Saunders NCLEX fundamentals exam with complete verified solutions ( VERIFIED FOR ACCURACY )
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
The nurse is performing a cardiovascular assessment and notes the presence of a blowing, swishing sound over the carotid artery. What should the nurse do?
Notify the physician of the abnormal finding of bruit which indicates blood flow turbulence.
Document the findings in the pt chart.
Describe a bruit. What does it indicate?
A low-pitched, "blowing," and swishing sound, indicating that an abnormal flow/blood flow turbulence exists. Can be heard on cardiac assessment.
Data that should be collected regarding the client's lifestyle includes:
alcohol, drug and tobacco use, sexual practices, tattoos, body piercings, travel history, and work setting.
When should the mental status exam take place?
while obtaining the subjective data from the client during the health hx interview.
What is assessed during a mental status assessment?
appearance: posture, dress, hygiene, movements
behavior: LOC, body language, facial expressions, speech pattern.
Cognitive level of functioning: recent memory, attention span, judgment.
What are the four types of health and physical assessments?
Complete: includes complete health hx and physical exam. Forms baseline database.
Focused: focuses on limited, short-term problem such as "cc"
Episodic/follow-up: evaluating a client's progress
Emergency: involves rapid collection of data often during a provision of life-saving measures.
Physical assessment uses auscultation, percussion, palpation and inspection. What orders are these done in? (except for abdominal assessments)
Inspection, palpation, percussion and auscultation
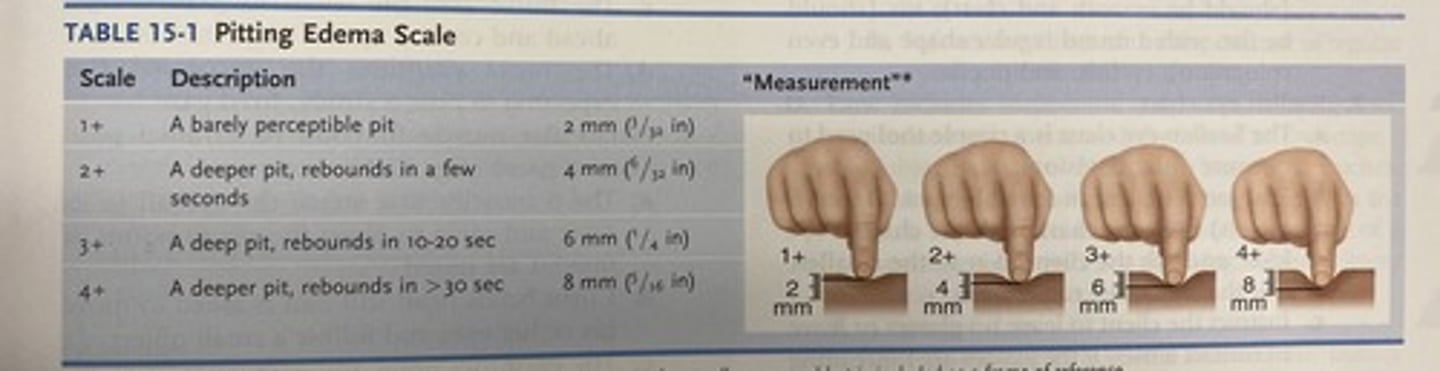
Pitting edema scale
1+ = barely perceptible pit- 2mm
2+ = a deeper pit, rebounds in a few seconds - 4mm
3+ = a deep pit, rebounds in 10-20 seconds - 6mm
4+ = deeper pit, rebounds in > 30 seconds - 8mm
When auscultating breath sounds, instruct the client to breathe through their ___________. Monitor the client for dizziness.
through the mouth.
When performing an abdominal assessment, the specific order is:
inspection, auscultation, percussion and palpation.
The nurse is performing a neurological assessment on a client and elicits a positive Romberg's sign. The nurse makes this determination based on which observation.
1. An involuntary rhythmic, rapid, twitching of the eyeballs.
2. A dorsiflexion of the ankle and great toe with fanning of the other toes
3. A significant sway when the client stands erect with feet together, arms at the side, and the eyes closed.
4. A lack of normal sense of position when the client is unable to return extended fingers to a point of reference.
A significant sway when the client stands erect with feet together, arms at the side, and eyes closed.
Describe Romberg's test
client is asked to stand w/ feet together and arms at the sides, and to close the eyes and hold the position. normally the client can maintain posture and balance. Positive Romberg's sign is a vestibular neurological sign that is found when a client exhibits a loss of balance when closing the eyes.
The nurse notes documentation that a client is exhibiting Cheyne-Strokes respirations. On assessment of the client, the nurse should expect to note which finding?
1. Rhythmic respirations with periods of apnea
2. Regular rapid and deep, sustained respirations
3. Totally irregular respirations in rhythm and depth
4. Irregular respirations with pauses at the end of inspiration and expiration.
Rhythmic respirations with periods of apnea.
A client diagnosed with conductive hearing loss asks the nurse to explain the cause of the hearing problem. The nurse plans to explain to the client that this condition is caused by which problem?
1. A defect in the the cochlea
2. A defect in cranial nerve VIII
3. A physical obstruction to the transmission of sound waves
4. A defect in the sensory fibers that lead to the cerebral cortex.
A physical obstruction to the transmission of sound waves.
- Conductive hearing loss occurs as a result of a physical obstruction to the transmission of sound waves.
Tip: the word conductive has a relationship to transmission therefore look for an answer with transmission in it.
While performing a cardiac assessment on a client with an incompetent heart valve, the nurse auscultates a murmur. The nurse documents the finding and describes the sound as which?
1. Lub-dub sounds
2. Scratch, leathery heart noise
3. A blowing or swooshing noise
4. Abrupt, high-pitched snapping noise
A blowing, swooshing noise.
Heart murmur: abnml heart sound described as a faint or loud blowing, swooshing sound w/ a high, medium or low pitch.
Pericardial friction rub is described as:
scratchy, grating, leathery heart sound
Click sound is described as
abrupt, high-pitched snapping sound
The nurse is testing the extraocular movement in a client to assess for muscle weakness in the eyes. The nurse should implement which assessment technique to assess for muscle weakness in the eye?
1. Test the corneal reflexes
2. Test the 6 cardinal positions of gaze.
3. Test visual acuity, using a Snellen eye chart.
4. Test sensory function by asking the client to close the eyes and then lightly touching the forehead, cheeks and chin.
Test the 6 cardinal positions of gaze is done to assess for muscle weakness in the eyes. Client is asked to hold head steady, follow the movement of an object through the positions of gaze.
Snellel eye chart assesses?
visual acuity and cranial nerve II (optic).
How does nurse test sensory function of eyes?
client closes eyes then lightly touching areas of the face and testing the corneal reflexes, assess cranial nerve V (trigeminal.)
The nurse is instructing a pt how to perform a testicular self examination. The nurse should explain that the best time to perform this is?
After a shower or bath when the hands are warm and soapy and the scrotum is warm. Perform while standing and at the same time monthly.
The nurse is assessing a client for meningeal irritation and elicits a positive Brudzinki's sign. What finding would the nurse observe?
Client passively flexes the hip and knee in response to neck flexion and reports pain in vertebral column.
Test tip: positive Brudzinki's sign = pain for pt. It involves passive flexing of hip in response to neck flexion.
In the event of a fire, what does RACE stand for?
Rescue client in immediate danger
Activate alarm
Confine the fire (close doors)
Extinguish
If a patient ingests poison, housecleaners, grease or other household harmful material, what should the nurse do first?
Call poison control before attempting an intervention