bio review unit 2
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
bottle neck effect
a large reduction in population size leading to a decrease in genetic diversity
Peripatric speciation
when a new niche i entered by a population and then they are isolated from the rest of the pop

parapatric speciation
when a population enteres a new niche without being isolated from the rest of the species

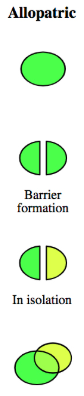
allopatric speciation
when a physical barrier comes between a population and isolates them from each other
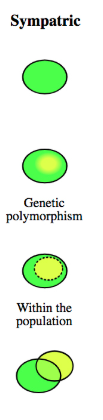
sympatric
when a population becomes reproductively isolated without any physical isolations withing the habitat.
mechanical isolation
physical differences in reproductive organs prevent mating between two species
gametic isolation
when the gametes (egg and sperm) can come into contact but they are incompatible and will not fertilize/make a zygote.
zygote mortality
the death of a zygote before it can develop into an embryo or offspring
hybrid inviability
when the offspring has a reduced chance of become reproductivly mature or viable
hybrid breakdown
a reproductive failure in F2 or later generations - since F1 was viable and fertile
adaptive radiation
an evolutionary process that produces new species from a single, rapidly diversifying lineage
importance of mass extinctions
lead to the diversification of surviving lineages, allowing them to occupy vacant ecological niches and evolve new adaptations
divergent evolution
when an ancestral species evolves into two or more new species
convergent evolution
when unrealted species form similar traits from adapting to similar environments
selective pressure
environmental traits that favor certain traits in a population
selective advantage
a trait that is favored by their environment and helps a species survives
evidence of natural selection
fossils, anatomy (homologous, analougous, vestigal), embryonology
what can you learn from fossils and how its formed briefly
evidence for evolution (anotomy), how old a species is/ what era their from, how they lived, where they lived and their environmental conditions (ex sea water or fresh water?)
vestigial structures
anatomical structures or traits that were once functional in an organism's ancestors but have since lost their original function, often becoming reduced or non-functional
embryology
we share many similar developmental phases while in utero
survival of the fittest/descent within modification
more offspring born than can survive
ressources are limited
variation between individuals
some will be better suited to the environment and have offspring while some won’t