Lecture 6&7: Multiple Dose Kinetics (IV and EV Drug Admin.) & Drug Distribution
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Predict the drug amount and plasma concentrations during and following a multiple dose regimen (CN,min, CN,max, CN,t, Abss,min, Abss,max) Determine the accumulation index (Rac) for a given regimen. Develop a dosing regimen to achieve a given plasma concentration. (Css,min, Css,max, and Css,ave). Estimate half-life, volume of distribution, and clearance from data obtained during and after a multiple dose regimen. 1. List the common sampling fluids. 2. Understand the process of drug distribution. 3. Define apparent volume of distribution. 4. List the major drug binding proteins in plasma. 5. Define fraction of drug unbound in plasma (fu) and unbound in tissue (fu t). 6. Derive the expression that relates the apparent volume of distribution to fraction of drug unbound in plasma and unbound in tissue. 7. Evaluate changes in the apparent volume of distribution with alterations in fraction of drug unbound in plasma and unbound in tissue.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
True or false: Multiple doses are the most common form of dosing.
True
How is τ (Tau) different to t?
Tau is the dosing interval.
t = time since the dose was administered
True or false: In multiple dose kinetics for steady state, the amount lost from the body in a dosing interval is equal to the amount given to the body during that same interval.
True
Why is the average concentration considered a steady state in multiple dose kinetics?
the concentration fluctuates btwn peaks and troughs after multiple bolus administrations
Css, ave = Dose/τ(CL)
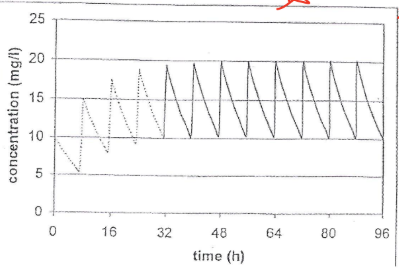
What does Accumulation Index (Rac) mean?
measures how much drug accumulates in the body
next dose is administered before previous dose has been completely eliminated —> accumulation
Increase in τ results in ___ accumulation
Decrease in τ results in ___ accumulation
more, less
What is Maximum Dosing Interval (τmax ) mean?
the maximum time interval to stay within the therapeutic window
can calculate when MTC (max. tolerated conc.) and MEC (min. effective conc.) are known
True or false: Loading/Maintenance doses do not have an effect to reach steady state concentrations faster. Multiple dose kinetics require you to wait.
False. Loading/Maintenance Dose (Dm) are just as helpful to reach steady state concentrations faster for a drug with a long half-life
True or false: Oral dosing is the most common form of multiple dosing.
True
For EV doses, what do you assume for absorption rate?
a. absorption rate constant (ka) is less than kel (ka < kel)
b. absorption rate constant (ka) is greater than kel (ka > kel)
c. absorption is complete within a short time peroid
b, c
Which is false when designing a Dosing Regimen Design:
a. Need to know MEC, MTC (target range of drug conc.) and choosing a Css,ave in the middle of range
b. Need to know drug half life (t1/2) and Vd
c. to determine the max dosing interval (τ max) —> have reasonable interval (q6h,8h,12h, daily)
d. Determine maintenance dose (DM), loading dose (DL) (if necessary)
e. Check if Css,max and Css,min falls within range
f. Adjust dosing regimen (dose only) if its not within required range
f. You can adjust dosing regiment with dose and τ
Time to steady-state is ___ half-lives
3.3
Select which are sampling fluids that determine drug concentrations:
a. urine
b. blood
c. bile
d. serum
e. plasma
b, d, e
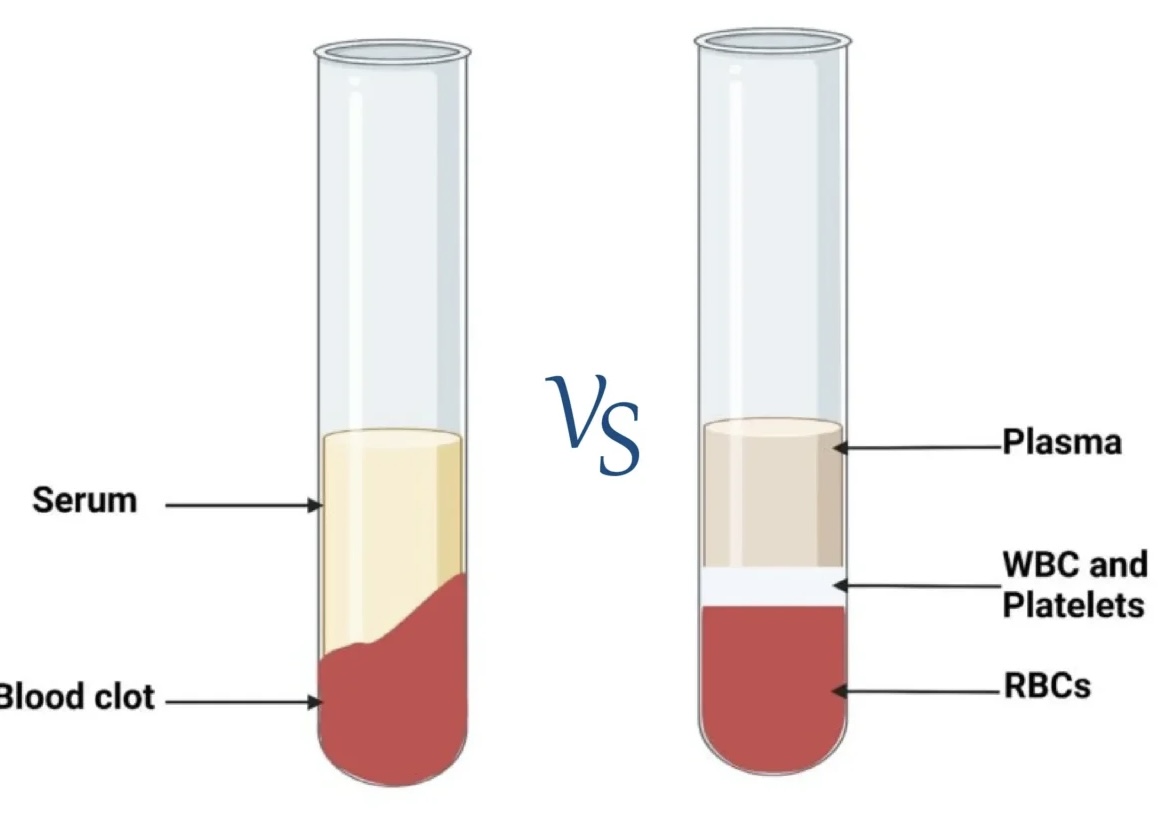
Which of the following is present in blood?
a. blood cells (RBC, WBC, platelets)
b. plasma proteins
c. fibrin
d. clotting factors
e. all of the above
e. All of the above
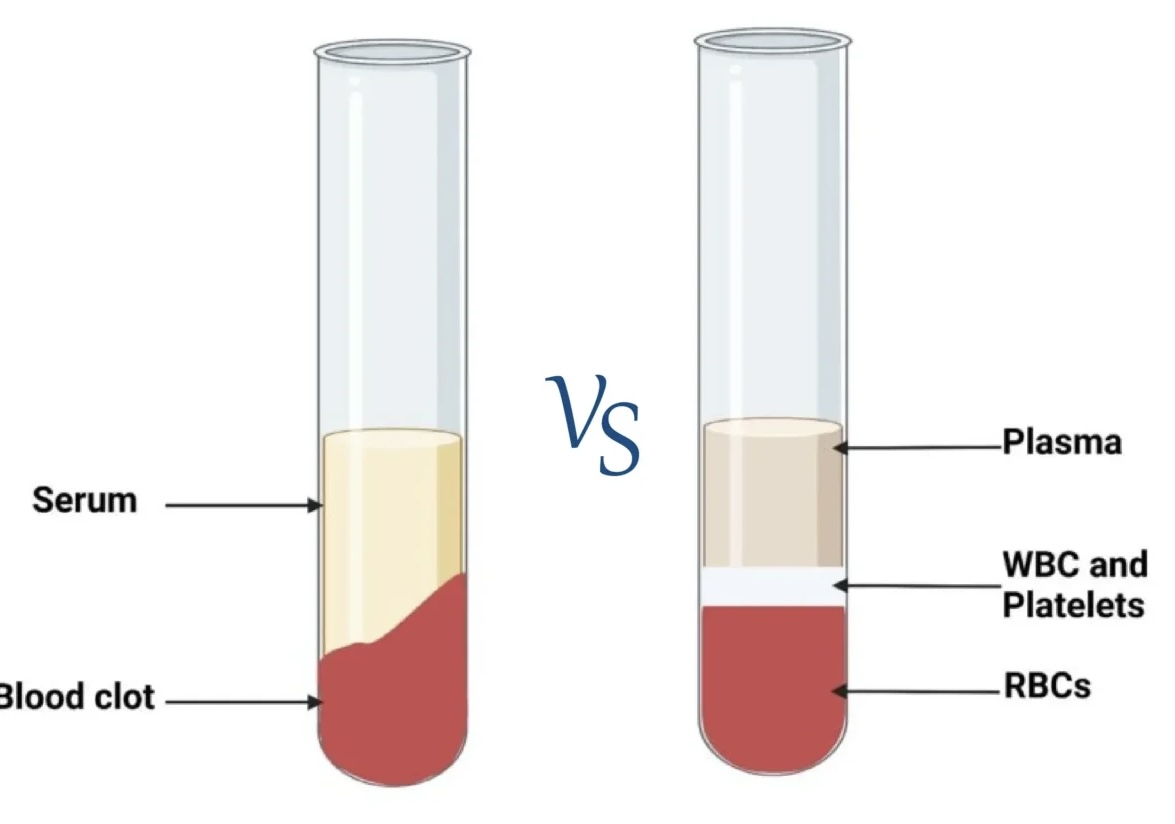
What is present in serum?
a. blood cells (RBC, WBC, platelets)
b. plasma proteins
c. fibrin
d. clotting factors
e. all of the above
b. plasma proteins
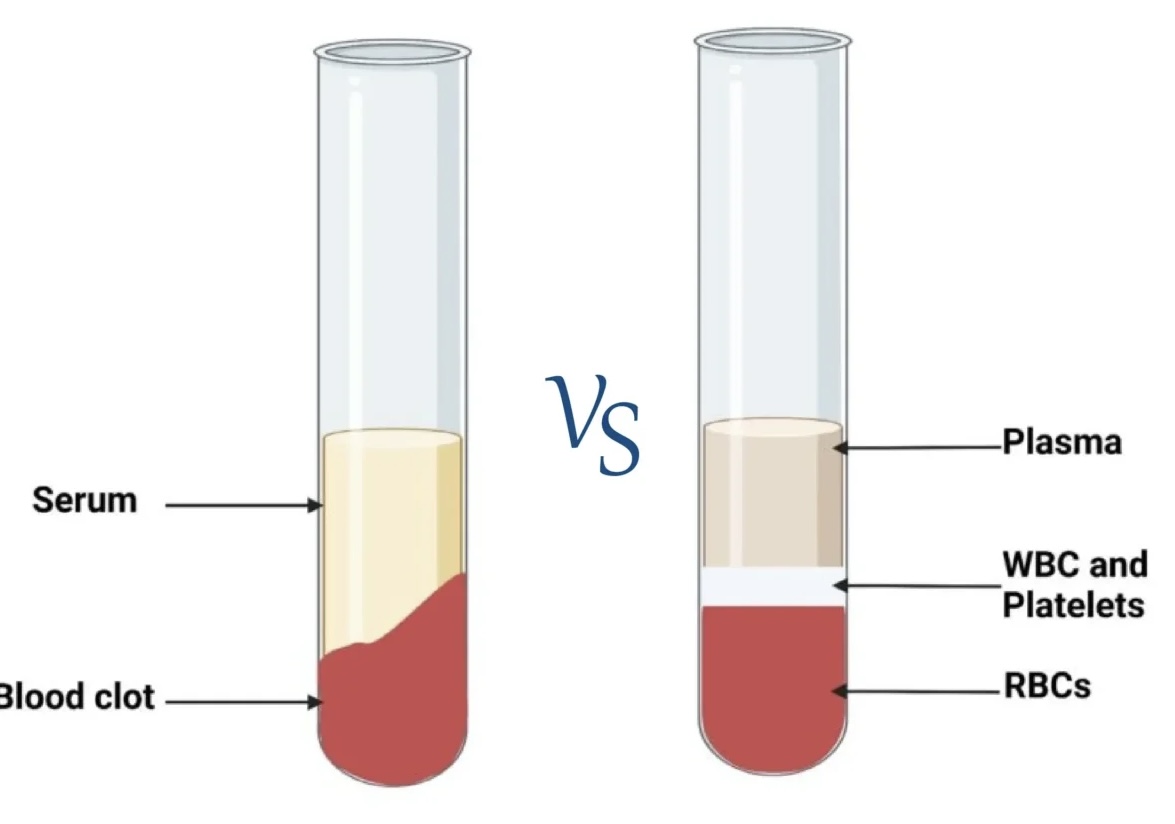
What is serum?
when blood coagulates, the fluid and the clot become separated. the fluid is called the serum
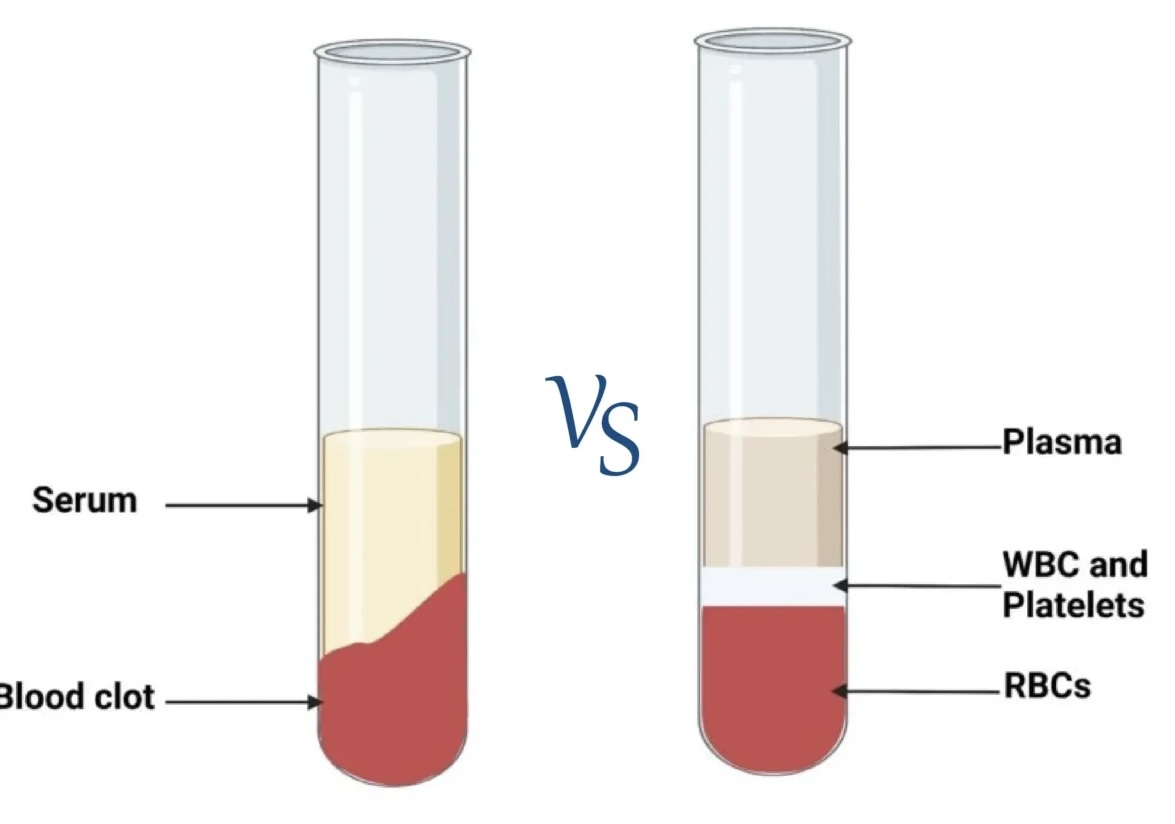
Which of the following is present in plasma?
a. blood cells (RBC, WBC, platelets)
b. plasma proteins
c. fibrin
d. clotting factors
e. b and d
e. b and d
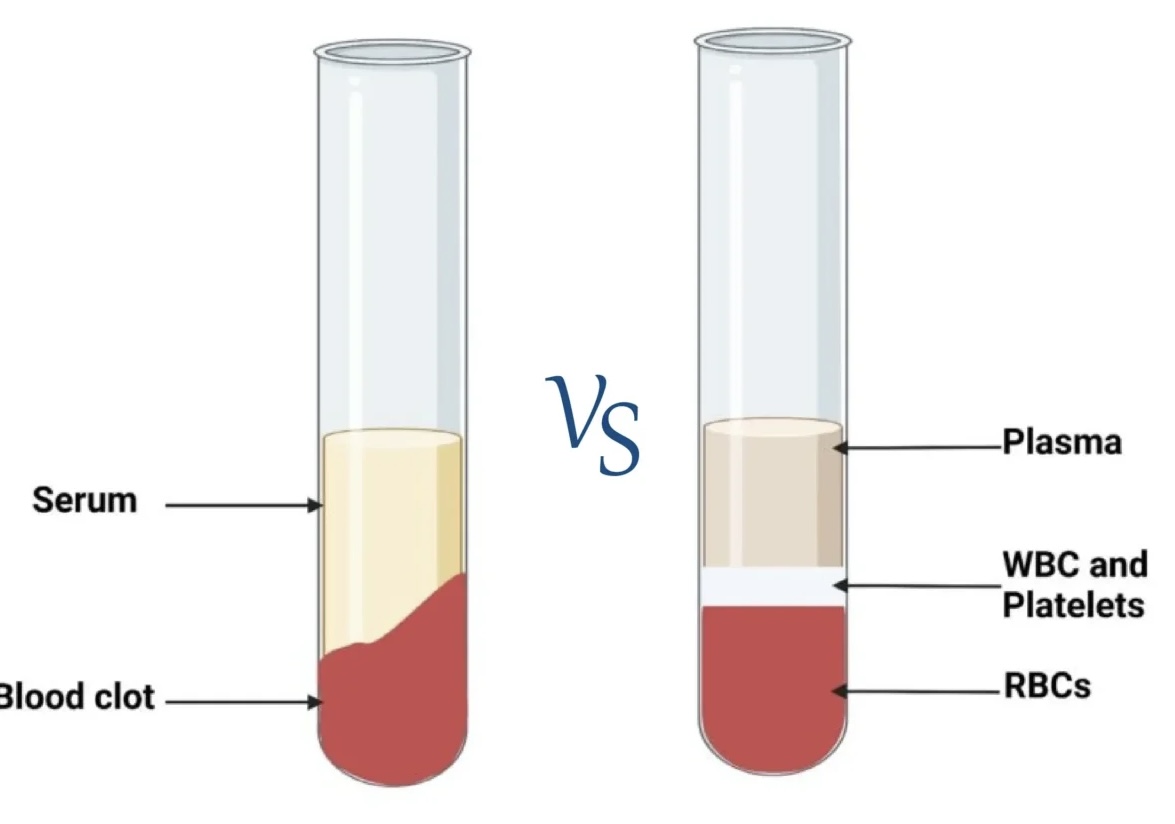
What is plasma and how do we obtain it?
Plasma is obtained when blood is centrifuged, having been collected with an anticoagulant
has plasma proteins and clotting factors
What is the difference between Cb and Cp/C?
Cb: drug concentration in blood
Cp/C: drug concentration in plasma —> Cp = Cbound + Cu
Cbound: bound drug
Cu: unbound drug
What does fu (fraction of drug unbound in plasma) mean?
the ratio of unbound conc. in plasma to total drug concentration in plasma
fu = Cu/C
For a drug with low plasma binding, its fu is ____
For a drug with high plasma binding, its fu is ____
large, small
What is ultracentrifugation?
a. membrane only allows unbound drugs to pass thru
b. pores in membranes allows unbound drug to pass thru but retains proteins
c. plasma proteins collect at bottom of tube while unbound drug is in the supernatant (serum)
c.
a = dialysis
b = ultrafiltration
Which of the following is not a plasma protein to which drugs bind to?
a. alpha 1-Acid glycoprotein
b. Lipoproteins
c. Leptin
d. albumin
c.
Leptin is a hormone that suppresses hunger
Which plasma proteins do acidic drugs bind to?
a. alpha 1-Acid glycoprotein
b. Lipoproteins
c. Leptin
d. albumin
b,d
Which plasma proteins do basic drugs bind to?
a. alpha 1-Acid glycoprotein
b. Lipoproteins
c. Leptin
d. albumin
a.
Example: propranolol
Which of the following does not determine plasma protein binding?
a. total protein concentration (Pt)
b. amount of unbound drug concentration (Cu)
c. affinity of protein to the drug (K)
d. available binding site (fup)
b
Conditions such as:
cirrhosis
burn
nephrotic syndrome (protein loss in urine)
end-stage renal disease
pregnancy
have ____ levels of what kind of plasma protein?
low levels of Albumin
Conditions such as:
Myocardial infarction
Surgery
Crohn’s disease (inflammatory bowel disease)
Trauma
Rheumatoid arthritis
have ____ levels of what plasma protein?
increased levels of alpha 1-Acid glycoprotein
True or false: Propranolol is an acidic drug.
False. It is basic. fu varies with plasma concentration of alpha1-acid glycoprotein
Which of the following isn’t a pattern of drug distribution?
a. drug always metabolized before excretion
b. drug distributes into body water
c. drug accumulates in one or more tissues
d. drug stays in the bloodstream
a
True or false: These are all the factors that influence drug distribution.
Membrane permeability
Perfusion (blood flow to and within) tissues
Plasma and tissue protein binding
Drug characteristics —> o/w partition coefficient, solubility, pKa
True
True or false: Vd (volume of distribution), Vu (unbound of distribution), and Vb (volume of distribution of blood) are all interchangeable
False
Amount in body is calculated in which way (3 ways):
a. V * C
b. Vu * Cu
c. Vr * Cr
d. Vb * Cb
a, b, d
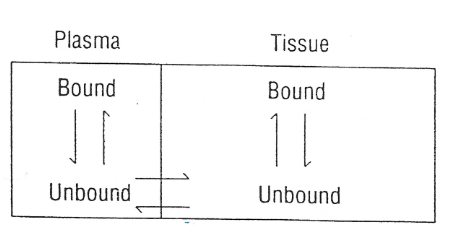
The fraction of drug in body located in plasma is ____ on the drug’s binding to both ____ and ____ components.
dependent, plasma and tissue
Define the factors involved in the Volume of apparent distribution:
V = Vp + VTW * (fu/fuT)
Vp = volume of plasma (3 L)
VTW = aqueous volume outside plasma into which the drug distributes
fu: fraction unbound
fuT: fraction unbound in tissue
True or false: The unbound drug can easily cross membranes and gets out of the plasma into tissues, thereby increasing the apparent volume of distribution.
True
Choose the true statements:
a. Increase of unbound drug conc. in the tissues (high Cu T) decreases the apparent volume of distribution V.
b. Decrease of unbound drug in tissues (low CuT) means that the concentration of drug in plasma is low which increases apparent volume of distribution V.
c. Increase of unbound drug in tissues (low CuT) means that the concentration of drug in plasma is low which decreases apparent volume of distribution V.
d. Decrease of unbound drug conc. in the tissues (high Cu T) decreases the apparent volume of distribution V.
a, b
True or false: V (apparent volume of distribution) tells you how spread out a drug seems to be in the body (tissues) compared to how much is left in your blood (plasma).
V = amount of drug in body/plasma concentration of drug
True
Choose the following statements:
a. High Vd means that drug stays mostly in blood
b. Low Vd means that drug stays mostly in blood
c. High Vd means that drug stays mostly in tissues
d. Low Vd means that drug stays mostly in tissues
b, c
Vd measures how much drug is distributed to tissues