exam 6 concepts
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Retroviruses
Single-stranded RNA viruses that use reverse transcriptase to make DNA from RNA.
DNA can be used to make mRNA or integrate into host DNA (lysogenic cycle).
HIV
Lichens
Lichens are symbiotic associations between fungi + algae/cyanobacteria.
Fungi provide protection, water, and nitrogen; algae/cyanobacteria provide carbohydrates via photosynthesis.
Fungi are eukaryotic, unlike viruses, which are non-cellular.
Archaebacteria
Archaebacteria are living prokaryotes, survive independently, and have polysaccharide cell walls.
bacteria have peptidoglycan cell wallsare non-living, lack metabolism, and must hijack a host cell to replicate.
X-linked Genetic Disorders
Found on the X chromosome, not the Y.
Males (XY) with the allele = fully affected.
Females (XX) with 1 affected X = carriers, may show partial or no symptoms.
Example: X-linked retinoschisis → causes partial/complete blindness by degrading the retina.
Y-linked disorders
Y-linked disorders affect only males; females can’t be affected (no Y chromosome).
X-linked disorders can affect both sexes:
Males with 1 affected X = fully affected
Females with 1 affected X = carriers, may show partial or no symptoms
Partial symptoms in females indicate the disorder is X-linked, not autosomal or Y-linked.
Ductus Venosus
Oxygenated blood from placenta returns via umbilical vein.
Half bypasses liver through ductus venosus directly to the heart.
Blood bypasses liver because fetal liver is not fully functional (filtering/detoxifying).
Other half flows through portal vein into the liver.
ductus venosus
foramen ovale
ductus arteriosus
Ductus venosus: Bypasses liver by directing half of umbilical vein blood to heart (fetal liver not fully functional).
Foramen ovale: Small opening between right and left atria; allows blood to bypass lungs by moving directly to left atrium (no fetal lung gas exchange).
Ductus arteriosus: Vessel connecting pulmonary artery to aorta; bypasses lungs by diverting blood away from pulmonary circulation.
Sperm Structure and Acrosome Function
Sperm parts: Head (contains acrosome), mid-piece (energy), tail (motility).
Acrosome: Lysosome-like organelle with enzymes that digest the zona pellucida.
Zona pellucida: Glycoprotein membrane around the oocyte with ZP3 receptor proteins.
Acrosome reaction: Triggered by sperm binding to ZP3, releasing enzymes to penetrate zona pellucida.
Importance: Without acrosome, sperm cannot penetrate zona pellucida or fertilize the egg.
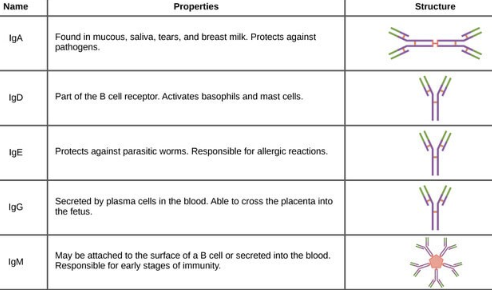
Antibody Structure & Classes
Structure: Y-shaped proteins with constant & variable regions; 2 heavy + 2 light chains linked by disulfide bonds.
Classes: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, IgM.
IgG: Most abundant in serum, monomeric, can cross placenta to protect fetus.
IgM: Pentameric structure, unique among antibodies.

Classes: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, IgM.
Menstrual Cycle Hormonal Regulation
Low estrogen & progesterone → Hypothalamus releases GnRH → Anterior pituitary releases FSH & LH.
FSH stimulates follicles → Follicles secrete estrogen → Estrogen causes positive feedback → More GnRH & LH surge.
LH surge triggers ovulation → Follicles secrete estrogen & progesterone → Thickening of endometrium for implantation.
Hormones in Lactation
Prolactin: Stimulates milk production in mammary glands.
Oxytocin: Causes milk ejection by contracting mammary smooth muscle.
Together, they enable feeding and provide nutrients plus antibodies to the baby.
Meiosis I vs Meiosis II
Meiosis I: Homologous chromosomes separate → daughter cells become haploid (half chromosome number).
Meiosis II: Sister chromatids separate → chromosome number stays haploid; no further reduction.
Gastrulation & Germ Layers
Gastrulation: Invagination of cells in blastula → forms gastrula with 3 germ layers: ectoderm (outer), mesoderm (middle), endoderm (inner).
Ectoderm: Nervous system, epidermis/hair, sensory structures (eye lens/retina), neural tube, facial bones, adrenal medulla.
Mesoderm: Musculoskeletal, circulatory/lymphatic, excretory, gonads, connective tissue, parts of digestive/respiratory, notochord, dermis, adrenal cortex.
Endoderm: Epithelial lining of digestive/respiratory tracts, liver, pancreas, gall bladder, thyroid/parathyroid, thymus, urinary bladder lining.
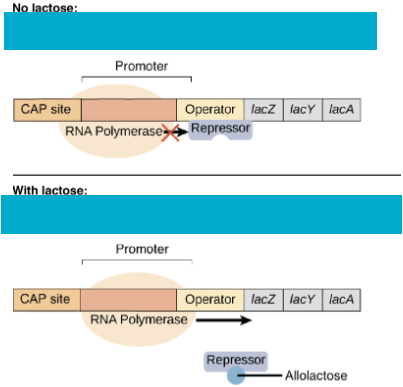
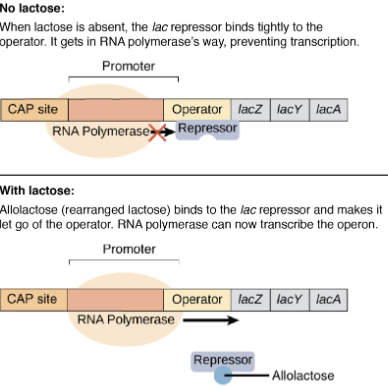
Lac Operon Regulation
Operon: DNA region with structural & regulatory genes controlled by promoter & operator.
Lac Operon (E. coli): Controls lactose breakdown via genes lacZ, lacY, lacA.
Regulation: Repressor protein binds operator, blocking RNA polymerase.
Lactose presence: LacZ converts lactose → allolactose, which binds repressor, inactivating it → RNA polymerase transcribes lactose digestion genes.
Result: Lactose enzymes made only when lactose/allolactose present.
Plant Energy Storage and Photosynthesis
Light-dependent reactions: Use sunlight to produce ATP & NADPH.
Dark reactions (Calvin cycle): Use ATP & NADPH to produce glucose.
Glucose use: Fuel for aerobic respiration in plant cells.
Energy storage: Excess glucose stored as starch (polymer of alpha-glucose).
Storage location: Starch stored in vacuoles and plastids called leucoplasts.
Alternative Splicing
Selective removal of introns and joining of exons in pre-mRNA to create different mRNA variants.
Allows one gene to produce multiple different proteins.
Only occurs in eukaryotes (prokaryotes lack introns and splicing machinery).
Increases protein diversity beyond the number of genes.
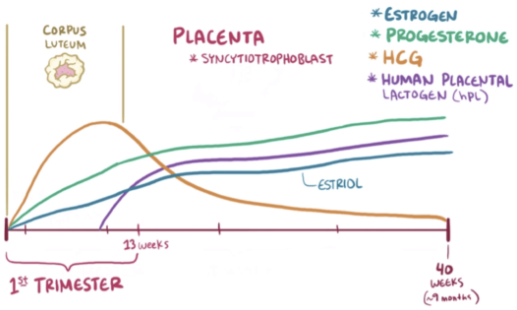
Role of hCG in Early Pregnancy
hCG is secreted by the placenta after implantation to maintain the corpus luteum.
The corpus luteum secretes estrogen and progesterone to maintain the endometrium for embryo support.
Without hCG, the corpus luteum degrades, progesterone and estrogen drop, and menstruation occurs.
Later in pregnancy, the placenta takes over progesterone production directly.
TSH
TRH from the hypothalamus stimulates the anterior pituitary to produce TSH.
TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) stimulates the thyroid gland to grow and secrete thyroid hormones T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine).
TSH regulates metabolism, not reproduction.
Species Diversity
Species diversity = species richness + relative abundance.
Species richness = total number of different species in a community.
Relative abundance = number of individuals per species.
Island Biogeography
Species richness increases with island size due to more habitats and resources.
Species richness decreases with greater distance from the mainland because of less immigration and more local extinctions.
When distance is unknown, island size is the key factor for predicting species richness.
Gastrin and HCl in Digestion
G cells (stomach) secrete gastrin, a peptide hormone absorbed into blood.
Gastrin stimulates parietal cells to secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl).
HCl keeps stomach pH very acidic (~2), killing bacteria and activating pepsin.
Pepsinogen (from chief cells) is converted to pepsin by HCl for protein digestion.
HCl also helps absorb vitamin B-12 in the ileum.
Gastrin is secreted and acts within the same organ (stomach).
Role of T3 (Triiodothyronine)
Secreted by the thyroid gland.
Targets most cells in the body (not a specific organ).
Essential for growth and neurological development in children.
Increases basal metabolic rate (BMR) by boosting cellular metabolism.
Insulin
Secreted by beta cells of the pancreas.
Targets liver, muscle cells, and adipose (fat) tissue.
Stimulates glucose absorption and storage, lowering blood glucose levels.
Does not target the pancreas itself.
Works alongside glucagon to regulate blood sugar
Epinephrine
Secreted by the adrenal medulla.
Targets multiple tissues throughout the body, not the adrenal medulla itself.
Activates the sympathetic nervous system — triggers “fight or flight” response.
Epinephrine effects
Increases blood glucose, blood pressure, and heart rate.
Increases blood flow to skeletal muscles.
Dilates pupils.
Bronchodilation (relaxes airway smooth muscles).
Decreases blood flow to non-essential organs (intestines, bladder).
Increases overall metabolic activity.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Secreted by the anterior pituitary.
Targets the ovaries (females) and testes (males).
In females:
Stimulates formation of the corpus luteum.
LH surge triggers ovulation (release of secondary oocyte).
In males:
Stimulates Leydig cells in testes to produce testosterone.
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Transcription and Translation
Lack membrane-bound organelles and a nuclear membrane.
Genetic material is in the nucleoid (no nucleus).
Transcription and translation occur simultaneously in the cytoplasm.
Ribosomes can begin translating mRNA immediately after transcription starts.
bacteria/archae kingdoms
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Transcription and Translation
Have a nucleus separating DNA from cytoplasm.
Transcription occurs inside the nucleus.
mRNA must be exported to cytoplasm for translation by ribosomes
animalia, plantae, fungi, protists kingdoms
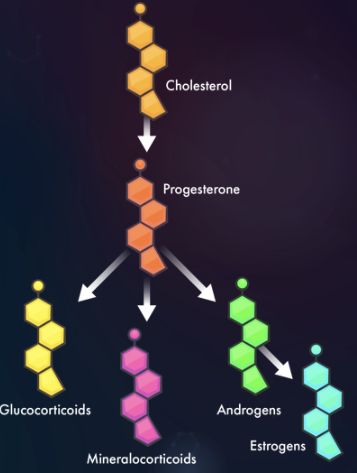
Steroid Hormones
Synthesis: Made from cholesterol in smooth ER.
Structure: Retain cholesterol’s 4-ring backbone; variations arise from diff functional groups.
Types:
Sex hormones: Androgens (testosterone), estrogens (estradiol), progestogens (progesterone).
Others: Mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids.
Functions: Regulate sexual dev (puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, sperm prod), physiological processes.
Hormones Derived from Tyrosine
Synthesized from AA tyrosine.
Include melatonin, epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin.
Mostly function as neurotransmitters or hormones affecting mood, stress response, and circadian rhythms.
Hormones Derived from Polypeptides
Synthesized by ribosomes, coded by genes in the genome.
Examples: FSH, LH, ACTH, hGH, TSH, prolactin, ADH, PTH, glucagon, insulin.
Typically water-soluble, act via membrane receptors to trigger cell signaling cascades.
Coevolution
Coevolution is when two species reciprocally influence each other’s evolution.
Seen in relationships like predator-prey (e.g., faster predators → faster prey).
Coevolution involves adaptive changes in both species due to close interactions.
Coevolution EX
Also occurs in mutualistic relationships, like:
Hummingbirds & trumpet creeper flowers:
Hummingbirds evolved long beaks for tubular flowers.
Flowers evolved long petals to match beak shape → improves pollination.
Carbon Cycle
Carbon reservoirs include the atmosphere (CO₂), producers, consumers, and decomposers.
Producers absorb CO₂ via photosynthesis and convert it to organic carbon.
Consumers eat producers and release CO₂ back through cellular respiration.
Decomposers in the Carbon Cycle
Decomposers/saprophytes (fungi, bacteria) break down dead matter using cellular respiration.
They secrete enzymes to digest organic compounds into absorbable units.
Their respiration releases CO₂ into the atmosphere & supply C for plants photosynthesis
Fossil fuel combustion also contributes CO₂ to the air.
Voltage-Gated Ion Channels & Neuron Transmission
Voltage-gated ion channels open in response to membrane potential changes.
Na⁺ influx depolarizes the axon; K⁺ efflux repolarizes it.
An action potential triggers sequential opening of these channels along the axon.
Motor End Plate & Muscle Fiber Activation
Acetylcholine at neuromuscular junction opens ligand-gated Na⁺ channels.
Sufficient depolarization activates voltage-gated channels in sarcolemma.
Action potential travels via T-tubules, triggering Ca²⁺ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Calcium & Muscle Contraction
Ca²⁺ binds troponin, enabling myosin-actin crossbridge formation.
Sarcomeres shorten → muscle contracts.
Ca²⁺ is actively pumped back into sarcoplasmic reticulum to end contraction.
Ligand-Gated and Mechanically-Gated Ion Channels
Ligand-gated channels open in response to neurotransmitter binding (e.g. acetylcholine).
Mechanically-gated channels open in response to physical stimuli (pressure, vibration).
Both types generate graded potentials that may trigger an action potential if threshold is reached.
DNA Microarray
Detects gene expression by hybridizing cDNA to gene-specific wells.
mRNA is isolated and converted to cDNA via reverse transcriptase.
Fluorescence indicates gene expression; intensity reflects expression level.
Only expressed genes produce signal—unexpressed genes show no binding.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Amplifies DNA (not RNA or gene expression).
Involves 3 steps: denaturation, annealing, and elongation.
Uses primers and DNA polymerase to replicate target DNA.
DNA amount increases exponentially with each cycle.
Karyotyping
Used to visualize number and structure of chromosomes.
Can detect large chromosomal abnormalities (e.g. trisomy 21 in Down Syndrome).
Involves staining and photographing chromosomes.
Cannot assess gene expression.
Gel Electrophoresis
Separates DNA, RNA, or proteins by size and charge.
Smaller molecules migrate farther through the gel.
Used before sequencing or probing for specific sequences.
Does not measure gene expression.
Thyroid Hormones (T3 & T4)
Lipid-soluble tyrosine derivatives made by the thyroid gland.
Increase basal metabolic rate; needed for growth & brain development in children.
Iodine is required for their synthesis.
Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism: ↓ metabolism, HR, RR; leads to fatigue, weight gain, decrease in gastric motility
Hyperthyroidism: ↑ metabolism, sweating; causes weight loss, thinness.
Both can cause goiter (thyroid enlargement).
Calcitonin vs Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Calcitonin: lowers blood Ca²⁺ by stimulating osteoblasts (build bone) and inhibiting osteoclasts (break down bone).
PTH: raises blood Ca²⁺ by stimulating osteoclasts (release Ca²⁺ from bone) and increasing osteocyte calcium absorption.
Homeotic (HOX) Genes
Homeotic genes control body structure development during embryogenesis by regulating gene expression in body segments.
HOX genes specifically determine segmentation and anatomic placement by turning genes on/off in each segment via the homeobox DNA sequence.
Small changes in HOX gene expression lead to major structural differences between related species (e.g., shrimp vs. grasshopper).
Mutations in HOX genes can cause misplacement of structures (e.g., leg growing on head) and often cause developmental failure due to their conserved nature.
lac Operon and lacZ Gene
The lac operon regulates lactose metabolism in prokaryotes
lacZ codes for β-galactosidase, an enzyme that breaks lactose into glucose and galactose.
Regulatory genes produce a repressor protein that binds the operator, blocking RNA polymerase and preventing transcription.
When lactose is present, it binds the repressor, inactivating it and allowing transcription of lac genes for lactose metabolism.
p53 gene
tumor suppressor gene encoding a protein that regulates cell repair and apoptosis.
Downregulation or mutation of p53 impairs its ability to control abnormal cell growth.
Loss of p53 function can lead to unchecked cell proliferation and cancer development.
SRY gene
located on the Y chromosome and produces the testis-determining factor protein.
It is essential for male sexual development, especially Sertoli cell formation.
Sertoli cells secrete signals that inhibit the development of Müllerian ducts (which form female reproductive structures).
Without SRY, the embryo develops ovaries and female reproductive organs.
trp operon
trpE is a part of
controls tryptophan synthesis in prokaryotes by producing enzymes needed for tryptophan production.
Regulatory genes produce an inactive repressor allowing RNA polymerase to transcribe tryptophan genes.
When tryptophan is abundant, it binds to the repressor, activating it.
The active repressor binds the operator, blocking RNA polymerase and stopping tryptophan synthesis (negative feedback).
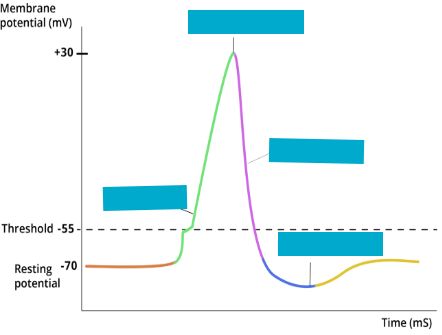
Resting & Graded Potential
Resting potential = -70mV (normal polarized neuron state)
Stimulus opens gated Na⁺ channels → Na⁺ enters → depolarization begins
Graded potential = small, local change in membrane potential (Graph A)
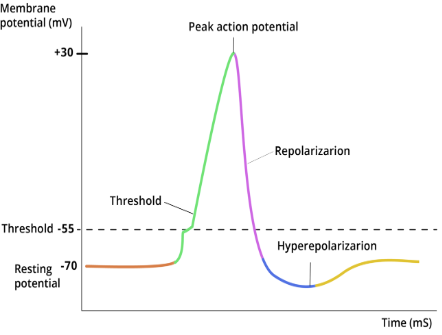
Action Potential & Threshold
Threshold: -50 to -55mV → triggers action potential
Action potential = rapid depolarization from voltage-gated Na⁺ channels opening along axon (Graph B, peak = Graph C)
At peak, voltage-gated Na⁺ channels close
Repolarization & Hyperpolarization
Repolarization: voltage-gated K⁺ channels open → K⁺ leaves cell → membrane potential returns toward resting (Graph D)
Hyperpolarization: K⁺ channels slow to close → excess K⁺ leaves → membrane potential dips below resting (Graph E)
Refractory Period & Ion Restoration
Refractory period: neuron temporarily unresponsive to new stimulus
Sodium-potassium pumps restore resting ion balance and membrane potential
Aposematic Coloration
Bright, conspicuous colors/patterns warning predators to avoid the animal
Example: Poisonous frogs use bright colors to signal toxicity
Chitin Function & Organisms
Chitin = β-glucose polymer used for structural support
Found in fungal cell walls & arthropod exoskeletons
Yeast (unicellular fungus) has a chitin-containing cell wall
Enzymes degrading chitin would damage yeast the most
Diatoms
Plant-like protists that perform photosynthesis
Cell walls made of silica (not chitin)
Segmentation in Animals
Segmentation = division of body into repetitive segments
Seen in: arthropods, annelids, and chordates
Cnidarians (e.g., Jellyfish)
No body segmentation
Two body forms:
Medusa: free-floating, umbrella-shaped with tentacles
Polyp: immobile, cylindrical with upward tentacles
Life cycle may alternate between medusa (sexual) and polyp (asexual) stages
Analogous vs. Homologous Structures
Analogous: similar function, different ancestry → from convergent evolution
Homologous: similar ancestry, may differ in function → from divergent evolution
Bird vs. Bat Wings (DAT Tip
Bird & bat wings = analogous (flight, different ancestors)
Their forelimbs = homologous (inherited from a common ancestor)
Smooth ER vs. Rough ER
Smooth ER: no ribosomes; synthesizes lipids & steroid hormones, detoxifies
Rough ER: has ribosomes; folds, modifies, and transports proteins
Rough ER performs post-translational modifications (e.g., adding chemical groups)
Lysosomes
Contain hydrolytic enzymes for digestion of biomolecules
Functions: apoptosis, autophagy, and pathogen breakdown (e.g., in phagocytes)
Formed from the Golgi apparatus
Phospholipids
Made of: 2 fatty acids (hydrophobic) + 1 phosphate group (hydrophilic) on a glycerol backbone
Hydrophobic tails: nonpolar hydrocarbons
Hydrophilic head: glycerol + negatively charged phosphate
Amphipathic → form bilayers: hydrophobic interior, hydrophilic exterio
Albumins
Simple, water-soluble functional proteins
Act as carriers for fatty acids, hormones, ions, and vitamins
Help maintain blood osmotic pressure
Recessive vs. Dominant Inheritance
A recessive trait is likely if two unaffected parents have an affected child.
A dominant trait usually does not skip generations; at least one parent is affected.
A skipped generation (e.g., affected grandparent → unaffected parent → affected child) suggests recessive inheritance.
Autosomal vs. X-linked Recessive Inheritance
X-linked recessive traits: Affected mothers will have all affected sons.
If an affected mother has an unaffected son, the trait is not X-linked recessive.
Autosomal traits affect males and females equally; X-linked recessive traits affect more males.
Y-linked traits occur only in males (never in females).
Centrifugation
most to least dense: 1st pellet: Nuclei
2nd pellet: Mitochondria & chloroplasts
3rd pellet: Microsomes & small vesicles
4th pellet: Ribosomes, viruses, macromolecules
Denser components pellet first; lighter components pellet after repeated spins
Key Transcription Facts
RNA polymerase reads DNA 3′→5′; synthesizes RNA 5′→3′
Uracil (U) replaces thymine (T) in RNA
Transcription occurs in the nucleus
Uracil is used in RNA because it’s less energetically costly than thymine
Transcription Example
DNA (coding strand): 5′ – ATATATGCGCACGC – 3′
Template strand: 3′ – TATATACGCGTGCG – 5′
mRNA (5′→3′): GCGUGCGCAUAUAU
Parallel Evolution
Occurs in related species with a common ancestor
Species evolve similar traits independently
Example: Two monkey species with similar features
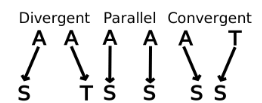
Convergent Evolution
Occurs in unrelated species
Similar traits evolve due to similar environments/functions
Example: Insect wings vs. bat wings (flight, no shared ancestor)
Divergent Evolution
Occurs in related species that become increasingly different
Caused by speciation and different environmental pressures
Example: Galapagos finches’ beaks evolving for different food sources
Open vs. Closed Circulatory Systems
Open system: Blood (hemolymph) pumped into hemocoel, bathes organs; returns via ostia
arthropods, insects, mollusks have this
Closed system: Blood circulates in vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries)
Efficiency of Closed Circulatory Systems
Higher blood pressure → faster flow
Separates oxygenated & deoxygenated blood
Greater oxygen-carrying capacity (more hemoglobin)
More efficient oxygen transport → supports higher metabolism
Feathery Gills
Feathery gills = large surface area for gas exchange
Important for aquatic organisms due to low dissolved oxygen in water
Maximized surface area improves respiratory efficiency
Moist skin
Moist skin or tracheal endings enhance gas diffusion
Found in annelids (mucus-secreting skin) and arthropods (e.g., grasshoppers)
Moisture helps O₂ and CO₂ dissolve and diffuse more easily
Miller–Urey Experiment
Simulated early Earth using CH₄, NH₃, H₂, H₂O, and electric sparks (lightning)
Produced organic molecules (e.g., amino acids, fatty acids, aldehydes) from inorganic components
Demonstrated possible chemical origin of life in a closed system