Theory of Rotor Wing Flight Exam (copy)
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Torque effect is an example of which newtons laws
Action/ reaction
More power is needed to obtain a desired RPM than is needed to maintain the RPM is which newton law
Inertia
Greater load, less acceleration is which newton law
Acceleration
If the airflow atop of the airfoil increases, static pressure will _____ and dynamic pressure will _____
Decrease, increase
Define center of pressure
The point along the cord line of an air foil to reach. All aerodynamic forces are considered to act.
Define airfoil
Any surface designed to produce lift when air is passed over it
What are 2 basic types of of airfoils?
Symmetrical and Non-symmetrical
Description of airfoil:
Rounded edge
Leading edge
Description of airfoil:
Straight line from the leading edge to to trailing edge
Chord
Description of airfoil:
Upper curvature
Upper camber
Description of airfoil:
Lower shape
Lower camber
Description of airfoil:
The length of the rotor blade from the point of rotation to the tip of the blade
Span
Description of airfoil:
Tapered edge
Trailing edge
Define rotational relative wind as applied to an airfoil
The flow of air parallel to an opposite the flight path of an air foil.
Define induced flow
Downward flow of air through the rotor blades
Define resultant relative wind
Rotational relative when modified by induced flow
How is the angle of incidence measured in a rotary wing aircraft?
The angle between the cord line of an air foil in the plane of rotation (tip path plane)
Define angle of attack
The angle between the cord line of an air foil and the resultant relative wind
Which flight control changes the angle of incidence differently around the rotor system
Cyclic pitch control
With an increase in the speed of air over a surface, What happens to dynamic and static pressure?
Dynamic increases and static decreases
List the two components of total aerodynamic force
Lift and drag
Describe the relationship of lift to resultant relative wind
Perpendicular
Describe the relationship between drag and resultant relative wind
Drag is parallel to, and in the same direction of the resultant relative wind
What type of drag is:
Rotor tip vortices
Induced
What type of drag is:
Lift and total aerodynamic force titling reward on the airfoil
Induced
What type of drag is:
Skin friction on the fuselage
Parasite
What type of drag is:
Skin friction on the airfoil
Profile
What type of drag is:
Non-streamlined fuselage
Parasite
What type of drag decreases with an increase in airspeed?
Induced drag
Which type of drag increases with an increase in airspeed
Parasite drag
Define dissymmetry of lift
Differential (unequal) lift between between advancing and retreating halves of the rotor disk
Relative wind velocity on the advancing blade equals blade speed ______ airspeed
Plus (+)
Relative wind velocity on the retreating blade equals blade speed ____ airspeed
Minus (-)
What causes the advancing blade to flap up?
An increase in lift
What causes the retreating blade to flap down?
A decrease in lift
How does the helicopter compensate for dissymmetry of lift?
Flapping
How does the pilot control the dissymmetry of Lift?
Cyclic feathering
Define blowback
Change in attitude of the rotor system
How does the pilot correct for blowback?
Cyclic feathering
Which forces in the lift equation can the pilot control?
Coefficient of lift (CL) through angle of attack, and relative wind velocity or airspeed (V2)
What are the three factors in air density (1/2 rho) that will affect lift
Pressure, temperature, humidity
A semi rigid disk tilt relative to _____
Mast
An articulated disk tilt relative to the_______
Hub
Define centrifugal force
Outward force produced whenever a body moves in a curved path
Define rotor blade conning
Upward flexing of the rotor blades
Rotor blade conning is a compromise between which two forces
Lift and centrifugal force
Define gyroscopic procession
When a force is applied to a rotating body, it will manifest 90° after application in the direction of rotation
Why is blade twisting necessary?
To distribute the lifting force more evenly along the blade
A pedal turn to the right requires ______ Power than a pedal turn to the left
Less
Define translating tendency
Tendency of a single rotor helicopter to drift right while hovering
List four methods used to overcome, translating, tendency and single rotor helicopters
Rigging the cyclic
Tilting the mast
Left cyclic
Automatic flight control/stabilization argumentation system
List the four rotor blade actions
Rotation
Flapping
Feathering
Hunting
Describe the relationship of total force to the tip path plane
Perpendicular
When the rotor disk is tilted, what are the two components of total force?
Lift and thrust
What are the two flight conditions?
Balanced and unbalanced
At what altitude would the aircraft be in ground effect?
Less than one rotor diameter
Loss, or apparent loss, of ground effect is caused by?
An altitude greater than one rotor diameter
Trees and bushes
Tall grass and uneven terrain
Hovering over water
Beginning of translational movement
Hovering into wind
Define effective translational lift (ETL)
When the rotor completely outruns the recirculation of old vertices and begins to work in relatively undisturbed air
Effective translational lift occurs at an airspeed of
14-24kts
Transverse flow effect is noticeable at an airspeed of
10-20 kts
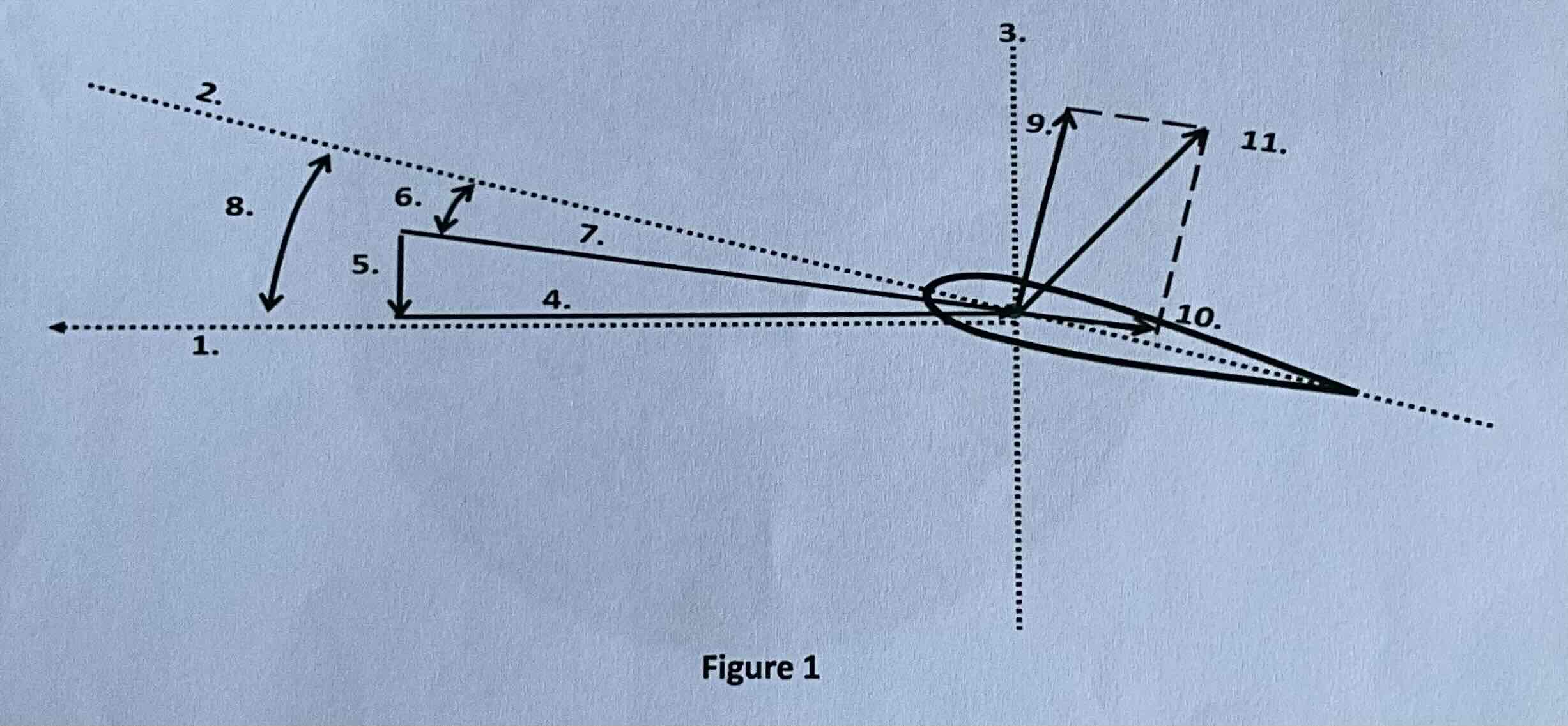
#1
Tip path plane
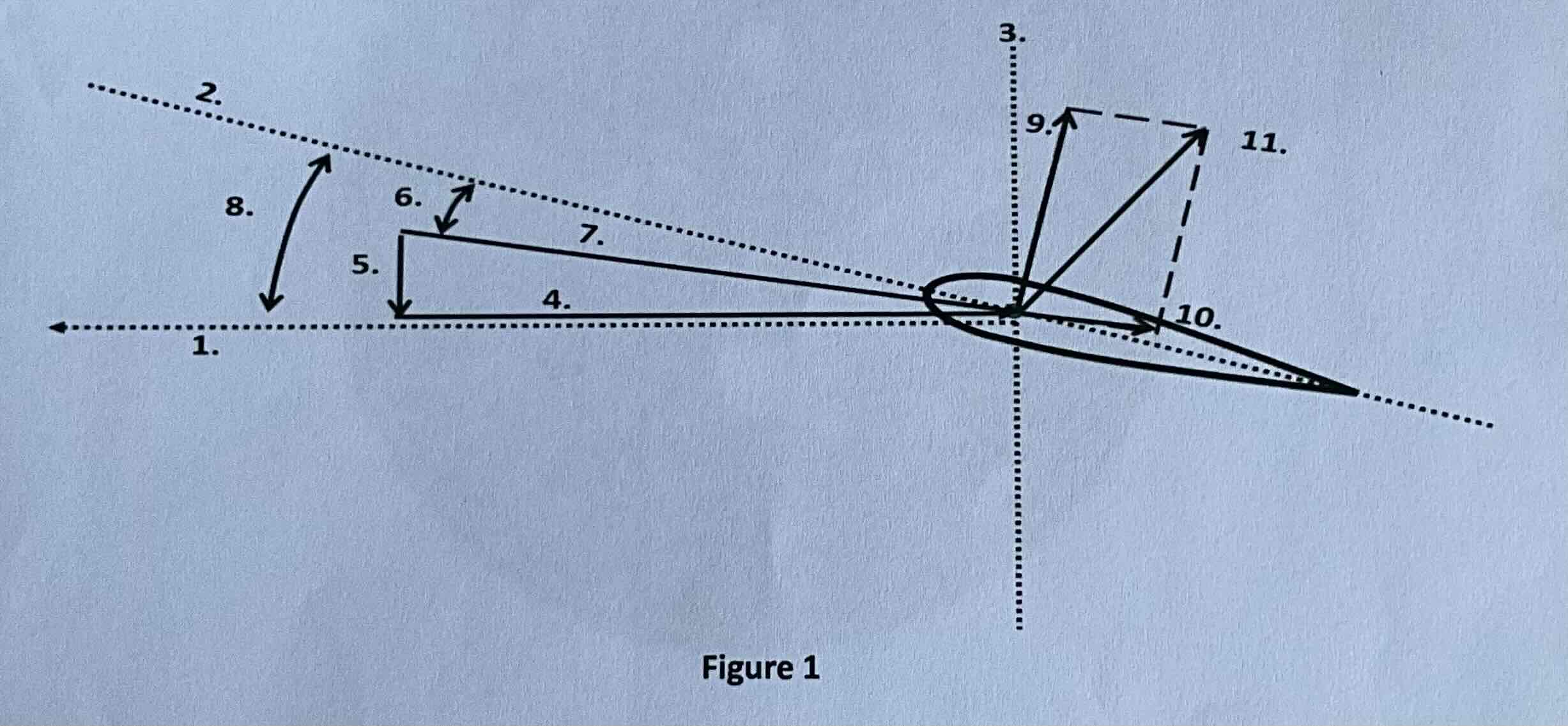
#2
Chord line
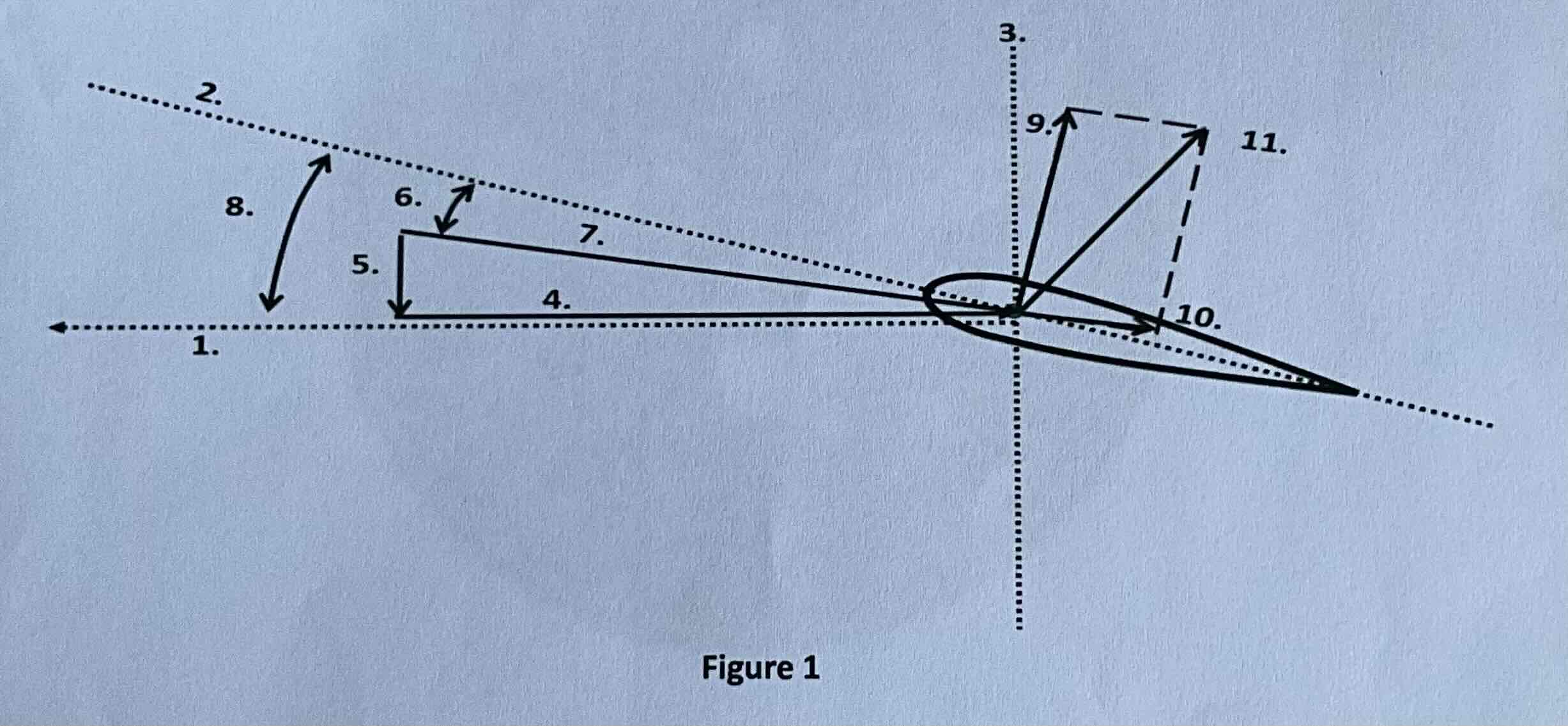
#3
Axis of rotation
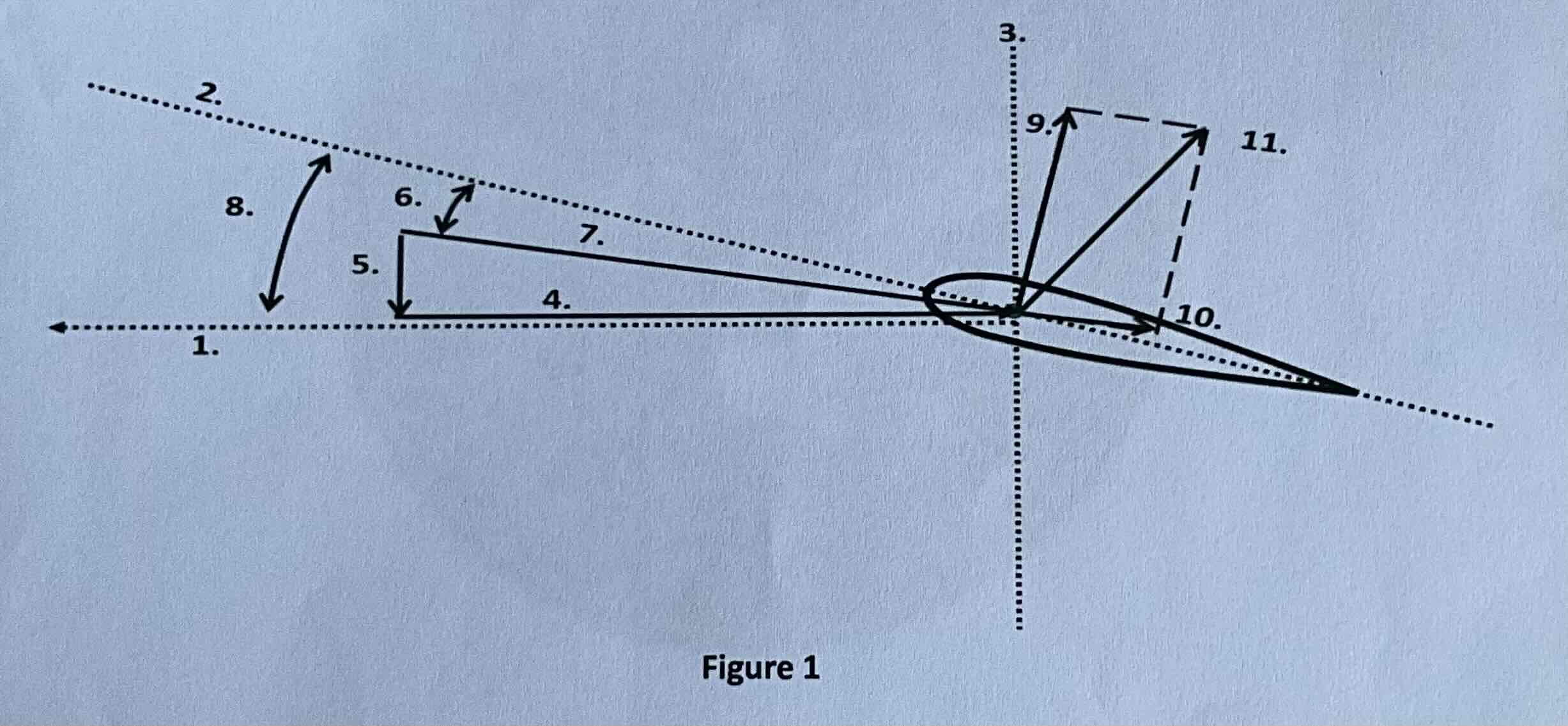
#4
Rotational relative wind
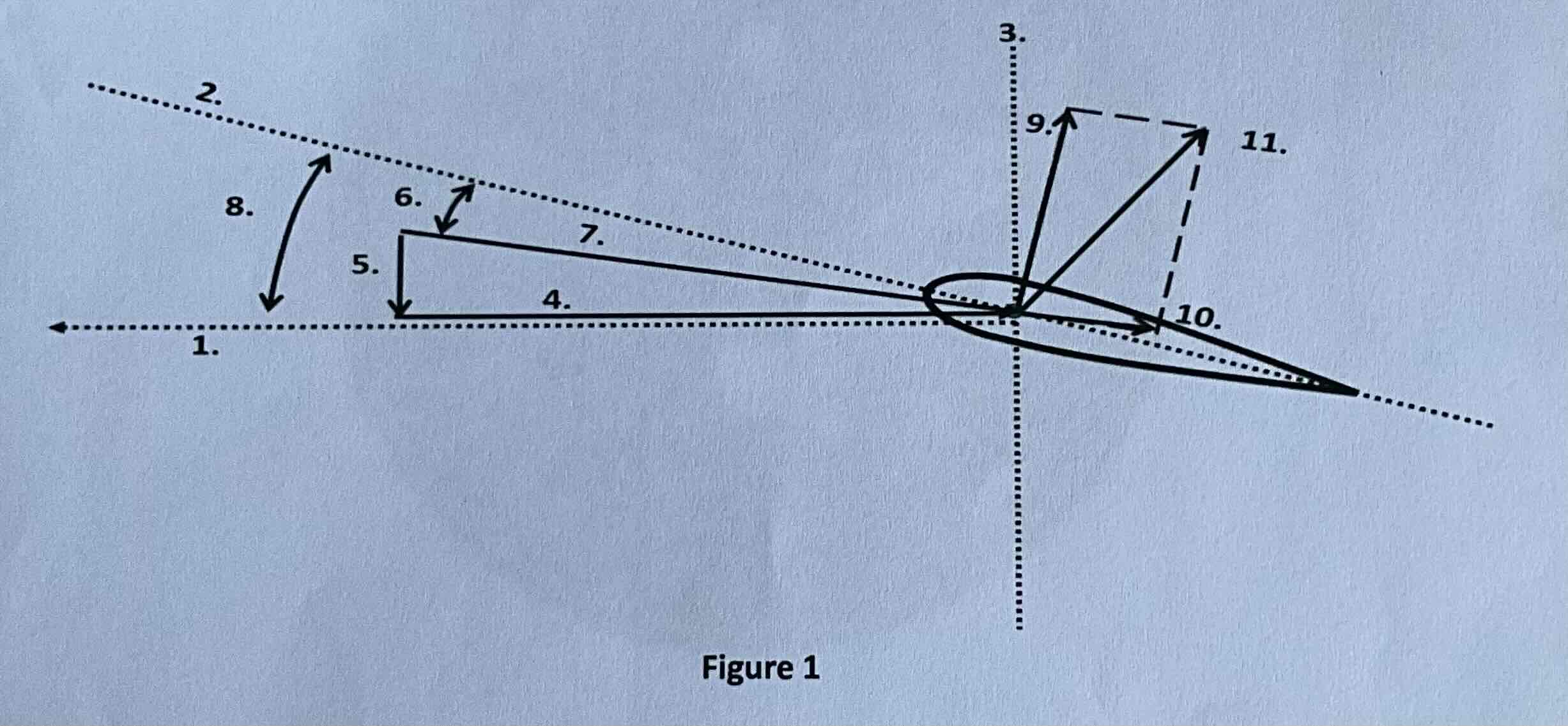
#5
Induced flow
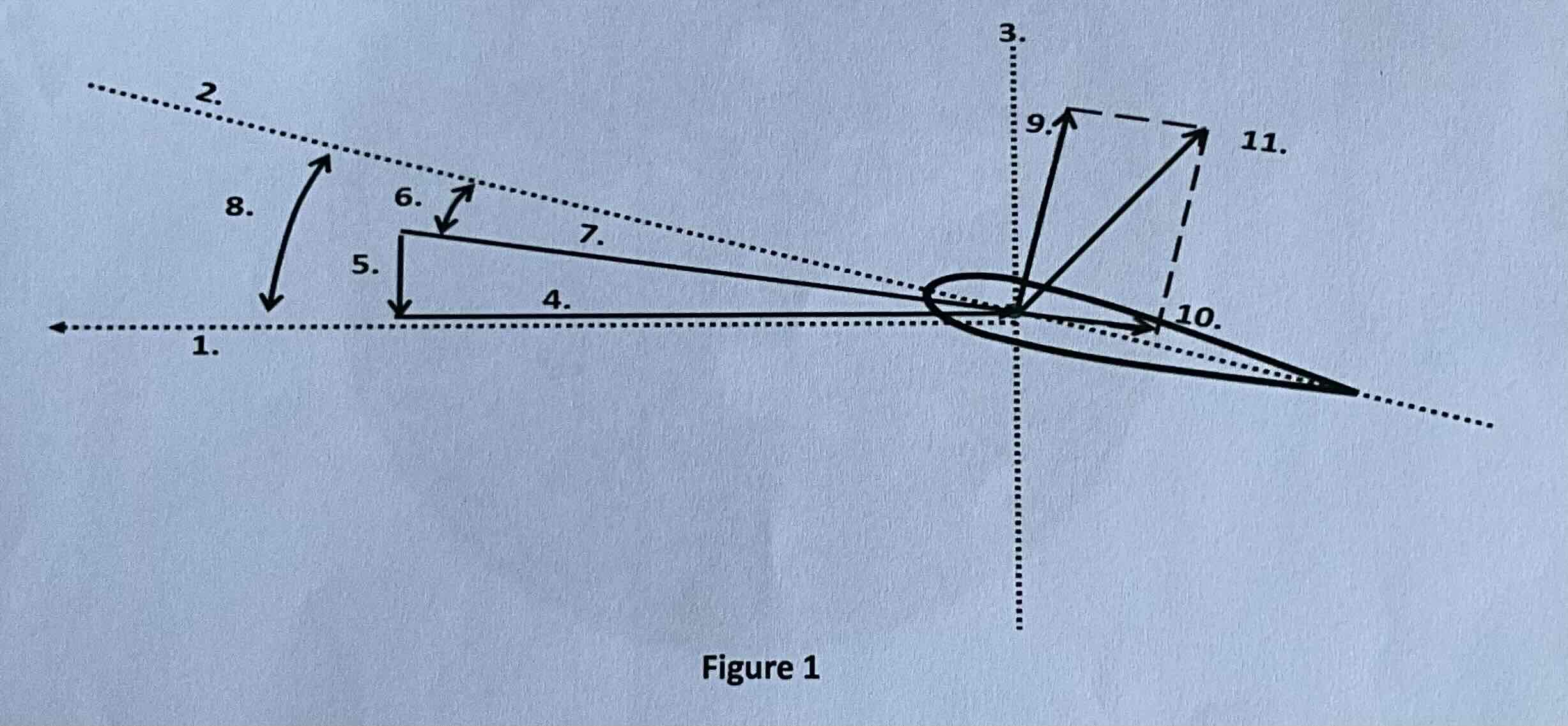
#6
Angle of attack
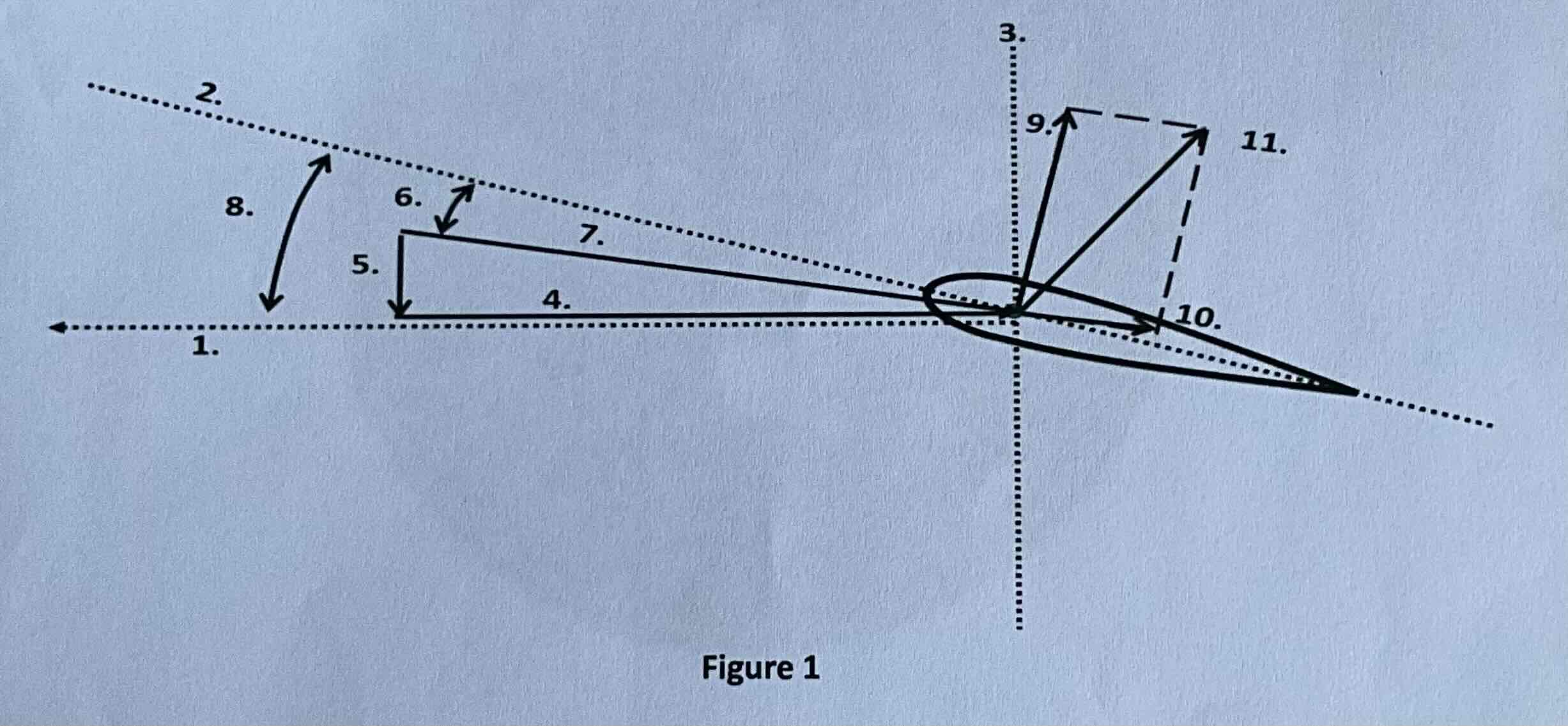
#7
Resultant relative wind
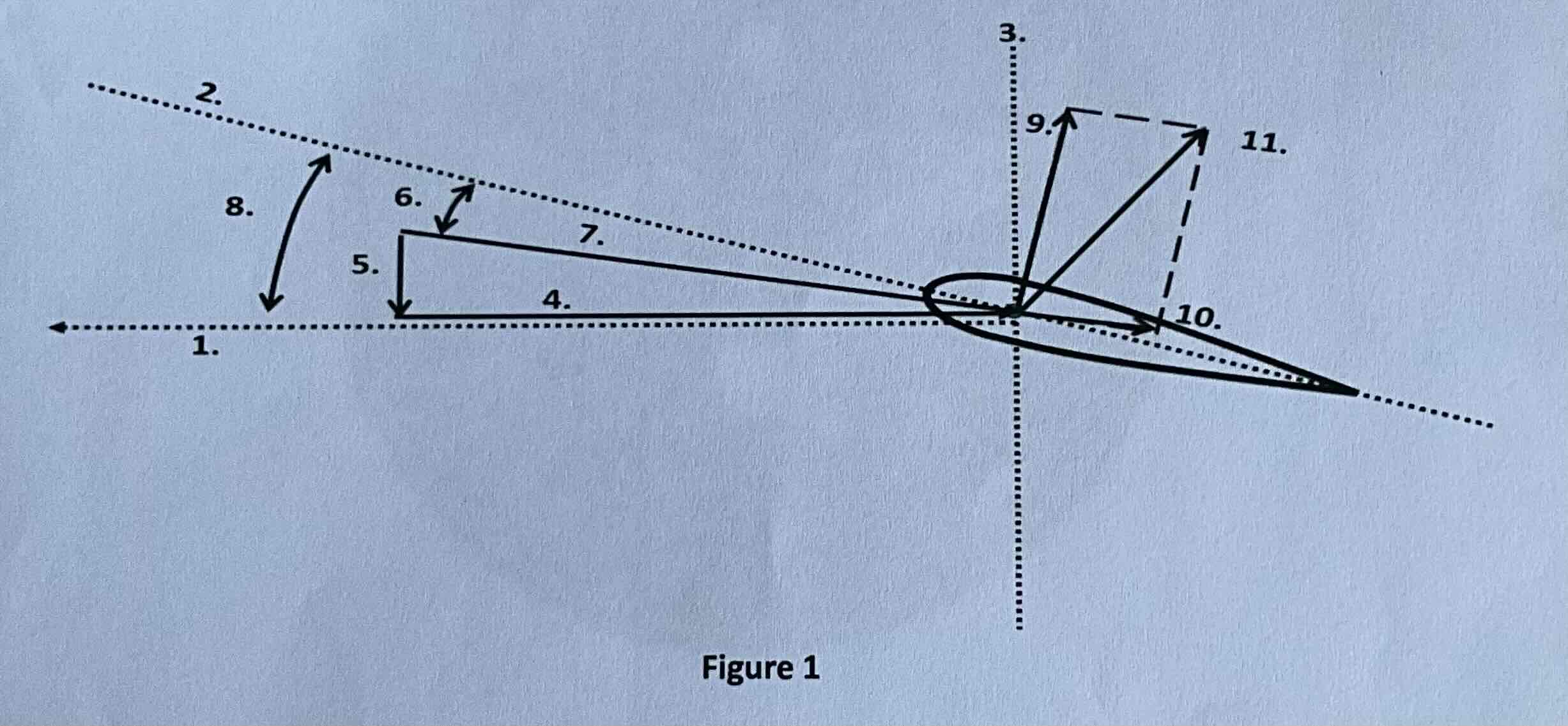
#8
Angle of incidence
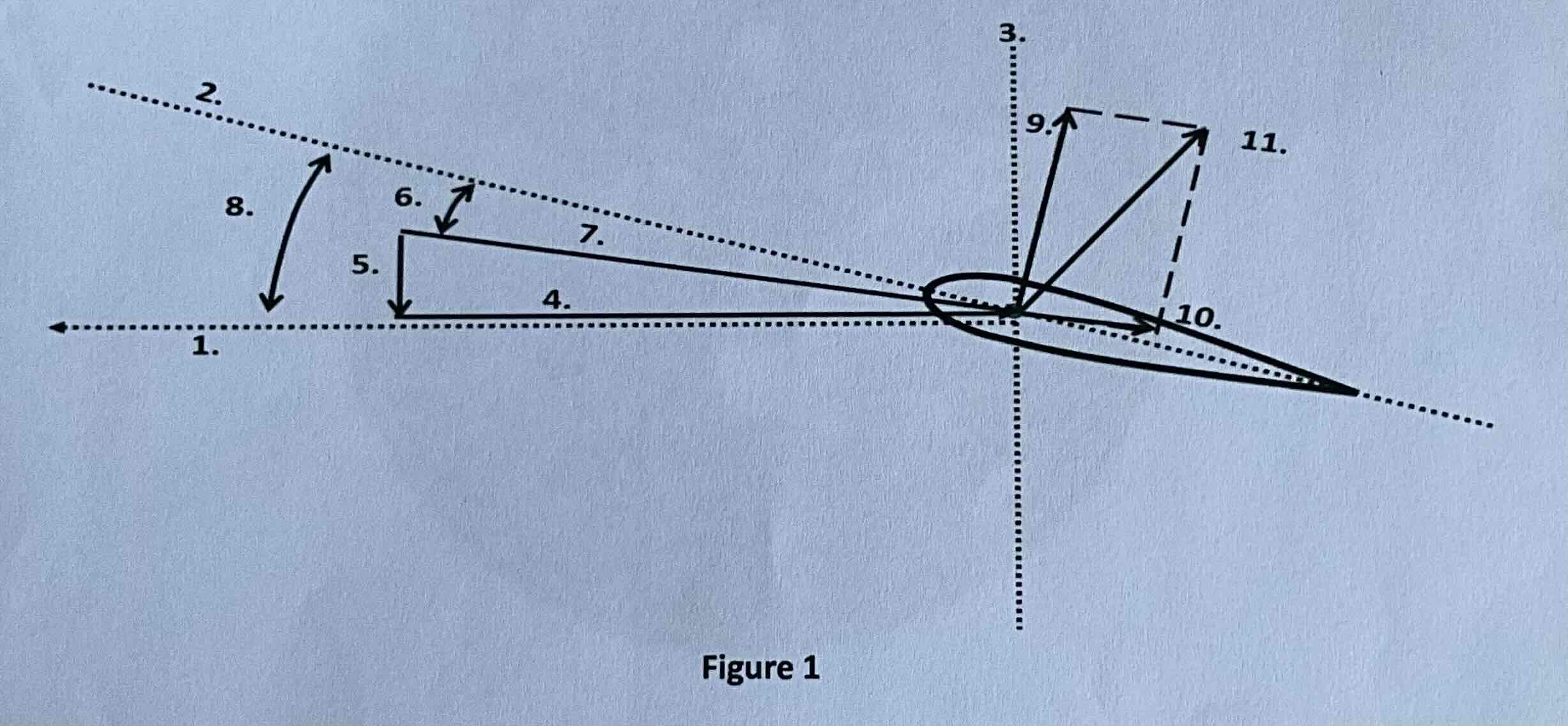
#9
Lift
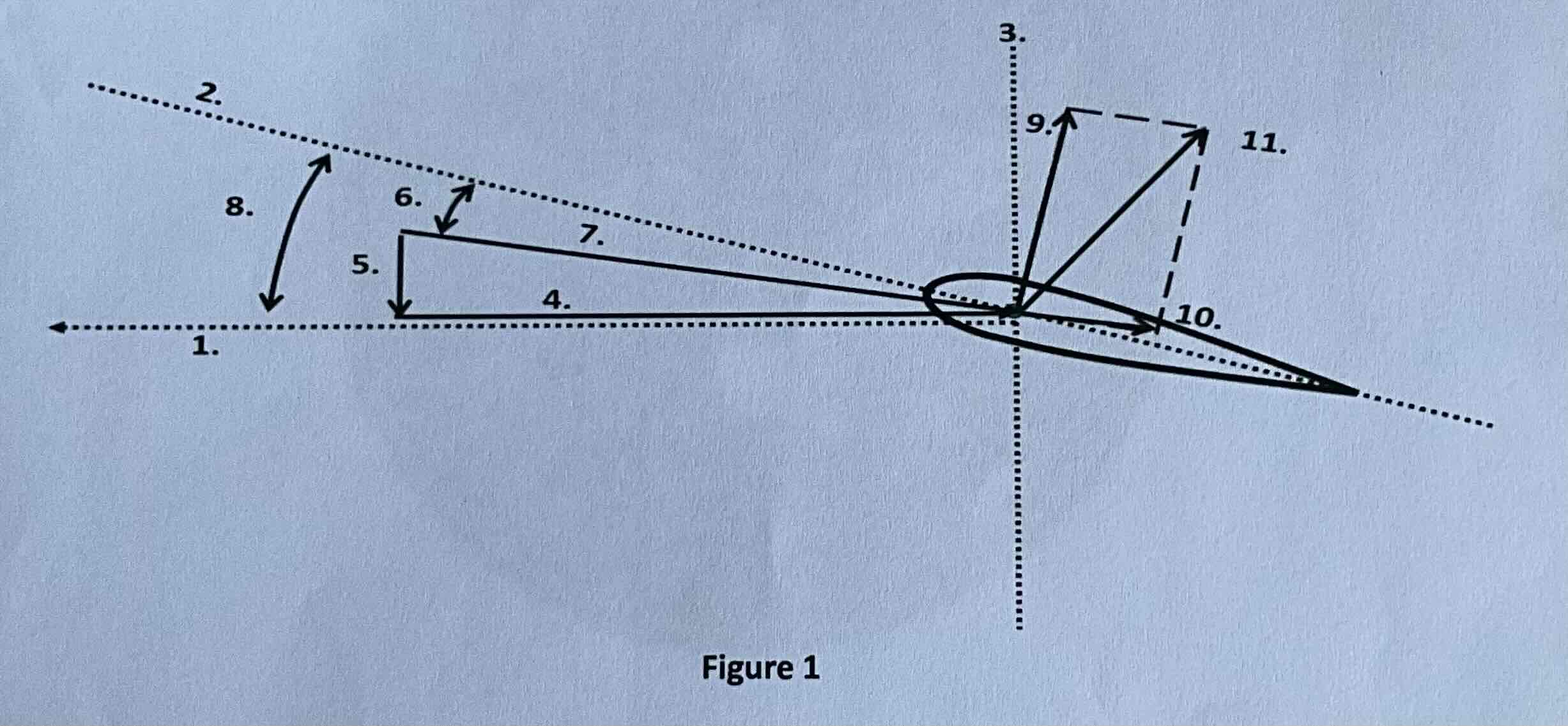
#10
Drag
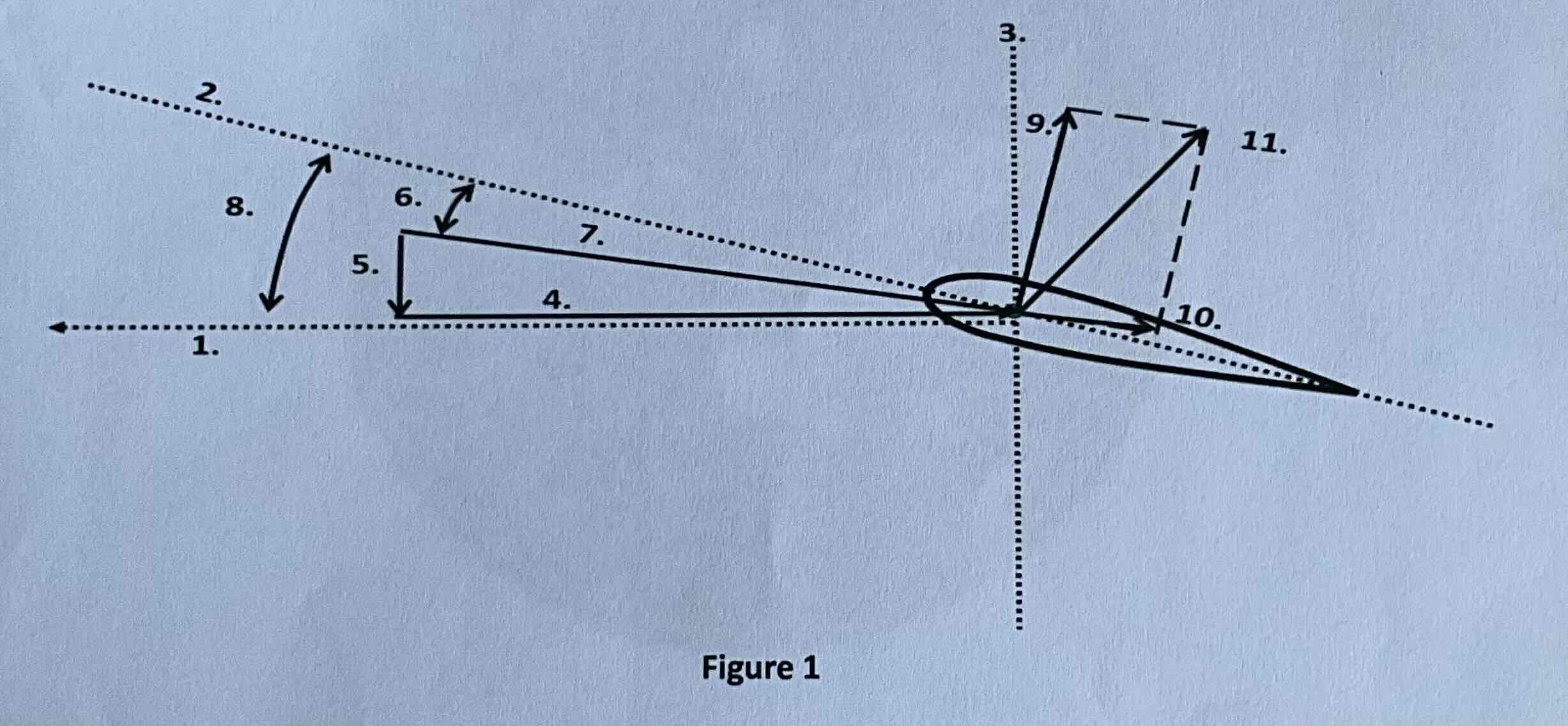
#11
TAF (resultant force)
Define settling with power?
A condition of powered flight in which the helicopter settles and its own downwash
List the three simultaneous conditions required for settling with power
Vertical or near vertical descent of at least 300 feet per minute
20% to 100% engine power
Slow airspeed less than ETL
List the required discovery procedures for settling with power
Increase airspeed with cyclic
Reduce collective as altitude permits
Adjust rotor RPM to normal operating range
Define autorotation
The flight condition during which no engine power is supplied, and he main rotor is driven only by the action of the relative wind
Describe how a pilot prevents a rotor RPM over speed during an auto rotation with turn
Collective control (increase)
List the three conditions required for dynamic rollover to occur
Pivot point
Rolling motion
Exceed critical angle
Dynamic rollover occurs due to a combination of which two factors
Physical and human factors
Which control input is required to recover from dynamic rollover on level ground
Smooth, moderate collective reduction
Operating at what speed is most likely to produce retreating blade stall
High forward speed
Describe the symptoms of retreating blade stall in a single rotor helicopter
Abnormal vibrations
Pitch up of the nose
Left roll
Loss of control (If corrective action is not applied)
Describe the recovery procedure from retreating blade stall
Reduce collective pitch
Regain control of aircraft
Reduce speed
Increase rotor RPM to normal operating range
Minimize maneuvering
Descend to a lower altitude