Chapter Four Bio Exam
5.0(2)Studied by 17 people
Card Sorting
1/86
Last updated 3:51 AM on 2/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
1
New cards
Identify the functions of the skin
1. protects your body against infections and extreme temperatures
2. maintains your balance of fluids
3. synthesizes vitamin D for personal use
2
New cards
Identify the layers of the skin
Epidermis, (stratified squamous), dermis (dense, irregular connective tissue) , hypodermis (adipose tissues)
3
New cards
Describe features of the epidermis
first layer of skin (outermost), layer that always flakes off, avascular (wont bled if scraped), stratified squamous, regeneration happens lower
4
New cards
describe features of the dermis
many collagen/elastin fibers, contain nerve fibers and blood vessels
5
New cards
describe features of the hypodermis
made of adipose tissue, provides insulation/energy storage, and helps anchor skin
6
New cards
Describe the layers of the epidermis outermost to innermost
stratum corneum, stratum lucideum (only found in thick skin), stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale (connects epidermis to dermis and cell regeneration happens here)
7
New cards
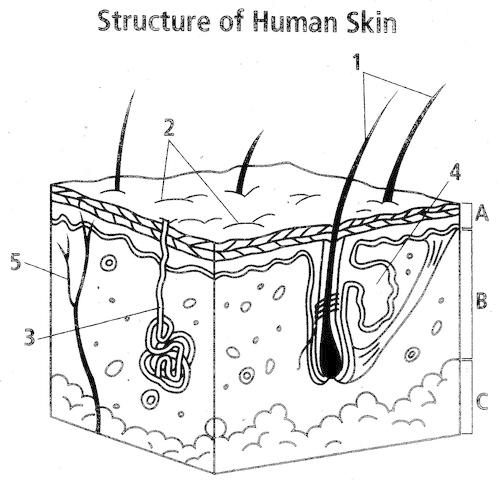
Label the following diagram
1. hair shaft
2. stratum corneum/sweat pores
3. sweat gland
4. sebaceous gland
5. blood capillaries
Also pictured: arrector pili muscle, hair follicle, adipose tissue, blood vessels, viable epidermis
a. epidermis
b. dermis
c. hypodermis
8
New cards
What are the functions of bone (the skeletal system)
1. support- anchors organs, holds the body upright
2. movement- bones act as levers for muscles to pull
3. protection-prevents damage to soft tissue and organs
4. storage- stores minerals like calcium and phosphorus, fat stored in the marrow
5. hematopoiesis- produces blood cells within the marrow
9
New cards
What is compact bone?
\-dense with few spaces
\-is primary component in long bones (arm and leg bones where greater strength is needed)
\-is primary component in long bones (arm and leg bones where greater strength is needed)
10
New cards
What is spongy bone?
\-”coral-like” or lattice appearance
\-lots of space
\- hold red bone marrow
\-ends of long bones, ribs, skull, pelvis, and vertebrae
\-lots of space
\- hold red bone marrow
\-ends of long bones, ribs, skull, pelvis, and vertebrae
11
New cards
What is yellow bone marrow and where is it found?
\-Found in the shaft of long bones
\-Used for fat storage
\-Used for fat storage
12
New cards
What is red bone marrow and where is it found?
\-Only found in some bones within adults- more in infants
\-found at the ends of long bones in spongy bone
\-Blood cell formation
\-found at the ends of long bones in spongy bone
\-Blood cell formation
13
New cards
What is the structure of an osteon?
1. Structural unit of compact bone
2. Osteocytes (bone cells) arranged in concentric circles (lamella) around the central canal
3. Lacuna = space in the hard extracellular matrix - osteocytes here
4. Tiny canals (canaliculi) within the osteon connects the osteocytes to each other and the central canal
14
New cards
Use packet to label the structures of long bones!!
15
New cards
Describe the steps of bone formation
Step 1-a cartilaginous model of the future bone forms
Step 2-Osteoblasts form a collar of bone around the shaft of the model
Step 3-The shaft of the cartilage model begins to hollow and spongy bone fills the space. Blood vessels continue to penetrate the area
Step 4-Secondary centers of bone formation develop in the ends of the bone
Step 5- cartilage remains only on the surfaces that rub and in the growth plates
Step 2-Osteoblasts form a collar of bone around the shaft of the model
Step 3-The shaft of the cartilage model begins to hollow and spongy bone fills the space. Blood vessels continue to penetrate the area
Step 4-Secondary centers of bone formation develop in the ends of the bone
Step 5- cartilage remains only on the surfaces that rub and in the growth plates
16
New cards
Describe the step of fracture repair
1. Hematoma: Blood clot forms at spot of break
2. Fibroblasts form a cartilage/collagen callus around the break
3. Osteoblasts convert cartilage to bone (bony callus)
4. Bony callus broken down to remodel the bone back to normal size
17
New cards
What is the role of osteoblasts?
build and create bone
18
New cards
What is the role of osteoclasts?
break down bone
19
New cards
What is the role of fibroblasts?
production of the rich ECM of connective tissues
20
New cards
What makes up the axial skeleton?
\-the bones in your skull, small bones of your middle ear, hyoid bone of your neck, vertebra, and your ribcage
\-supports the upright position and protects internal organs
\-supports the upright position and protects internal organs
21
New cards
What makes up the appendicular skeleton?
\-the upper and lower extremities, which include the shoulder girdle and pelvis.
\-aids in the movement of the body
\-aids in the movement of the body
22
New cards
Name the three types of joints
Fibrous-immovable/synarthrosis (found in the skull)
Cartilaginous-semi movable/ amphiarthrosis (found in vertebrae)
Synovial-freely movable/ diarthrosis (found in hips)
Cartilaginous-semi movable/ amphiarthrosis (found in vertebrae)
Synovial-freely movable/ diarthrosis (found in hips)
23
New cards
Name the different synovial joints and provide an example for each
Plane-Between tarsal bones
Hinge- elbow
Pivot- between vertebrae
Condylar-between radius and carpals bones of wrist
Saddle-between carpal and metacarpal bones
Ball & Socket-Hip
Hinge- elbow
Pivot- between vertebrae
Condylar-between radius and carpals bones of wrist
Saddle-between carpal and metacarpal bones
Ball & Socket-Hip
24
New cards
Refer to packet for structure of synovial joints!
25
New cards
What is extension and flexion?
\
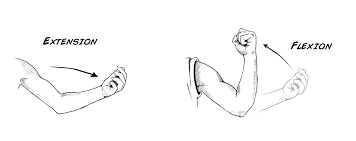
26
New cards
What is abduction and adduction?
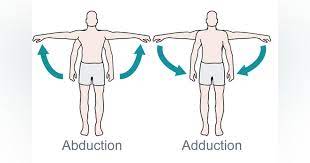
27
New cards
What is rotation?
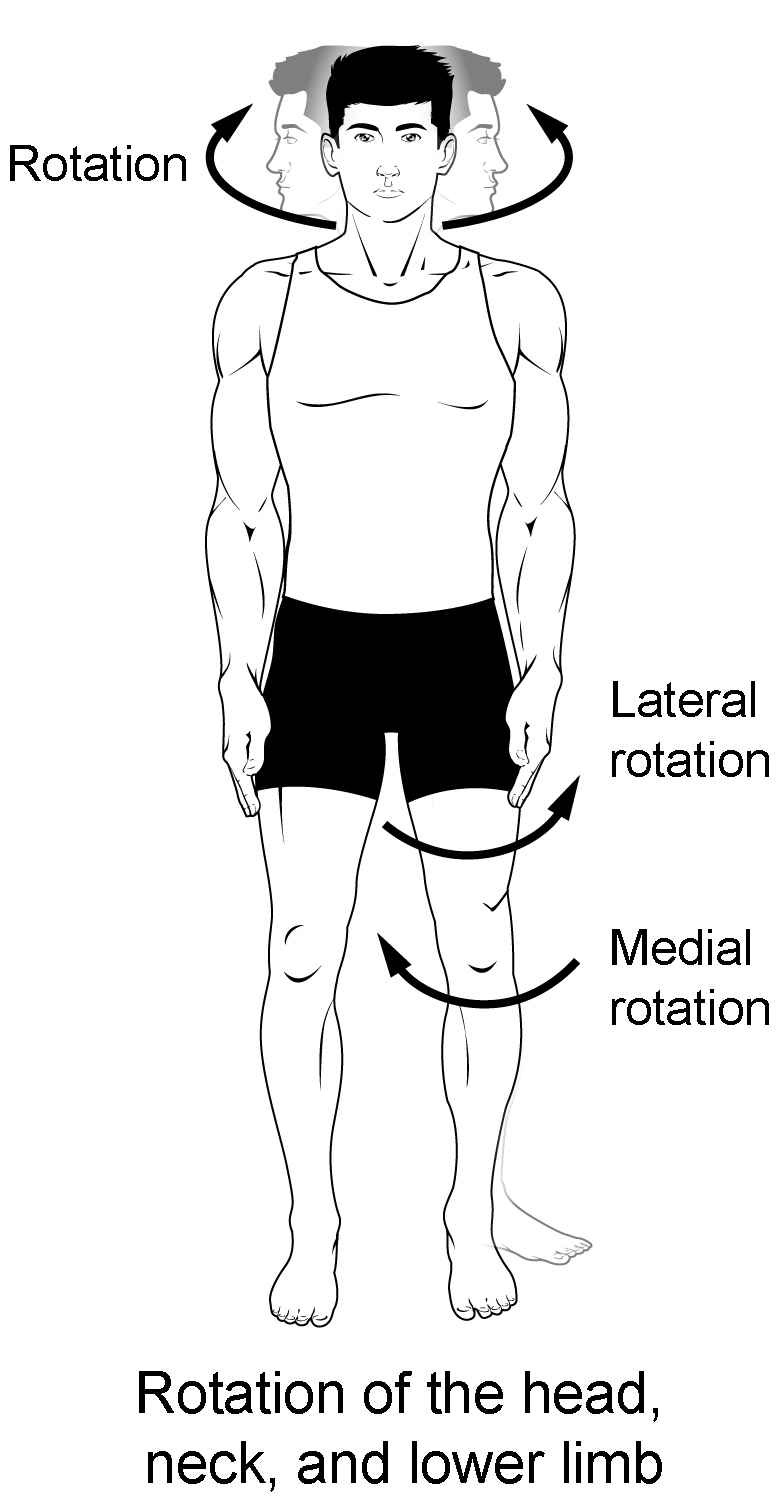
28
New cards
What is dorsiflexion vs. plantar flexion?
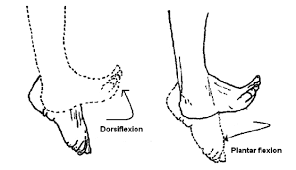
29
New cards
What is inversion and eversion?
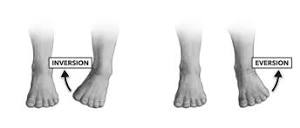
30
New cards
What is supination and pronation?
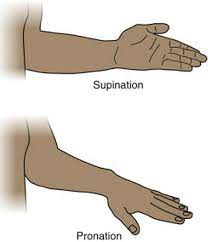
31
New cards
Name four characteristics of all muscle types?
1. Excitable-Respond to stimulus
2\. Contractile- tissue can shorten
3. Extensible- ability to stretch
4\. Elastic- can return to original size
32
New cards
How do synergistic muscle work? provide an example
\-They create the same movement.
\-Example: the liacus, psoas major, and rectus femoris all can act to flex the hip joint.
\-Example: the liacus, psoas major, and rectus femoris all can act to flex the hip joint.
33
New cards
How do antagonistic muscle work? provide an example
\-They cause opposing movement
\-When you perform a bicep curl the biceps will be the agonist as it contracts to produce the movement, while the triceps will be the antagonist as it relaxes to allow the movement to occur.
\-When you perform a bicep curl the biceps will be the agonist as it contracts to produce the movement, while the triceps will be the antagonist as it relaxes to allow the movement to occur.
34
New cards
What is the origin of a muscle?
The anchor/ point of attachment that does not move during contraction
35
New cards
What is the insertion of a muscle?
The “pull point”/ the point of attachment that moves during contraction
36
New cards
Use the packet to remember the structure of a muscle and structure of a sarcomere!!
37
New cards
What is the sliding filament theory?
1. Myosin head split ATP and become reoriented and energized
2. Myosin heads bind to actin forming cross bridges
3. Myosin heads rotate toward the center of the sarcomere (know as a power stroke)
4. As myosin heads bind ATP, the cross bridges detach from actin
5. Repeat
38
New cards
Name the steps of contraction by a motor nueron
1. Action potential arrives at a neuromuscular junction
2. Acetylcholine is released, then binds to receptors, and opens sodium ion channels, leading to action potential in the sarcolemma
3. Action potential travels down the t-tubles
4. Calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
5. Calcium binds to troponin causing cross bridges to form between actin and myosin- causing contraction
39
New cards
What is the role of troponin in contraction?
Calcium interacts with tropomyosin to unblock active sites between the myosin filament and actin allowing cross-bridge cycling.
40
New cards
What is the role of tropomyosin in contraction?
Tropomyosin blocks myosin binding sites on actin molecules, preventing cross-bridge formation, which prevents contraction in a muscle without nervous input.
41
New cards
Know the action of muscles from the table in lab 8!!
42
New cards
What is a motor unit?
All muscle fibers stimulated by one motor neuron
* Small motor unit- small number of fibers stimulated
* Large motor unit-large number of fibers stimulated
* Small motor unit- small number of fibers stimulated
* Large motor unit-large number of fibers stimulated
43
New cards
What is recruitment?
Stimulation of multiple motor units to trigger a stronger contraction
44
New cards
What is a muscle twitch?
Single stimulus, weak contraction
45
New cards
What is a summation?
Repeated stimulus that occur prior to full relaxation, leads to a stronger contraction
46
New cards
What is a tetanus?
Rapid, repeated stimulus that occurs without relaxation, strong/smooth contraction
47
New cards
What is ATP used for in muscles?
Reactivates myosin in cross bridge cycling, pumps calcium back into sarcoplasmic reticulum, resets sarcolemma ion balance so it can be triggered again by motor neuron.
48
New cards
What is creatine phosphate used for in muscle contraction?
formed during time of rest, during active periods it is converted to creatine and produces useable ATP
49
New cards
Describe an anaerobic pathway
without oxygen, uses glucose then lactic acid, used for high intensity/ short duration activity
50
New cards
Describe aerobic cellular respiration
with oxygen, glucose + oxygen= carbon dioxide + water, used for prolonged activity
51
New cards
Define the properties of a slow twitch muscle
● Contract slowly when stimulated
● High endurance (can contract for longer amount of time before becoming fatigued)
● Darker in color due to high amount of myoglobin (which stores oxygen)
● Can produce ATP aerobically for long periods of time
● High endurance (can contract for longer amount of time before becoming fatigued)
● Darker in color due to high amount of myoglobin (which stores oxygen)
● Can produce ATP aerobically for long periods of time
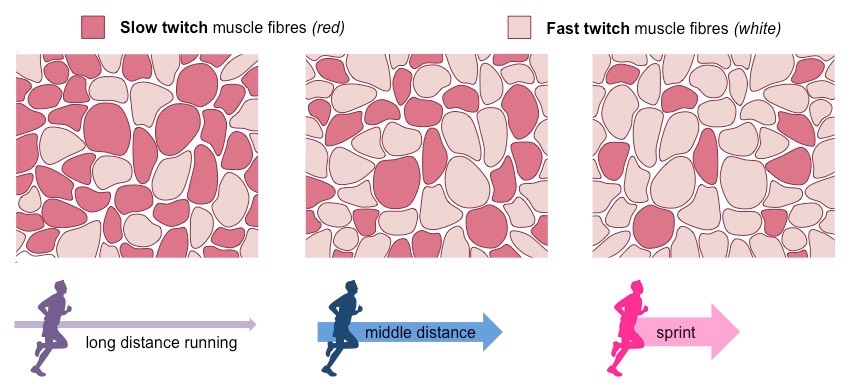
52
New cards
Define the properties of a fast twitch muscle
● Contracts quickly and powerfully when stimulated
● Fatigues easily
● Lighter in color
● Relies more heavily on anaerobic respiration
● Fatigues easily
● Lighter in color
● Relies more heavily on anaerobic respiration
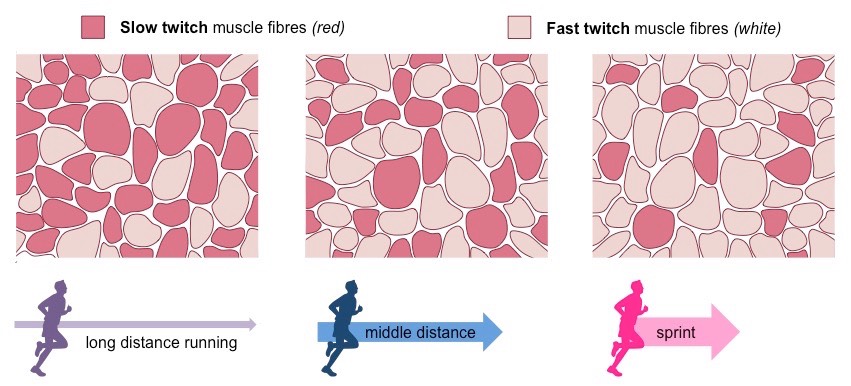
53
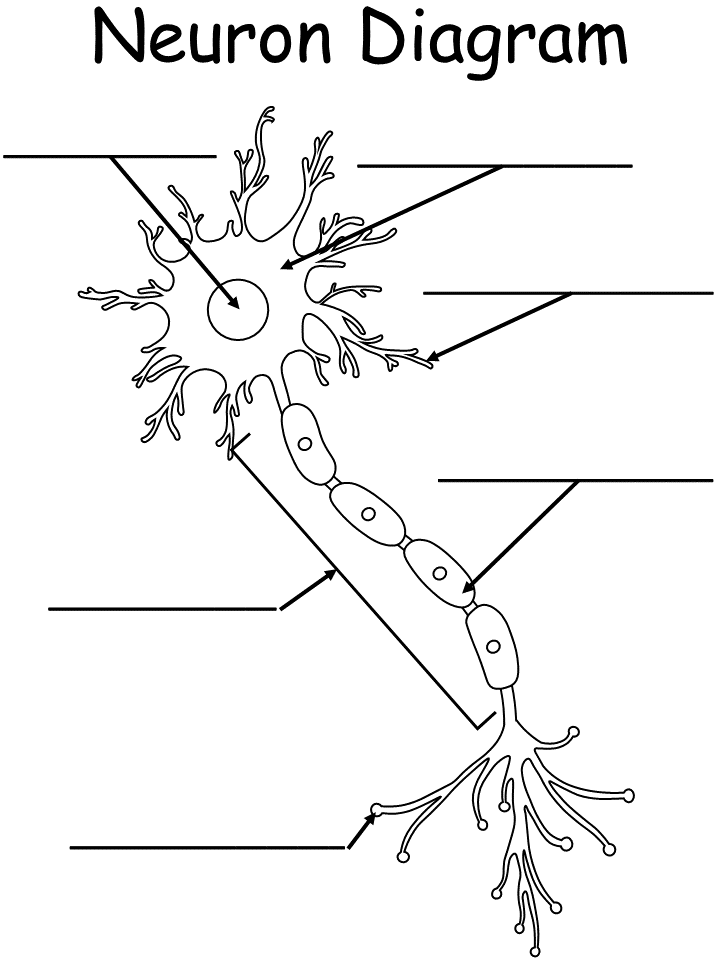
New cards
Label the neuron diagram
54
New cards
What are oligodendrocytes
Oligodendrocytes are the myelinating cells of the central nervous system (CNS).
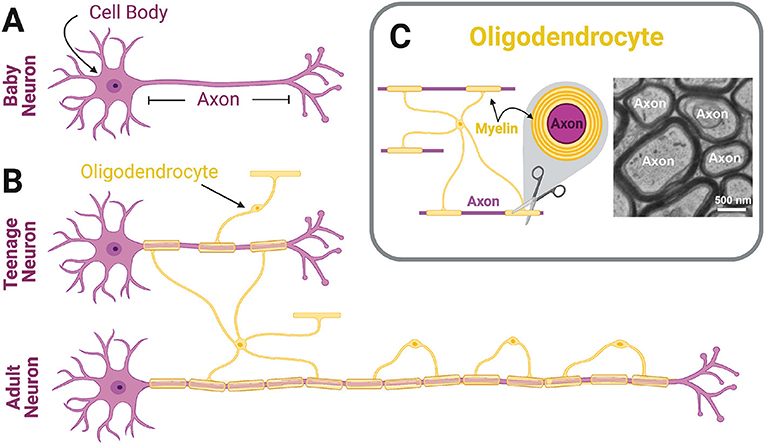
55
New cards
What are Schwann Cells
A type of glial cell of the peripheral nervous system that helps separate and insulate nerve cells.
56
New cards
What is the function of an axon
electrical impulses from the neuron travel away to be received by other neurons.
57
New cards
What is the function of a dendrite
Dendrites receive synaptic inputs from axons
58
New cards
What is the resting membrane potential of neuron?
\-70 Mv
59
New cards
At rest, where is there a high concentration of sodium ions (Na+), potassium (K+),
and larger, organic anions?
and larger, organic anions?
Outside = more Na
Inside = more K+ and negative ions
Inside = more K+ and negative ions
60
New cards
How does the sodium-potassium pump maintain resting membrane potential?
\-Pumps three sodium ions out and two potassium ions in
Uses ATP
Uses ATP
61
New cards
Describe how action potential works
1. Depolization- voltage-gated sodium channels open, Na+ enters the cell, membrane potential increases (becomes more positive)
2. Repolarization- voltage gated potassium channels open, potassium ions leave the cell, membrane potential decreases/ becomes more negative
3\. Return to rest- All voltage-gate channels closed and Na-K pump restores resting membrane potential (-70 mV)
62
New cards
Describe the process of synaptic transmission
Step 1: Impulse reaches synaptic knob opening calcium channels and calcium enters the cell
Step 2: Vesicles release neurotransmitters into the cleft
Step 3: Neurotransmitter moves across the cleft and binds to receptors
Step 4: Ion channels open and ions move
Step 2: Vesicles release neurotransmitters into the cleft
Step 3: Neurotransmitter moves across the cleft and binds to receptors
Step 4: Ion channels open and ions move
63
New cards
What are excitatory neurotransmitters
opens sodium channels, allows sodium to enter, causes depolarization- creates action potential
64
New cards
What are inhibitory neurotransmitters
they open potassium channels, allows potassium to enter, causes hyperpolarization
65
New cards
What makes up the CNS and what is the function?
the brain and the spinal cord; controls how we think, move, learn and carries messages to body
66
New cards
What makes up the PNS
cranial and spinal nerves
67
New cards
What does the sensory division of the PNS do?
sensory=input, somatic (voluntary movements)
68
New cards
What does the motor division of the PNS do?
Motor= output, somatic and autonomic
69
New cards
What is the parasympatheic condition?
adjust body function to conserve energy- calm mode
70
New cards
What is the sympathetic condition?
prepares body for fight or flight response
71
New cards
What are meninges?
Protective layers of the CNS
72
New cards
List three types of meninges
dura, arachnoid, pia
73
New cards
What is the function of the frontal lobe
thinking, planning, decision making
74
New cards
Label the lobes of the brain
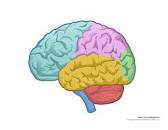
75
New cards
what is the function of the parietal lobe
perception and spelling
76
New cards
what is the function of the occipital lobe
Vision
77
New cards
what is the function of the temporal lobe
memory, understanding, and language
78
New cards
What is the function of the cerebellum
Responsible for sensory-motor coordination, balance and equilibrium, posture, etc.
79
New cards
What makes up the brain stem (in order from top to bottom)
midbrain, pons, medulla oblangada
80
New cards
What is the function of the brainstem
Controls reflexes, breathing, heart rate, blood pressure
81
New cards
What makes up the dienceophalons and what are their functions
thalamus (sorts and relays impulses to cerebrum), hypothalamus (regulates body temp and thirst) and the pituitary gland
82
New cards
What is reflex arc
Allows for rapid response
to a stimulus
to a stimulus
83
New cards
What does a mechanoreceptor sense
Physical force
84
New cards
What does a thermoreceptor sense
tempature
85
New cards
What does a photoreceptor sense
light
86
New cards
What does a chemoreceptor sense
chemicals
87
New cards
What does a nociceptors sense
pain and physical damange