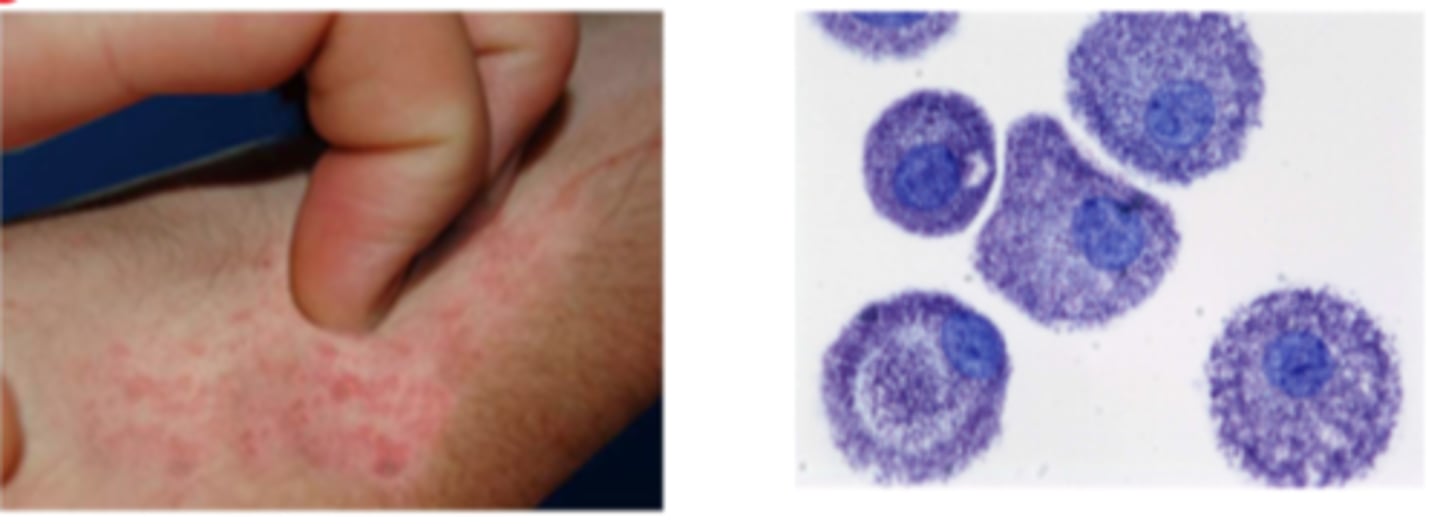
Why does pruritus occur with opioid use & what do we do about it
- d/t mast cell stimulation & histamine release
- patient may scratch skin to a point where wounds form & end up not healing as quick as immunity may also be suppressed
What is ketamine
- downer drug
- sedative hypnotic, dissociative anesthetic (mood changes, amnesia) => date rape drug
- higher doses: sedation, amnesia, respiratory depression
(the higher the dose the higher the sedation)

What is PCP (phencyclidine)
- downer drug, developed to mimic ketamine
- relative of ketamine; higher doses: trance state
What are mushrooms aka "shrooms"
- hallucinogenic, psychedelic downer drug
- ingested orally by eating
- active ingredients: psilocin & psilocybin
- relatively low addiction risk

What are the desired effects of mixed drugs (eg. alcohol, cannabis, nicotine)
- relaxation (euphoria)
- altered mood
- uninhibited behavior

What are the recreational use dangers of mixed effect drugs
- increased Dopamine => addiction?
- Gateway drugs?
- neuromodulation: lasting alterations in emotional & cognitive processes
- Cannabinoids: risk of psychosis (2%) (dose dependent)

What is alcohol (ETOH/ethanol)
- excitatory & inhibitory effect drug
- dose dependent
- stimulates endorphins & dopamine
- increases Serotonin & GABA
- decreases & blocks Glutamate
- stimulates excitement/relaxation => sedation with higher doses
- Often combined with other drugs => DANGEROUS!!!!

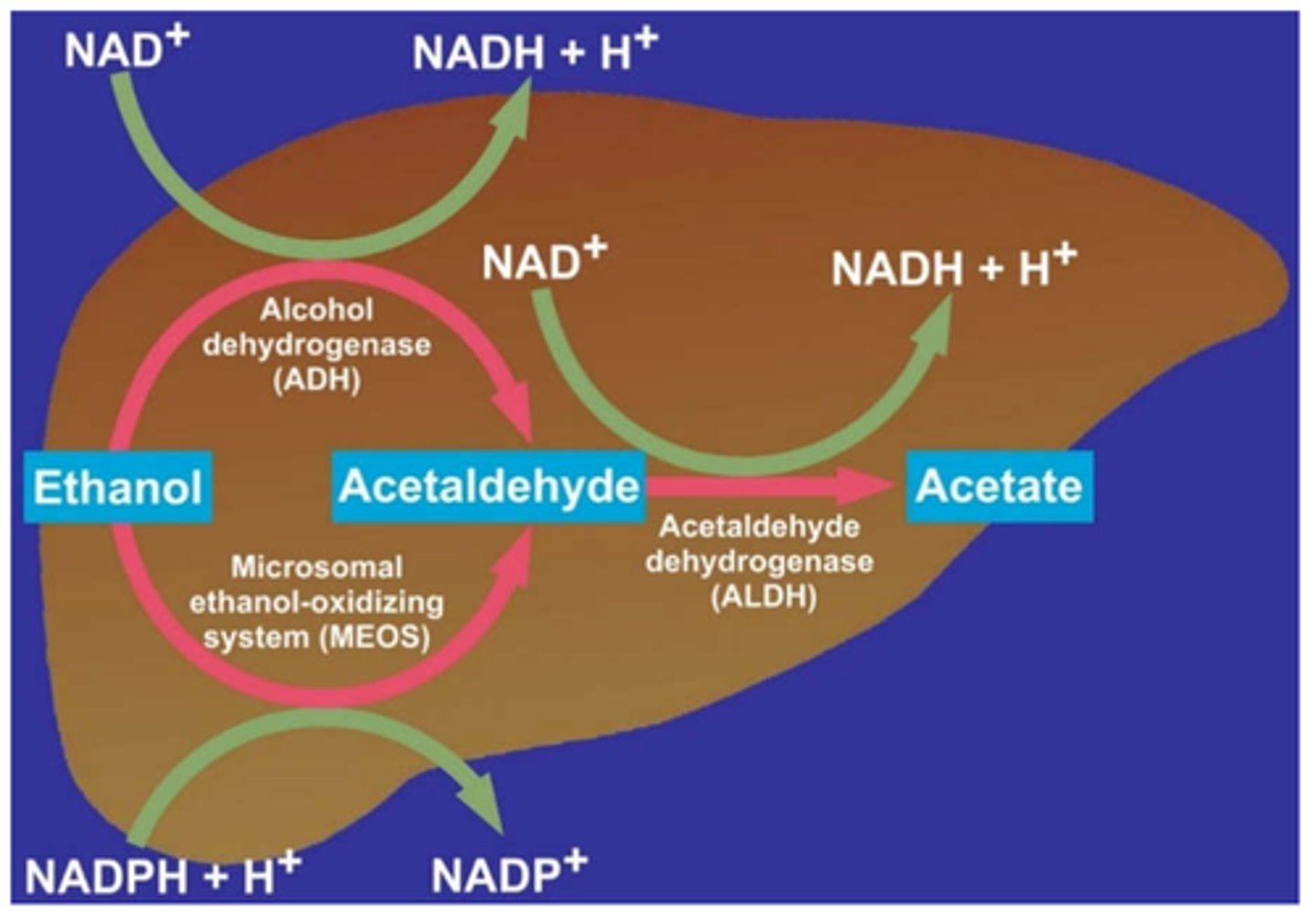
What is the ADME of alcohol
- liver & GI metabolized:
- phase #1: alcohol is 1st pass metabolized via enzyme called alcohol dehydrogenase into acetaldehyde (which creates hangover feelings such as headache or nausea)
- phase #2: active ALDH enzyme metabolizes acetaldehyde into acetate
- inhibits adrenal ADH => causing diuresis (& dehydration, electrolyte imbalances)
- Zero order kinetics
How does tolerance of alcohol work in chronic use (hint: domestic's brain is filled with GABA receptors)
• GABA receptor #s increase, requiring more & more alcohol to create the same effect
• depletes Vitamin B during metabolism
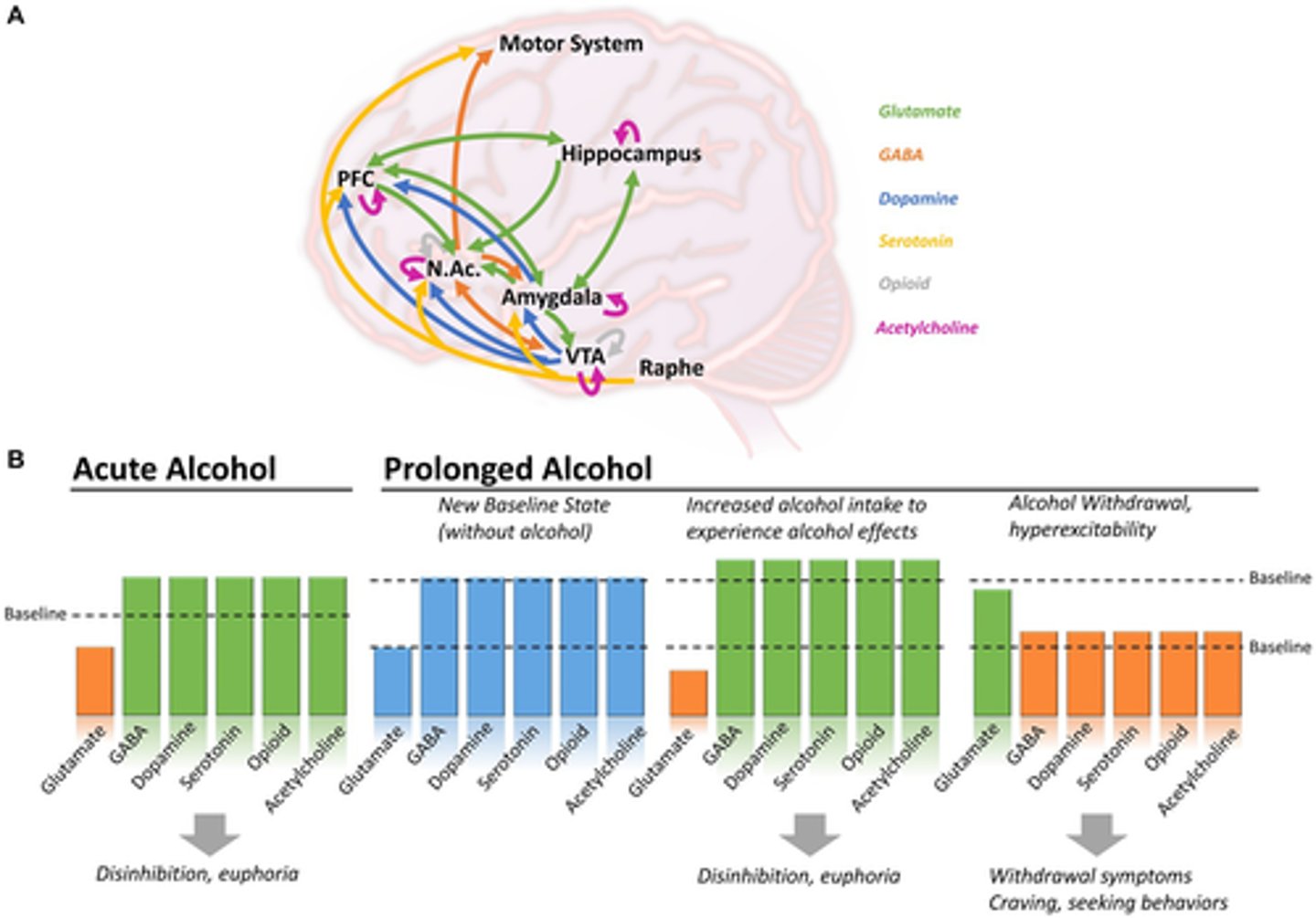
What is ALDH (metabolizing enzyme) polymorphism
- when the body cannot metabolize acetaldehyde, resulting in toxic accumulation of it
- increased acetaldehyde inhibits ADH, causing diuresis which in chronic use can result in dehydration & electrolyte imbalances
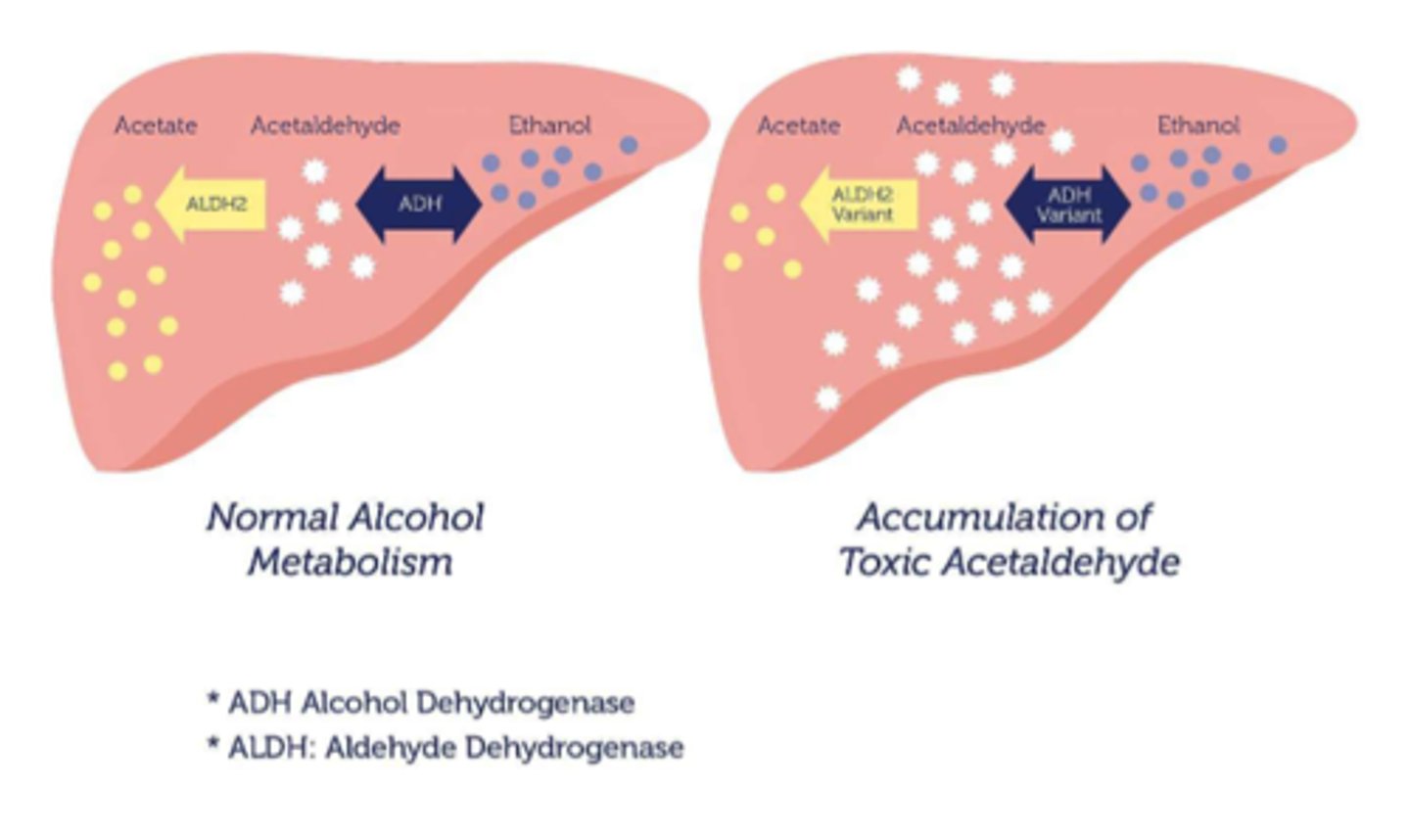
What are the S&S of alcohol intolerance
- cognitive disturbances, brain fog, vertigo
- poor/decreased sleep
- rashes, flushing (d/t vasodilation)
- stomachache, heartburn, tachycardia
- fatigue, weakness, headaches, muscle aches
- asthma, wheezing
- mood: depression, anxiety & irritability
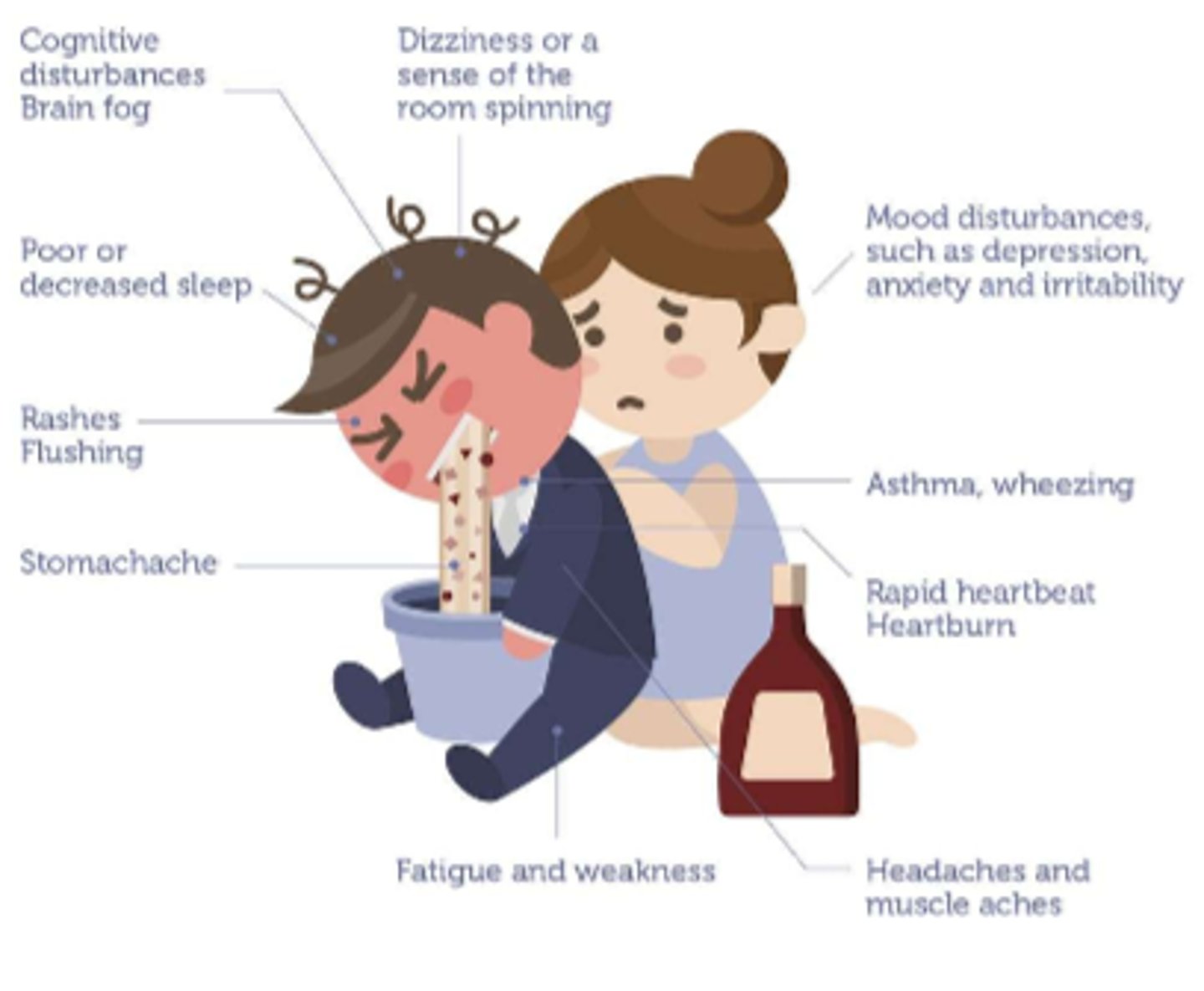
How do we tx alcohol addiction pharmacologically
- Disulfiram PO qd: increases acetaldehyde, makes pt feel when they drink & want to stop
- Naltrexone PO qd: long acting Narcan, decreases cravings
How do we tx alcohol addiction with adjunct therapy
- Vitamin B
- Nutritional support (replenish depletions in the body)
- Support group meetings (AA)
What is withdrawal s&s called with alcohol
'Delirium Tremens'

S&S of alcohol poisoning
- bradypnea/apnea
- hypothermia
- vomiting
- seizures
- stupor, unconsciousness

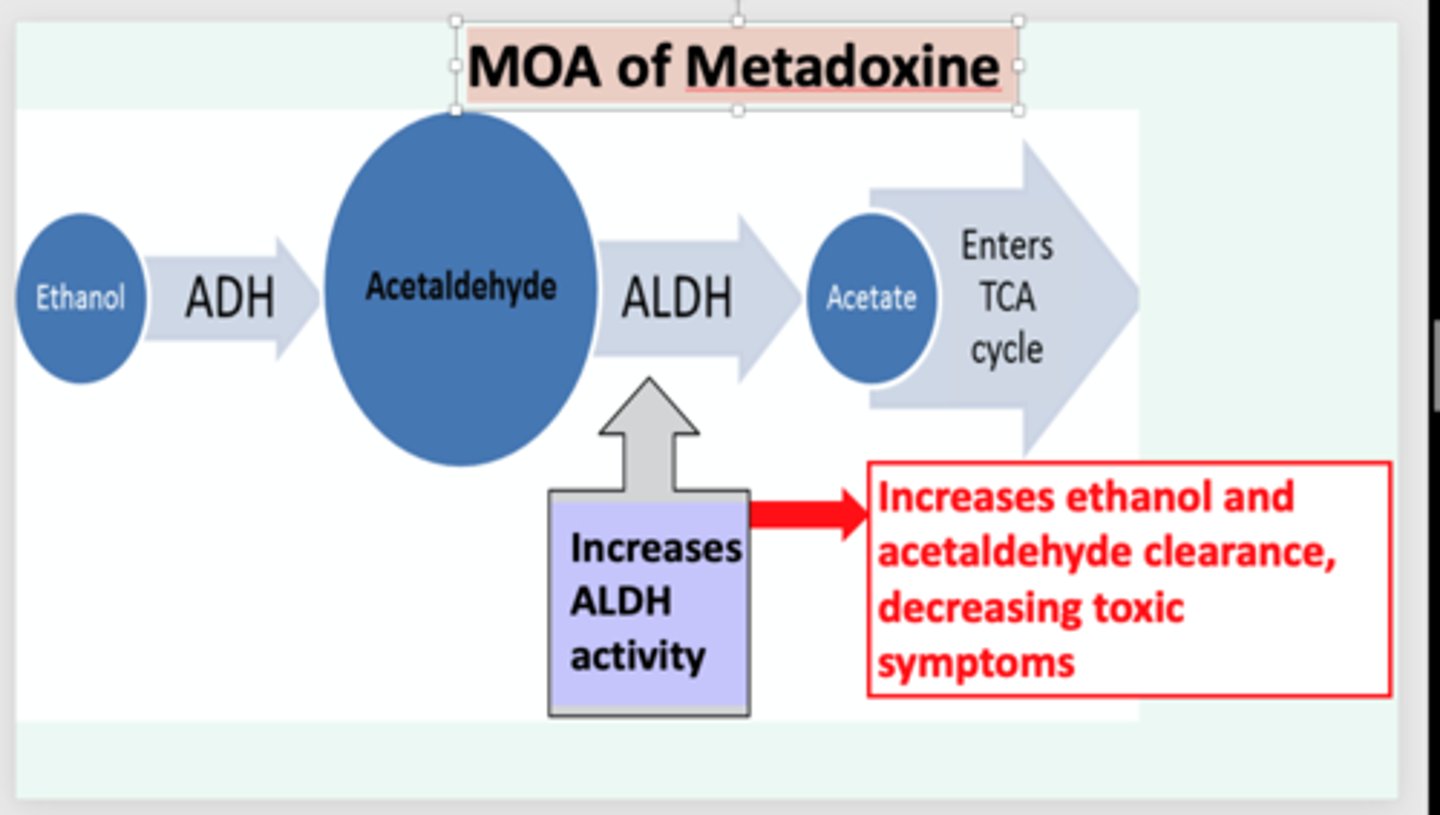
How do we tx alcohol toxicity
- Metadoxine, IV
- fx: induces alcohol dehydrogenase metabolism
- IV fluids
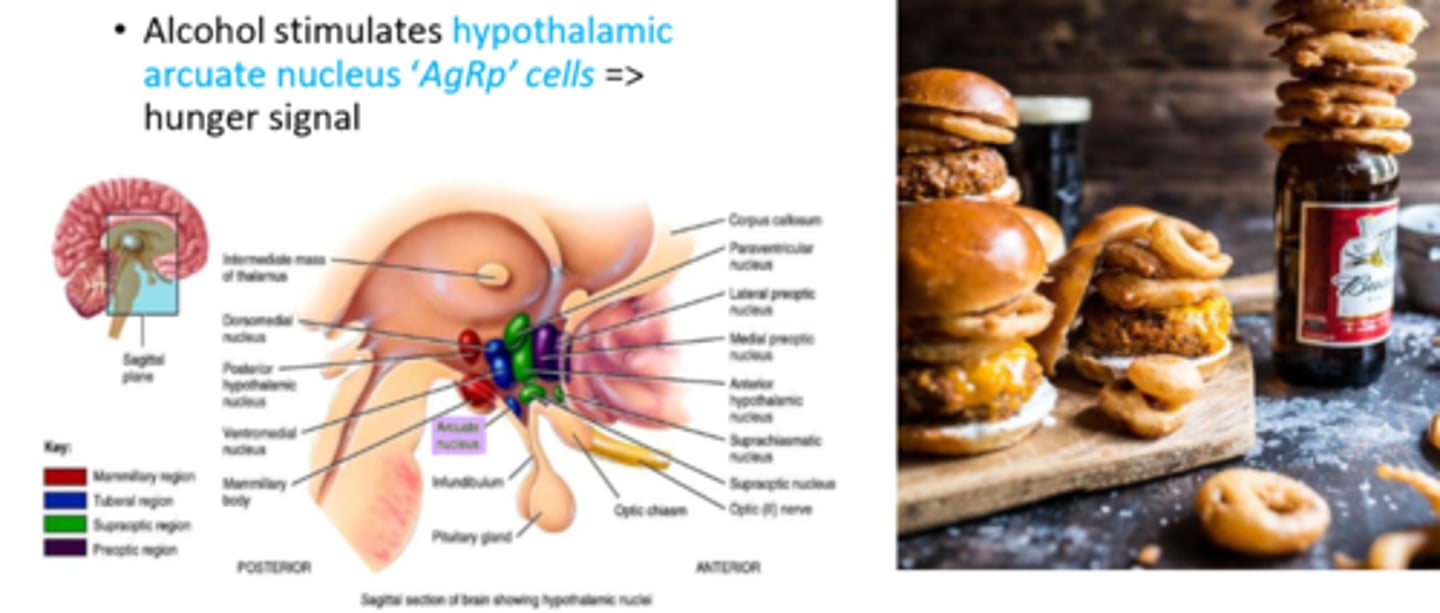
Why does alcohol stimulate hunger
- alcohol stimulates hypothalamic arcuate nucleus 'AgRp' cells => hunger signal
What are the emerging effects of vaping
- "temperature of aerosolization and the mixing of various juices may result in novel toxic components that are uniquely injurious"
- juice safety testing is based on ingestion not inhalation
- aerosols generated from present formaldehyde, glycidol, acetol & others => more toxic when heated
"the vape pen itself may be toxic, for example different atomizers may contain several different heavy metals"

What are cannabinoids used for therapeutically and what are the drugs (Nabil and nabin)
- therapeutic: nausea, complex pain, seizures (decreases neuro excitability)
- drugs: Nabilone (Cesamet), Dronabinol

What is Cannabis and its routes of admin
- plant = Marijuana => various preparations from various part of the plant
- Routes: smoked, PO (edibles), dabbing (temperature regulated vapes)
- > 400 different chemicals; 61 cannabinoids
- main parts used: Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) & Cannabidiol (CBD)

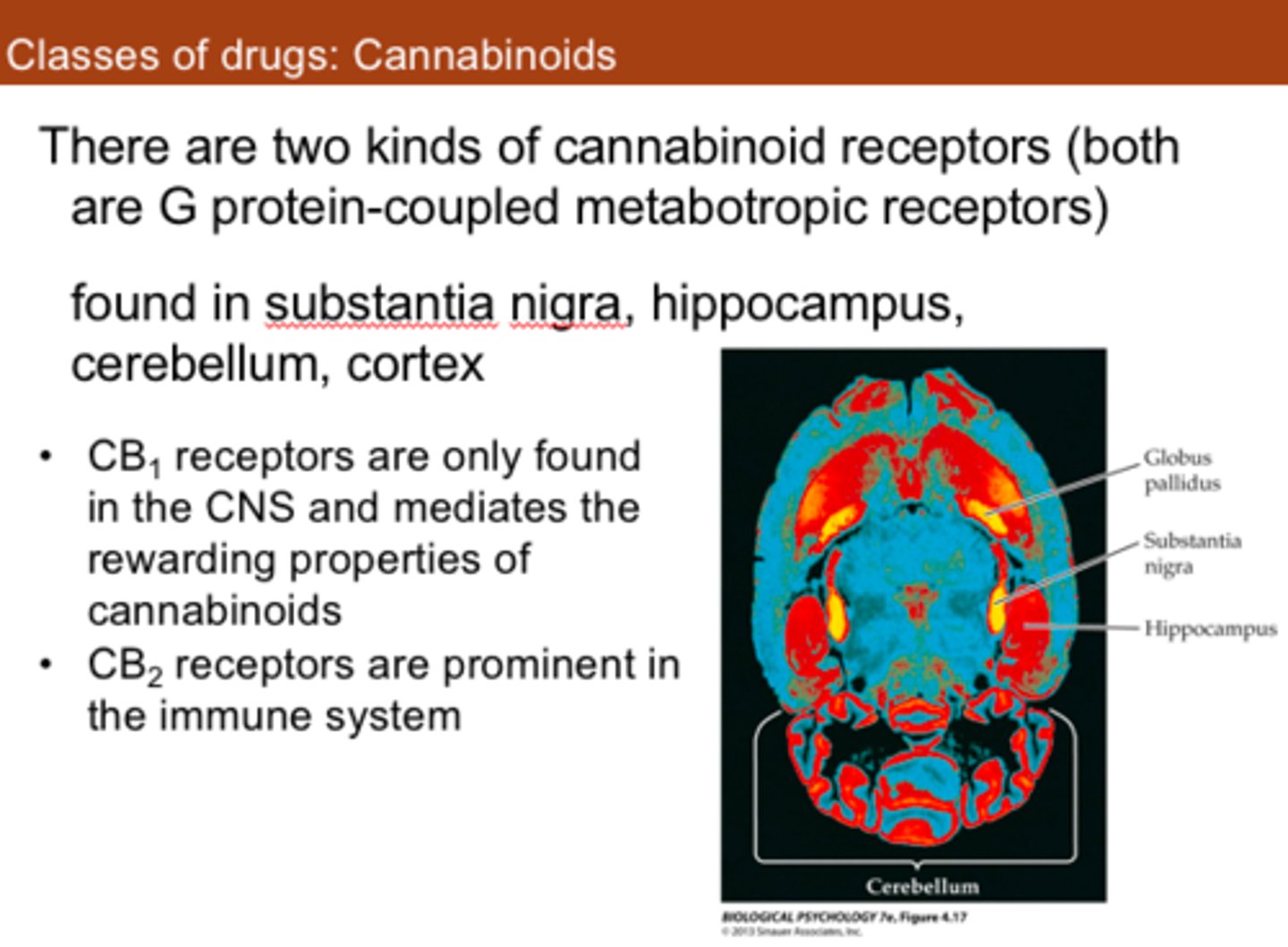
What is the PKPD of cannabis
- Receptor binding: agonises CB1 & CB2 (in CNS & PNS)
- Serotonin = CNS mood alterations
- Anandamide agonist = memory loss (anandamide is body's protection against overstimulation, makes so you don't remember everything)
- stimulate dopamine release (reward pathway)
How do CBD & THC work
- compete at receptors
- THC (full agonist): high levels adrenergic NS stimulant
- CBD (partial agonist): balances THC effect; low psychoactivity

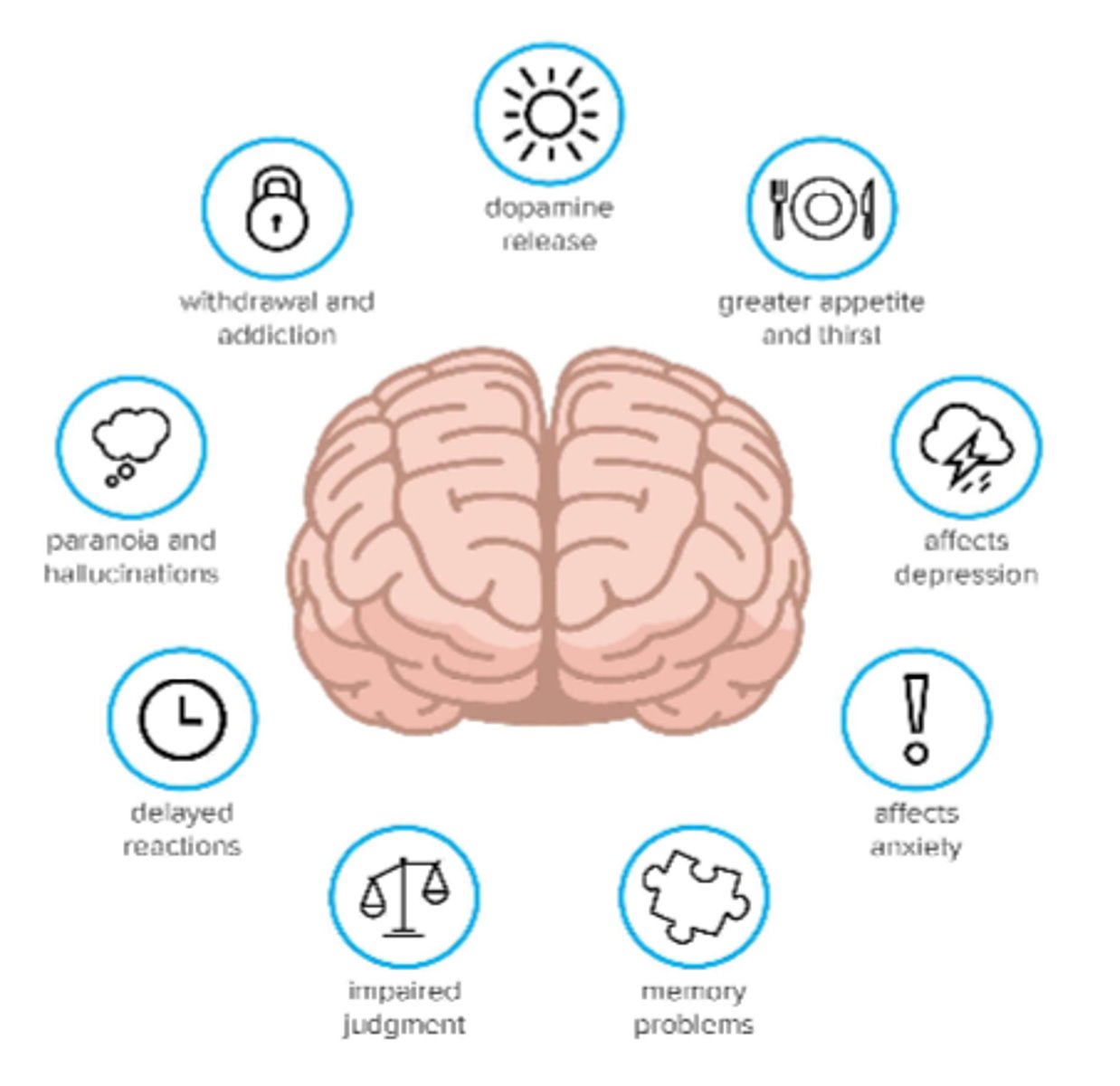
What are the long term effects of marijuana on the brain
- dopamine release (addiction), withdrawal
- GI alterations, either increased or decreased appetite
- affects depression & anxiety (may decrease short term but stim. in long term use)
- memory problems, may decrease IQ
- impaired judgement & reactions
- paranoia & hallucinations (chronic use)
What are the main routes of cannabis admin and how would we tx if necessary
- inhalation - 15-30 min onset, bioavailability 50%
- PO - 1-2 hr onset (variable => age varies), bioavailability 20% (OD risk d/t slow onset with edibles)
- Tx: supportive; no antagonist

What does cannabis toxicity look like
- neurocognitive effects, variable presentation:
- VS changes (tachycardia, hypertension)
- seizures, N&V
- acute psychosis, agitation
- coma
What are the fx of nicotine
- 1 cigarette = 10 mg of Nicotine
- binds nicotinic receptors: Cholinomimetic & Adrenergic
- dominant adrenergic effects: vasoconstriction (eg. cold hands), decreased GI motility, alertness
- CNS - stimulates dopamine release
- very lipophilic, gets to the brain very quickly
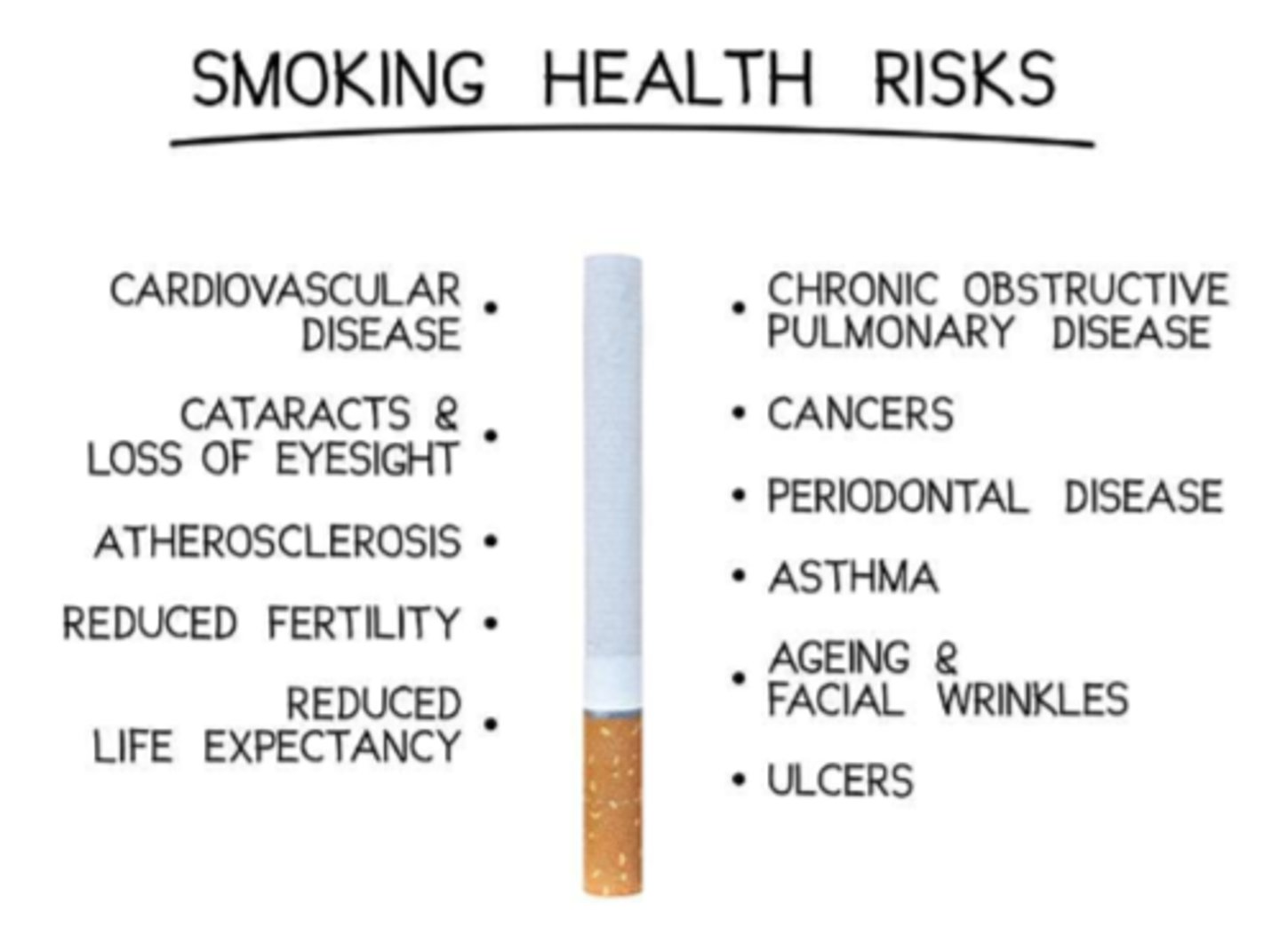
What are the main smoking health risks
- CVD, atherosclerosis
- cataracts & loss of sight
- reduced fertility
- reduced life expectancy, cancers
- COPD, periodontal disease, asthma
- aging & face wrinkles
- ulcers
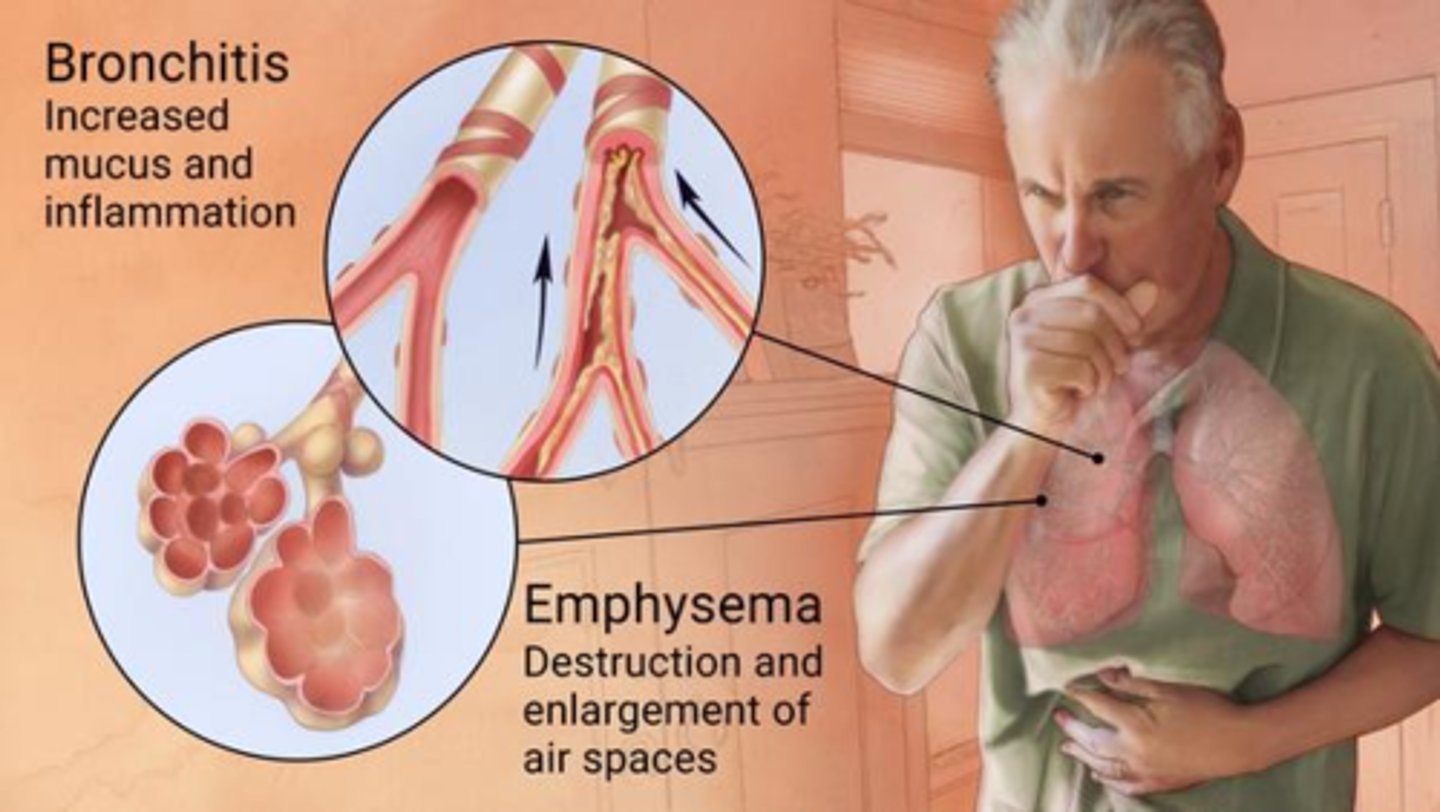
What is COPD and the 2 types
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 2 types: emphysema (alveoli enlargement, hyperinflation & inefficient fx) & bronchitis (excess mucous)
- most COPD: overlapping features, s&s are mixed, tx is the same
What is the etiology of COPD
- smoking
- other environmental (occupational, eg. mining)
- genetic (alpha1 antitrypsin deficiency)
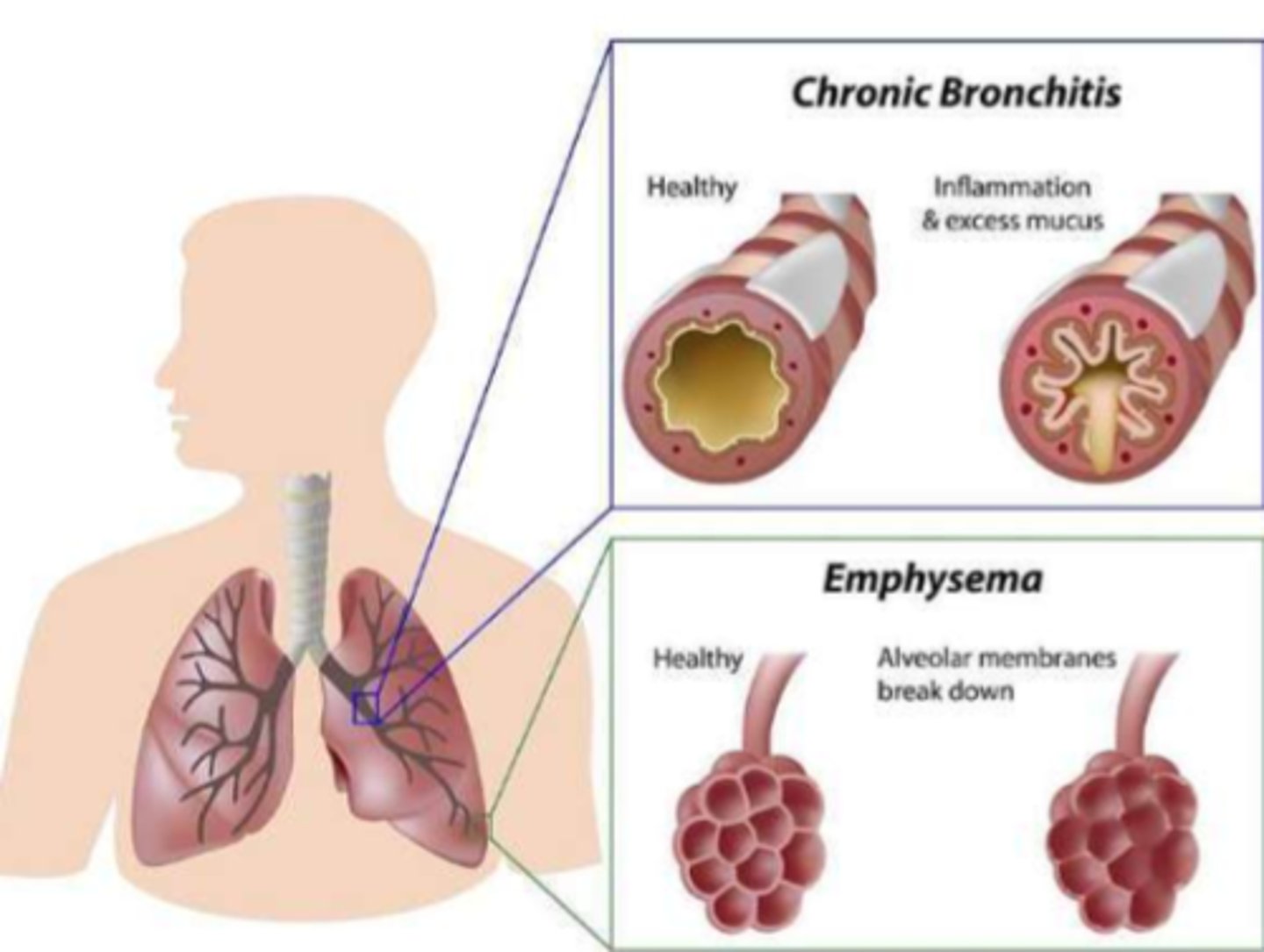
What is the pathological sequelae of COPD
- chronic inflammation (diagnosed later in life) => fibrous tissue/scarring/low tissue elasticity/loss of fx
= air trapping & hyperinflation of alveoli => insufficient oxygenation/ventilation
What are the s&s of COPD
- SOB, accessory muscle use
- prolonged expiratory phase, low O2 sats & very hard to breathe out (therefore drive to breathe will decrease)
- hypoxemia, hypercapnia (excess CO2), CHF
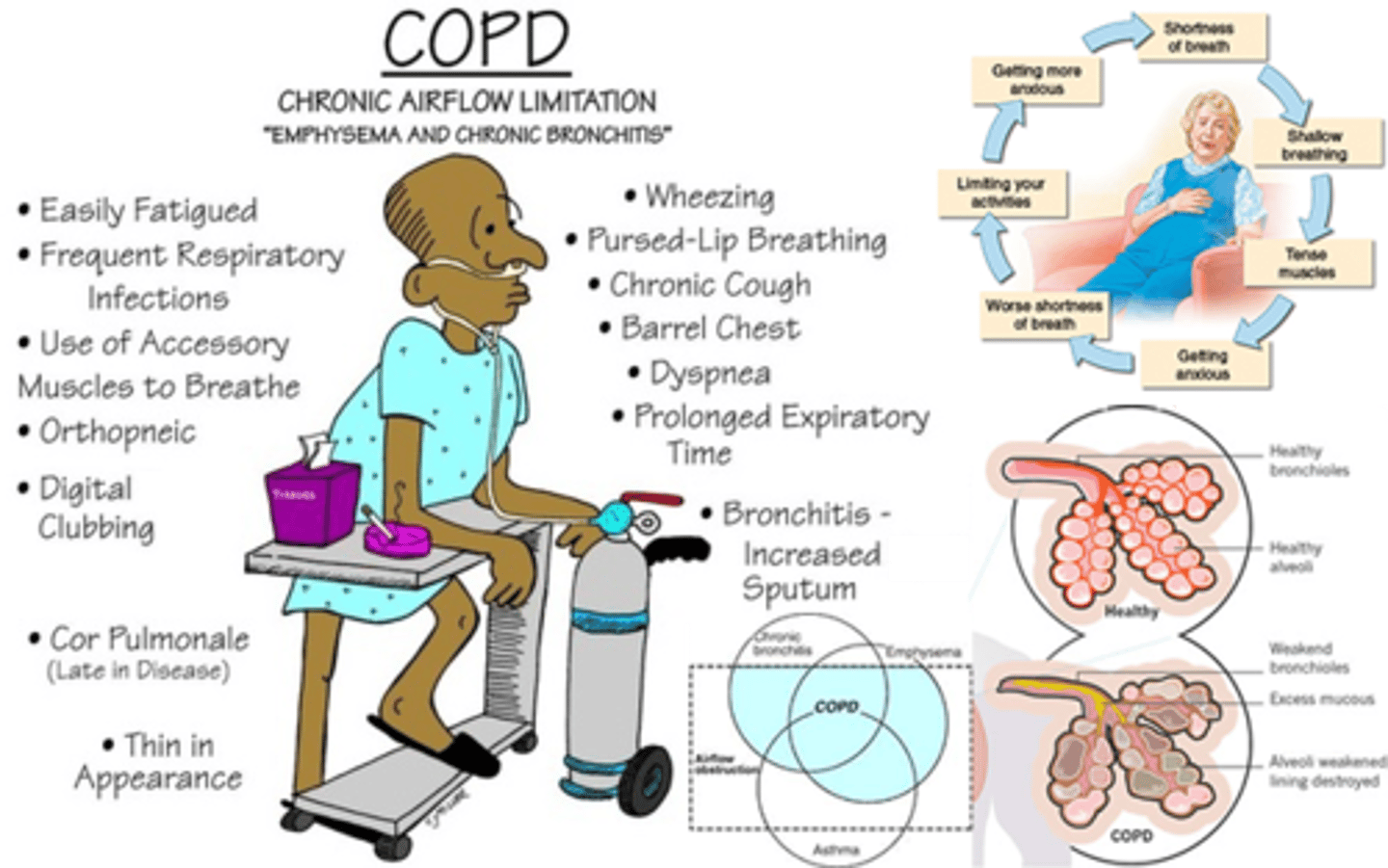
How do we tx COPD
- smoking cessation => biggest advocation for this as it is most impactful (eg. wean pts with nic patch)
- drug: Serevent (long acting B2 agonist, like Ventolin) => not very effective

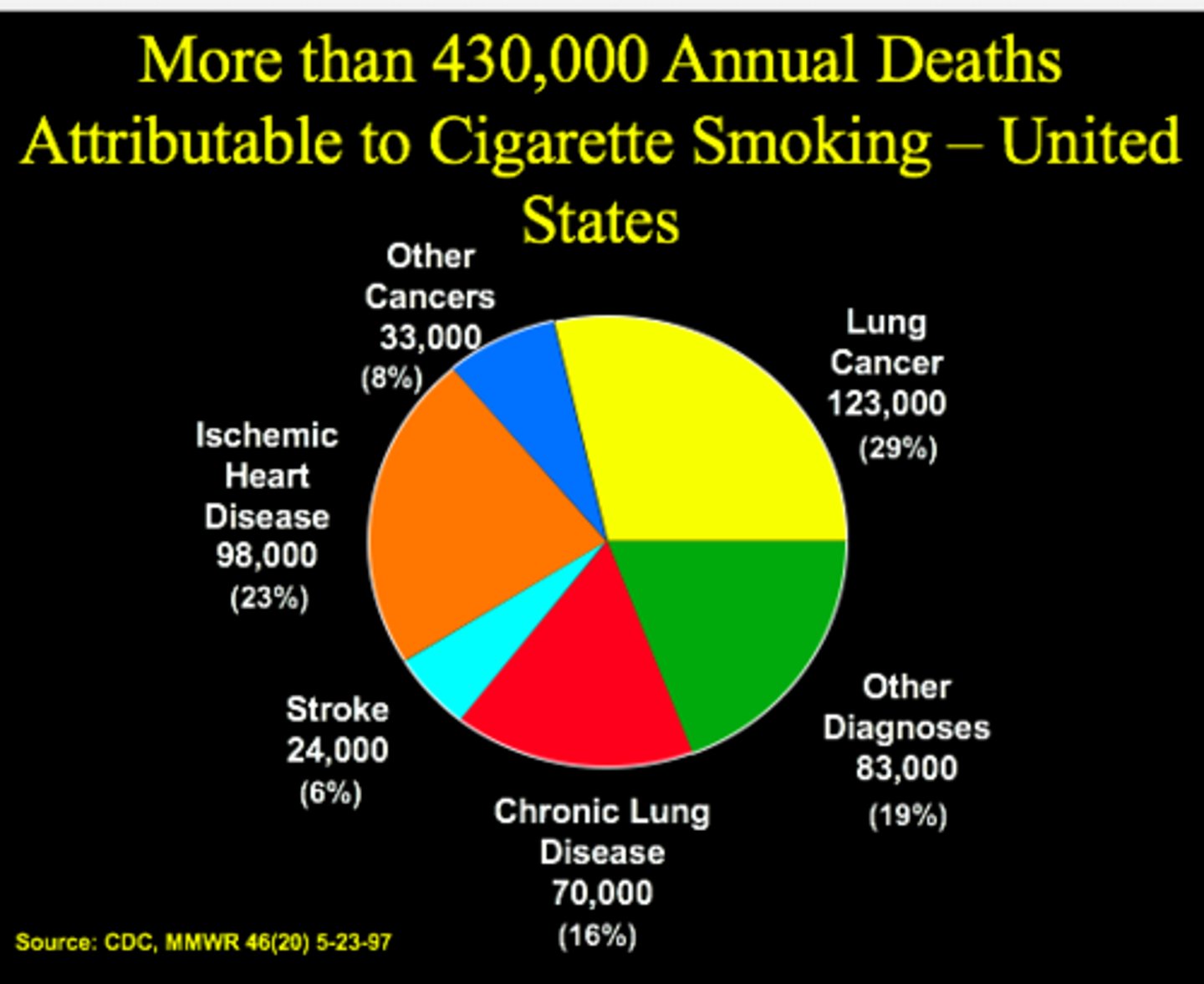
What is nicotine addiction overall
- smoking kills half of all those who do it, plus 600,000 people a year who don't, via second-hand smoke => making it the world's biggest preventable killer
- evidence - affects adolescent brain development, especially to the parts responsible for intelligence, language and memory
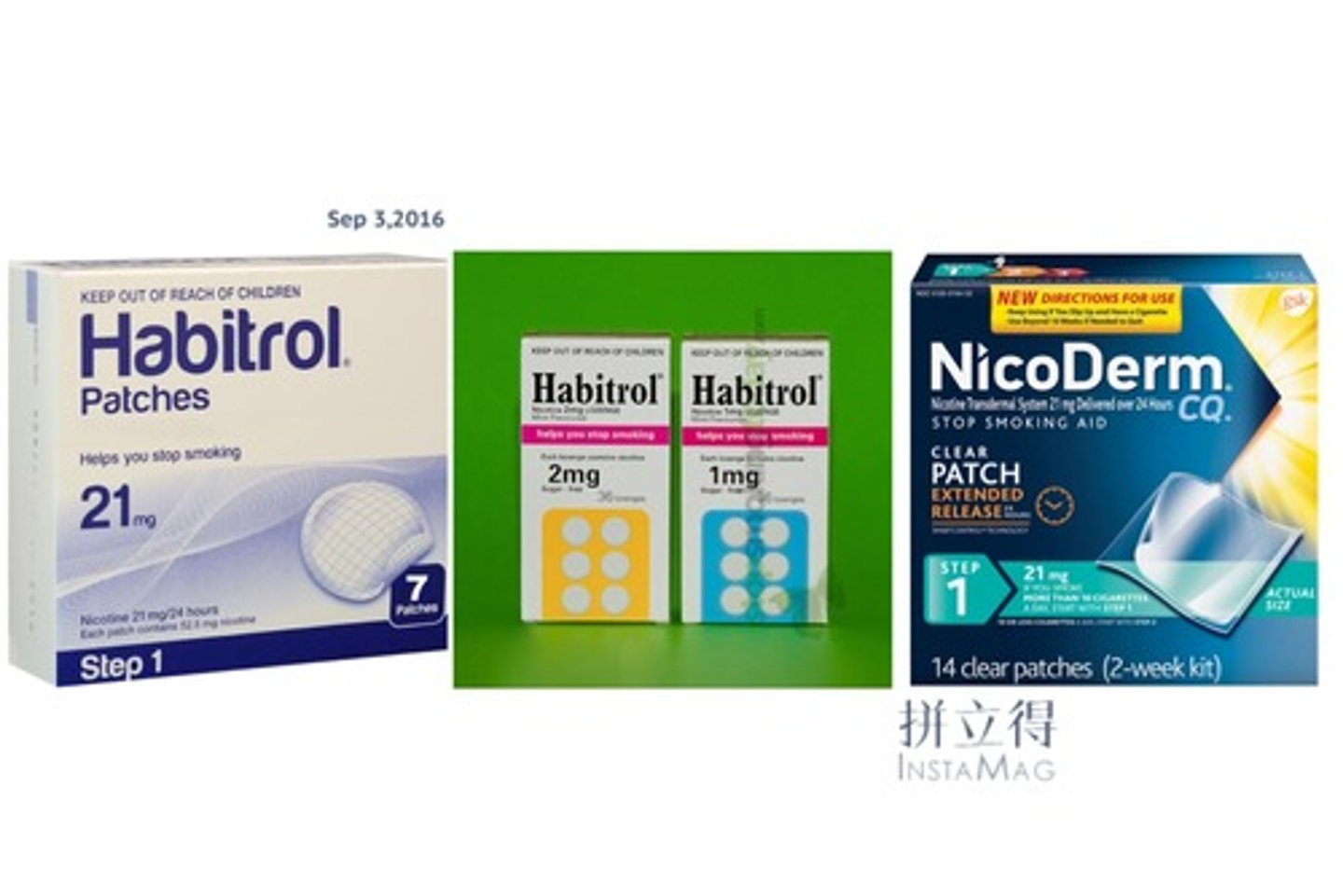
What is Nicotine Replacement Therapy
- 'weaning' therapy
- Decreases bioavailability
- Decreases toxic substances other than nicotine
eg. transdermal nicotine patch
What is the function of 'upper' drugs
- stimulants & psychoactive stimulants
- stimulant fx: Excitation (euphoria), uninhibited behavior (cocaine, Crystal Meth)
- psychoactive stimulant fx: altered reality (eg. hallucinations) (Ecstasy, LSD)

What is the PKPD of 'upper' drugs
- Increases: NE, serotonin, dopamine
=> increase performance, confidence

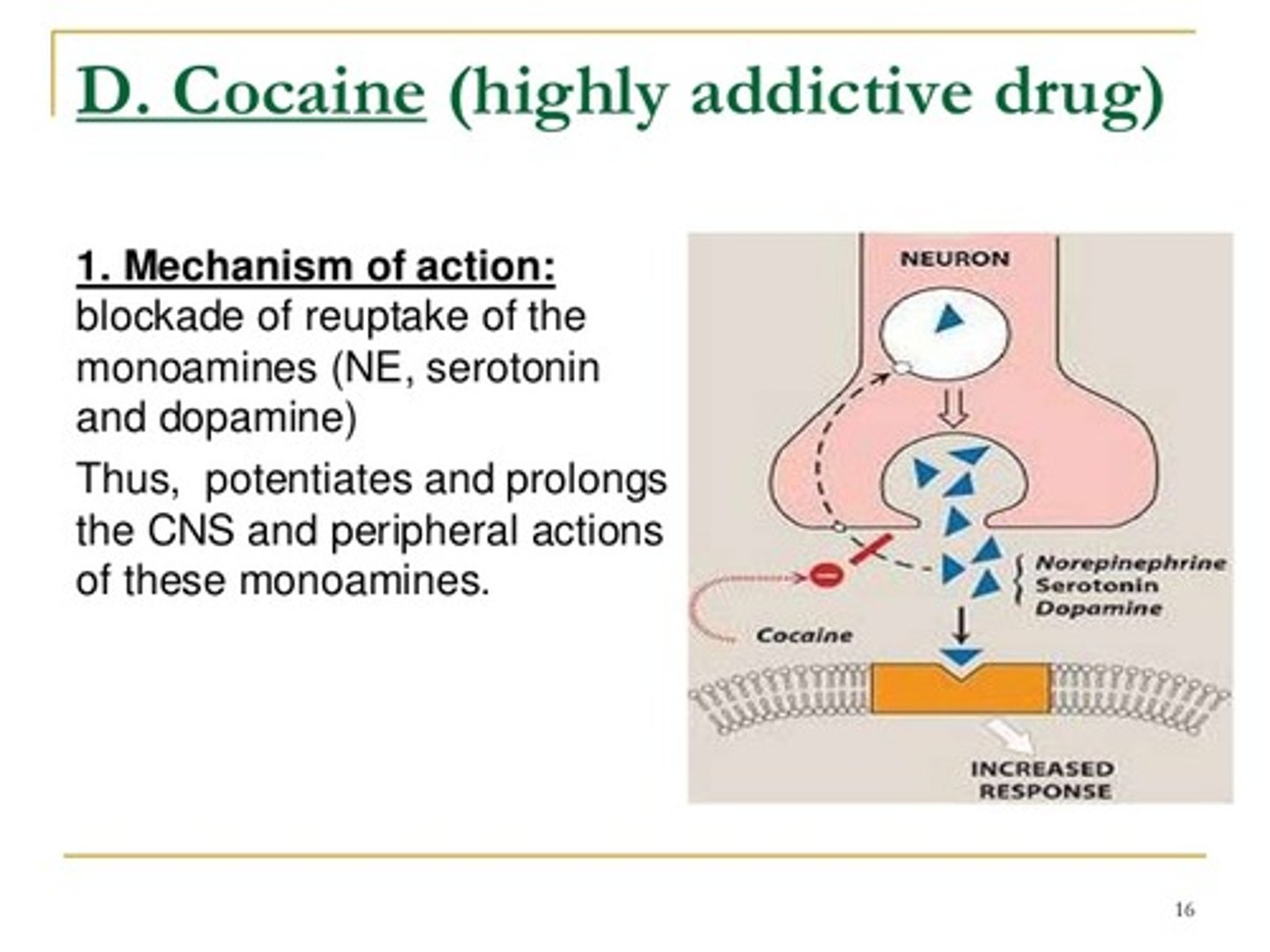
What is cocaine
- upper drug
- powder, insufflated (snorted)
- lipophilic; crosses BBB
- high Dopamine release
- Onset of action: seconds
- Duration of action: up to an hour, avg 45 min (short duration leads to binging behavior)
What is crack cocaine
- rock, inhaled (smoked)
- Cocaine hydrochloride + ammonia or baking soda + water = rock (alkalinized to get rock formation)
- heated to remove the hydrochloride ("freeing the base"), resulting in a solid, rock-like substance form
- even faster onset of action, danger of binging to maintain 'high'
- one use of crack cocaine does lead to addiction!

What is 'cocaethylene'
combo of Cocaine and ETOH, long t1/2

What is Crystal Meth
- upper drug
- methamphetamine derivative, up to 200x more potent than therapeutic use (eg. ADHD tx like concerta)
"Enters the brain quickly and produces an intense "rush" or euphoria that also ends quickly"
- 'high': elation, talkativeness, happiness
- high doses: LOC impairment
- long term use: paranoias, seizures, insomnia, memory loss

What is LSD (acid)
- upper drug
- potent hallucinogen/altered reality
- less addictive than cocaine; hallucinations can be addictive
- can cause psychological distress
- Onset: 15-20 minutes
- Duration: 8-20 hrs VERY LONG ACTING (clear your schedule)
"doses as small as 1-1.5 mcg/kg can produce psychoactive effects; an oral dose of 25 µg is capable of producing potential deleterious psychedelic effects"

What is ecstasy (MDMA/molly)
- not a potent hallucinogen, however dose dependent
- can induce altered reality
- high addiction potential
- mood elation, connectivity, sociability; "rave/dancing drug"

What are the long term addiction effects
- impaired CNS synapses: negative neuroplasticity
- poor memory, IQ decline with use, altered personality
- impulsive behavior; violence
- hallucinations, paranoias, seizures
- depression, socio-economic decline, malnutrition, immunosuppression
- infections (eg. Hepatitis B & C, HIV; opportunistic)
- electrolyte & Vitamin deficiencies
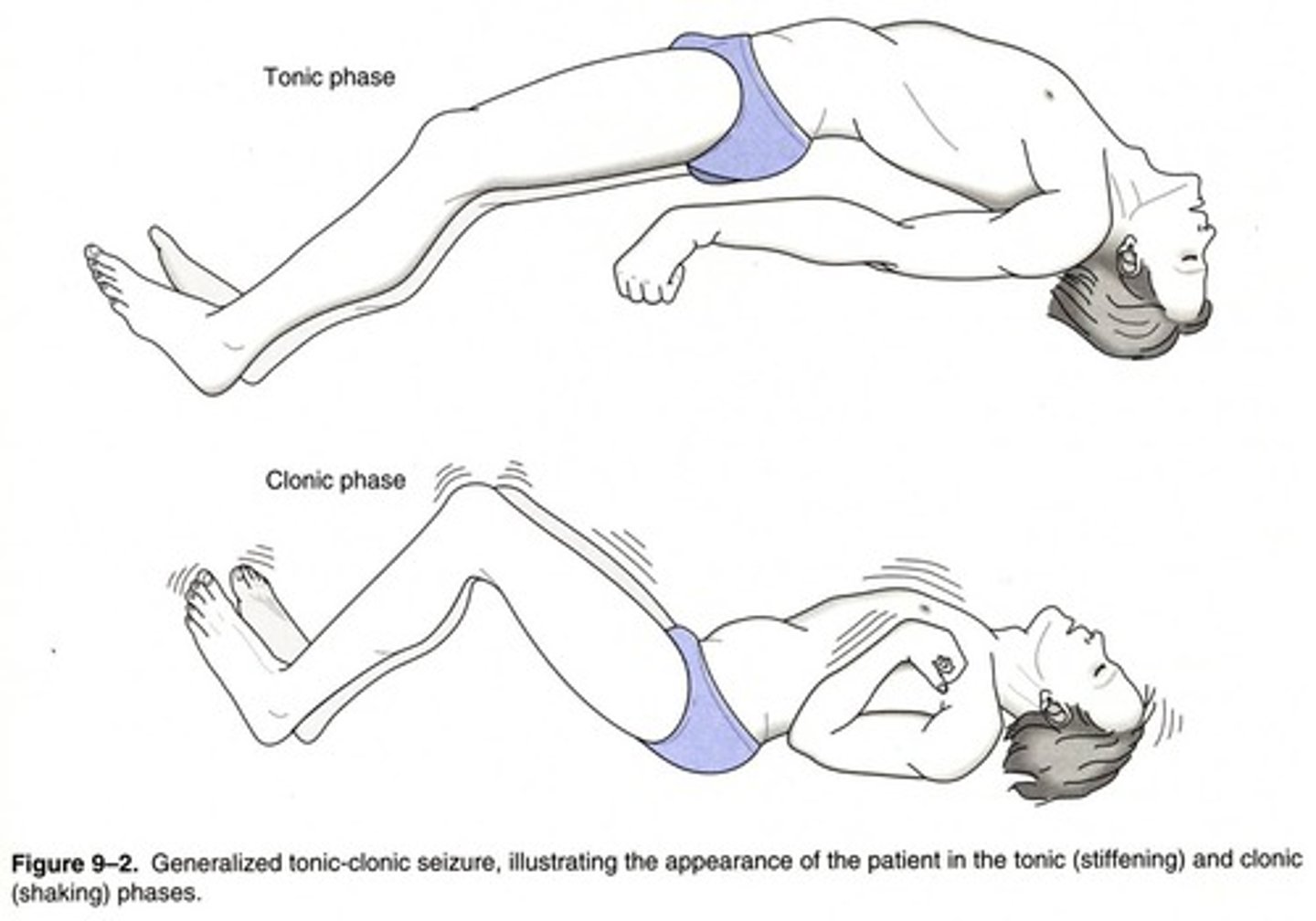
What are the withdrawal S&S in drug addiction
- adrenergic like S&S:- anxiety, restlessness, tremors, insomnia
- GI distress (nausea, cramping)- diaphoresis, tachycardia
- unpredictable behaviours
- drug craving

What is the adjunct tx for addiction
- treat as per s&s
- according to long term effects: antidepressants, anxiolytics (panic/anxiety tx)