unit 1b psychological research (full)
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Basic Research
Builds psychology's knowledge base through exploration.
Applied Research
Addresses practical problems using psychological concepts.
Scientific Attitude
Curiosity and skepticism towards unsupported claims.
Hindsight Bias
Belief that outcomes were predictable after they occur.
Overconfidence (secret term!!)
Excessive confidence in one's own correctness.
Critical Thinking
Evaluates evidence and assesses conclusions critically.
Validity
Accuracy of a test in measuring intended concepts.
Reliability
Consistency of results across multiple trials.
Scientific Method
Systematic process for observing and testing theories.
Theory
Integrated set of principles predicting observations.
Hypothesis
Testable prediction derived from a theory.
Null Hypothesis
Assumes no relationship between studied variables.
Operational Definitions
Specific procedures to define research variables.
Replication
Repetition of study to confirm findings.
Descriptive Studies
Observational methods to describe behavior patterns.
Case Study
In-depth study of an individual to reveal principles.
Naturalistic Observation
Observing subjects in their natural environment.
Surveys
Questionnaires to gather data from a population.
Industrial Psychologists
Focus on workplace behavior and productivity.
Cognitive Psychologists
Study mental processes like perception and memory.
Personality Psychologists
Examine individual differences in behavior and traits.
Social Psychologists
Investigate how individuals influence and are influenced by others.
Developmental Psychologists
Study psychological growth and change across the lifespan.
Biological Psychologists
Explore the relationship between biology and behavior.
Patient H.M.
Subject with anterograde amnesia after hippocampus removal to treat his seizures.
Retrograde amnesia
Memory loss of past events.
Anterograde amnesia
Inability to form new memories.
Hippocampus
Brain region crucial for memory formation.
Hausa tribe
Cultural group studied for attraction preferences, deeper voices led to stronger attraction.
Case study
In-depth analysis of an individual or group.
False consensus effect
Overestimating others' agreement with personal beliefs.
Survey
Method for gathering self-reported attitudes or behaviors.
Framing effect
Influence of question wording on responses.
Naturalistic observation
Recording behavior in natural settings without interference.
Field experiment
Research in real-world settings with some control.
Subjects
Individuals or animals involved in a study.
Sample
Subset of a population for analysis.
Population
Entire group targeted for research.
Random sampling
Each member has equal chance of selection.
Stratified sampling
Dividing subjects into subgroups for representation.
Double-blind procedure
Neither researchers nor participants know treatment status.
Counterbalancing
Technique to control for order effects in experiments.
Correlation studies
Examine relationships between variables without control.
Correlation coefficient
Statistical measure indicating relationship strength.
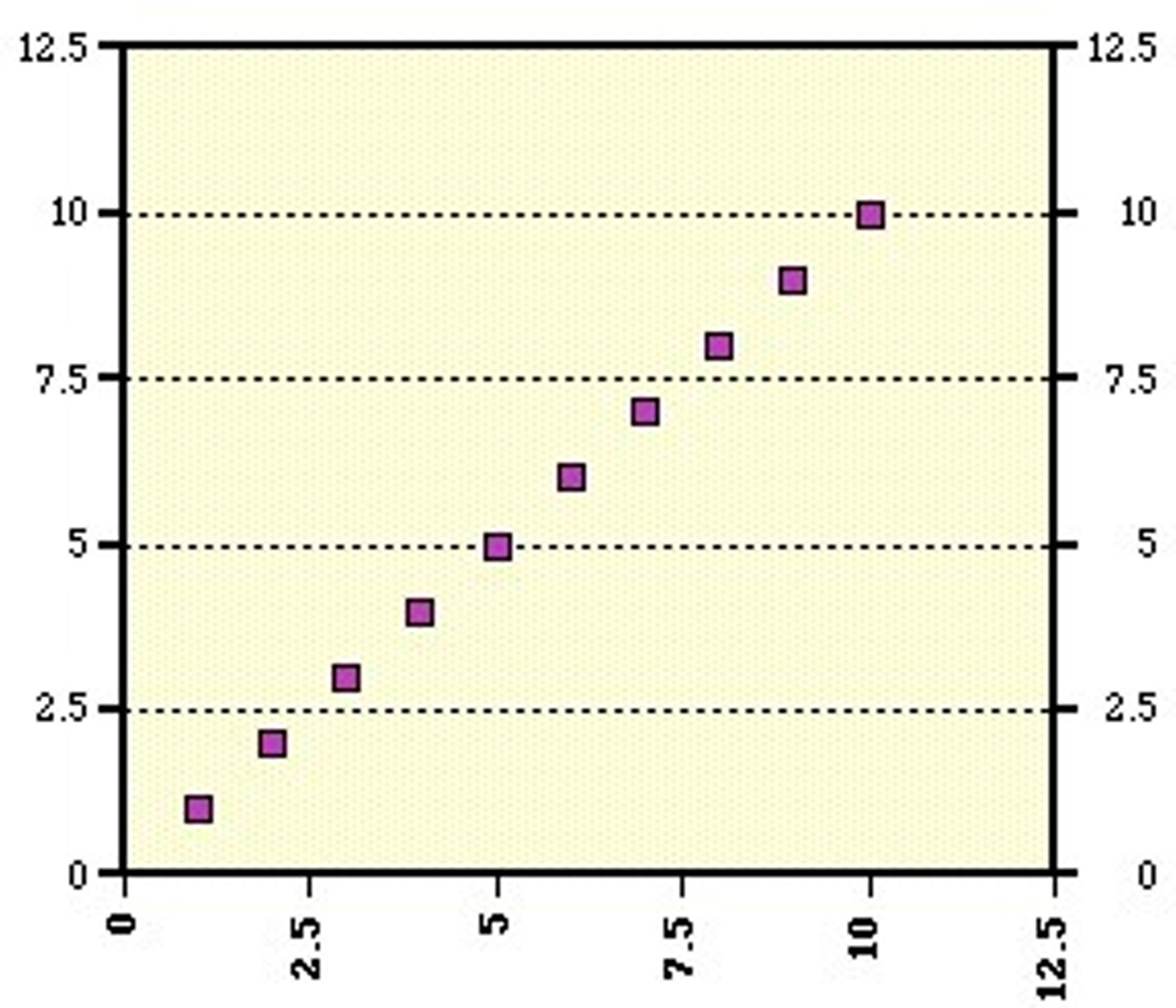
Positive correlation
Both variables increase together.
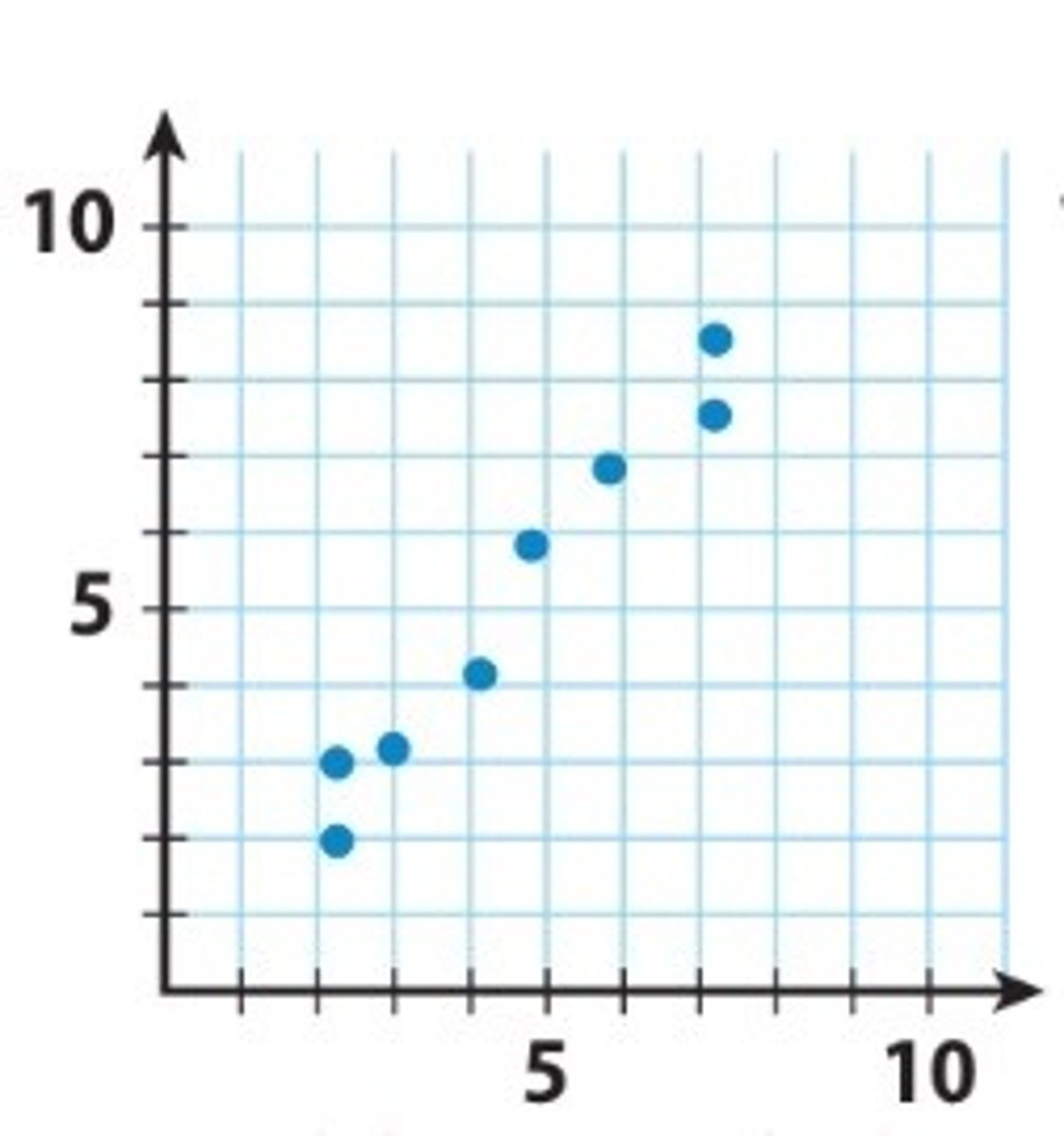
Perfect positive correlation
+1.00 indicates direct proportional increase.
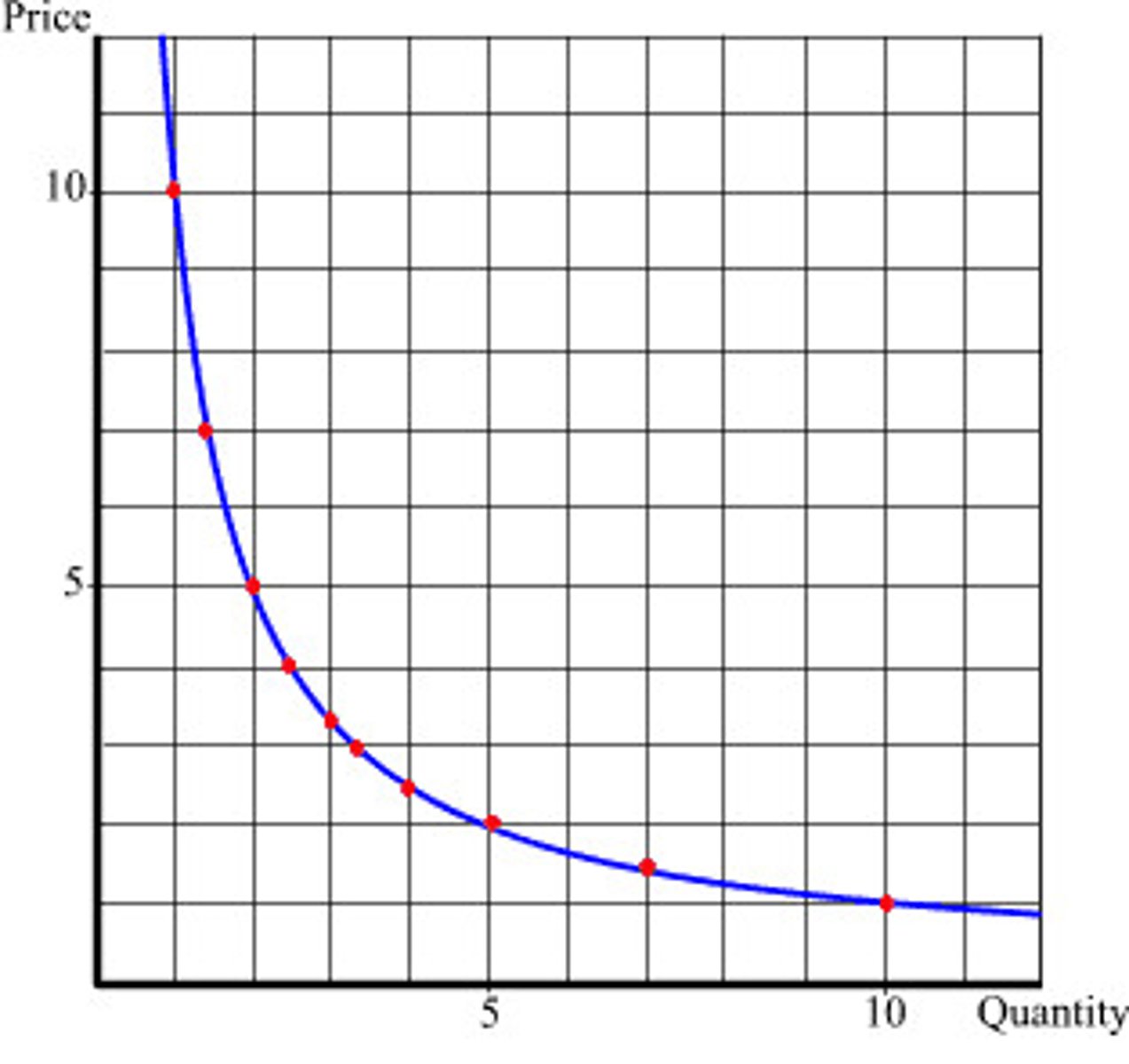
Negative correlation
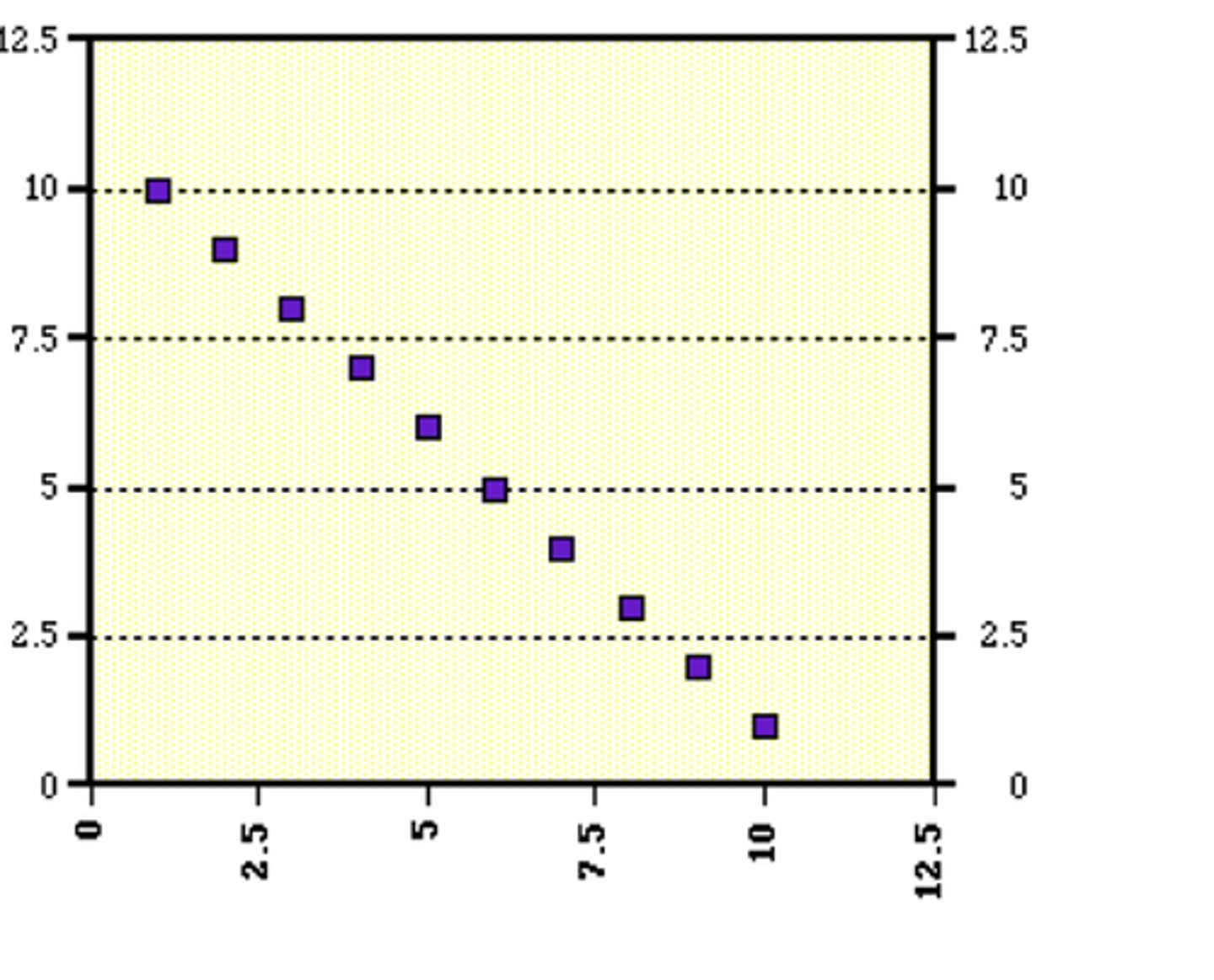
One variable increases while the other decreases.
Perfect negative correlation
-1.00 indicates inverse proportional relationship.
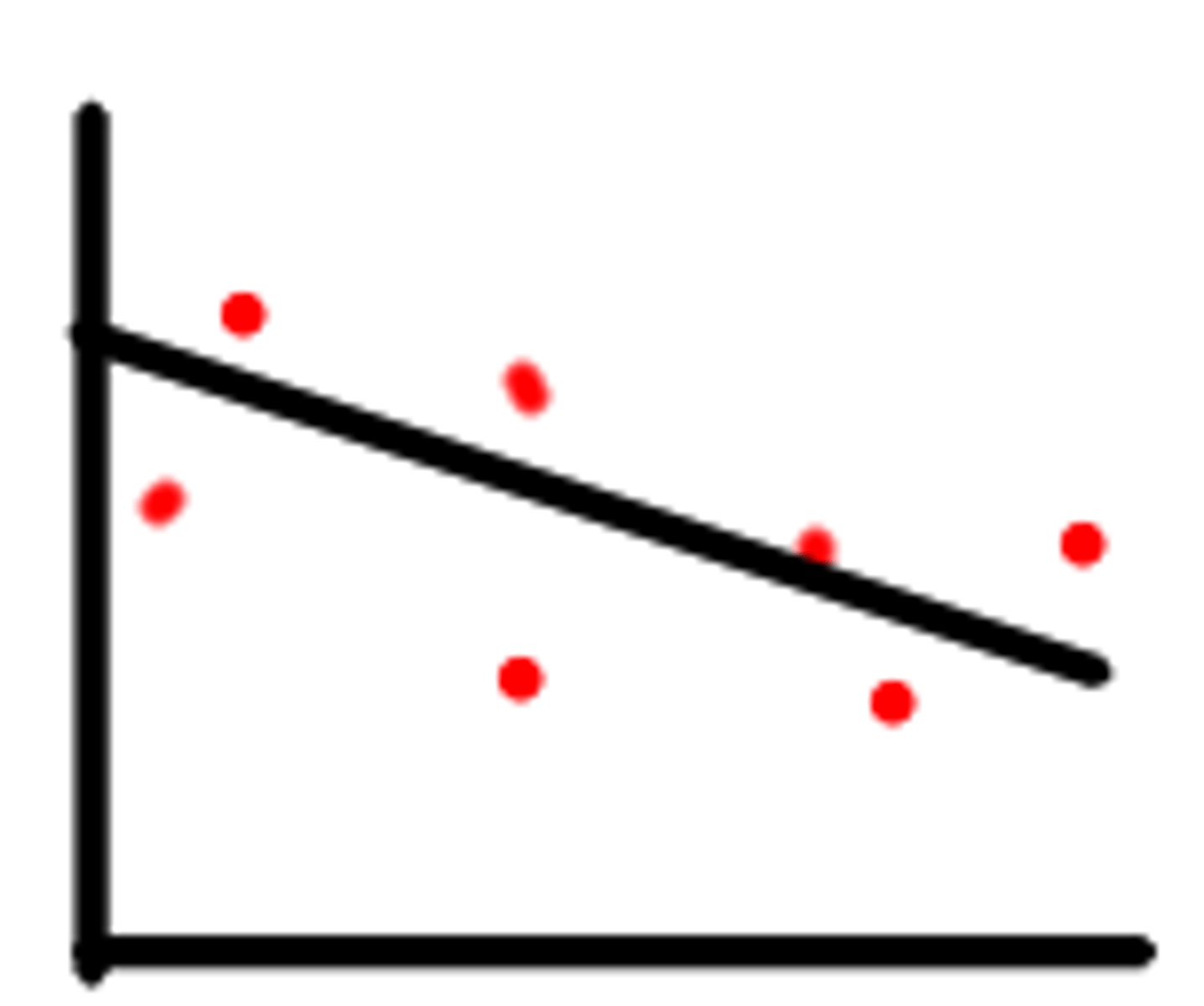
Weak correlation
Near 0 indicates little to no relationship.
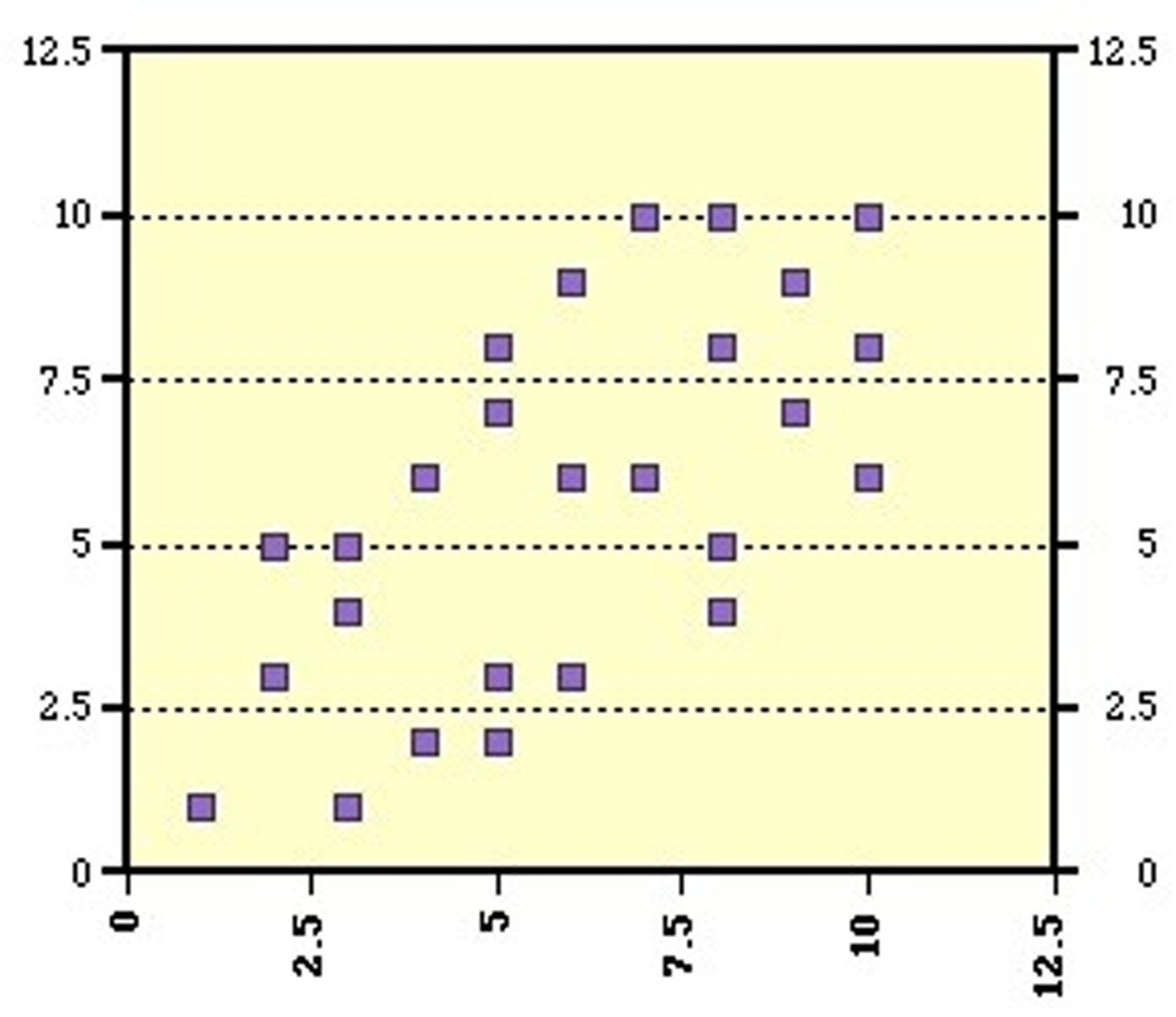
Direct relationship
One variable predicts another's behavior.
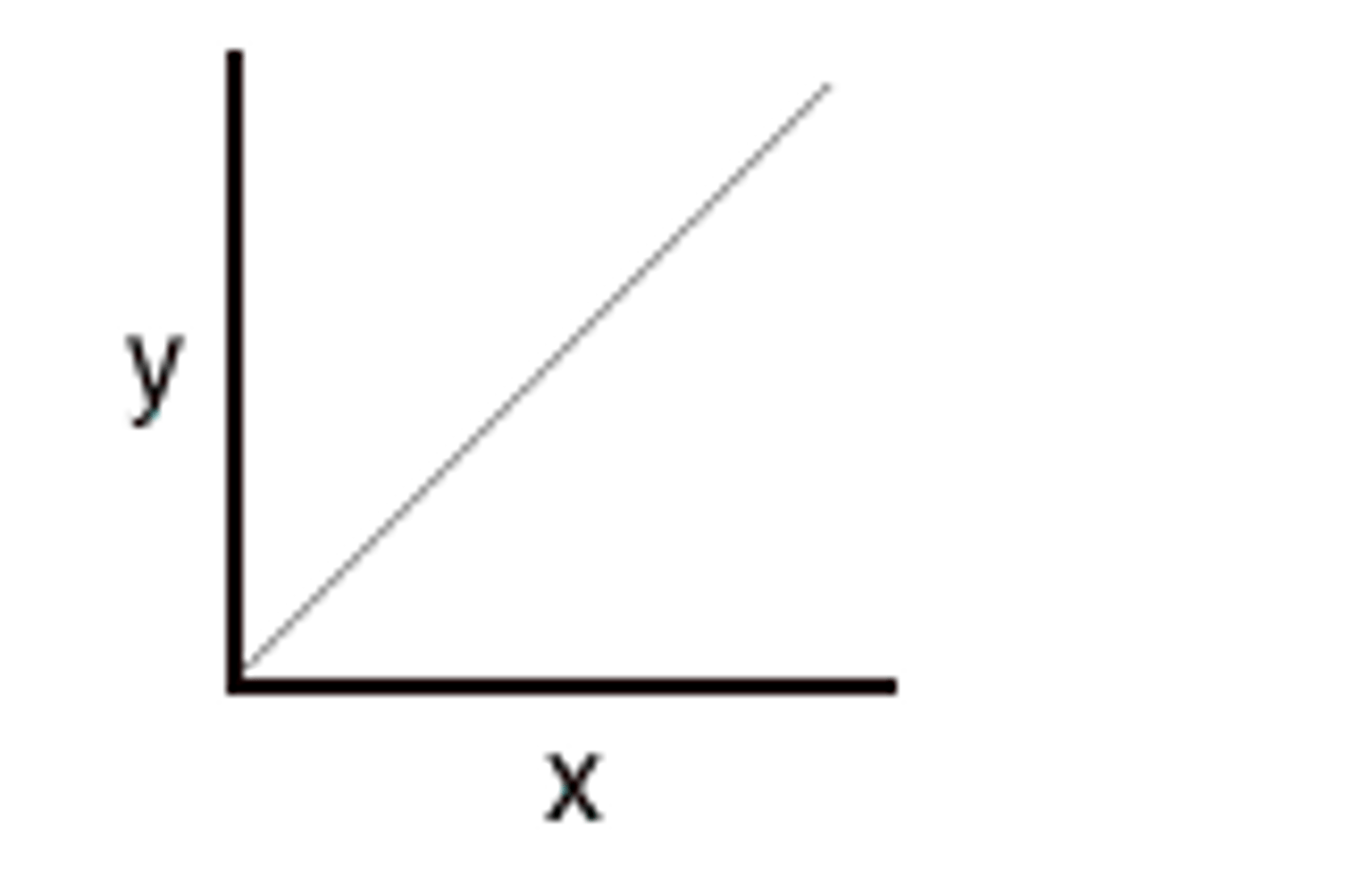
Inverse relationship
Two variables relate inversely to each other.
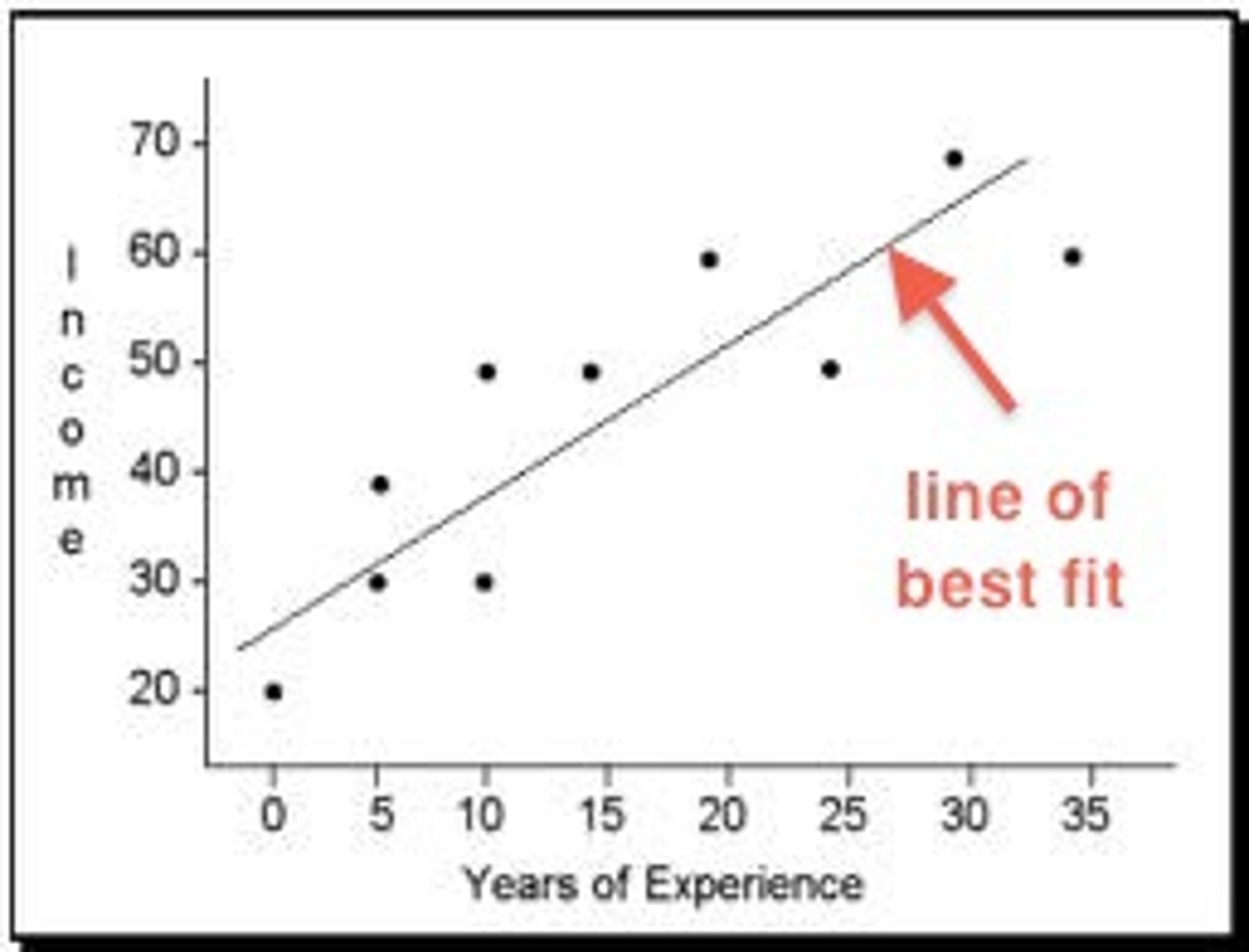
Scatterplots
Graph showing relationship between two variables.
Line of best fit
Minimizes distance between data points and line.
Illusory correlation
Perception of a relationship where none exists.
Correlation does not equal causation
Correlation does not imply one variable causes another.
Experimental studies
Controlled settings manipulate factors to show effects.
Laboratory experiment
Research method manipulating independent variables.
Experimenter bias
Researcher unintentionally influences experiment outcomes.
Independent variable (IV)
Factor manipulated to observe its effect.
Dependent variable (DV)
Measured factor that may change due to IV.
Confounding variable
Other factors that may interfere with results.
Random assignment
Assigning participants by chance to minimize differences.
Experimental condition
Group receiving the treatment or independent variable.
Control condition
Group that does not receive the treatment.
Hawthorne effect
Behavior changes due to awareness of observation.
Blind/subject bias
Participants' knowledge affects study outcomes.
Placebo
Treatment that appears real but has no effect.
Placebo effect
Improvement due to belief in treatment's efficacy.
Longitudinal study
Repeated measures over an extended time period.
Cross-sectional study
Analyzes data from different groups at one time.
Measures of central tendency
Summarizes data with mean, median, and mode.
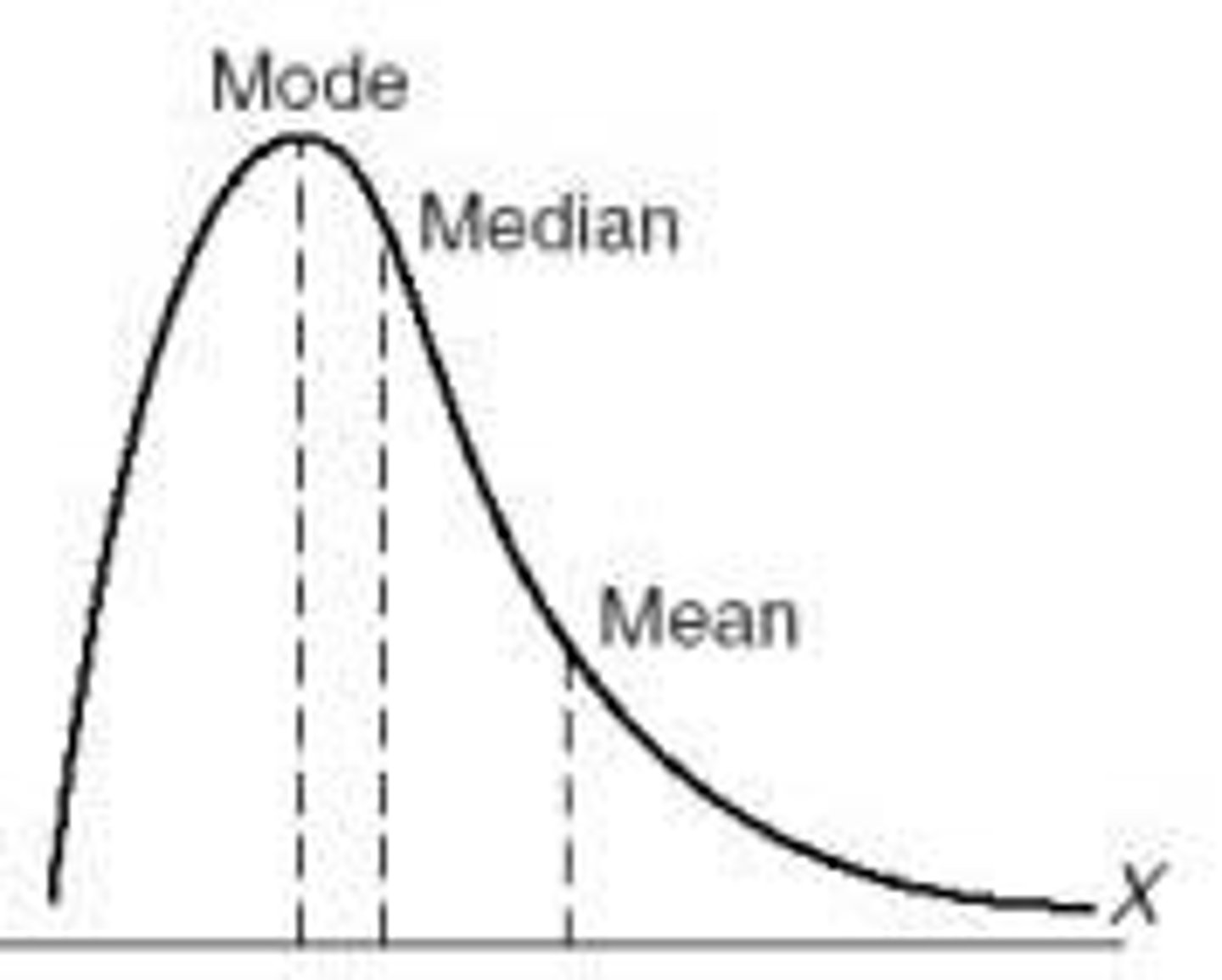
Mode
Most frequently occurring score in a distribution.
Mean
Average score calculated by total divided by count.
Median
Middle score when data is ordered.
Extreme scores
Lowest and highest scores in a distribution.
Measures of variation
Show diversity and spread of data distribution.
Range
Difference between highest and lowest scores.
Standard deviation
Measure of score variability around the mean.
Z-score
Describes the value's relation to the mean. Indicates how many standard deviations a specific data point is from the mean of a normal distribution.
Normal distribution
Bell curve representation of data distribution.
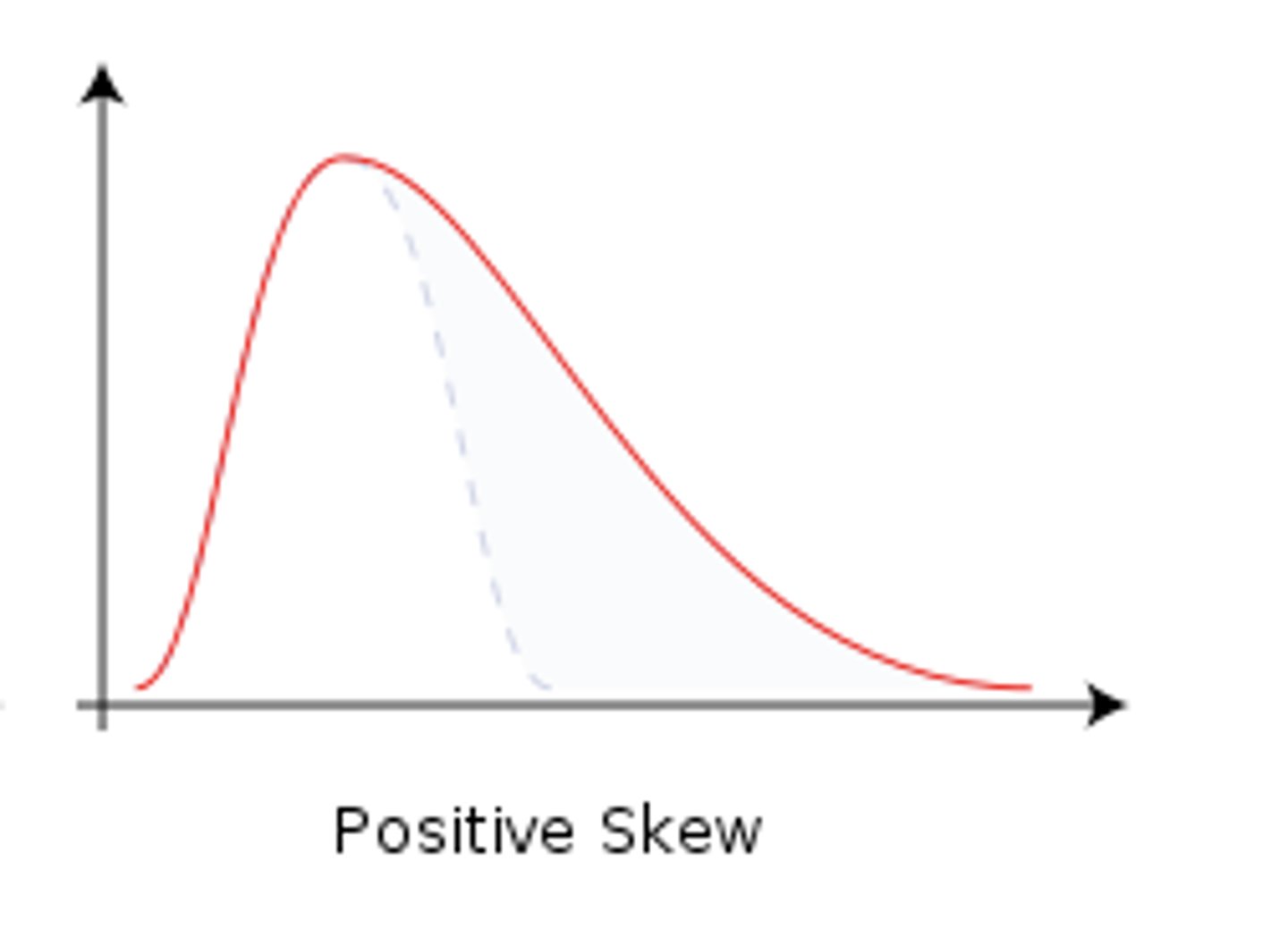
Positively skewed
A distribution of scores in which scores are concentrated in the low end of the distribution (more low scores than high scores)
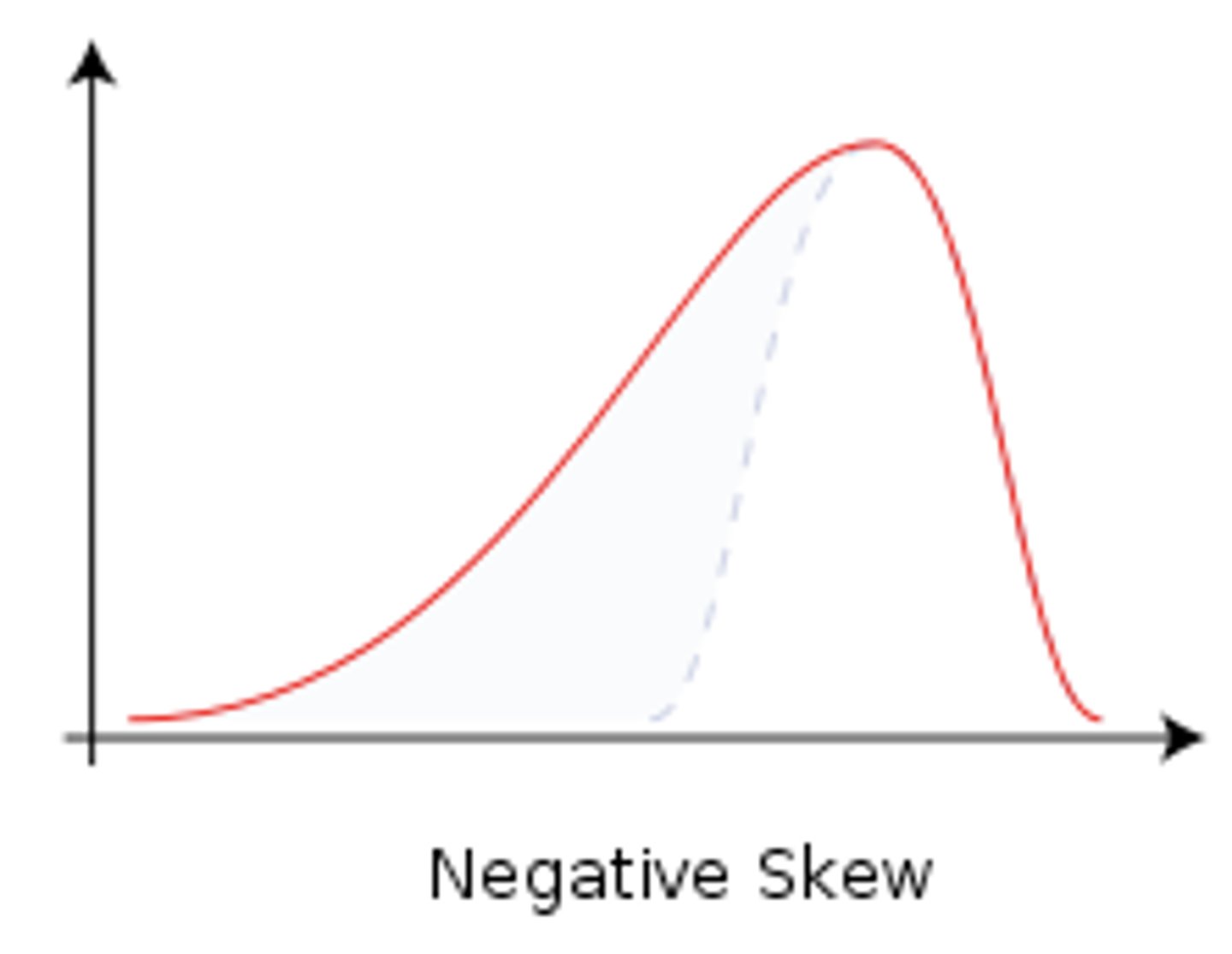
Negatively skewed
A distribution of scores in which scores are concentrated in the high end of the distribution (more high scores than low scores)
Variance
The spread between numbers in a data set
Statistical significance
A statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance
P-value
A statistical measurement used to validate a hypothesis against obtained data.
IRB
Stands for Institutional Review Board; they review research in advance to ensure ethical considerations are met
Type I error
A false positive error, the incorrect rejection of a null hypothesis
Type II error
A false negative error, when they accept the null hypothesis when it failed (found more of type II than type I)
APA ethical guidelines
APA ethics code has research standards and guidelines established for protected the animal and human participant's well being
Animal research
1) clear scientific purpose
2) must house and care for the animals in a humane way
3) acquisition: animals acquired legally
4) least amount of suffering feasable
Human research
1) informed consent (very important)
2) coercion, must be voluntary
3) anonymity/confidentiality (eg. patient H.M)
4) no significant mental/physical risk (eg. Milgram)
5) must debrief the purpose of experiment