AP World Cookbook Project Yellow Folder Blue Folder 25-26
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
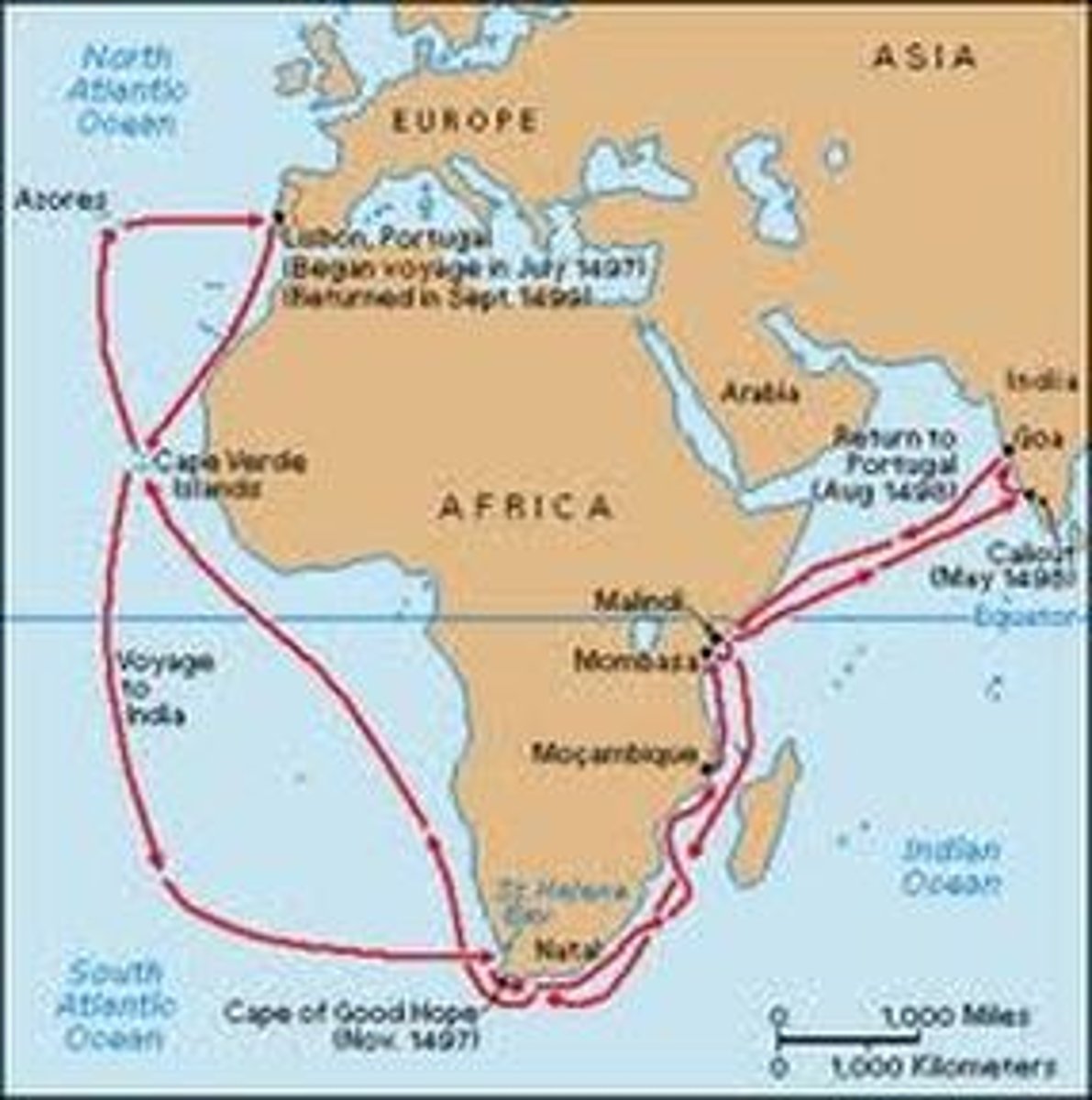
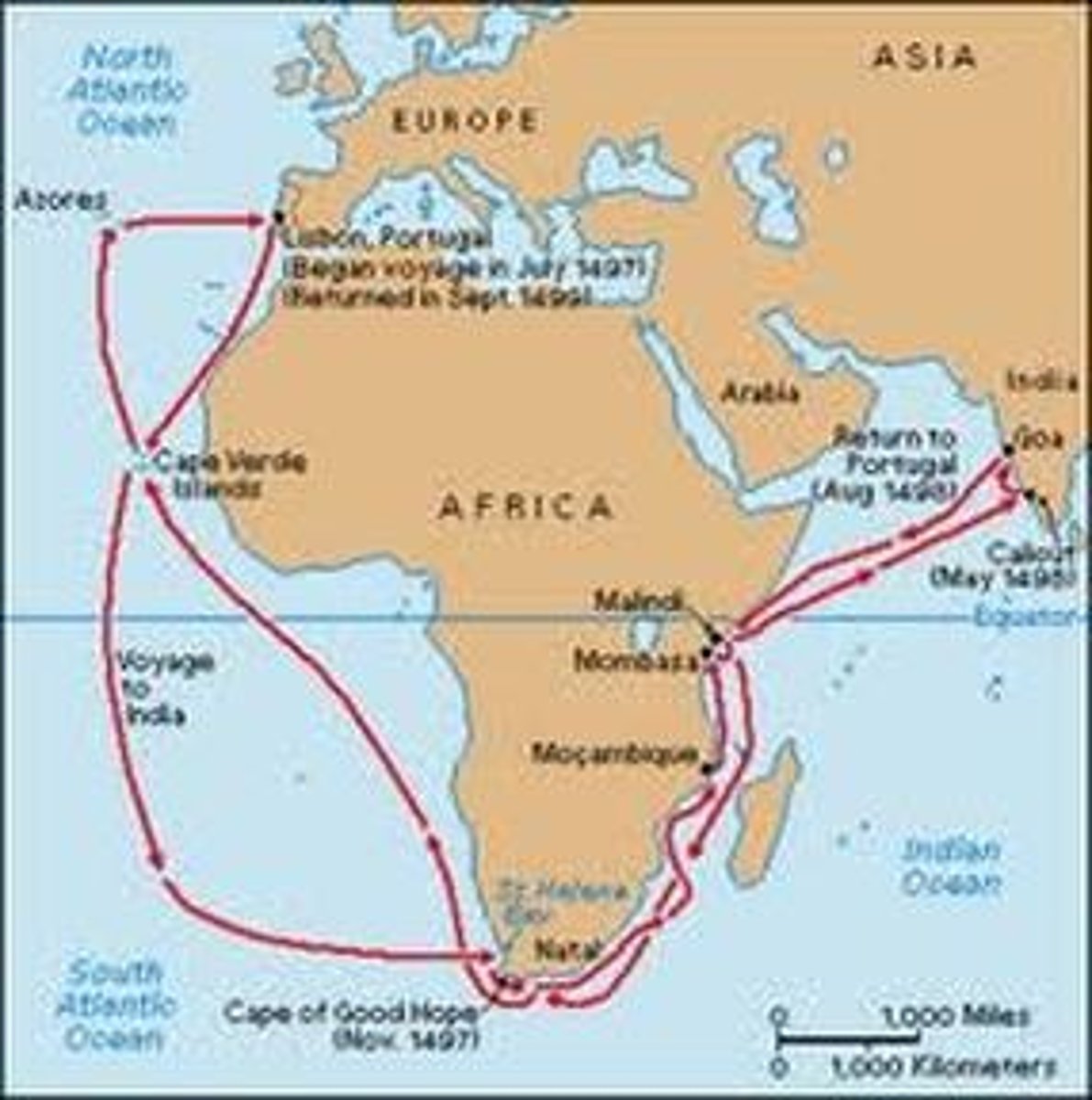
Prince Henry the Navigator
(1394-1460) Prince of Portugal who established an observatory and school of navigation at Sagres and directed voyages that spurred the growth of Portugal's colonial empire.
Portuguese Empire
took an early lead in European exploration (sponsored by Prince Henry); went East and established trading posts in West Africa, East Africa (Swahili City States) and India for spice trade
Global Silver Trade
Trade between the Americas and Europe and onward to China from the 16th to 18th centuries. It had a profound effect on the world economy could also be considered the beginning of the global economy.
cash crop
a crop produced for its commercial value rather than for use by the grower.
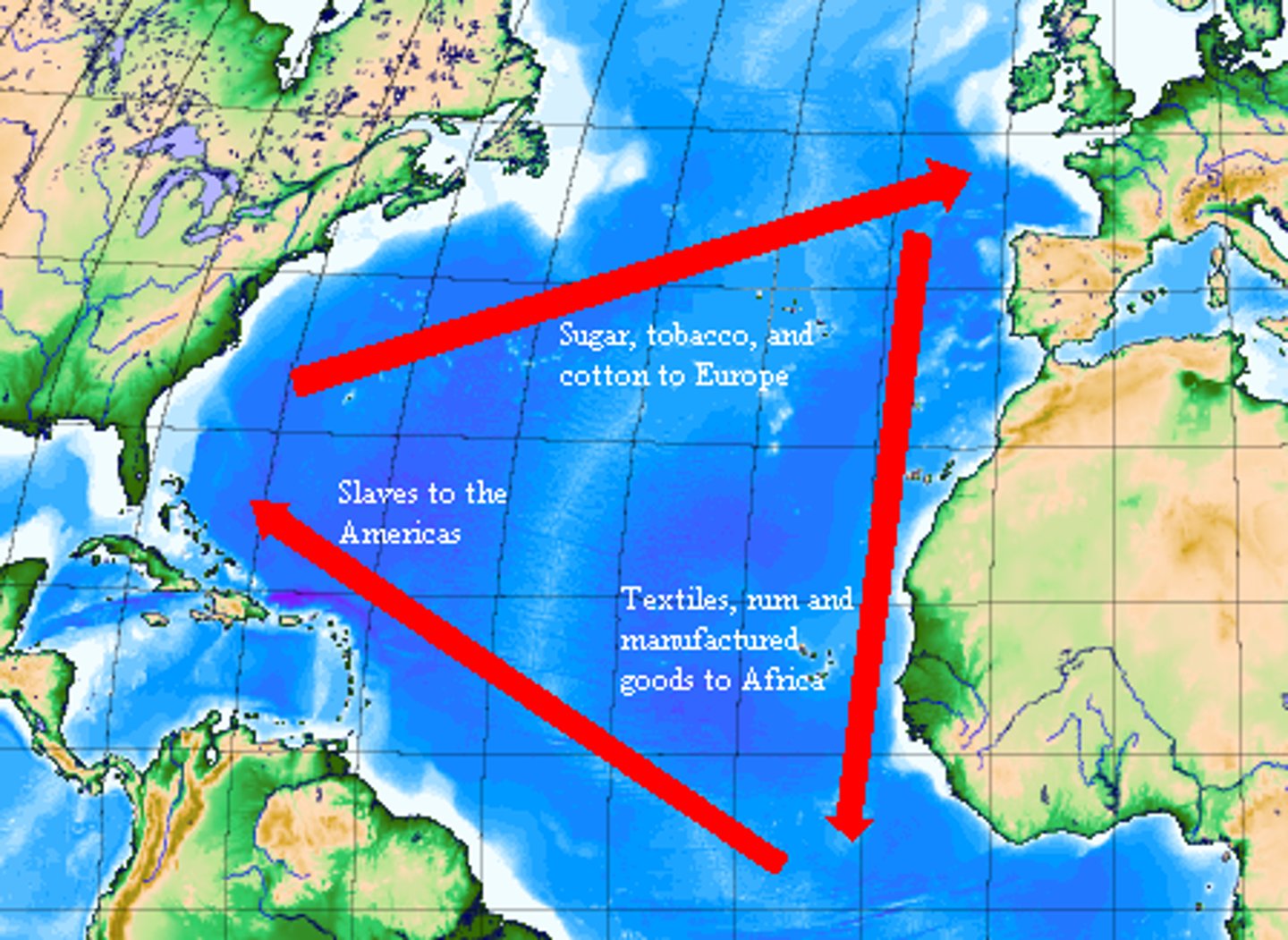
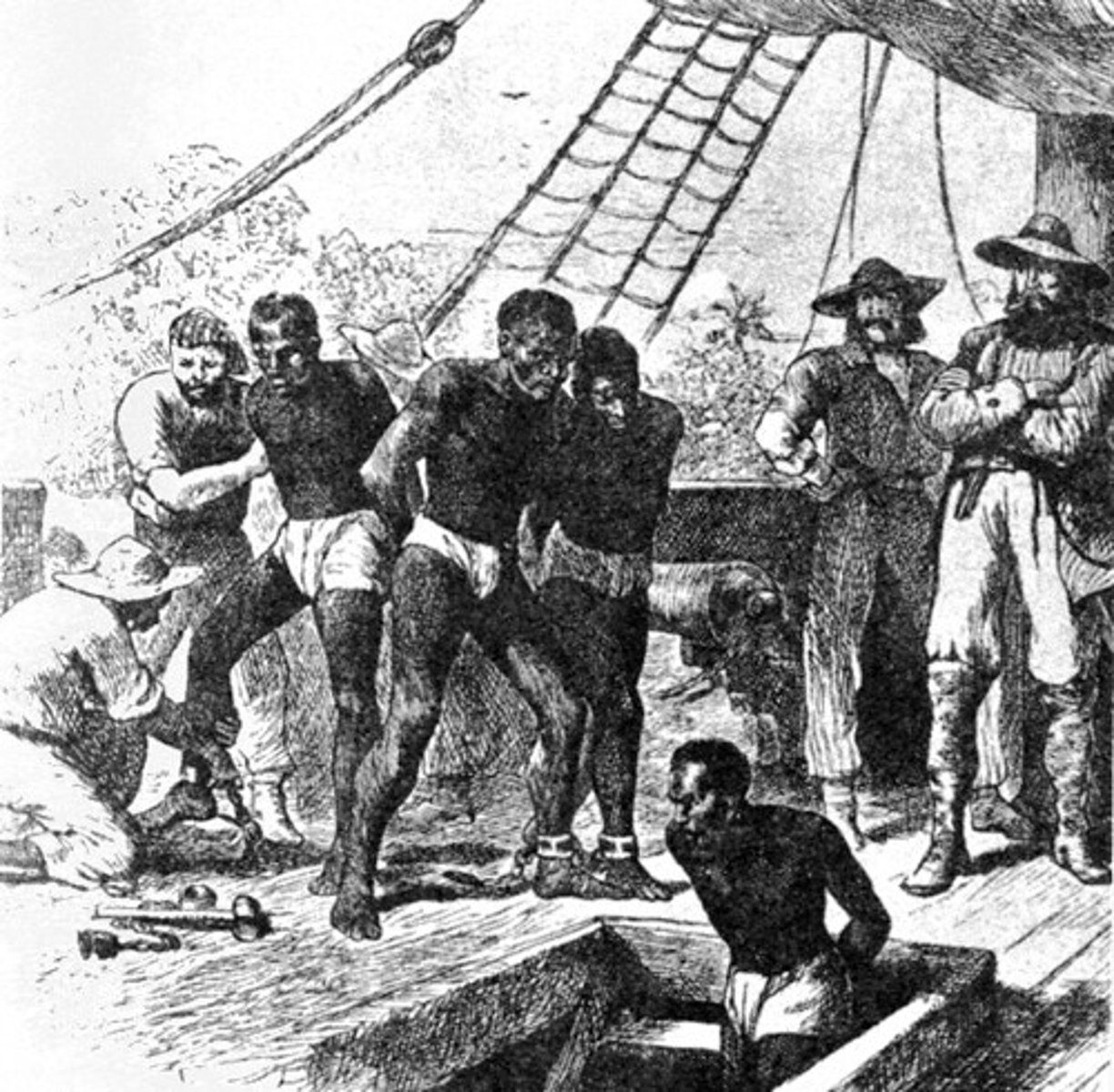
Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade
The forced migration of between 12 - 15 million people from Africa to the Western Hemisphere from the middle of the 15th century to the end of the 19th century.

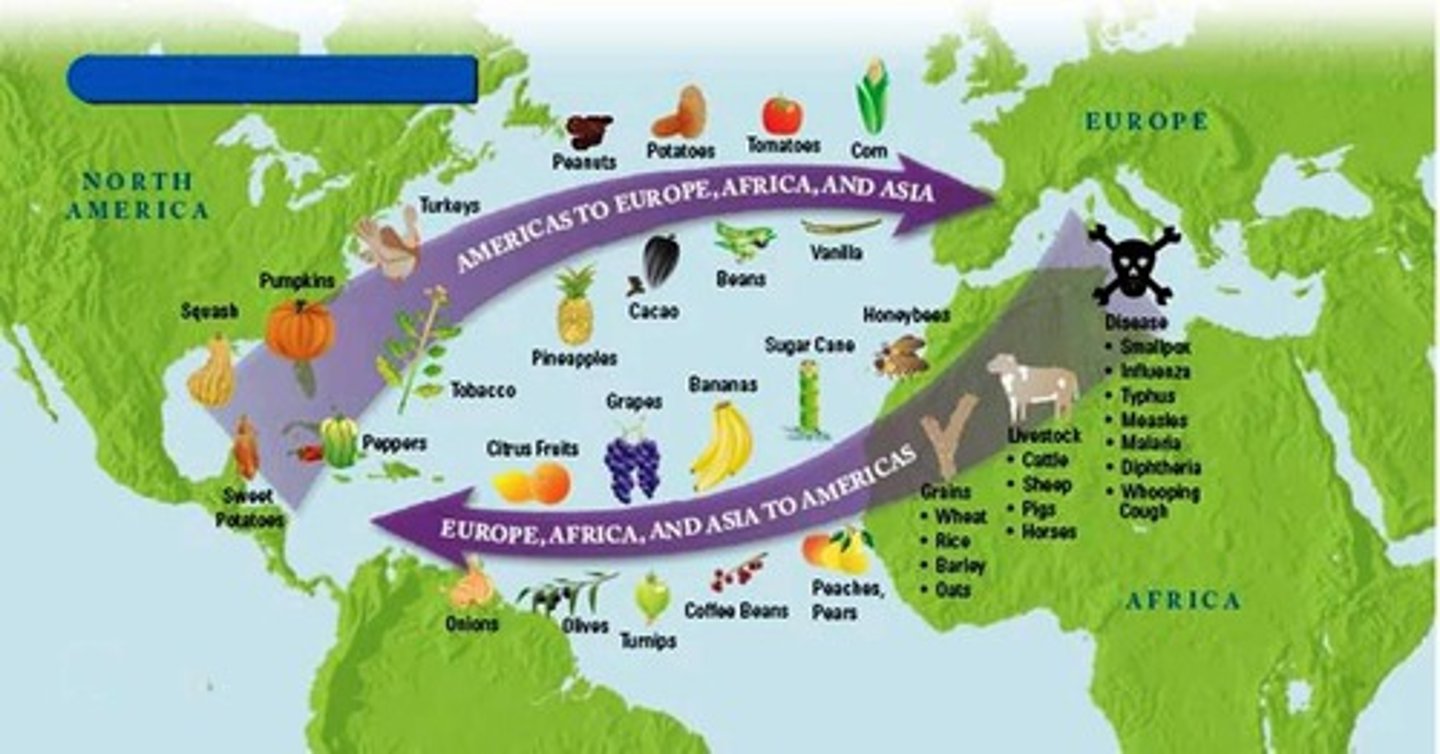
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus's voyages.
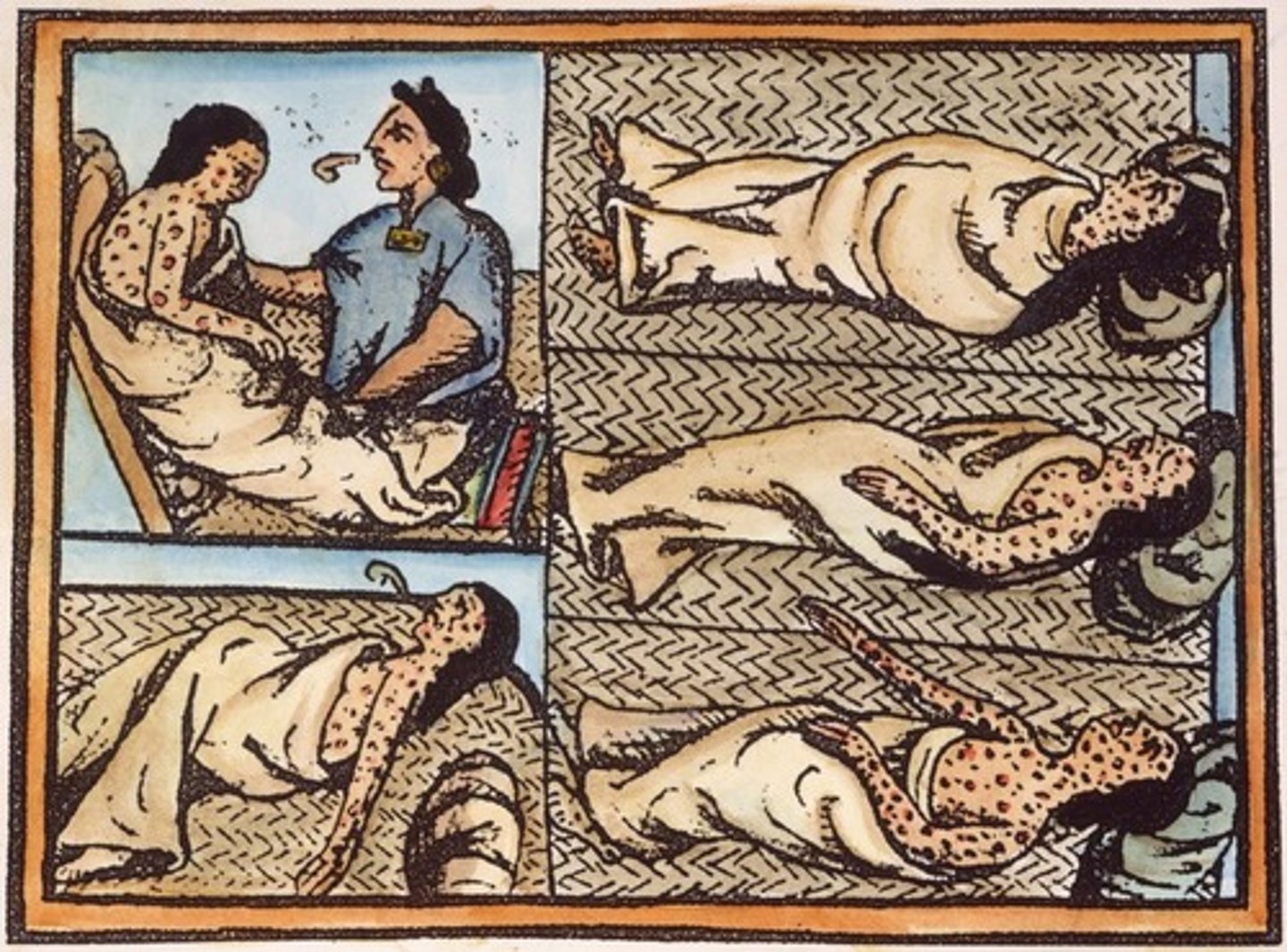
Smallpox
A highly contagious viral disease characterized by fever, weakness, and skin eruption with pustules that form scabs; responsible for killing Native Americans.
coercive labor
Any labor system that involves force (ex: slavery, serfdom, and encomienda)
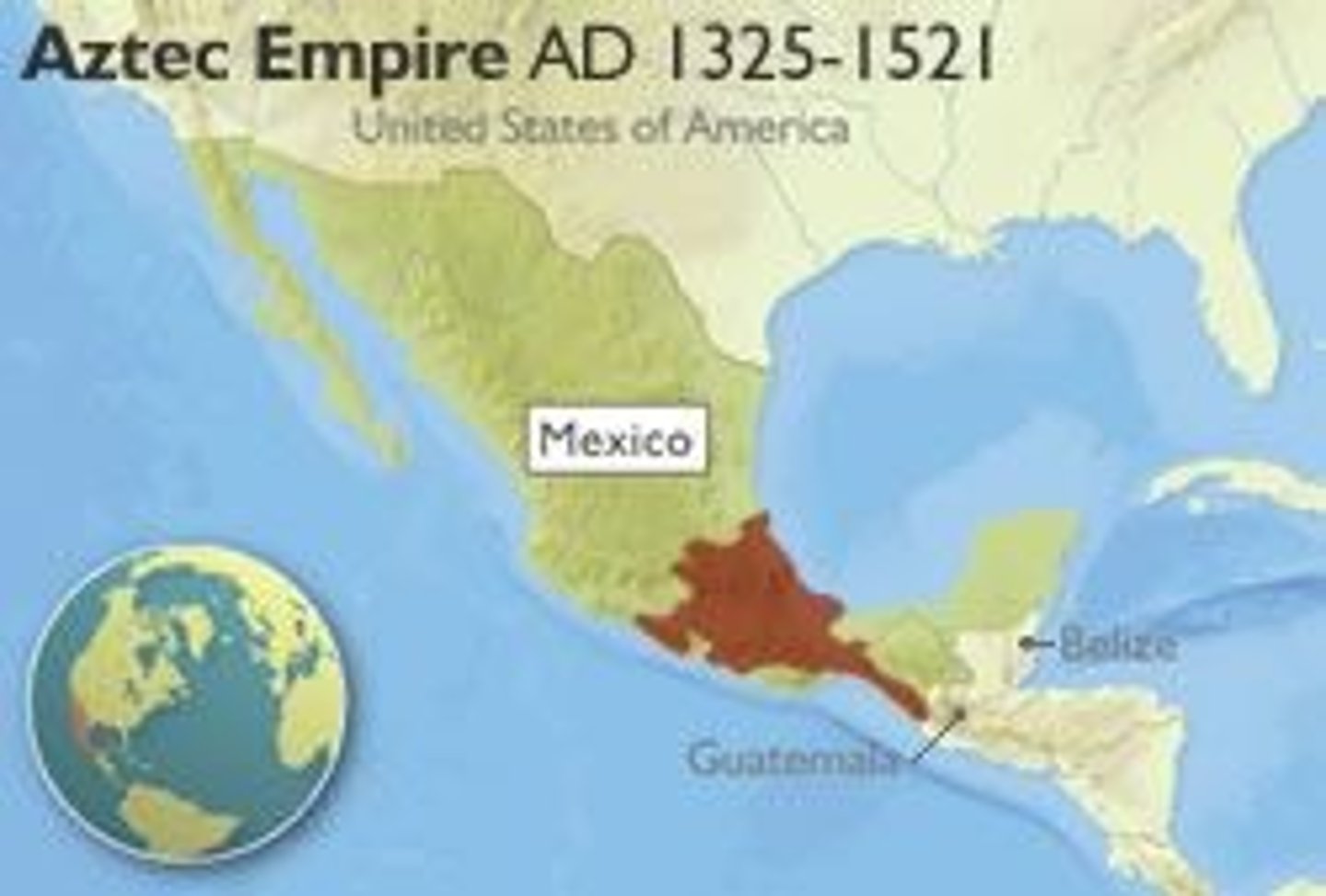
Aztec Empire
Central American empire constructed by the Mexica and expanded greatly during the fifteenth century during the reigns of Itzcoatl and Motecuzoma I.
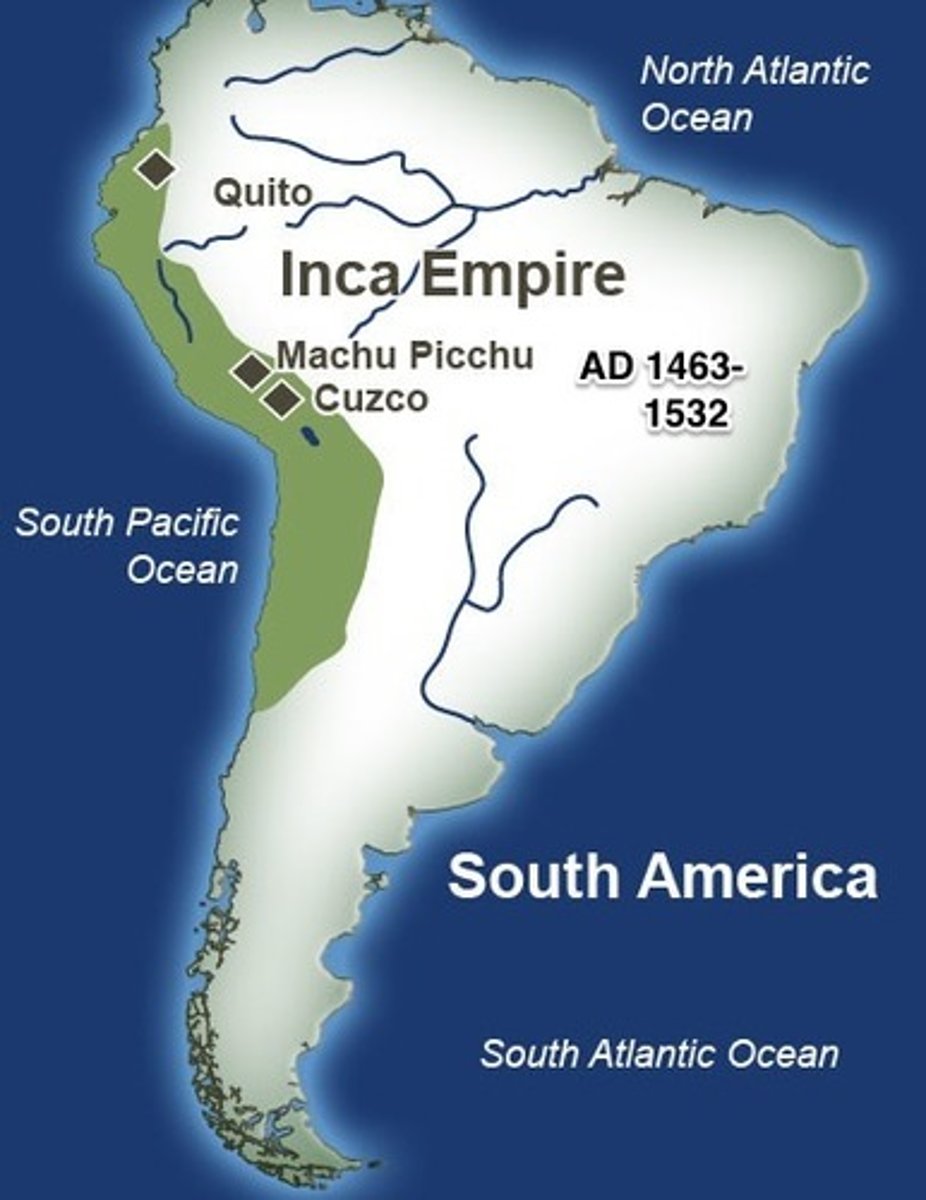
Inca Empire
Empire in Peru. conquered by Pizarro, who began an empire for the Spanish in 1535
Maroon Societies
Communities formed by escaped slaves in the Caribbean, Latin American. and the United States.
Resistance of Enslaved People
Enslaved resisted by working slowly, damaging goods, or running away; one of the largest uprisngs in the US was the German Coast Rebellion of 1811 in Louisiana; Nat Turner led a revolt in Virginia in 1831; Southern slaveowners enforced strict slave codes severe punishments and made it illegal to help run-away slaves;
Mulattoes
People with mixed races between European and African descent
Potosi
Mine located in upper Peru (modern Bolivia); largest of New World silver mines; produced 80 percent of all Peruvian silver.
Chattel Slavery
Absolute legal ownership of another person, including the right to buy or sell that person.
Astrolabe
An instrument used by sailors to determine their location by observing the position of the stars and planets
Continuity in enslavement in Africa between 1200-1750
Encorporation of enslaved persons into households and the export of enslaved persons to the Mediterranean and the Indian Ocean regions
Mit'a
Incan labor system used by the Spanish to coerce labor in the Americas, including in the mining of silver.
Demographic impact of slavery in Africa
The population of men declined and women became more central to economic and political systems as result.
Cultural synthesis
The blending of religious and other traditions, including food, that resulted from long-distance interactions between cultures.
Cause of Chinese demand for silver
Ming dynasty taxation policies to reduce the use of paper money
What was the Abbasid Caliphate?
Vast Islamic empire from 750 to 1258 CE, promoting scholarly and cultural development, with its capital in Baghdad.
Who were the Turkic peoples?
Nomadic tribes from the Central Asian steppes; they played significant roles in Islamic empires, including the Seljuk and Ottoman empires.
What was the Baghdad House of Wisdom?
An intellectual center during the Islamic Golden Age, where scholars translated, studied, and preserved classical works of antiquity.
What were the contributions of Muslim Scholars and Scholarship?
Pioneered advancements in various fields; they preserved and expanded upon Greek/Roman Philosophy, developed algebra in mathematics, and made significant contributions to medicine.
What were the characteristics of Islam in Spain?
Islam entered Spain in the 8th century; Al-Andalus became a center of learning and culture, with tolerance for multiple religious communities.
What were the characteristics of Islam in South Asia?
Islam spread to South Asia through trade and conquest, influencing regional cultures and sparking both cooperation and conflict with Hindu and Buddhist communities.
What were the characteristics of Islam in Southeast Asia?
Introduced largely through trade, Islam blended with local traditions and established lasting Muslim communities, especially in Indonesia and Malaysia.
What were the characteristics of Islam in East Africa?
Islam influenced coastal regions, enriching Swahili culture and facilitating trade between East Africa, the Middle East, and Asia.
What were the characteristics of Islam in West Africa?
Islam entered through trans-Saharan trade, influencing local kingdoms like Mali and Songhai, and fostering Islamic scholarship.
What are Sufis / Sufism?
Mystical Islamic tradition focusing on personal experience of God and aiming to attain truth and divine love through direct encounters with God.
What is the Islamic Golden Age?
A period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century.
Who were the Seljuk and Ottoman empires?
Two significant Islamic empires that emerged from Turkic peoples and had a lasting impact on the region.
What is the significance of trade in the spread of Islam?
Trade routes facilitated the spread of Islam to various regions, allowing for cultural exchange and the establishment of Muslim communities.
What is the role of Islamic scholarship in preserving and expanding knowledge?
Islamic scholars played a crucial role in translating, studying, and preserving classical works of antiquity, as well as making significant advancements in various fields.
What is the significance of the House of Wisdom in Baghdad?
A part of the Abbasid Caliphate, this served as a center for intellectual exchange and translation, contributing to the preservation and expansion of knowledge during the Islamic Golden Age.
What is the importance of the Umma in Islam?
The concept emphasizes the unity of Islamic believers, transcending ethnic and geographic differences, and fostering a sense of community and solidarity.
What are the main characteristics of Sufism?
This group of Muslims emphasized the personal experience of God, seeking truth and divine love through direct encounters with God, often through practices such as meditation and chanting.
What is the Sunni/Shia divide?
Fundamental division within Islam over Prophet Muhammad's successor.
What is Jizya?
Tax on non-Muslims in Islamic states for religious freedom.
Who was Ibn Battuta?
14th-century Moroccan traveler and scholar.
Who was Mansa Musa?
14th-century ruler of Mali, known for his pilgrimage to Mecca and wealth.
What was the Incan Empire known for?
Largest empire in pre-Columbian South America, with advanced infrastructure and a road system.
What was the Inca road system?
Sophisticated network of roads built by the Inca Empire.
What were the Aztecs known for?
Mesoamerican civilization known for complex social and political structures.
What was Tenochtitlan?
Capital city of the Aztec Empire.
What was the significance of Aztec agriculture?
increased production of crops, including maize cultivation and the use of chinampas techniques
What was the Song Dynasty known for?
Chinese dynasty in 1200, known for technological innovations, flourishing arts, and development of Neo-Confucianism.
Who established the Yuan Dynasty?
The Mongols under Kublai Khan.
What was the impact of Confucianism on China?
Shaped social, political, and educational systems, promoting hierarchical social order and moral conduct.
What was the Imperial Bureaucracy in China?
Centralized administrative system staffed by officials chosen through Civil Service Examinations.
What were Civil Service Examinations in China?
Exams for selecting bureaucrats based on Confucian texts, promoting social mobility and meritocracy.
What were canals used for in China?
Facilitating transportation and trade, notably the Grand Canal linking the north and south.
What was the significance of paper money in China?
Revolutionized the economy, making transactions easier and promoting trade.
What led to increased market activity in China?
Urbanization, trade, and innovations like paper money.
What is filial piety?
Confucian value emphasizing respect and care for elders and ancestors.
What impact did gunpowder have?
Initially used for fireworks, this had a profound impact on warfare and spread along trade routes.
What was the purpose of foot binding in China?
To reflect and reinforce patriarchal norms, restricting women's mobility and enforcing feminine ideals.
What was the significance of Champa Rice?
Boosted agricultural productivity in China during the Song Dynasty.
What were the Silk Roads?
Ancient trade networks connecting East and West, involved trade over land across geographic areas, such as the Central Asian steppe
What was porcelain used for?
Fine ceramic ware, major Chinese export
What were caravanserais?
Roadside inns along Sillk Roads trade routes
What were the luxury goods?
High-value, non-essential goods traded along long-distance routes
What was important about the manufacture of iron and steel in China?
These are examples of how China's economy was productive and innovative, especially with China's advancements in metallurgical techniques
What was the tribute system?
Diplomatic practice in East Asia acknowledging China's supremacy
What was feudalism?
Socio-economic system based on landowners and vassals
What was serfdom?
Labor system in medieval Europe where peasants were bound to the land
What was the manorial system?
Economic and social structure of medieval Europe that utilized feudalism and agricultural production
What was the caste system?
Social hierarchy intertwined with Hindu beliefs
Who were Buddhist Monks?
Religious practitioners following Buddha's teachings
What was Mahayana Buddhism?
Buddhist sect emphasizing universal enlightenment
What was the Bubonic Plague?
A deadly pandemic in the 14th century, known as the Black Death, causing massive fatalities and socio-economic disruptions in Eurasia.
What were Hindu states in Southeast Asia?
Indianized kingdoms in Southeast Asia, adopting Hinduism, Sanskrit, and Indian political concepts, notably in regions like Cambodia and Java.
What were Buddhist states in Southeast Asia?
States like Srivijaya and Sukhothai adopted Buddhism, shaping political and cultural developments in the region.
What are diasporic communities?
Communities of people who have migrated and settled in different regions.
What is a lateen sail?
A triangular sail used in ancient and medieval navigation.
What is an astrolabe?
An instrument used to measure the altitude of celestial bodies.
What is a stern post rudder?
A type of rudder attached to the stern of a ship.
How were camels and the saddle used?
Technologies used for transportation in desert regions, such as the Trans-Saharan trade network.
What are monsoon winds?
Seasonal winds that bring heavy rainfall in certain regions.
What is the significance of gold?
A valuable metal used for trade and currency.
What are caravans?
Groups of travelers and merchants traveling together for safety and trade.
What are trading cities?
Cities that serve as major centers for trade and commerce.
What are new forms of credit and money economies?
Emerging systems of borrowing and monetary exchange.
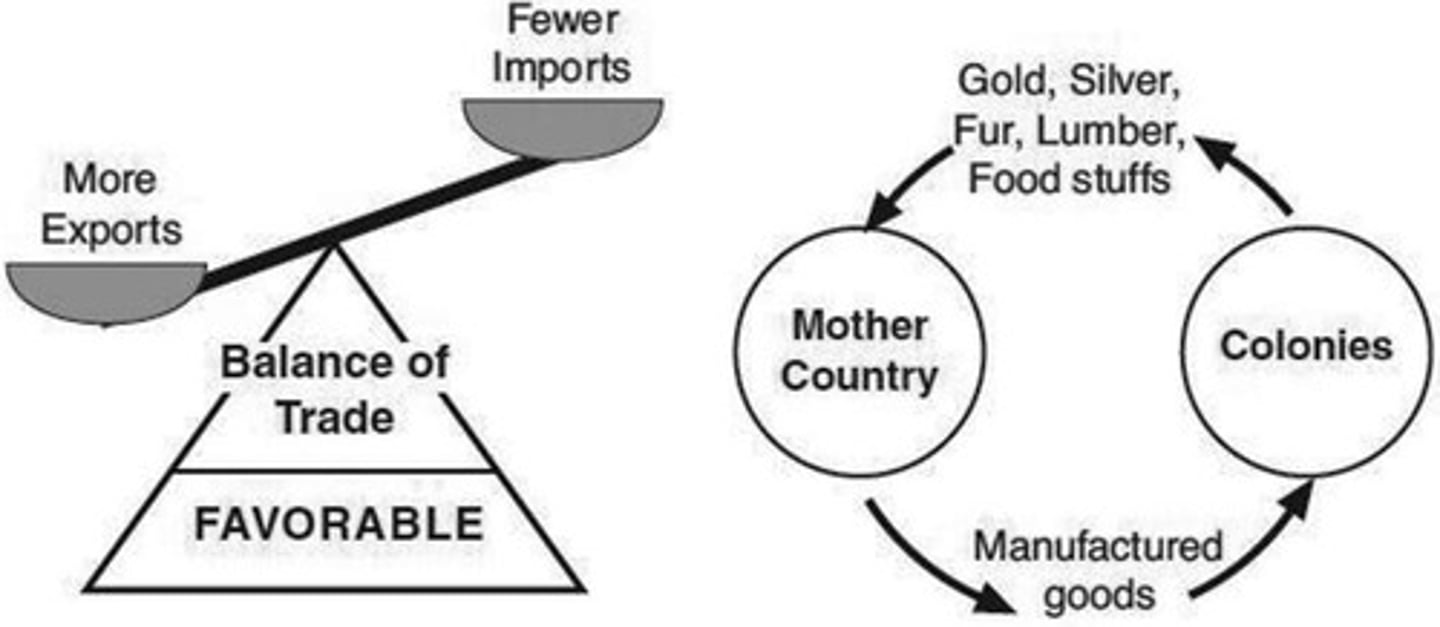
Mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase by selling more goods than they bought and utilizing colonies
Prince Henry the Navigator
(1394-1460) Prince of Portugal who established an observatory and school of navigation at Sagres and directed voyages that spurred the growth of Portugal's colonial empire.
Portuguese Empire
took an early lead in European exploration (sponsored by Prince Henry); went East and established trading posts in West Africa, East Africa (Swahili City States) and India for spice trade
Global Silver Trade
Trade between the Americas and Europe and onward to China from the 16th to 18th centuries. It had a profound effect on the world economy could also be considered the beginning of the global economy.
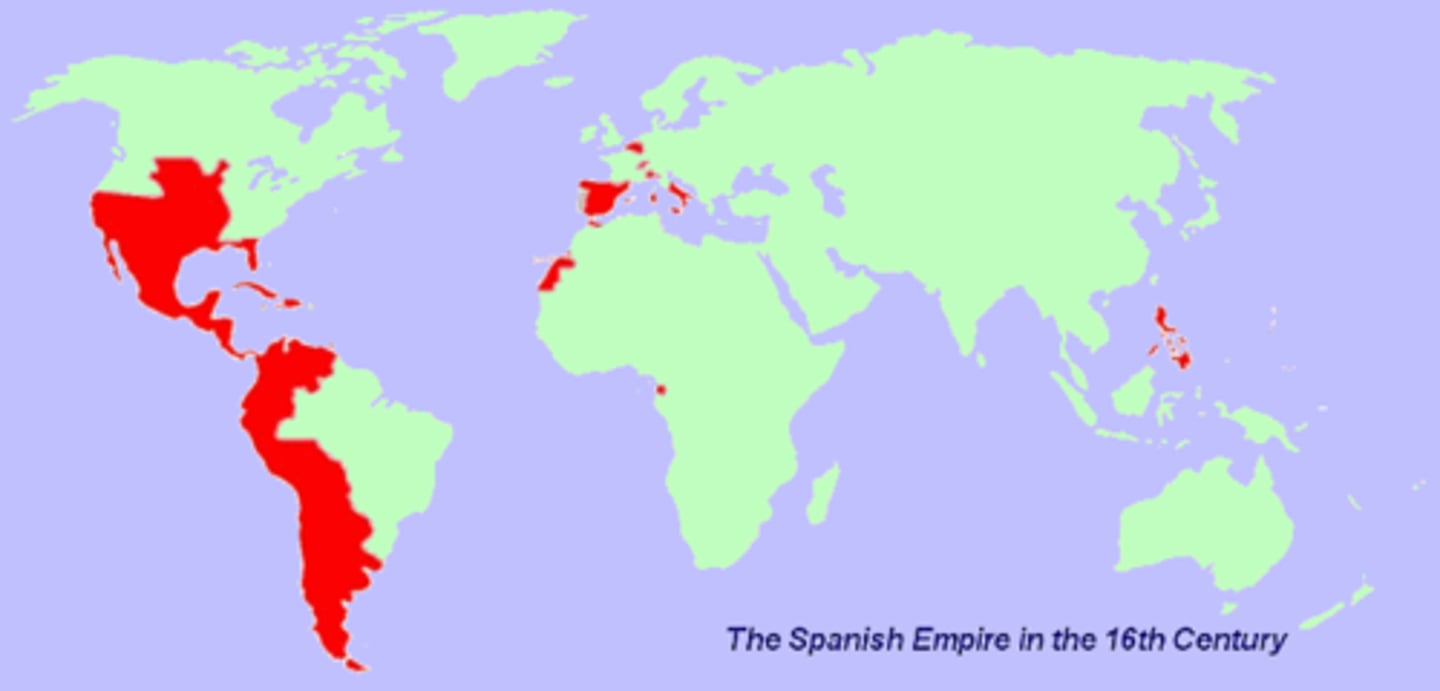
Spanish Empire
Made up of territories and colonies in Europe, Africa, and Asia controlled from Spain. At its strongest, it was one of the biggest empires in world history according to how much land they had, and one of the 1st global empires.
cash crop
a crop produced for its commercial value rather than for use by the grower.
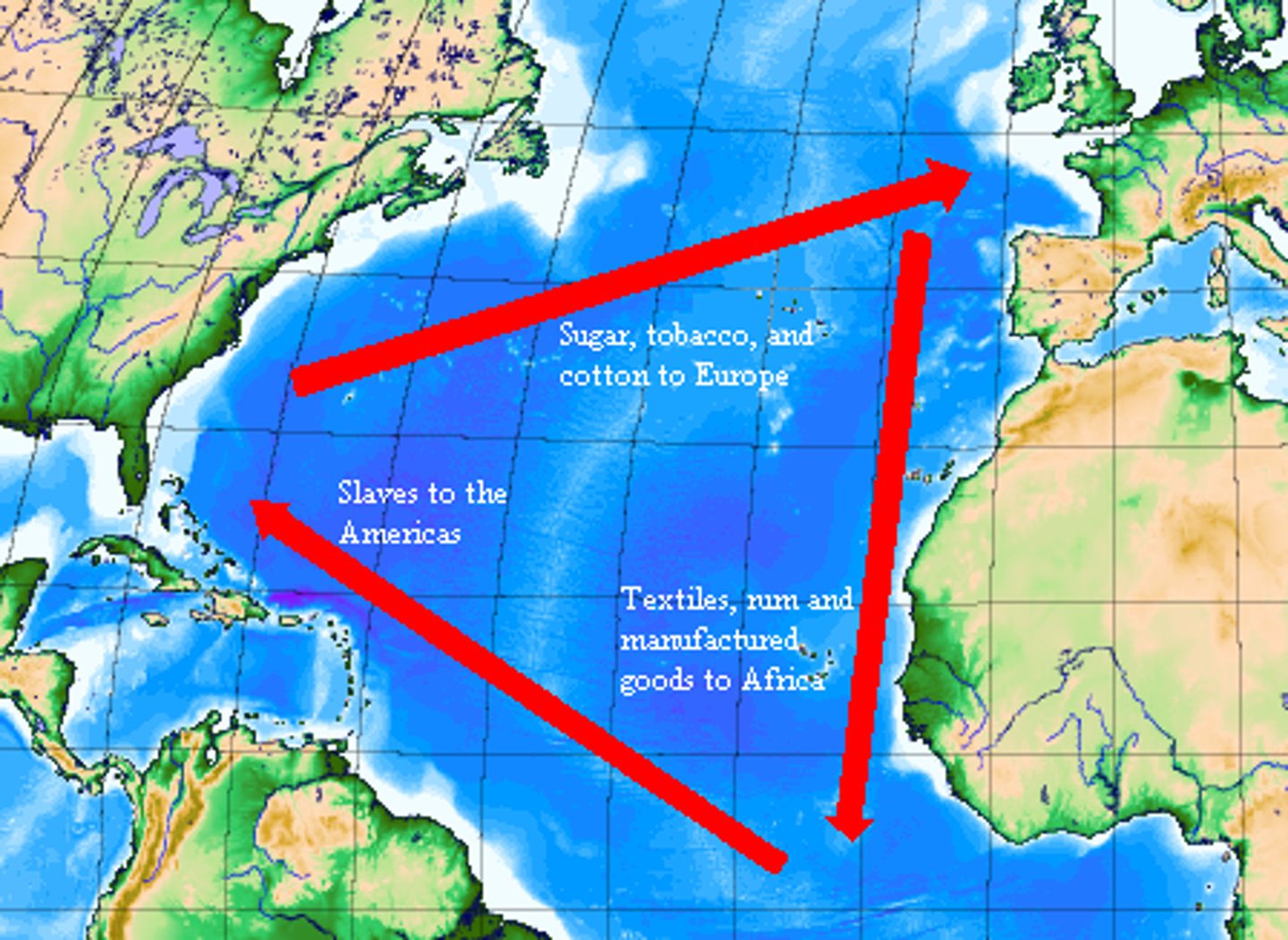
Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade
The forced migration of between 12 - 15 million people from Africa to the Western Hemisphere from the middle of the 15th century to the end of the 19th century.
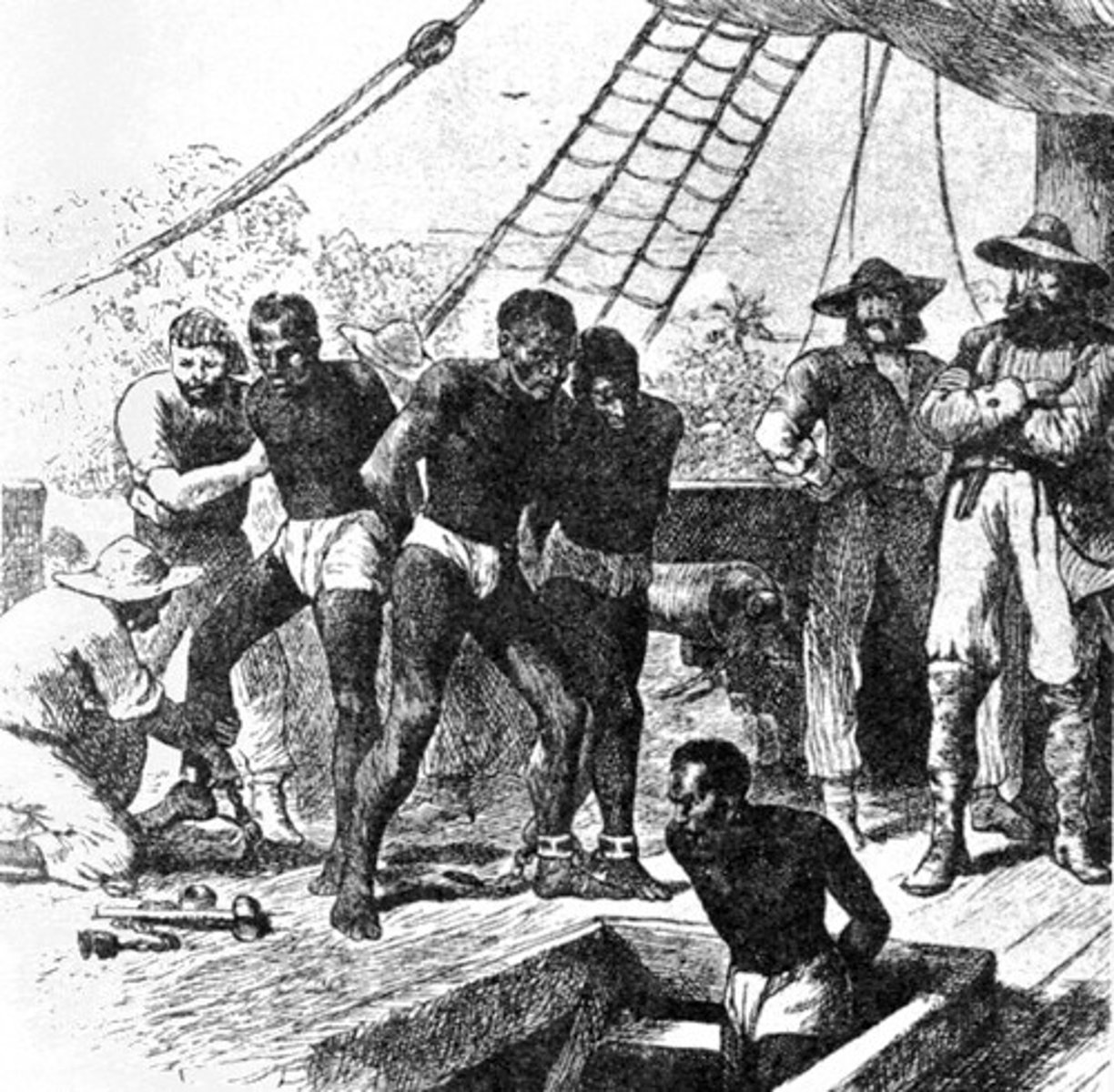

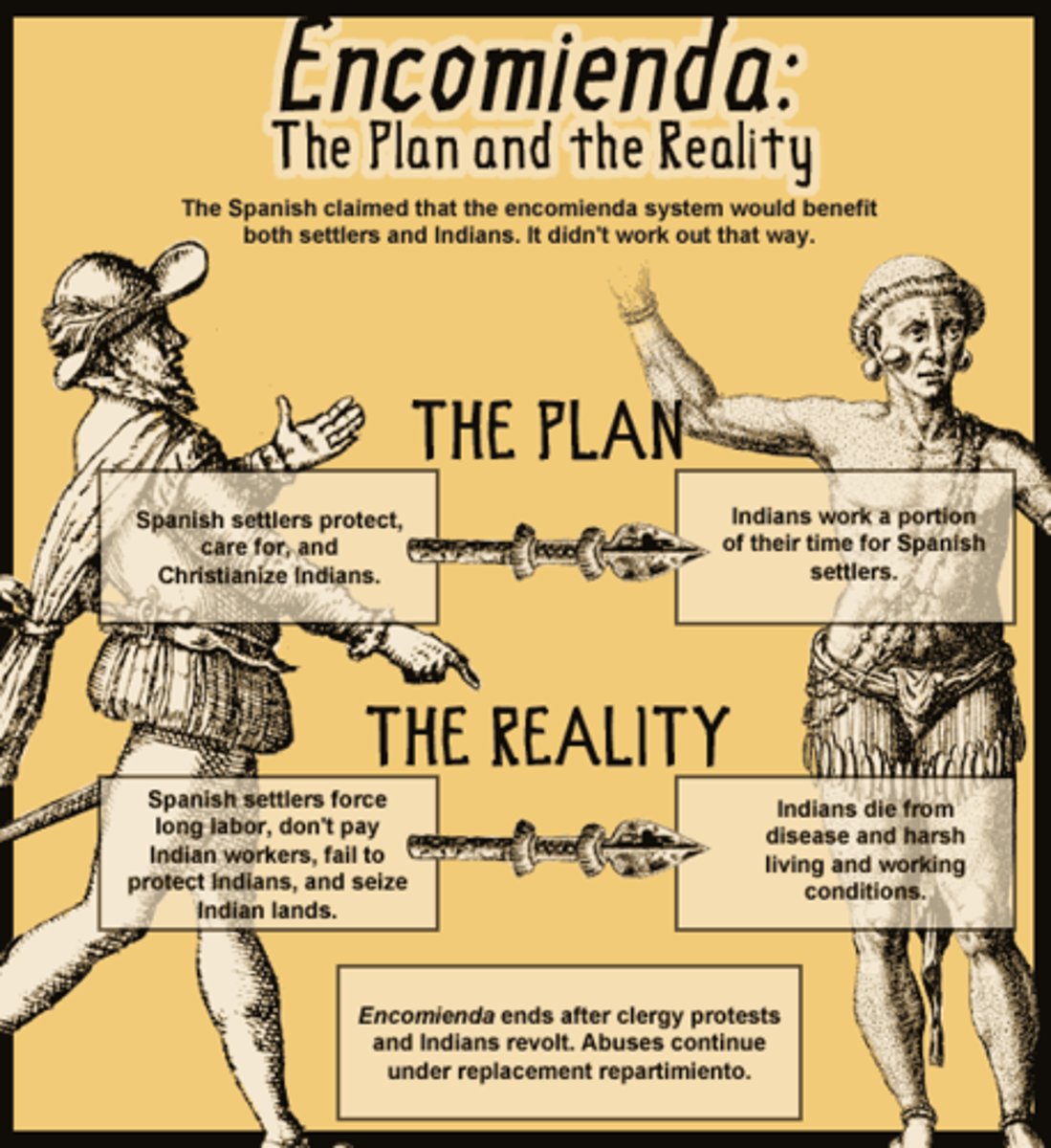
Encomienda System
It gave settlers the right to tax local Native Americans or to make them work and convert them to Christianity. It was a form of coercive labor.
Dutch East India Company
Government-chartered joint-stock company that controlled the spice trade in the East Indies.

British East India Company
set up trading posts in India in the 1600s, beginning the British economic interest there

joint-stock company
A business, often backed by a government charter, that sold shares to individuals to raise money for its trading enterprises and to spread the risks (and profits) among many investors.
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus's voyages.
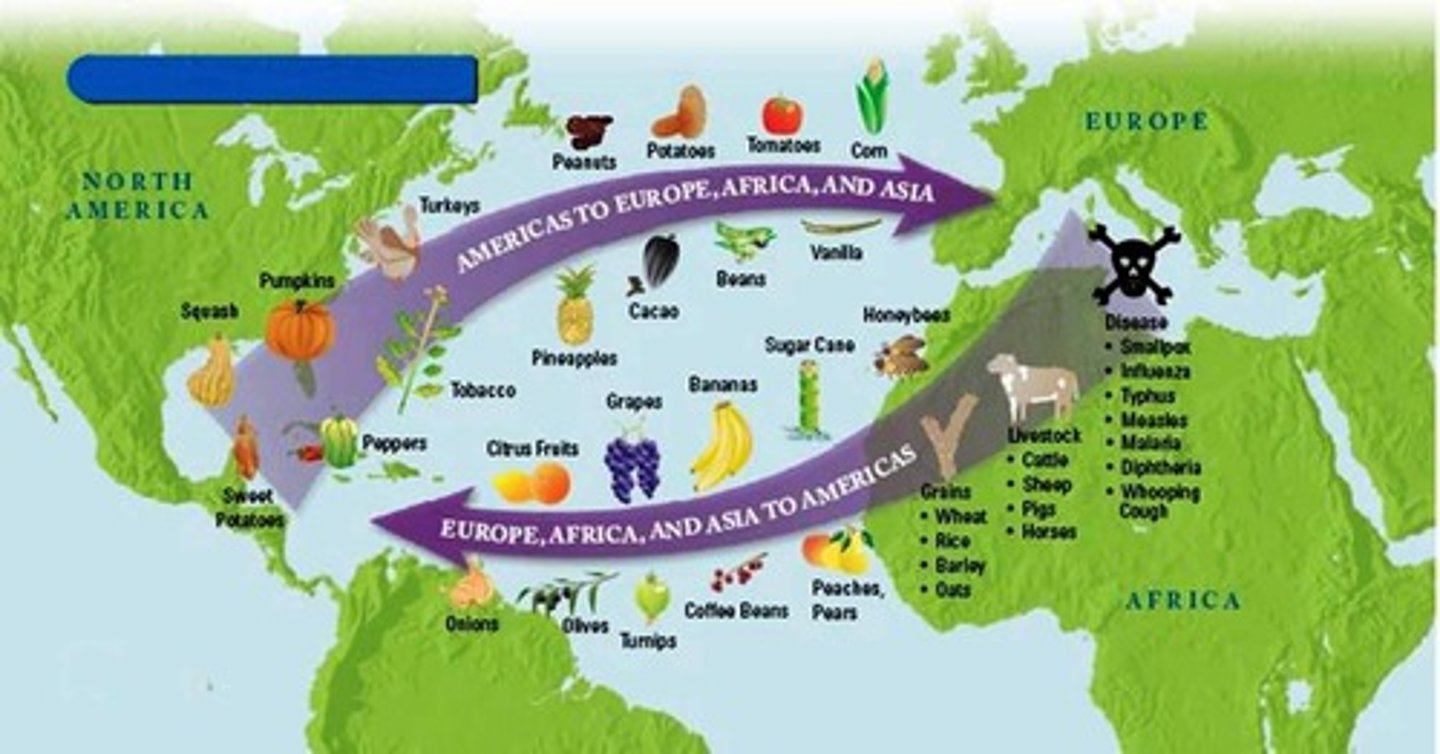
Smallpox
A highly contagious viral disease characterized by fever, weakness, and skin eruption with pustules that form scabs; responsible for killing Native Americans.
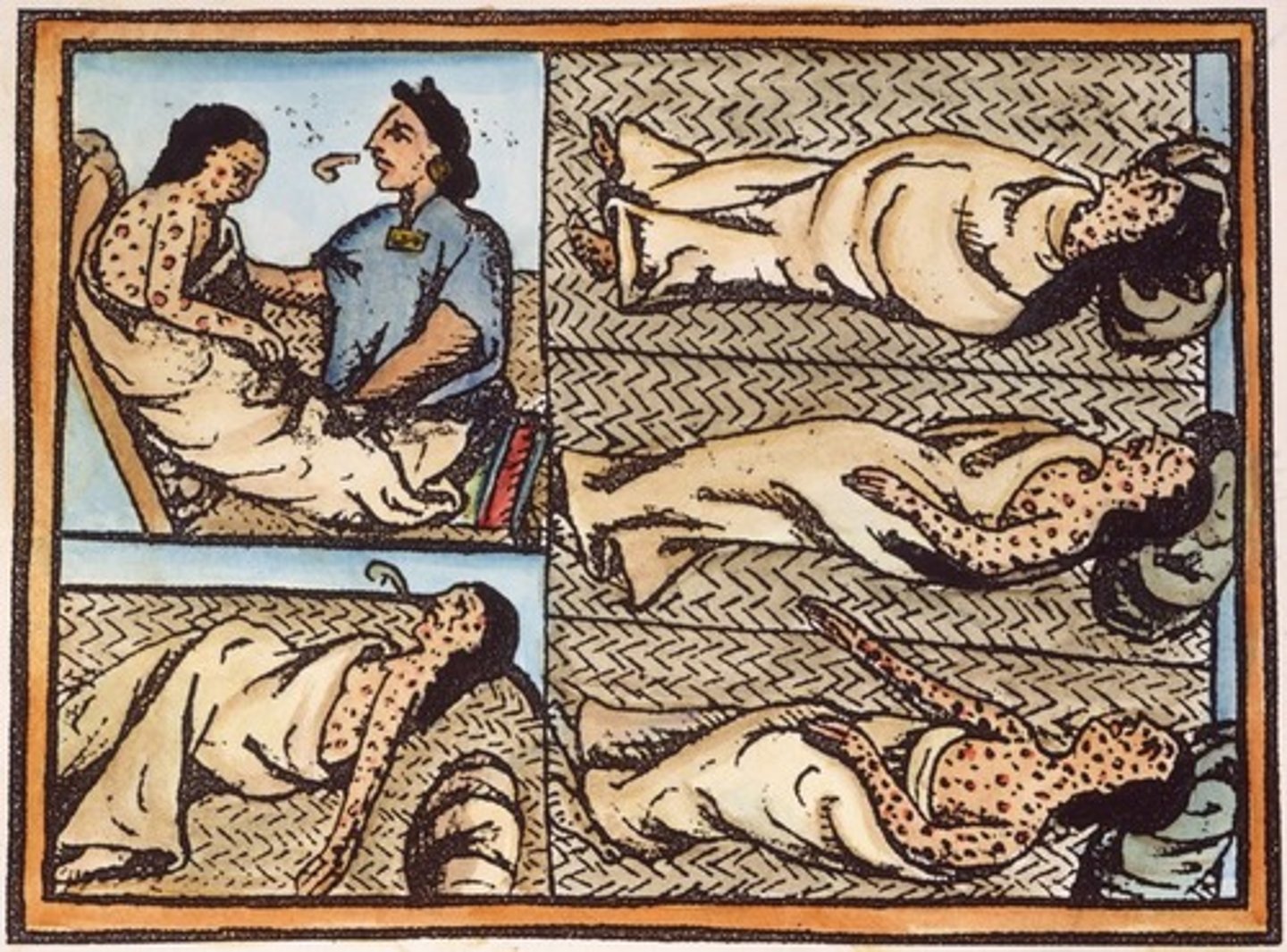
coercive labor
Any labor system that involves force (ex: slavery, serfdom, and encomienda)
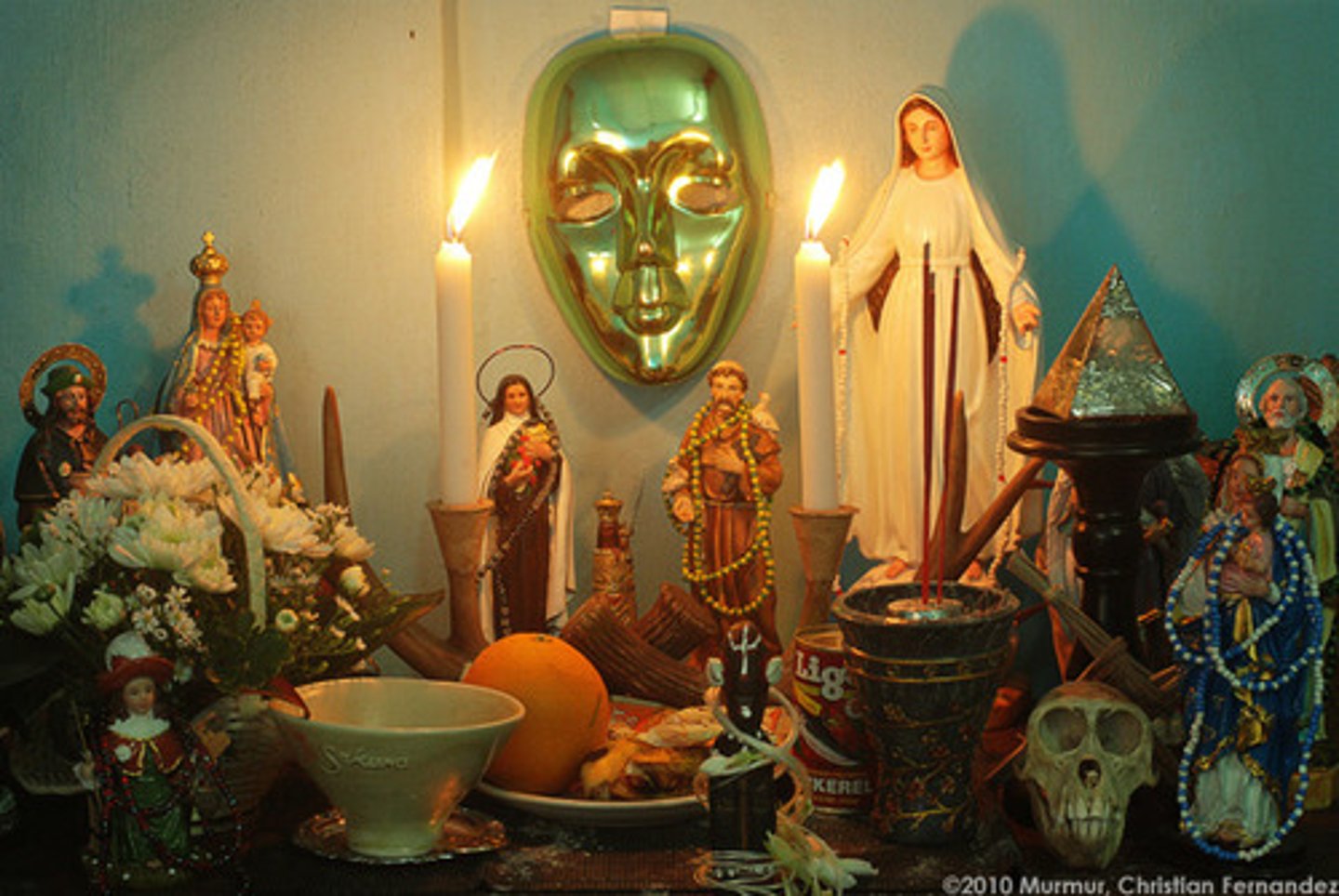
Voodoo
syncretic belief system that combines traditional African religious beliefs with elements of Christianity.
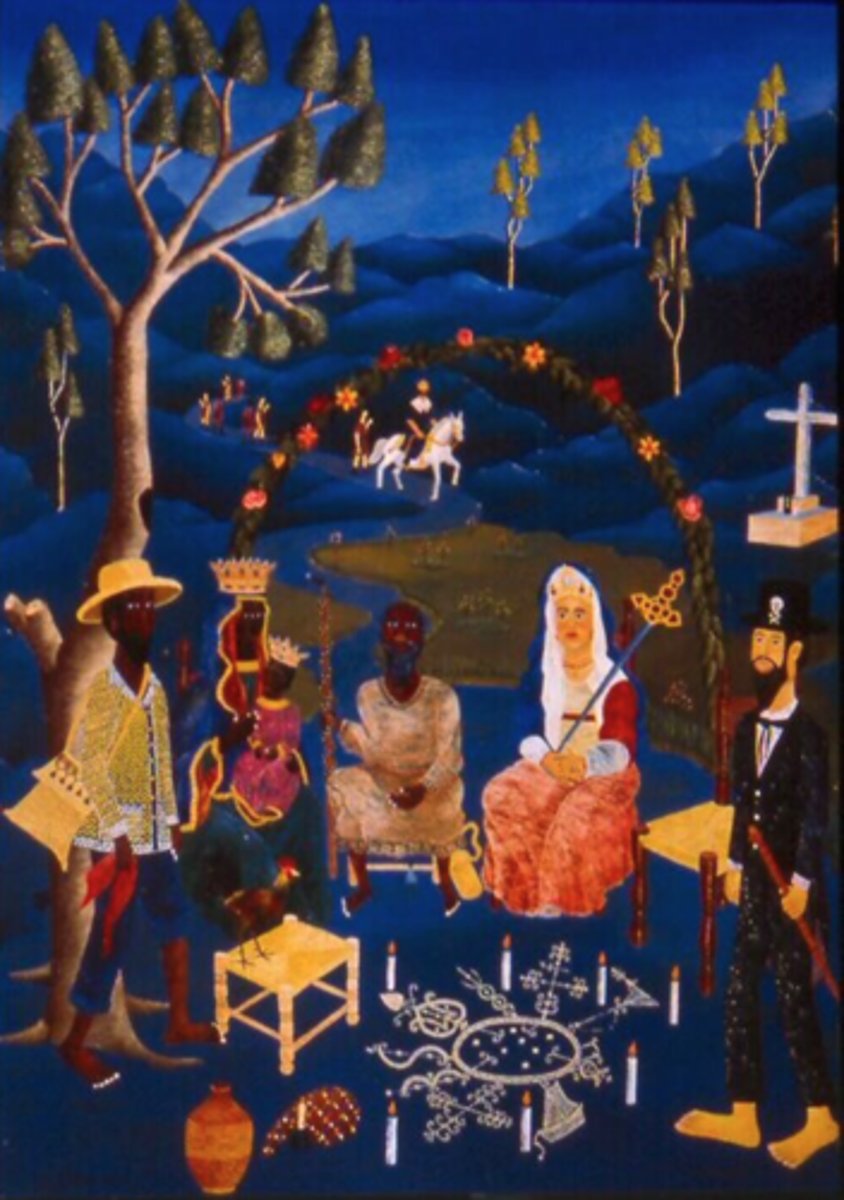

Santeria
Cuban religion that combines Catholic and West African beliefs
