A&P - Chapter 1 McGrawHill
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Anatomy
Studies the form and structure of the body
Physiology
examines how the body functions
What is the scientific method
Systematic process where scientists
- examine natural events through observation
- develop a hypothesis for explaining a phenomenon
- experiment and test hypothesis by collecting data
- determine if the data supports the hypothesis or if the hypothesis should be rejected or modified
What are the four core steps to the Scientific Method
Observation
Hypothesis
Experiment
Conclusion
Microscopic Anatomy
- Examines structures that cannot be observed by unaided eye
- Specimens are examined under a microscope
What are the two divisions of Microscopic Anatomy?
Cytology and Histology
What is Cytology?
it's the study of body cells and their internal structure
What is Histology?
Study of tissues
What is Gross anatomy (macroscopic anatomy)
- investigates structures visible to the unaided eye
- normally specimens are dissected for examination
Divisions of Gross anatomy
-Systematic anatomy
-Regional anatomy
- Surface anatomy
- Comparative anatomy
- embryology
Definitions of Gross anatomy divisions
• Systemic anatomy: studies the anatomy of each body system
• Regional anatomy: examines the structures in a body region
• Surface anatomy: focuses on superficial anatomic markings and internal body structures
• Comparative anatomy: examines anatomical similarities and differences in different species
• Embryology studies: developmental changes from conception to birth
Divisons focusing on diagnosis or research
Pathologic Anatomy
Radiographic anatomy
Pathologic anatomy
examines macroscopic and microscopic anatomic changes resulting from disease
Radiographic anatomy
investigates internal structures visualized by scanning procedures
True of False: physiologists examine the function of body structures, focusing on molecular and cellular level?
True
Physiology Subdisciplines
- Cardiovascular physiology
- Neurophysiology
- Respiratory physiology
- Reproductive physiology
- Pathophysiology
Cardiovascular physiology
Examines the function of the heart, blood vessels, and blood
Neurophysiology
Studies functioning of nerves and nervous system organs
Respiratory Physiology
Explores functioning of respiratory organs
Reproductive Physiology
Investigates functioning of reproductive hormones and the reproductive cycle
Pathophysiology
Focuses on the function of a body system during disease or injury to the system
What is the relationship between anatomy and physiology?
form and function are interrelated
Which field of physiology examines how the heart, bloodvessels, and blood function?
Cardiovascular physiology
properties common to all organisms
Organization
Metabolism
Growth and Development
Responsiveness
Regulation
Reproduction
Anabolism
Small molecules joined to form larger ones
Catabolism
large molecules broken down into smaller ones
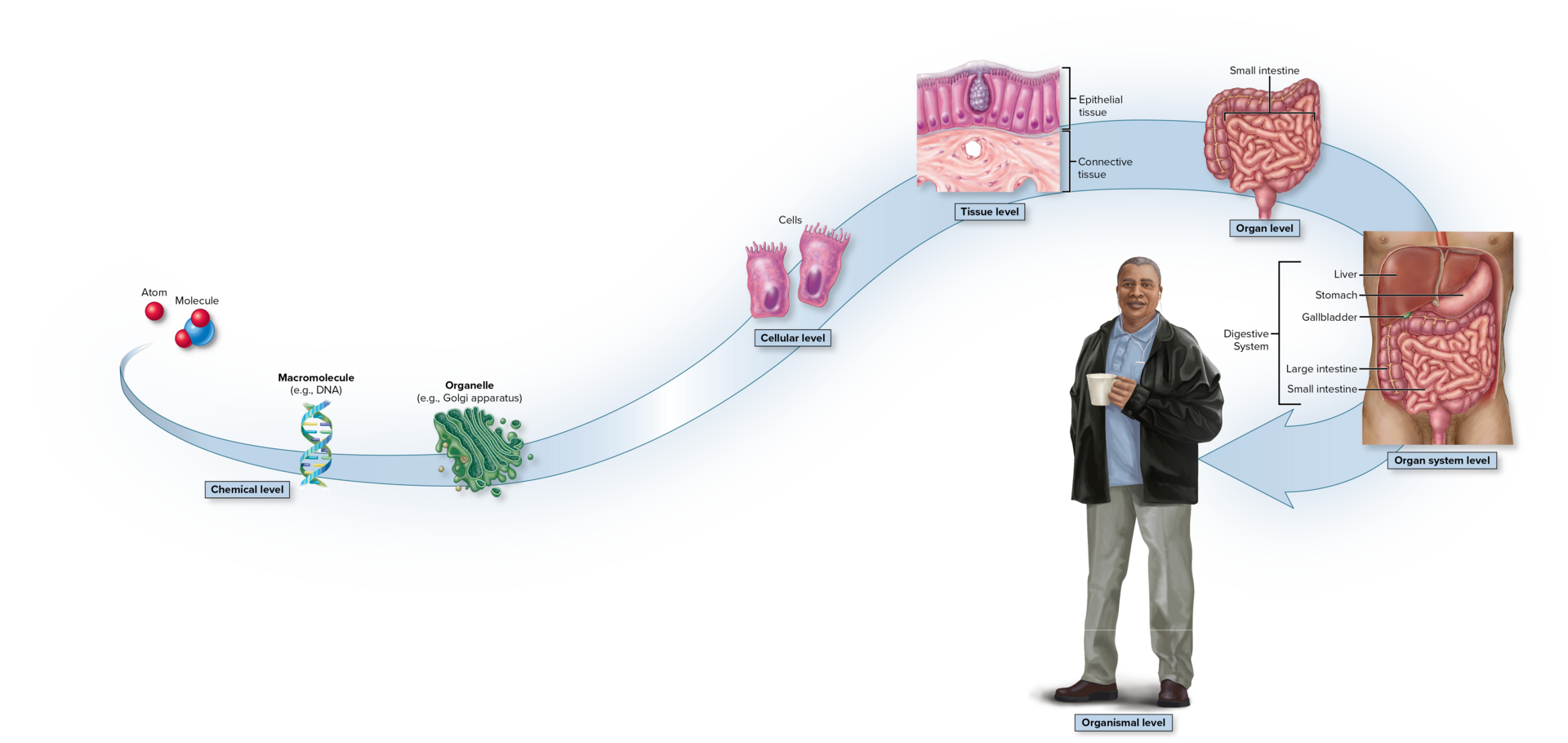
Levels of organization from simplest to most complex
Chemical Level - atoms. molecules, macromolecules
Cellular Level- cells, basic units of life
Tissue level- tissues, similar cells performing common function
Organ level- multiple tissues working together
Organ system Level- related organs work together
Organismal level- organ systems function together
Integumentary System
provides protection, prevents water lose and gain, regulates body temp
Skeletal System
Provides support and protection. Site of hematopoiesis (blood cell production), stores calcium, provides sites for ligament and muscle attachement