A-Level Geography (AQA) - Physical Geography
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
178 Terms
What are inputs?
Refers to where matter or energy is added to a system.
What are outputs?
Refers to where matter or energy leaves the system.
What are stores?
Refers to where matter or energy builds up in a system
What are flows?
Refers to where matter or energy moves in a system
What are boundaries?
Refers to the limits of a system (etc, the watershed)
What are open systems?
Refers to when systems receive inputs and transfer outputs of energy or matter with other systems.
What is a closed system?
Refers to when a systems’ inputs are equal to its outputs.
What is dynamic equlibrium?
Refers to where a systems’ inputs equal its outputs despite changing conditions.
What is positive feedback?
Refers to when a chain of events amplifies the impacts of the original event.
What is negative feedback?
Refers to when a chain of events nullifies the impacts of the original event.
What kind of systems are carbon and water cycles locally?
Open systems
What kind of systems are carbon and water cycles globally?
Closed systems
What are some examples of flows in a local drainage basin system?
1) Evaporation
2) Precipitation
3) Condensation
4) Transpiration
5) Baseflow
What is percipitation?
Refers to any water that falls to the surface of the Earth from the atmosphere, e.g, rain and hail
What is convectional rainfall?
Refers to when heating from the sun causes warm air to rise, leading to condensation at higher altitudes, which falls as rain.
What is relief rainfall?
Refers to when warm air is force upward by a natural barrier, such as mountains, causing water to condense at higher altitudes and falls as rain.
What is frontal rain?
Refers to when warm air rises over cool air when 2 bodies of air at different temperatures meet, because warm air is less dense and lighter, leading to condensation at higher altitudes and rainfall.
What is evapotranspiration?
Refers to net evaporation and transpiration.
What is evaporation?
Refers to when water is heated by the sun, causing it to become a gas and rinse into the atmosphere.
What is transpiration?
Refers to when plants release water through their roots, which then evaporates due to heating by the Sun.
What is streamflow?
Refers to when all the water which enters a drainage basin will either leave through the atmosphere or through streams which drain basins.
What is infiltration?
Refers to the process of water moving from above the ground into the soil.
What is infiltration capacity?
Refers to the rate of infiltration.
What is percolation?
Refers to when water moves from the ground into porous rock or fractures in rocks.
What is the perconlation rate dependent on?
1) Rock fractures
2) Percolation rate
What is throughflow?
Refers to when water moves through the soil into streams and rivers.
What is throughflow dependent on?
1) Soil type
2) Field capacity
What is surface run-off/ overland flow?
Refers to when water flows above the ground as sheetflow (lots of water flowing over a large surface area) or rills (small channels similar to streams).
What is groundwater flow?
Refers to when water moves through the rocks.
What is stemflow?
Refers to the flow of water that has been intercepted by plants and trees, e.g, down a stem, leaf or branch.
What is soil water?
Refers to water stored in the soil which is utilised by plants.
What is groundwater?
Refers to water that is stored in the pore spaces or rock.
What is a river channel?
Refers to water stored in a river.
What is interception?
Refers to water intercepted by plants or trees via branches and leaves before reaching the ground.
What is surface storage?
Refers to water stored in puddles and ponds.
What is a water table?
Refers to the upper level at which the porse spaces and fractures in the ground become saturated.
Why is the water table important for research?
Used by researchers to assess drought conditions, health of wetland systems and the success of forest restoratio programmes.
What is the water balance?
Refers to the formula used to express the process of water storage and transfer in a drainage basin system.
What is the formula for a drainage basin system?
Precipitation = Total Runoff + Evapotranspiration +/- (change in) storage
What are the human factors which effect the water cycle?
1) Deforestation
2) Agriculture
3) Urbanisation
What are the physical factors which effect the water cycle?
1) Storm events
2) Seasonal changes
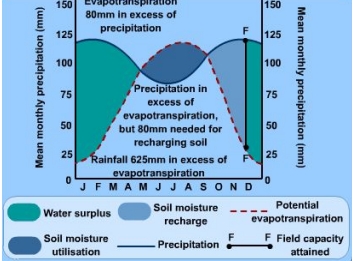
What is the soil-water budget?
Refers to the annual balance between inputs and outputs in the water cycle.
Why is understanding the soil water budget important?
This shows how inputs and outputs in the water cycle impact the soil and water storage.
What are water levels like during winter for the soil-water budget?
In surplus
What are water levels like during autumn for the soil-water budget?
In recharge
Why do water levels recharge during autumn?
The inputs of precipitation exceed the outputs of evapotranspiration due to weather being significantly cooler.
What are water levels like during spring and summer for the soil-water budget?
In deficit
Why are water sources depleted during spring and summer?
Evapotranspiration rates are greater than precipitation due to warmer weather, leading to soil water deficits.
What is field capacity?
Refers to the maximum storage of water in the soil.
What features of the water basin is the water budget dependent on?
1) Type depth
2) Soil and bedrock permeability
What is the hydrosphere?
Refers to any area where there are large volumes of water.
What is the lithosphere?
Refers to any area which is within the crust and upper mantle.
What is the cryosphere?
Refers to any area where there are large areas of frozen ice.
What is the atmosphere?
Refers to any area within the Earth’s atmosphere which stores gaseous fluids.
What is the biosphere?
Refers to any place within living organisms.
What are the areas water can be stored in?
1) Hydrosphere
2) Lithosphere
3) Cryosphere
4) Atmosphere
5) Biosphere
What are aquifers?
Refers to underground water stores.
What is the residence time of shallow groundwater aquifers?
Up to 200 yr/s
What is the residence time of deeper fossil aquifers?
Up to 10,000 yr/s
What is the residence time of glaciers?
Around 20-100 years
What is the residence time of lakes?
Around 50-100 years
What is the residence time of seasonal snow cover?
Around 2-6 months
What is the residence time of soil water?
Around 1-2 months
What are some examples of seasonal changes which effect the water cycle?
1) Less precipitation and increased evapotranspiration in summer due to higher temperatures.
2) Reduced interception and reduced flows in winter due to water being stored as ice.
What are some examples of farming practises which effect the water cycle?
1) Ploughing breaks up surface soil, increasing infiltration.
2) Arable farming increases interception and evapotranspiration
3) Pastoral/Animal farming causes soil to compact, which reduces infiltration.
What are some examples of land use changes which effect the water cycle?
1) Deforestation reduces interception and evapotranspiration, but infiltration increases.
2) Construction reduces infiltration and evapotranspiration, but increases surface run-off.
What are the effects of abstraction on the water cycle?
1) Reduces the volume of water in surface stores.
2) Decline in global long-term water stores.
What is a flood hydrograph?
Refers to the graph which represents rainfall for the drainage basin of a river and the discharge of the same river on the graph.
What is the rising limb?
Refers to the section of a hydrograph where discharge increases rapidly after rainfall, as surface runoff and throughflow enter the channel.
What is lag time?
Refers to the time delay between peak rainfall and peak river discharge.
What is the falling limb?
Refers to the section of a hydrograph where discharge decreases as runoff decreases, as water returns slowly to stores via groundwater flow.
What is baseflow?
Refers to the normal background flow of a river supplied mainly by groundwater between rainfall events.
What is bankfull discharge?
Refers to the maximum discharge a river can hold before it overflows its banks and flooding begins.
What does a “flashy” hydrograph look like?
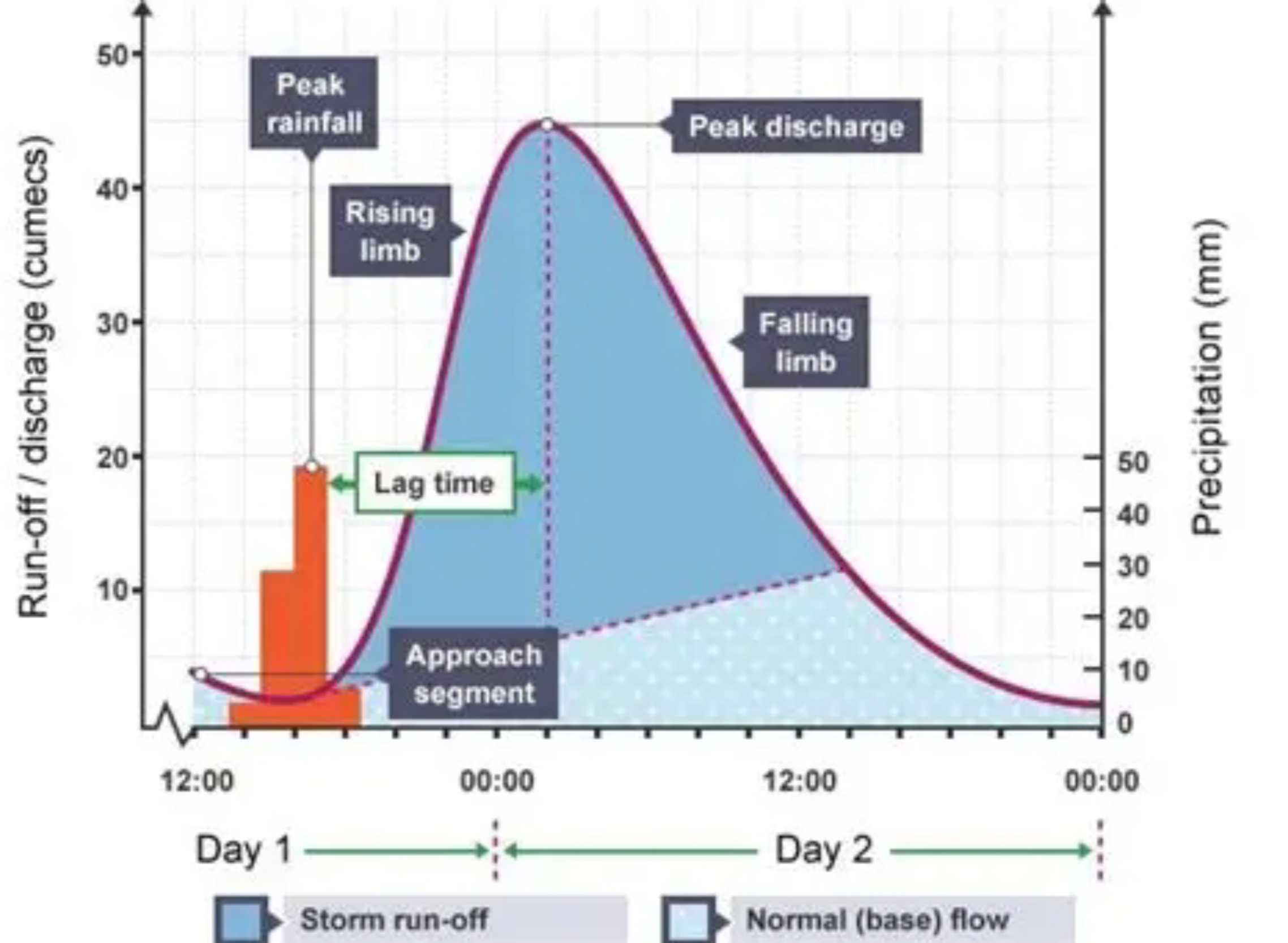
What characterises a flashy hydrograph?
1) Short lag time
2) Steep rising and falling limb
3) Higher flood risk
4) High peak discharge
What does a “subdued”/low-flat hydrograph look like?
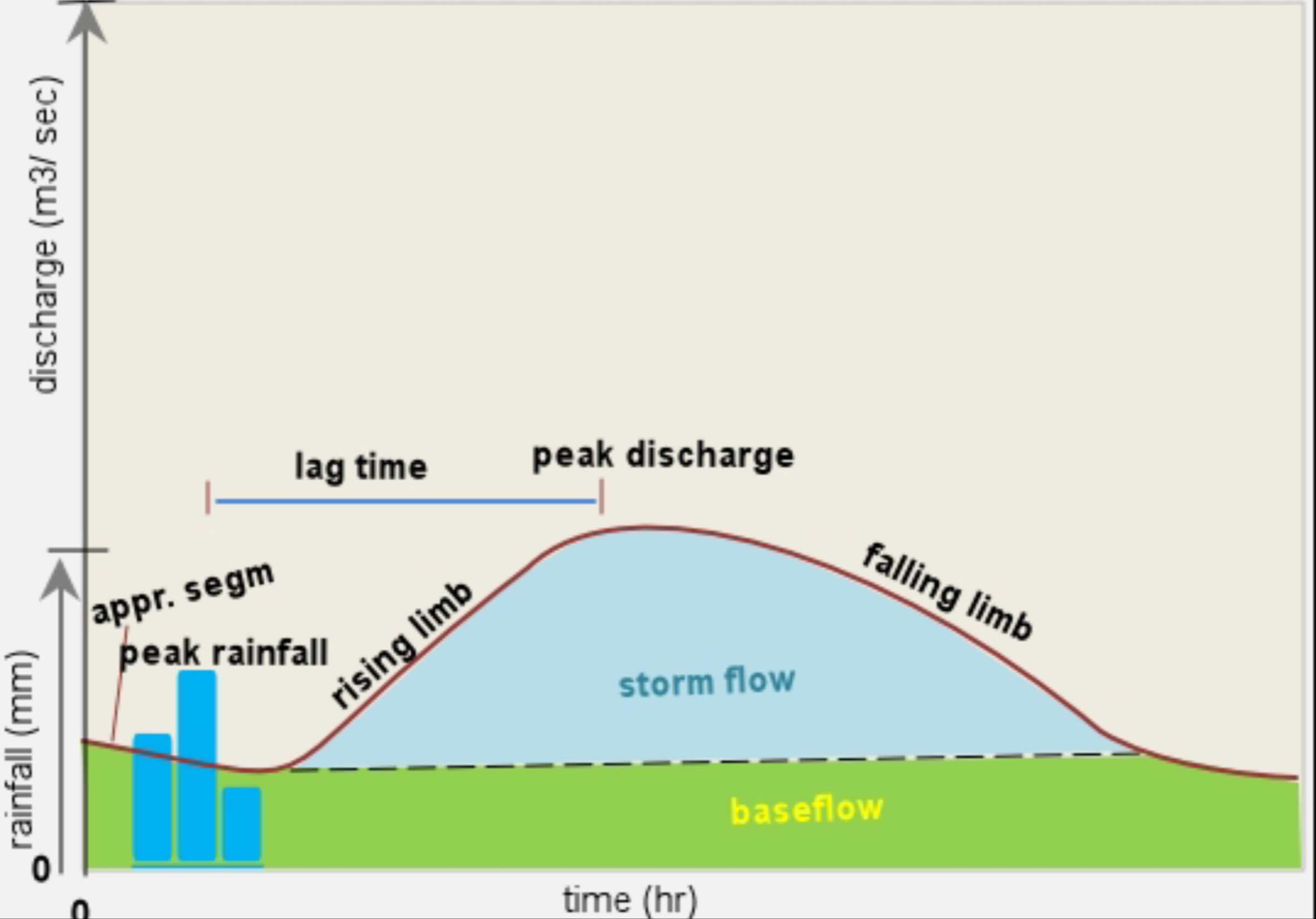
What characterises a subdued hydrograph?
1) Long lag time
2) Gradually rising and falling limb
3) Lower flood risk
4) Low peak discharge
What is a system?
Refers to a group of interacting parts connected by flows or transfers of energy, material or matter.
What is cascading systems?
Refers to a system where energy and material are transferred from one subsystem to another.
What kind of system is the Eath?
Closed system
What is equilibrium?
Refers to the state of balance within systems where inputs and outputs are equal, and processes involved operate to maintain the balance.
What is dynamic equilibrium?
Refers to changes and processes within a system which maintain the balance of a system.
What percentage of freshwater makes up the Earth’s water? (STAT)
~2.5%
What percentage of freshwater is locked and inaccessible to humans? (STAT)
~1.6% (~70% in the cryosphere, ~30% as groundwater)
What is climate change a significant factor in the change in water cycles? (STAT)
Approx. 18000 yr/s ago => Roughly a third of the Earth’s surface was covered in ice sheets => Climate change => Increase in sea levels to increase by around 100m
What are the two primary sources which drive the hydrological cyle?
1) Solar energy
2) Gravitational forces
What is the largest flow in the water cycle?
(Oceanic) evaporation
What is the largest input into the hydrological cycle?
Precipitation above oceans
What is the residence time of oceans/seas? (STAT)
~4000 yr/s
What is the residence time of swamps? (STAT)
~1-10 yr/s
What is the residence time of biospheric water? (STAT)
~1 week
What is the rainshadow effect?
Refers to how most rain is in the West U.K., due to being mountainous compared to the flatter East U.K.
What is surplus in terms of the soil moisture budget?
Refers to when the soil water store is full, which fills soil moisture capacity for plant use and surface run-off.
What is recharge in terms of the soil moisture budget?
Refers to when precipitation exceeds evapotranspiration, so soil moisture levels increase.
What is depletion in terms of the soil water budget?
Refers to when evapotranspiration exceeds precipitation, so moisture levels decrease.
What does NASA research show about human impacts on the water cycle? (STAT)
“Majority of negative changes in the global water cycle are due to human activities, for example, agriculture.”
What is a drainage basin?
Refers to the area of land drained by the river and tributaries.
What are confluences?
Refers to smaller streams which join with the main courses of the river.
What are tributaries?
Refers to smaller streams which branch off from the main course.
What is a source?
Refers the the starting point of a river.