Microeconomics Theme 1 <3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
1
New cards
Ceteris paribus
all other things remaining constant
2
New cards
positive statement
a statement with facts and is value free scientific approach.
3
New cards
normative statement
statement with opinion and value judgement and is a nonscientific approach
4
New cards
The basic economic problem
how to allocate scarce resources given unlimited want
5
New cards
3 economic agents
1. Households
2. Firms
3. Government
2. Firms
3. Government
6
New cards
3 key questions
1. What to produce?
2. How to produce it?
3. Who to produce for?
2. How to produce it?
3. Who to produce for?
7
New cards
Difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources
nonrenewable resources are finite whereas renewable resources can replenish themselves and are infinite
8
New cards
Rational consumer
wish to maximise their satisfaction or utility
9
New cards
Rational Producers
wish to maximise profits by producing at the lowest cost
10
New cards
Rational Government
wish to improve the economic and social welfare
11
New cards
opportunity cost
the value of the next best alternative forgone when a choice is made
12
New cards
Production Possibility Frontier (PPF)
the maximum potential output combination of two goods an economy can achieve when all its resources are fully and efficiently employed
13
New cards
factors causing an outward shift in ppf
increase in quality or quantity of factors of production
14
New cards
factors causing an inward shift in ppf
decrease in quality or quantity of factors of production
15
New cards
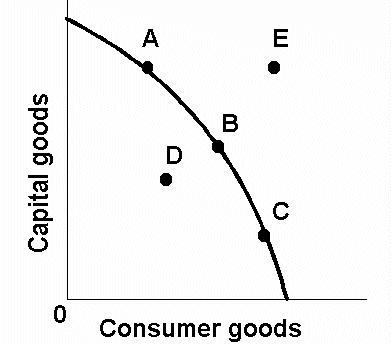
Efficient allocation of resources
B
16
New cards
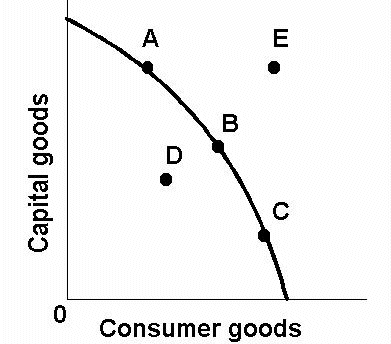
inefficient allocation of resources (we could produce more given FoP at no OC)
D
17
New cards
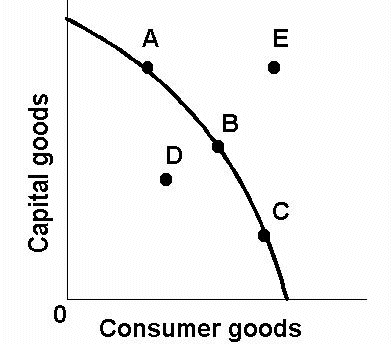
unattainable (given current FoP)
E
18
New cards
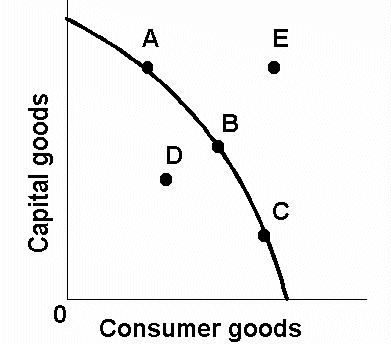
maximum productive potential of an economy
A/B/C
19
New cards
economic growth on ppf
outward shift
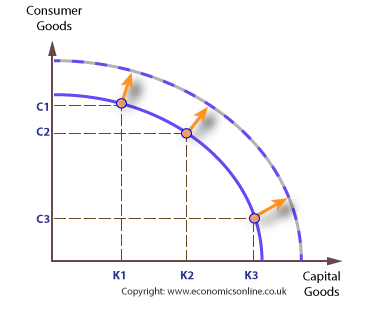
20
New cards
economic decline on ppf
inward shift
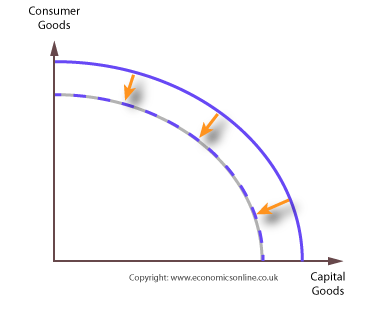
21
New cards
division of labour
splitting the production process into different parts to increase output
22
New cards
specialisation
the process of becoming particularly skilled in a task
23
New cards
Adam smith concept of division of labour
a worker will be able to make 20 pins a day if he worked alone but if 10 workers who are specialised in different parts of production then they'll produce 48000 pins a day
24
New cards
4 Advantages of division of labour
1. Increased productivity
2. Lower cost per unit
3. Workers can concentrate on one task
4. Increased output
2. Lower cost per unit
3. Workers can concentrate on one task
4. Increased output
25
New cards
3 Disadvantages of division of labour
1. Work can become tedious
2. Workers can get bored and leave
3. All stages of production will become co reliant on each other so if one stage breaks down the others are affected as well
2. Workers can get bored and leave
3. All stages of production will become co reliant on each other so if one stage breaks down the others are affected as well
26
New cards
4 Functions of money
1. Medium of exchange
2. Store of value
3. Measure of value
4. Standard of deferred payment
2. Store of value
3. Measure of value
4. Standard of deferred payment
27
New cards
free market economy
an economy in which decisions on the three key economic questions and the problem of scarcity is determined by the market force (demand and supply)
28
New cards
command economy
a centrally planned economy in which the role of the state is to be a social planner and the decisions on the three key economic questions and the problem of scarcity is determined by the government
29
New cards
mixed economy
a mixture of free market economy and command economy
30
New cards
Adam Smith and the free market
he thought when individuals follow their own self interest they indirectly promote the good of society then the free market producers would respond to changes in consumer wants in a way that reduces waste and the governments role should be limited to proving public goods
31
New cards
Friedrich Hayek and the free market
he thought when the government plans economies it leads to failure, requires force and restricts freedom
32
New cards
Karl Marx
he thought capitalism was inherently unstable because workers were exploited and there would be a revolution and the economy would follow communism
33
New cards
5 characteristics of command economy
1. State ownership of resources
2. Price determined by the state
3. Resources allocated by the state
4. The role of the state is to be a social planner
5. A greater equality of income and wealth
2. Price determined by the state
3. Resources allocated by the state
4. The role of the state is to be a social planner
5. A greater equality of income and wealth
34
New cards
5 characteristics of free market economy
1. Private ownership of resources
2. Producers aim to maximise profits
3. Consumers aim to maximise utility
4. Resources are allocated by the price mechanism
5. The role of the state is to reduce constraints
2. Producers aim to maximise profits
3. Consumers aim to maximise utility
4. Resources are allocated by the price mechanism
5. The role of the state is to reduce constraints
35
New cards
the role of the state in a mixed economy
fix market failure
36
New cards
demand
the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy
37
New cards
movement along the demand curve
change in price
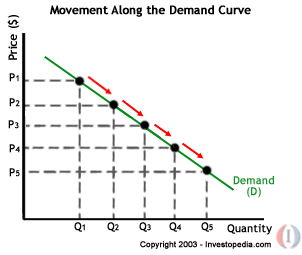
38
New cards
shift in demand curve
Population
Advertisement
Substitutes
Income
Fashion/trends
Interest rates
Complements
Advertisement
Substitutes
Income
Fashion/trends
Interest rates
Complements
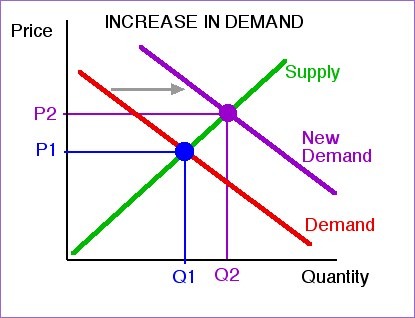
39
New cards
diminishing marginal utility
Decreasing satisfaction or usefulness as additional units of a product are acquired
40
New cards
contraction and extension in demand
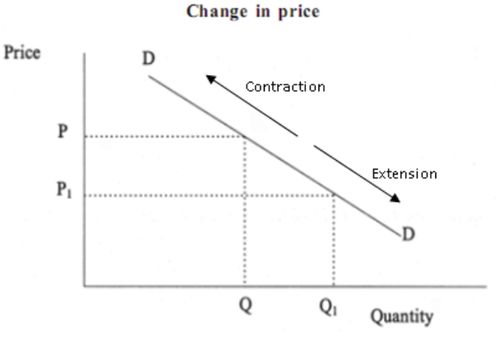
41
New cards
percentage change formula
change/original x 100
42
New cards
elastic demand
%change in price leads to a more than proportional %change in quantity demanded (more than 1)
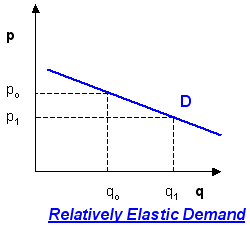
43
New cards
inelastic demand
%change in price leads to a less than proportional %change in quantity demanded (less than 1)
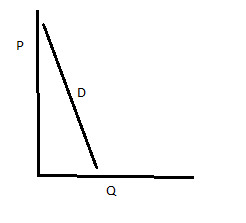
44
New cards
price elasticity demanded (PED)
how responsive quantity demanded is to a change in price
45
New cards
PED formula
% change in Qd / % change in P
46
New cards
Determinants of PED
Substitutes
Proportion of income
Luxury/necessity
Addictive
Time period
Proportion of income
Luxury/necessity
Addictive
Time period
47
New cards
Income elasticity demanded (YED)
how responsive quantity demanded is to a change in income
48
New cards
YED formula
% change in Qd / % change in Y
49
New cards
inferior goods
there are other alternatives so when income rises demand falls (negative YED)
more than 1 - income elastic
less than 1 - income inelastic
more than 1 - income elastic
less than 1 - income inelastic
50
New cards
normal good
there are no other alternatives so when income rises demand rises (positive YED)
more than 1 - income elastic (normal luxury)
less than 1 - income inelastic (normal necessity)
more than 1 - income elastic (normal luxury)
less than 1 - income inelastic (normal necessity)
51
New cards
Cross Elasticity of Demand (XED)
how responsive quantity demanded of good A is to a change in price of good B
52
New cards
XED formula
%change in Qd of Good A / %change in P of Good B
53
New cards
Joint demand (complements)
two goods are complements so if price increases for one demand would decrease for the other (negative XED)
54
New cards
competitive demand (substitutes)
a good has substitutes so if the price of the good increases the demand for the substitute increases (positive XED)
55
New cards
supply
the quantity of a good the producer is willing and able to sell
56
New cards
movement in supply
change in price
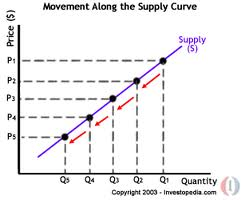
57
New cards
shift in supply
cost of production changes
government subsidy
entry of new things into the market
government subsidy
entry of new things into the market
58
New cards
contraction and extension in supply
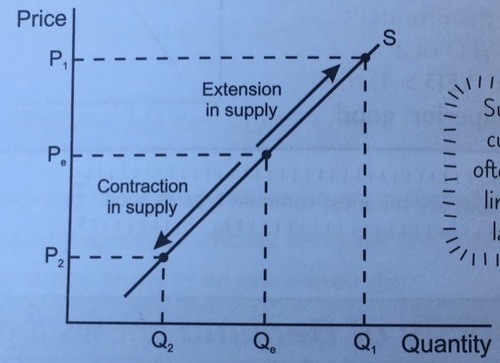
59
New cards
price elasticity supplied (PES)
how responsive quantity supplied is to a change in price
60
New cards
PES formula
% change in Qs / % change in P
61
New cards
perfectly elastic
infinity
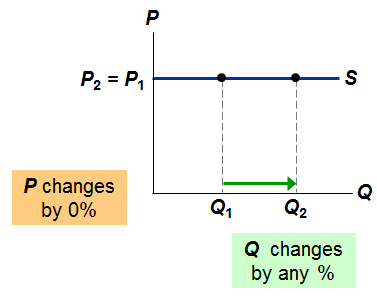
62
New cards
relatively elastic
greater than 1 but less than infinity
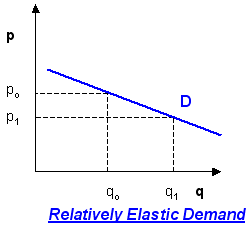
63
New cards
perfectly inelastic
0
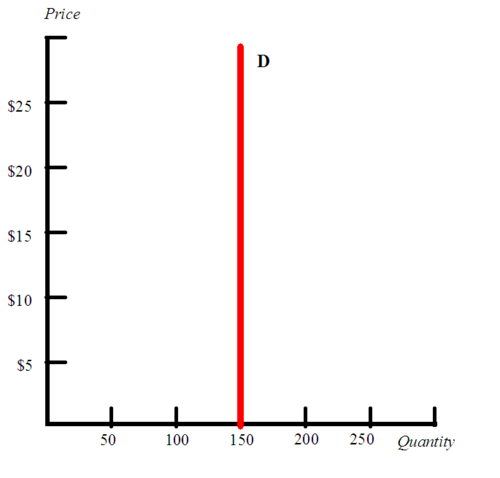
64
New cards
relatively inelastic
less than 1 but greater than zero
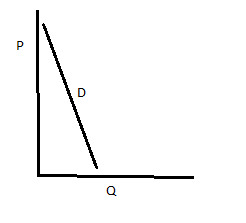
65
New cards
determinants of PES
Time period
Production time
Factor mobility
Spare capacity
Production time
Factor mobility
Spare capacity
66
New cards
Factors of production
Land
Labour
Capital
Entrepreneurship
Labour
Capital
Entrepreneurship
67
New cards
Price mechanism
signals to producers that the price is too high/too low
incentive to change the price
rations excess demand/supply
successfully allocates scarce resources
incentive to change the price
rations excess demand/supply
successfully allocates scarce resources
68
New cards
consumer surplus
difference between how much a consumer is willing and able to pay and the market price
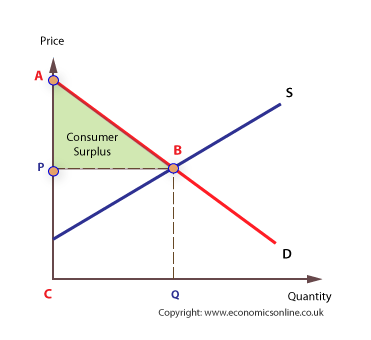
69
New cards
producer surplus
difference between how much a producer willing and able to sell a good for and the market price
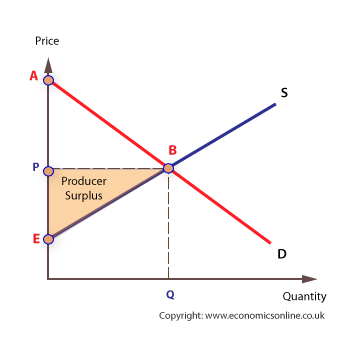
70
New cards
indirect tax
a tax imposed on goods
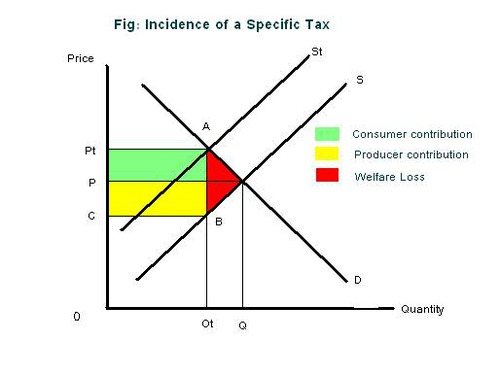
71
New cards
ad valorem tax
a percentage tax imposed on good
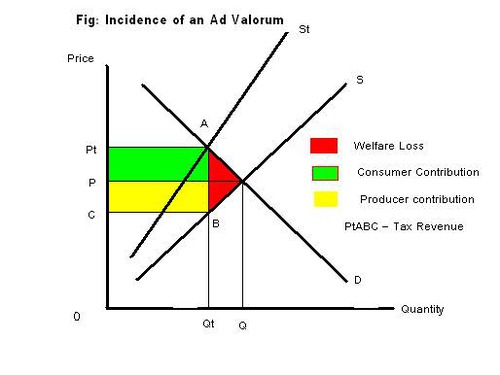
72
New cards
elastic/inelastic demand in indirect tax
elastic demand more of the incidence of tax is paid by the producer
inelastic demand more of the incidence of tax is paid by the consumer
inelastic demand more of the incidence of tax is paid by the consumer
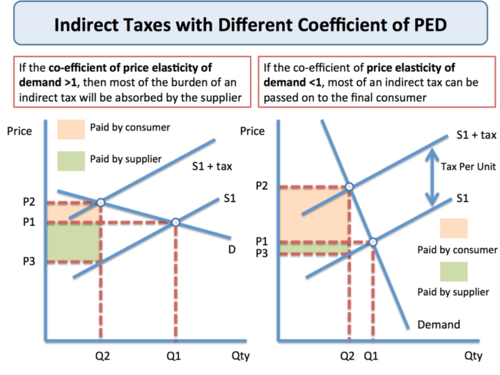
73
New cards
subsidy
money granted by the government
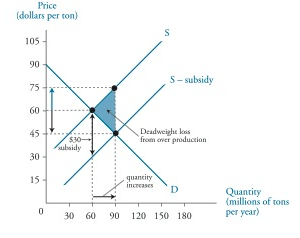
74
New cards
herd thinking
Making decisions based on what other people do.
75
New cards
habitual thinking
people prefer to carry on behaving as they always have
76
New cards
market failure
the market misallocates resources and isn't operating at the socially optimum level
77
New cards
types of market failure
Negative externality
Positive externality
Public good
Asymmetric information
Positive externality
Public good
Asymmetric information
78
New cards
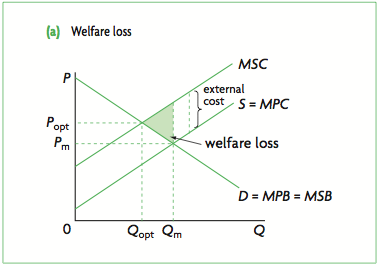
negative externality
cost to the third party and social costs exceeds private costs
79
New cards
private cost
cost faced by producers directly involved in a transaction
80
New cards
external cost
cost to the third party
81
New cards
social cost
private cost + external cost
82
New cards
marginal private cost (MPC)
the cost of producing an additional unit of output
83
New cards
Marginal External Cost (MEC)
the cost to the third party for producing an additional unit of output
84
New cards
Marginal Social Cost (MSC)
The total cost to society of producing an additional unit of output MSC=MPC+MEC
85
New cards
negative externality causes market failure
social costs exceed private cost
overproduction of the good
misallocation of resources
not operating at the socially optimum level
market failure
overproduction of the good
misallocation of resources
not operating at the socially optimum level
market failure
86
New cards
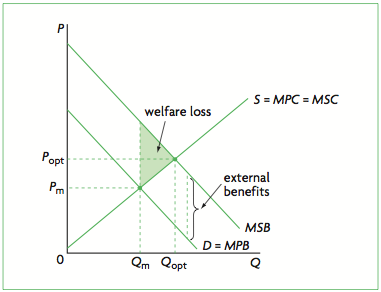
positive externality
benefit to the third party and social benefits exceed private benefits
87
New cards
private benefit
benefits for consumers directly involved in a transaction
88
New cards
external benefit
benefit to the third party
89
New cards
social benefit
private benefits + external benefits
90
New cards
Marginal Private Benefits (MPB)
benefits to consumers for consuming an additional unit of output
91
New cards
marginal external benefit (MEB)
Benefit to third parties from the consumption of extra unit of output.
92
New cards
marginal social benefits (MSB)
total benefits to the consumer consuming an additional unit of output MSB=MPB+MEB
93
New cards
positive externality causing market failure
social benefits exceed private benefits
under consumption of the good
mis allocation of resources
not operating at the socially optimum level
market failure
under consumption of the good
mis allocation of resources
not operating at the socially optimum level
market failure
94
New cards
public goods
good that are non excludable and non rivalrous
95
New cards
non excludable
can't be confined solely to those who have paid for it and non payers can enjoy the benefits at no financial cost
96
New cards
non rivalrous
each persons enjoyment of a good doesn't stop others enjoyment
97
New cards
free rider problem
difficulty of charging consumers and they will benefit from the product without paying for it
98
New cards
public goods cause market failure
a good is non excludable and non rivalrous
you can't charge people to use it (free rider problem)
firms have to incentive to provide it
under provision of the good
misallocation of resources
market failure
you can't charge people to use it (free rider problem)
firms have to incentive to provide it
under provision of the good
misallocation of resources
market failure
99
New cards
asymmetric information
one party to an economic transaction has more information than the other
100
New cards
asymmetric information causes market failure
information gaps
consumers don't have all the information to make a rational decision
market failure
consumers don't have all the information to make a rational decision
market failure