Nerves and Spinal Cord
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the 4 main ions involved in muscular contractions? Explain the relative amounts intercellular vs extracellular.
*intercellular
Na+ (5mM 1:28)
K+ (130mM 43:1) ← Only one that has more internal
Cl- (25mM 1:28)
Ca2+ (0.001mM 1:10000)
Explain the Sodium Potassium Pump
ATP is used to push 3Na+ out of the cell and 2K+ ions are then pumped into the cell. This creates a net positive extracellular environment (negative intercellular).
The potassium gradient is essential in secondary transport of other ions within the cell (like Cl-)
Polarized → Negative intracellular
Depolarized → Trying to make positive intracellular
EPSP
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential
Generated by activation of neurotransmitters produced through the synapses of neurons that depolarize neurons → regulation
Promotes action potentials
Multiple EPSP causes action potentials
IPSP
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential
Generated by activation of neurotransmitters produced through the synapses of neurons that hyperpolarize neurons → regulation
Inhibits action potential
Depolarize membrane to reduce chance of action potential
Action Potential Curve (simple)
Dependent on the regulation of Sodium and Potassium gated channels
Sodium floods into cell to trigger action potential → rise in potential
Potassium exits cell to maintain membrane potential → decrease in voltage bc gradient returns back to normal
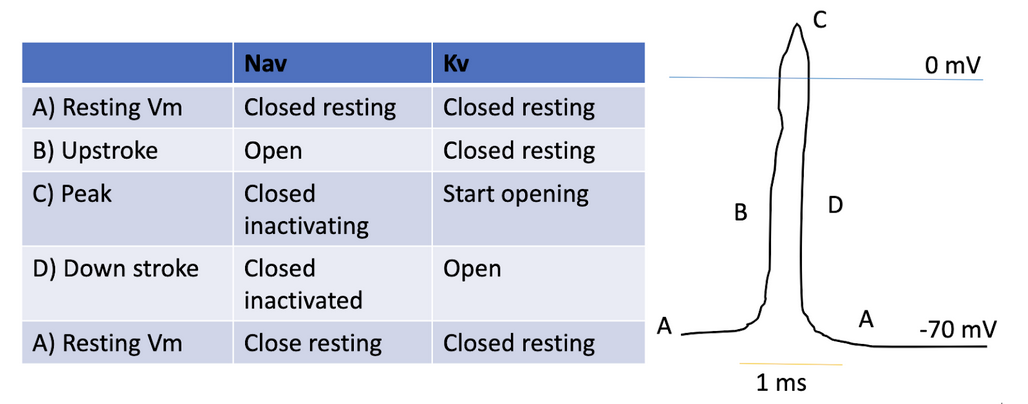
Polarization
Na+ channels are triggered, Na+ floods into cell → cell inside becomes more positive
-70mV → -55mV (must reach 55mV)
Voltage gated Na+ channels open in response to intermembrane charge reaching -55mV
Due to the voltage gated Na+ ions, Na+ ions flood into the cell rapidly → cell becomes very positive or depolarised (+40mV)
Action potential transfers down the neuron
YAY ACTION POTENTIAL
Depolarization
YAY ACTION POTENTIAL
Potassium ion channels open → potassium floods out of the cell to rebalance charges
Hyperpolarization occurs where too much potassium flows out so the intermembrane voltage dips to -75mV (more negative than resting) → relapse here where it cannot have another action potential
Gates close and the sodium potassium pumps work to redistribute the sodium and potassium ions back to the resting state
End Plate Potential
Triggered initially by neurotransmitters where sodium channels open (typically ACh to nAChRs)
Must reach a certain threshold to trigger the action potential and spread to the whole muscle for contraction
Local depolarization of muscle endplate at neuromuscular junction
Resting Membrane Potential
Slightly more negative inside than outside set by non-voltage gated channels
Voltage Amounts
Resting: -70mV
Max Voltage/Action Potential: 30mV
Hyperpolarization: -100mV
Return to Resting: -70mV
Types of Nerve Fibers
Type A
Type B
Type C
A-type Nerve Fibers
Large diameter and myelinated
Fastest of all nerve fibers
Rapid signals for motor and sensory control
B-type Nerve Fibers
Small diameter, thinly myelinated
Autonomic nervous system
Preganglionic fibers
C-type Nerve Fibers
Small diameter, unmyelinated
Slow conduction
Dull and diffusing pain, temperature
Postganglionic fibers
Associated for chronic and achey pain
Neuropathies most likely affect this
Ia: A-alpha fibers
Sensory Fiber
Proprioception
Muscle spindles + primary endings
Knee-jerk reflex
II: A-beta
Clinical test: Proprioception test, two point differentiation test
Touch, pressure, vibrations
Like feeling a textured surface
III: A-delta
Clinical test: Light touch, pin prick, cold temperature
Sharp pain, cold, light touches like tickle or stroke
Pain from a cut
IV: C type fibers
Clinical test: hot temperature
Dull pain, aches, warmth, itch, autonomic functions
Cauda Equina
The spinal cord goes from brainstem down to L1 or L2 where it “ends”. At that point, nerve roots split down and branch out, forming the cauda equina.
Grey Matter
Unmyelinated nerves synapse and conduct information. On the inside of vertebrae and surrounded by white matter.
White Matter
Myelinated and one way tracts that conduct information vertically up and down vertebrae. Ascending tracts are sensory, descending is motor.
Spinal Nerves
Mixed - contain both sensory and motor
They split off just before reaching the vertebrae where the sensory fibers enter on the dorsal side and the motor fibers enter on the ventral side
Sensory Pathway
First Order Neurons - Nerve enters dorsal root and synapse with 2nd order
Second Order Neurons - Ascend tract to brainstem
Third Order Neurons - Conduct information from brainstem to the sensory cortex
Motor Pathway
Upper Neurons - Start in motor cortex to brainstem/spinal cord
Lower Neurons - Starts from spinal cord vertebrae and travels to effector organs or muscles
Somatic Reflexes
Doesn’t usually require brain input (sometimes can)
Reflex arc
Somatic Receptor
Sensory neuron
Interneuron
Motor Neuron
Effector muscle