climate change unit test friday!
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
greenhouse effect
a natural process whereby gases and clouds absorb infrared radiation emitted from Earth’s surface and radiate it, heating the atmosphere and Earth’s surface
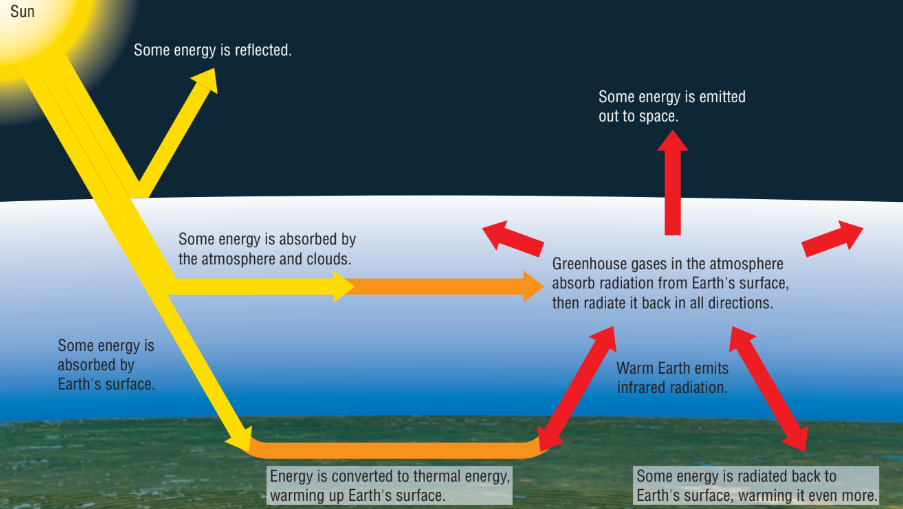
greenhouse gas definition and what are some names
any gas in the atmosphere that can absorb infrared radiation
Examples: CO2, H2O, N2O, Ozone, CFCs, CH4
carbon sink
a reservoir that absorbs CO2 and stores it in a different form
Example: Trees take in CO2 to turn it into sugars for energy
how (why) do greenhouse gases absorb infrared radiation
they consist of more than one atom, and different atoms:
Examples:
Bad Absorbers
H2, O2
Can only vibrate one way
Good Absorbers
H2O, N2O, CH4, CO2, CFCs
Can vibrate in more than one way, and can absorb different types of energy
Continental Drift
Theory that Earth was big super continent called Pangaea
Plate Tectonics
Theory explaining the slow movement of the Earth’s large plates
How do Volcanic Eruptions affect the climate
They erupt rock, dust, and sulfur dioxide gases high into the air, causing some of the sun’s radiation to be reflecting back into space
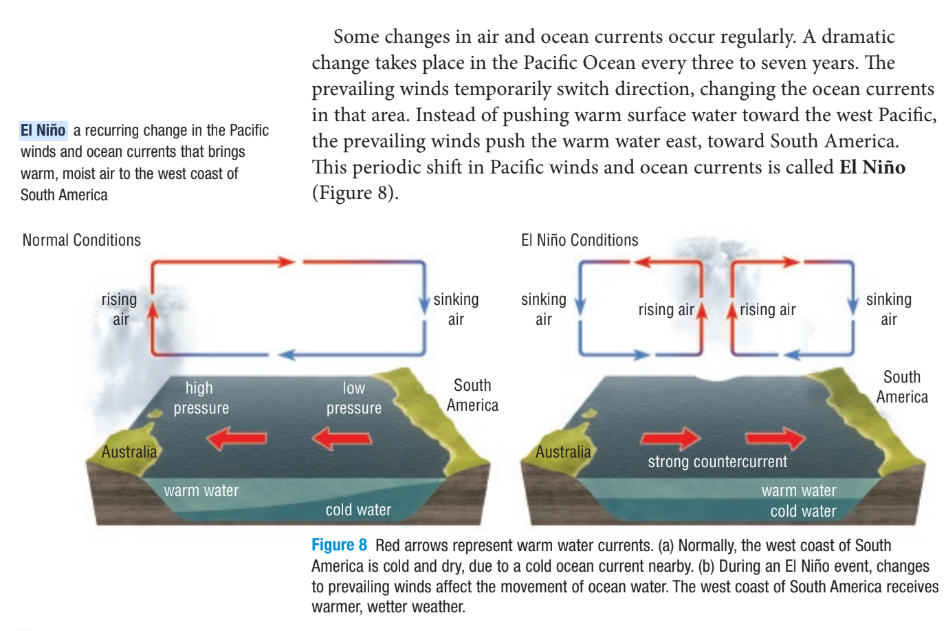
El Niño
a recurring change in both the pacific winds and ocean currents, causing warm, moist air (and warm water) to be pushed from Australia to South America
Anthropogenic sources of Greenhouse Gases
CO2, N2O, CH4, CFCs
Name a source for each greenhouse gas
CO2
CH4
N2O
CFCs
CO2: Burning fossil fuels, Deforestation
CH4: Agriculture (Cattle, Rice Farming), decay of organic material, and coal mining and natural gas extraction
N2O: Livestock feed and waste
CFCs: Leaks out from fridges, air conditioners, or industrial processes
7 signs of climate change
Rising Sea Levels
Rising Temperatures
Melting sea ice, glaciers, & ice sheets
Change in precipitation
Change in severe weather
Change in seasons
Change in ecosystems
Past Clues of Climate Change?
Ice Cores, Tree Rings, Coral Reefs, Cave, Rock, Ocean Sediments,
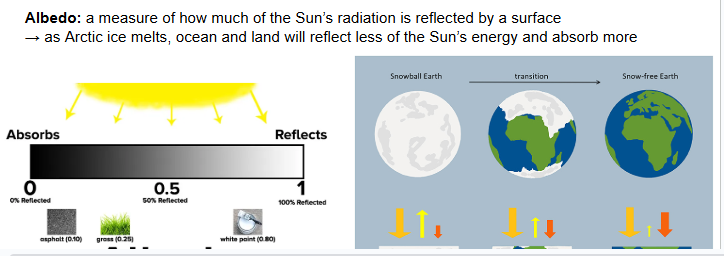
Albedo Effect
The measure of a surface’s reflectivity from the sun’s radiation
Melting Glaciers - Impact from Climate Change
Glaciers disappear = water shortage
Artic sea ice melting = loss of biodiversity: habitats of animals like polar bears
What is Thermal Expansion
Water expands slightly when it warms up. Sea levels are believed to rise due to thermal expansion
Melting Permafrost - Artic Effects on World
Enhanced release of CO2 and Methane
Stored in higher amounts in permafrost
How does an ICE CORE reveal past clues of climate?
Ice cores are cut into very thin slices to test the air bubbles in each slice for various gases to establish how much carbon dioxide, methane, & nitrous oxide was in the air when the air bubble formed.
How does a TREE RING reveal past clues of climate?
Trees create one growth ring per year. You can assemble clues from both living and dead trees to collect records of climate going back as far as 10 000 years
What is the Rainshadow effect?
When clouds are blown upward over a mountain, and lose their moisture as rain falls on the windward side, resulting in less rainfall for the leeward of the mountain.
What is Convection current?
A circular current of air and other liquids as the result of warm liquid rising, and cold liquid sinking.
Meaning it happens during uneven amounts of heating liquid or gas which creates the current.
What is Thermohaline circulation?
The continuous flow of water as a result of the temperature differences and salinity in the oceans.
How does CORAL REEFS reveal past clues of climate?
Like trees, coral reefs grow a layer each season, and scientists (or wtv) can research the temperature of the surface ocean water when each layer was growing
How does Rock, Ocean Sediment, and Caves reveal past clues of climate?
Layers of rock build up overtime. Information from these buildups can contain clues about plant pollen or fossils to the climate at that time in that location.