Module 6 Chemistry of phenol
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
what type of acid is phenol
weak acid
what happens to phenol when dissolved in water
will partially dissociate making it a weak acid. more acidic than alcohols but less acidic than carboxylic acids
why is phenol less soluble in water than most alcohols
OH group is polar and can undergo hydrogen bonding with water but benzene ring is non polar
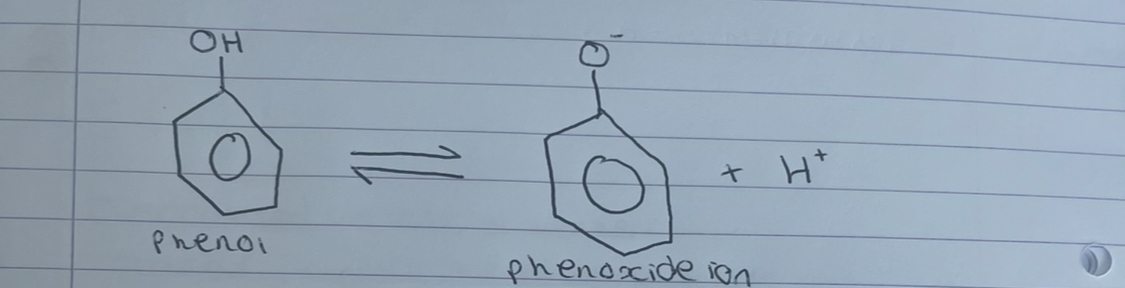
what does this show
phenol is a weak acid
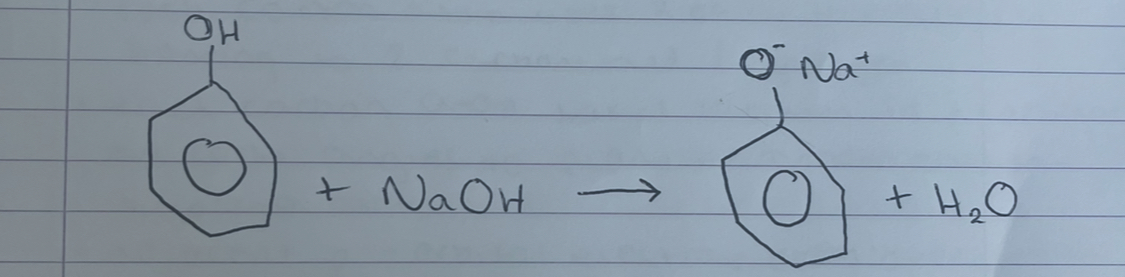
what does this show
neutralisation of NaOH, produces sodium phenoxidesalt
what is the electron density like in bromination of phenol
high electron density in benzene ring to polarise bromine molecule
what is not needed in bromination of phenol
without halogen carrier
what does bromination of phenol form
2,4,6-tribromophenol
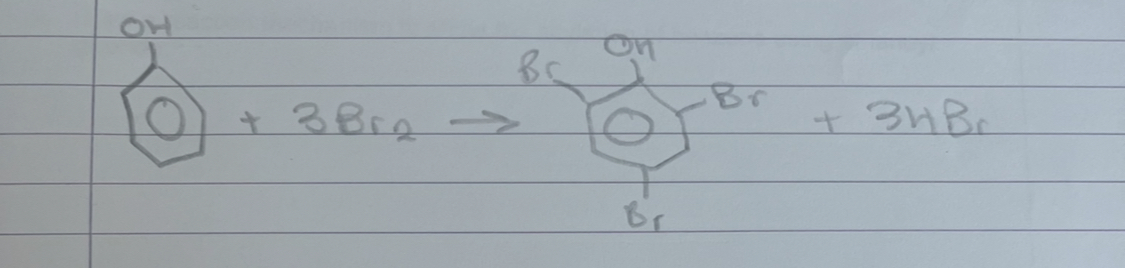
what is this
bromination of phenol
what temp does nitration of phenol happen
room temp
what is nitration of phenol without
without H2SO4 present
what products are formed in nitration of phenol
2-nitrophenol or 4-nitrophenol
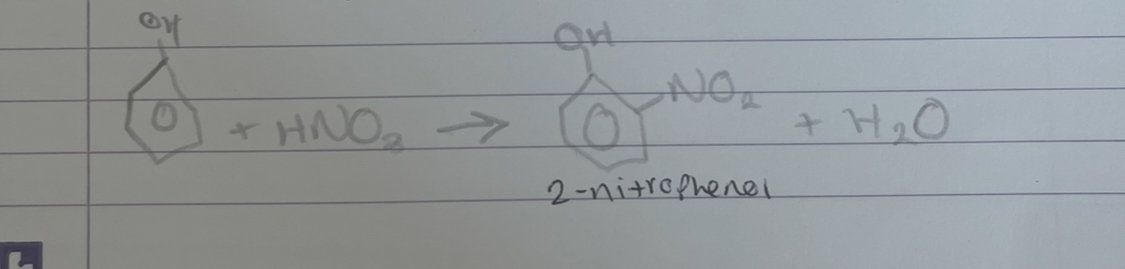
what is this
nitration of phenol
what happens in electrophilic substitution of phenol
lone pair on oxygen overlaps with delocalised ring and merge and distort the shape (donation into the pi system)
what will the lone pair on oxygen overlapping with delocalised ring and merging and distorting the shape (donation into the pi system) causing in the electrophilic substitution of phenol
increase electron density, increase reactivity of aromatic ring
what is not needed in electrophilic substitution of phenol
catalyst not usually needed
what conditions does electrophilic substitution of phenol happen under
under milder conditions than benzene
what is more common in electrophilic substitution of phenol
multi substitutions are more common
what happens if nitration of phenol happens with concentrated nitric acid
multi substitution occurs and produces 2,4,6-trinitrophenol
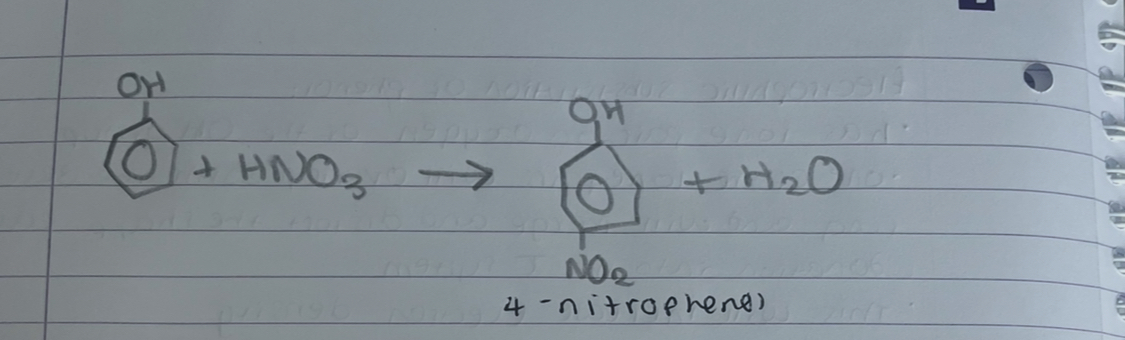
what is this
nitration of phenol
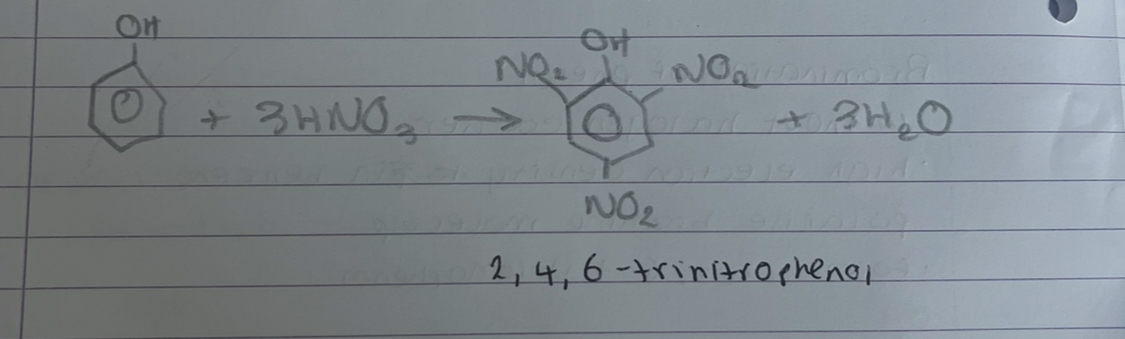
what is this
nitration of phenol with concentrated nitric acid