Molecules and Cells in Human Disease
1/415
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
416 Terms
Cancer is driven by molecular changes in signaling proteins
Either by activating mutations in oncogenes or inactivating mutations in tumor suppressor genes
Src
Tyrosine kinase that was the first oncogene identified
Protein kinases
Catalyse a chemical reaction used in cells as a form of information transfer. This can control key enzymes in cell proliferation and can turn target proteins on/off
Kinase inhibition
Small molecules can be developed that inhibit enzymes like kinases
Philadelphia chromosome
Common translocation in chronic myologenous leukemia patients that generates a fusion BCR-ABL gene. ABL is a tyrosine kinase so imatinib is used to inhibit BCR-ABL.
Cell death regulation defects cause diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases involve loss of cells like neurons. Your immune system can kill your own cells. Cancer cells are resistant to apoptosis. Ischemia results in death of surrounding cells
Necrotic cell
Swelling of cell, loss of plasma membrane integrity, releases content into surrounding tissues.
Apoptotic cell
Shrinkage of cell, maintenance of plasma membrane integrity, and the cell is phagocytosed by macrophages.
Autophagy cells
Maintenance of plasma membrane integrity. Organelles are broken down and reused as nutrients
Cellular stress causes apoptosis
It protects from infected, damaged, or unwanted cells. Apoptosis will minimize collateral damage to the tissue. It achieves this as apoptotic cells are phagocytosed by other cells
Apoptosis morphological changes
Cell shrinkage, cytoskeleton collapses, loss of nuclear membrane, chromatin condenses and DNA is cleaved into fragments. The membrane blebs which breaks off into apoptotic bodies and the cell surface alters to attract phagocytes. This requires energy in form of ATP
Signalling pathway resulting in biological effect
A signal is detected by a receptor which activates enzyme 1 which activates enzyme 2 and causes a biological effect
Signalling pathway resulting in transcription factor
A signal is detected by a receptor and activates kinase 1 which activates kinase 2. This gets phosphorylated and so does the then activated transcription factor
Caspases
Endopeptidases which cleave within a protein. They cleave specific substrates and sites. They cleave proteins after an aspartate in the substrate
Caspase substrate cleavage
Substrate cleavage often results in activation of function of CAD. Makes caspase signalling enzymes acting on downstream effectors
CAD
Caspase activated DNAase
On/Off point for apoptosis
By activation of caspases
Executioner caspases
Have a small pro-domain
Initiator capsases
Have a large pro-domain
Caspases are expressed as inactive proenzymes
Become activated during apoptosis
Initiator caspases activate executioner caspases by proteolytic cleavage.
A signal is detected by a receptor and activates the initiator caspase which then activates the executioner caspase. This has an effect on the biological substrate.
Executioner dimers
Proenzyme executioner caspases are dimers. Cleavage by initiator caspases causes rearrangement of the active site
Initiator dimers
Exist as monomers but need to dimerize to activate via the pro-domain.
Caspase 9 is activated by the apoptosome
The apoptosome is a large multimeric complex.
APAF 1
A cytosolic monomer that assembles into a heptameter after binding to cytochrome c. The heptameric APAF1 can bind caspase 9 through CARD. Caspase 9 is now concentrated enough to dimerize
Cytochrome c release
It is released from the mitochondria right before caspase activation. It is the point of no return for a cell and is controlled by Bcl-2 protein family
MOMP
Bcl-2 family of proteins controls apoptosis by mediated mitochondrial outer membrane permeablisation
Bcl-2
Identified in follicular lymphoma - a cancer of B cells. It was the first identified in a family of related proteins. Some Bcl-2 proteins keep cells alive whilst some like Bax promote apoptosis
Bax
Bcl-2 associated X protein functions to promote cell death and antagonise Bcl-2
Anti-apoptotic Bcl-2
Have shared domain structure and block OMM permeabilisation. Includes Bcl-2, Bbl-X, Bbl-W, and Mcl-1
Pro-apoptotic Bcl-2s
Make holes in the OMM. Include Bax, Bak, and Bok
BH3-only proteins
Regulate pro and anti apoptotic proteins. They are activated by a range of damage signals a cell can receive.
Pro and anti apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins interact
On the OMM to regulate MOMP. BH3-only proteins will either inhibit anti-apoptotic proteins or activate pro-apoptotic proteins
Mutations affect Bcl-2 threshold
Mutations in oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes can shift the threshold for Bcl-2 regulation of MOMP.
BH3-only protein regulation
Some are regulated by growth factor signalling. Some are regulated by DNA damage
PUMA regulation by p53
DNA damage can regulate PUMA by p53, a tumour suppressor which gets mutated in 50% of cancers. Chemotherapy often tries to activate BH3-only proteins to kill cancer cells but if p53 is mutated then the tumour cells don't respond
Mimic BH3 domain
NMR spectroscopy used to identify small molecules that bound in the same region as the BH3 domain. Compound joined to generate high affinity binding. Lead to a compound being produced which was the first BH3-mimetic
Further modification
To generate an orally active variant, and further to increase target specificity and reduce side effects.
Caspase 8 activation
By extrinsic signals like receptors on the cell surface. Needs death domain and death effector domain
CD95
Also called Fas it binds to Fas ligand. It is a trimeric receptor with a single transmembrane spanning domain
FADD
Fas associated death domain containing protein
DISC
Death inducing signalling complex
Caspase 8 cleavage
It undergoes autocatalytic cleavage to stabilise the active dimer
ALPS
Autoimmune condition where mutations mean there is an accumulation of T-lymphocytes which are normally controlled by apoptosis. Causes autoimmune symptoms and lymphoid tumours. Caused by inactivating mutations in CD95, FasL, or caspase 9
Non-apoptotic caspase activation
Same as apoptotic caspases but the signal and substrate are different
PAMPs
Pathogen associated molecular patterns recognise bacterial cell walls or microbial DNA
DAMPs
Damage associated molecular patterns
Necrosis characteristics
Cells and organelles swell, and the plasma membrane ruptures. This releases DAMPs so can induce inflammation
Repurfusion damage
Restoration of blood flow can affect movement of many ions and deplete cellular energy levels by activating enzymes like PARP. This can be even more damaging
Autophagy
Cells eating themselves. They form large vacuoles in the cytoplasm but the plasma membrane stays intact. There is no membrane blebbing, nuclear condensation, DNA fragmentation, or caspase activation. The autophagosome fuses with lysosomes and the contents get degraded
Nutrient deprivation
Can initiate autophagy as cells try to survive. Turns off mTOR so the ATG13 complex is active and causes autophagy
Cancer cells can enter autophagy
If resources are limited cells enter autophagy. Tumour cells resistant to apoptosis stay alive using autophagy by making tumour cells dormant and hard to kill. Removal of stress allows dormant cells to activate again
Mitophagy
Specialised form of autophagy that protects cells from damaged mitochondria
PINK and Parkin
Label defective mitochondria and target them to autophagosomes for destruction
Kidney connective tissue
Majority of the kidney is made of connective tissue, not cells
Cells and ECM are linked
Helps to resist mechanical forces and give mechanical integrity.
Collagen
Most abundant protein in the body. Needed to hold tissues together
Collagen isoforms
There are 28 different types but collagen I is most common and makes up over 80%. It makes up tendons and ligaments but different types are used to form different ECM structures
Collagen structure
All have a repeating sequence with proline, glycine, and another amino acid. These form chains and three chains form a tight helical structure
Proline
Causes tight wrapping of the three chains around each other
Glycine
Gives flexibility
Proline and glycine hydroxylation
Forms hydroxyproline and hydroxyglycine which form antrachain hydrogen bonds to stabilise the triple helix.
Hydroxylase
Need vitamin C as a cofactor. Converts proline or lysine to their hydroxy version
Basement membrane
Specialised to organise cell layers in metazoans. First recognisable ECM to form during metazoan development. Mutations in genes for early BM cause no development beyond this stage.
Basement membrane strength
It's very mechanically strong and diseases in it cause loss in mechanical strength.
Collagen IV
Specific to basement membranes. It assembles into 2D mats rather than fibres. This is because the N and C terminus don't get cleaved.
Collagen IV N terminus
Called 7S domain and is rich in cysteine and leucine. Domains interact to form a teamer of collagen trimers which contain extensive crosslinks holding the tetramer together.
Collagen IV C terminus
Called NC1 and is 230aa long. Drives triple helix formation and hexamer formation through end-end interactions
Crosslinking
4 triple helices crosslink through disulfide and lysine/hydroxylysine crosslinks
Interruptions
Interruptions in Gly-X-Y repeats cause increased flexibility and sites for cross linking
NC1 groove
All NC1 monomers have a groove which fits a finger-like projection from a collagen monomer
Collagen IV genes
There are 6 types of collagen IV genes which means there are 56 possible trimers. However only 3 are made
Glomerular BM
Specialised BM in the kidney that acts as a filter. It forms a thicker BM and is between the endothelial cells of blood vessels, and podocytes which are a specialised epithelial cell
Different parts of the kidney express different isoforms
The Bowmans capsule and globular basement membrane are made of different collagen isoforms. Bowmans has α1α1α2 whilst GBM has α3α4α5
Alport syndrome
Discovered by Albert Alport in 1927 as he witnessed physical symptoms of a hereditary form of nephritis. Found a loss of a3a4a5 in the 90s
Col α3α4α5 vs Col α1α1α2
α3α4α5 has more inter and intra chain crosslinks which protect it from increased pressure, and proteolysis from proteases in serum/the filtrate. If the wrong collagen is in the GBM it will undergo proteolytic degradation
Collagen mutations
X-linked Alport's are most common and caused by a mutation in the Col Iv α5 gene. It is severe in hemizygous males but varies depending on nature of mutations. It can be mild to non-existent in heterozygous females
Lysil Oxidase
Deaminates hydroxylysine and lysine to generate reactive aldehyde groups. These form covalent bonds with other lysines and hydroxylysines to form intermolecular crosslinks
Hydroxylysine and Hydroxyproline
Form intrachain hydrogen bonds that stabilise the triple helix
Collagen IV heterotrimers
α1α1α2
α3α4α5
α5α5α6
Most basement membranes
Made of collagen IV made of α1α1α2
BM protein isoforms
Different isoforms are found in different tissues and give these BM specific properties. In development α1α1α2 is expressed in the kidney but as the kidney matures it switches to expression of α3α4α5
Collagen IV gene pairs
Genes are in pairs because they have arisen through gene duplication. They share a common bi-directional promoter. 1 and 2, 3 and 4, and 5 and 6 are paired
α3 α4 mutations
Associated with autosomal recessive form of Alpert's
Collagen IV alport mutations
Can occur throughout the molecule but are mostly in the coiled domain.
Early onset disease mutations
Include large gene rearrangements. Non-sense mutations and splice sites lead to truncations
Late onset adult type mutations
Include missense mutations disrupting Gly-X-Y repeats. Conserved cysteine residues affect cross linking.
α3 knockout in mice
Develop progressive glomerulopathy. Phenocopies human autosomal dominant Alports
Alports mouse model
Been used to evaluate ACE inhibitors to reduce onset of symptoms. They reduce pressure in the glomerulus by vasodilation of efferent vessels to increase the life span of Alports mice.
Cure Alport's
Genetically engineered mice where α3 has been turned back on the glomerulus has been developed. Results show repair and return of function to defective GBM when added to Col IV
Laminin
A major component of BMs that self assembles into a network to present binding sites for cells. It is a high MW glycoprotein with a cruciform structure.
Laminin structure
Made of three protein chains from three separate genes. They assemble into the cruciform structure. The α chain is the longest, and then there are β and γ chains. The β and γ wrap around the α chain, with their N terminus forming the short arms. The globular part is the C terminus of the α chain
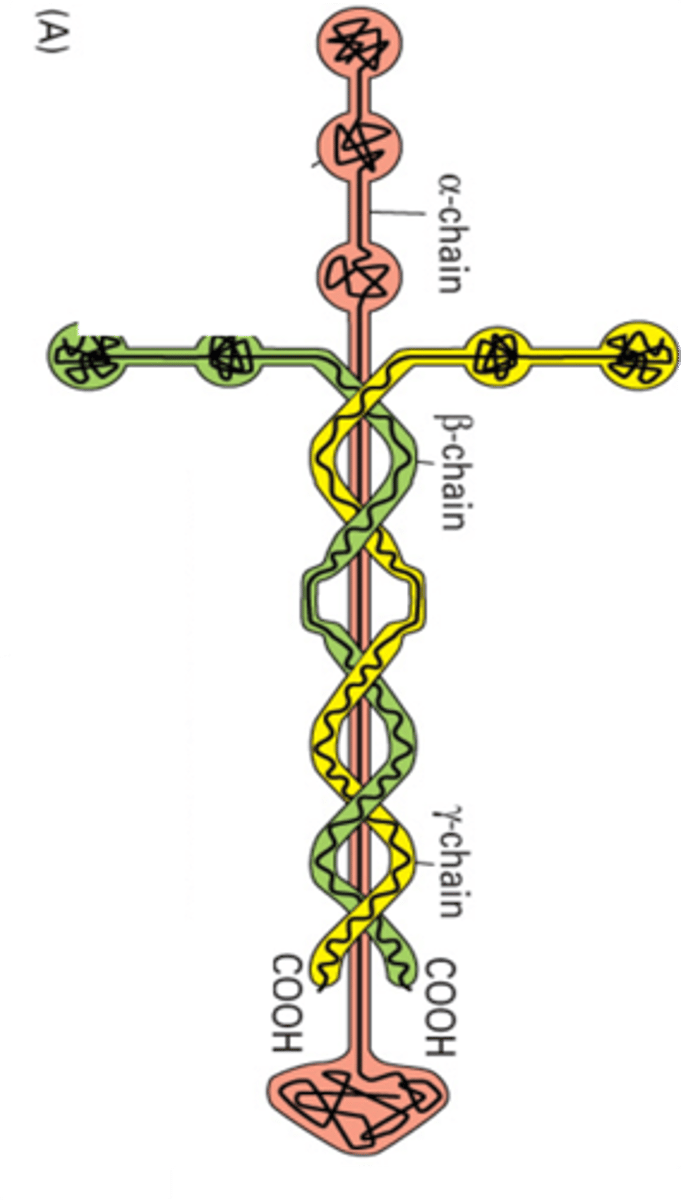
Globular domains
On the α chain and are spread out by spacers which are comprised of EGF repeats
N terminal globular domains
Promote polymerisation into a network. Laminin 1 spontaneously forms a network in vitro
α chain globular domain
At the C terminus there are 5 LG domains that interact with cell surface receptors
Integrin binding site
LG1 LG2 LG3
Dystroglycan and Heparin binding site
LG4 LG5
11 laminin genes
There are 5α 3β and 3γ chains but only 15 different heterotrimeric combinations are formed. Different laminin isoforms show tissue specific expression
α1β1γ1
Present in embryonic BM so if there is a mutation and these isoforms aren't expressed, the embryo will not continue developing
Pierson syndrome
Caused by loss of laminin β2 isoform. Causes congenital nephrotic syndrome progressing to end stage renal disease, eye abnormalities, and severe muscular hypotonia. Laminin 11 containing β2 is expressed in the GBM, eye, and synaptic BM so explains symptoms.