Fossil fuels
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Coal
Steam engines, cooking, industry
Pollution, hazardous, hard to operate
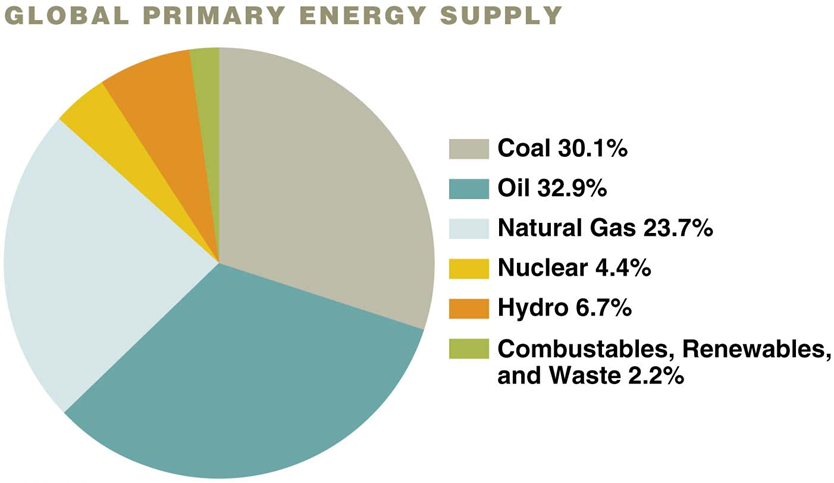
Oil
Alternative to coal. Refinement of oil into fuel. Main energy source for the world
More convenient and burned cleaner
Combustion engine lighter than steam engine
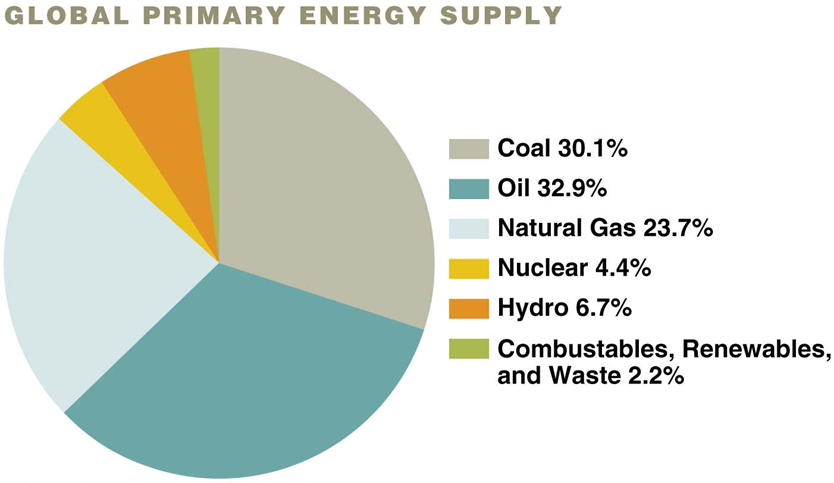
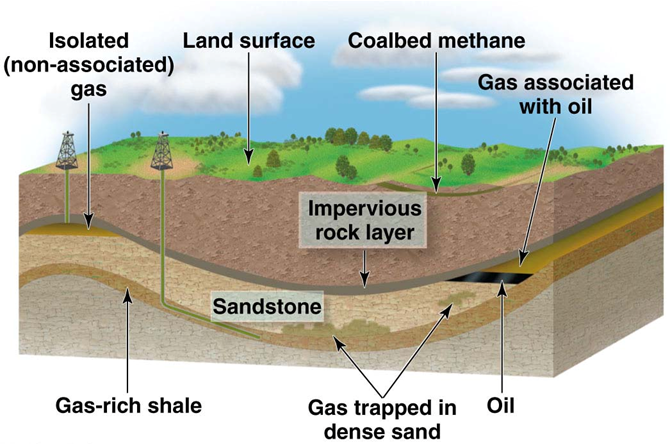
Natural gas 1
Drilling oil. Consists of methane (CO2 and H20 when burned.
More convenient, burned cleaner, inexpensive
Pipelines able to be transported instead of atmospheric
21% of world energy demand
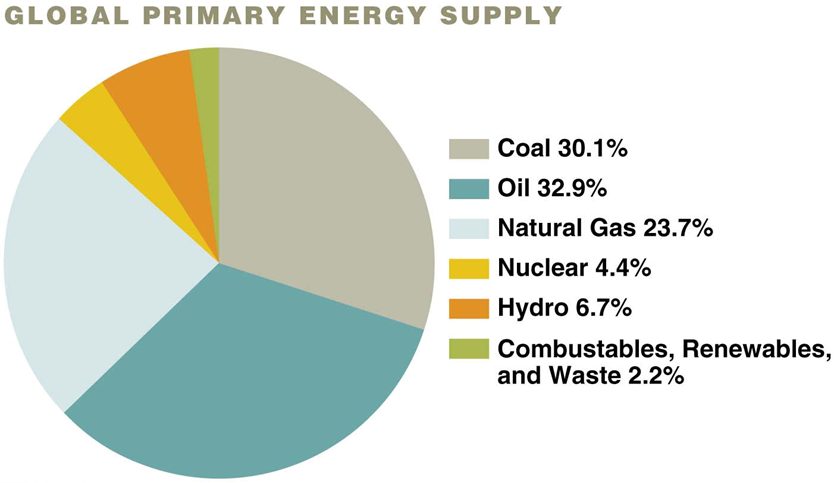
Electrical power
amount of work done by an electric current over time
Watt: 1J per second
kWh: 3.6 x 10^6J of energy
Energy carrier
electricity itself that transfers energy from primary energy source to point of use
Generator
Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy
Electrical generator
coil of wire that rotates in a magnetic field
Energy lost by conversion from primary source to electricity
33% efficient
Energy lost as heat by wire resistance
Turbogenerator
turbine and generator
Coal/oil/nuclear produce steam which drives turbine
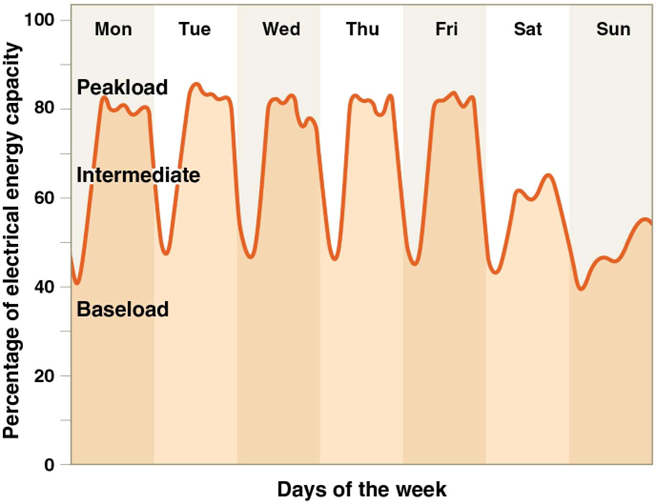
Brownout
result from deficiency of available power. Causes a reduction in voltage
Blackout
total loss of power. Occur during peak demand.
Demand rising faster than supply
Reserve capacity has declined to 15%
Summer heat waves are the greatest cause of sudden increased demand
Utilities are being pushed to the edge of their ability to provide electricity on demand
Self-healing electrical grid
Can prevent major blackouts
monitors problems
reacts to trouble
isolates troubled areas to prevent cascading failures
The U.S. Department of Homeland Security rates this as one of its highest priorities
Baseload
constant supply of power provided by large coal-burning/nuclear power plants
Heat energy
Produced by boiling water to drive turbines. Cannot be recycled into turbine.
Condenser turns steam into water for reuse
Heat energy lost to atmosphere
Alternative to cooling tower
Waste heat transfer to river/ocean
Kill planktonic organisms
Thermal pollution
waste heat discharged into natural water
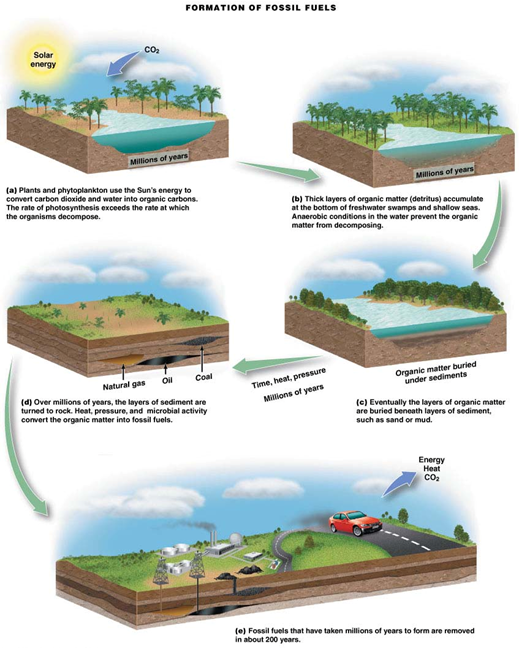
Crude oil
Extracted from deep wells on land/seafloor. Formed millions of years ago
Anaerobic conditions slow decomposition
Pressure/heat convert vegetation to fossil fuel
Composed of
Nitrogen compounds
Oxygen compounds
Sulfur compounds (e.g. toxic Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S))
Heavy metal contaminants (Fe, Ni, Cu, Cr, V, etc.)
Hydrocarbons (the vast majority):
Oil production
withdrawal of oil/gas from field. Does not proceed at a steady rate.
Oil trapped in pore spaces of sedimentary rock
Primary recovery
25% of oil can be removed using regular conventional pumping
Secondary recovery
remove up to 50% of oil by injecting steam/brine into wells.
Enhanced recovery
increases yield from well by injecting CO2 to break up oil
Impact of higher oil prices
Increased domestic production
the Alaskan pipeline, re-opening old fields
Increased fuel efficiency standards
lowered speed limits (to 55 mph)
Promoted appliance and building efficiencies
Developed alternative energy sources
Created a strategic oil reserve in Louisiana
Store 702 million barrels of oil (33 days of oil at 21 million barrels/day use)
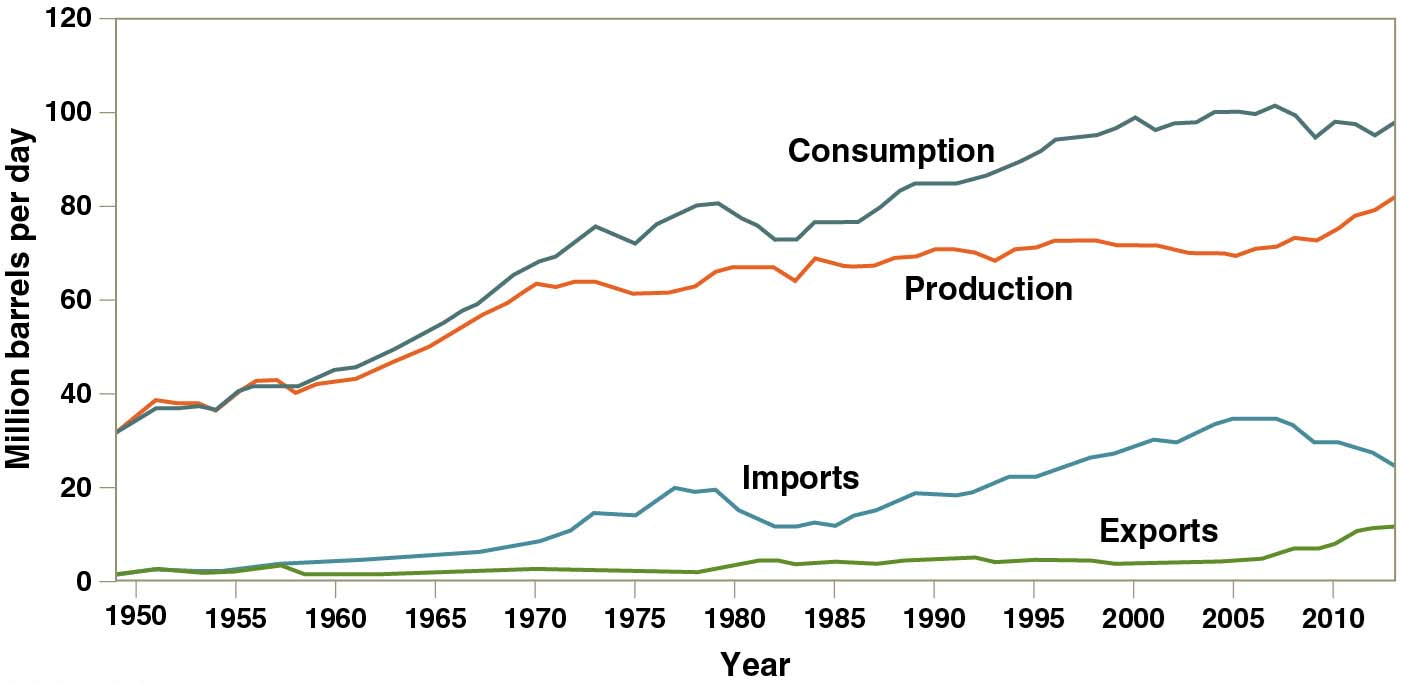
Oil limitations
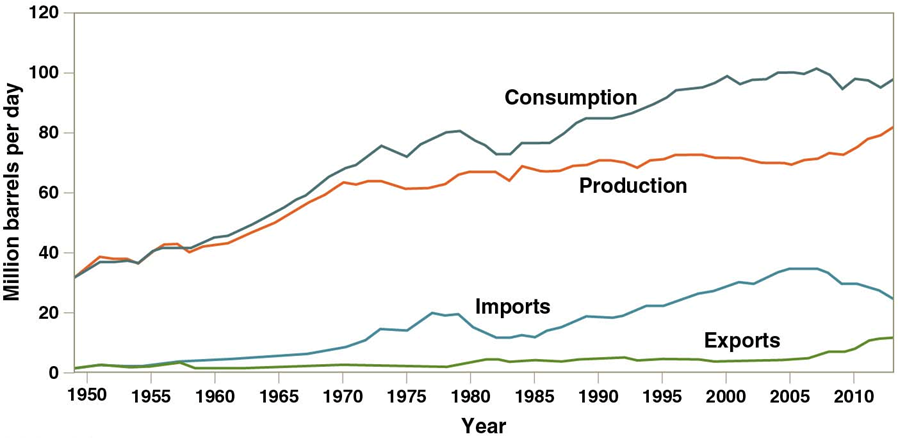
US oil production decreasing. Offshore and foreign oil used.
Alaskan oil field or isolated pockets
Offshore oil
30% of domestic production
Drilling for Gulf oil reserves with high prices
World use of oil: 92mil barrels/day
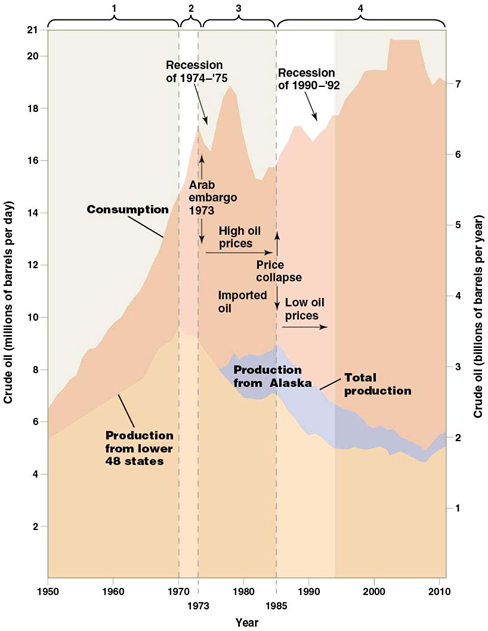
Hubbart’s peak
oil production follow bell-shape curve
Peak between 1965 - 1970
Available oil decline
Production decline
Decrease supply and demand
USA import from other countries
Fracking
Injecting a fluid mixture of water, sand, and chemicals into shale
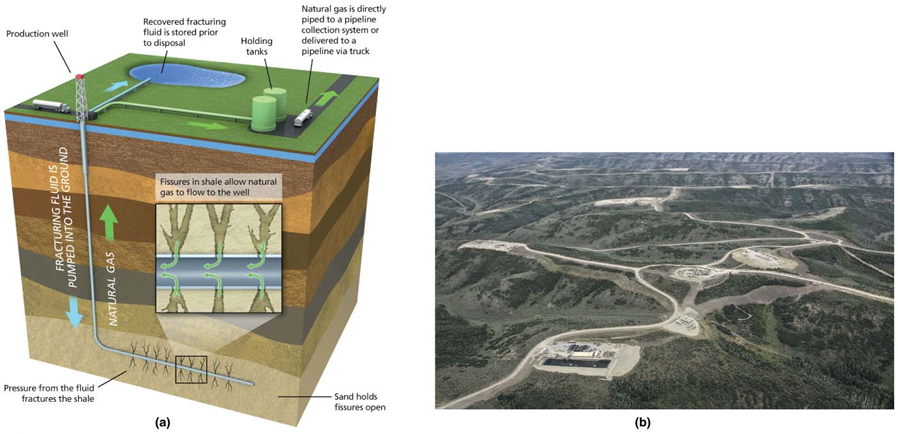
Light crude oil
low paraffin wax content
Heavy crude oil
higher density, high paraffin wax content, flow rate is slow
Sweet crude oil
low sulfur content
Estimated reserves
random guess on where and how much oil exists. drilling is required for accurate guess
Proved reserves
an accurate estimate of how much oil can be economically obtained from a field
1 barrel = 42 gallons
P05 = 5% probability the field contains given number of oil barrels
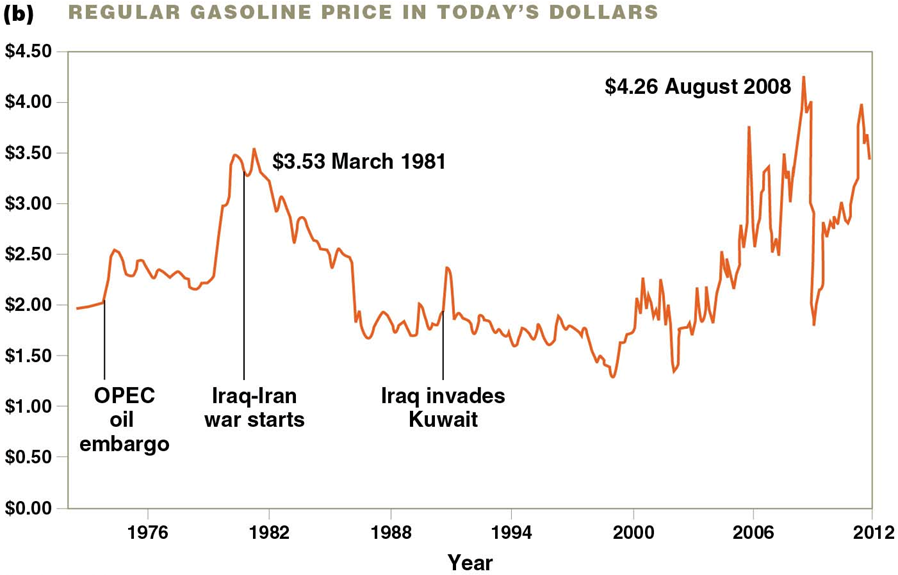
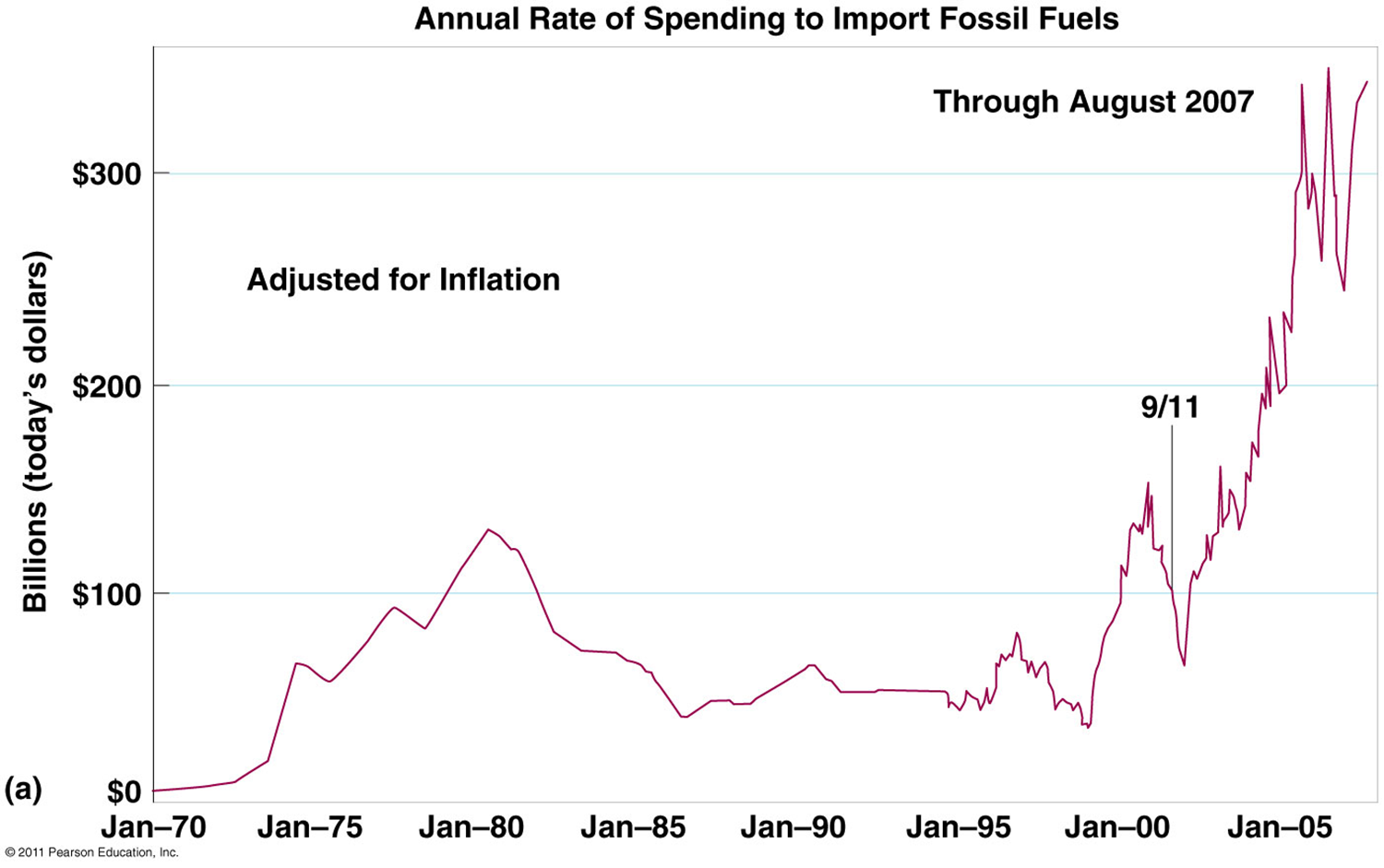
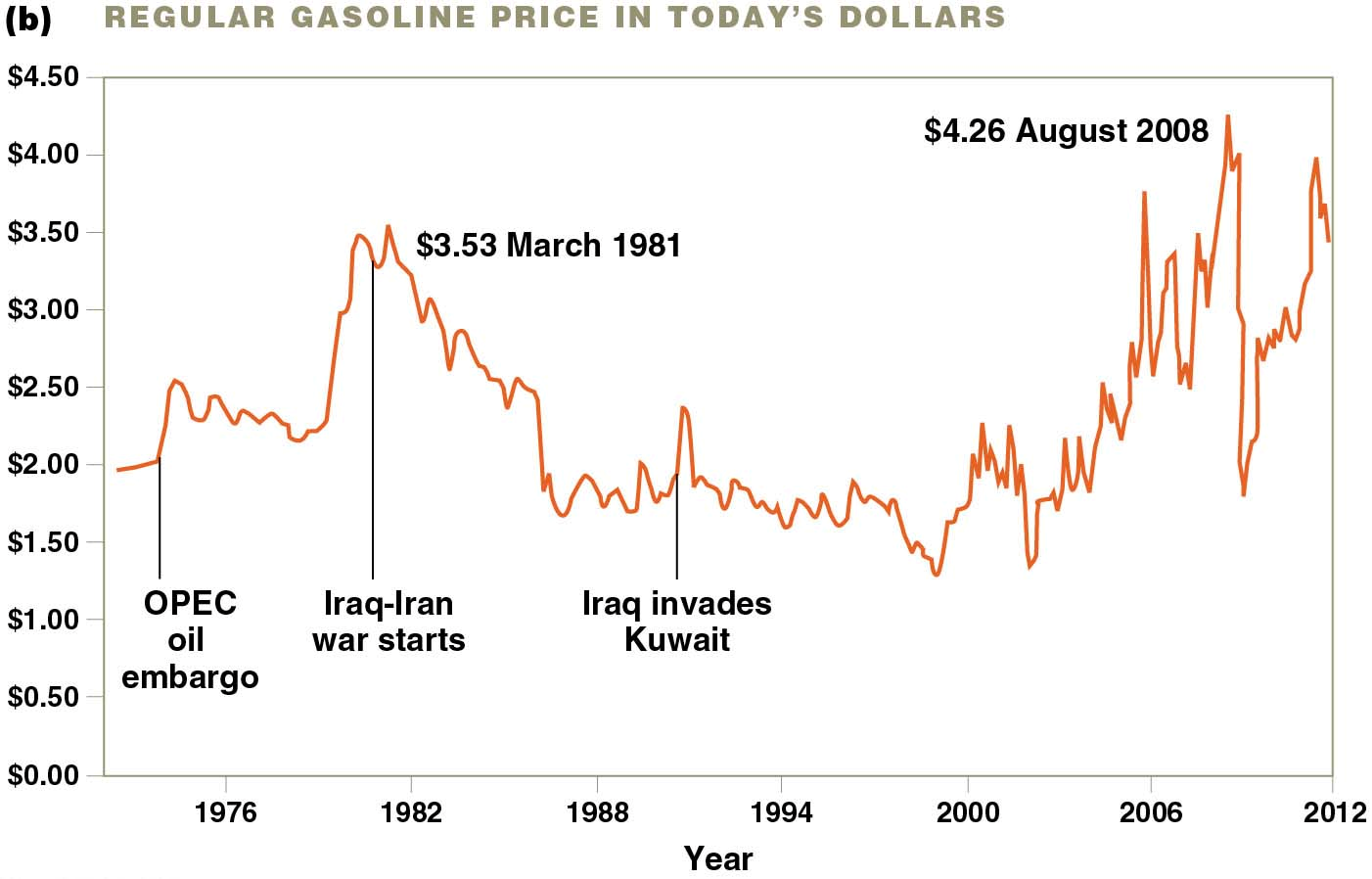
1970 Oil crisis
•The U.S. and other industrialized countries increased their dependence on imported oil
•The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
•Mostly Arab countries
•Restrained production and initiated an embargo to increase prices
•Resulted in shortages, panic, and long lines at gas stations
•The U.S. willingly paid four times the previous price
•Devastating results: inflation, unemployment, and recessions
Response to high oil prices
Increased domestic production
the Alaskan pipeline, re-opening old fields
Increased fuel efficiency standards
lowered speed limits (to 55 mph)
Promoted appliance and building efficiencies
Developed alternative energy sources
Created a strategic oil reserve in Louisiana
Store 702 million barrels of oil (33 days of oil at 21 million barrels/day use
US became less reliant on oil imports
Natural gas 2
Industry, residential, electrical power. Cost fluctuates with supply/demand.
New deposits/drilling: supply 50 years
Piped or liquified (LNG)
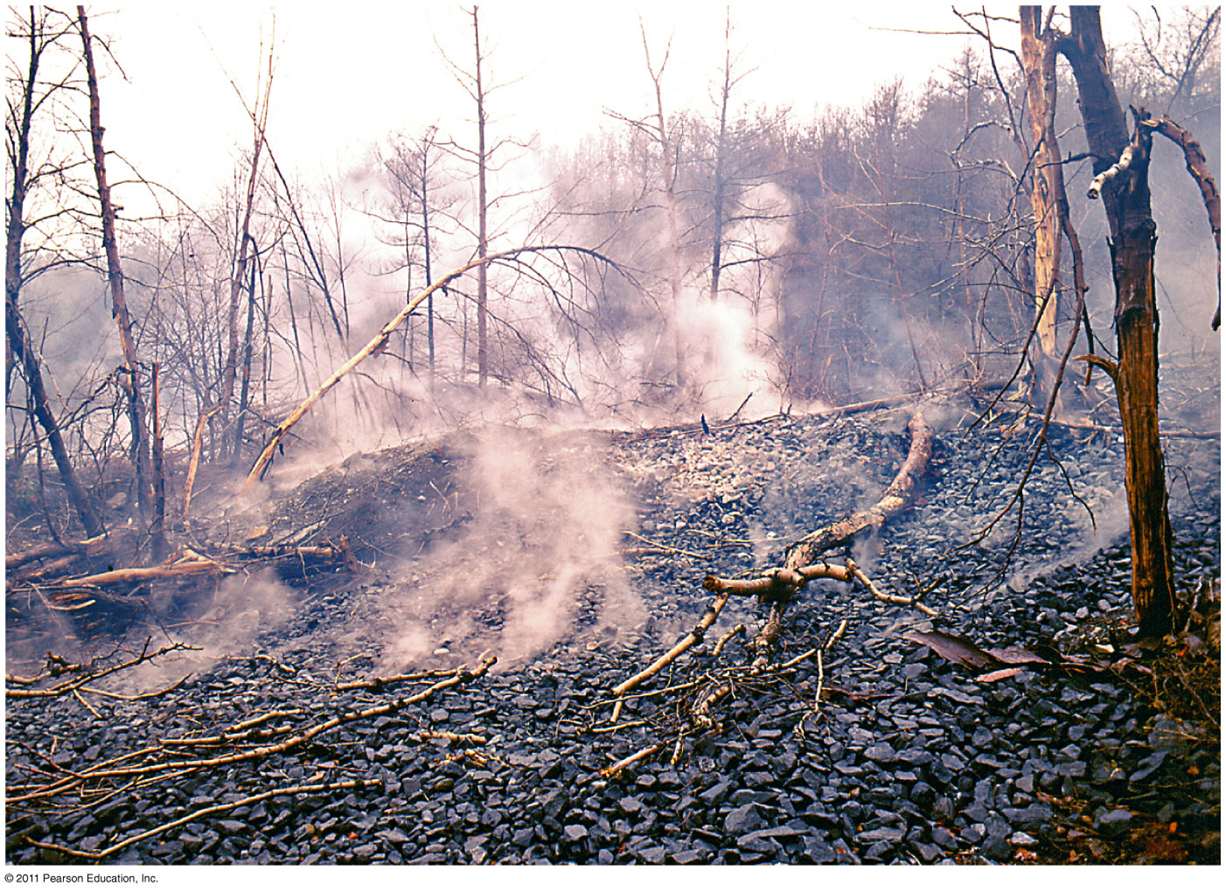
Impacts of coal
•One of the biggest environmental problems from coal mining results from the release of sulfuric acid from underground
mines.
•The acid poisons thousands of miles of streams in the eastern United States
•Underground mines cause land subsidence, toxic metals and sulfuric acid runoff, and fires
•Centralia, Pennsylvania’s fire started 40 years ago
•It could burn another 100 years
•The federal government bought the town
•Worldwide coal fires release as much carbon dioxide as all cars and trucks in the U.S.

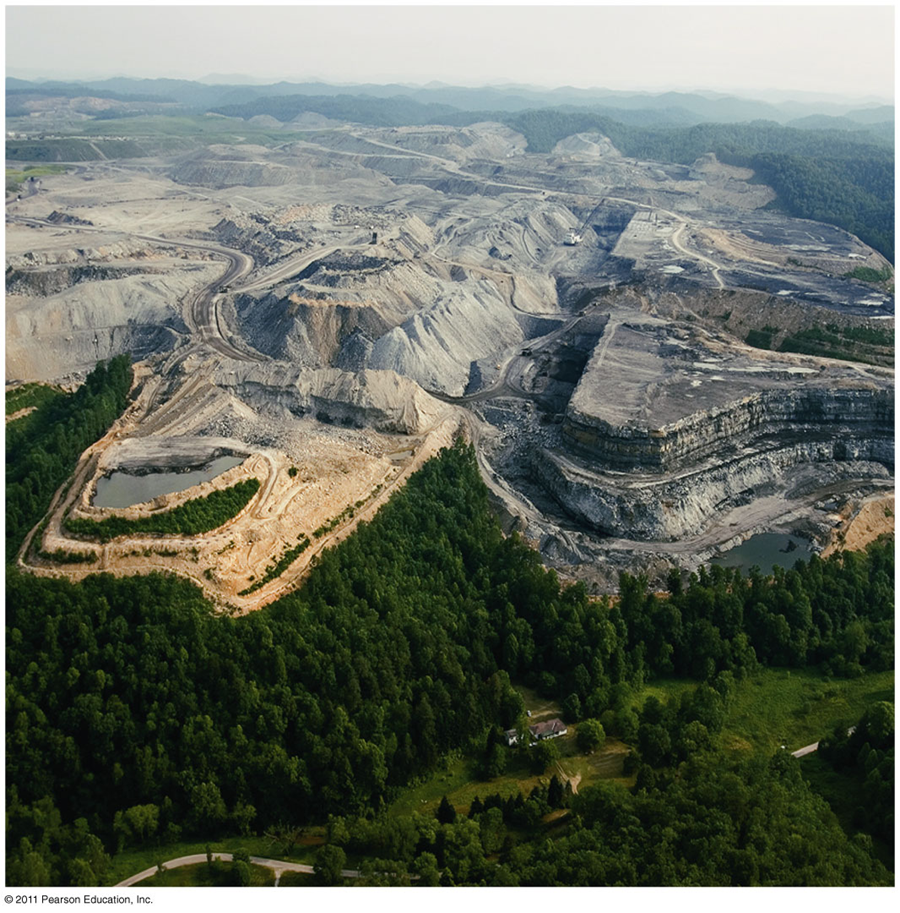
Strip mining
•Dynamite breaks overlying areas
•Giant power shovels remove overlying rocks and coal
•Deforestation and burying streams destroy ecosystems
•Federal regulations require reclamation (grading, replanting)
•It takes decades for recovery at the most basic level
•Erosion, acid leaching, and mine wastes affect surface and ground water

Oil shale
a fine sedimentary rock containing kerogen
Developing oil shale and sand will occur with high oil prices
Kerogen
a solid, waxlike hydrocarbon
•One ton of shale produces ½ barrel of oil
•Mining, transportation, and waste disposal are cost prohibitive
•Deposits contain 800 BBs of oil
Oil sand
a sedimentary material containing bitumen
Bitumen
a hydrocarbon that can be refined like oil
Alberta, Canada has the largest deposits (152 BBs)
The cost is competitive with oil
U.S. imports = 10% of our imported oil
Mining oil sand causes significant environmental damage
82,000 acres of boreal forest and wetlands have already been heavily disturbed in Canada
Developing oil shale and sand will occur with high oil prices