881 - Physical Determinants
1/180
Earn XP
Description and Tags
midterm one
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
Draw the COTIPP diagram
COTIPP diagram

Step one in COTIPP
seek understanding about context
what is involved in seeking understanding about context
listen to personal histories, identities, and experiences
use critical reflexivity and humble self-reflection
seek to understand layers of structural factors that impact occupational participation
step two of COTIPP
reflect, critically reflect, and reason
what is involved in reflect, critically reflect, and reason
reflect on OT practice
critically reflect on systems and structures
reasoning guides what OTs say and do from their values and beliefs
third step in COTIPP
Justice, equity and rights based lenses
what is involved in justice, equity, and rights-based lenses
recognize occupational rights as human rights
taking action to remove barriers to participation
advocacy to uphold the rights of clients and collectives
fourth step in COTIPP
connect
what is involved in the connect stage
rapport building, considering referal, discuss benefits of OT, obtain consent, determine to continue or refer
fifth step in COTIPP
seek to ounderstand and define purpose
what is involved in seek to undertsand and define purpose?
client sharing their story, ensuring you have the knowledge required before continuing, ensure their is a role for OT, obtain consent
sixth step of COTIPP
explore occupational partiicaption
what is involved in exploring occupational participation
co-creating assesment plan for occupational participation
seventh step of COTIPP
co-design priorities, outcomes, goals, and plans
what is involved in co-desigining priorities, outcomes, goals, and plans
co-create priorities, goals, and outcomes, co-design a treatment plan, involve family and community
what are sternal precautions?
no lifting more than 10 pounds, no reaching behind the back or above head, no pushing or pulling the arms
what is the order of blood flow through the heart and lungs?
right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary veins, left atrium, bicuspid valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, aorta, body
isometric contraction
contration occurs with no muscle shortening
isotonic contraction
muscle contraction occurs, causing movement of the body
agonist
prime mover responsible for concentric contraction
antagonist
opposite of agonist, controls, slows and resists movement using eccentric contraction
synergist
additional muscles that assits agonist muscles
what is the central nervous system made of
brain and spinal cord
basic unit of nervous system
neuron
myotome vs dermatome
myo - muscle, derma - skin
How can damage to a peripheral nerve produce loss of sensation and movement to the
skin and muscles it supplies?
nerve sends information from peripheral systems (sensory) to the brain which allows them to respond in the peripheral (motor) systems, damage causes a break in this system
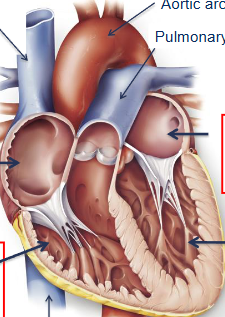
label this diagram
superior vena cava, right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve, pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, left atrium, bicuspid valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, aorta, inferior vena cava chordae tendinae, papillary muscle,

label the diagram
coronary sinus
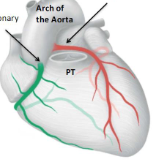
label the diagram
right and left coronary artery
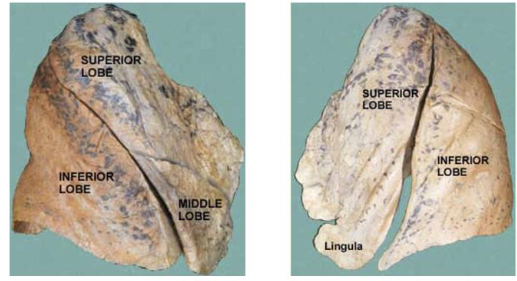
label this diagram
superior, middle, inferior lobes, horizontal and oblique fissures
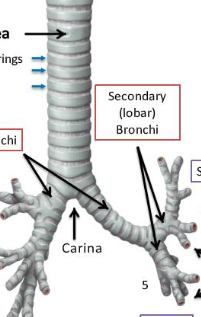
label this diagram
trachea, primary, secondary, tertiary bronchi
label this diagram
bronchioles, alveoli
what are the segements of the spinal cord and nerves
C1-C8, T1-T12, L1-L5, S1-S5, 1 coccygeal segment
where is their differences in spinal nerve entry and exit?
C1-C7 exit above the vertebrae, C8 and below exit below the verterbae
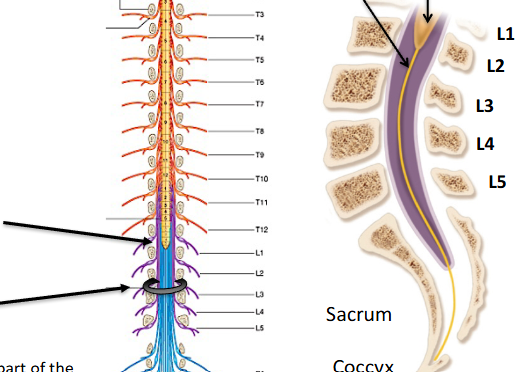
label the diagram
filum terminale, conus medullaris, cauda equina
what is remediation
restoring a skill or ability that was impaird
what is adaptation
modifying the activity to faciliate performance
what is compensation
use of alternative strategies or devices when skills are not possible
what is grading
increasing or decreasing difficulty of an intervention based on client response
what does occupation as means mean?
us of occupation as treatment to improve a clients capacities which enables another occupational function
what is occupation as end?
using the occupation as the therapy activity
which approaches are bottom up and top down
biomechanical/person focused = bottom up
rehabilitative approach/occupation focused = top down
what is the biomechanical frame of reference?
remediation or prevention of limitations in ROM, strength, and endurance
what is the rehabiliation frame of reference?
looks at overall client functioning and performance including context to teach compensation or adaptations while collaborating with the client
what is an activity analysis?
an assesment which focuses on understanding an activities components and the skills required for participation
what are the 4 steps of an activity analysis?
activity, steps, activity demands, analysis for intervention
what is a performance analysis?
observing the client perform an activity and grading it based on their performance
what is a frame of reference?
perspective or paradigm based on theoretical principles that guide the evaluation and treatment of impairments and injuries
what does the SMART acronym stand for?
Specifc, Measureable, Achievable, Realistic, Time-bound
what is an occupational performance problem?
an occupation a person wants to do, needs to do or is expected to do but cant do, doesnt do, or isnt satisfied with
what is the 2 minute walk test? What type of measure is it?
the client walks for two minutes without assistance and the distance is measured, biomechanical
what is the borg rate of percieved exertion test? what type of measure is it?
a measure used to rate the clients percieved exertion in relation to exercise intensity, biomechanical
what is the scale for the borg test? list the levels

what is the minnesota living with heart failure questionnaire? what type of measure is it?
a measure to asses physical and emotional quality of life of those with heart failure, rehabilitative
what are the ranges for the minnesota living with heart failure questionnaire?
less than 24 is good quality of life, 24-45 is moderate quality of life, greater than 45 is poor quality of life
what is the health promting activities scale? what type of measure is it?
asseses participation in leisure that promtoes or maintains well-being, rehabilitative
what is the Barthel index? what type of measure is it?
it asseses activities of daily living for acute or rehabilitative contexts, rehabilitative
what is the Katz scale? what type of measure is it?
is a graded assesment scale for six primary and psychosocial functions, rehabiliataive
what are the six things the katz tests
bathing, dressing, going to the toilet, transferring, feeding, contienence
how is the barthel index scored?
using increments of 5, which are then totaled
how are the katz assesments scored
1 for independant, 0 for dependant, then totaled
draw the basic units of a muscle
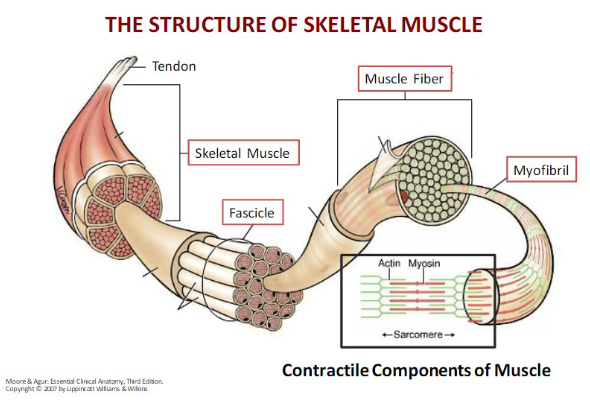
what must occur for movement to happen?
the muscle must cross the joint
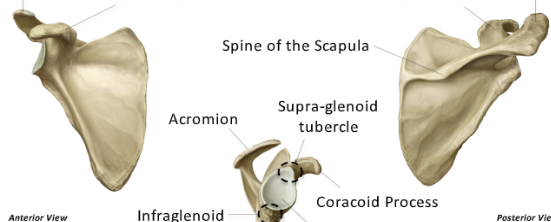
label these structures
acromion, coracoid process, spine of scapula, medial and lateral borders, gelnoid fossa, inferior angle
which joint is commonly dislocated? what is it called?
acromioclavicular joint, shoulder seperation
where is the scapulothoracic joint? why is it not a true joint?
between the scapula and thoracic cage, it is an articulation
what is the ratio of scapulohumeral rhythm
2:1 of glenohumeral to scapulothoracic movement
what is subluxation? what are the three types at the glenohurmeral joint?
when the bone comes partially out of its socket, anterior, posterior, inferior
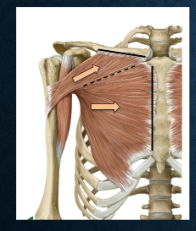
which muscles are these? functions?

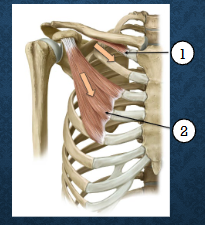
which muscles are these? functions?
Pectoralis Major - glenohumeral flexion, internal rotation and adduction
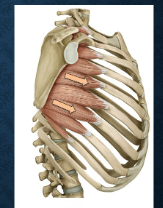
which muscles are these? functions?
Subclavius - depression of clavicle
Pectoralis minor - depression of scapula
which muscles are these? functions?
serratus anterior - protraction of the scapula
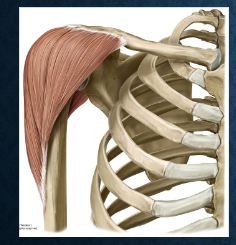
what muscle is this? functions?
deltoid - Glenohumeral flexion, extension, and external rotation
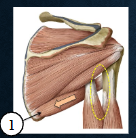
what muscles? Function?
teres major - extension, adduction, internal rotation of arm at GH joint
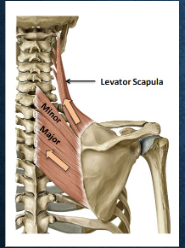
what muscles? function?
levator scapulae - elevation of scapula
rhomboid major and minor - retraction of scapula
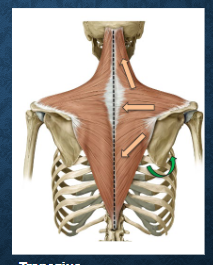
what muscles? function?
trapezius - elevation of scapula, retraction of scapula, upward rotation of scapula
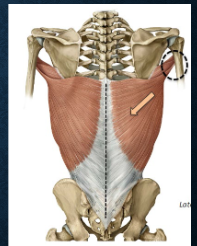
what muscles? function?
latissimus dorsi - extension, adduction, internal rotation of arm at GH joint
what is the brachial plexus? where is it located?
network that carries motor and sensory information to the chest, shoulder, arm, and hand, from the anterior rami of c5 to T1
draw the brachial plexus
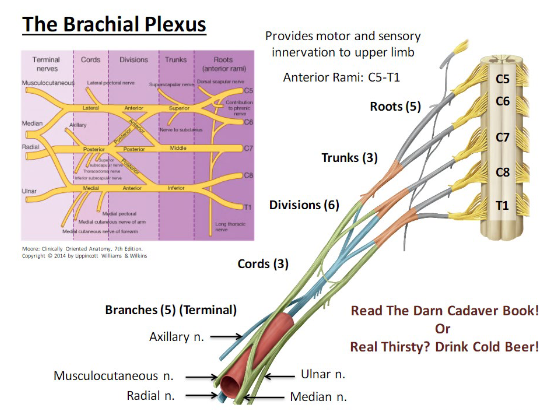
what does the long thoracic nerve inneravte? if this is imparied what is caused?
serratus anterior, winged scapula
what is the axilla? what are its borders?
area of the armpit, where many important structures pass through

what is adhesive capsulitis? what does it cause?
frozen shoulder, stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint with a loss of range of motion
what are the characteristics of adhesive capulitis?
ROM loss greater than 25% in two movement planes, with 50% loss of passive external rotation, sudden or gradual onset, impacts flexion, abduction, and external rotation
what is the DASH assesment? what type of assesment?
the disability of arm, shoulder, and hand assesment which measures the difficulty, ability to use the extremity, and pain, rehabilitative
what is ROM testing? what type?
range of motion testing, biomechanical
what is manual muscle testing? what type of test?
testing the strength and tension of muscles, biomechanical
what is the visual analogue scale (VAS)? what type of measure?
it is the numercal pain rating scale 1-10, biomechanical
what are the steps to a job analysis? what type of test is this?
rehabilitative

what is the most common type of arthritis?
Osteoarthritis
what is oseoarthritis
the slow onset of bony formations or spurs form on the affected joint causing pain and stiffness, resulting from wear and tear on joints, particularly in the protective cartilage that cushions ends of bones
how long does it take to develop osteoarthritis? what interventions can be used?
it is a gradual condition that develops over years, treatments include self-management, education, muscle strengthening, exercise, ergonomic education, medication and assitive devices
how many people with osteoarthritis have to leave work? or have issues with ADLS
1 in 5 have to leave work or retire early, 82% report having difficulty with ADLs
what is rheumatoid arthritis? causes?
it is an inflammatory autoimmune disease, which causes the body to attack the lining of joints, causes thickening of synovial memebrane and increased synovial fluid which causes stretching and swelling, weakening the ligaments and the joints
how long does it take to develop rheumatoid arthritis?prevalance?
rapid or sudden onset, 1 in 100 canandians have it, more common in women
symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis
pain, fatigue, discomfort, swelling
how to manage rheumatoid arthritis?
medication, education, ergonomic education, exercise, fatigue management, assistive devices
what joints are most affected by rheumatoid arthritis?
wrist, mcp, elbow, pip, shoulder
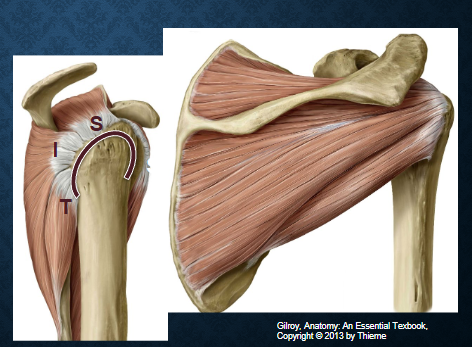
which bones are these? Label them
What does the Penn Shoulder Score measure? what type of measure is it?
Activities of daily living and pain of shoulder assesment, rehabilitative
what is the rapid upper limb assesment (RULA)? What type of assesment?
measures posture, muscle use, and force of the upper body, biomechanical