General Biology Exam 2
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Genome
A cell’s total genetic material
Prokaryote
usually 1 circular DNA molecule
Eukaryotes
usually > 1 linear DNA molecules
Chromosomes
Molecule of DNA in a cell
Chromatin
DNA / protein complex in dispersed state thread- or fiber-like, DNA in this state when cell not actively dividing
Chromosomes (different definition)
“colored body”, DNA wrapped around proteins, Highly organized- high density, Only present during cell division
Haploid
(n), Having one complete set of chromosomes, Haploid cells have 1 of each chromosomes
Diploid
(2n), Having 2 complete sets of chromosomes, 2 of same chromosomes: homologous chromosomes or a homologous pair, same length, centromere location, genes
What cells are presented in humans they are diploid
Somatic cells
Haploid Example
n=2, gametes (male or female germ cells)
Diploid Example
2n=4, blood cells, skin cells, and muscle cells, somatic cells
Prokaryotes (Cell Cycle), How do they divide?
Binary Fission
Interphase
Time between cell divisions, Not a resting stage- cell highly active, Growth, synthesis, metabolic activity, Long- at least 90% of cell cycle, DNA is chromatin
What are the 3 phases of Interphase?
G1 (Gap 1), S Phase, G2 (Gap 2)
G1 (Gap 1)
Growth and normal development and functions, Preparation for S phase, Many cells spend most of there lives in G1
S Phase
S = Synthesis, Chromosomes duplicated- DNA and chromosomal protein synthesis-Does not change ploidly
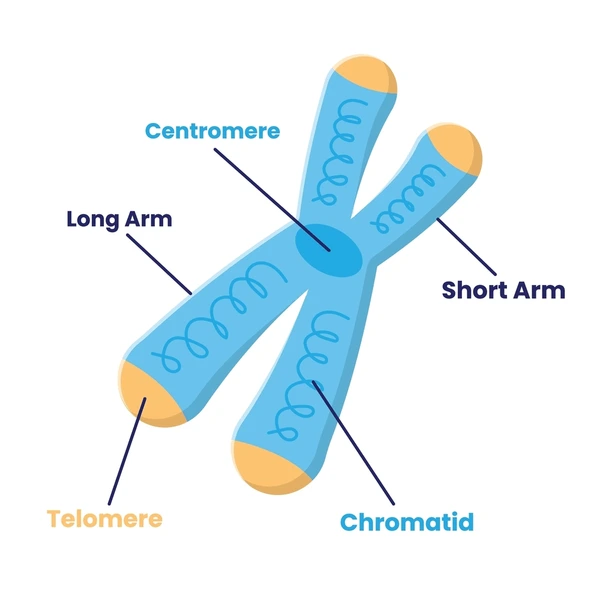
What part are both of the sister chromatids are connected to?
Centromere
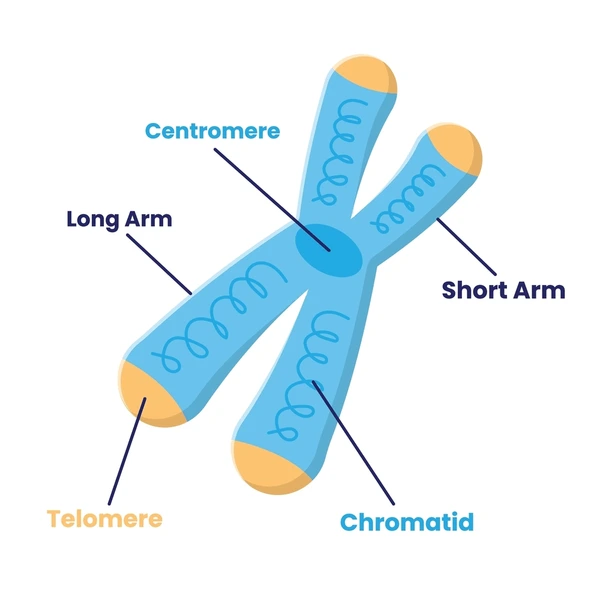
What part of the 2 sisters chromatids are located?
Telomere
What do 2 sister chromatids have in common?
Identical Copies
Is DNA is still presented in the chromatin during the S phase?
Yes
G2 (Gap 2)
Usually shorter than G1 or S Phase, DNA still as chromatin, High metabolic activities, preparations for mitosis
M Phase
Mitosis and cytokinesis, Shortest part of the cell cycle (<10%)
Mitosis
Nuclear division of somatic cells, Continuous process, Divided in 4 stages: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
What are the 4 stages of Mitosis?
Prophase, 2.Metaphase, 3.Anaphase, 4.Telophase
Prophase
3 big things happen":
Chromosomes condense
Nucleus breaks down
Mitotic spindle forms
Mitonic Spindle
Fibers within cell oriented from pole to pole of cell, Guide chromosomes movement during mitosis
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at metaphase plated
Anaphase
Sister chromotids sperate, move to opposite poles, Pulled by Kinetochores, After seperation, each chromatid considered to be a chromosomes
Kinetochores
proteins attached to centromeres
Telophase
Opposite of prophase, chromosomes start to de-condense, Nuclear envelope reforms, New nuclei identical to parent nucleus-that’s the point!
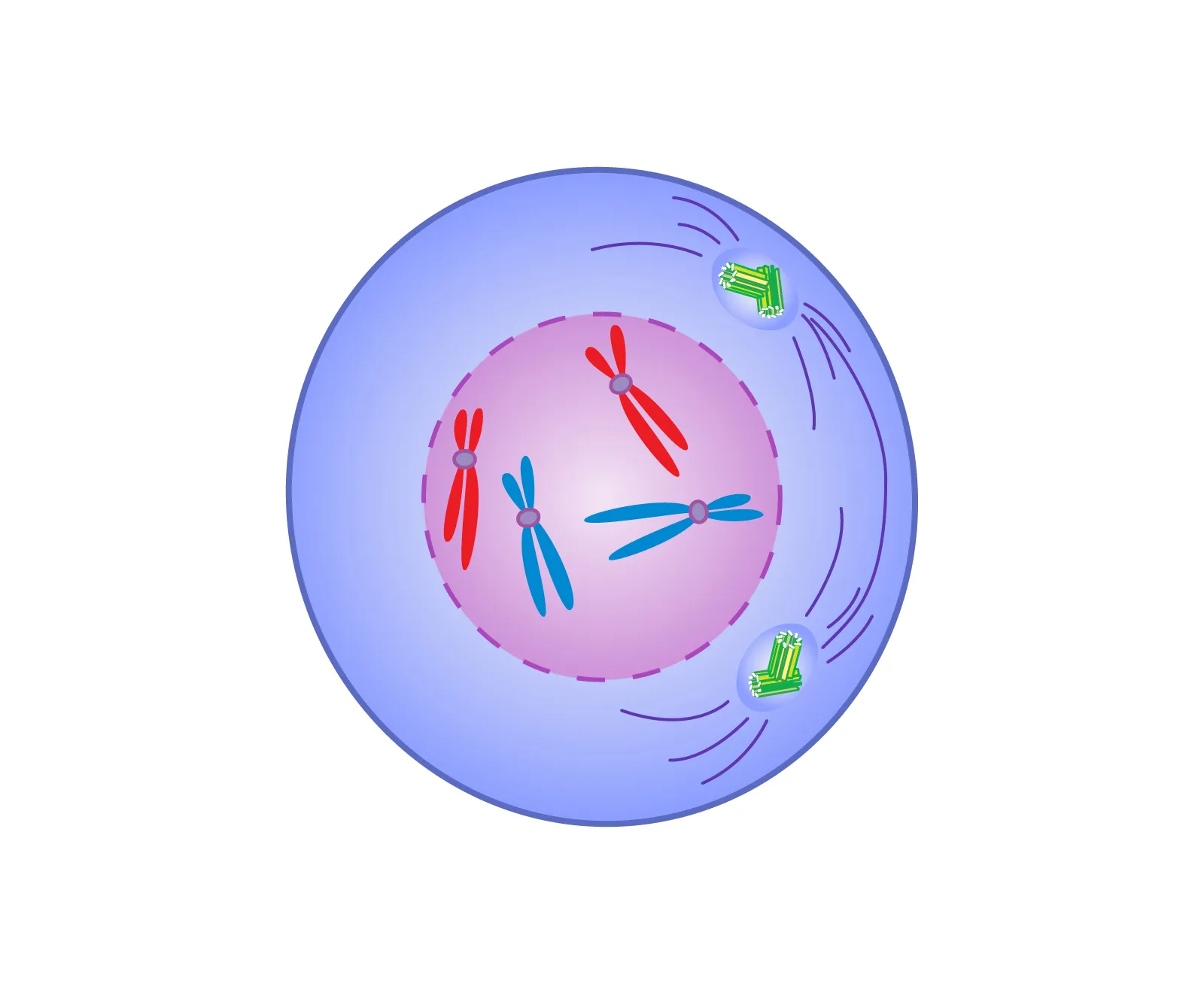
What phase is this?
Prophase
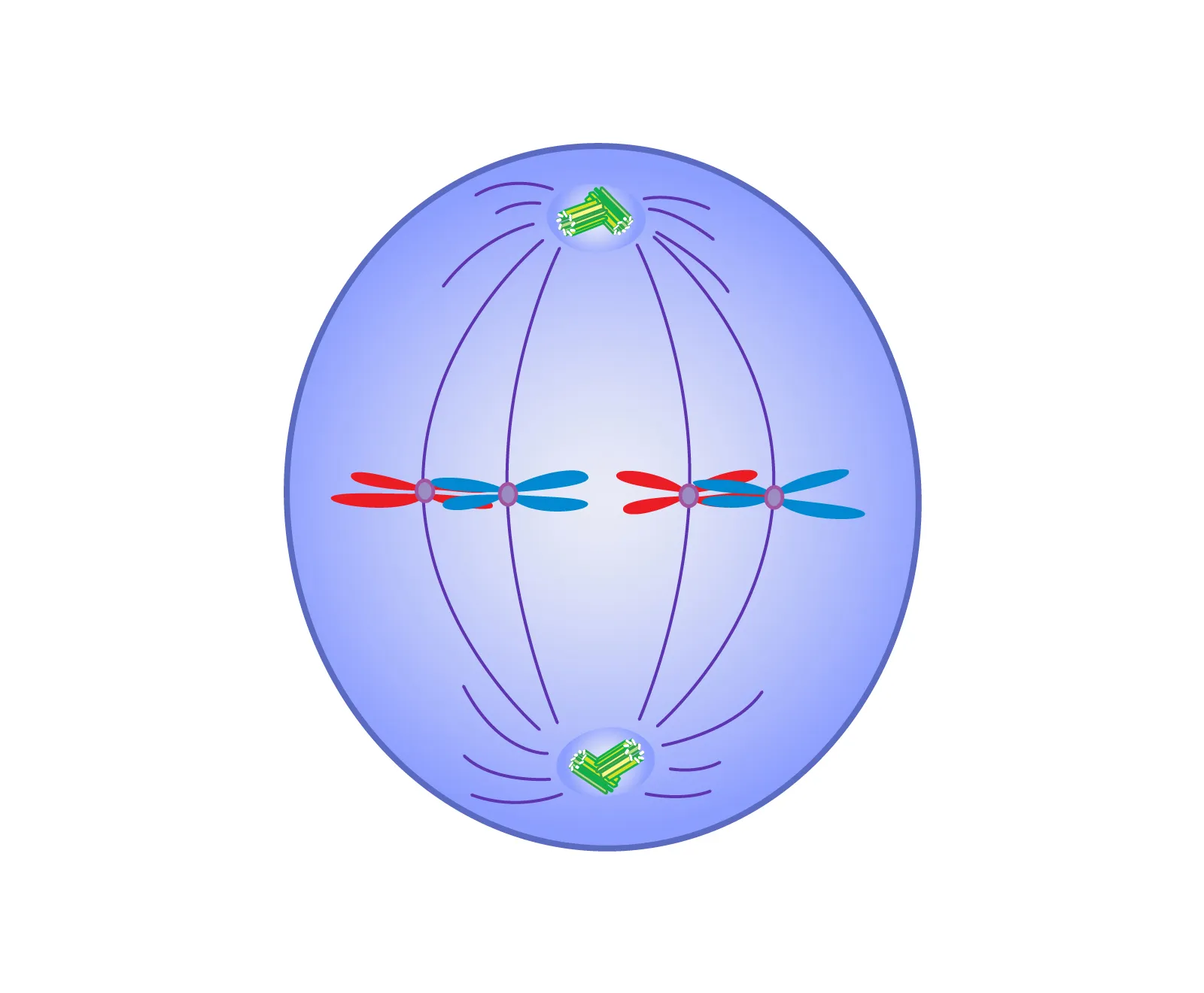
What phase is this?
Metaphase
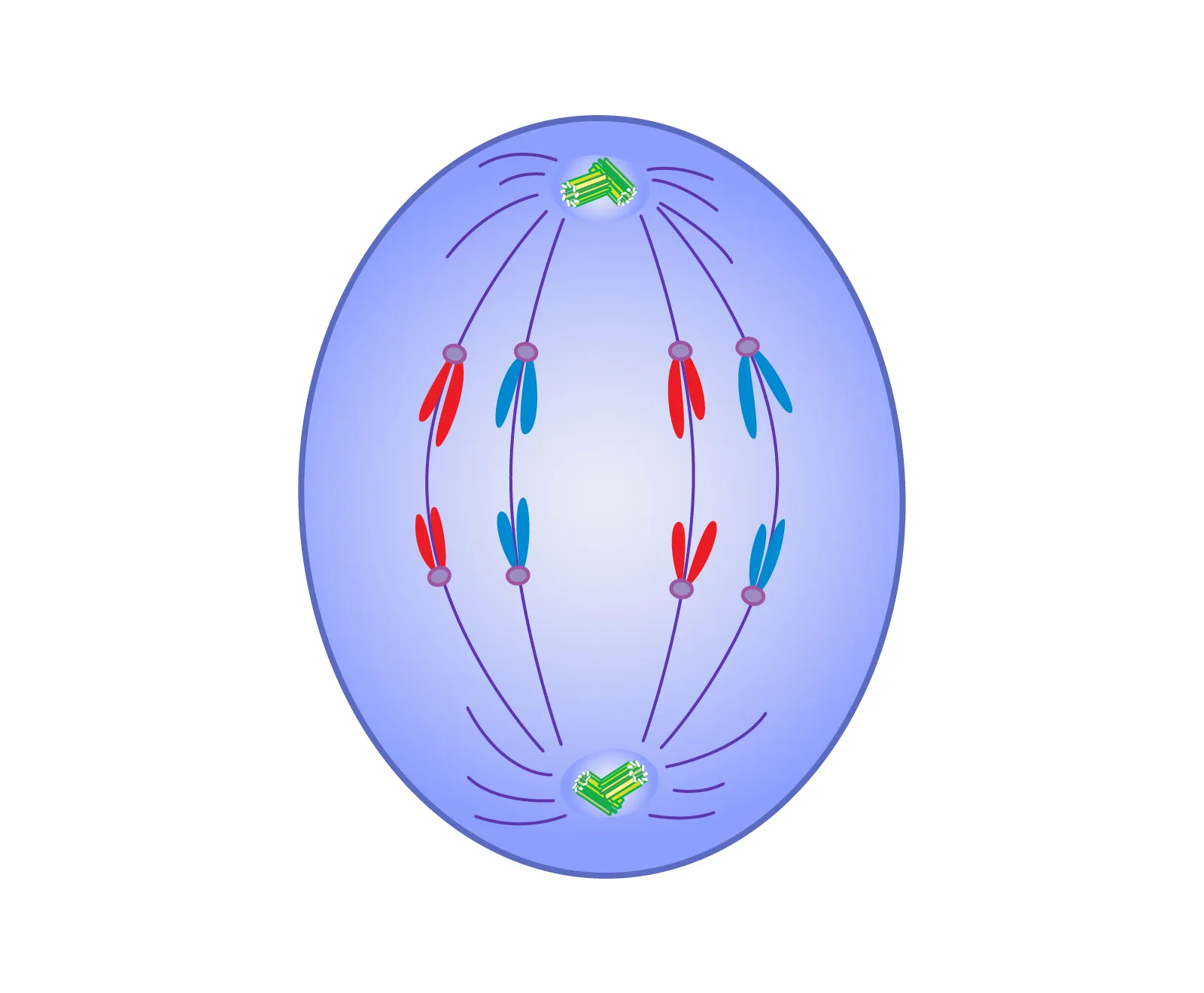
What phase is this?
Anaphase
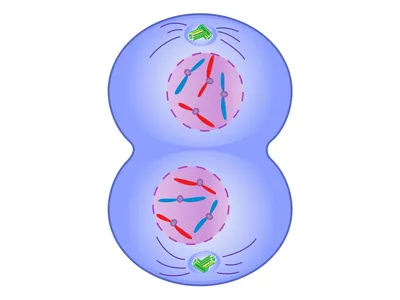
What phase is this?
Telophase
What is the number of daughter cells being produced after mitosis? (2n=4)
two daughter cells with 2n=4 in each
What is the number of daughter cells being produced after meiosis? (2n=4)
four daughter cells with n=2 in each
Cytokinesis
Part of M phase, Cytoplasmic divison —> 2 cells, each with 1 nucleus, Distinct process from mitosis, but generally overlaps with telophase
Cleavage Furrow
Contacts until parent cell pitched into two, Part of cytokinesis for “animal” cells
Cell Plate
new membrane at location of metaphase plate, fuses with plasma membrane, divides daughter cells, part of cytokinesis for “plant” cells
How many sister chromatids are in G1? (2n=4)
0
How many chromosomes are in G1? (2n=4)
4
How many chromosomes are presented in S phase?
8
How many homologous pair are presented in S phase?
2
How many sister chromatids are in S phase?
8
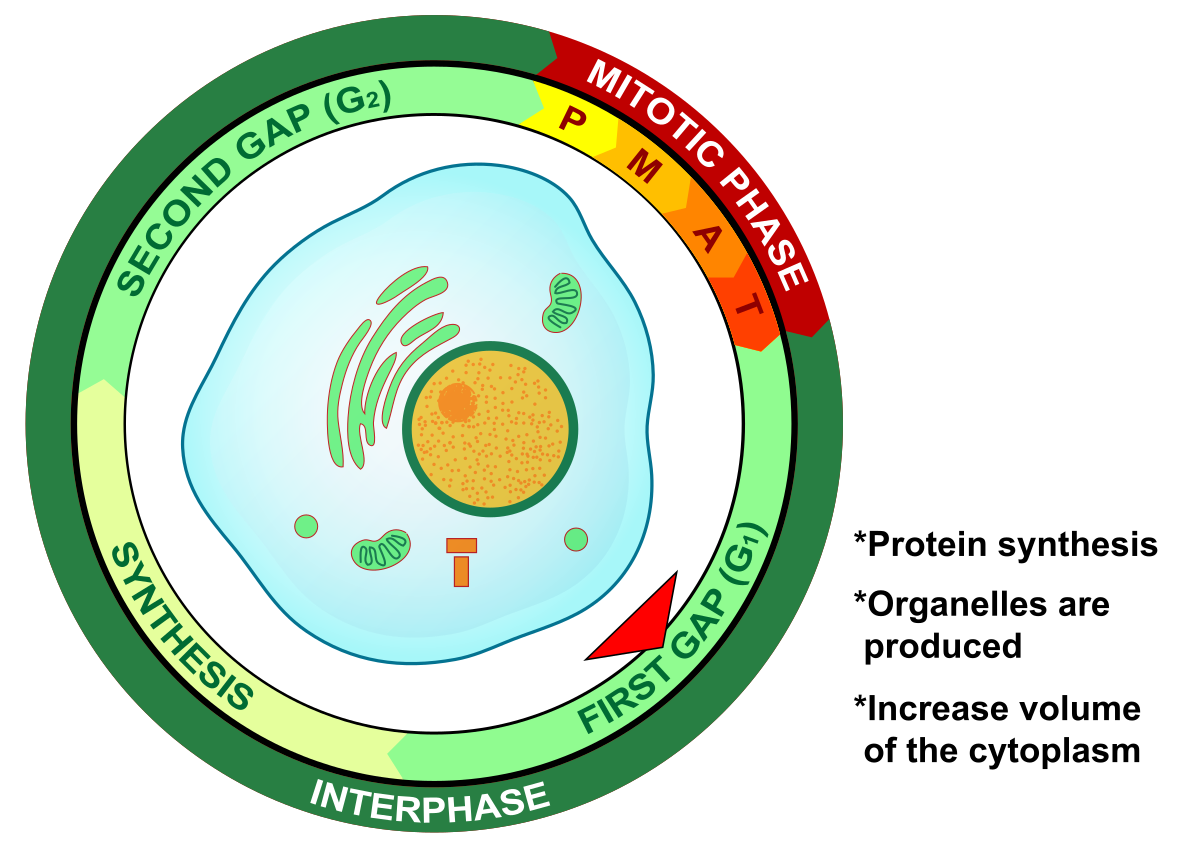
What phase is this?
G1 (Gap 1)
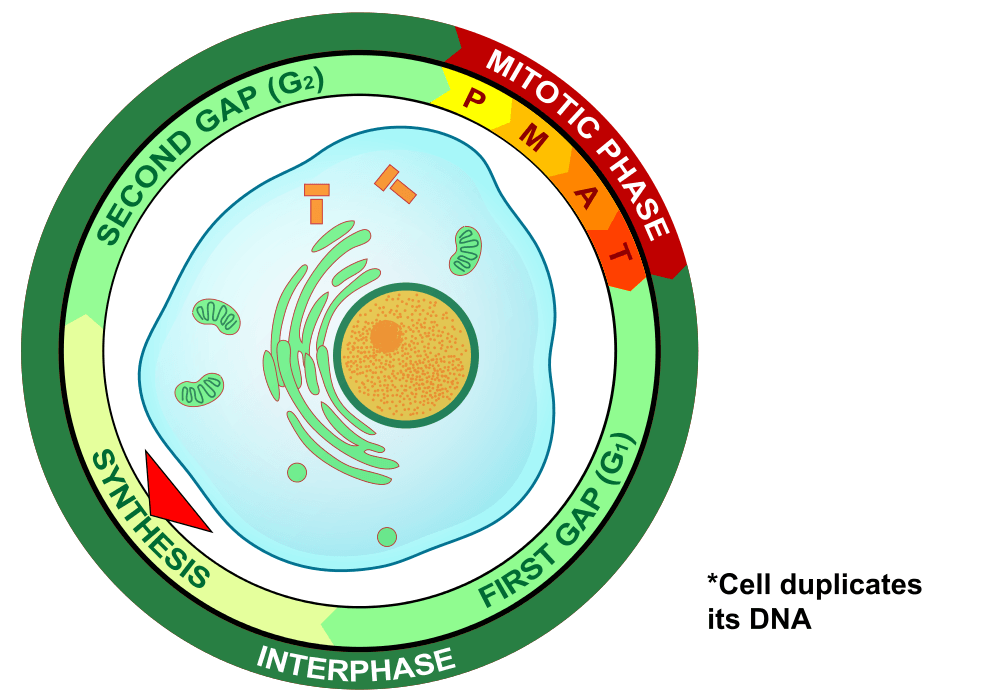
What phase is this?
S Phase
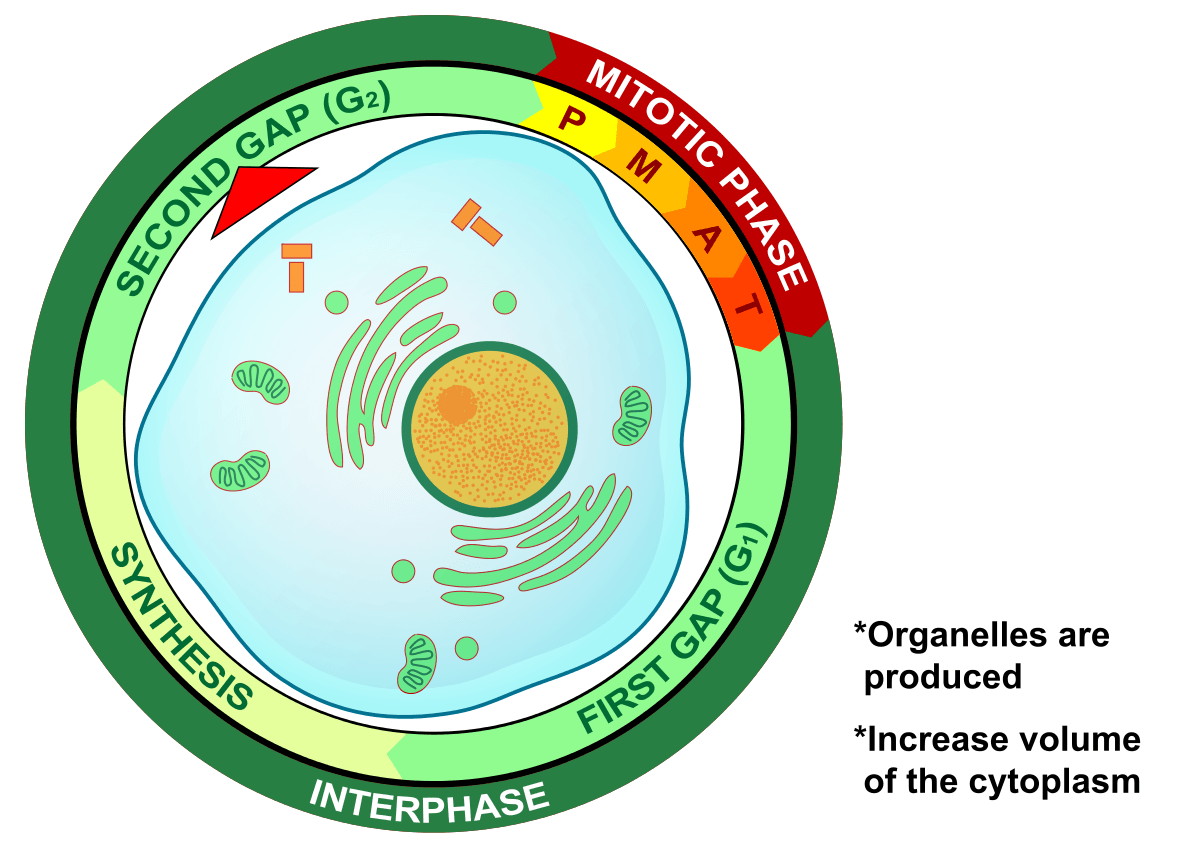
What phase is this?
G2 (Gap 2)
Heredity
Transmission of traits from one generation to the next (inheritance)
Variation
Differences between individuals
Genetics
The study of heredity and hereditary variation
Gametes
Reproductive cells that transmit genes from one generation to the next.
What can reproduction be?
Asexual and Sexual
Asexual Reporduction
Single parent produces offspring, Unicellular-split, Multicellular-budding or fragmentation
Where does Asexual reproduce?
Eukaryotes
Is Asexual a mitotic divison?
Yes
Asexual: How many offspring can 1 diploid (2n) parent produced?
2 diploid offspring
Asexual: How many offspring can 1 haploid (n) parent produced?
2 haploid offspring
Clones
offspring genetically identical to parent
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
Fast, Low E required, Safe, Lots of offspring, Well adapted?, Don’t change
Sexual Reproduction
Fusin of 2 gametes to form a zygote
What does gamete (n) + gamete (n) equal to?
Fertilization—> zygote (2n)
Sexual: Are offspring genetically identical to their parents?
No
Are gametes usually from different parents?
Yes (but not always)
Costs of Sexual Reproduction
Slow, High E requirement, Dangerous-predation, decease often fewer offspring, Well adapted? Offspring only get half of your genes-genome dilution
Advantages of Sexual Reproduction
Genetic variation, Offspring represent novel combinations of parents’ genes, More likely able to survive environmental change of stress
What’s the problem about sexual reproduction?
If gametes have the same number of chromosome as parents --> chromosome number doubles when they fuse
What is the solution to this problem about chromosomes number double?
Meiosis
Meiosis
Reduction division, Cell divides twice
How many cells are produced when 1 diploid (2n) cell is split in meiosis?
2 haploid (n) cells
What are the 4 stages involve in Meiosis (including 2 cell divisions)?
interphase
Meiosis I
Interkinesis
Meiosis II
Interphase
Like before mitosis, chromosomes duplicate, Each chromosomes now 2 sisters chromatids (still chromatin)
How many chromatids are in humans (2n=46) during the interphase?
92
Meiosis I
First meiotic division-homologous chromosome separate, ploidy reduced, First and second meiotic divisions are indicated in the name of each stage:
Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I
Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II
Prophase I
The same 3 prophase things as mitosis, plus new thing, Synapus, Genes in chromosomes align,
Synapus
Homologous chromosomes pair up
What does Prophase I result in?
Tetrad
Tetrad
2 homologous chromosome (4 chromatids) held together by proteins
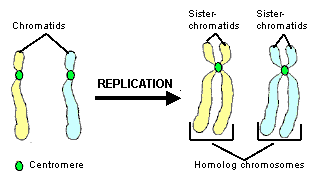
Chromosomes Term
sister chromatids, duplicated chromosome (2 sister chromatids), Homologous pair (as a tetrad)
What’s the point of synapsis?
Crossing over (Homologues Recombination)
Crossing over (Homologues Recombination)
Exchages between non-sister chromatids in tetrad, Results in new combinations of genes, Important source of genetic diversity
At the End of Prophase I in Humans? (2n=46)
46 chromosomes, 23 tetrads, 92 chromatids
Metaphase I
Tetrads align at metaphase plate, Homologous chromosomes orient towards opposite poles
Anaphase I
Disjunction: Homologous chromosomes separate, Sister chromatids still connected, Chromosomes acted independently, Direction depends on orientation of tetrad.
Telophase I and Cytokinesis
Chromosomes may decondense, Nuclear envelope may reform, Cytokinesis occurs, results in 2 haploid cells, with duplicated chromosomes (sister chromatids still together)
At the end of Telophase in Humans ? (2n=46)
23 chromosomes in each cell, 46 chromatids, 0 tetrad
Interkinesis
Time between 1st and 2nd meiotic divisions, Usually short, interphase-like stage, No S phase, no DNA replication occurs
Meiosis II
2nd meiotic division, Chromatids separate into daughter cells, Very similar to mitosis (it’s basically just mitosis)
Stages of Meiosis II (separate sister)
Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II
At End of Telophase II in Humans? (2n=46)
23 Chromosomes in each cell, 0 tetrad, 0 chromatids
Which cell division involves in 2n cells?
Mitosis and Meiosis
Which cell division involves in n cells?
Mitosis
Number of Divisions in Mitosis
1
Number of Divisions in Meiosis
2
Delta chromosomes number in Mitosis
none
Delta chromosomes number in Meiosis
reduced by 1/2
What separates in anaphase in Mitosis?
sister chromatids
What separates in anaphase in Meiosis?
Homologous, then sister chromatids
Are there identical daughter cells in Mitosis?
Yes
Are there identical daughter cells in Meiosis?
No
Homologous Pairing in Mitosis?
No