l8 amines part 2
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
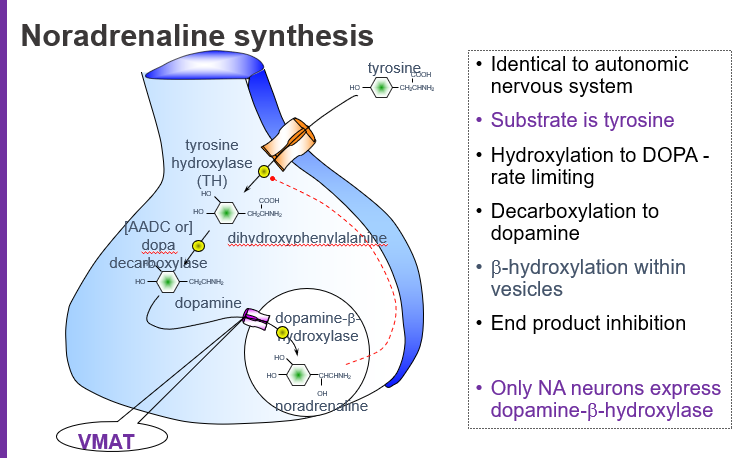
What is the starting molecule (substrate) for noradrenaline synthesis?
Tyrosine, an amino acid that serves as the precursor for catecholamines.
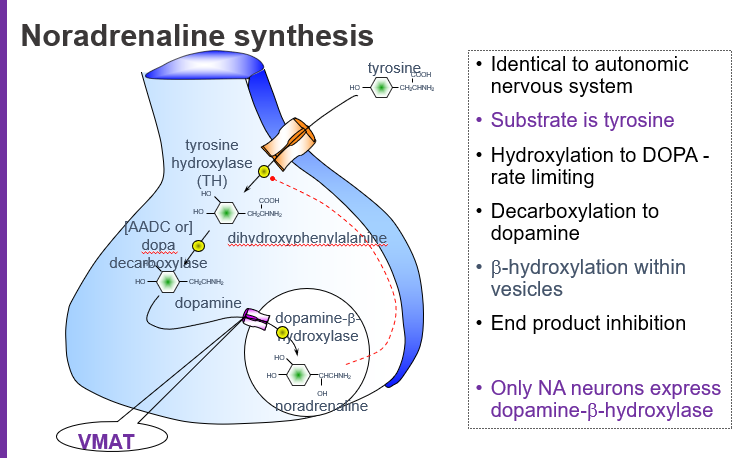
Which amino acid is used to begin noradrenaline synthesis?
Tyrosine.
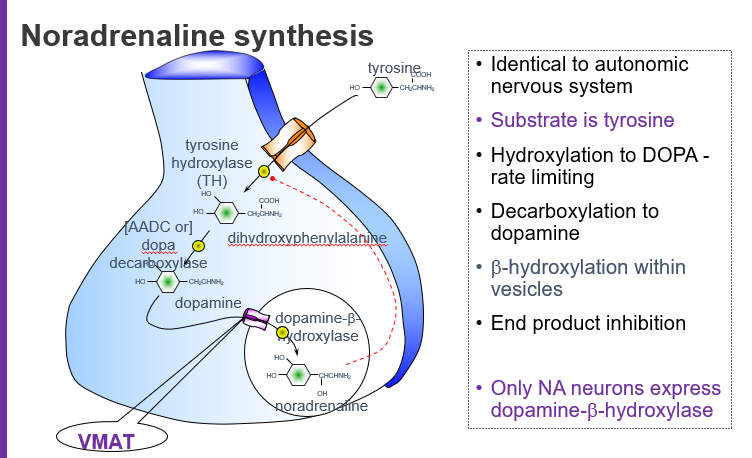
What is the rate-limiting step in noradrenaline synthesis?
The hydroxylation of tyrosine to L-DOPA by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (TH).
Which enzyme controls the rate of noradrenaline production by acting first on tyrosine?
Tyrosine hydroxylase (makes L-DOPA).
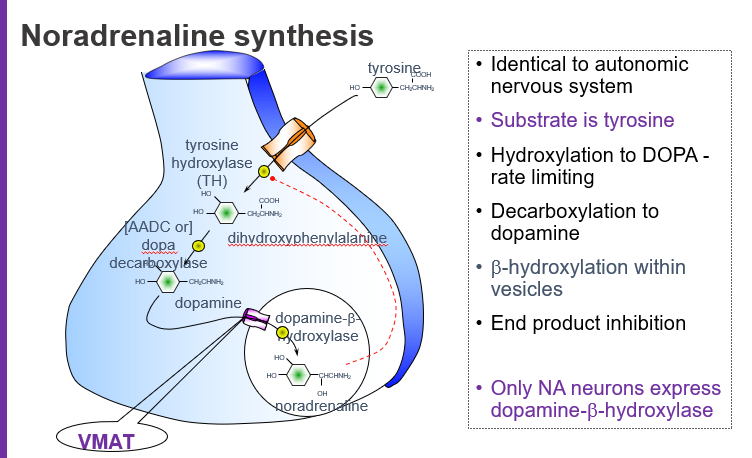
What intermediate is formed when tyrosine is hydroxylated?
L-DOPA (L-dihydroxyphenylalanine).
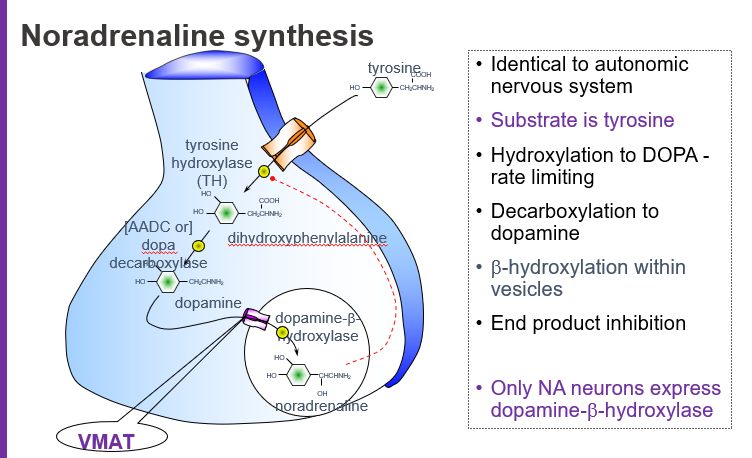
What molecule is produced directly from tyrosine before dopamine?
L-DOPA.
Which enzyme converts L-DOPA to dopamine?
Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC), also called DOPA decarboxylase.
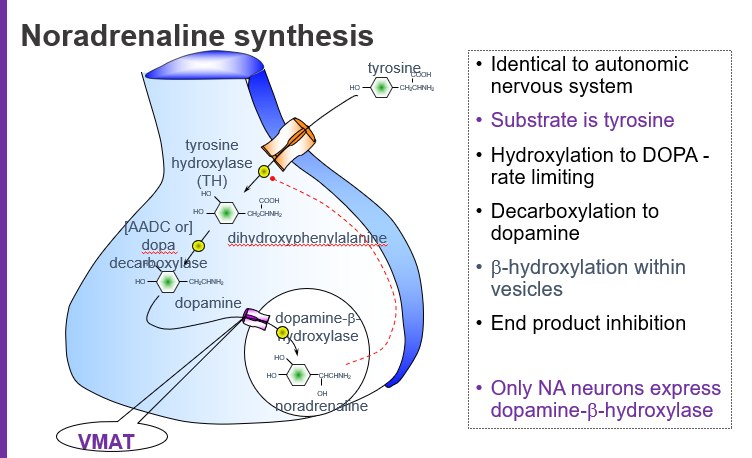
What is the name of the enzyme that makes dopamine from L-DOPA?
DOPA decarboxylase (AADC).
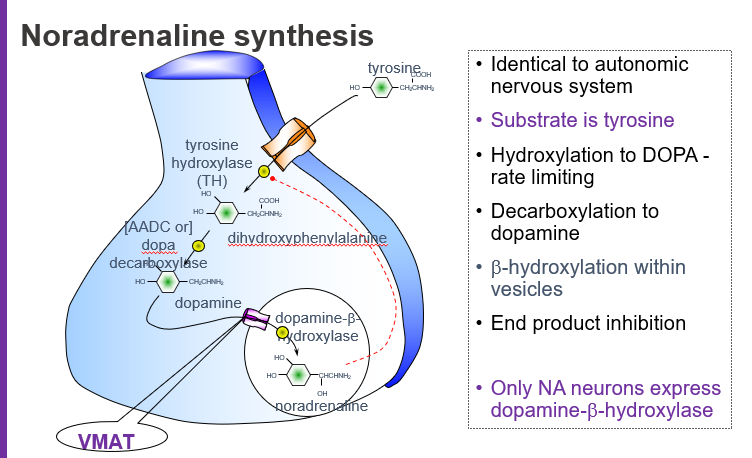
Where does the conversion of dopamine to noradrenaline occur?
Inside synaptic vesicles via dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH).
In which part of the neuron is dopamine converted into noradrenaline?
Inside vesicles, by DBH.
Which enzyme is only found in noradrenaline-producing neurons?
Dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH).
What enzyme distinguishes NA neurons from dopaminergic ones?
DBH, because only NA neurons express it.
What does VMAT do in noradrenaline synthesis?
VMAT (Vesicular Monoamine Transporter) moves dopamine into vesicles where it is converted to noradrenaline.
What transporter loads dopamine into vesicles for conversion to noradrenaline?
VMAT.
What is end-product inhibition in noradrenaline synthesis?
Noradrenaline inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase, reducing its own production when levels are high.
How does noradrenaline regulate its own synthesis?
Through feedback inhibition of tyrosine hydroxylase.
Is noradrenaline synthesis the same in the CNS and autonomic nervous system?
Yes, the synthesis pathway is identical in both systems.
Do noradrenaline neurons in the brain and peripheral nervous system use the same synthesis steps?
Yes — the pathway is the same.
summary of the pathway
Tyrosine → (Tyrosine hydroxylase) → L-DOPA → (DOPA decarboxylase) → Dopamine → (VMAT loads into vesicles) → (DBH) → Noradrenaline
How do neurons increase noradrenaline production during high demand?
By increasing TH and DBH synthesis, boosting NA output.
Tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine β-hydroxylase.
Which enzymes are upregulated when more noradrenaline is needed?
Tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine β-hydroxylase.
What is the cellular mechanism behind increased NA production over time?
Increased gene expression of enzymes like TH and DBH.
How does long-term stimulation lead to more NA synthesis?
Through enhanced transcription of the enzymes.
What happens when tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) is blocked?
Noradrenaline synthesis is inhibited, which can lead to depression
Blocking which enzyme reduces NA levels and may trigger depressive symptoms?
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH).
Why doesn't giving more tyrosine increase noradrenaline levels?
Because TH becomes saturated, and can't work faster even with more substrate.
What limits further NA synthesis even when tyrosine is abundant?
Saturation of tyrosine hydroxylase.
How does L-DOPA affect noradrenaline synthesis?
It bypasses the rate-limiting step, boosting dopamine and noradrenaline level
What precursor can increase NA by avoiding the TH bottleneck?
L-DOPA.
What is the effect of blocking VMAT with a drug like reserpine?
It prevents vesicular storage of NA, leading to depression.
Which drug causes depression by depleting stored NA?
Reserpine, by blocking VMAT.
Why can altering NA synthesis cause autonomic side effects?
Because noradrenaline also acts in the autonomic nervous system.
Modulating NA levels affects which body system besides the brain?
The autonomic nervous system, causing side effects like hypotension and dry mouth
What is the main way noradrenaline is cleared from the synaptic cleft?
Reuptake by NET (Norepinephrine Transporter) into the presynaptic neuron (Uptake 1).
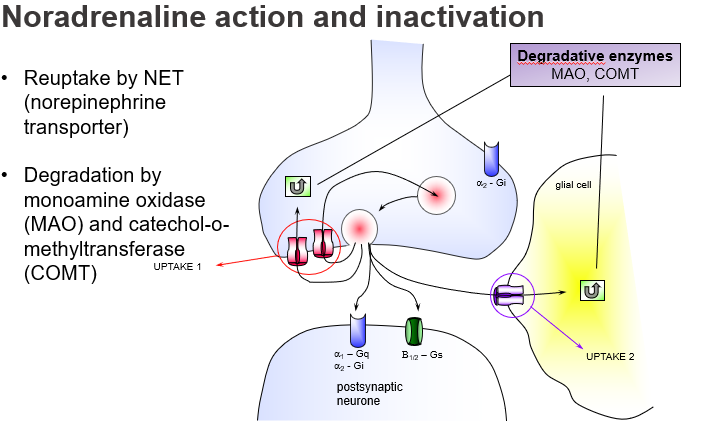
Which transporter is responsible for removing noradrenaline from the synapse?
NET, responsible for Uptake 1.
What is Uptake 2 in noradrenaline clearance?
A non-neuronal reuptake mechanism, often in glial cells, that plays a minor role unless Uptake 1 is blocked.
What pathway clears noradrenaline via glial cells and non-neuronal tissues?
Uptake 2.
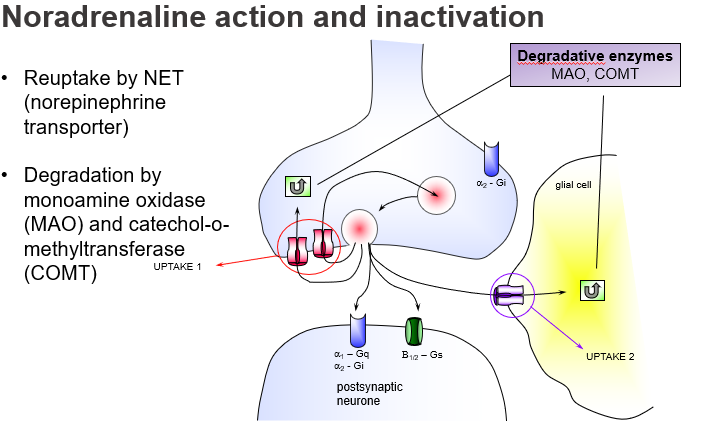
Which two enzymes break down noradrenaline?
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) and Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT).
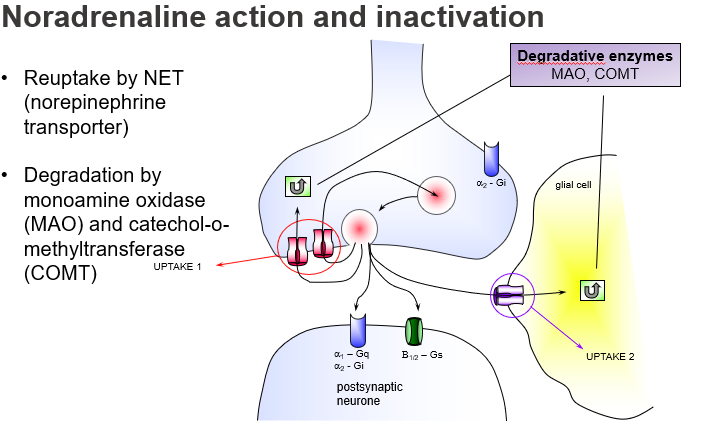
What enzymes degrade NA after reuptake or in glial cells?
MAO and COMT.
Where is monoamine oxidase (MAO) primarily active?
In the presynaptic neuron and glial cells, degrading NA after reuptake.
Which enzyme acts inside the neuron to break down noradrenaline?
MAO.
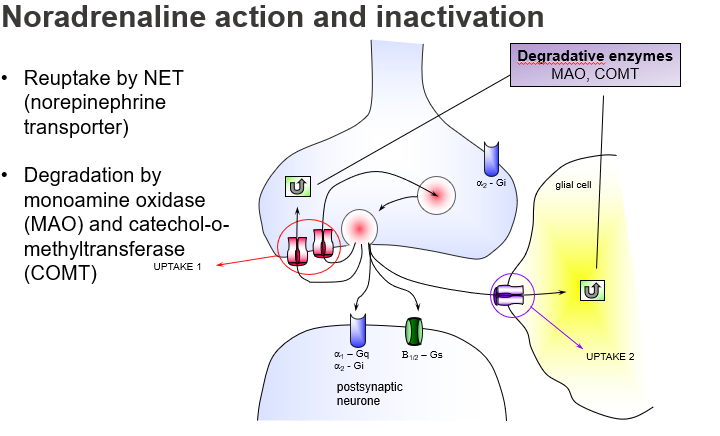
What is the function of α2-adrenoceptors in NA synapses?
They act as presynaptic autoreceptors to inhibit further NA release (negative feedback), and are Gi-coupled.
which noradrenaline receptor reduces further NA release and how?
α2-adrenoceptor, via Gi protein inhibition.
What G-protein pathway is α1-adrenoceptor linked to, and what is its effect?
Gq-coupled, activating phospholipase C for excitatory postsynaptic effects.
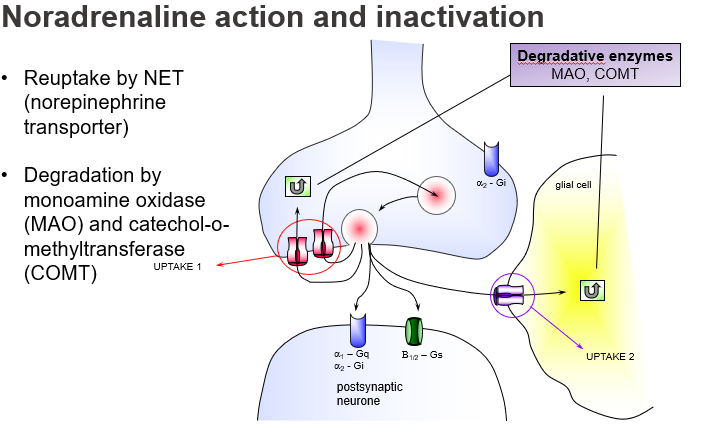
Which postsynaptic receptor mediates excitation via Gq signalling?
α1-adrenoceptor.
Which cell types contribute to NA breakdown outside the neuron?
Glial cells, via both MAO and COMT enzymes.
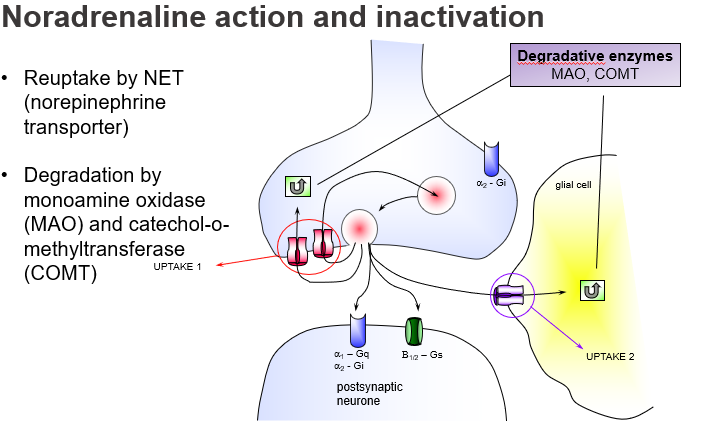
Where does enzymatic NA degradation also occur besides the neuron?
In glial cells.
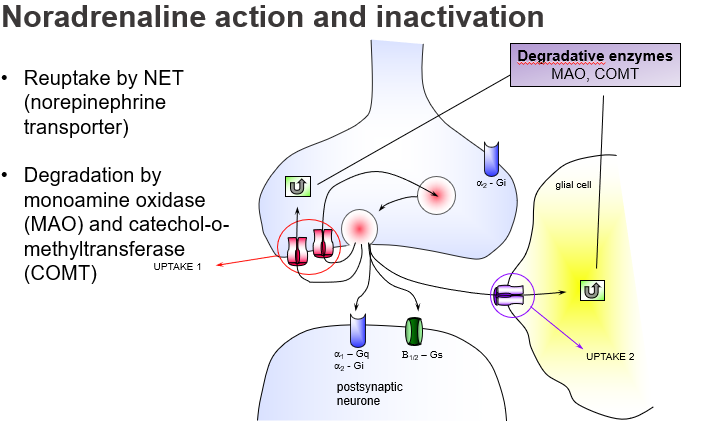
What happens if NET is blocked by drugs (e.g. antidepressants)?
NA stays longer in the synapse, enhancing its effect, useful in treating depression.
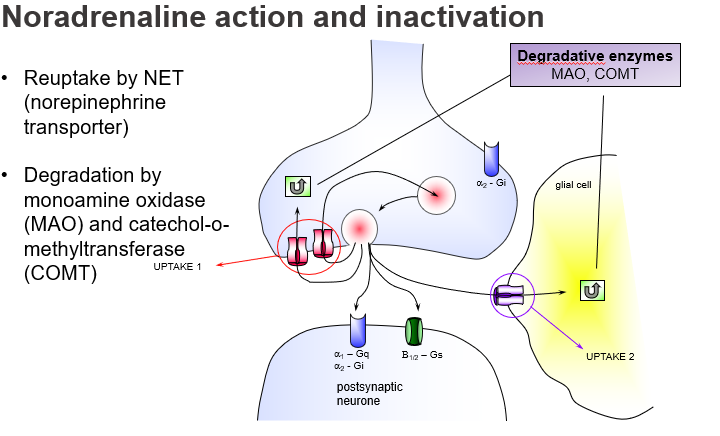
Why are NET inhibitors used as antidepressants?
They increase synaptic noradrenaline by blocking reuptake.
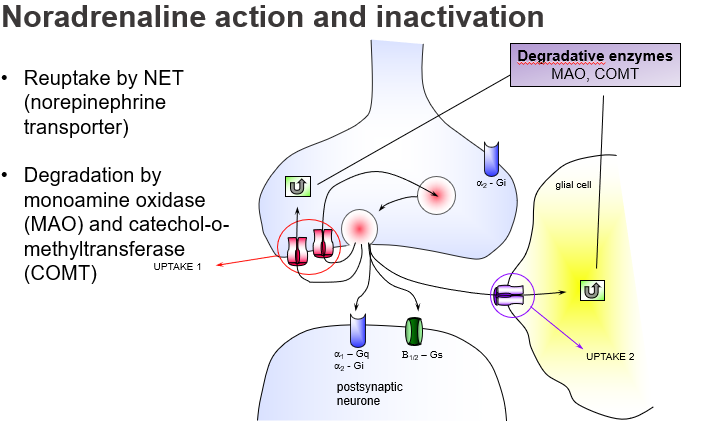
How do MAO inhibitors treat depression?
By preventing breakdown of NA, increasing its levels in the synapse.
What is the effect of MAOIs on synaptic noradrenaline?
They raise NA levels by blocking its degradation.
What mental illness is associated with overactive COMT?
Schizophrenia, due to excessive breakdown of dopamine and NA in the brain.
Overexpression of which enzyme contributes to a schizophrenia-like phenotype?
COMT.
What is the main method of noradrenaline inactivation in the CNS?
Uptake 1, via the NET transporter on the presynaptic neuron.
Which reuptake pathway plays the biggest role in NA clearance?
Uptake 1 (neural reuptake by NET).
Why are NET uptake blockers used as antidepressants?
they prevent reuptake, increasing NA activity and improving mood.
Which type of drugs treat depression by enhancing NA in the synapse?
Uptake 1 inhibitors like TCAs and SNRIs.
How does cocaine create a feeling of reward and euphoria?
It blocks NA and dopamine reuptake, leading to synaptic build-up.
Which drug blocks uptake of monoamines and causes strong reward effects?
Cocaine.
What is the mechanism of action of amphetamine?
It enters neurons via NET and displaces NA from vesicles, causing massive release into the synapse.
How does amphetamine increase noradrenaline levels in the synapse?
By displacing it from vesicles and promoting release.
Where do central dopamine pathways originate in the brain?
The substantia nigra (SN) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) of the midbrain.
What two midbrain structures are the main sources of CNS dopamine neurons?
SN and VTA.
What is the nigrostriatal pathway and what does it control?
A dopamine pathway from the substantia nigra to the striatum, involved in movement control.
Which dopamine pathway is crucial for motor function and is lost in Parkinson’s disease?
The nigrostriatal pathway.
Which dopamine pathways arise from the VTA and are involved in emotion and cognition?
The mesolimbic (emotion, reward) and mesocortical (cognition, planning) pathways.
What are the roles of the mesolimbic and mesocortical dopamine systems?
Mesolimbic: reward/emotion; Mesocortical: cognition/attention.
What psychiatric condition is linked to mesolimbic and mesocortical dopamine dysfunction?
Schizophrenia: mesolimbic overactivity → positive symptoms; mesocortical underactivity → negative symptoms.
How is schizophrenia related to dopamine pathway imbalance?
Too much dopamine in mesolimbic; too little in mesocortical areas.
What is the function of the tuberoinfundibular dopamine pathway?
It controls prolactin secretion by inhibiting it in the anterior pituitary.
Which dopamine pathway regulates prolactin and where does it originate?
The tuberoinfundibular pathway, from the hypothalamus.
Why is dopamine called the “reward chemical”?
Because it's involved in reward, motivation, and reinforcement learning, mainly via the mesolimbic pathway.
Which neurotransmitter is linked to reward and addiction, and via which pathway?
Dopamine, especially through the mesolimbic system.
What types of dopamine receptors exist in the CNS?
There are five dopamine receptors, D1 to D5, all of which are GPCRs (G protein-coupled receptors).
How many dopamine receptor subtypes are there and what kind of receptors are they?
Five subtypes (D1-D5), all are GPCRs.
Which dopamine pathway controls movement, and what disease results from its dysfunction?
The nigrostriatal pathway controls movement; its loss causes Parkinson’s disease.
What is the role of the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway and what condition is associated with its degeneration?
It regulates movement; degeneration causes Parkinsonism.
What brain system is involved in attention, emotion, and reward, influenced by dopamine?
The mesocorticolimbic system, involving VTA projections to cortex and limbic areas.
Which dopamine system affects motivation and emotion by projecting from the VTA?
The mesocorticolimbic pathway.
How is dopamine linked to schizophrenia?
Dopamine overactivity in the mesocorticolimbic system causes positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
What role does dopamine play in schizophrenia symptoms?
Excess dopamine in certain pathways leads to hallucinations and delusions.
Which drugs of abuse act on dopamine pathways?
Cocaine, heroin, and amphetamine increase dopamine activity, especially in reward pathways.
Name some addictive drugs that increase dopamine signaling.
Cocaine, heroin, and amphetamines.
How does dopamine regulate endocrine function?
Via the tuberoinfundibular system, dopamine inhibits pituitary hormone (prolactin) secretion.
Which dopamine pathway controls pituitary hormones?
The tuberoinfundibular dopamine pathway.
What role does dopamine play in the brainstem?
It is involved in vomiting; dopamine antagonists are used as antiemetics.
How does dopamine affect the emetic reflex?
Dopamine in the brainstem triggers vomiting; blocking dopamine receptors can prevent it.