International Air Laws
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Define “law”
Law = Sovereignty (อำนาจอธิปไตย)
A rule of human conduct imposed upon and enforced among members of a given state
What are the 4 things that made up sovereignty? (Hint : AEOJ)
A = Authority (อำนาจในการบังคับใช้)
E = Enforcement (การบังคับใช้)
O = Order
J = Jurisdiction (ขอบเขตการควบคุม)
True or false: “Nations have sovereignty over the airspace above their territories”
True!
What are the 3 solutions to solve the conflict of laws in aviation? (Hint : CCA)
C = International Co-operation
C = International Convention (อนุสัญญาระหว่างประเทศ)
A = International Agreement
Give 3 examples of international conventions in aviation. What are they responsible for?
Warsaw Conventions (airline liability in the event of accidents)
Montreal Conventions (airline liability in the event of accidents)
Chicago Conventions (framework of basic rules for international flight)
Define “international conventions”
Agreement between nations
In order to form an international convention, what does each country has to do?
Sign a convention
Ratifies the convention (ทำสัตยาบันร่วมกัน)
Making the laws part of the international regulatory framework
Legally binding the convention.
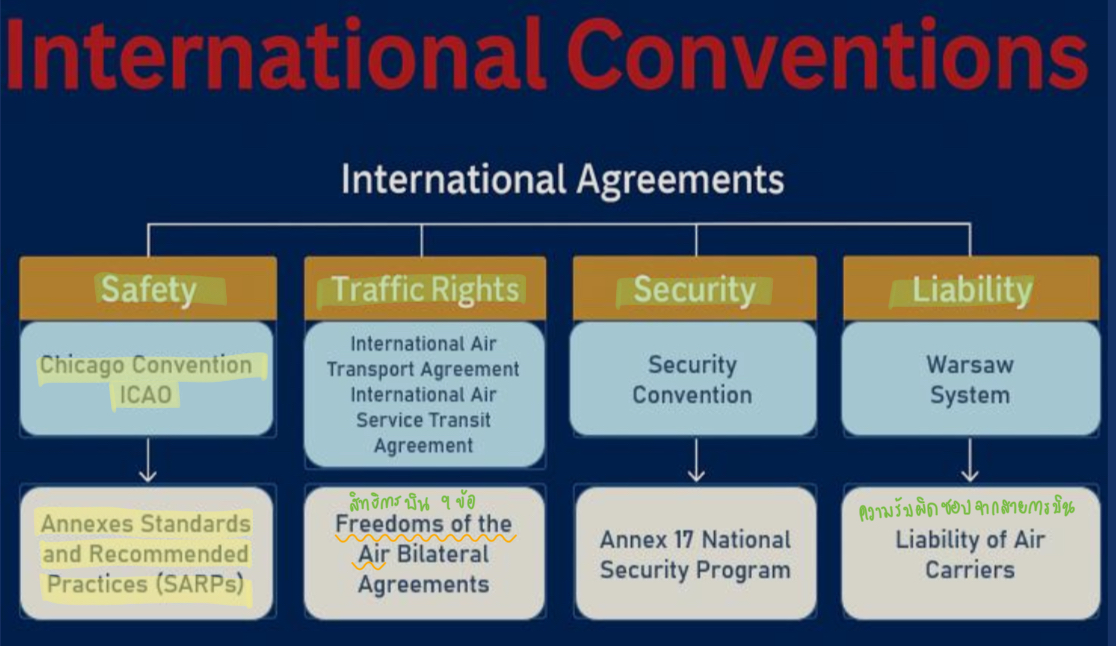
What are the 4 agreements that is included as parts of the international convention? Which solution do they fall under?
Safety (Chicago Conventions & ICAO)
Traffic Rights (International Air Transport Agreement)
Security (Security Conventions)
Liability (Warsaw System)
Describe the “Chicago Convention”
Signed in December 1944 by representatives of 52 nations
A source of international air law
193 countries have ratified the Chicago Convention (a.k.a contracting states)
What are the key words stated by the Chicago Conventions 1944?
“safe and orderly”
Air transport service may be established on the basis of “equality of opportunity and economy”
What are some issues occurring under the Chicago Conventions?
Traffic rights
Aircraft
Airport
ICAO
True or false: “every state has complete and exclusive sovereignty over their airspace”
True! (Art.1)
True or false: “every state can freely operate over/into the territory of a contracting state”
False! (Art.5-6)
(You need to have a special permission/other authorization of that state)
True or false: “According to Art.17-21, aircraft have nationality of the state where it was registered”
True!
(An aircraft can only be registered in one state, but can change from one state to another)

Which article of the Chicago Convention mention about “airworthiness”?
Art.31
“Every aircraft engaged in international navigation shall be provided with a “certificate of airworthiness” issued by the state in which it is registered”
Which article of the Chicago Convention mention about “personnel licensing”?
Art.32
“Every person operating every aircraft shall be provided with certificates of competency and licensed issued by the state in which the aircraft is registered”
True or false: “contracting states have the right to refuse or recognize for the purpose of flight above its own territory”
True!
According to Art.26, who are involved in investigation of accidents involving death and serious injury? What is their role?
The state in which the accident occurs = initiate an enquiry into the circumstances of the accident.
The state in which the aircraft is registered = given an opportunity to appoint observers.
When one state does not comply with ICAO international standards, what do other contracting states have to do?
Notify ICAO immediately of the differences.
True or false: “ICAO gave birth to the Chicago Convention”
False!
(It’s the other way around. The Chicago Convention gave birth to the ICAO)
Describe “ICAO” in a very simple term
A specialized agency of the United Nations that looks after aviation
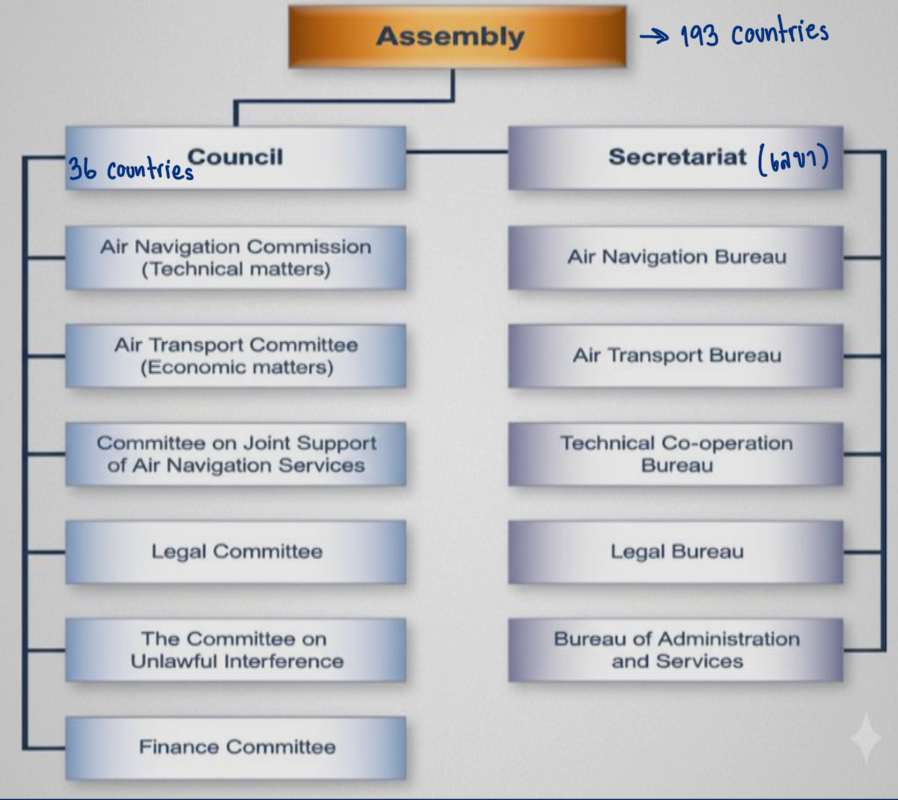
How many countries are chosen as “the governing council” of the ICAO assembly?
36 countries
What are the 3 parts (categories) within the governing council? Name 2-3 countries for each part
States of chief importance in air transport (e.g. Brazil, China, UK, US, Germany)
States which make the largest contribution to the provision of facilities for international civil air navigation (e.g. Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, South Africa)
States ensuring geographical representation (e.g. Malaysia, Korea, UAE)
What are the 3 non-governmental organizations which cooperate with ICAO?
IATA (International Air Transport Association)
ACI (Airport Council International)
CANSO (Civil Air Navigation Services Organization)
What are the 2 compliances of ICAO Audits?
USOAP (Universal Safety Oversight Audit Program) = ความปลอดภัย
USAP (Universal Security Audit Program) = ความมั่นคงทางความปลอดภัย
Explain “International Standards and Recommended Practices”
“SARPs”
Contain standards which are mandatory and recommended practices which are desirable.
What is the purpose of Airline Liability Conventions?
To establish a common standard for compensation
Explain the “Warsaw Convention”
Introduced in 1929
Defines liability compensation per passenger, documents of carriage and claim limitations.
Explain the “Montreal Convention”
Signed in 1999
Adopted from the old Warsaw system
Applies to all international carriage of persons, baggage or cargo.
What are some liabilities of the Montreal Convention? Simply explain them
Death and injury of passengers (death/injury took place on board the aircraft or in the course of embarking and disembarking)
Baggage (destruction/loss/damaged to checked baggage)
Cargo (took place during the carriage by air)
Delay (delay in carriage of passengers, baggage, and cargo)