EKG, Sensitivity & Specificity, BP Wrap Up
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Electrocardiogram
- A graph of the hearts electrical impulses and patterns as measured by electrodes
- versatile, immediate

Electrocardiograms are NOT __________ and NOT _____________
- NOT invasive
- NOT expensive
Electrocardiograms detect normal (or abnormal) rhythms of the heart and....(4)
• Arrhythmias
• Myocardial ischemia/infarction
• Drug toxicities
• Other cardiac abnormalities
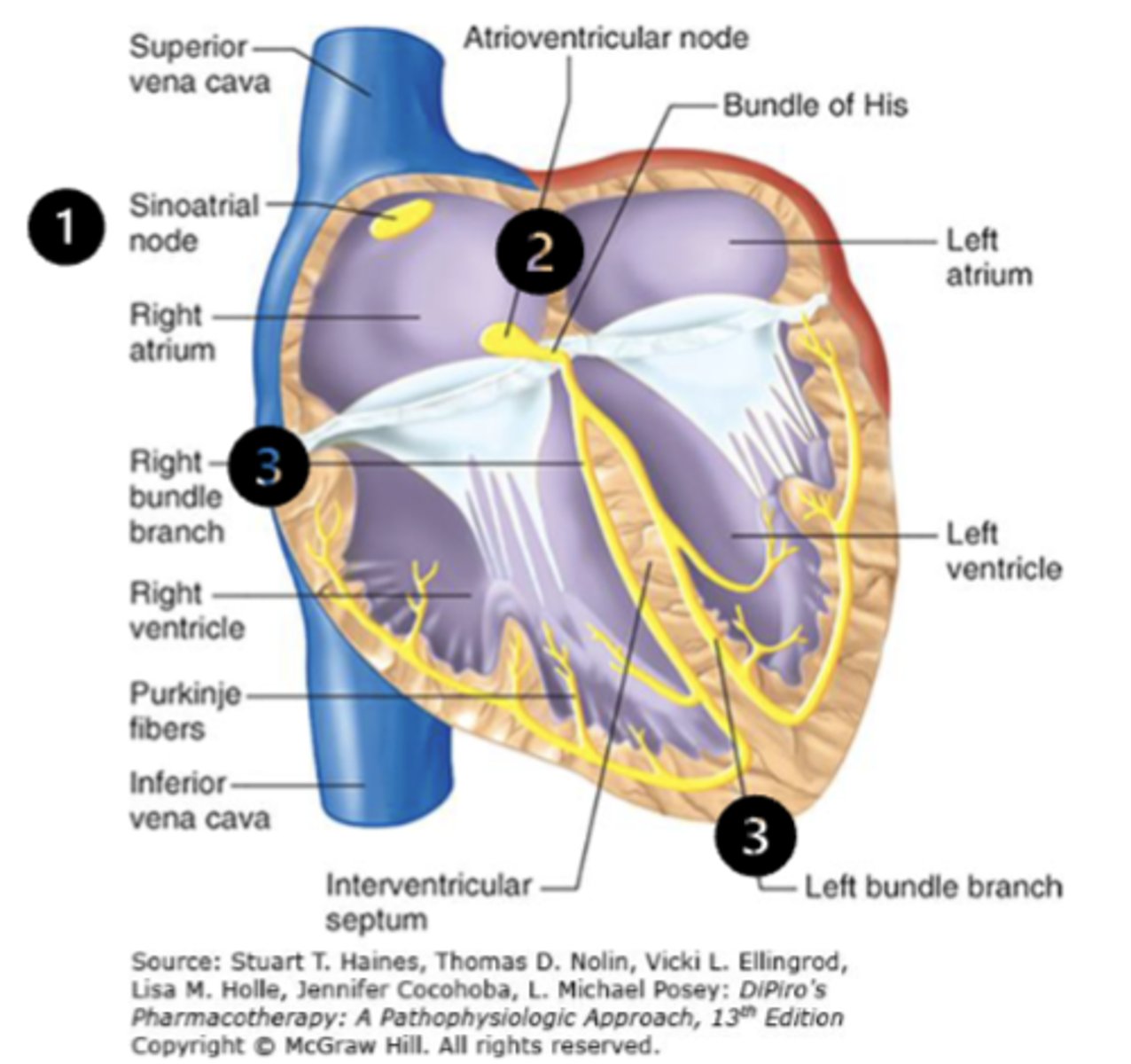
• Electrical impulse starts at the ___________________ node of the ______ atrium
• Then a wave of _________________ occurs across the atria to the ___________________ node
• Conduction goes down the left and right ________________, and into the ____________________ system where it transmits to the ___________________
• The electrical stimulation of heart muscle cells cause __________ to enter into the cell, more calcium is released causing a __________________
• After the contraction, myocytes ________________ and get ready for the next impulse
• Electrical impulse starts at the sinoatrial (SA) node of the right atrium
• Then a wave of depolarization occurs across the atria to the atrioventricular (AV) node
• Conduction goes down the left and right bundle branches, and into the His-Purkinje system where it transmits to the ventricular myocardium
• The electrical stimulation of heart muscle cells cause calcium to enter into the cell, more calcium is released causing a contraction
• After the contraction, myocytes repolarize and get ready for the next impulse
Depolarize- _____________
Repolarize- __________
Depolarize- contract
Repolarize- relax
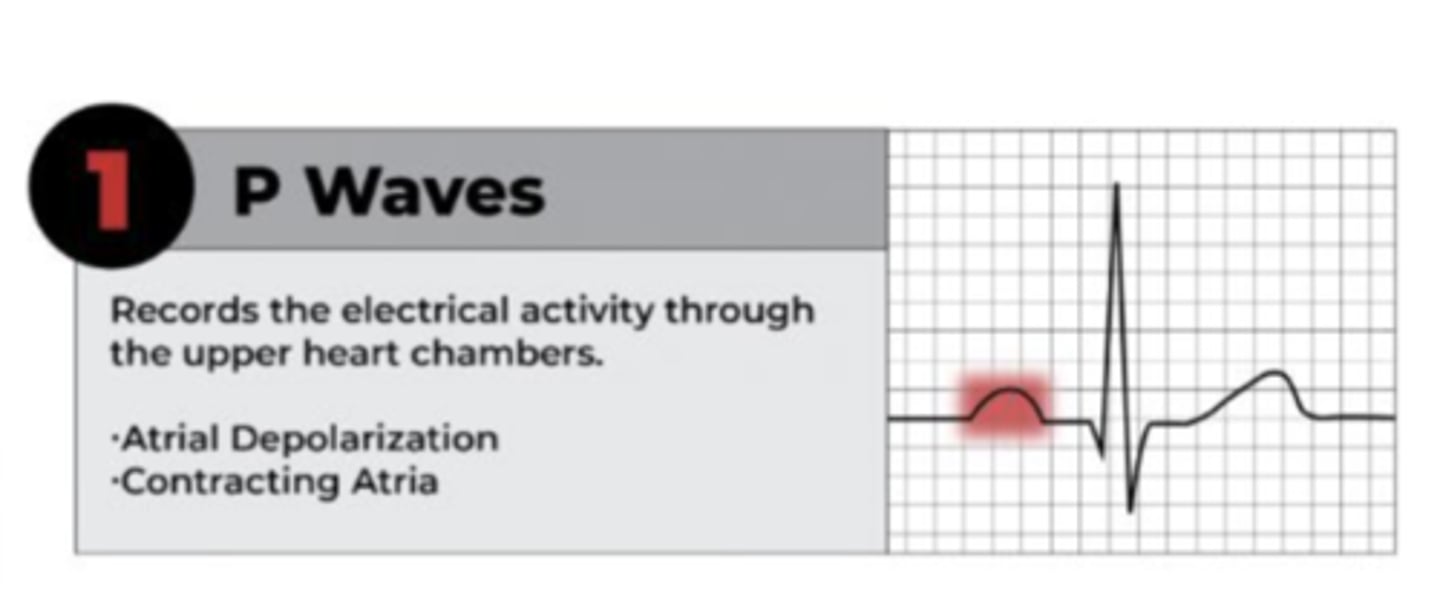
P wave
• Upper heart chambers
• Represents atrial depolarization or contraction of atria
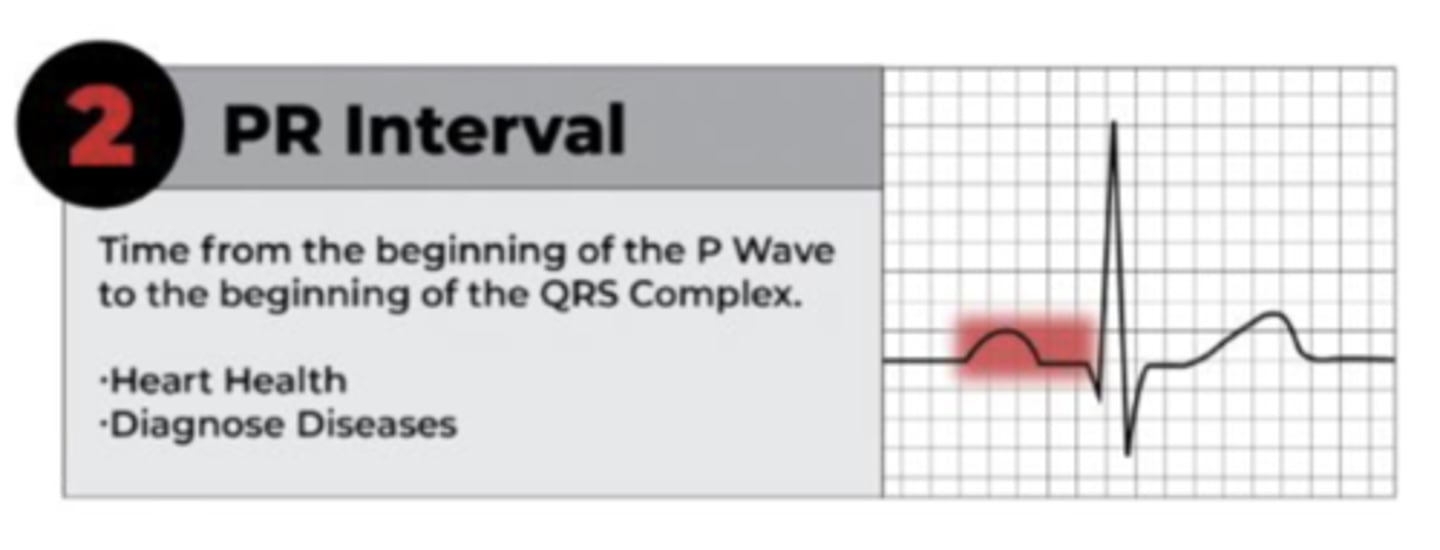
PR interval
• End of the P wave to the start of the QRS complex
• Reflects how conduction is slowed through the AV node and the time delay between atrial and ventricular depolarization
QRS Complex
• Lower heart chambers
• Ventricular depolarization (or ventricular systole (contraction))
• Q wave: first downstroke
• R Wave: first upward spike
• S Wave: downward dip

T Waves
ventricle repolarizes at the beginning of ventricular diastole (relaxation)

What do boxes on the EKG strip mean?
Boxes measure time and distance
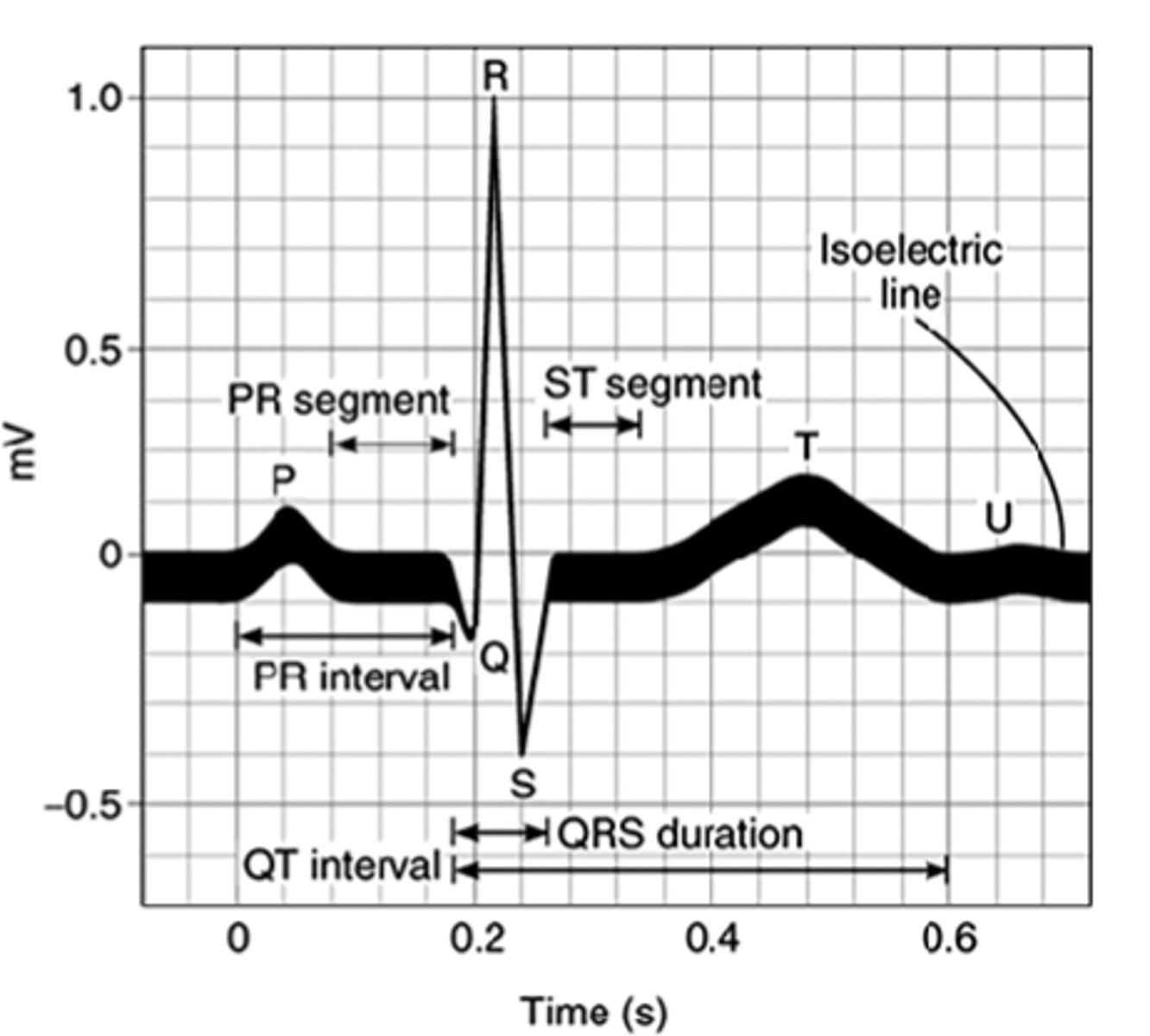
A large "big" box (5 mm) mean) =
= 0.20 seconds
A small box (1 mm)=
= 0.04 seconds
Dips and spikes are called ____________ identifying different phases of the activity of the ___________
- waves
- heart
EKG has _____ "leads" with _____ electrodes. _____ on chest, _____ at limbs
- 12 "leads"
- 10 electrodes
- 6 on chest
- 4 at limbs
QT Prolongation (or long QT syndrome)
Abnormal heart electrical system where it takes the heart longer to recharge between beats
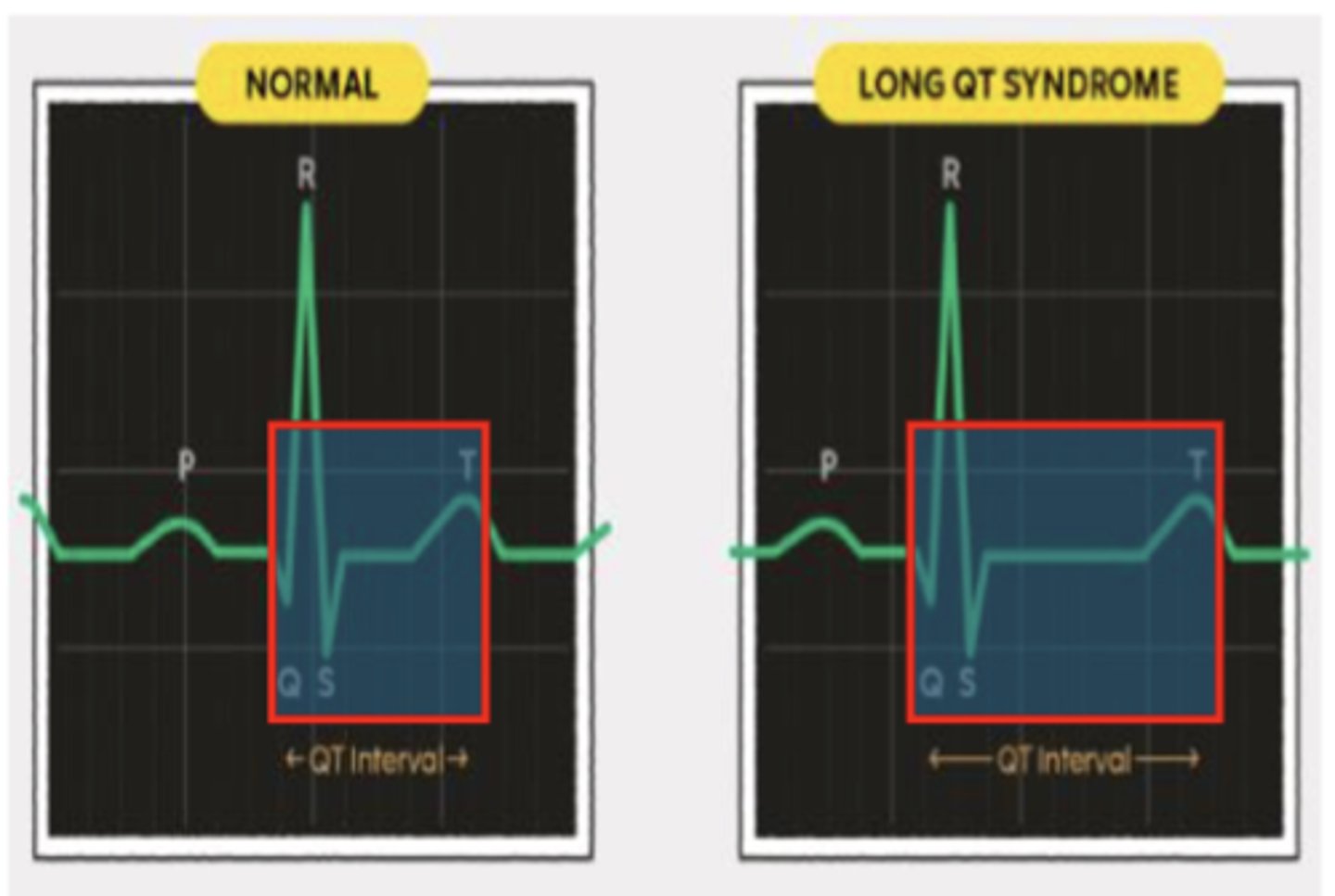
What can QT Prolongation lead to?
a potentially life-threatening arrhythmia called torsades de pointes (pronounced torsad de pwant)
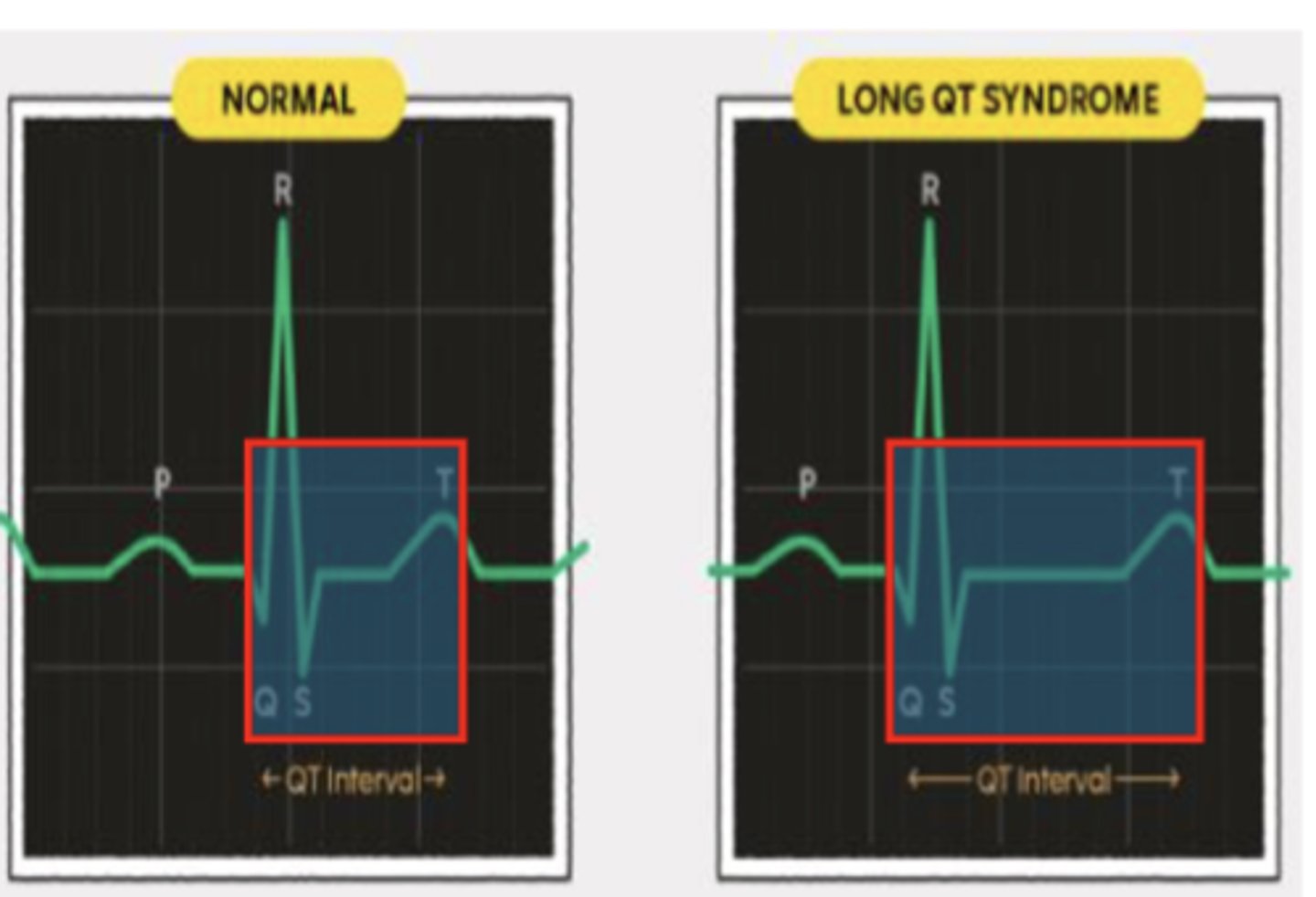
Medications may cause QT prolongation
• Antiarrhythmic: Amiodarone
• Antibiotic: Eryrthromycin, Ciprofloxacin
• Antipsychotic: Amitryptyline, citalopram
• Antihistamine: Diphenhydramine
Comparing PQRST!
Sensitivity & Specificity
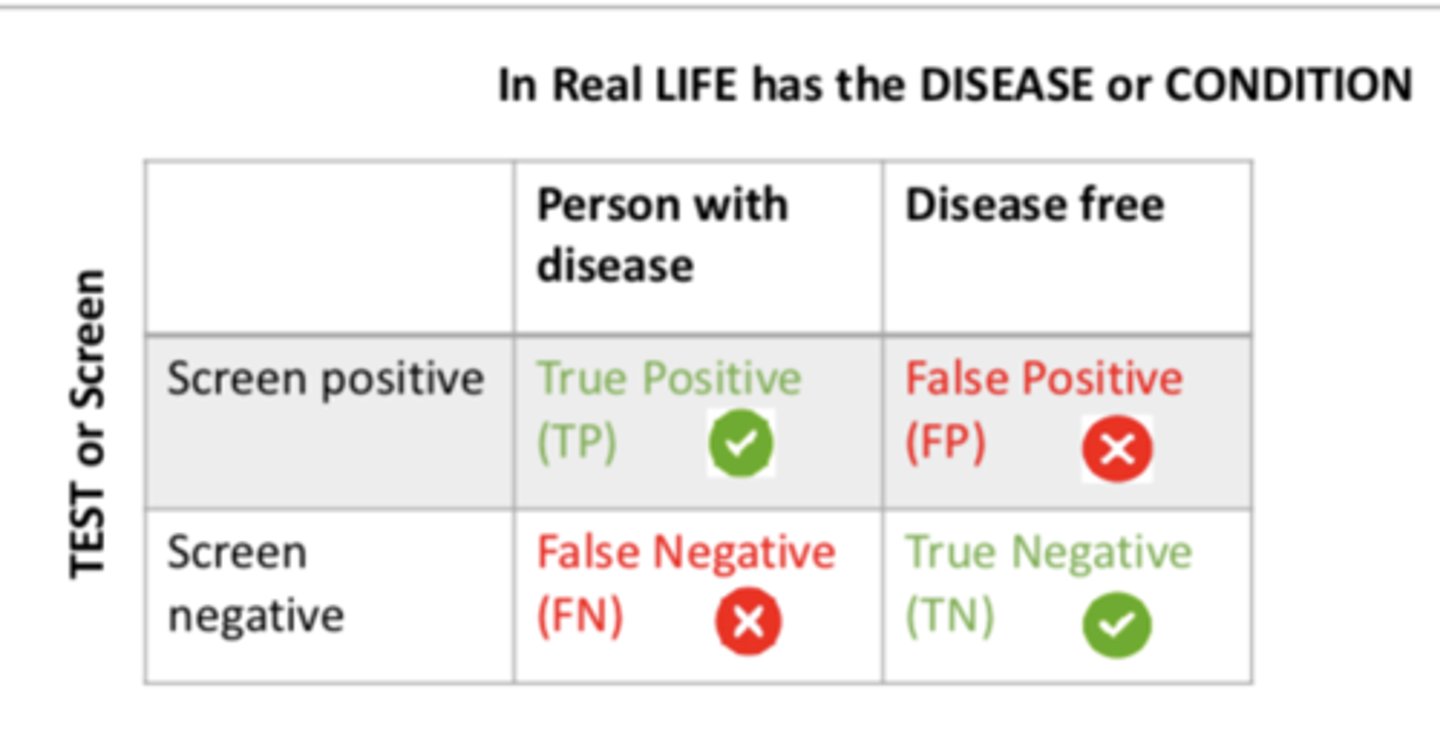
If a person screened positive and is a person with the disease, it is a...
TRUE positive (TP)
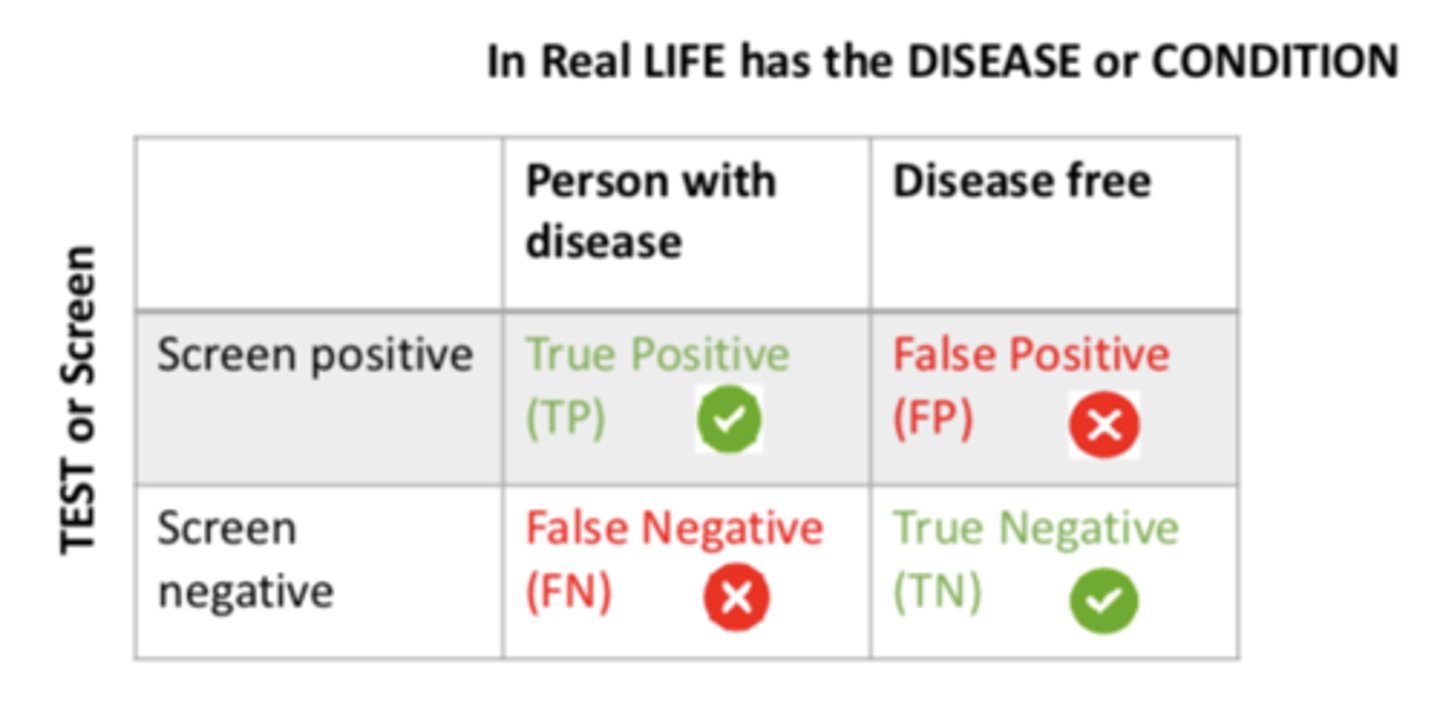
If a person screened positive and is disease free, it is a...
FALSE positive (FP)
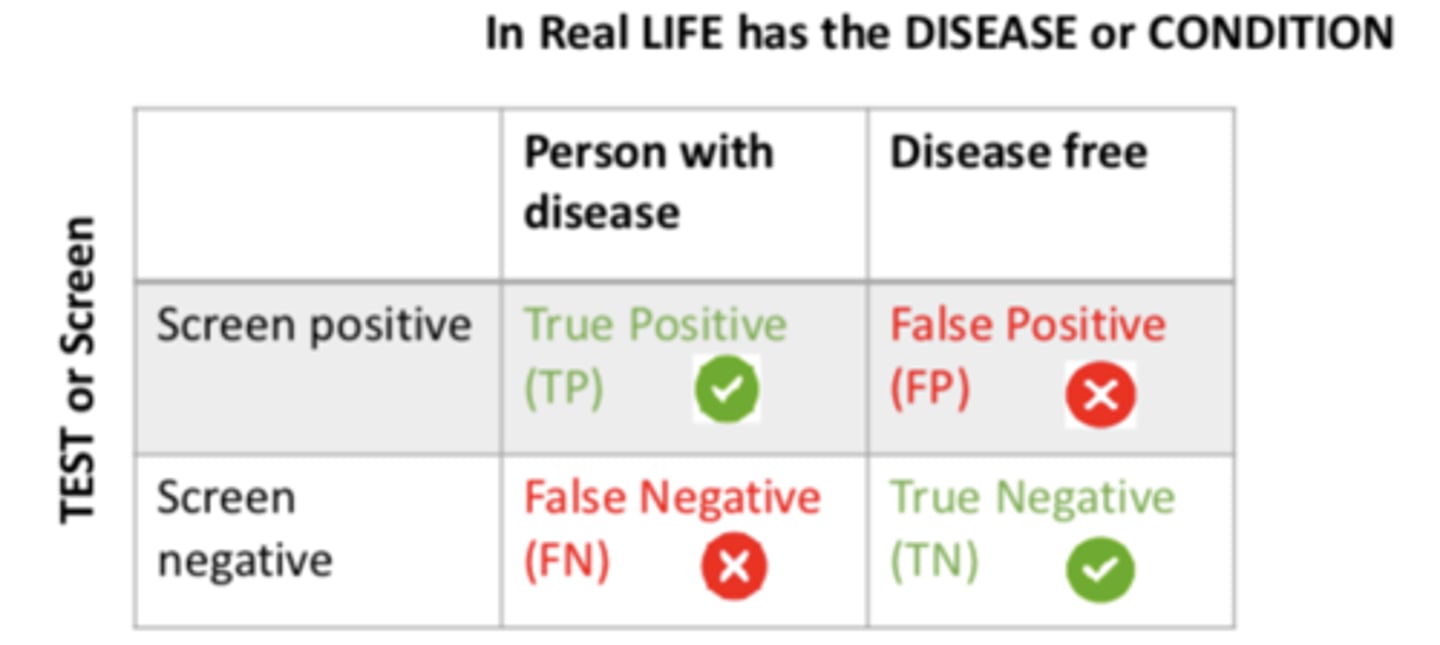
If a person screened negative and is a person with the disease, it is a....
FALSE negative (FN)
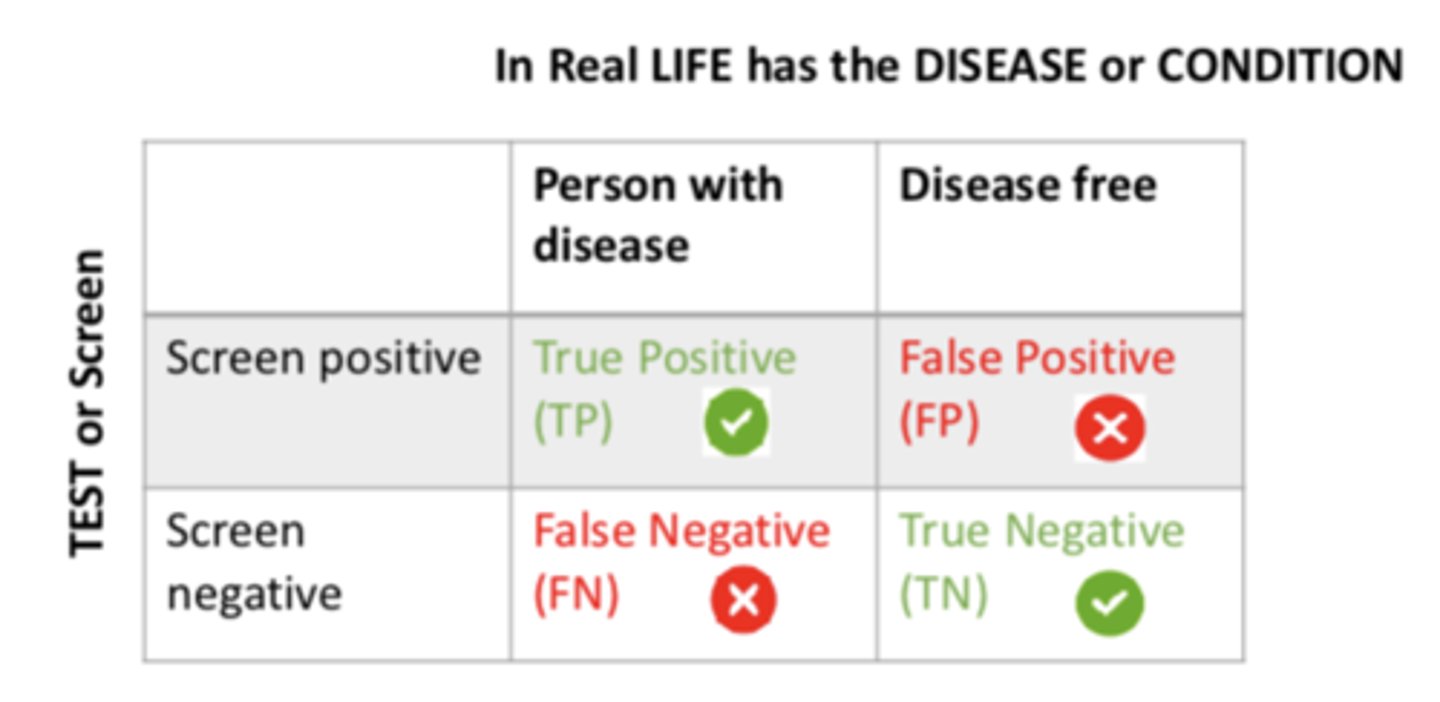
If a person screened negative and is disease free, it is a...
TRUE negative (TN)
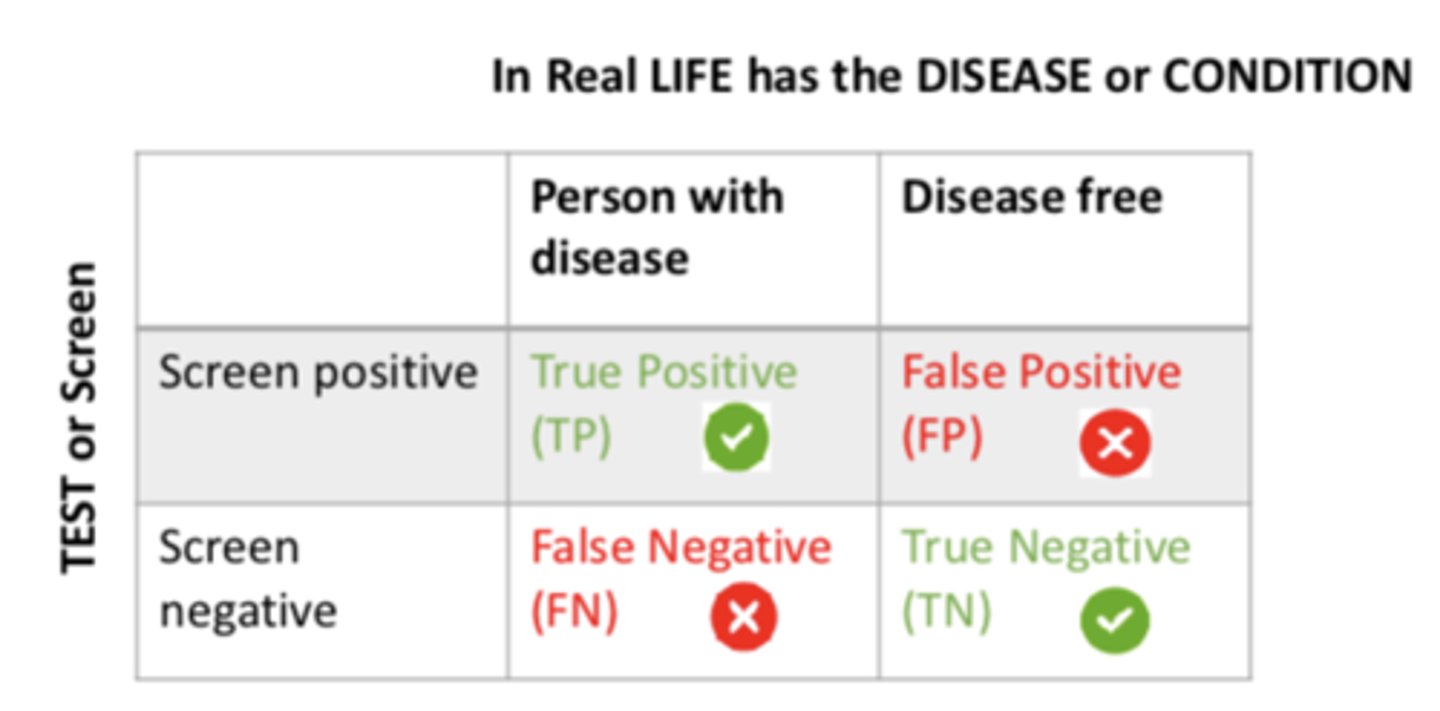
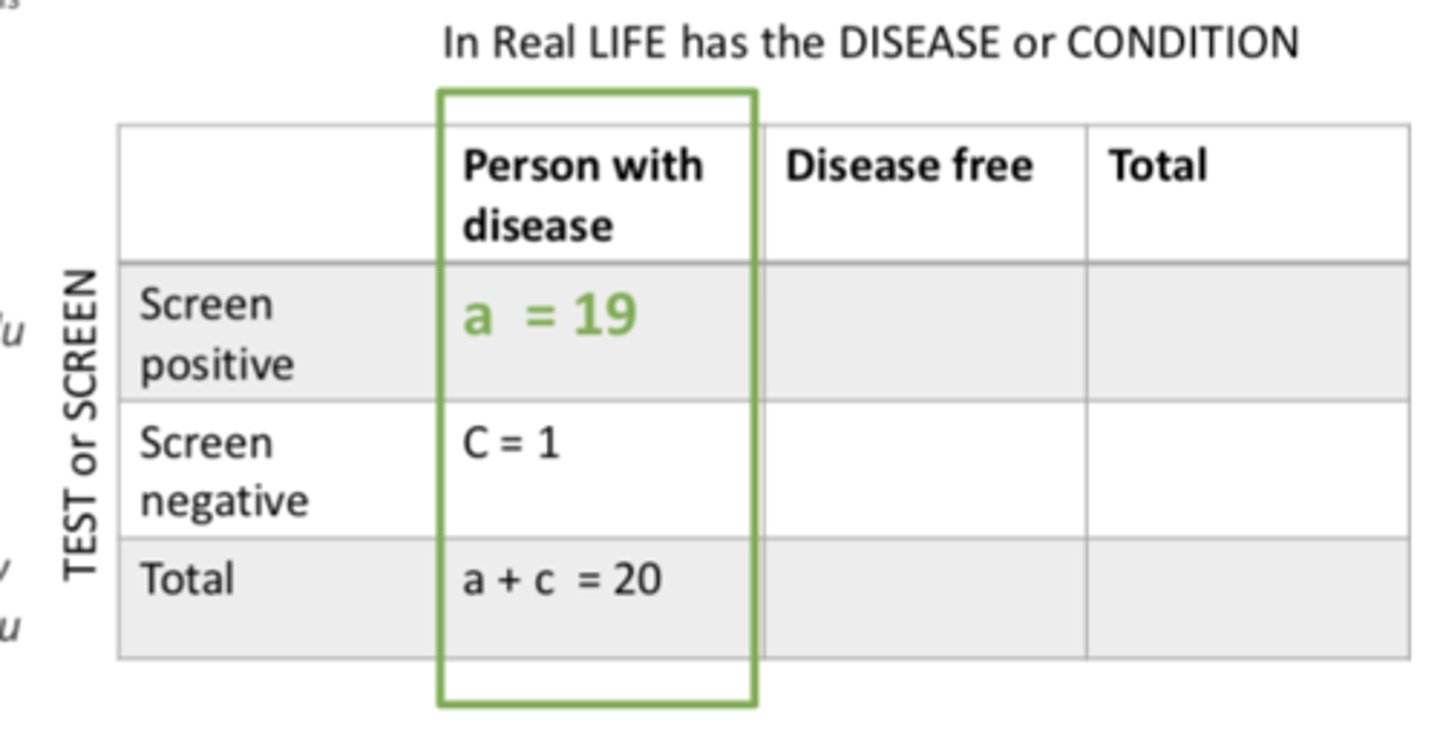
Sensitivity focuses on...
- people who really have a disease
- True positive (+) fraction
- probability that a person who really has a certain disease screens positive (+)
- (a /a +c) X100
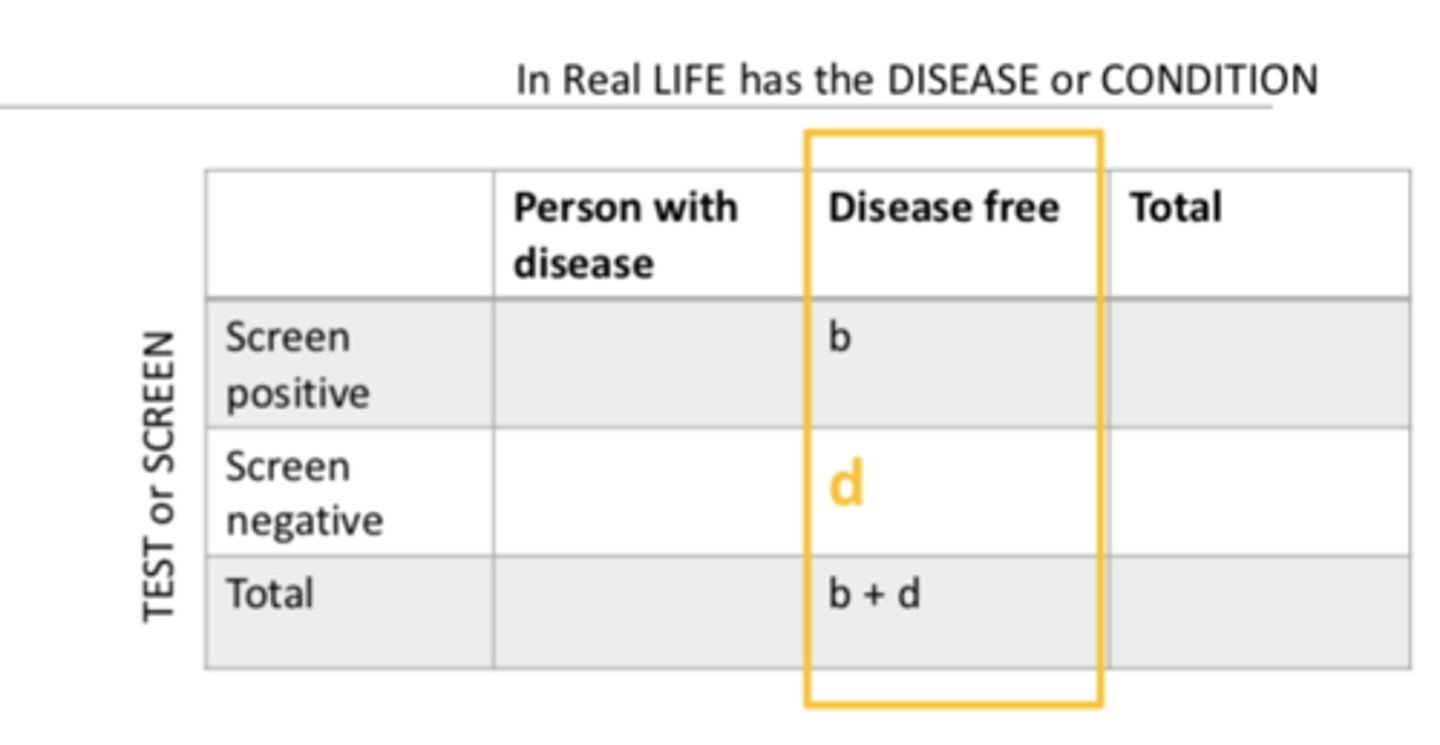
Specificity focuses on...
- people who do NOT have disease
- True negative fraction
- probability that a disease-free person screens negative
- (d /b + d) X 100
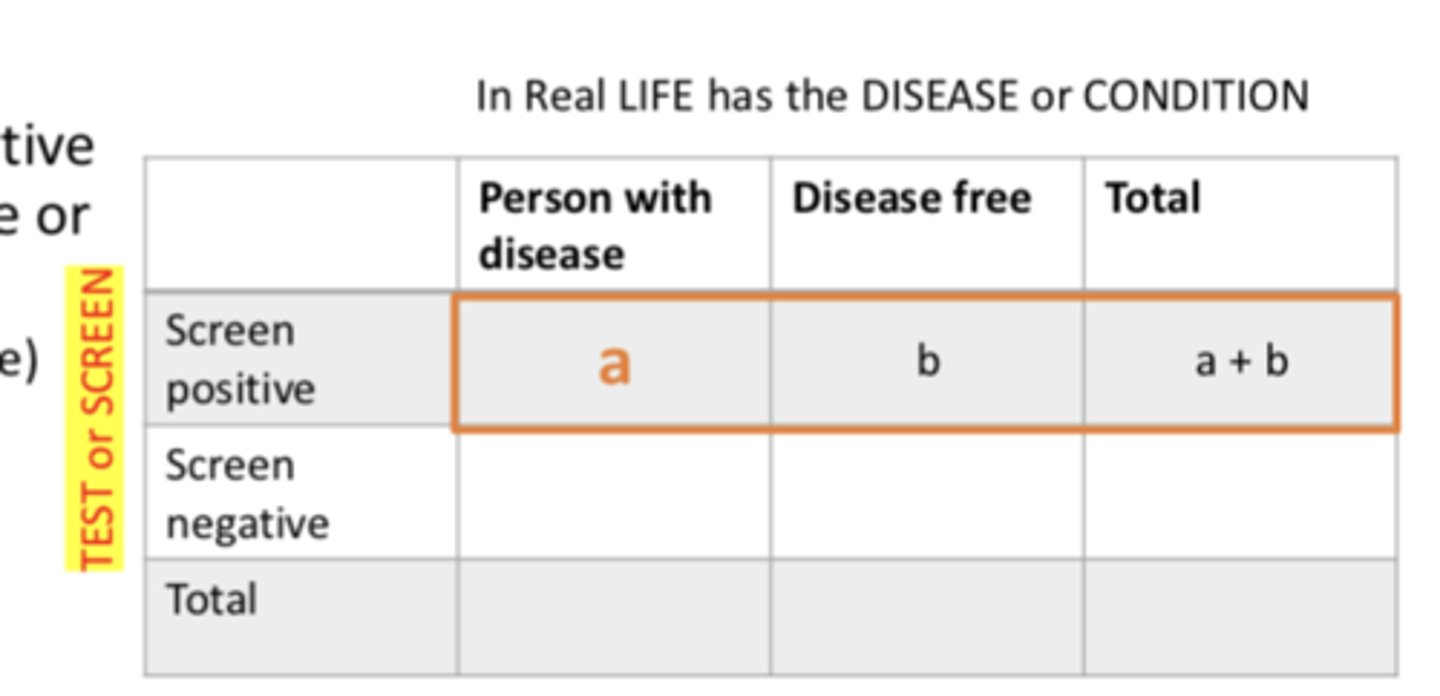
Positive Predictive Value (PPV)
- focuses on people who test positive
- probability that subjects with a positive screening test truly have the disease or condition
- true positive/(true positive + false positive)
- (a /a + b)X 100
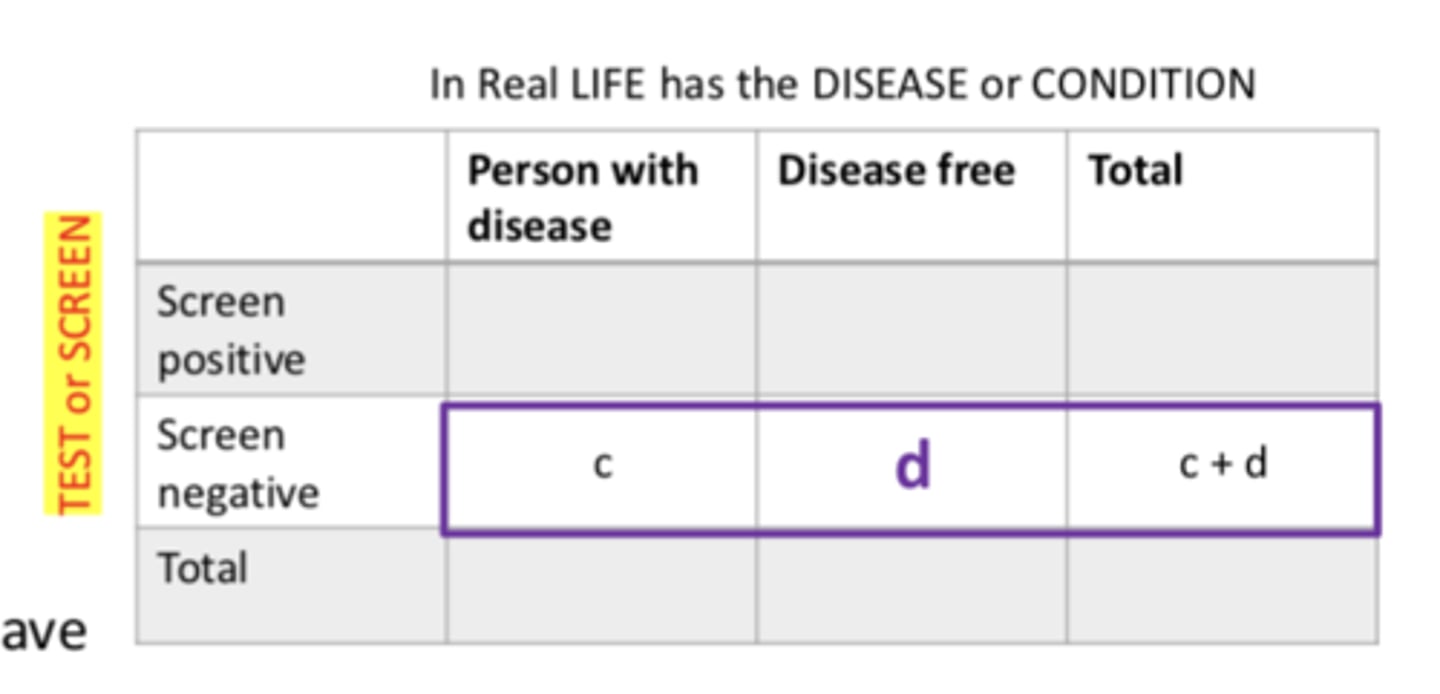
Negative Predictive Value
- focuses on people who test negative
- probability that subjects with a negative screening test truly don't have the disease
- true negative/ (true negative + false negative)
- (d/d + C) X100
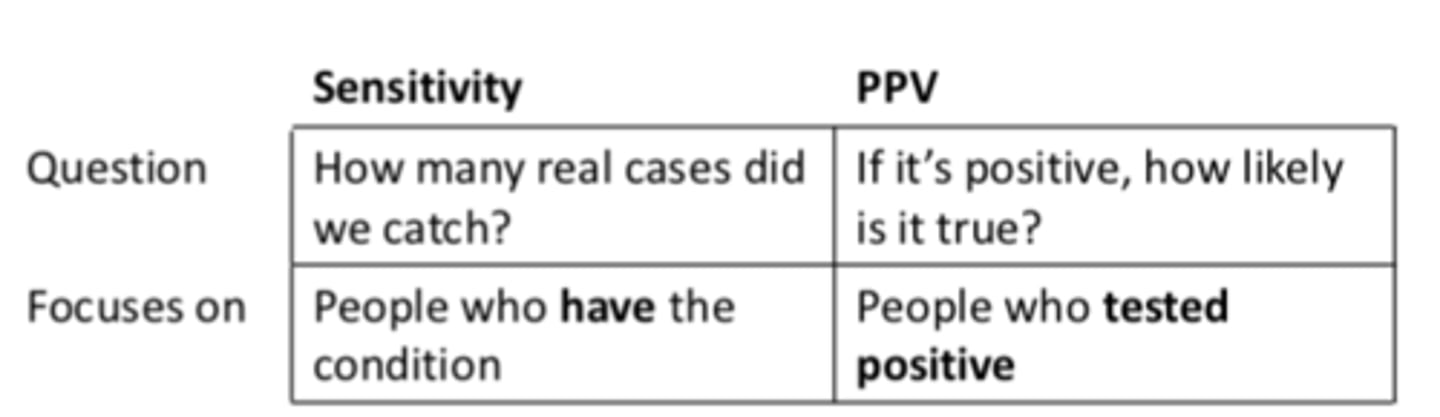
Sensitivity and PPV chart
Specificity and NPV chart

Sensitivity vs. PPV
Sensitivity: how many REAL cases did we catch? People who HAVE the condition, accuracy of identifying sick ppl
PPV: If it's positive, how likely is it to be true? People who TESTED POSITIVE, chance that a positive test actually means disease
Specificity vs. NPV
Specificity: How well does the test avoid false positives? People who DON'T HAVE the condition, accuracy of identifying healthy ppl
NPV: If it's negative, how likely is it correct? People who TESTED NEGATIVE, chance that a negative test actually means no disease
Auscultatory Gap & Blood Pressures: Korotkoff sounds become...
inaudible
Auscultatory Gap & Blood Pressures can lead to...
falsely LOW blood pressure
Auscultatory Gap & Blood Pressure is the reason we use what?
using palpable systolic with radial artery