Periodic classification
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chemistry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
mnemonic of f block actinoid
thapa u nappu
aam kam bikay
cafe aise farmao madam nashtha lao
Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr
atomic number of starting and ending of
d block
f block
p block

C

C

A
Number of electrons filled in 4th period
number of electrons that can be filled in 4th shell
number of electrons or elements in given period= 2,8,8,18,18,32,32
number of electrons in a shell= 2n²
general electronic configuration of d block
ns0-2 n-1d1-10
general electronic configuration of p block
ns2 np1-6

D
diagonal relation dekhte time Be, Boron carbon ko ek saath lo, d block beech me mat lo
In nomenclature of elements after 100, suffixes used are for numbers
everything same just remember quad for four and sept for seven
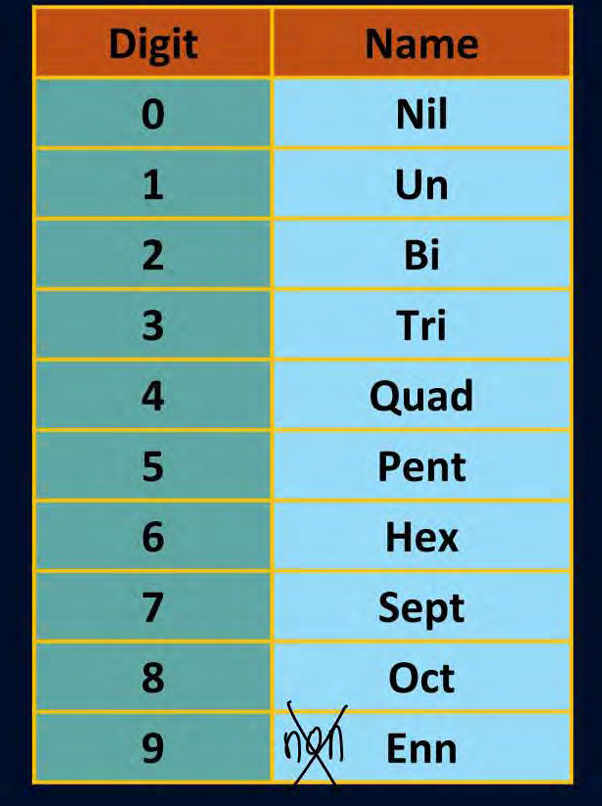
pnemonic for elements after 100
Modi ka number lahore ke refugee ne dubai sea ke bahar
has mat das rang ka konsa nhi flower
mc lover tussi ogod
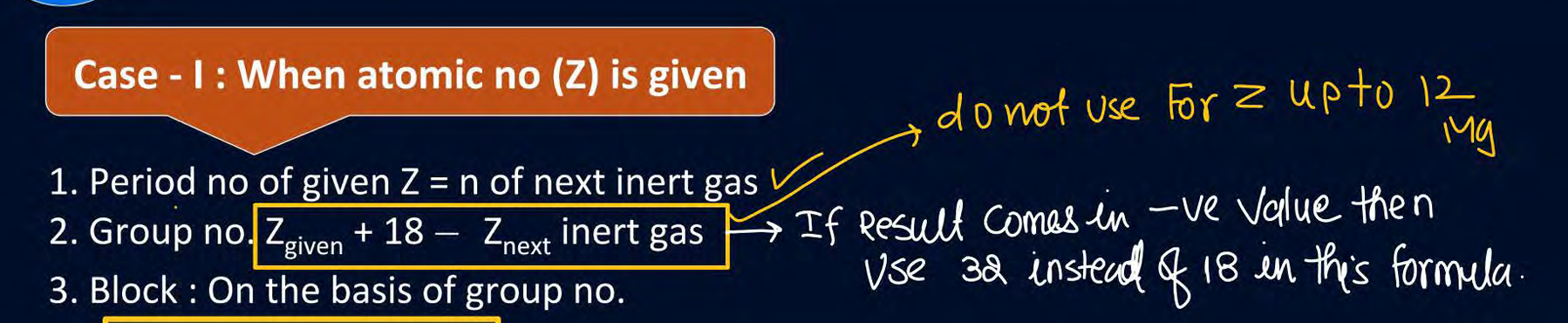
how to find group number of actinoids, lanthanoids and atomic numbers after 104

How to find group number after atomic number Z=12
why position of helium in p block is justified
Strictly helium belongs in the s block but its position in p block is valid because it has completely filled valence shell ns² and as a result exhibit characteristic properties of noble gases
Why hydrogen is placed separately at the top of periodic table
Because it has one electron it can be placed in group 1 but it can also gain an electron to achieve noble gas configuration and act as halogen so can be placed in group 17. So it is placed separately
how metallic character and reactivity changes down the group in s block.
metallic character and reactivity increases down the group in s block
reactivity is high thats why s block is never found in pure form in nature
what are the exceptions of s block compounds which are predominantly ionic
s block element compounds are predominantly ionic except lithium and berilium
Metals or non metals which are liquid at slightly high temp or room temp
Cs and Ga are liquids at slightly high temp
Hg is liquid at room temp
non metal bromine is liquid at room temp
exceptions of s block elements
hydrogen and helium

A
A
dobereiner triad method and examples
said that atomic weight of middle element is the arithmetic mean of other two elements
examples
Li Na K
Cl Br I
Ca Sr Ba
Who was first scientist who related properties of elements with atomic mass
Newlands law of octaves
what was newlands law of octaves and why did it fail
if we arrange elements in acc to atomic mass then every 8th element will have same property as 1st element
it was only valid upto calcium and failed after discovery of inert gas
mendeleevs periodic law statement and drawbacks
It stated that physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic masses
drawbacks
no place for isotopes
no separate place for hydrogen
in some places, element having higher atomic mass was placed before lower atomic mass
moseleys experiment benefits
It challenged mendeleevs periodic law
and basis of modern periodic table
what was moseleys experiment
He bombarded electrons on metal surfaces and obtained x rays
he observes that the frequency of x rays was in relation with atomic number of metal used
root of frequency= a(Z-b) a and b are constant. So root of frequency is proportional to atomic number Z
exception in alkaline earth metals
Beryllium is not included in alkaline earth metals
because it does not form alkaline hydroxide or oxide, its oxide is amphoteric
What are transurenic or transurenium elements
elements after atomic number 92 uranium
they are man made synthetic and not known in nature
what are representative or main group elements
elements of s and p block
what is period number of 1s²2s²2p63s²3p64s²3d104p64d10
acc to electronic configuration 4th period
but it is in 5th period
it is palladium
atomic no. 46
penetration effect and shielding effect order
s>p>d>f
across a period, effective nuclear charge
increases

D
successive ionisation enthalpy increase


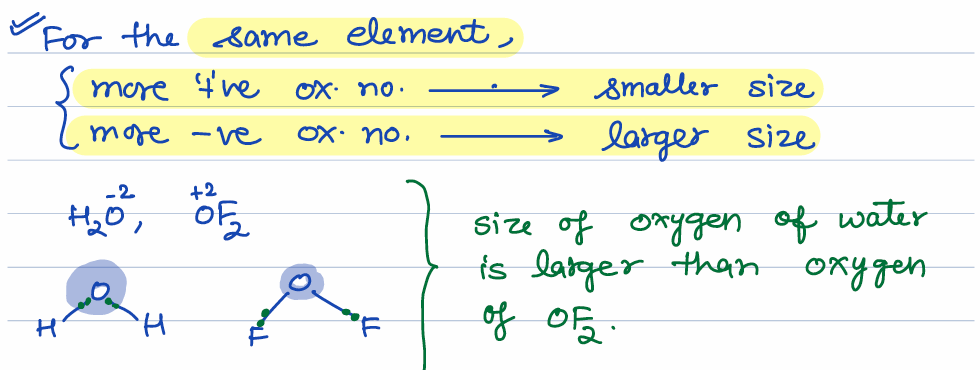
for same element, order of vanderwall, covalent and metallic radius
Vanderwall> metallic> covalent
VMC
vanderwall almost double of covalent
Trend in size for elements in s block
E banao aur N banao
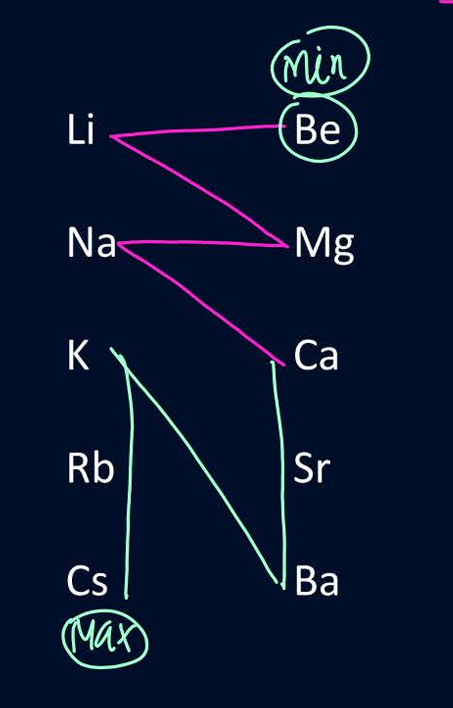
atomic size order for cations in s block
everything same like normal except Li>Mg
Li+ greater or equal to Mg2+ in cationic form
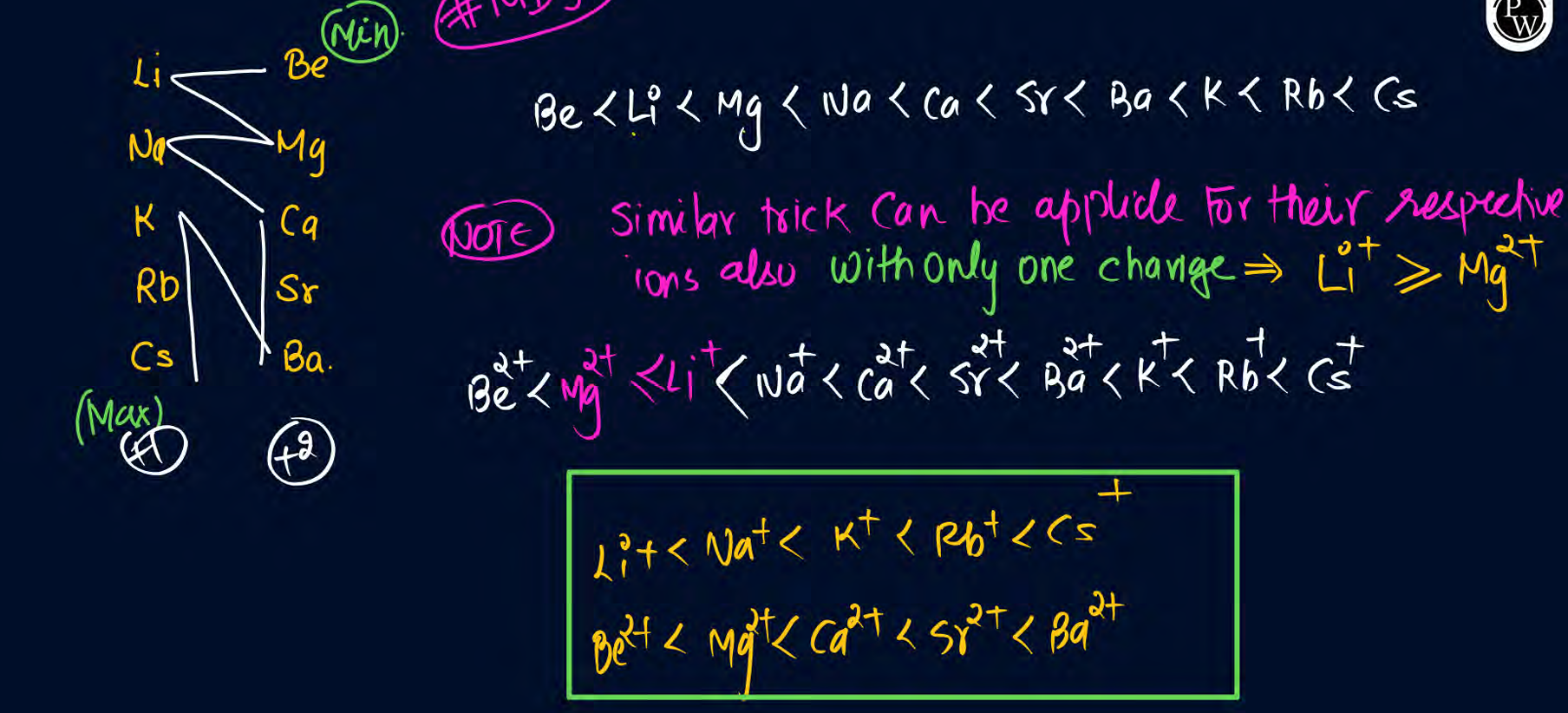
size order in p block
in 13th group B<Ga<Al<In<Tl
Al>Ga because of transition contraction
rest groups are normal khushiyon ka pitara
how does size of element depend on oxidation number
size of oxygen in water and OF2 is not same because of oxidation number
-ve oxidation number means larger atom
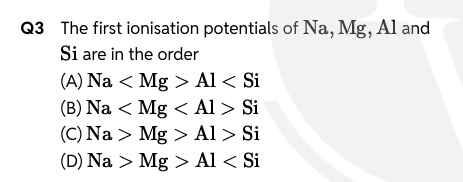
A

D
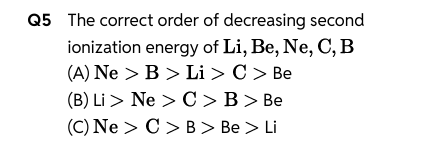
Neon (Ne):
Has the highest second ionization energy because its first ionization energy is to remove an electron from its outermost shell, making it much higher than the first ionization energy of the other elements, and removing a second electron is extremely difficult.
Lithium (Li):
Has the lowest second ionization energy because after losing its single valence electron, it achieves a noble gas configuration, making it very easy to remove a second core electron.