AP Psychology: Unit 7 Part 2: Personality
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Aggression
A central force in humans that must find a socially acceptable outlet.
Albert Bandura
Believes that personality is the result of an interaction that takes place between a person and their social context.
Alfred Adler
Believes that a child struggles with an inferiority complex during growth and strives for superiority and power.

Archetypes
the universal symbolic images that appear across cultures in myths, art, stories and dreams.
Big Five Factor
Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, Neuroticism
Cardinal Trait
characteristics or feature so important to that a person is identified by it.
Carl Jung
Believed in the collective unconscious, which contained a common reservoir of images derived from our species' past.

Carl Rogers
Agreed with Maslow's ideas people are basically good and driven to self-actualize UNLESS inhibited by environment
Central Trait
traits that make us predictable in most situations
Compensation
Excelling in one area to make up for shortcomings in another.
Congruence
self-concept meshes well with actual experience
Conscious Mind
Everything we are aware of
Defense Mechanisms
Help to shield the ego from the anxiety created by conflicts between the id, superego, and reality.
Denial
Refusal to admit or recognize that something has occurred or is currently occurring.
Displacement
Taking out our frustrations, feelings, and impulses on people/objects that are less threatening.
Dreams
The release of repressed urges and impulses that Freud referred to as "the royal road to the unconscious". Seen as safe outlets for unconscious material and wish fulfillment.

Ectomorph Body Personality
Physically, narrow shoulders and hips; thin and narrow face, with a high forehead; very little body fat, self-conscious, private, artistic, emotionally restrained and thoughtful
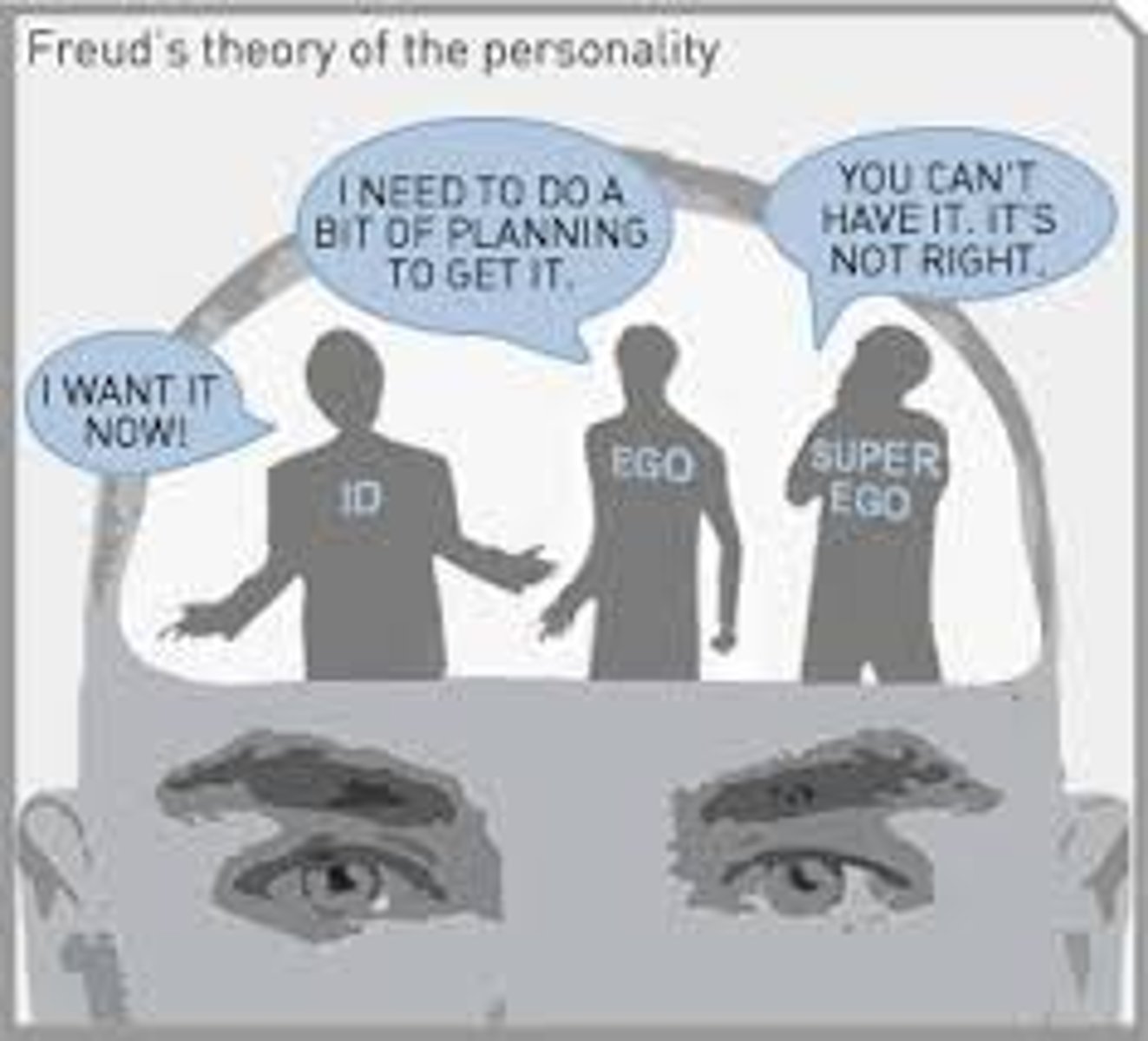
Ego (or I)
Mediates between the Id and the real world. Operates according to the reality principle.
Electra Complex
During the phallic stage of psychosexual development, girls begin to see their mothers as rivals for the fathers affection. Girls also experience penis envy, and Freud believed girls remain somewhat fixated at the phallic stage because they never resolve their penis envy.
Elements of personality
- Relatively enduring qualities in our behavior; uniqueness; comprehensiveness
Emotional instability
moody, anxious & restless
Emotional stability
easy-going, relaxed, well-adjusted and even tempered
Empirically Tested
testing that is based on science/research
Endomorph Body Personality
Physically quite 'round', and is typified as the 'barrel of fun' person.
Extraversion
sociable, outgoing, active & lively
Free association
Method of therapy which involves reporting the first thing that comes to mind in response to a given stimuli without censorship as a way to learn more about how the person things and feels.

Freudian slip
A verbal or memory mistake that is believed to be linked to the unconscious mind. According to Freud, those errors reveal an unconscious thought, belief or wish.
Gordon Allport
identified some 4,500 traits for personality (3 main categories)

Hans Eysenck
believed there are 2 distinct traits in personality (extraversion vs. introversion; emotional stability vs. emotional instability)
High self-efficacy
Person is CONFIDENT - and believes they can achieve goals
Humanistic Perspective
People are viewed as seeking personal growth and striving toward becoming their full selves. (Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow)
Iceberg Analogy
The mind is like an iceberg, with the largest part (unconscious) hidden from awareness.
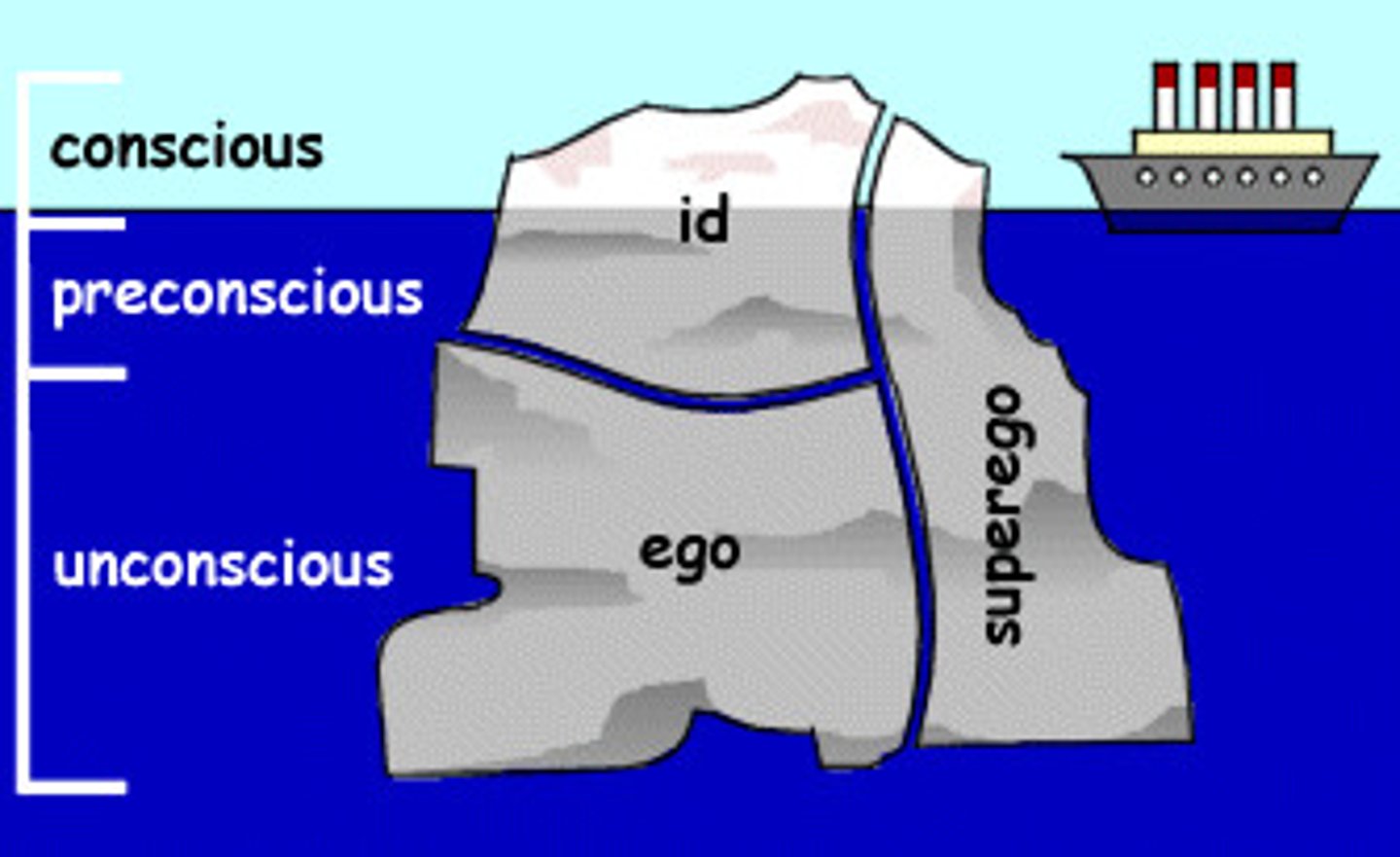
Id
The impulsive and unconscious part of the psyche that responds directly and immediately to the instincts. Demands immediate satisfaction and when satisfied, we experience pleasure. When left unsatisfied we experience pain or "unpleasure." Not affected by reality, logic, or everyday life. Operates on the pleasure principle.
Ideal-Self (Ego-Ideal)
An imaginary picture of how you ought to be. The superego can reward us for fulfilling this with certain behavior by making us feel pride.
Identification
Children cope with threatening feelings by repressing them and by identifying with the rival parent. Through this process the childs superego gains strength that incorporates their parents' values.
Incongruent
self-concept does not mesh well with actual experience
Introversion
thoughtful, reserved & quiet
Karen Horney
Believed in the social aspects of childhood growth and development and that children were trying to overcome a sense of helplessness. Countered Freud's assumption that women have weak superegos and suffer from "penis envy."

Latent Content
The underlying meaning of the manifest content.
Low Self-Efficacy
Person is UNCONFIDENT and many not try to obtain goals
Manifest Content
The actual literal subject matter of a dream
Mesomorph Body Personality
Physically they have a "desirable" body; Muscular body, with strong forearms and thighs; adventurous, competitive, desire for power and dominance

Moral Principle
The superego provides standards for jthe BEST judgment (the conscious) and for future aspirations. Starts developing around age 4-5.)
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
Test has widely been used in business and career counseling; 16 distinct combinations.
Negative self-concept
Ideal-self + Real-self = different
Neo-Freudian
A group of loosely linked American theorists of the mid-twentieth century, who were all influenced by Sigmund Freud, but who extended his theories, often in social or cultural directions.
Oedipus Complex
During the phallic stage of psychosexual development, boys begin to see their father as rivals for the mothers affection. They desire to possess the mother and replace the father. The child also fears that he will be punished by his father (castration anxiety), so instead identifies with the father in order to reduce this anxiety.

Personality Inventories
Used to assess a person's traits by use of questionnaires (often with true-false or agree-disagree items) designed to gauge a wide range of feelings and behaviors assessing several traits at once.
Pleasure principle
The principle the id operates on which requires satisfaction regardless of consequences.
Positive self-concept
Ideal-self + Real-self = same
Preconscious Mind
Represents ordinary memory. May not always be aware of information at this level, but we can retrieve it and pull it into consciousness easily.
Projection
Taking our own unacceptable feelings or qualities and ascribing them to other people.
Projective Test
A test that allows for evaluating personality from an unconscious mind's perspective would by how someone reveals themselves onto a drawing, ink blot, etc.,
Psychosexual Stage: Anal
- 1 to 3 years; Erogenous zone: bowel and bladder control; Primary focus: controlling the bladder and bowel movements; Major conflict: toilet training (parents are vital; too lenient--anal expulsive personality: messy, wasteful, or destructive. Too strict--anal-retentive personality: stringent, orderly, rigid, and obsessive).
Psychosexual Stage: Genital
-Puberty to death; Maturing sexual interests; Strong sexual interest in the opposite sex; Goal is to establish balance between the various life areas;
Psychosexual Stage: Latency
6-12yearsofage;Sexual feelings are inactive; Development of the ego and supergo; Development of social and communication skills and self-confidence
Psychosexual Stage: Oral
- Birth to 1 year; Erogenous zone: mouth; Pleasure is derived from oral stimulation; Primary conflict: the weaning process; If fixation occurs: the child will have issues with dependency or aggression (can result in problems with drinking, eating, smoking, or nail biting).
Psychosexual Stage: Phallic
- 3 to 6 years; Erogenous zone: genitals; Children discover the differences between males and females; Oedipus and Electra complex;
Rationalization
Justifying behavior or feelings that cause guilt.
Reaction Formation
Reduces anxiety by taking up the opposite feeling, impulse, or behavior.
Reality principle
The principle the ego operates on which works out realistic ways of satisfying the Id's demands.
Reciprocal Determinism
Personality is shaped by an interaction among cognitive (internal personal) factors, behaviors and environmental factors. (Specific ways in which individuals, behaviors and environments interact.)
Regression
A reversion to immature patterns of behavior.
Repression
Keeps information out of conscious awareness.
Rorschach Inkblot Test
The most widely used projective test uses a set of 10 inkblots and was designed by Hermann Rorschach.
Secondary Trait
convey's our preferences to items such as music or food
Self-Actualizing Person
Fulfilling our unique potential.
Self-concept
the central feature of personality. "Who am I?" refers to this.
Self-Efficacy
Your belief in your ability to perform behaviors that should lead to expected outcomes --confidence in our own ability to reach goals & complete tasks.
Sigmund Freud (Psychoanalysis)
He believed personality is instinct-driven and our behaviors are motivated by unconscious forces. We are all bundles of instinctual drive energy

Social-Cognitive Perspective
People behave according to how they cope with social pressures and solve social problems; Emphasize the interaction of our traits with our situations.
Sublimation
Allows us to act out unacceptable behaviors by converting them into more acceptable forms.
Superego
Incorporates the values and morals of society which are learned from parents or other people in the environment. Develops around 4-5 years during the phallic stage. Functions between the conscience and the ideal-self (ego-ideal), which are both developed during childhood; based on the moral principle.
The Person-Situation Controversy
Traits may be enduring and on average as a whole are pretty predictable, but the resulting behavior in various situations is different.
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
Developed by Henry Murray, this projective test allows people to express their inner feelings and interests through the stories they make up about ambiguous scenes.
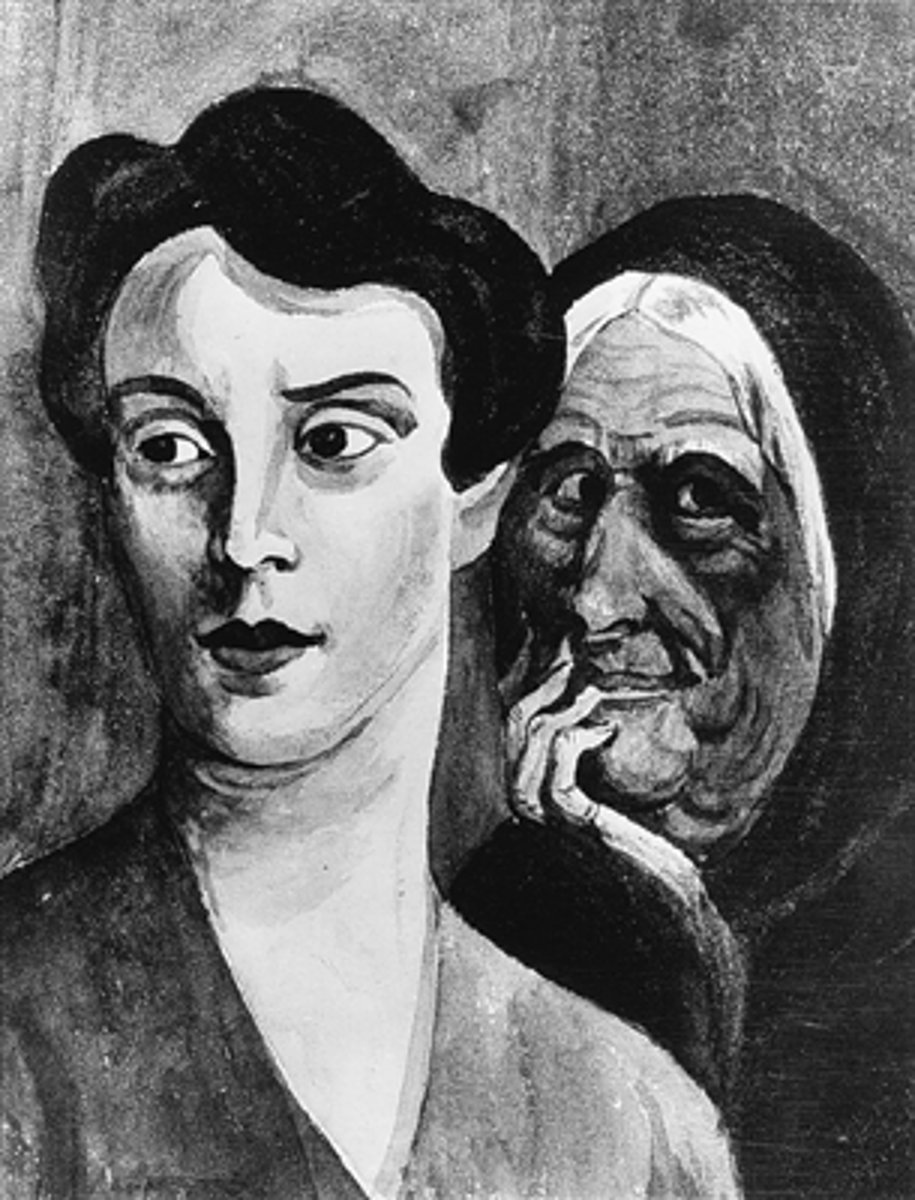
Trait Perspective
Believes people exhibit consistent psychological traits such as extraversion or deceitfulness; looks to describe and not explain. (Gordan Allport and Hans Eysenck)
Unconscious Mind
A reservoir of thoughts, feelings, urges, and memories beyond our conscious awareness. Much of our behavior is driven by this force according to Freud.
Personality psychology
The study of why people act the way they do and also the study of individual differences.
Positive Psychology
the scientific study of optimal human functioning; aims to discover and promote strengths and virtues that enable individuals and communities to thrive
Attributional style
way of explain explaining positive or negative events (optimistic or pessimistic)
Self
organizing of our thoughts, feelings and actions; most important item in personality according to humanistic psychologists
Self-Esteem
feelings of self-worth
Self-serving bias
our readiness to perceive ourselves favorably
Individualists
more emphasis on independent self; self defined by personal values, personal goals and personal attributes
Collectivists
Self defined by connections with family and friends meaning with the goals of the group having a higher priority than individual goals
Spotlight Effect
overestimating our concern that others evaluate our appearance, performance, and blunders

Fixation
according to Freud, a lingering focus of pleasure-seeking energies at an earlier psychosexual stage, in which conflicts were unresolved
unconditional positive regard
according to Rogers, an attitude of total acceptance toward another person
MMPI (Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory)
the most widely researched and clinically used of all personality tests. Originally developed to identify emotional disorders (still considered its most appropriate use), this test is now used for many other screening purposes.
collective unconscious
Jung's name for the memories shared by all members of the human species; we all see "evil" with similar ideas in mind