APES U6 Review - Energy Resources and Consumption
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Explain how coal is obtained from the environment.

Coal
a solid fuel formed primarily from the remains of trees, ferns, and other plant materials that were preserved 280 to 360 million years ago.
→ Typically used for electricity generation and industrial processes, and can be found in many forms
→ Forms ONLY through organic matter becoming buried quickly.
4 Kinds of Coal
Peat, Lignite, Bituminous, Anthracite
Peat
partly-decomposed organic material, like mosses.
Lignite (brown coal)
soft sedimentary rock with traces of plant structure (60-70% carbon).
Bituminous (asphalt)
black or dark brown coal that has bitumen.
Dirtier → have sufficient amounts left.
Anthracite (hard coal)
contains greater than 90% carbon, the highest energy per volume.
Cleaner → running out
How is coal obtained?
mining
- Subsurface mining
Miners dig tunnels to reach coal deposits that are deeper underground.
- Surface mining
Coal that is close to the Earth's surface is extracted by removing soil and rock above it.
→ Once mined, coal is processed, transported, and then burned mainly in power plants to produce electricity.
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of coal as an energy source.

Advantages of Coal
Energy-Dense and Plentiful
→ EROEI really high*
Provides heat to industrial processes and electricity generation
Mining cost is low
Easy to move
LOTS OF COAL LEFT*
Disadvantages of Coal
Tailings have environmental consequences
→ mining
Subsurface mining is expensive and dangerous
Impurities of coal can be harmful: sulfur, Hg, Pb, As
→ Nurotoxins
Pollutants like sulfur dioxide and particulates are emitted by combustion.
→ Combustion
Carbon in coal is converted into CO2
→ Contributes to climate change
Explain how petroleum is obtained from the environment.

Crude Oil
a mixture of hydrocarbons such as oil, gasoline, kerosene, as well as water and sulfur that exists in a liquid state underground, and when brought to the surface.
Petroleum
a nonrenewable fossil fuel formed from the remains of ancient marine organisms that were buried under heat and pressure over millions of years
→ Used for fuels like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel.
How is Petroleum obtained?
Crude oil/petroleum is formed from ocean-dwelling phytoplankton (microscopic algae).
Oil is found in porous rock covered by non-porous rocks.
Extracted by drilling wells on land or offshore
Oil is pumped to the surface using natural pressure or mechanical pumps
Transported by pipelines, ships, or trucks to refineries for processing
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of oil as an energy source.

Advantages of Petroleum (oil)
- Liquid form is easy to transport and use
- Energy-dense
- Cleaner than burning coal
- Ideal for mobile combustion engines
- Produces only 85% as much CO2 as coal.
Disadvantages of Petroleum (oil)
- Also contains sulfur and other trace metals
- Oil may leak into the ground or the ocean when extracted
- Tankers and pipelines may break/spill
- Habitats can be destroyed to mine for oil or to create pipelines to transport it.
→ Ex. Alaska National Wildlife Refuge is near known oil reserves
- Oil flaring - Burning off excess natural gas
→ Can lead to air pollution
→ Still emits CO2
Explain how natural gas is obtained from the environment.
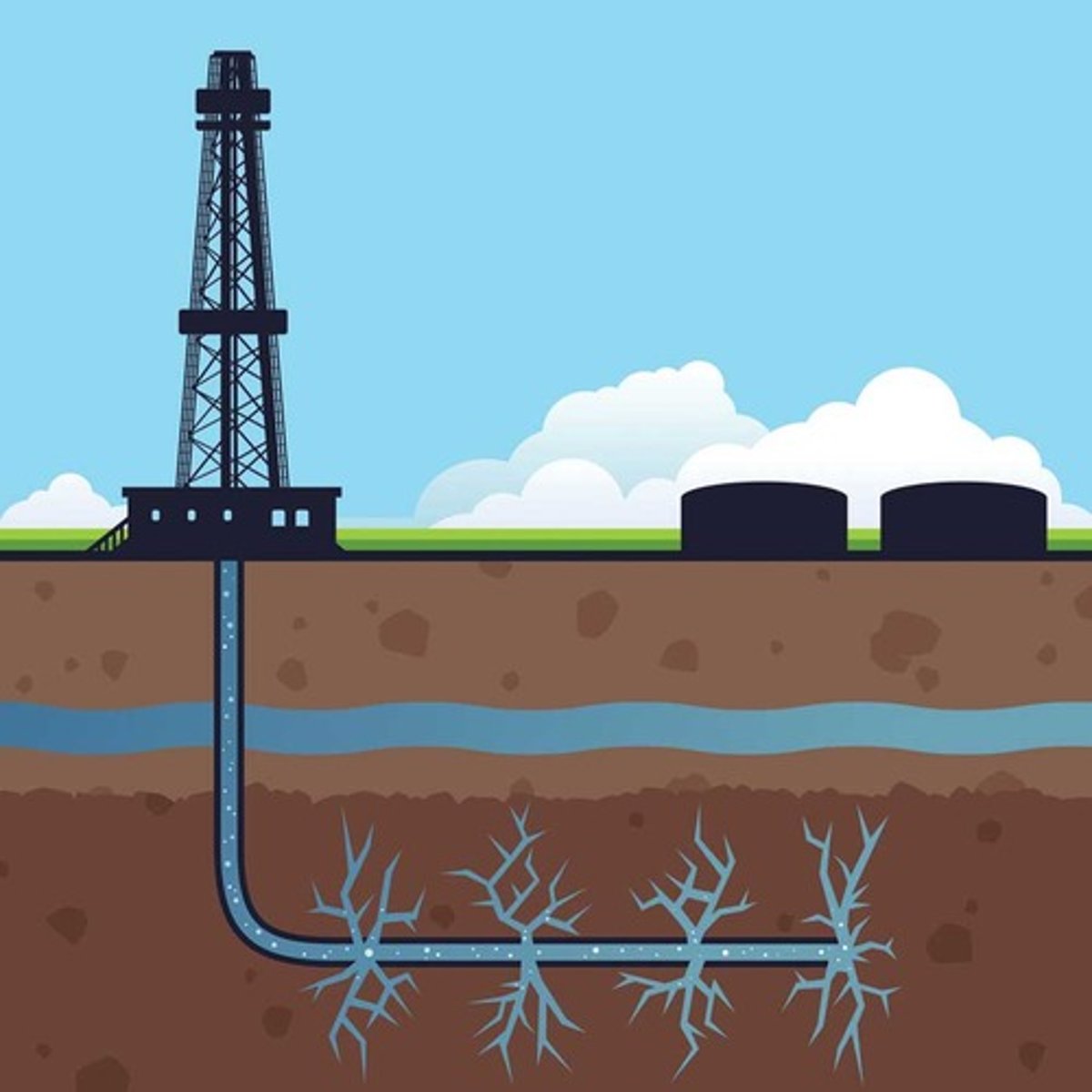
Fracking
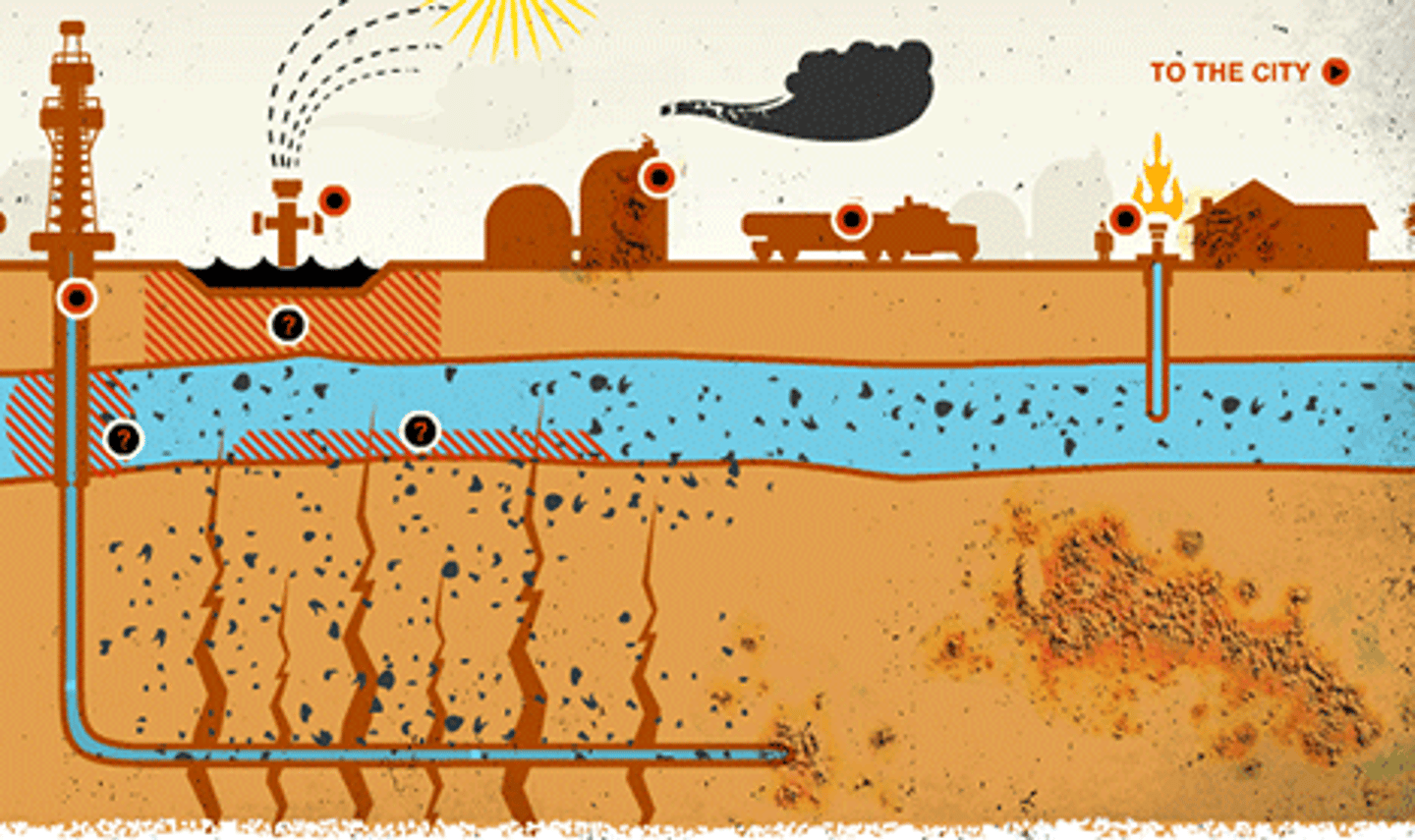

Fracking
short for hydraulic fracturing, a method of oil and gas extraction that uses high-pressure fluids to force open existing cracks in rocks deep underground.
Natural Gas
relatively clean fossil fuel containing 80-95% methane (CH4) and 5-20% ethane, propane, and butane.
- Can be compressed and liquified for transport
- Natural gas comprises of 24% of total energy consumption globally
- Some natural gas is burned to prevent an explosion
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
a type of organic compound air pollutants that evaporate at typical atmospheric temperatures.
→ enter the gas phase easily
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of natural gas as an energy source.
Advantages of Natural Gas
- Extensive gas pipeline system is already in place
- Fewer impurities than coal and oil
- Almost zero amounts of sulfur dioxide and particulates are released.*
- Only released about 60% as much CO2 as coal*
- Can be liquified to provide fuel for homes and businesses.
Disadvantages of Natural Gas
- Unburned natural gas (methane) can be released and is 25x more potent than CO2
- Extraction leads to large extraction fields, destroying the habitat
- Hydraulic fracturing (fracking) can contaminate the water table
→ Water is contaminated instead of being used for homes and businesses
- Fracking releases volatile organic compounds, which evaporate quickly at atmospheric temperatures
Explain the process of nuclear fission of U-235 atoms and the role of control rods in a nuclear reactor.
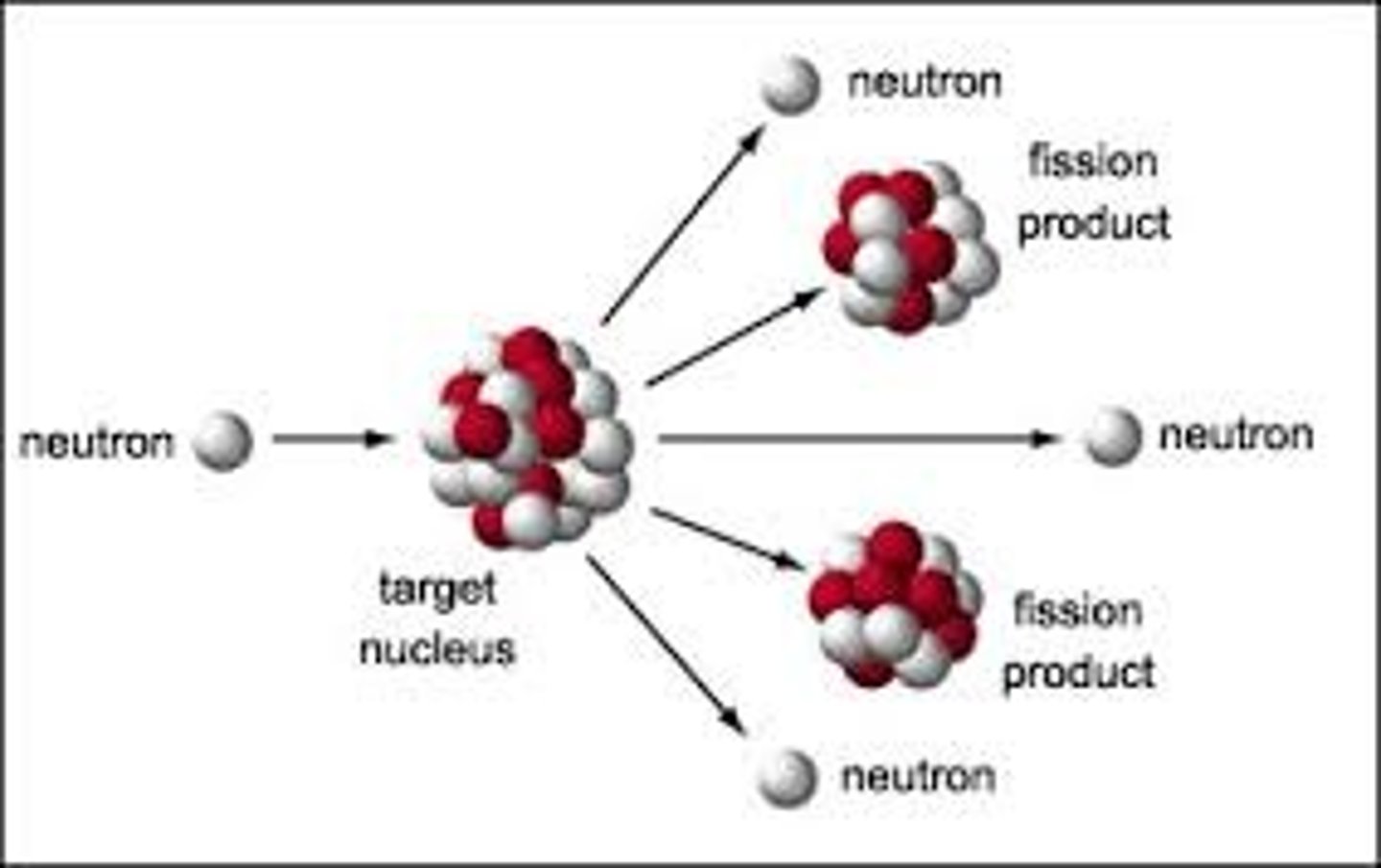
Nuclear Power
electricity generated from the nuclear energy contained in nuclear fuel.
Radioactive
The emission of ionizing radiation or particles caused by the spontaneous disintegration of atomic nuclei → UNSTABLE
→ Energy is harnessed from nuclear fuel by causing a fission reaction.
Fission
a nuclear reaction in which a neutron strikes a relatively large atomic nucleus, which then splits into two or more parts, releasing additional neutrons and energy in the form of heat.
Fuel Rods
a cylindrical tube that encloses nuclear fuel within a nuclear reactor
Control Rods
a cylindrical device inserted between the fuel rods in a nuclear reactor to absorb excess neutrons and slow down or stop the fission reaction.
→ Prevents overheating and keeps the reactor safe and stable*
Radioactive Decay
When a radioactive parent isotope emits alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays.
Half-life
The time it takes for one-half of the original radioactive parent atoms to decay.
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of nuclear power as an energy source.
Advantages of Nuclear Power
- No air pollution produced
- Allows for energy independence if fossil fuels are scarce for countries
- Little to no greenhouse gases are produced by power plants.
- Statistically, the safest form of energy production.
Disadvantages of Nuclear Power
- Expensive to build a power plant.
- Uncertainty of nuclear waste and storage of waste
- Security concerns of having nuclear waste
- Greenhouse gases produced by mining and construction
- The possibility of dangerous nuclear accidents
NIMBY**
Not In My Back Yard
People don't want nuclear power plants anywhere near them
Emotionally → dangerous
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of biomass (e.g., wood, charcoal, animal dung, ethanol, biodiesel...) as an energy source.
Biomass
a renewable energy source made from living or recently living organic material, such as plants and animal waste, used to produce heat, electricity, or fuel.
Biofuel
liquid fuel created from processed or refined biomass (ex. biodiesel and ethanol)
Ethanol
alcohol made by converting starches and sugars from plant material into alcohol and CO2
→ Can cause food shortages from using crops like corn and sugarcane
→ Made from coal
→ Doesn't release fossil carbon
→ US is the leading producer
When used as a fuel → efficiency is reduced → needs to refuel more frequently.
Biodiesel
a diesel substitute produced by extracting and chemically altering oil from plants.
→ Direct substitute for petroleum-based diesel
→ Made from: soybean oil, vegetable oil, and algae
→ Can emit carbon monoxide
→Takes more land to grow soybeans than corn (ethanol)
→ Can be carbon neutral → doesn't use fossil fuels
Advantages of Biomass
- Renewable
- Reduces waste: Uses agricultural, animal, and food waste
- Reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels
Disadvantages of Biomass
- Air pollution: Burning biomass releases particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and other pollutants
→ Major air pollutants
- Deforestation: Overharvesting wood can destroy forests and habitats
- Lower energy density: Produces less energy per unit than fossil fuels
Wood and Charcoal drawback
Major Air Pollutants
Particulates/Particulate Matter
Solid/liquid particles suspended in the air (soot)
Carbon Monoxide
A colorless, odorless gas that is formed during the incomplete combustion of most minerals
Nitrogen Oxides
A by-product of the combustion of any fuel in the atmosphere
→ contains 75% nitrogen
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) - air particulate
Organic Compound that evaporates easily
Carbon Dioxide
Byproduct of all combustion, modern carbon from woody material
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of solar energy, including passive solar, photovoltaic panels, and concentrated solar farms.

Solar Energy
renewable energy that comes from sunlight and is converted into usable heat or electricity.
Passive Solar
a use of energy from the sun that takes advantage of solar radiation without active technology
→ energy can't be stored
→ south-facing windows.
Advantages of Passive Solar
- Uses building design (south-facing windows, materials that absorb heat)
- No fuel or moving parts
- Reduces heating and lighting needs
Disadvantages of Solar Passive
- Depends on building location and design
- Less effective in cloudy or cold climates
Active Solar Energy
a use of technology that captures and stores the energy of sunlight with electrical equipment and devices.
→ Can provide: domestic warm water, heated swimming pools, and heated homes.
Photovoltaic Solar Cells (solar panels)
a use of energy from the sun as light, not heat, and converting it directly into electricity.
Advantages of Photovoltaic Systems
- Convert sunlight directly into electricity
- Renewable and produces no air pollution during operation
Disadvantages of Photovoltaic Systems
- High upfront installation cost
- Energy production depends on sunlight and weather*
- Not aesthetically pleasing
Concentrated Solar Farms
Large-scale solar power systems that use mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight onto a small area, producing intense heat that is used to create steam and spin turbines to generate electricity.
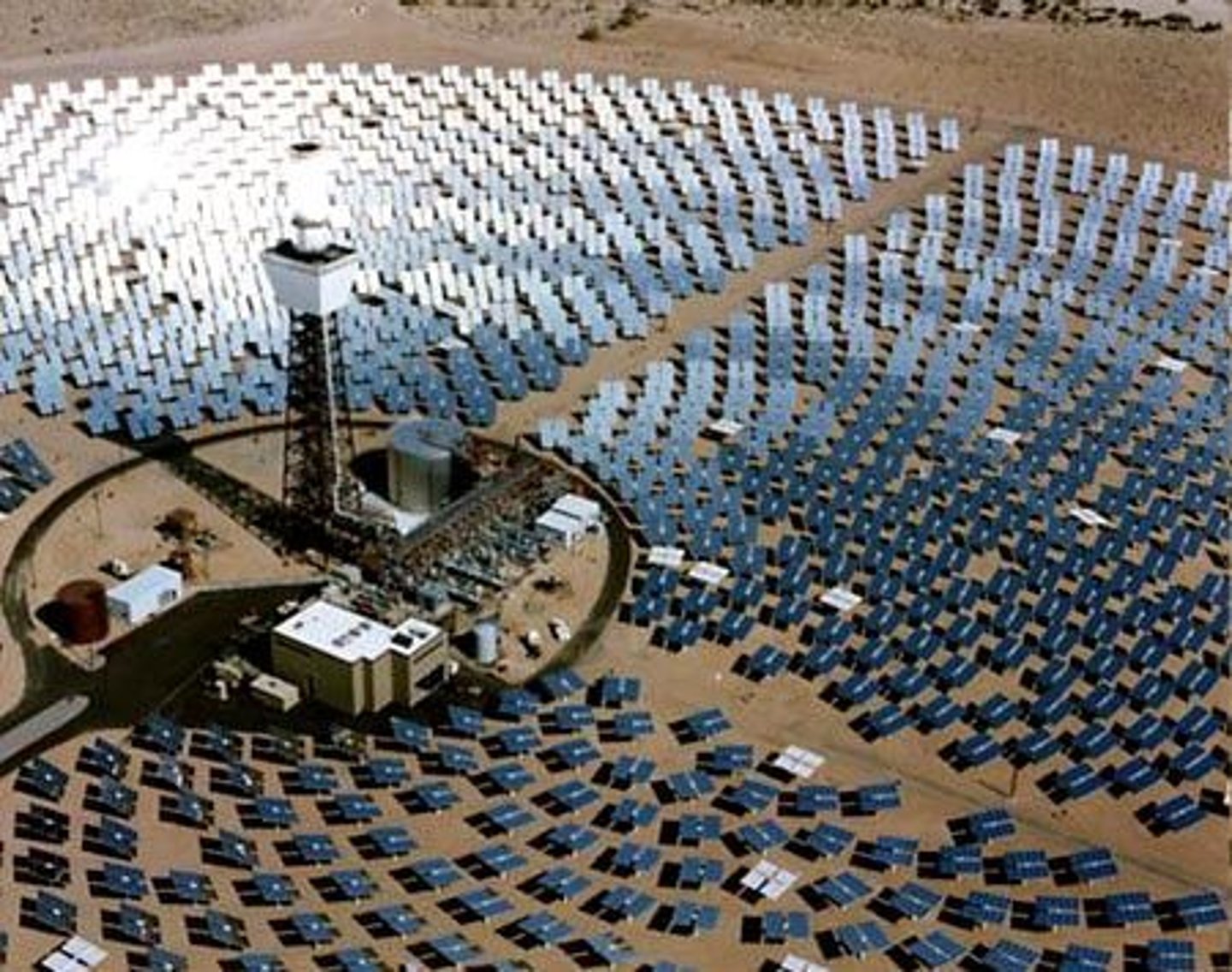

Advantages of Concentrated Solar Farms
Use mirrors to focus sunlight and produce large amounts of electricity
- Produces little air pollution
- Can store heat for energy production after sunset
Disadvantages of Concentrated Solar Farms
- Expensive to build
- Requires large amounts of land
- Best suited for sunny, desert regions
- Can impact wildlife and local ecosystems
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of hydroelectric power as an energy source.

Hydroelectricity
electricity generated by the kinetic energy of moving water.
Water Impoundment Systems (dams)
the storage of water in a reservoir behind a dam.
Run-of-the-River Systems
hydroelectricity generation in which water is retained behind a low, small dam or no dam.
Tidal energy
energy that comes from the movement of water driven by the gravitational pull of the Moon.
Advantages of Hydroelectricity
- A renewable energy source powered by the water cycle
- Produces little to no air pollution
- Reservoirs can provide flood control and water storage
- Highest EROEI**
Disadvantages of Hydroelectricity
- Building dams is expensive
- Floods land, destroying habitats and displacing people
- Disrupts fish migration and aquatic ecosystems
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of geothermal as an energy source.

Geothermal Energy
heat that comes from the natural radioactive decay of elements deep within the Earth.
In what areas of the US is geothermal energy most effective?
Western states have more geothermal energy because they are located near tectonic plate boundaries and hotspots, where magma is closest to the Earth's surface.
Ground Source Heat Pumps
a technology that transfers heat from the ground to a building.
→Highly efficient process*
→ very low greenhouse gas emissions*
Advantages of Geothermal Energy
- Renewable and sustainable
- Produces very low greenhouse gas emissions
- Reliable, constant energy source (baseload power)
Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy
- Limited to regions with geothermal activity
- High upfront costs for drilling and infrastructure
- Risk of land subsidence or induced earthquakes
Fuel Cell
an electrical-chemical device that converts fuel, such as hydrogen, into an electrical current.
Drawbacks of a fuel cell
Energy is required for electrolysis, and hydrogen is dangerous to transport
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of wind turbines as an energy source.

Wind Energy
energy generated from the kinetic energy of moving air.
→ Denmark generates 47% of its electricity from wind.
Wind Turbines
a turbine that converts the kinetic energy of moving air into electricity.
→ Installed in rural areas near electrical transmission lines
Advantages of Wind Energy
- Nondepletable
- No pollutants from energy generation
- Once manufactured and installed, no/low cost
- Land can be shared with other uses
Disadvantages of Wind Energy
- Batteries are needed if turbines are off-grid
- Birds and bats are killed by collisions with turbines
- Visually unappealing (big, ugly)
- Sounds from turbines are bothersome
- High installation costs
Explain the concept of EROEI and how this impacts the viability of an energy source.

Energy Conservation
methods for finding and implementing ways to use less energy.
Energy Efficiency
the ratio of the amount of energy expended in the form you want to the total amount of energy that is introduced into the system.
Energy Return on Energy Investment (EROEI)
the amount of energy we get out of an energy source for each unit of energy expended (used) on its production.

What is considered a good/bad EROEI ratio?
1:1 → Not good (produced : invested)
3:1 → Good/viable (produced : invested)
want AT LEAST a 3:1 ratio; (produced : invested)
How high EROEI impacts energy viability
- Produces much more energy than it consumes
- More efficient and economically viable
- Supports large-scale energy needs (ex. oil in the past, hydropower)
How low EROEI impacts energy viability
- Produces little net energy
- Requires more resources, money, and infrastructure
- Less sustainable long-term (ex. tar sands, some biofuels)
Why EROEI matters
- Determines whether an energy source is worth using
- Impacts energy cost and availability
- Low EROEI sources leave less energy for society (transportation, food production, healthcare)
- Helps compare renewable vs. nonrenewable energy options
How can we conserve energy?
- Turn off the lights
- unplug appliances
- Reduce hot water usage (shorter showers)
- Switch to electric/hybrid vehicles
- carpool
Phantom Loads
electrical demand that draws electrical currents even when it is turned off
ex. gaming systems, cable boxes, appliances, etc.