Bio 305: Urinary System
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Functions of the kidney
1. Regulation of water, inorganic ion balance, acid base balance
2. Removal of metabolic waste
3. Removal of foreign chemicals
4. Gluconeogenesis
5. Production of hormones
Kidneys use a lot of _____
energy
Hormones made in the Kidneys
1. Erythropoietin
2. Renin
3. Conversion of inactive Vitamin D to active Vitamin D (acts on small intestine to increase calcium absorption)
Erythropoietin (EPO)
hormone secreted by the kidney to stimulate the production of red blood cells by bone marrow (secreted when oxygen levels in the blood are low)
blood doping
inject extra red blood cells before competition to improve performance
3 Most common nitrogenous waste
1. Urea - amino acid metabolism waste
2.Creatinine - Breakdown of creatine phosphate
3. Uric Acid- Metabolic processing of nucleotides
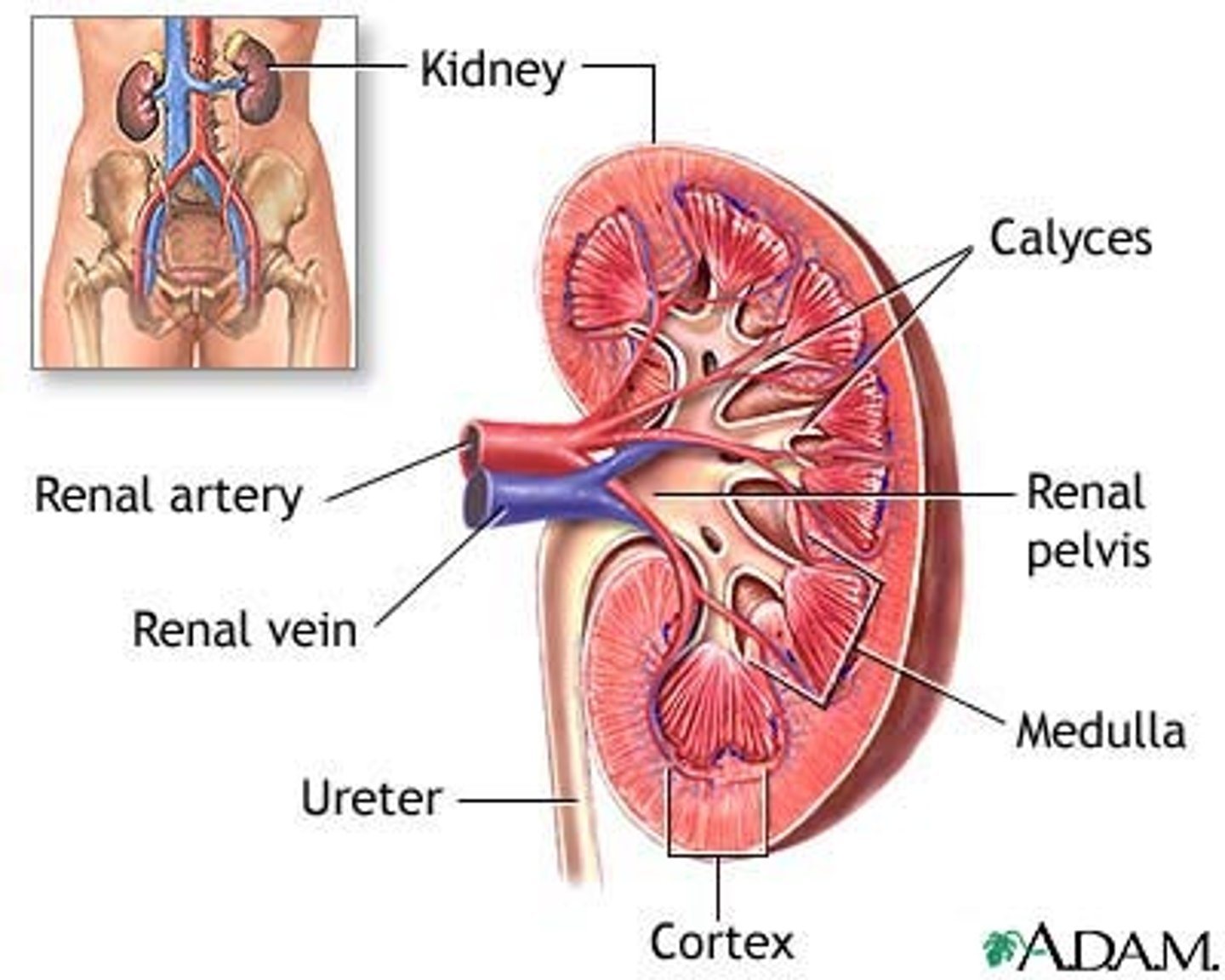
Anatomy of the Kidneys
-2 bean shapes that are red-ish brown
- covered by renal capsule
- Renal artery enters; renal veins and ureter exit
Kidneys have over _______ _______ nephrons
1 million
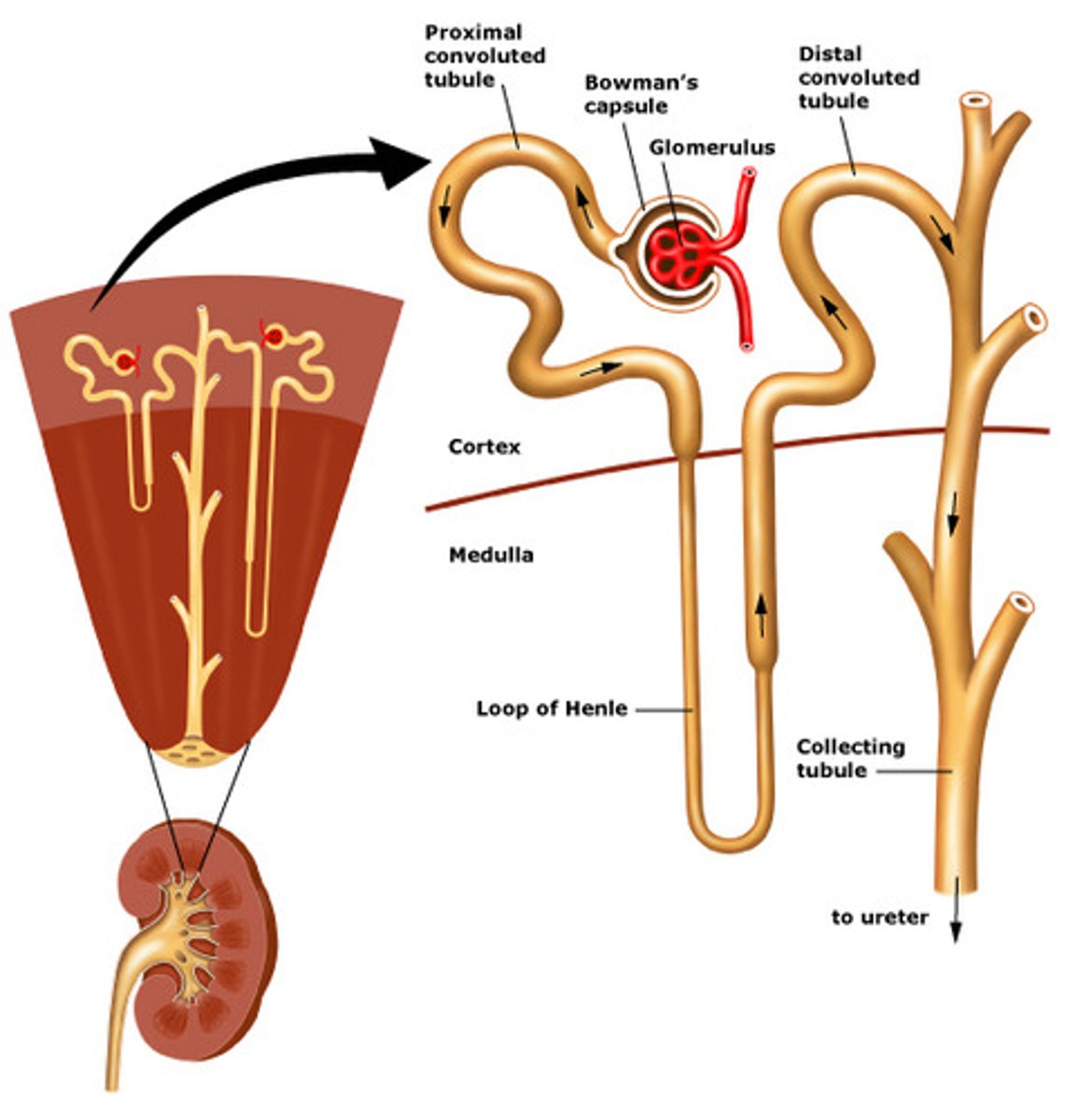
Nephrons
functional unit, filter blood and produce urine
Nephron's empty urine into one __________ ________
collecting duct
Collecting Ducts empty into _________ _________
renal Pelvis (can't be changed at this point)
structure of nephron that filters blood
interstitial fluid in the kidneys are
salty
cortical nephrons
85% of nephrons; almost entirely in cortex
Boman's capsule
surrounds the glomerulus
juxtamedullary nephrons
-Long nephron loops deeply invade medulla
-Ascending limbs have thick and thin segments
-Important in production of concentrated urine
Where does Urine first begin being filtered
Bowman's Capsule
Loop of Henle
the part of a kidney tubule that forms a long loop in the medulla of the kidney, from which water and salts are resorbed into the blood.
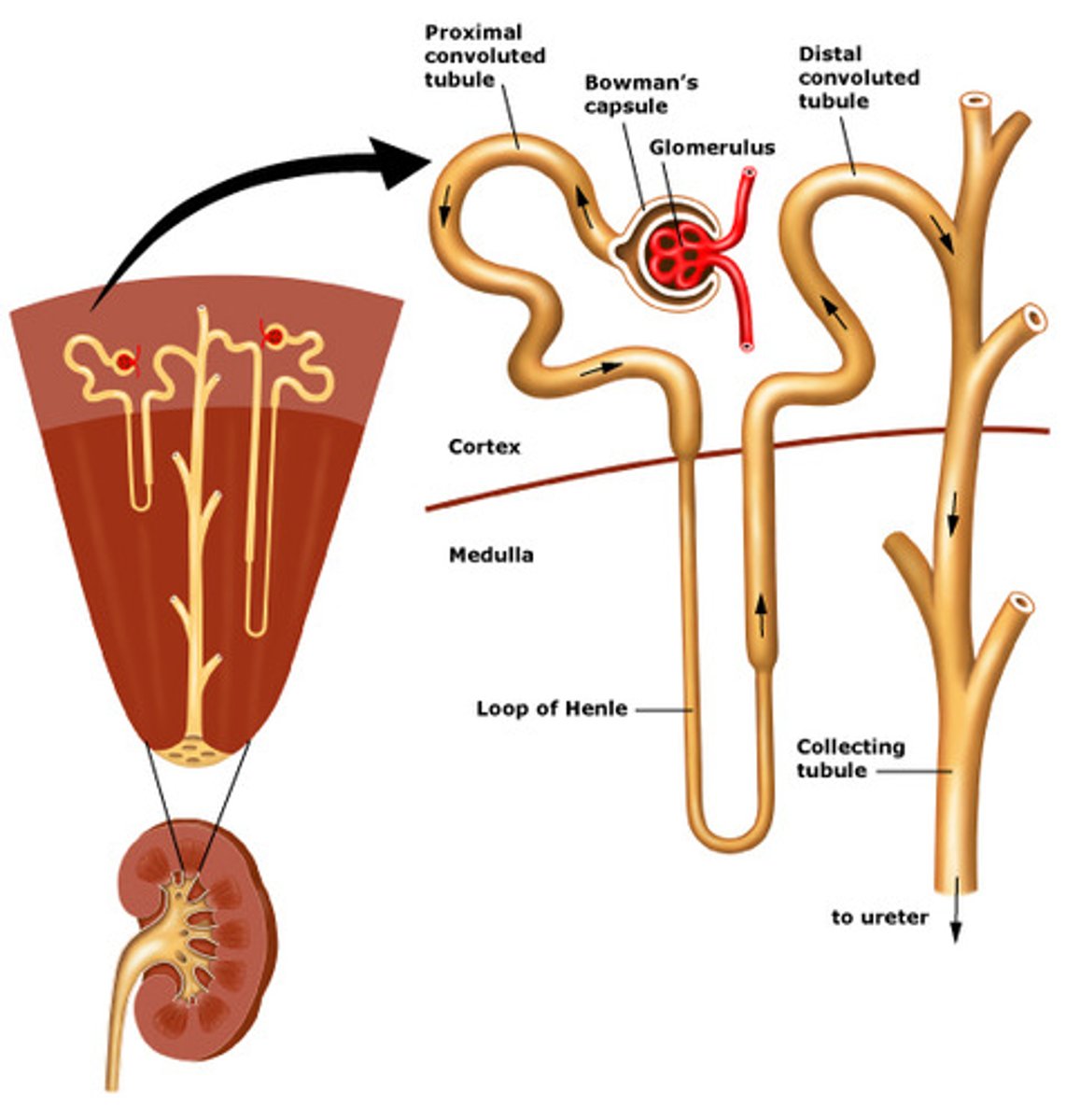
Which loop of Henle is longer ?
Juxtamedullary (it makes the saltiness)
Collecting Ducts are shared by ______ to _____ nephrons
6-8
Collecting ducts drain into the _____ ______ and can not be modified
Renal Pelvis
Apparent atrial
carries blood into the glomerulus
Efferent arterial
Carries blood away from the glomerulus
Glomerulus have smooth muscle and can change their diameter due to _______ and ______ ______ in cordial nephrons
Appharent and Efferent arterials
Path of blood in the cordical nephrons
1. Afferent arteriole enters corpuscle
2. Glomerular capillaries
3. Efferent arteriole leave corpuscle
4. Peritubular Capillaries
5. Drain into venules
3 Basic Renal Processes
1. Glomerular filtration
2. Tubular secretion
3. Tubular reabsorption
glomercular filtration
hydrostatic pressure causes fluid to pass through pores of glomerular capillaries and split pores between podocytes to enter the capsule (about 20% of blood is filtered)
Distal convoluted arterial pass .....
between afferent and efferent arterioles.
renal copuscle
glomerulus and bowman's capsule
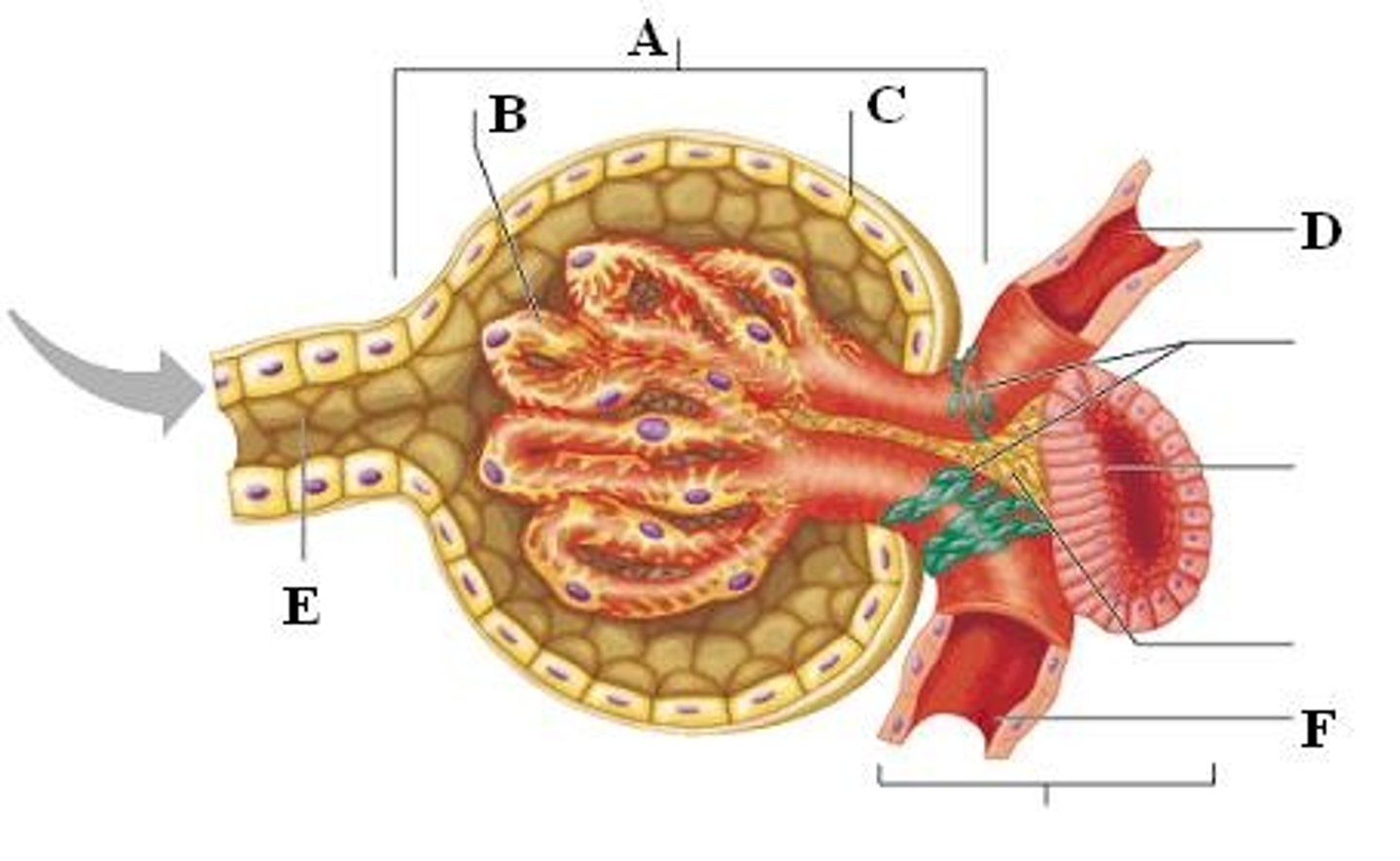
Podocytes:
cells in the Bowman's capsule in the kidneys that wrap around capillaries of the glomerulus and make the inner wall
filtration slits
Gaps between podocyte processes surrounding the glomerulus
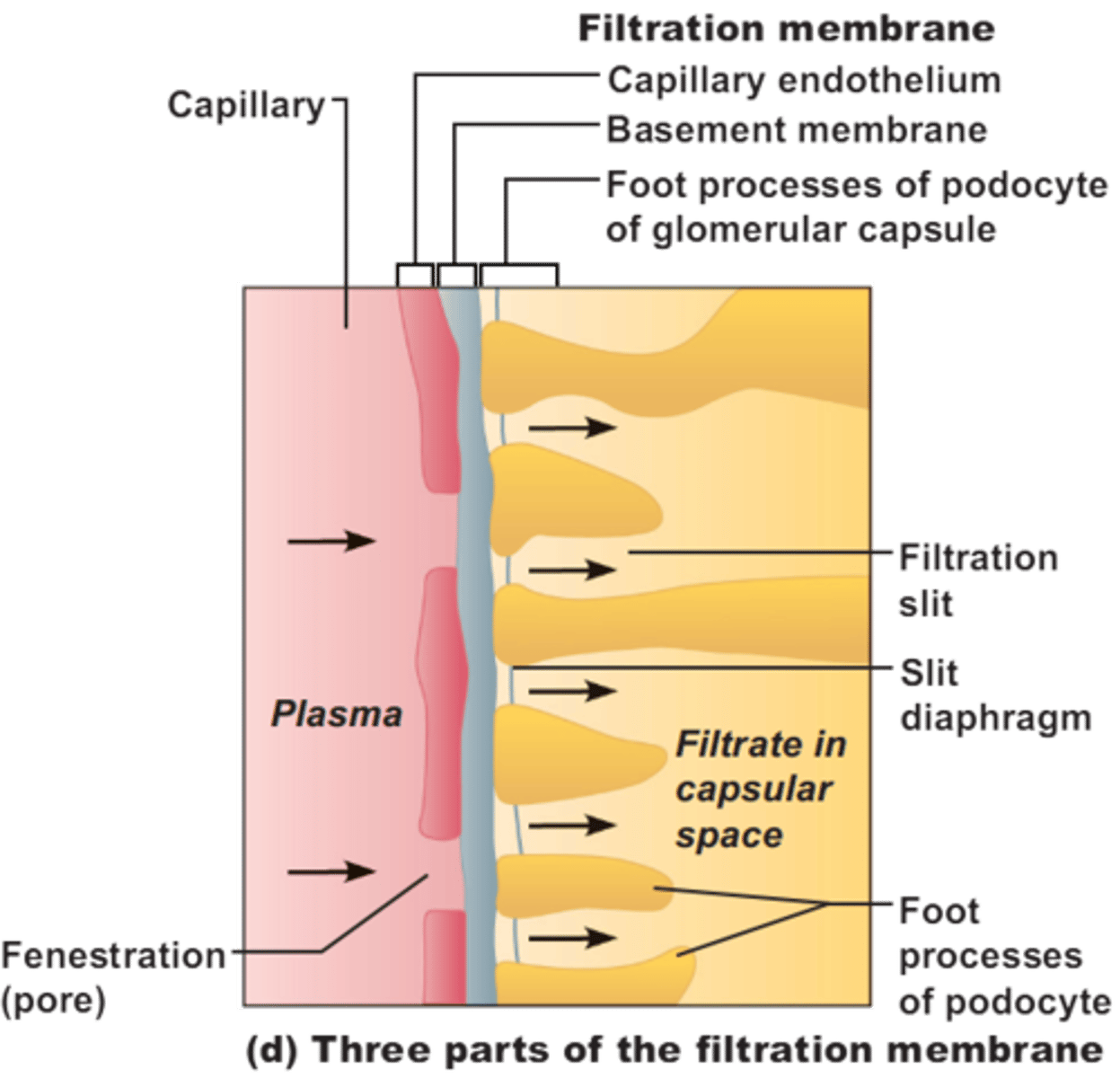
fenestrated capillaries
have pores in vessel wall; found in kidneys, intestines, and endocrine glands
Things small enough to pass through the filter slits
-water
-electrolytes
-glucose
-amino acids
-fatty acids
-vitamins
-urea
-Uric acid
-creatine
tubular secretion
secretion of solutes from blood in peritubular caps into filtrate tubules
Tubular reabsorption
movement material from filtrate in tubules into blood of peritubular caps
Amount Excreted =
amount filtered + amount secreted - amount reabsorbed
filtration =
secretion =
reabsorption +
nonspecific
specific
specific
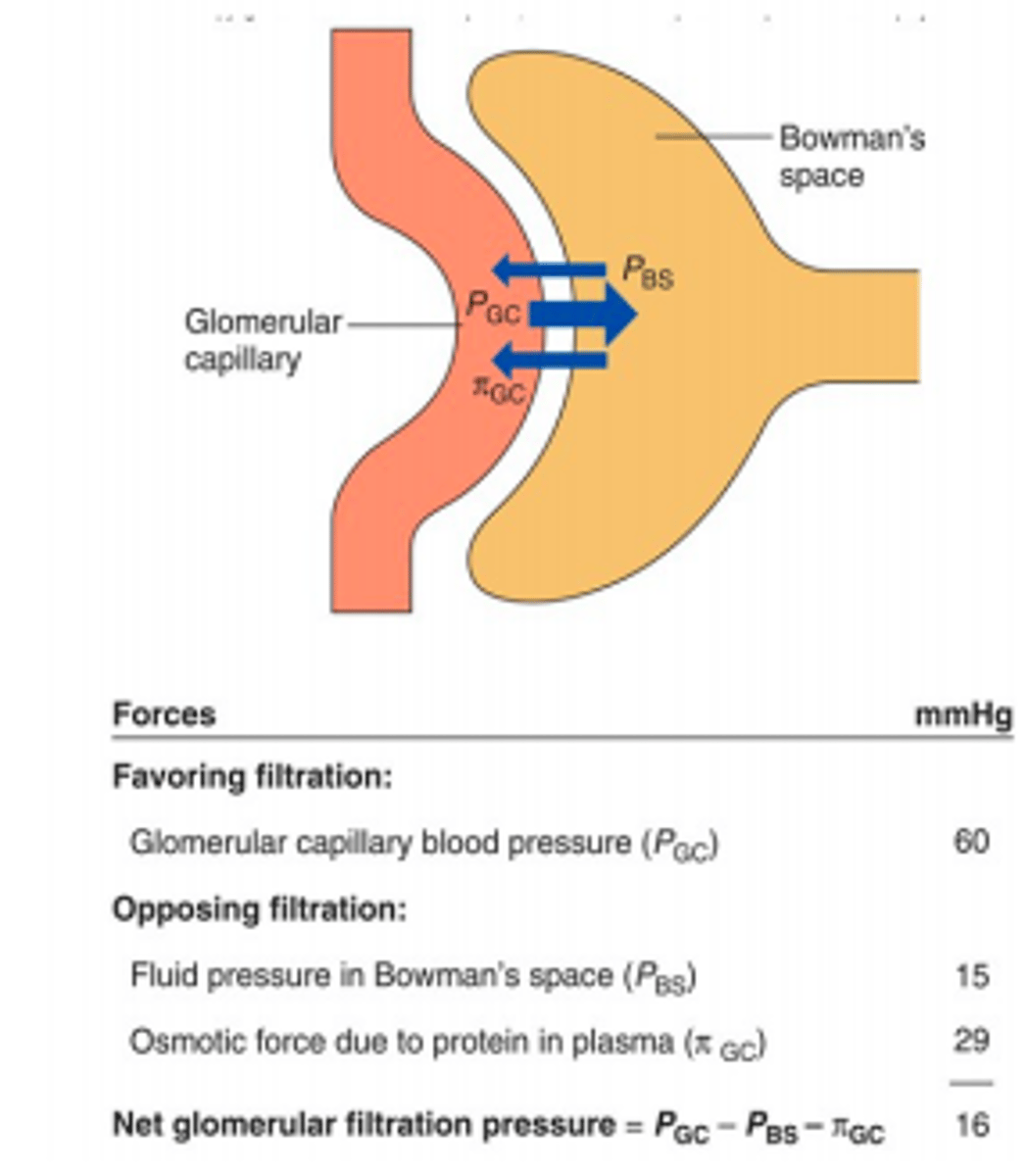
Hydrostatic (blood) pressure
favors filtration
Osmotic pressure of glomerulus and hydrostatic pressure of filtrate ______ __
oppose it
GFR=
volume fluid filtered/time (180 liters/day)
Favors filtration:
glomerular capillary blood pressure
opposes filtration
-Fluid pressure in Bowmans capsule
-Osmotic force due to protein in plasma
net glomerular filtration pressure
Pgc - Pbs - πgc
What alters blood flow through glomerular capillaries and leads to changes in GFR
Afferent and Efferent Vasodilation and vasoconstriction
Mesangial cells
contractile cells that help regulate glomerular filtration
Filtered load of substance =
GFR x [substance in plasma]
Reabsoprtion occurs by _____ or ___ ______
diffusion ; mediated transport
if a substance is lipid soluble it can be reabsorbed passively by
simple diffusion of facilitated diffusion
Micturition
Release of urine from bladder, coordinated by combination of smooth and skeletal muscle relaxation / contraction
Sodium and water balance are maintained by
varying urine output
Things that trigger aldosterone
- renal sympathetic nerves (increase) to the JGA cells (increase in Renin)
- JGA cells
- Macula densa in DCT
JGA cells
intrarenal baroreceptors that produce renin
(decrease in blood pressure = decrease in stretch = increase in renin)
macula densa of DCT
Glomerular filtrate rate regulation
(decrease in sodium= paracrine factory - JGA secrete renin)
Renin
hormone (enzyme) secreted by the kidney that raises blood pressure by cutting angiotensin to angiotensin 1
ACE
Cuts angiotensin 1 to 2
Aldosterone increases synthesis of Na+ channels and pumps in the ______ ______ _____
cortical collecting ducts
ADH is produced when there is a drop in ________
blood pressure/volume
ADH
Hormone regulating water reabsorption in kidneys. produced by pituitary gland
What causes the secretion of ADH
-osmoreceptors (decrease in water= increase in plasma osmolarity)
-
Thirst center is in the _________
hypothalamus
ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide)
Secreted in response to excess blood volume in the heart ,(stretch) promotes salt and thus water excretion.
ADH is always low unless you have
low blood pressure