Physics- Mechanics + Electricity
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Speed Formula and units:
v=d/t,
v = speed (m/s)
d = change in distance (m) [final distance - initial distance]
t = change in time (s) [final time - start time]
Acceleration Formula and units:
a=v/t
a = acceleration (m/s²)
v = change in speed (m/s)
t = change in time (s)
Formula for net force and units
Fnet=ma
Fnet = net force (N)
m = mass (kg)
a = acceleration (m/s²)
Formula for weight force and units
Fweight=mg
w = weight force (N)
m = mass (kg)
g = acceleration due to the force of gravity (9.8m/s²) or 9.8Nkg-1
Formula for pressure and units
P=F/A
P = pressure (Pa) OR N/m²
F = force (N)
A = area (ms2)
Kinetic Energy formula and units
Ek= 1/2 x m x v2
m = mass (kg)
v = (speed (m/s)
Potential Energy formula and units
Ep= mgh
m = mass (kg)
g = acceleration due to gravity (ms-2)
h = change in height (m)
Work formula and units
W= Fd
W = work (J)
F = force (N)
d = displacement (m)d
Power formula and units
P = W/t or P= E/t
P = power (W)
W = work (J) OR N/m
t = seconds
E= energy (J)
What is scalar quantity
Only has a value (magnitude) associated with it - speed and distance
S for speed, speed measured in distance and time
What is vector quantity
Has a value (magnitude) and direction associated with it - velocity and displacement
V for velocity, velocity measured in displacment and time
Definition for Speed
the rate of change of distance, m/s
Defintion for Velocity
the rate of change of displacment, m/s
Definition for distance
the total ground covered by an object (m)
Definition for net force/resultant force
overall force acting on an object (N)
Definition for displacement
the change in position of an object or the shortest distance between the final and initial position (m)
Definition for constant speed
when an object travels the same distance every period of time (m/s)
Definition for acceleration
change of speed over time, m/s²
Definition for force
a push or pull that changes the direction, speed, or shape and has magnitude and direction (N)
Definition for mass
the amount of matter an object is made of, measured in kilograms (kg)
Definition for weight
The downward force caused by gravity acting on an object, measured in Newtons (N)
Definition for Density
how close together particles in a substance are g/cm³
Definition for contact force
force between two objects that are touching e.g. friction
Definition for non-contact forces
Force between two objects that are not touching e.g. gravity
Definition for balanced forces
Opposite forces that are equal of size
Definition for unbalanced forces
Opposite forces that are not equal of size
Definition for friction
Force that always act to oppose motion or attempted motion
Definition for drag and air resistance
Type of frictional force that acts opposite to the relative motion of an object moving through a fluid (could be liquid or gas). Air resistance is this through the air.
Definition for pressure
Measure of a force appiled to a particular area, measured in pascals (Pa), or in weird situations Newtons per square metre (N/m²)
Definition for work
The amount of energy transformed to move an object in the direction of the force, measured in joules (J)
Definition of Active Energy
Form of energy that causes the movement of either objects, particles, or waves.
Power Definition
The amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time, measured in watts (W)
Definition of Potential Energy
Form of stored energy that can be turned into active energy, e.x. gravitational potential energy
How to describe forces
-What force
-Unbalanced? Direction
-Net force
-Accelerating/Decelerating
What does a balanced force diagram mean
The object is stationary or is moving at a constant speed in the direction it is heading
What does an unbalanced force diagram mean?
The object is accelerating or decelerating in the direction of the arrow.
What are some examples of contact forces
Support, Thrust, Drag, Buoyancy, Tension, Lift
What are some examples of non-contact forces
Magnetic, Electrostatic, Gravitational Force/Weight Force
What is the advantages friction
It provides necessary traction because of more collisions with particles.
What are disadvantages of friction
It creates wear and tear and excess heat. It may also use too much fuel.
What is terminal velocity? Give explanation on how it works.
Air resistance occurs due to an object colliding with air particles, if the number of collisions increase, air resistance increases.
starts falling → small level of air friction, higher weight force → large net force in downward motion → speed increases downward
then speed increase (down) = air friction up increases
until air friction = weight force down →balanced forces = no net force = no acceleration → reached max velocity and falls at constant speed = TERMINAL VELOCITY (remains unless other elements are added)
What happens when a parachute is opened during terminal velocity?
when the parachute opens → surface area increases → increases air friction upwards → air friction no longer balanced with weight force → net force goes upwards moment parachute is deployed = acceleration in opposite direction to weight force → object slows
until air friction = weight force (no net force, no acceleration)→ once again terminal velocity (new), but falls at a slower constant speed
What does ━ mean on distance-time graphs
Stationary
What does ╱ mean on distance time graphs
Constant Speed (away from start)
What does ╲ mean on distance time graphs
Constant Speed (towards the start/ journey ended)
What does a steeper line mean?
Faster the speed
What does ╯ mean on a distance-time graph?
Positive Acceleration
What does ╮ mean on a distance-time graph?
Deceleration (Negative Acceleration)
What is ━ on a speed-time or velocity-time graph?
Constant Speed
What is ╱ on a speed-time or velocity-time graph?
Positive Acceleration
What is ╲ on a speed-time or velocity-time graph?
Deceleration (Negative Acceleration)
Where can you find the distance on a speed-time graph or displacement under a velocity-time graph.
The area under the graph.
What is Newton’s first law?
An object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion continues in the motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force.
What is Newton’s Second Law?
F=ma, or net force is equal to mass times acceleration. A larger net force acting on an object causes a larger acceleration, and objects with a larger mass require more force to accelerate.
What is Newton’s Third Law?
For every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction.
What is the “Law of Conservation of Energy”?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred (movement of energy from one location to another (same energy)) or transformed (when energy changes from one type to another).
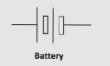
What does the circuit symbol for battery look like?
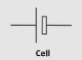
What does the circuit symbol for a single cell battery look like?
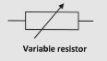
What does the circuit symbol for a variable resistor look like?
What does the circuit symbol for a bulb look like?
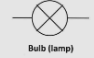
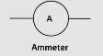
What does the circuit symbol of an ammeter look like?
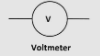
What does the circuit symbol of a voltmeter look like?
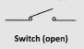
What does the circuit symbol of a switch (open) look like?
What does the circuit symbol of a thermistor look like?

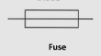
What does the circuit symbol of a fuse look like?
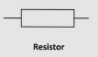
What does the circuit symbol of a resistor look like?
Why is that an object that has the same weight force and mass experience different accelerations when falling? ex. piece of paper vs scrunched up piece of paper
Even though weight force and mass is the same, there is less air resistance/drag force on scrunched paper, so the net force of the scrunched paper is greater towards the floor → acceleration is greater
What are the current-voltage laws
Series - Current = Same
Series - Voltage = Divide
Parallel - Current = Divide
Parallel- Voltage = Same
What is the voltage law?
The sum of the potential difference around any closed loop is equal to the potential difference across the supply.
What is the current law?
The sum of the current into any single point in a circuit is equal to the current out.
What is mA
Milliamphere (0.001A = 1mA)
What is kJ
Kilojoule (1000J = 1kJ)
What is MW
Megawatt (1MW= 1000kW= 1,000,000W)
How is resistance in series calculated?
Total Resistance = R1 + R2 + R3…etc.
How is resistance in parallel calculated?
1/Total Resistance = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 ..etc. then reciporcal of 1/RT
What routes do current like to flow through?
Current in parallel splits accordingly to the amount of resistance each branch has. Use ratios to figure out how the current splits according to the number of “things.”
What determines the brightness of bulbs? And the process in which this occurs.
The amount of power a bulb has determines how bright it will be. This can be calculated through the findings of its current and voltage (maybe even resistance).
The chemical potential energy from the battery through the bulb gets converted electrical potential energy then into light energy (and other waste energies). Power is the amount of energy transferred per second, the more power the more energy that can be transferred, then converted into light energy, the brighter the bulb will be.
What are some common resistances that affect circuits?
Thickness and Length of Wire, and Temperature
Why does a thickness of a wire cause resistance?
The thicker the wire, the more space inside the wire “cross-section",” →giving more space for the electrons to pass through
however, if thickness of the wire is decreased, less space for electrons to pass through → more collisions between electrons → more resistance
Why does the length of the wire cause resistance?
The longer the wire, the more resistance there will be because the longer the electrons have to travel, the more collisions will occur → making it difficult and more resistance
Why does temperature cause resistance?
The higher the temperature, the greater the kinetic energy transferred to the particles and electrons, making them begin to vibrate. For example in a wire, the higher temperature causes the atoms and electrons in the wire to vibrate faster causing more collisions and thus more resistance.
How does chemical potential energy and electrical potential energy relate and power usage relate to battery life?
A battery stores chemical energy →converted into electrical energy → this process called discharge
higher power usage→ more chemical energy converted into electrical energy (discharge) →decrease in battery life because the chemical energy in the battery is being converted into electrical energy and other forms as the battery is being used.
Why does parallel circuits have an advantage over series circuits?
Advantage for parallel (disadvantage for series is just the opposite):
-more than one pathway
↪if a break in the circuit there are other pathways, entire circuit won't break down
-voltage same each loop
-resistance decreases with each loop added ->because more pathways for current to flow
↪decrease in resistance = increase in total current
-brightness of bulbs stay the same in parallel
Disadvantage: current splits in loops
Why do series circuits tend to use less battery?
In a series circuit the current stays the same, but the resistance gets larger with each component added. Since resistance is inversly proportional to power (P=V2 /R) this means that less power is used, thus less battery is used.
How does voltage and current in batteries in series work?
Each battery has a system capacity (the total amount of electrical energy a battery can store before it needs to be recharged, e.g. 100Ah can supply 100A for 1 hour before it has to be recharged again) and the amount of voltage a battery outputs (system voltage).
When batteries are in series, the system voltage gets added together, but the system capacity stays the same.
How does voltage and current in batteries in parallel work?
Each battery has a system capacity (the toal amount of electrical energy a battery can store before it needs to be recharged, e.g. 100Ah can supply 100A for 1 hour before it has to be recharged again) and the amount of voltage a battery outputs (system voltage).
When batteries are in parallel, the system voltage stays the same, but the system capacity is added together, this is because the workload they have to handle is halved so they can last longer.
What are cations
Cations are postively charged ions because they are atoms or molecules that have lost one or more electrons resulting in a net positive charge.
How do cations usually move?
Typically stationary within a solid material or solution because they are bound to specific lattice sites (in solids) or are surrounded by solvent molecules (in liquids). So when there is electrostatic induction they don’t usually move.
What are bulk electrons?
Also known as free electrons which are negatively charged particles that are not bound to atoms or molecules. These materials have a significant number of free electrons due to the nature of their atomic structure.
How do free electrons move?
Can move relatively freely within certain materials, such as metals or semiconductors.
What are delocalised electrons?
Electrons that are not bound to any particular atom but instead move freely throughout the metal’s structure.
What do like charges do?
Repel electrostatically
What do unlike charges do?
Attract electrostatically
What does static charge/electrostatic charge mean?
Charges at rest acccumuated causing an imbalance of charges within or on the surface of an object. Usually caused by friction resulting in the transfer of electrons from one object to another.
What does Q (q) stand for?
Electric charge
What does C stand for?
Coulomb
What charge does an individual electron have?
1.6 × 10-19 C
How many electrons are in 1C of charge?
6.25 × 1018
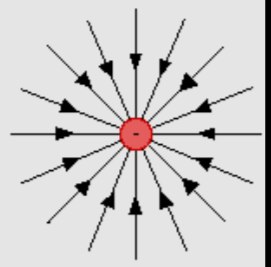
What does an electric field with positive charge look like?
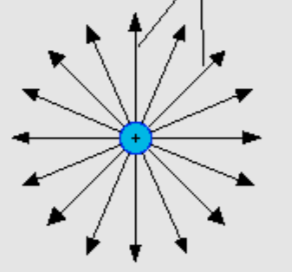
What does an electric field with negative charge look like?