Spring Reading Quiz #10
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
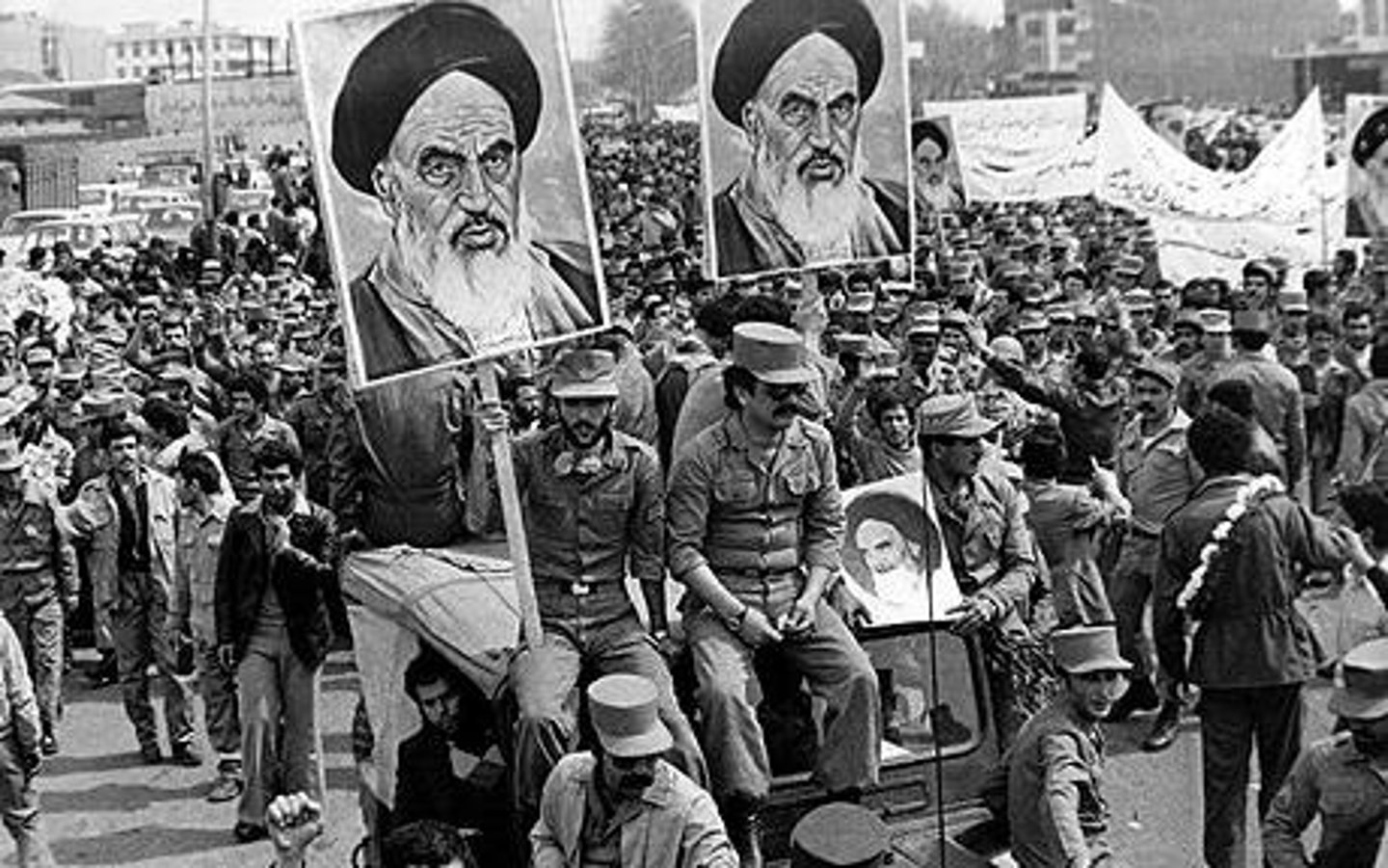
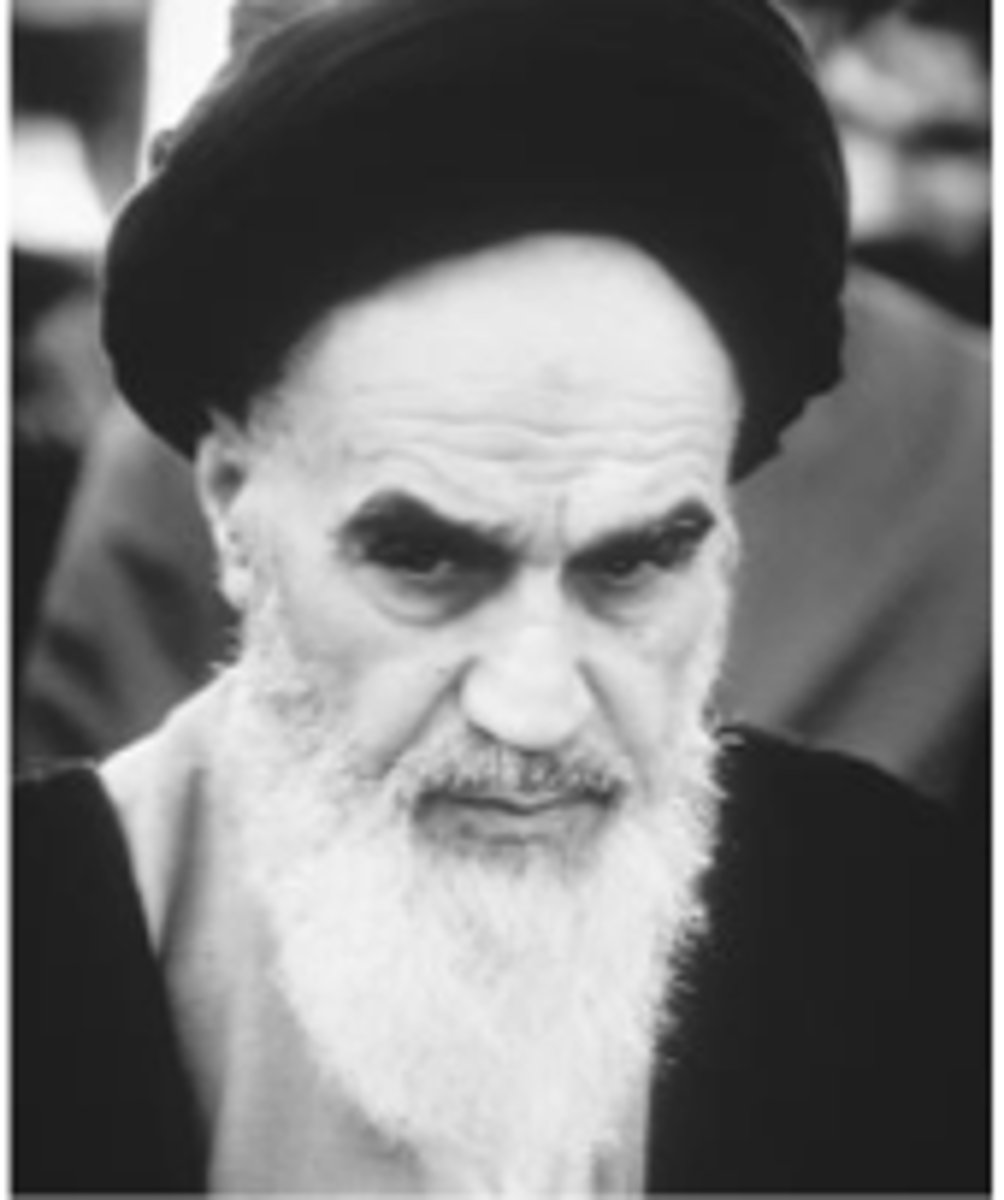
Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini
Shi'ite philosopher and cleric who led the overthrow of the shah of Iran in 1979 and created an Islamic republic.

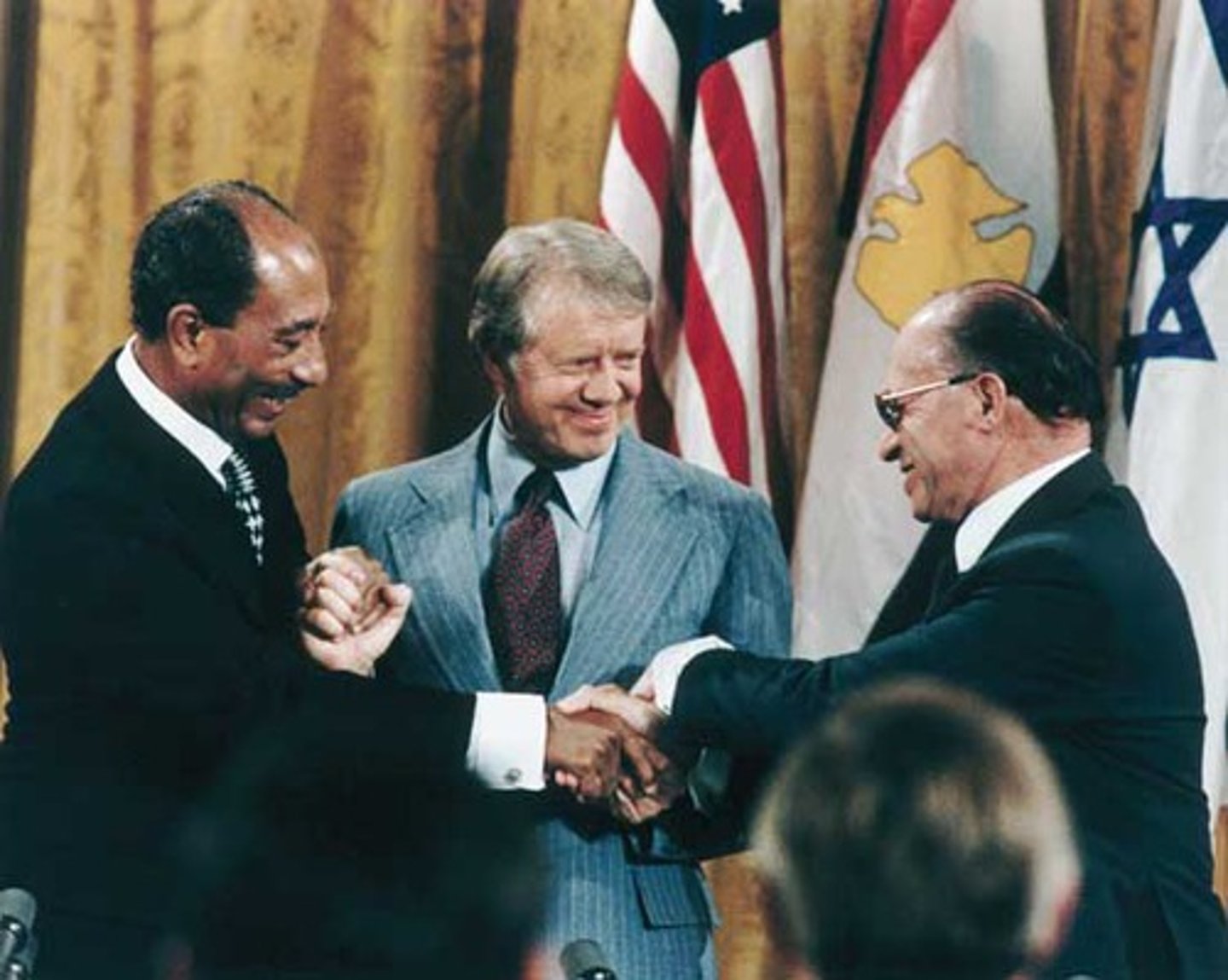
Camp David Accords
A peace treaty between Israel and Egypt where Egypt agreed to recognize the nation state of Israel

Community Action Program
Invited local communities to establish community action agencies (CAA's) to be funded through the office of economic opportunity; allowed poor to run antipoverty programs in their own neighborhoods.

counterculture
A culture with lifestyles and values opposed to those of the established culture.

George McGovern
A Senator from South Dakota who ran for President in 1972 on the Democrat ticket. His promise was to pull the remaining American troops out of Vietnam in ninety days which earned him the support of the Anti-war party, and the working-class supported him, also. He lost however to Nixon.
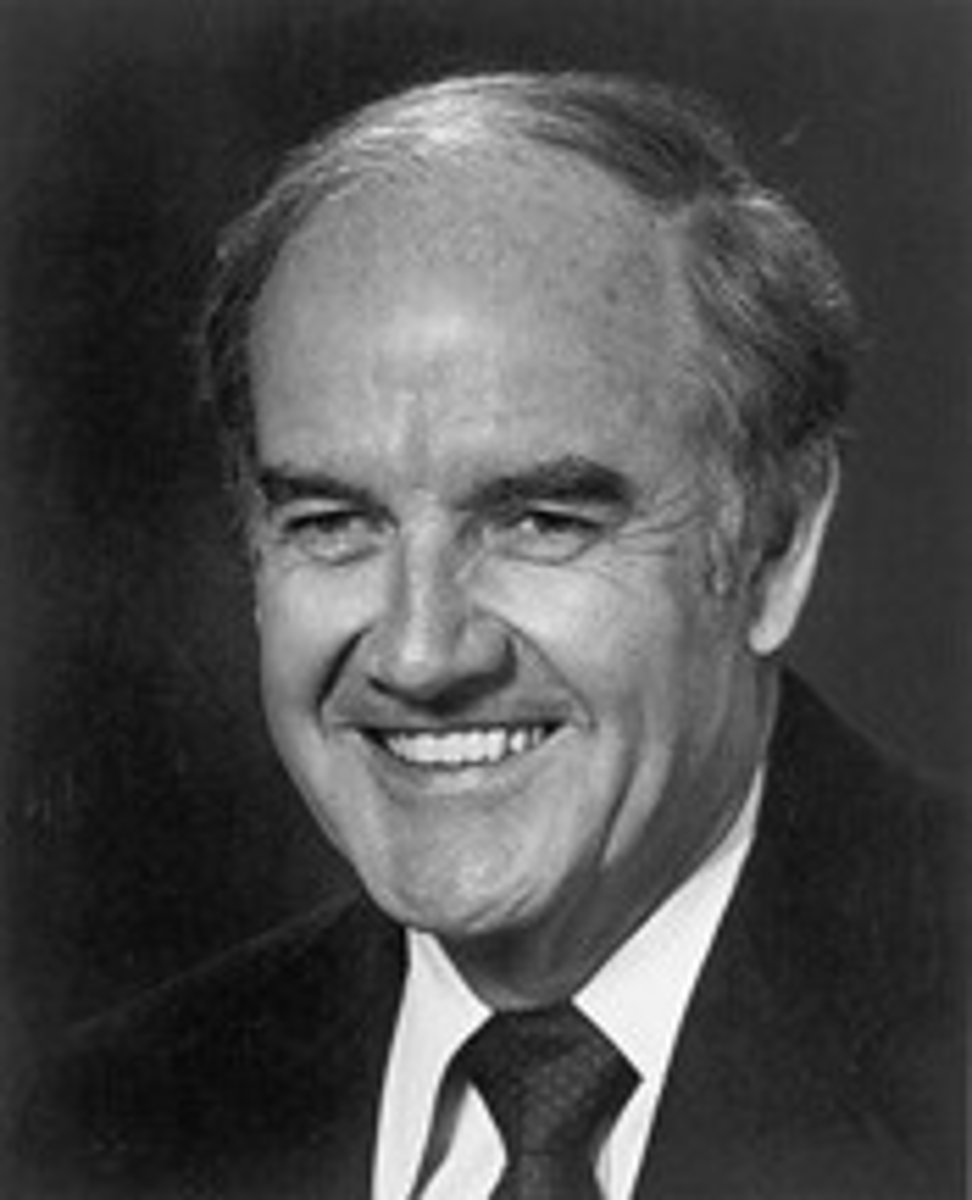

Gerald Ford
1974-1977, Republican, first non elected president and VP, he pardoned Nixon
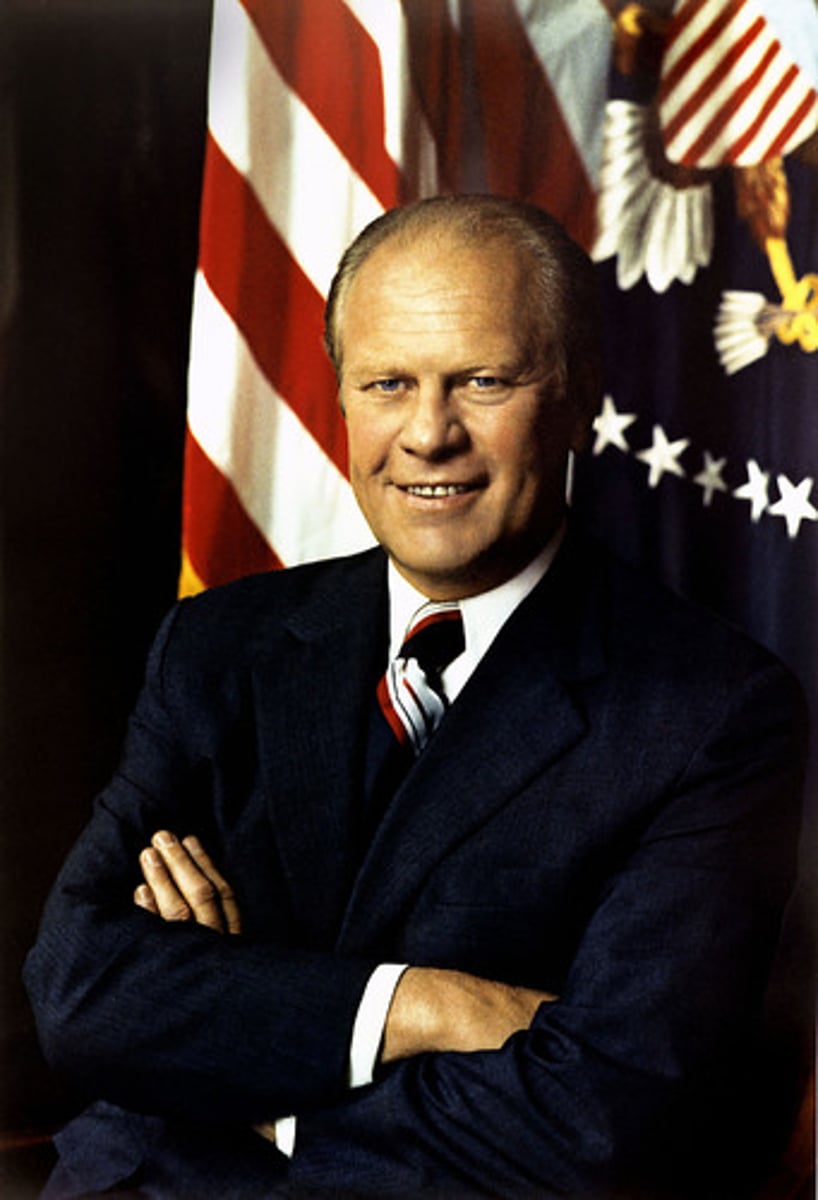

Great society
President Johnson called his version of the Democratic reform program the Great Society. In 1965, Congress passed many Great Society measures, including Medicare, civil rights legislation, and federal aid to education.

Immigration Act of 1965
Abolished the national-origins quotas and providing for the admission each year of 170,000 immigrants from the Eastern Hemisphere and 120,000 from the Western Hemisphere

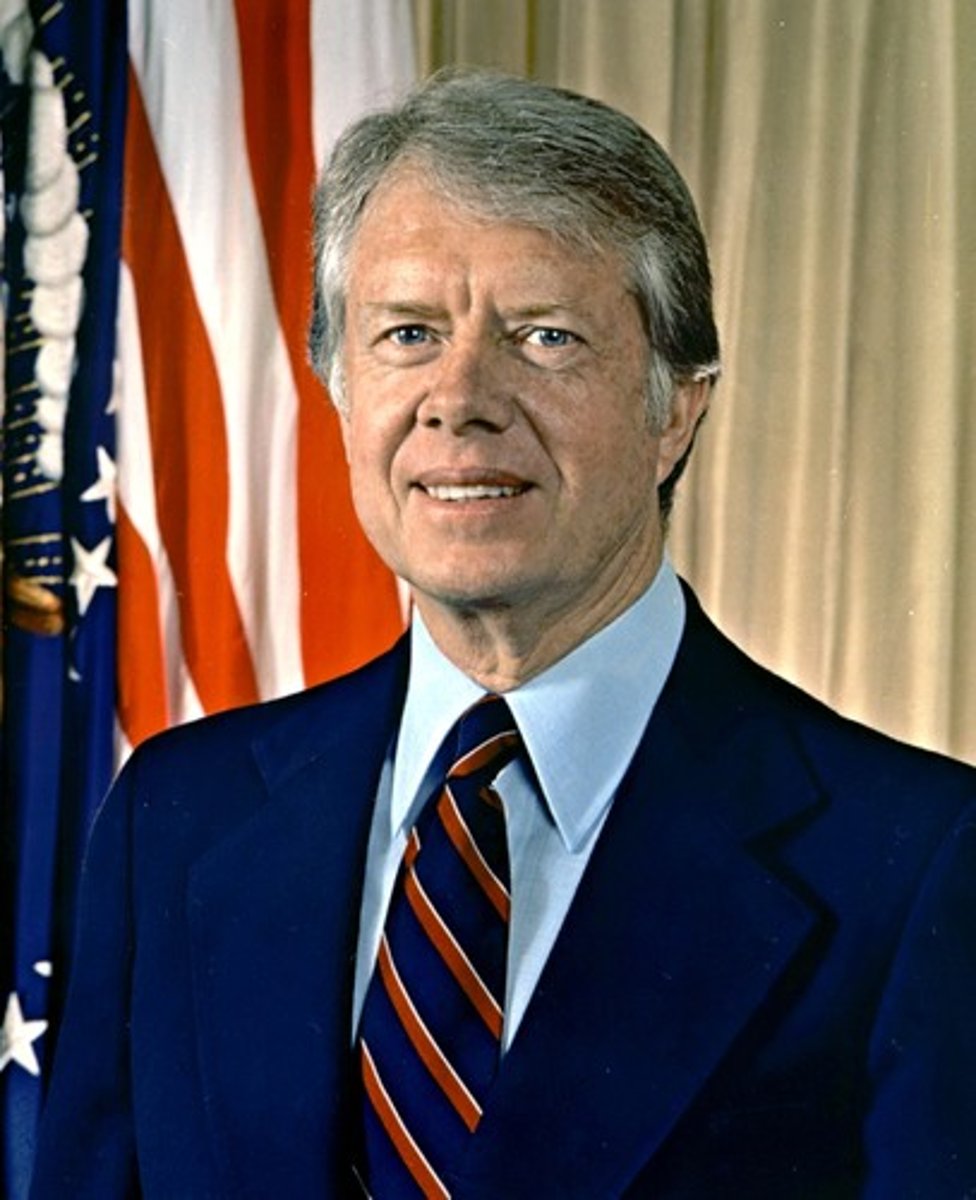
Jimmy Carter
39th U.S. President. 1977-1981. Democratic

Medicaid
A federal and state assistance program that pays for health care services for people who cannot afford them.
Medicare
A federal program of health insurance for persons 65 years of age and older

New Left
Coalition of younger members of the Democratic party and radical student groups. Believed in participatory democracy, free speech, civil rights and racial brotherhood, and opposed the war in Vietnam.

OPEC
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries

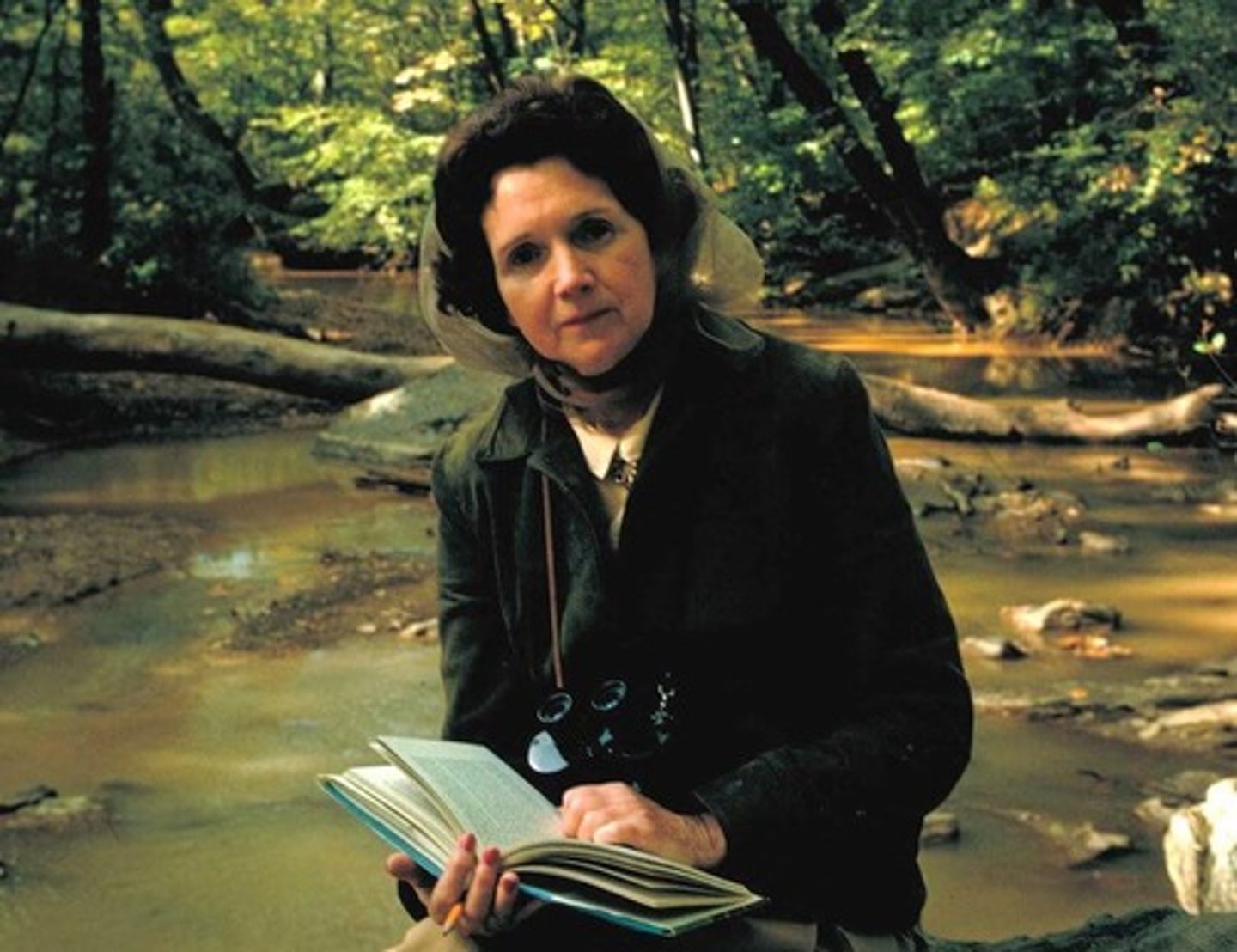
Rachel Carson
United States biologist remembered for her opposition to the use of pesticides that were hazardous to wildlife (1907-1964)

"silent majority"
A phrase used to describe people, whatever their economic status, who uphold traditional values, especially against the counterculture of the 1960s

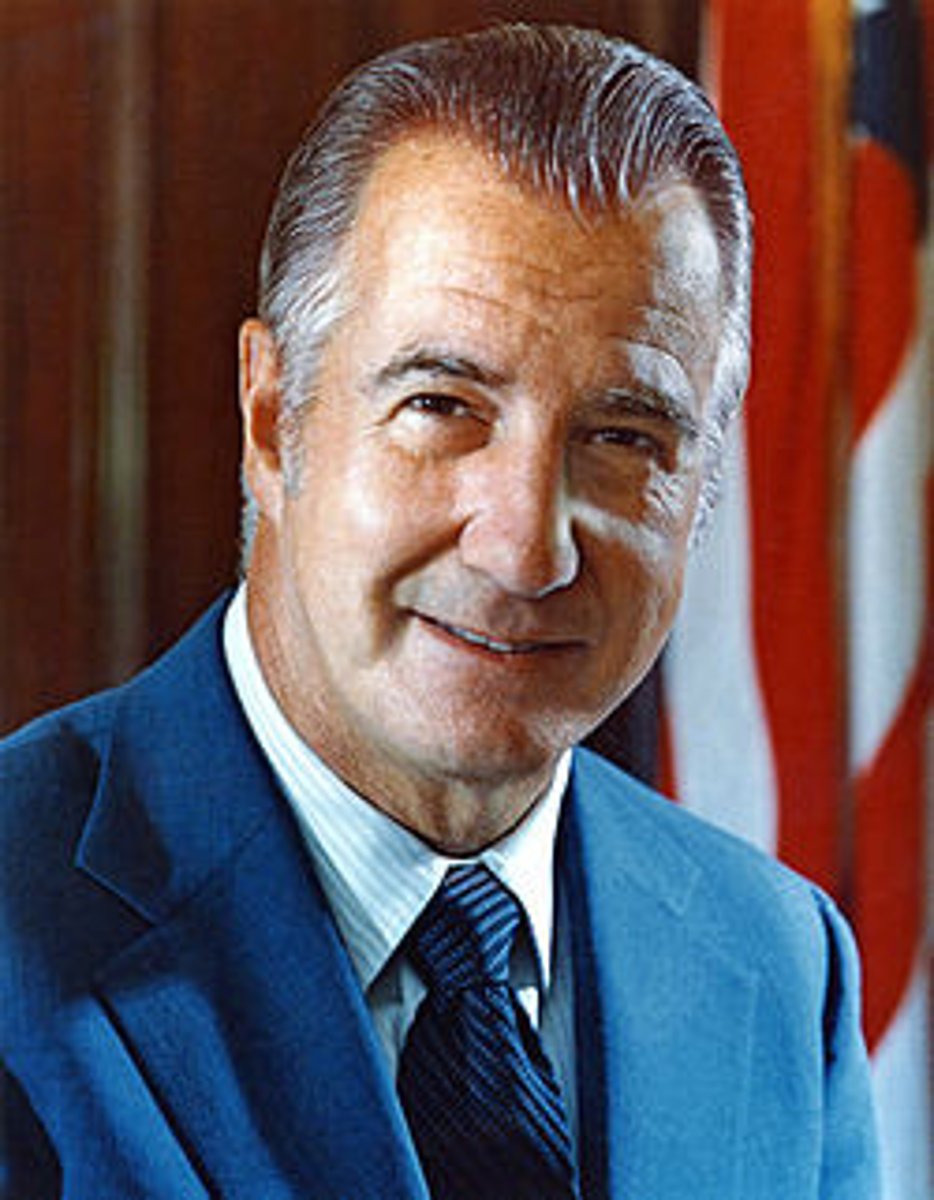
Spiro Agnew
Nixon's vice-president resigned and pleaded "no contest" to charges of tax evasion on payments made to him when he was governor of Maryland. He was replaced by Gerald R. Ford.

"stagflation"
a period of slow economic growth and high unemployment (stagnation) while prices rise (inflation)

SDS (Students for a Democratic Society)
organization founded in 1960 at the University of Michigan to fight racism and poverty

Watergate
The events and scandal surrounding a break-in at the Democratic National Committee headquarters in 1972 and the subsequent cover-up of White House involvement, leading to the eventual resignation of President Nixon under the threat of impeachment.

Weathermen
a radical protest group apart of the student democratic gov program

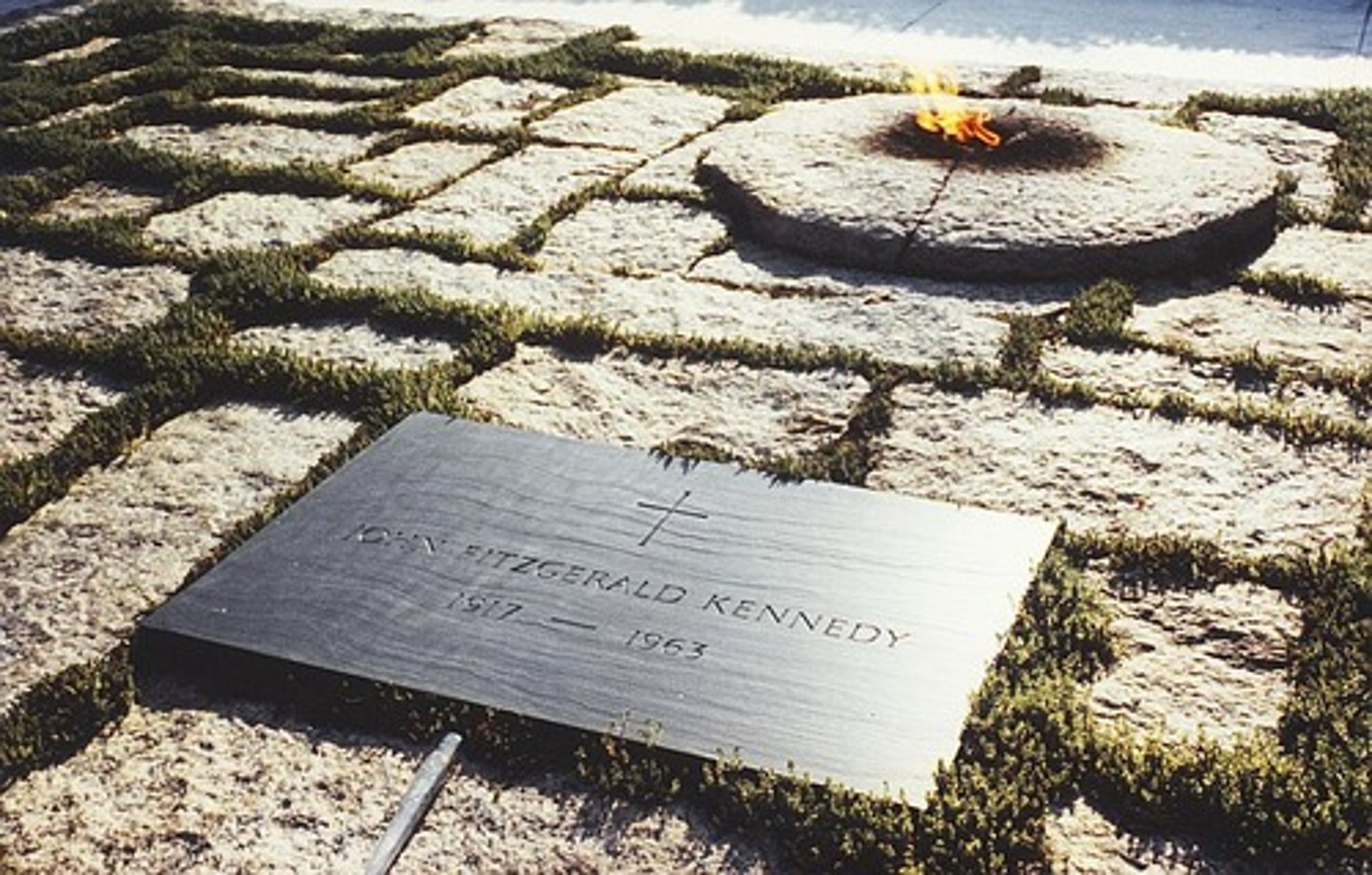
The eternal flame
National Monument present at JFK's grave site

Department of Housing and Urban Development
the United States federal department that administers federal programs dealing with better housing and urban renewal

Secondary Education Act
The act provides federal funding to primary and secondary education, with funds authorized for professional development, instructional materials, resources to support educational programs, and parental involvement promotion.

The Johnson treatment
LBJ's tactic of "negotiation" with members of congress. He used his size and abrupt manner to manipulate them

Youth culture 1960s
Emergence of counterculture and youth activism.

Free Speech Movement
(Berzerkley 1964) Mario Salvo. Students protested against limits on passing out of literature ---> questioned university & society that created it and this signaled the beginning of numerous campus protests: People's Park protest (Berzerkly 1969) was the longest campus protest
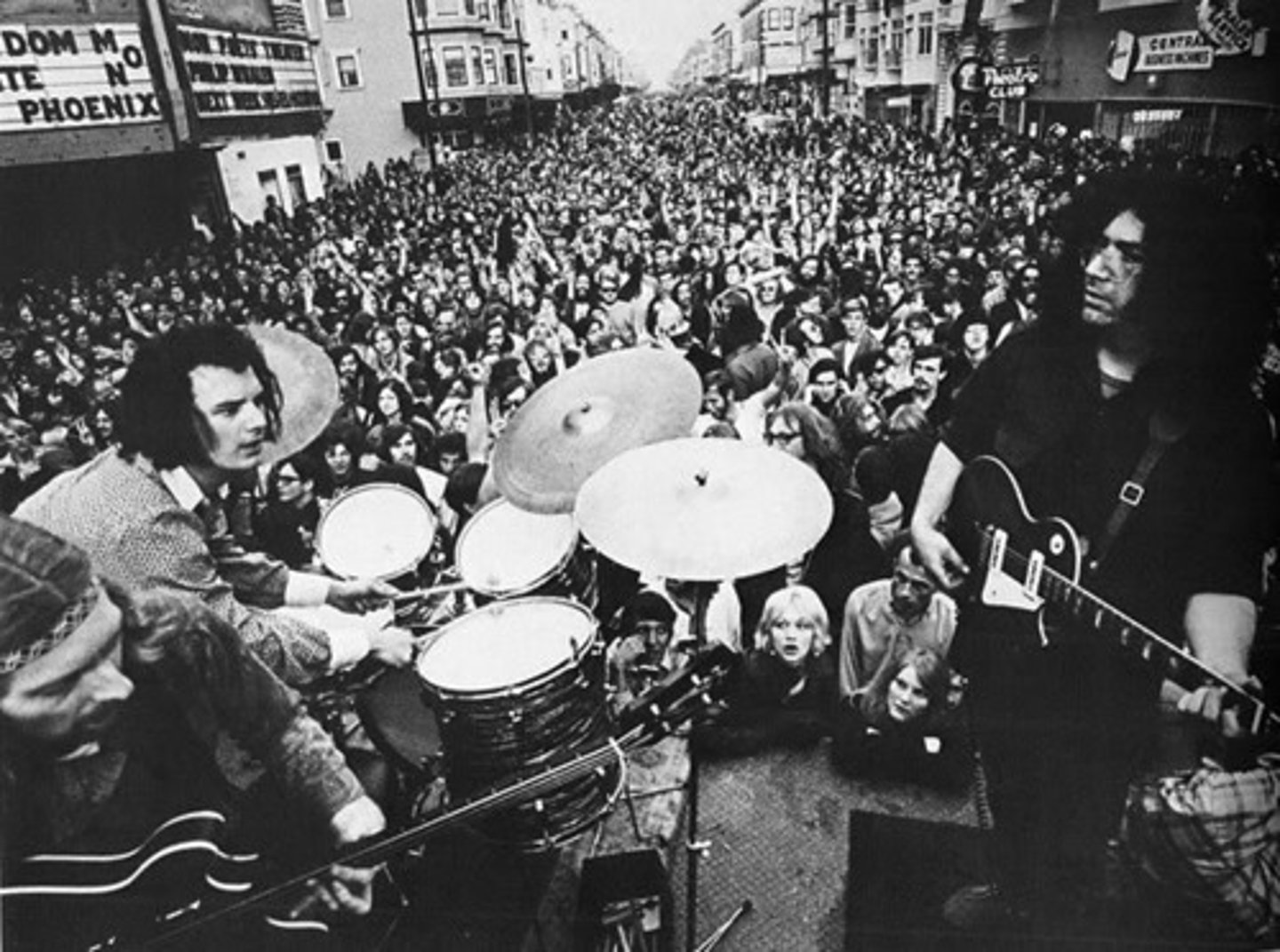
Rock Music in the 60s
Artists like Janis Joplin, Jimi Hendrix, Jim Morrison and the Doors, Jefferson Airplane dominated the music scene in the US

Woodstock
3 day rock concert in upstate N.Y. August 1969, exemplified the counterculture of the late 1960s, nearly 1/2M gather in a 600 acre field
Altamont
Site of a free concert staged by The Rolling Stones in December 1969 that was marked by violence from the Hell's Angels.

The Beatles
a British band that had an enormous influence on popular music in the 1960s

People's Park
A public park in Berkley. The site of many FSM speeches and events. Governor REGAN sent police to People's Park. Police clear the park. Protests demanding the park back lead to violence. JAMES RECTOR killed.

Hippies
Believed in anti-materalism, free use of drugs, they had a casual attitude toward sex and anti-conformity, (1960s) practiced free love and took drugs, flocked to San Francisco- low rent/interracial, they lived in communal "crash pads", smoked marijuana and took LSD, sexual revolution, new counter culture, Protestors who influenced US involvement in Vietnam
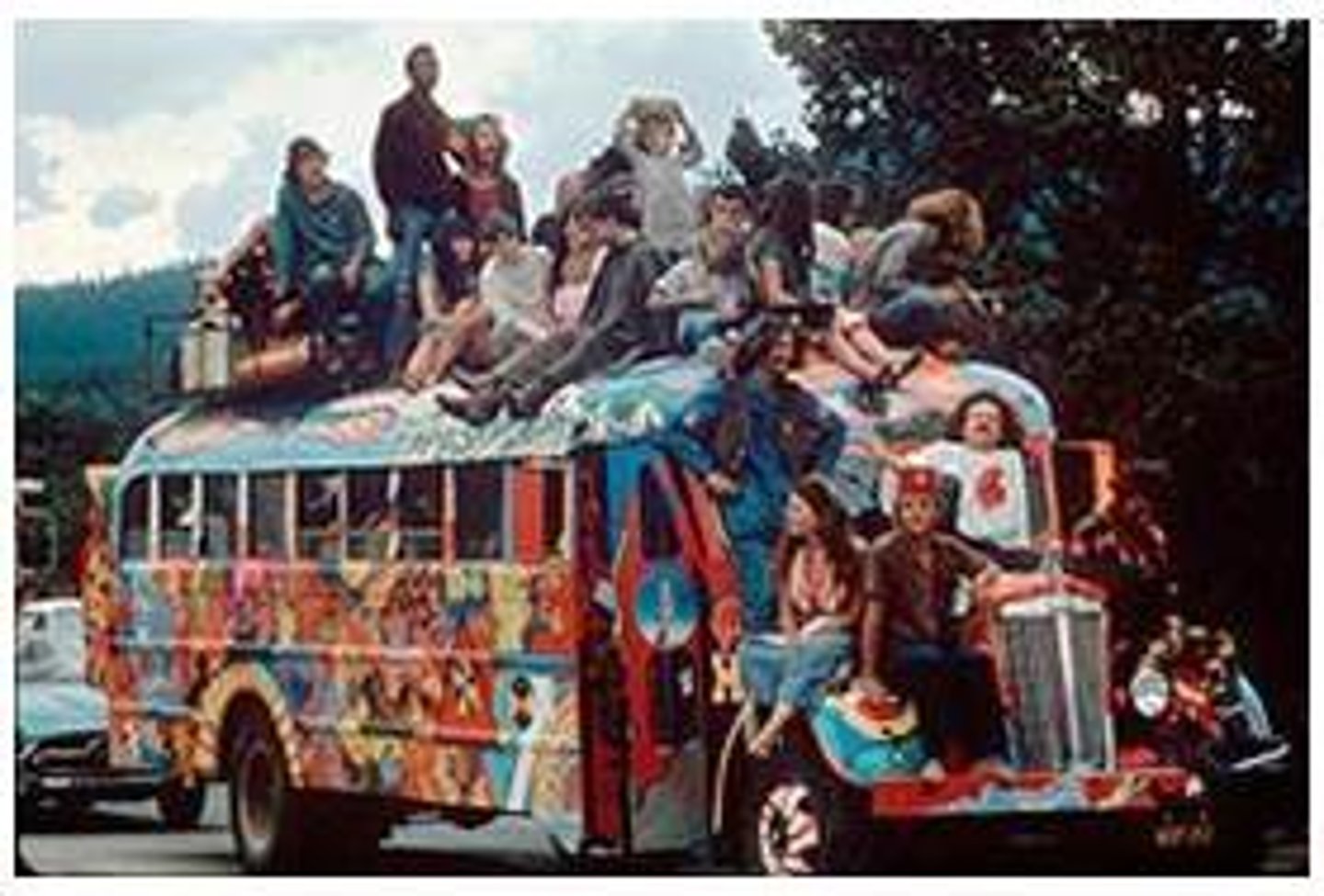

Haight-Asbury
The hippie capital of California; these two streets represented the center of the counter culture movement.

Ecology
Scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment

Silent Spring
A book written by Rachel Carson to voice the concerns of environmentalists. Launched the environmentalist movement by pointing out the effects of civilization development.

Wilderness society
Along with the Sierra Club, these were some of the most important environmental organizations. They predated the rise of modern ecological science, but all of them entered the last decades re-energized and committed to the new concepts of environmentalism.

Water and Air Pollution
Most water pollution is the result of human activities; wastes produced by households,

The first "Earth Day"
April 22, 1970

EPA
Environmental Protection Agency
An independent federal agency established to coordinate programs aimed at reducing pollution and protecting the environment

FAP (Family Assistance Plan)
families of 4 without an outside income received $1,600 a year and $4,000 in supplement income (Nixon)

Baker v. Carr
One man, one vote

Bakke v. Board of Regents of California
Supreme Court decision that upheld the legality of affirmative action
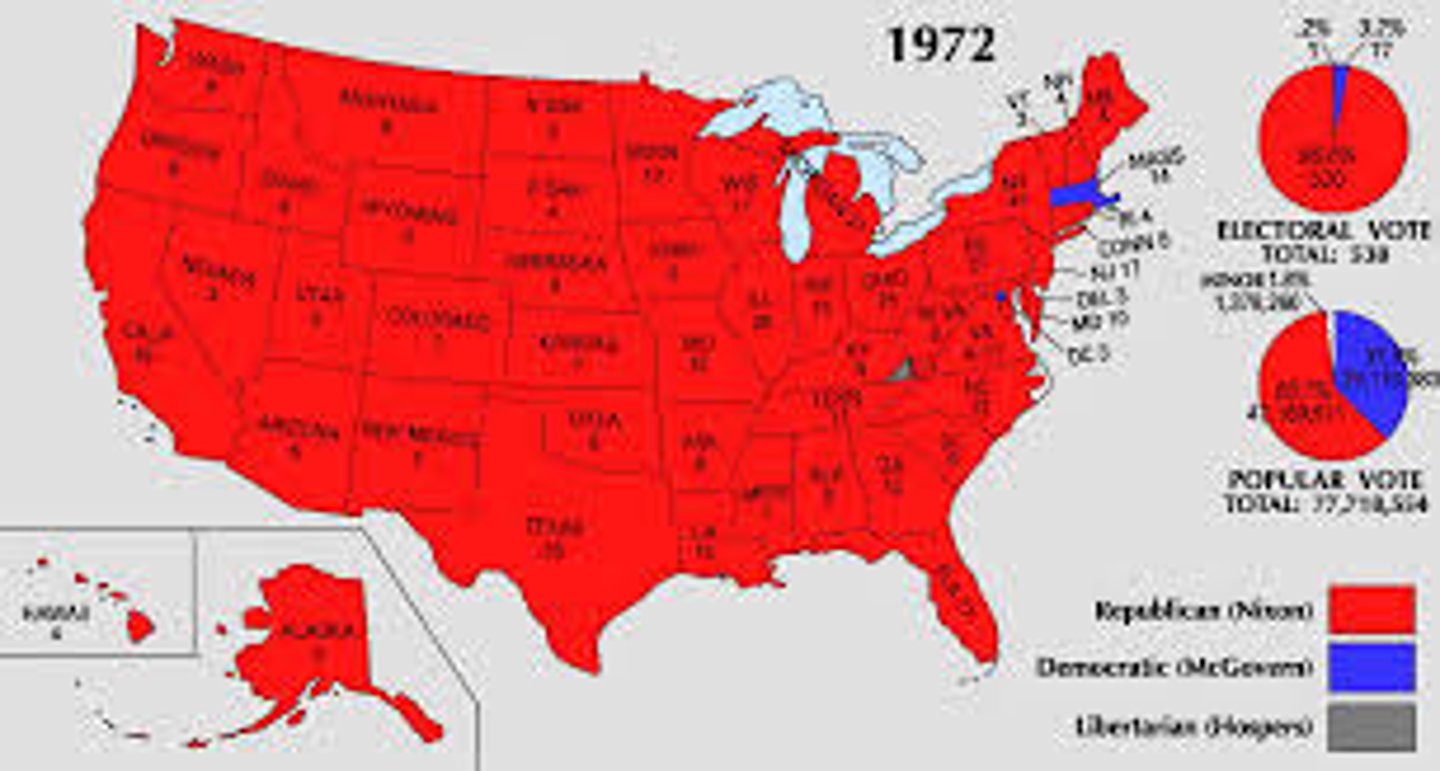
Election of 1972
Placed Nixon against Democrat George McGovern, with the former being the embodiment of the radical movements Nixon's "silent majority" of middle-class Americans opposed, resulting in a landslide victory for Nixon
Inflation 1970s
stock market is a mess. It loses 40% in an 18-month period, and for close to a decade few people want anything to do with stocks. Economic growth is weak, which results in rising unemployment that eventually reaches double-digits

Deindustrialization
process by which companies move industrial jobs to other regions with cheaper labor, leaving the newly deindustrialized region to switch to a service economy and to work through a period of high unemployment

Saturday Night Massacre
A name given to the resignation of the U.S. attorney general and the firing of his deputy in October 1973, after they refused to carry out President Nixon's order to fire the special prosecutor investigating the Watergate affair
U.S. v. Richard M. Nixon
Nixon gives up tapes and ahead of impeachment, he resigns

Election of 1976
Ford vs Carter, Carter wins. Importaint because he was the first president from the south for a while and people thought he would bring fresh ideas
Iranian Revolution
(1978-1979) a revolution against the shah of Iran led by the Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, which resulted in Iran becoming an Islamic republic with Khomeini as its leader
