In Semester Exam L11 Fungi
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is a spore?
Microscopic biological particles that allow fungi to reproduce, serving a similar purpose to that of seeds in the plant world.
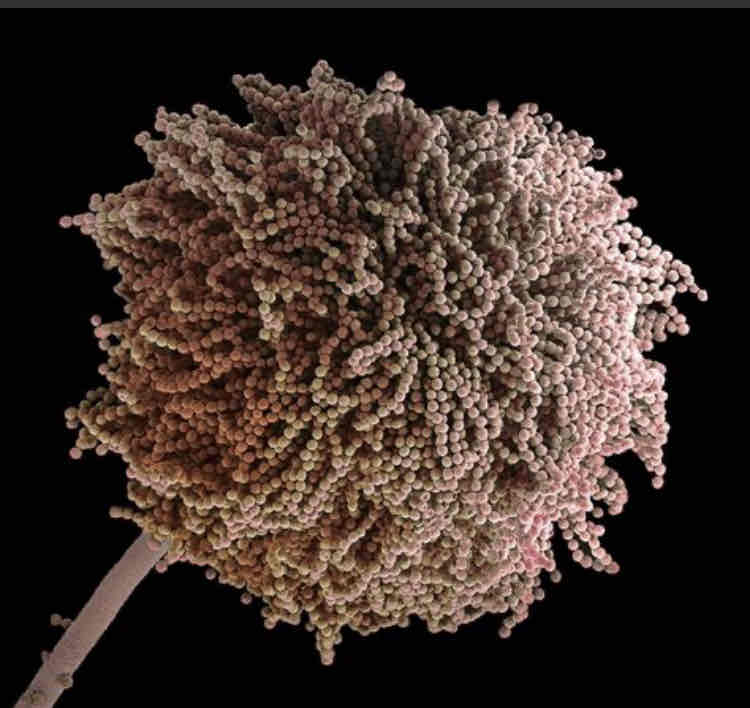
What are hyphae?
Extensions that grow from each fungi designed to increase the surface area for the absorption of nutrients.
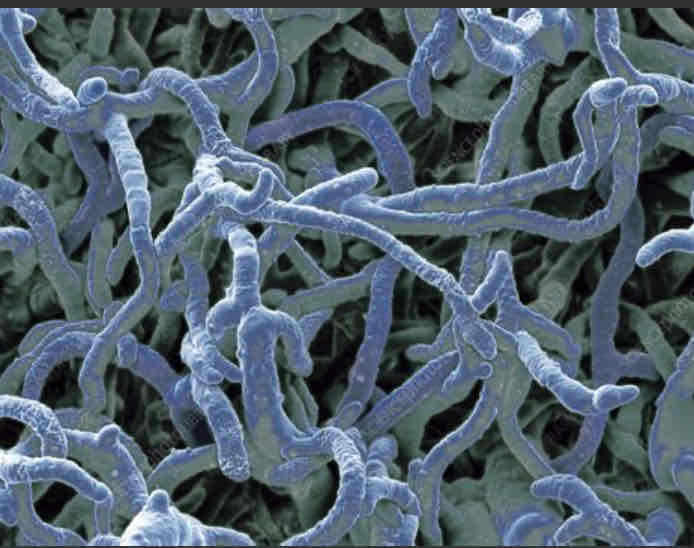
What is mycelium?
Matt of entwining hyphae.
What are septa?
The hyphae of most fungi are divided into cells by internal walls called septa.
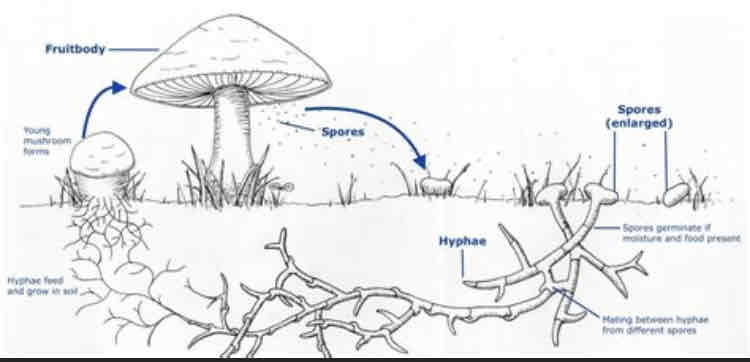
Describe the fruiting bodies of fungi.
The fruiting bodies of fungi contain spores, which are dispersed for reproduction. Mushrooms are a familiar example of a fruiting body. They are formed from hyphae.
What criteria classify an organism as a member of the kingdom of fungi?
They are a eukaryote
A member of a opisthokonta
They have a rigid cell wall like plants, but unlike plants, it is composed of chitin.
The cell membrane is bilayered
When are fungi most pathogenic?
They are most pathogenic when they are budding. They can also evade white blood cells at this stage.
What is a single cellular type of fungi?
Yeast
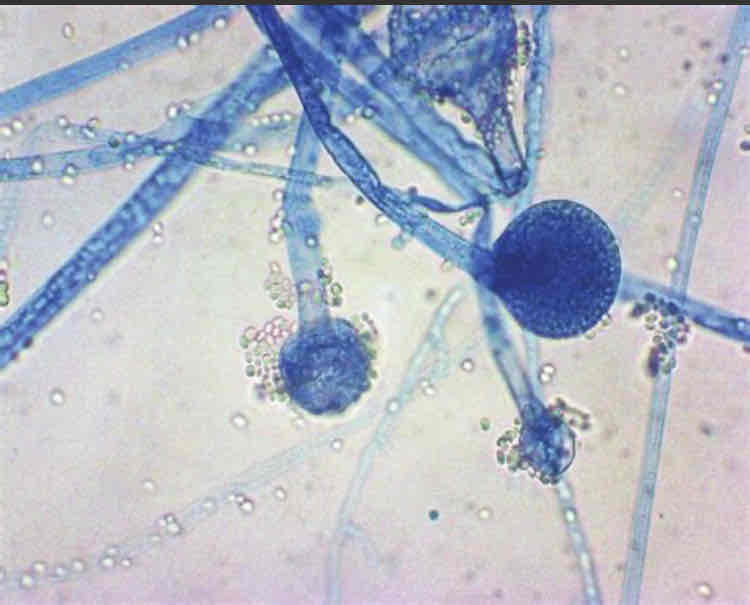
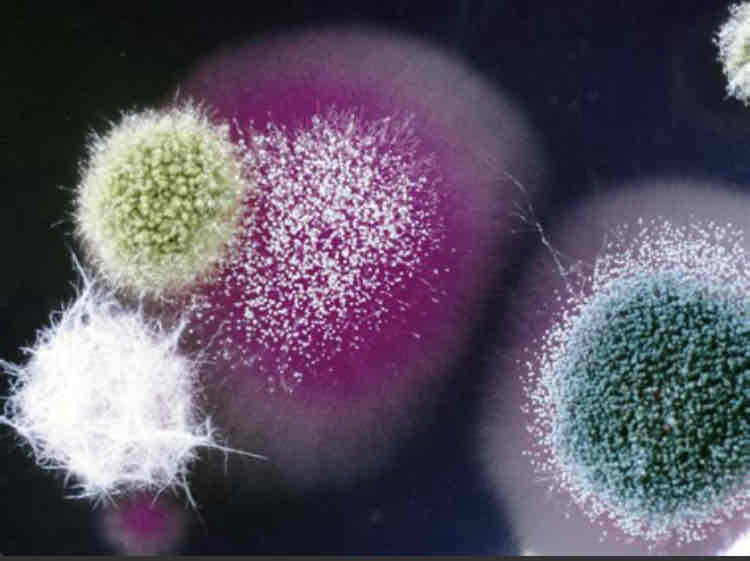
Describe what fungi culture looks like microscopically.
Microscopically, you can see the spores and hyphae.
What does fungi look like macroscopically in culture?
It looks like a growth on the top side and underside may be a different colour.
Roughly what percentage of the time do fungi reproduce asexually?
About 80% of the time.
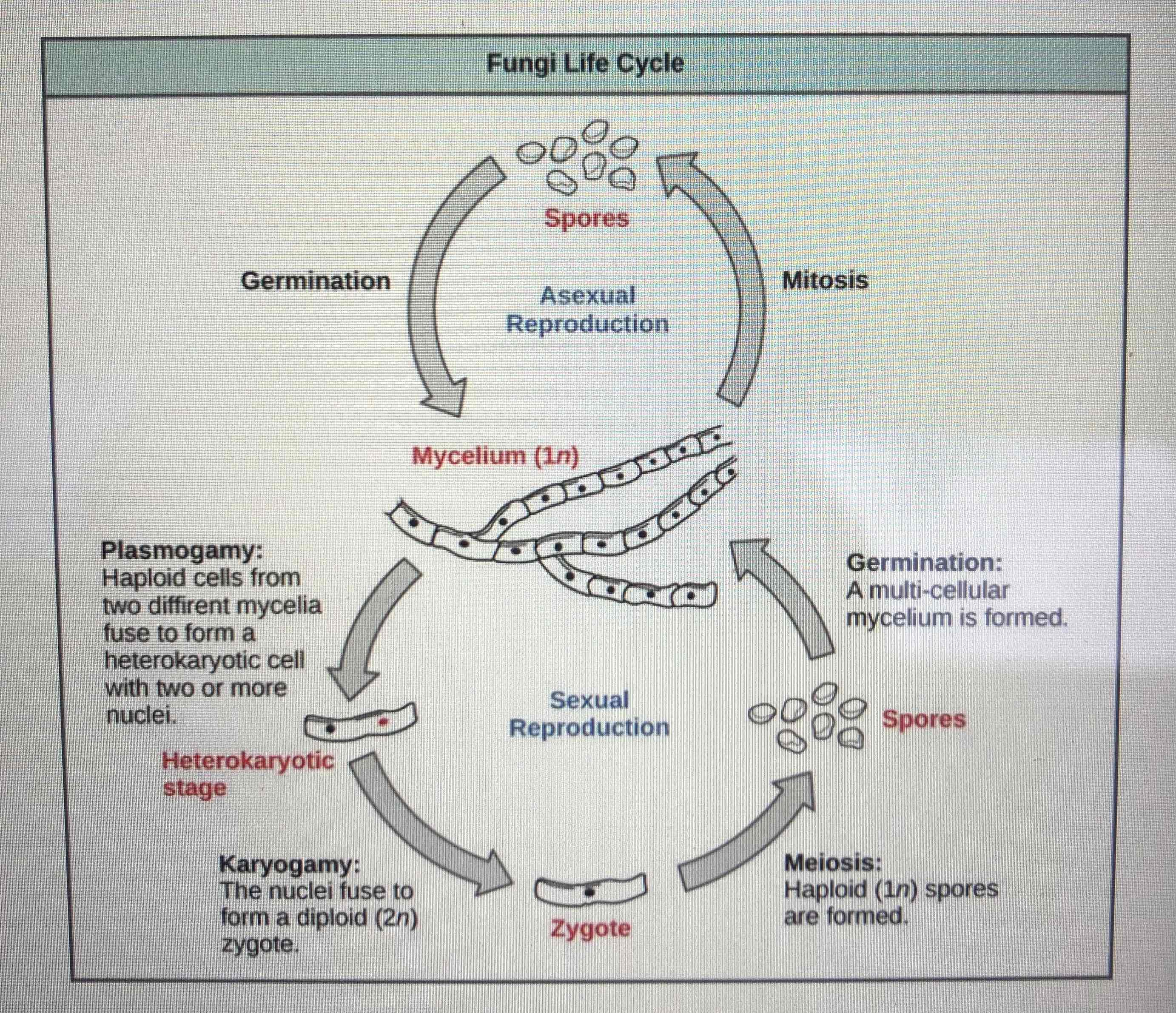
There are different terms used for asexual and sexual stages of fungi reproduction. Sexual reproduction increases genetic variation into a population of fungi. In what conditions does sexual reproduction usually occur?
Sexual reproduction usually occurs in response to adverse environmental conditions.
Describe asexual reproduction.
The fungi produce spores through mitosis.
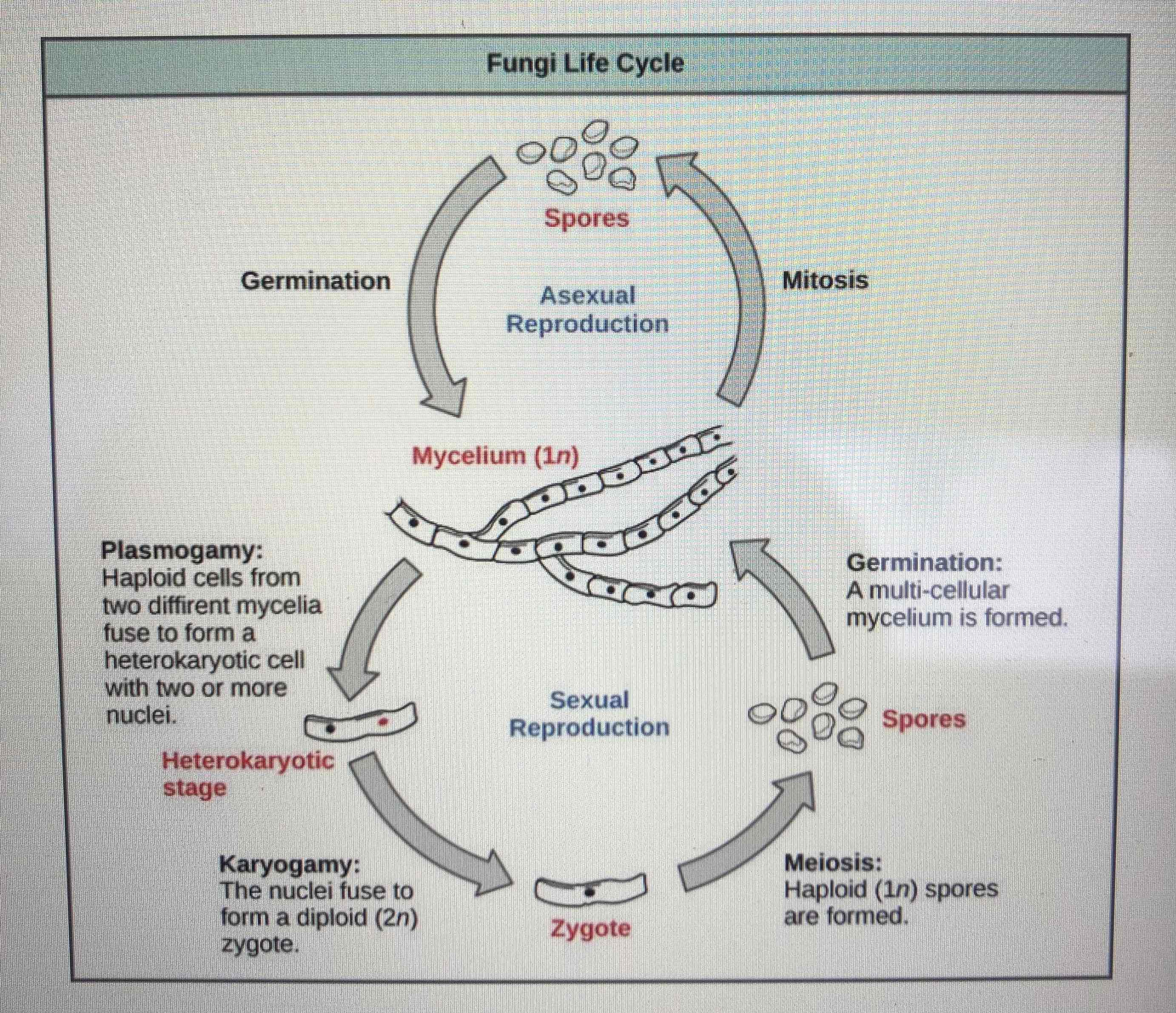
Describe sexual reproduction.
Cells from two different mycelia fuse. They then form a zygote.
Through meiosis spores are formed.
Fungi can be classified according to their taxonomy or according to their morphology, which is their appearance. One of the groups are known as chytrids (chytridiomycota) describe their morphology.
The name means little pot, which describes the structure containing unreleased zoospores.
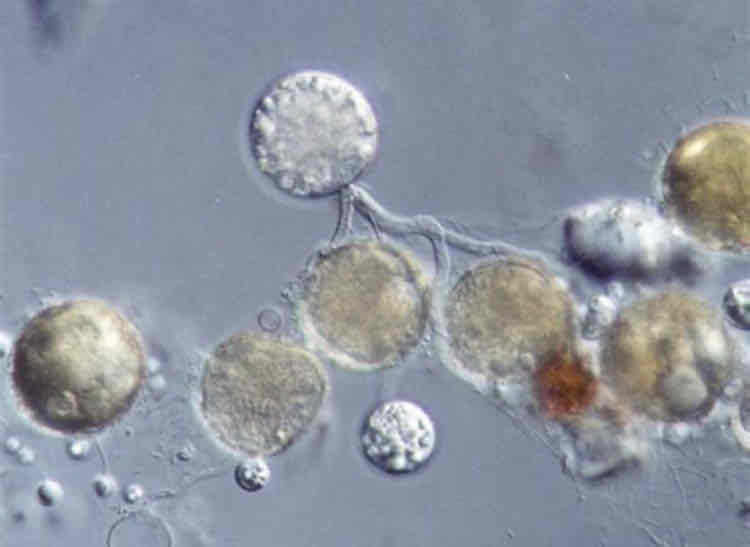
Zygomycota lives in soil and looks like bread mould. Glomeromycota is another division of fungi. Where do they live?
They live in soil and plants.
With respect to morphology, what are multicellular fungi that form microscopic, fruiting bodies referred to?
Moulds
With respect to morphology, what are multicellular fungi that form macroscopic, fruiting bodies referred to?
Mushrooms
With respect to morphology, what are single cellular fungi referred to?
Yeast
When grown on agar, what does yeast resemble?
Bacterial colonies
Fungi are heterotrophs and are important for the environment. What kind of relationship do they have with most plants species?
Mutualistic
What is fungal disease called?
Mycosis
What happens in nasal aspirgillosis?
The fungi get inhaled by dogs and can degrade the bone. This causes a discharge of the nose. It is treatable if found.
What are fungi on the skin, hair and nails called?
Dermatophytes. A Woods lamp will light these up.
Animals can get yeast infections on their skin and in their ears. When looking at yeast under a microscope is it larger or smaller than bacteria?
Larger
What are fungal infections beneath the skin called?
Subcutaneous mycosis