BioLab REPORTS
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Laboratory Reports
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
How many amount of cheek cell to put?
Temporary amount
What are the six content of our lab reports?
Introduction
Materials and Set-Up
Procedure
Results
Interpretation and Analysis
Conclusion
References
What are the 12 materials needed in human cheek cell experiment?
➢ Blotting paper
➢ Compound microscope
➢ Distilled water
➢ Glass microscope slides
➢ Glycerine
➢ Methylene Blue solution (0.5% to 1%)
➢ Needle
➢ Plastic cover slips
2 Plastic pipette or dropper
➢ Papertowels or tissue
➢ Sterile toothpick
➢ Tweezer/Forceps
A cell is shielded by its _______, often known as its _______
plasma membrane; cell membrane
gelatinous fluid that fills a cell's inside; made up of several organic compounds, salts, and water.
Cytoplasm
membrane-enclosed; houses genetic material,
nucleus
A subcellular structure known as an ______ serves one or more specific purposes inside the cell
organelle
assemble proteins
ribosomes
supply chemical energy; powerhouse of the cell
mitochondria
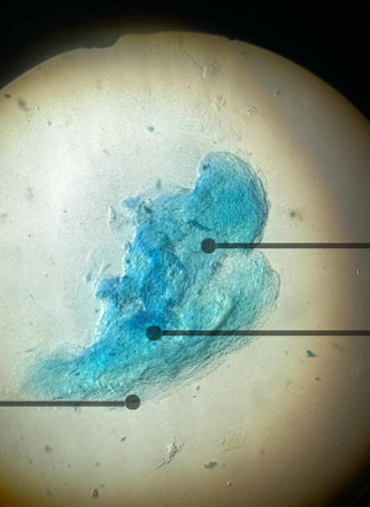
Label the ff:
Cytoplasm, nucleus, cell membrane
After ________ minutes remove any excess water and stain from the slide using a ______
2-3; blotting paper.
Concentrated methylene blue is toxic if ingested.
True or false?
True
Cheek cells are what kind of cell?
Epithelial
Place the slide on the microscope, with _____objective in position, and find a cell. Then view at higher magnification.
4x or 10x
What are th 5 materials used in Diffusion experiment?
Materials:
Petri dish
Jelly Cork
Borer or glass
Pasteur pipette
Needle
Dropper
pour the plates to a depth of stirred jelly in approximately what centimeters?
~ 0.8 cm
Take a petri dish of gelatin that has been sitting at room temperature for how many minutes?
5-10 minutes
The position of the hole in the plate is not important, but it should be far enough from the edge of the plate
True or false
true, it should be where diffusion of the spot can be easily observed
Carefully pipette a small drop ______ of dye solution into the hole using a Pipetman or Pasteur pipette.
(2-10 µl); a pinch
measure the diameter of the dye spot at different times after adding the dye, e.g., __________________ minutes
0, 5, 10, 30, 60, 150 minutes.
The increase in size of the dye spot will be easy to see even after 5 or 20 minutes
true or false
false: 5 or 10 minutes
After measuring the diameter of the dye spot, divide by two to find the_____
radius
Are the times required for Methylene Blue to diffuse a given distance, e.g., 0.5 cm, in gelatin or Jello the same or different for the different dyes?
a passive transport method that does not require energy and involves the transport of tiny molecules from a highly concentrated area to a less concentrated area
Diffusion
What is the significance of diffusion?
Diffusion is crucial to cells because it enables them to eliminate waste materials and acquire the beneficial elements needed for growth and energy
Through different temperatures, higher temperatures cause molecules to travel more energetically, which accelerates the diffusion process. Lower temperatures cause molecules' energy to drop, lowering the diffusion rate
True or false
True;
the colder, the lower diffusion rate
the hotter, the higher diffusion rate
What are the three percentages of the methylene blue solution in diffusion?
1% - cold
2% - hot
3% - room temp
CHR
Cell cytoplasm moves relatively slowly because it is low in viscosity and density.
True or false
false: exceeding in viscosity and density
Plants make their own food in a process called ______
photosynthesis
A by-product of photosynthesis, ______, will be released by the plant
oxygen
What are the 12 materials needed in the photosynthesis experiment?
Spinach Plant leaves (enough leaves to make 20 leaf disks using the puncher)
● Single hole puncher
● Baking Soda
● Water
● ⅛ measuring teaspoon
● Measuring Cup/Beaker
● Liquid Dish Soap
● Transparent Cups (4)
● Big Plastic Syringe (without needle)
● Light source
● Paper towels
● Timer
____ mL water
_____ drop of dish soap
____ teaspoon of baking soda.
300mL
1 drop
1/8 teaspoon
Stir the solutions gently in both cups to avoid creating _____.
foam
It is a process in which sunlight energy is used to make glucose
photosynthesis
Where does photosynthesis occur?
chloroplast
What are the two main functions of chloroplasts?
Chlorophyll absorbs most of the colors i
Why do most leaves appear green?
Chlorophyll absorbs most of the colors in the color spectrum and reflects only green and yellow wavelengths of light
What is the primary pigment found in the chloroplast?
Chlorophyll
What is the formula for photosynthesis?
CO2+ H2O+sunlight----> C6H12O6+ O2

What three things are used to make glucose in photosynthesis?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Where does the water come from?
Where does the water enter the plant?
The water comes from the ground and absorbed through roots
Name 3 sources of CO2
Exhaled, Factory smokestacks, car fumes
What type of energy does the plant use to convert CO2and H2O into sugar?
Light energy
What is produced in photosynthesis?
Glucose and oxygen
What is the glucose used for?
for energy and growth.
What process happens in the mitochondria?
Chemical reactions
What is the purpose of the process of cellular respiration in mitochondria (what does it create)?
generate usable ATP energy to support many other reactions in the body
Some organisms perform photosynthesis to produce energy. Other organisms cannot do photosynthesis. What can they do in order to generate energy?
must eat the carbohydrates produced by plants, algae, and other animals.
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
Producing useable ATP energy to support several other bodily reactions is the aim of the process of cellular respiration.
What happens to carbohydrates during cellular respiration?
Cells take the carbohydrates into their cytoplasm, and through a complex series of metabolic processes, they break down the carbohydrates and release the energy
What is the chemical energy in the cell called?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
What is one product of cellular respiration?
product of cellular respiration: water, carbon dioxide, and energy (ATP).
Oxygen is a PRODUCT OR REACTANT of respiration?
Reactant
Genetic alteration refers to altering the ______ found in the nucleus of cells
DNA
What are the 7 materials in Cell energy production experiment?
Calcium hydroxide (3 mL of lime water)
glass pipette
phenolphthalein
goggles
beaker
graduated cylinder
stirring rod
What is the transformation of colors in cell energy production?
Pink or purple to Colorless
How do you blow?
Outward
How many drops of phenolphthalein solution are in the water?
10-12
How many ml of calcium hydroxide into the beaker?
10 ml of calcium hydroxide
What is the objective of cell energy production experiment?
To demonstrate the evidence of aerobic cellular respiratio
Since lime water is a base, the addition of _________caused the solution to turn pink
phenolphthalein
Water is created when the hydroxide ions in the calcium hydroxide combine with the hydrogen ions from the carbonic acid.
process of neutralization reaction
What is the chemical formula for the process of neutralization reaction
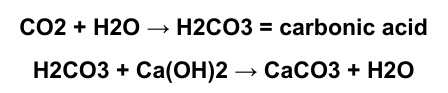
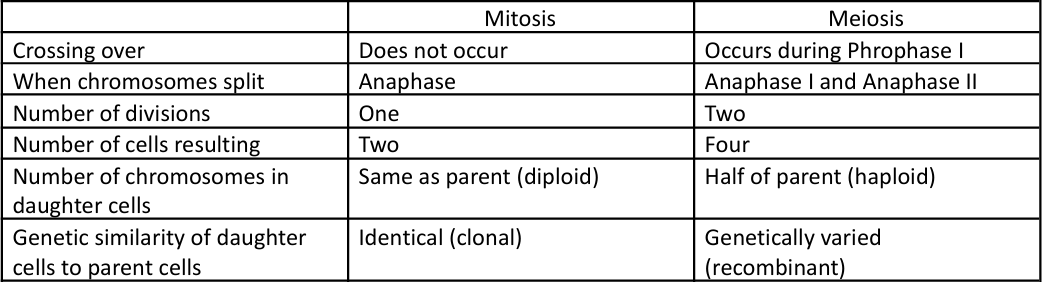
Summarize the major differences between mitosis and meiosis
appears as a constricted region of a chromosome and plays a key role in helping the cell divide up its DNA during division (mitosis and meiosis)
region where the cell's spindle fibers attach
centromere
_________ paired barrel-shaped organelles located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope. It plays a role in organizing microtubules that serve as the cell's skeletal system
Centrioles
cellular structure involved in pulling the chromatids apart during cell division
Centrosome
A large protein complex that forms on a specific part of a chromosome called the centromere.
kinetochore
The two _______ are joined at a constricted region of the chromosome called the centromere
“sister” chromatids
structure that forms when the cytoplasm of a plant cell divides
Cell plate
plasma membrane invagination at the cell division site
cleavage furrow
term that describes a cell or organism with two complete sets of chromosomes.
diploid
Refers to the presence of a single set of chromosomes in an organism's cells
haploid
What role would mitosis play in the body of an adult animal?
Produces new cells that are genetically similar to one another.
Allows organisms to expand in size and repair damaged tissues.
Required for tissue repair and regeneration in the adult body, allowing injured or dead cells to be replaced.
Promotes the growth of specific tissues.
What advantage does the process of crossing over bring to reproduction?
Crossing over during meiosis offers an important advantage by promoting genetic diversity.
Why would the method of cytokinesis in animal cells not work in plant cells?
Cytokinesis in animal cells, which involves pinching the membrane via a cleavage furrow, wouldn’t work in plant cells due to their rigid cell walls. Instead, plant cells form a cell plate that develops into a new wall, dividing the cell
What is the purpose of mitosis?
cell proliferation and replace worn out cells
What is the purpose of meiosis?
production of sex cells or gametes
Which organisms perform in mitosis?
Somatic cells
Which organisms perform in meiosis?
sex cellsA
How long does mitosis take?
18-20 hrs
How long does meiosis take?
72 hours or 3 days
What is an example of a disease caused by an error in mitosis?
Production of too much or too few chromosomes, leading to
chromosomal disorders
hereditary diseases
cancer
What is an example of a disease caused by an error in meiosis?
Medical Klinefelter conditions like
Klinefelter Syndrome
Down Syndrome
Turner Syndrome
Triple X Syndrom
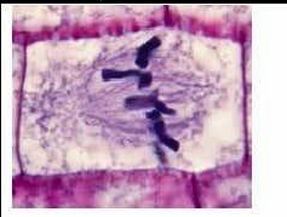
label this phase
metaphase
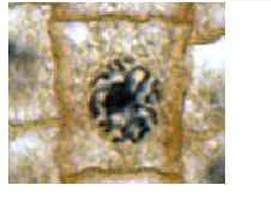
label this phase
prophase
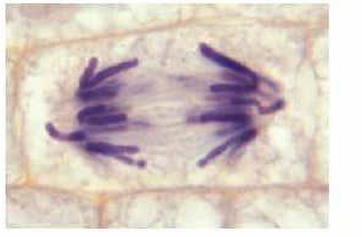
label this phase
Telophase
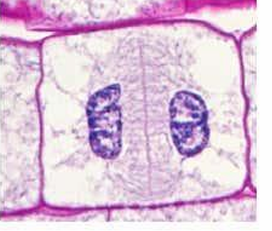
label this phase
Anaphase
label this phase
Interphase
They are coiled structures made out of DNA and proteins.
Chromosomes
There are __ pairs of chromosomes in a cell.
23
_____ is a disease that occurs when the cell cycle is no longer regulated.
Cancer
The ________ is a repeating series of events, including growth, DNA synthesis, and cell division
cell cycle
___________phase is when the cell’s DNA is copied in the process of DNA replication.
S phase or Synthesis Phase
Chromosomes: Coiled structure; Chromatins:
Grainy material and not coiled
The DNA was replicated after meiosis I during interphase since there were already two haploid daughter cells.
True or false
True
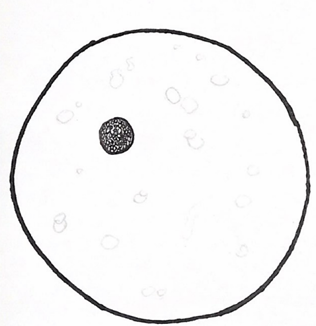
label this tonic
RBC with 0.2% NaCl solution
Hypotonic
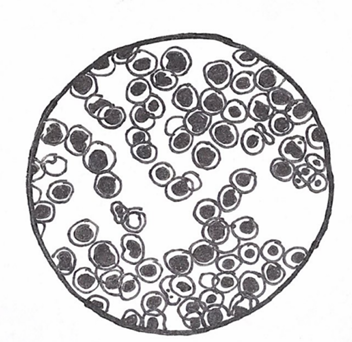
label this tonic
RBC with 0.9% NaCl Solution
Isotonic
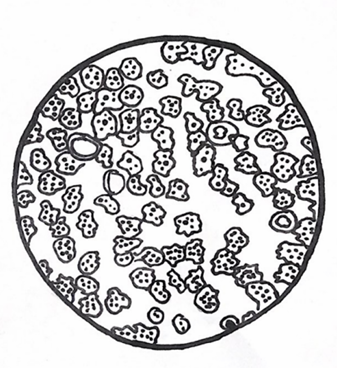
label this tonic
RBC with 2% NaCl solution
Hypertonic
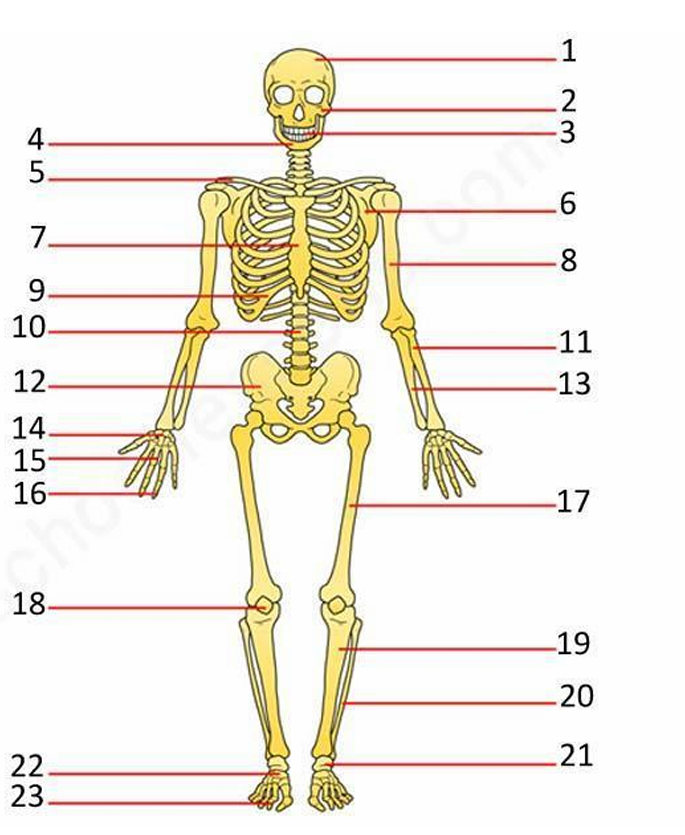
Label everything
