FBLA-Organizational Leadership
1/233
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
234 Terms
Leadership definition
-influencing process of leaders & followers to achieve organizational objectives through change
-a process of social influence in which one person can enlist the aid and support of others in the accomplishment of a common task
Leadership self-assessment
is a series of statements and reflective questions that offer insight into your leadership style to help you identify your strengths and opportunities for growth.
Characteristics of leaders
-initiative
-ability to function independently
-followthrough
-ethics
-ability to respond to ambiguity and change
-resiliency
-positive attitude
-confidence
-record of excellence
Harry Mintzberg's Managerial Roles
-Interpersonal
-Informational
-Decisional
interpersonal roles for managerial leadership
-Figurehead
-Leader
-Liaison
Figurehead Role (Interpersonal)
the interpersonal role managers play when they perform ceremonial duties/ Represents the company in a symbolic way
-Cutting the ribbon at ceremony for the opening of a new building
Leader Role (Interpersonal)
Guides and motivates employees to achieve organizational goals
-Helping subordinates to set monthly performance goals
Liason Role (Interpersonal)
Acts as a go-between among individuals inside and outside the organization
-Representing the retail sales division of the company at a regional sales meeting
informational roles for managerial leadership
-Monitor
-Disseminator
-Spokesperson
Monitor Role (Informational)
constantly searching for information to become more effective/Seeks out and gathers information relevant to the organization
-Finding out about legal restrictions on new product technology
Disseminator Role (Informational)
Provides information where it is needed in the organization
-Providing current production figures to workers on the assembly line
spokesperson role (informational)
Transmits information to people outside the organization
-Representing the company at a shareholders' meeting
Decisional Roles of managerial leadership
-Entrepreneur
-Disturbance handler
-Resource allocator
-Negotiator
entrepreneur role (decisional)
Searches out new opportunities and initiates change
-Implementing a new production process using new technology
Disturbance Handler role (decisional)
Handles unexpected events and crises
-Handling a crisis situation such as a fire
Resource Allocator role (decisional)
Designates the use of financial, human, and other organizational resources
-Approving the funds necessary to purchase computer equipment and hire personnel
negotiator role (decisional)
Represents the company at negotiating processes
-Participating in salary negotiations with union representatives
Important things to understand as a manager
-importance of effective research for leadership decisions
-appreciate perspectives of other individuals
-successful leaders use reflection and application in future challenges
-analyze situations to gain more comprehensive understanding
-leaders connect individual thinking with systems thinking
-evaluate different alternatives to make the best decisions
-problem solving and decision making are key
what elements of self-understanding contribute to leadership capabilities?
-personal values
-personal contributions
-scope of competence
Individual Thinking with Systems Thinking (used by managers)
Measuring individual performance in terms of a system (structure/culture in work group)
programed decisions
Decisions made in response to frequently occurring routine situations.
nonprogrammed decisions
Responses to infrequent, unforeseen, or very unusual problems and opportunities where the manager does not have a precedent to follow in decision-making.
Decision Making Process
1. Define the problem
2. Identify the choices
3. Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each choice
4. Choose one
5. Act on your choice
6. Review your decision
3 major managerial skills
-conceptual
-human relations
-technical
(Robert Katz)
conceptual skills
A manager's ability to view the organization as a whole, understand how the various parts are interdependent, and assess how the organization relates to its external environment.
human relations skills
A manager's interpersonal skills that are used to accomplish goals through the use of human resources.
technical skills
A manager's specialized areas of knowledge and expertise, as well as the ability to apply that knowledge
Leadership Styles
-Democratic Leadership.
-Autocratic Leadership.
-Laissez-Faire Leadership.
-Strategic Leadership.
-Transformational Leadership.
-Transactional Leadership.
-Coach-Style Leadership.
-Bureaucratic Leadership
-Spiritual Leadership
-Directive Leadership
-Path-Clarification leadership
democratic/ participative leadership style
sharing decision making with others and encouraging subordinates to be involved in setting goals
autocratic leadership style
centralizing authority, making decisions alone, and expecting followers or subordinates simply to follow instructions
laissez-faire leadership style
a leadership style characterized by complete freedom for the group in making decisions
strategic leadership style
is aimed at finding a balance between the long-term focus of styles, such as transformational leadership, and the short-term focused style of transactional leadership. -must look at the impact an action might have on the short- and long-term.
transformational leadership style
leaders encourage, inspire and motivate employees to innovate and create change that will help grow and shape the future success of the company
-more long term
Transactional Leadership Style
characteristic of leaders who focus on supervision and organizational goals achieved through a system of rewards and punishments; maintenance of the organizational status quo
-more short term
Coach leadership style
involves and facilitates the engagement of people, as well as drawing out and understanding and empathising with their specific and individual motivations.
directive leadership style
involves a leader giving clear directions, objectives, and expectations to employees. Directive leadership is probably most effective when a task is complex and employees are unskilled or inexperienced
path-clarification leadership style
refers to situations where the leader lets employees know what is expected of them and tells them how to perform their tasks, shows them how to accomplish tasks and receive organizational rewards
bureaucratic leadership style
fixed official duties under a hierarchy of authority, applying a system of rules for management and decision-making-relies on rules, regulations, policies, and procedures
Job-centered behavior
when a leader pays close attention to the work of subordinates, explains work procedures, and is keenly interested in performance.
Employee-centered behavior
when the leader is interested in developing a cohesive work group and in ensuring employees are satisfied with their jobs
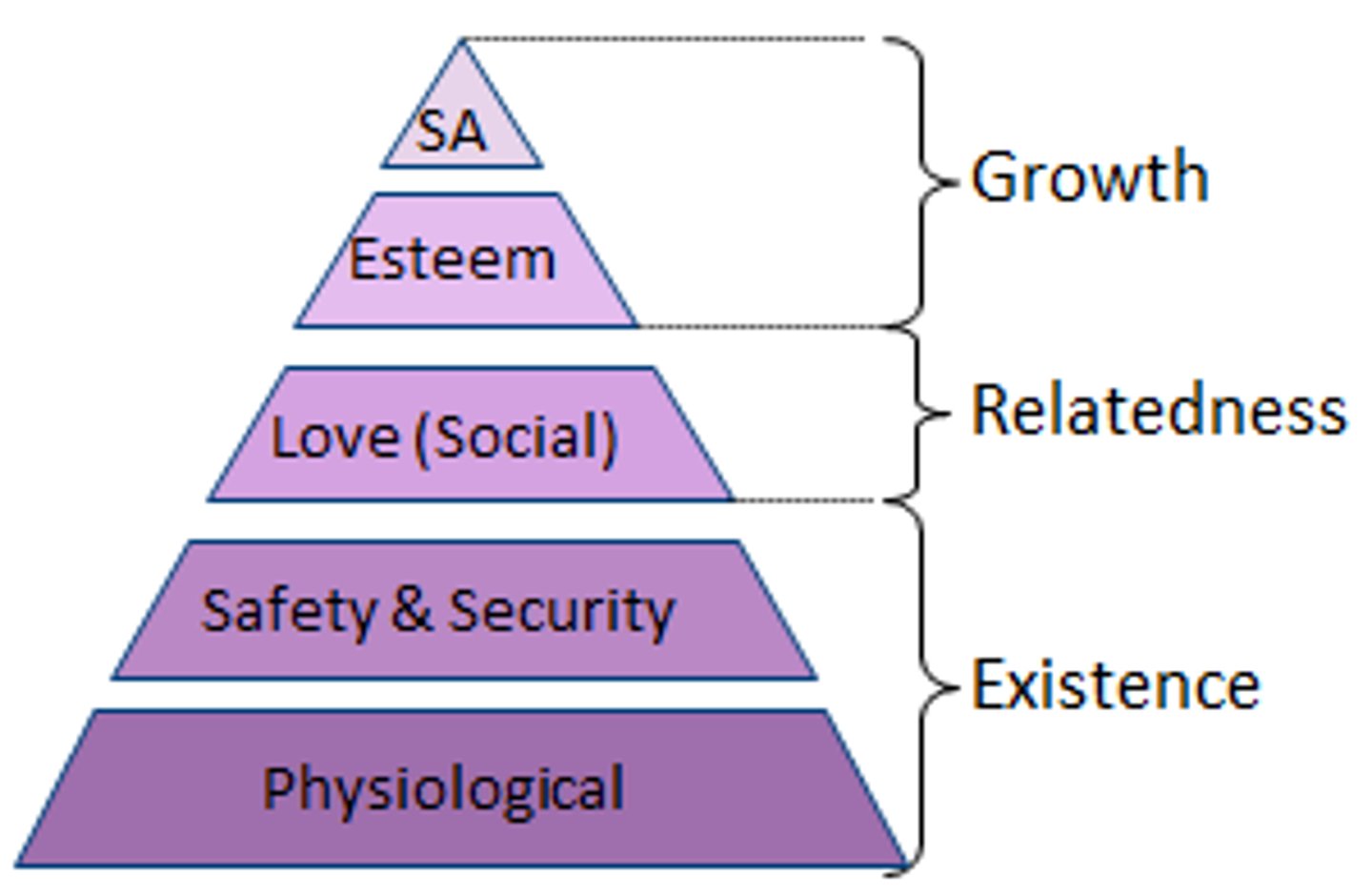
Alderfer's ERG Theory of Motivation
a simplified version of Maslow's hierarchy of needs that suggests that all human needs can be accessed and satisfied simultaneously, rather than from the bottom up. Either way, as needs are satisfied, employees are motivated to strive to satisfy a new need.
(existence needs, relatedness needs, growth needs)
Acquired Needs Theory of Motivation (McClelland)
individuals' needs and classifies them into three motivating drivers, need for achievement, power or affiliation. In acquired needs theory, McClelland proposes each person falls into one three types of needs based on personal preference and personal experience of that person
(Achievement, Affiliation, Power)
needs are acquired, not innate
Cognitive Evaluation Theory of Motivation
A version of self-determination theory which holds that allocating extrinsic rewards for behavior that had been previously intrinsically rewarding tends to decrease the overall level of motivation if the rewards are seen as controlling
intrinsic motivators: Achievement, responsibility and competence
extrinsic: pay, promotion, feedback, working conditions
Two Factor theory (Herzberg)
proposed that work satisfaction and dissatisfaction arise from two different factors -
MOTIVATING FACTORS= determine satisfaction (presence motivates)- these are intrinsic things esp
HYGIENE FACTORS= determine dissatisfaction (absence motivates)
Equity Theory of Motivation
Focuses on the desire to be treated with equity and to avoid perceived inequity
Reinforcement Theory of Motivation
the theory of motivation that focuses on positive and negative reinforcement and the motivational repercussions of the reinforcement.
Operant Conditioning- Positive and Negative Reinforcements, Positive and Negative Punishments
Expectancy Theory of Motivation (Vroom)
employee's motivation is an outcome of how much an individual wants a reward (Valence), the assessment that the likelihood that the effort will lead to expected performance (Expectancy) and the belief that the performance will lead to reward (Instrumentality).
Goal-Setting Theory of Motivation
a theory of motivation based on directing one's effort toward the attainment of specific goals that have been set or established
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory
A motivation theory that suggests that human needs fall into a hierarchy and that as each need is met, people become motivated to meet the next-highest need in the pyramid.
1-Physiological Needs
2-Safety/Security Needs
3-Love/Belongingness Needs
4-Esteem Needs
5-Self Actualization Needs
Individuals need to balance
professional and personal needs
Professional Networking
type of social network service that is focused solely on interactions and relationships of a business nature rather than including personal, non business interactions
interpersonal communication
direct, face-to-face communication between two or more people
-helps to create an open and honest work culture where employees feel they have the ability to communicate with all levels of the organization. Strong interpersonal skills help to make people more relatable to others, which is an important quality in the workplace.
leadership advantages of professional networks
helping you identify career opportunities, build a successful team, anticipate organizational changes, and stay on top of industry trends
characteristics of productive leaders
-appropriate interaction with others,
-empathy,
-mentoring
-helping others,
-motivation,
-empowerment,
-feedback,
-supervision,
-collaboration,
-other's contributions
Elements of the communication process
sender, receiver, message, and feedback
Sender
the originator of the message in the communication process
Receiver
person to whom message is sent during the communication process
message
the information transmitted by the source in the communication process
feedback
The receiver's response to a message in the communication process
common approaches to getting feedback on messages
-be open to feedback
-be aware of nonverbal communication
-ask questions
-paraphrase
nonverbal communication
communication based on a person's use of voice and body, rather than on the use of words (eye behaviors, facial expressions, movements and gestures, voice-tone and volume)
-can help to determine emotional states, power and dominance, and credibility
Conflict Negotiation
the process of negotiating an understanding between people in a conflict, so that a peaceful resolution can be reached.
-perception of fairness is crucial
-provides the team with faith in their ability to continue to co-operate with each other
listening skills
the ability to hear and understand messages that are being sent characterized by using eye contact, positive body language, and positive feedback
importance of listening skills
-make workers more productive
-allows workers to better understand assignments they are given
-listeners work better in a team environment
-allows workers to build a strong rapport with coworkers, managers, and clients
-good listeners also have a better track record resolving problems with customers.
Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory
-deals with how leaders influence member behavior, INDIVIDUAL dyadic relationship between leaders and subordinates
Highlights the importance of leader behaviors not just toward the group as a whole but toward individuals on a personal basis. (role taking, role making, routinization)
-creation of an in-group and an out-group
-aka VERTICAL DYADIC LINKAGE THEORY
group dynamics
the ways in which individuals affect groups and the ways in which groups influence individuals
team building
a process that consists of formal activities intended to improve the development and functioning of a work team
group dynamics impact.....
team building
effective leader feedback
-make it relevant
-stay focused
-provide context
-listen carefully
-be compassionate
-follow up
characteristics of an effective follower
1. Exemplify Core Values
2. Decision Maker
3. Commitment
4. Problem Solving
5. Organizational Understanding
6. Flexibility
7. Competence
8. Good Communication skills
9. Courage
10. Enthusiasm
being a leader and a follower
has a dual role of being both
Group vs. Team
-group is a collection of individuals who coordinate their individual efforts.
-team is a group of people who share a common team purpose and a number of challenging goals. Members of the team are mutually committed to the goals and to each other
Advantages of teamwork
-increased productivity
-increased speed
-reduced costs
-improved quality
-reduced destructive internal competition
-improved workplace cohesiveness
disadvantages of teamwork
1. groupthink
2. hidden agendas
3. social loafing
characteristics of effective teams
-Clear sense of purpose/direction
-Open and honest communication
-support risk taking and change
-defined roles
-communicate freely
-common goals
-encourage differences in opinion
-collaboration
-Creative thinking
-Accountability
-Focus
-Decision by consensus
-team trust
functional teams
A team whose members come from the same department or functional area
cross-functional teams
corporate teams whose members represent various functions of the organization, such as R&D, design, production, marketing, distribution, and customer service
self-managed teams
a group of employees that's responsible and accountable for all or most aspects of producing a product or delivering a service. Traditional organizational structures assign tasks to employees depending on their specialist skills or the functional department within which they work.
strategic vision
The long-term direction and strategic intent of a company.
Provides a perspective on where the organization is headed and what it can become in the future (analyze environment)
Strategic Planning
the managerial process of creating and maintaining a fit between the organization's objectives and resources and the evolving market opportunities
strategic implementation
the process of planning, allocating and controlling resources to support the chosen strategies
mission statement
a short, specific written statement of the reason a business exists and what it wants to achieve
evaluating leadership strategies
-create opprotunities for feedback
-make time for self-reflection
-check the clarity of your vision
crisis management
a coordinated effort to handle all the effects of unfavorable publicity or another unexpected unfavorable event
process for crisis management
-Risk identification
-Risk assessment and ranking
-risk reduction strategies
-crisis prevention simulations
-crisis management
Risk Identification
Identifying the potential project risks and documenting their characteristics.
risk assessment and ranking
evaluation of the short-term and long-term risks associated with a particular activity or hazard
Risk Reduction Strategies
1. Preparation for the activity
2. Conduct of the activity
3. Injury management
4. Records management
Crisis Prevention
involves activities that managers undertake to try to prevent crises from occurring and to detect warning signs of potential crises
what must leaders understand about change
recognize the need for change and understand why people resist change
Change Process
approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations using methods intended to re-direct the use of resources, business process, budget allocations, or other modes of operation that significantly reshape a company or organization
Change Management Process
the sequence of steps that a manager would follow for the successful implementation and adoption of change
mission
sentence describing a company's function, markets and competitive advantages; a short written statement of your business goals and philosophies
vision
an encompassing explanation of why the organization exists and where it's trying to head
goals
The broad, long-term accomplishments an organization wishes to attain.
leadership development plan
1) initial diagnosis
2) assessment
3) design
4)implementation
5) support
6) evaluation
a detailed plan that helps you set your career towards advanced leadership roles and senior management positions.
individual leadership
focus more on what is best for individuals
organizational leadership
a dual focused management approach that works towards what is best for individuals and what is best for a group as a whole simultaneously. It is also an attitude and a work ethic that empowers an individual in any role to lead from the top, middle, or bottom of an organization.
-try to get individuals to attain their goals and group goals, goals for groups and individuals
Leadership Theory
An explanation of some aspect of leadership; theories have practical value because they are used to better understand, predict, and control successful leadership.
-schools of thought brought forward to explain how and why certain individuals become leaders. The theories emphasize the traits
contingency theory of leadership
the idea that the effectiveness of a leader depends both on how task oriented or relationship oriented the leader is and on the amount of control the leader has over the group