IB Biology HL DNA and Protein
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is bacteriophage?
A virus that attacks bacteria
DNA is labeled as what in experiments
Radioactive phosphorous (32P)
Protein contains what kind of radioactive isotope?
Radioactive sulfur (35S)
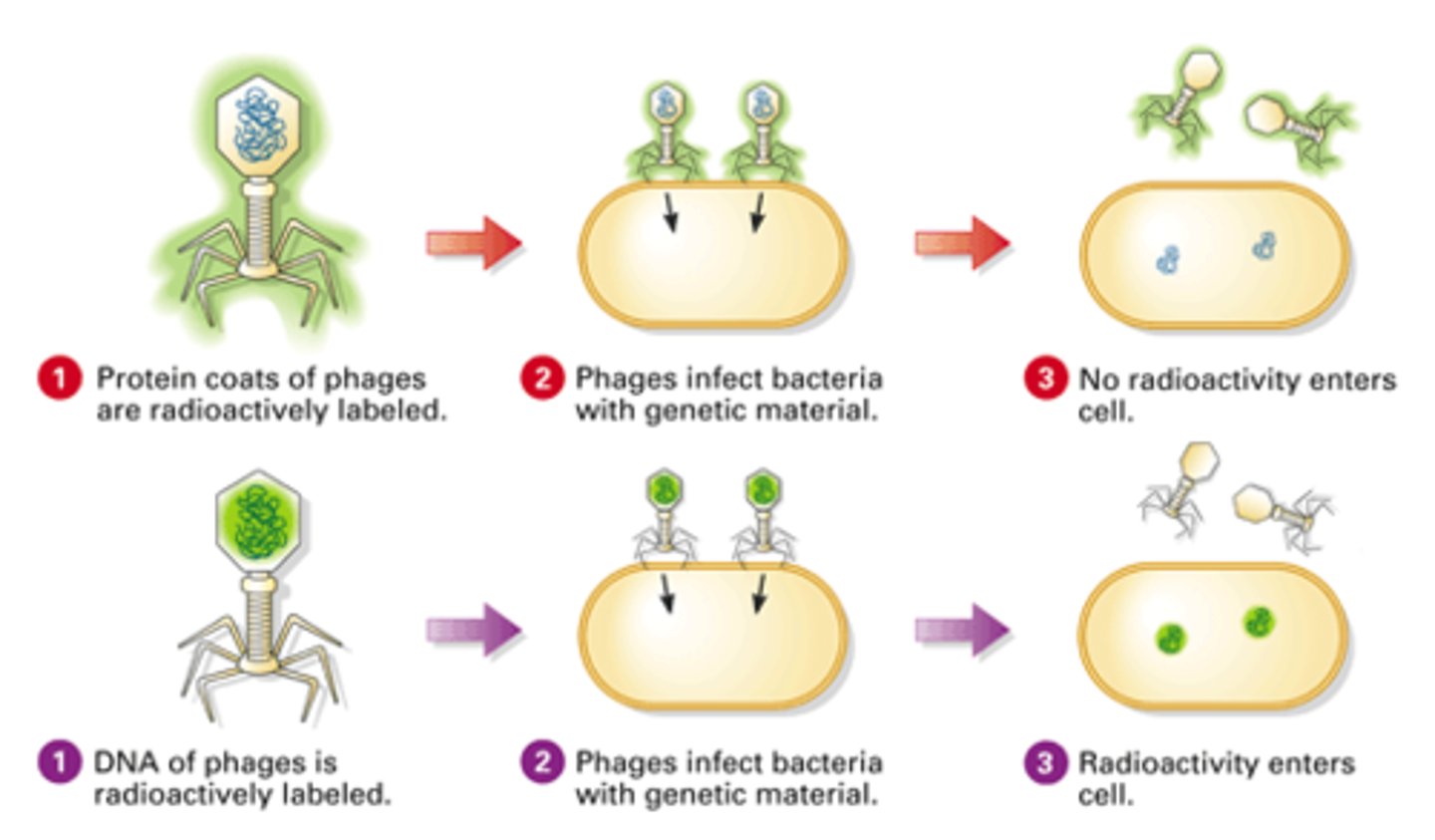
Hershey and Chase Experiment
A bacteriophage with 32P was labeled to have DNA. A bacteriophage with protein 35S was labeled to have protein. The bacteriophages were put in a medium with bacteria and later infected the bacteria.
Hershey and Chase Experiment Result
Found that 32P was present in the bacterial cells, while 35S remained in the bacteriophage
Hershey and Chase Experiment Conclusion
DNA from the bacteriophage entered the bacteria proving that DNA can pass from one organism to another
Hershey and Chase Experiment Diagram
Genetic Dogma
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
RNAP
-RNA Polymerase
-Copies a DNA sequence into an RNA sequence
Transcription for Eukaryotes
-Begins when RNAP binds to promoter sequence
-RNAP uses template strand
-Transcription factors bind to promoter which allows RNAP to bind and start transcription
-RNAP adds 5' end of free nucleotide to 3' end of growing mRNA molecule
-Transcription is finished at end of gene
Transcription for Prokaryotes
Same process but doesn't involve transcription factors as RNAP binds directly to promoter and starts binding
Exons
Regions of DNA that code for proteins and are not spliced out during RNA processing
Introns
Noncoding segments of nucleic acid that lie between coding sequences.
Difference between Exons and Introns
Exons code for proteins, introns don't.
Post Transcriptional Modifications
-Pre mRNA has introns and exons
-Spliceosome cut open useful exons
-Ligase glues exons together (alternative splicing may occur)
-End result is large protein or small proteins
Three Stages of Translation
initiation, Elongation, Termination
Start Codon
AUG (methionine)
Stop Codon
UAA, UAG, UGA
P-Site
-Starting site
-Holds the tRNA that carries the growing polypeptide chain
Initiation for Translation
1. Small sub-unit of ribosome binds to mRNA
2. tRNA with anticodon complementary to AUG binds
3. Large sub-unit of ribosome binds to small unit and tRNA with AUG is on P-site
4. Peptide bond forms between amino acids held by tRNAs in P and A sites
Initiation in summary
AUG gets on P site
Elongation for Translation
1. Ribosome moves three bases on along mRNA towards 3' end
2. tRNA in E site detaches and moves away
3. tRNA with anticodon complementary to next codon on mRNA binds to A site
4. Growing polypeptide that is attached to tRNA in P site is linked to amino acid on tRNA in A site by formation of a peptide bond
Elongation in Summary
Amino acids bond together
Termination for Translation
1. Ribosome moves along mRNA in 5' to 3' direction, translating each codon into amino acid on elongating polypeptide, until it reaches stop codon
2. No tRNA molecule haas complementary anticodon and instead release factors bind to A site, causing release of polypeptide from tRNA in P site
3. tRNA detaches from P site, mRNA detaches from small sub-unit, and large and small sub-unit of ribosome separte
Termination in Summary
Ribosome gets to stop codon
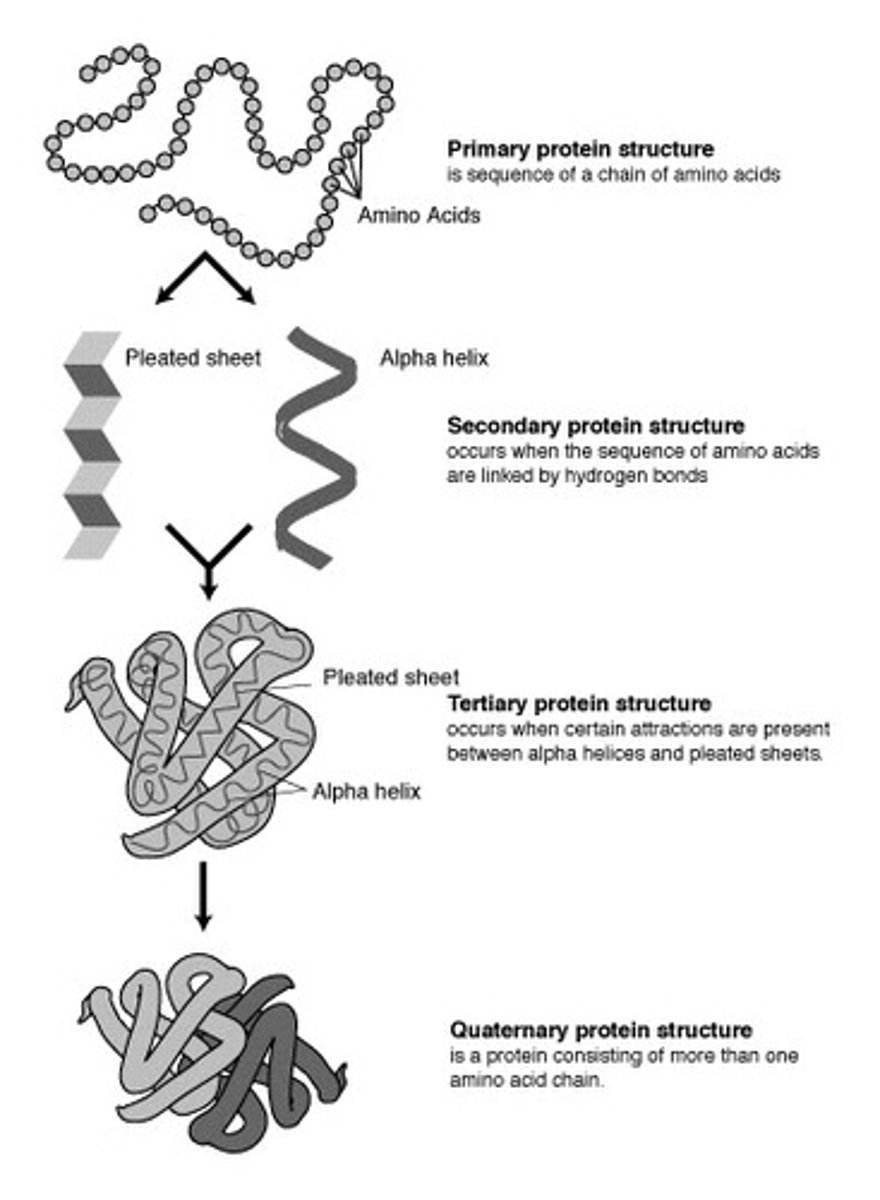
Primary Proteins
Sequence of amino acids
Secondary Proteins
-Alpha helix
-Beta pleated sheets
-Hydrogen bonds
Tertiary Proteins
-Disulfide bonds stabilize tertiary proteins
-Ionic bonds
-Vanderwaal forces
-Hydrophobic interactions (caused by R groups in amino acids)
Quaternary Proteins
-When multiple polypeptides are linked
-Same bonds as tertiary
-Ex: hemoglobin
Protein Structures Diagram
Epigenetics
Effect of environment on gene expression
DNA Methylation
-Methyl group (CH3) added to cytosine of DNA
-Represses transcription so DNA won't make RNA
-Thus, it stops production of protein
First Step of DNA Replication
DNA gyrase moves in advance of helicase loosens up DNA so it doesn't get tangled when unwinding
Second Step of DNA Replication
DNA helicase unzips DNA strands; single-stranded binding proteins keep strands apart
Third Step of DNA Replication
-DNA Polymerase III adds nucleotides 5' to 3' direction
-On leading strand, it moves same direction as replication fork (close to helicase)
Fourth Step of DNA Replication
DNA primase places RNA primers on lagging strand to help start DNA replication
Fifth Step of DNA Replication
-DNA Polymerase III starts replication next to RNA primer
-Adds nucleotides in 5' to 3' direction (moving away from replication fork on lagging strand)
Sixth Step of DNA Replication
Okazaki fragments are formed
Seventh Step of DNA Replication
DNA Polymerase I replaces RNA primers with DNA but leaves small gaps
Eight Step of DNA Replication
DNA Ligase seals up gaps by making sugar-phosphate bonds, completing new DNA strand