Anatomy and Physiology Fall Week 7
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
Hairs (pili)
flexible strands produced by hair follicles that consist of dead hard keratinized cells
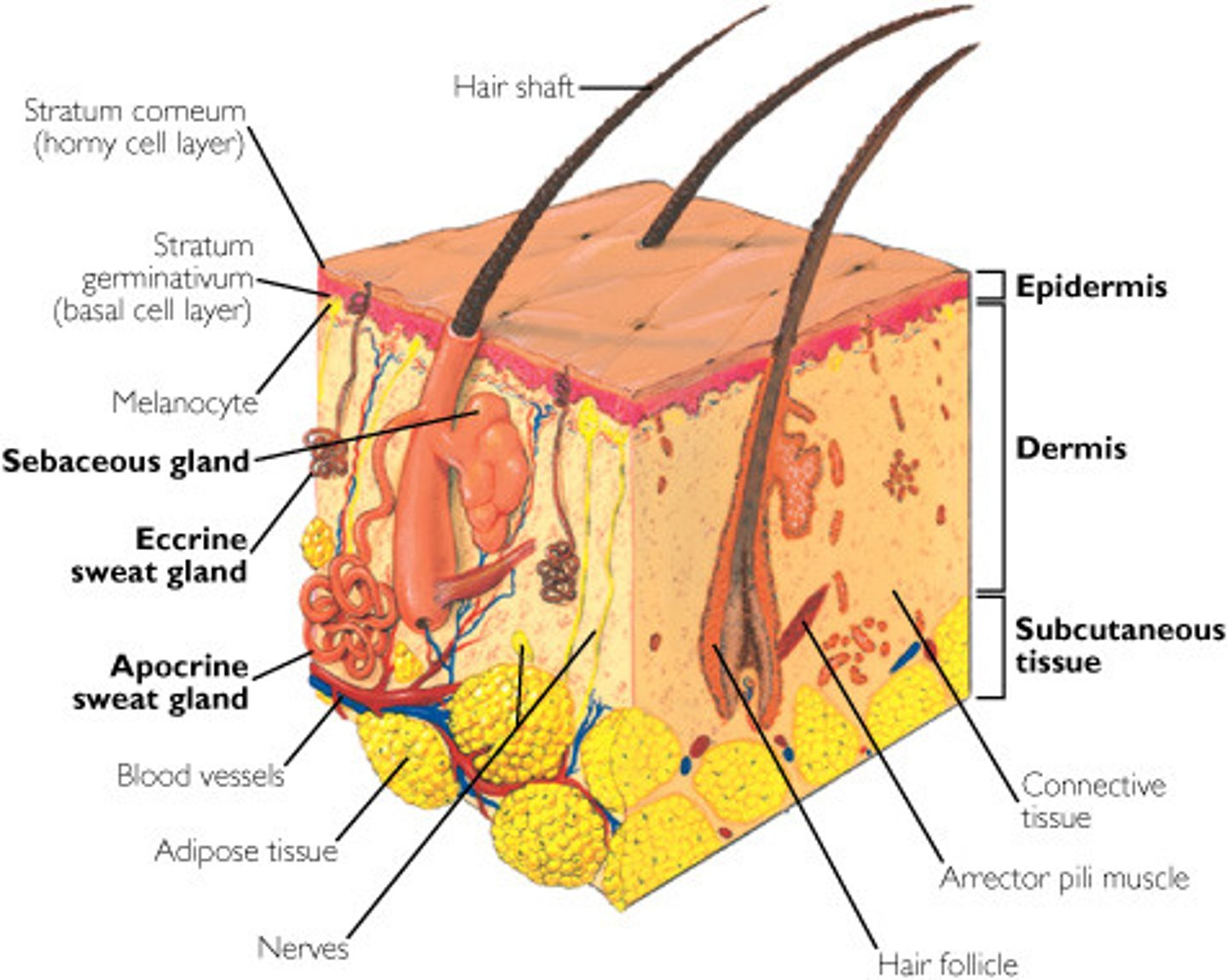
Function of hair
warning of parasites on skin; insulating, protecting the head from physical trauma, shielding the skin from sunlight

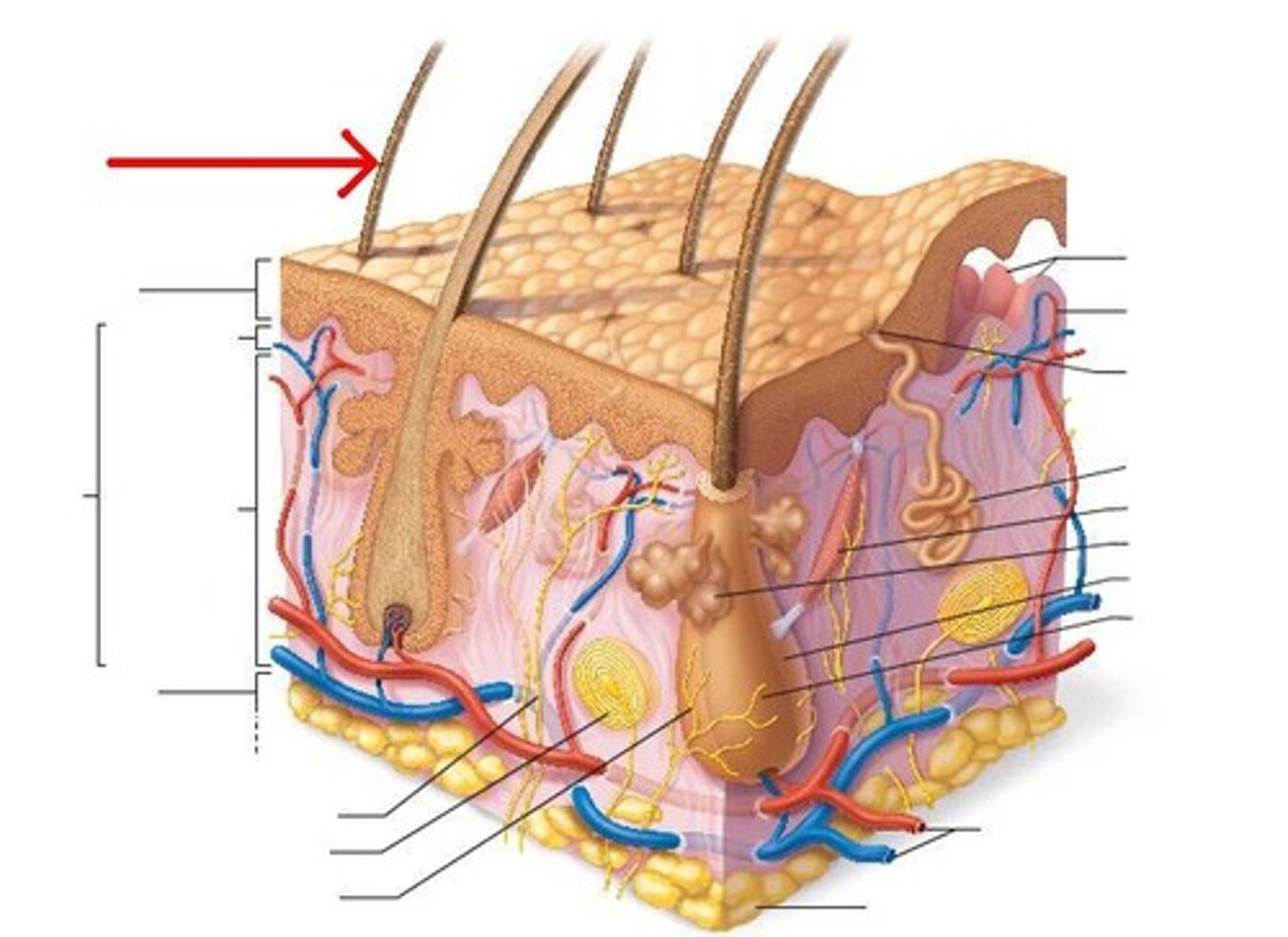
Shaft
part of the hair projecting from the skin
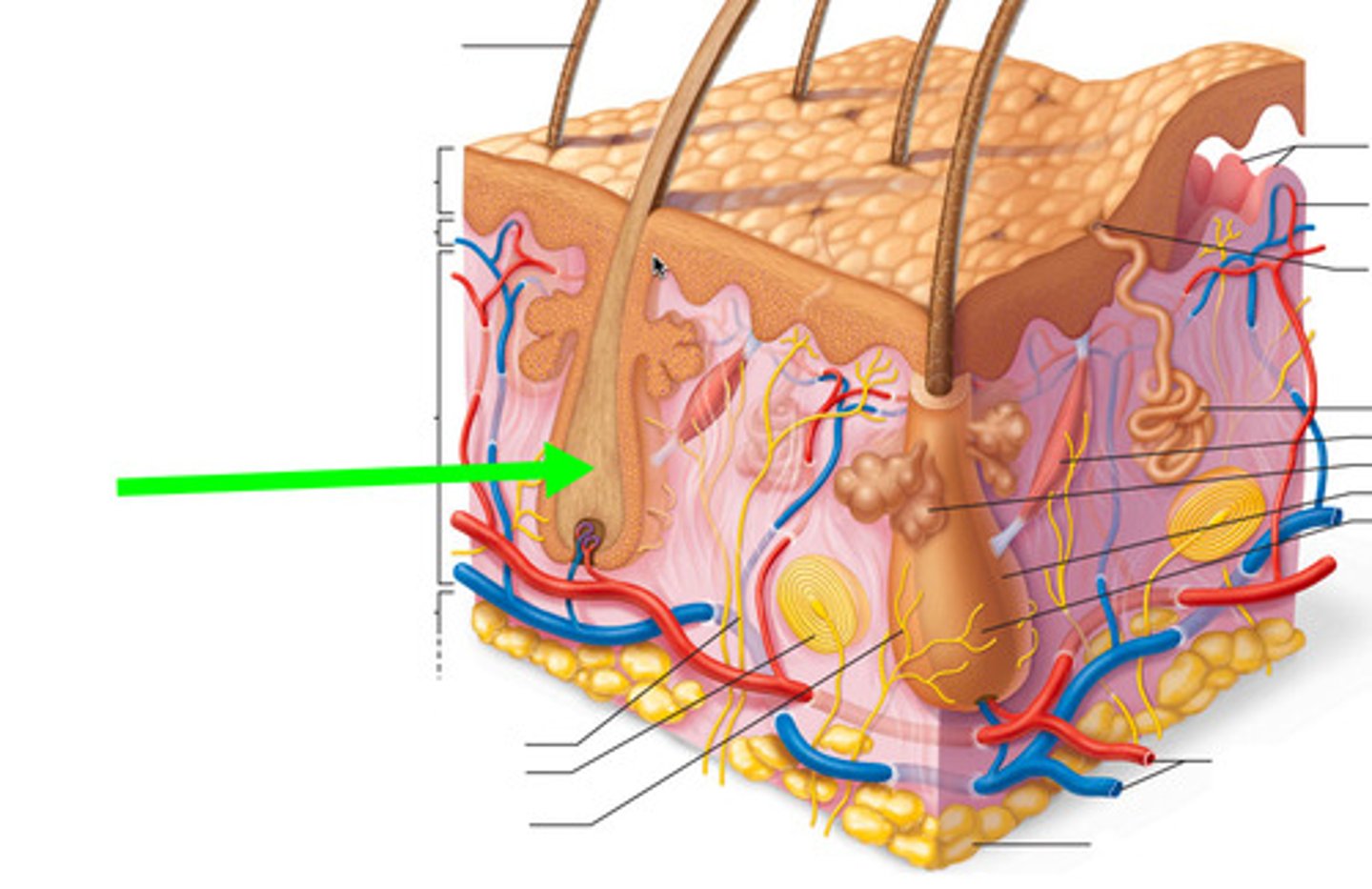
Root
part of the hair embedded in the skin
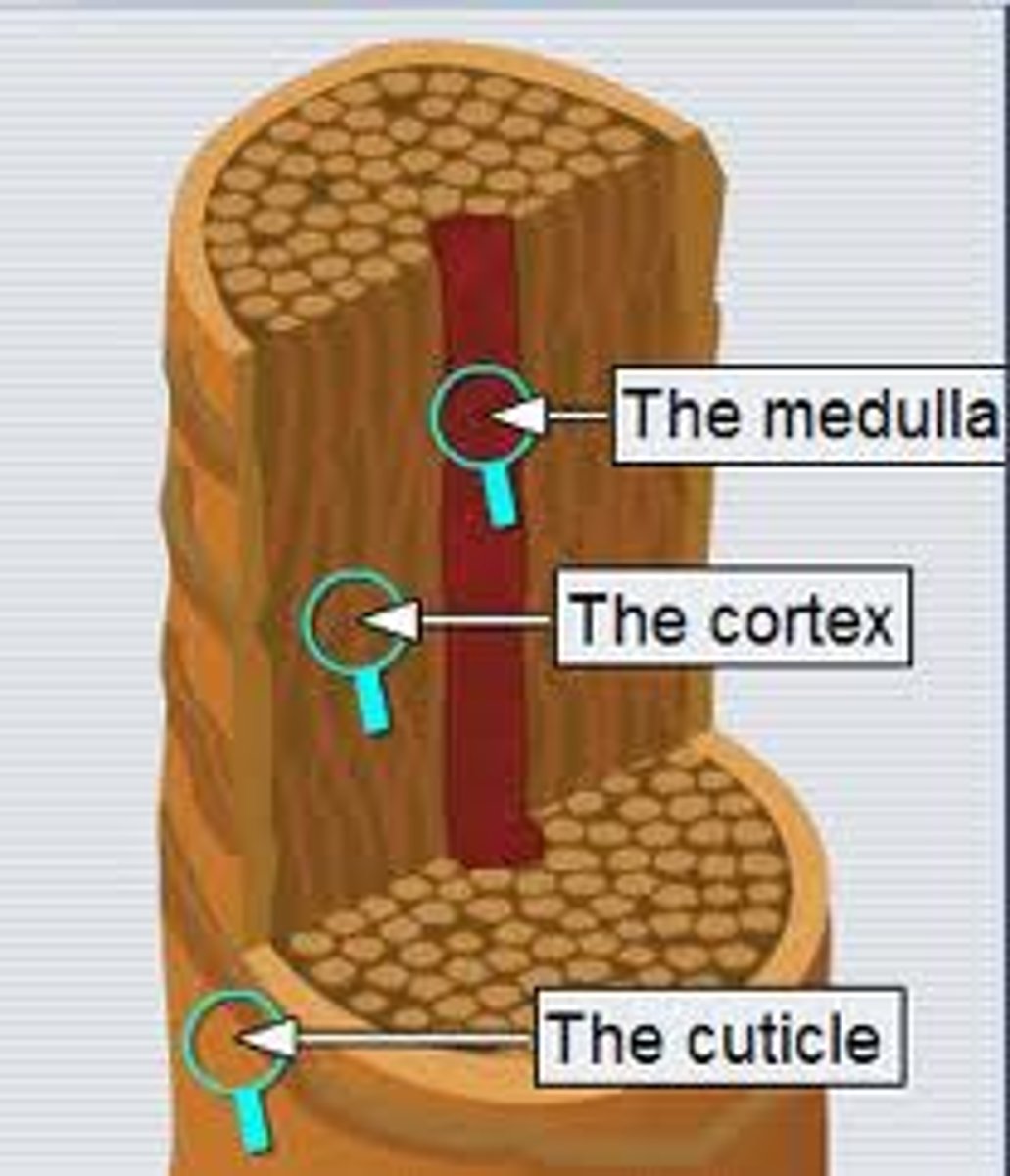
Medulla
inner core of keratinized cells in hair (not all hairs have this)
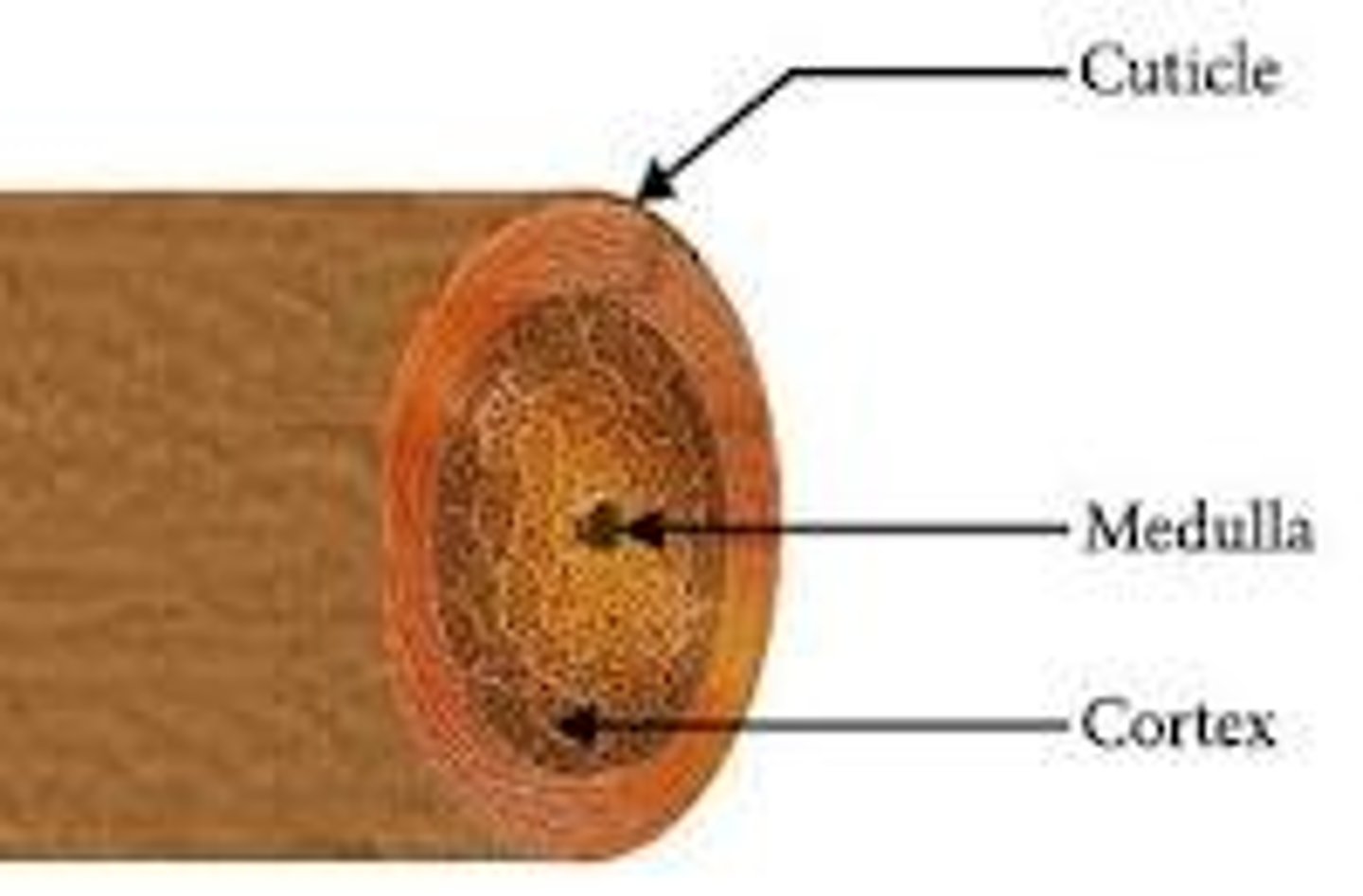
Cortex
middle layer of keratinized cells in hair
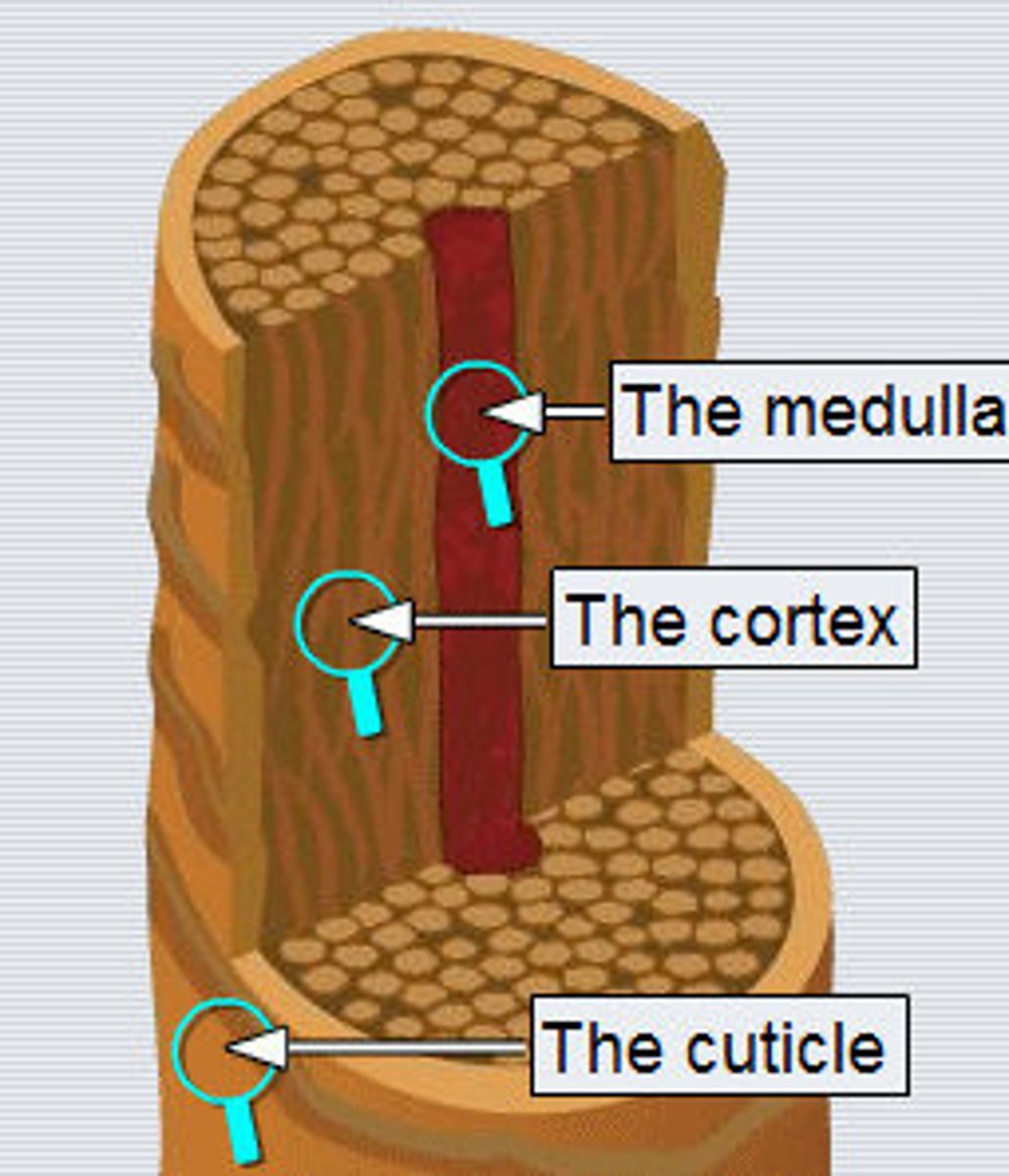
Cuticle
outer layer of keratinized cells in hair
Hair pigments
made by melanocytes at the base of the hair follicle and transferred to the cortical cells

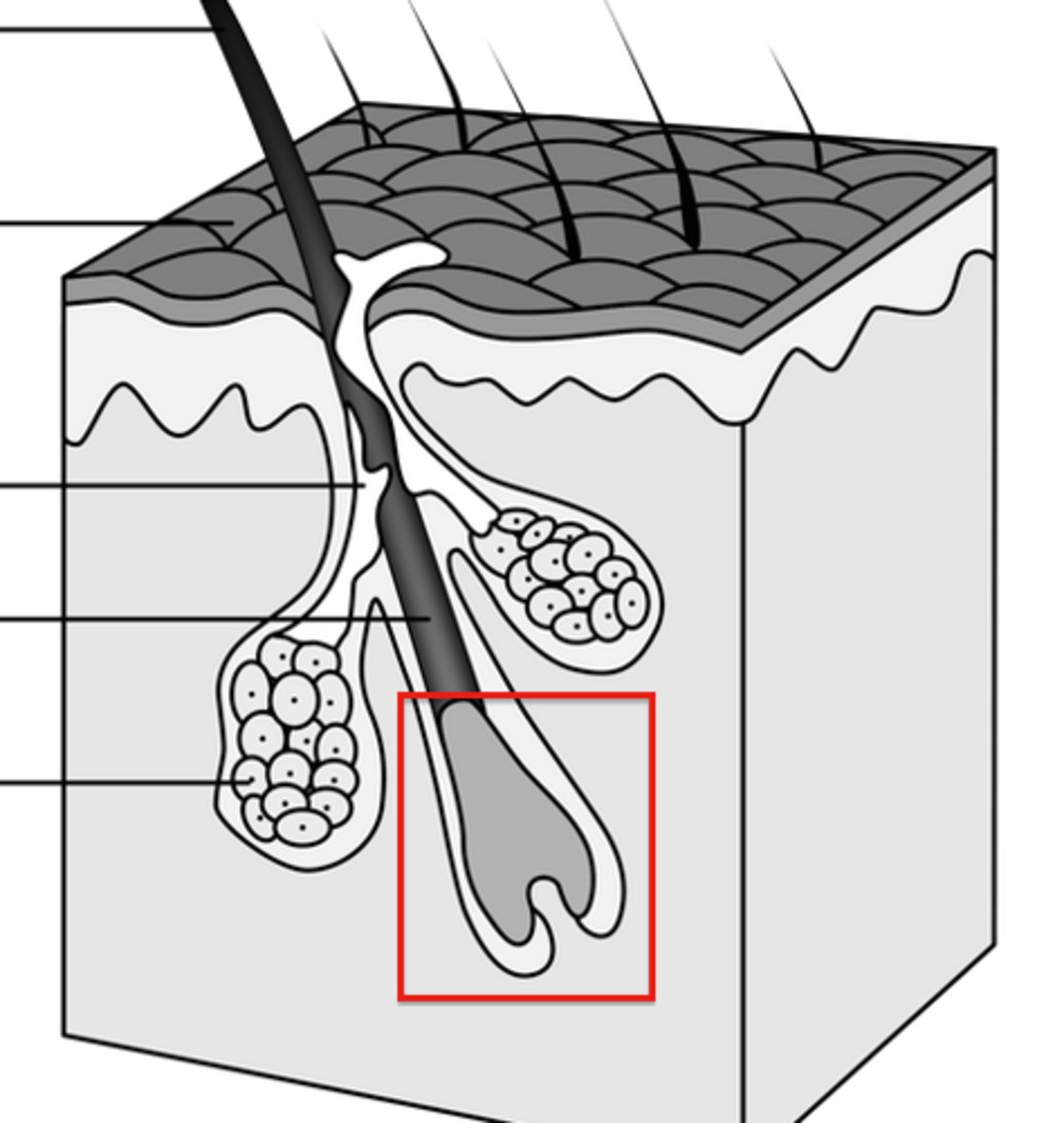
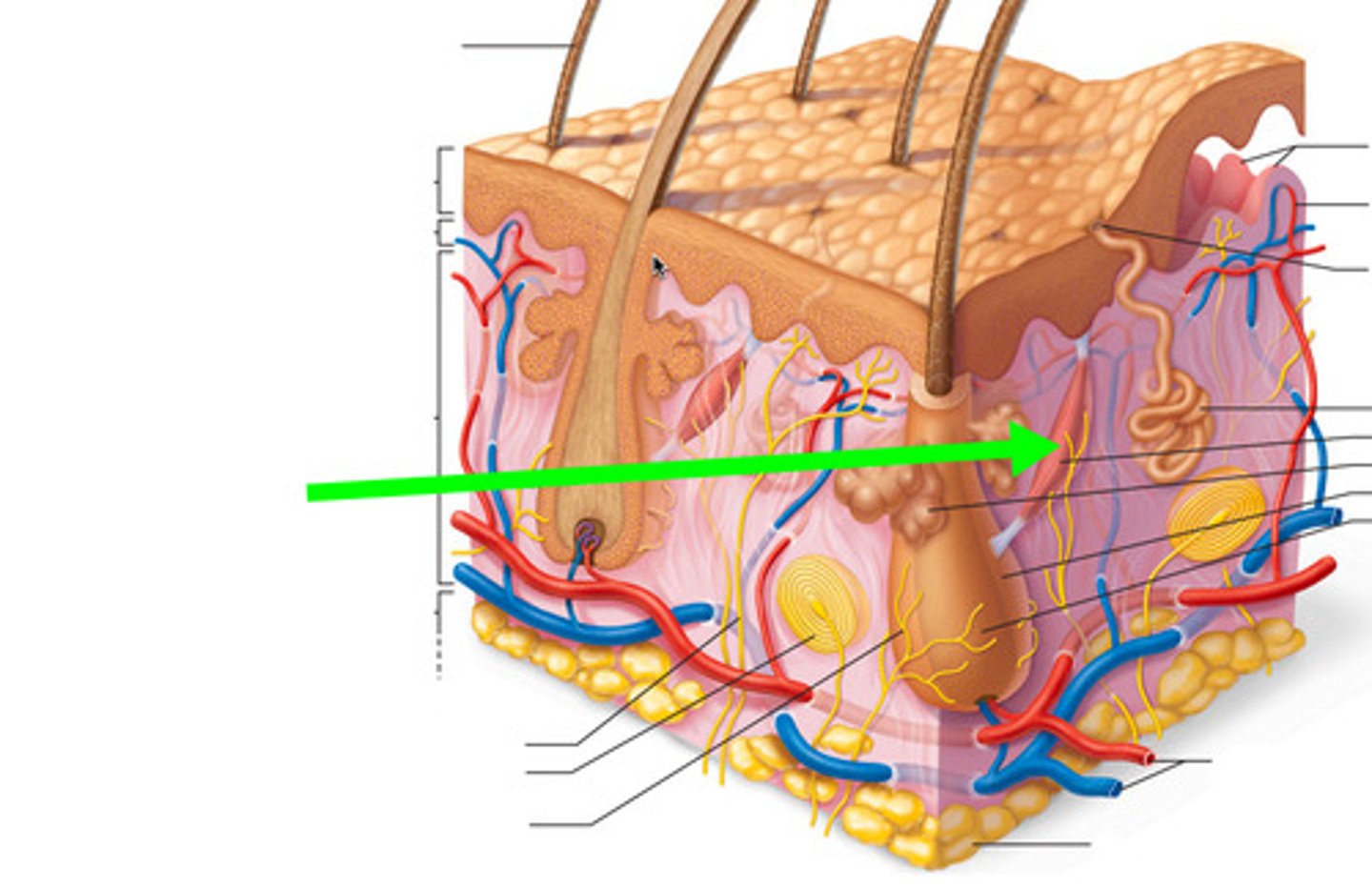
Hair follicles
fold down from the epidermis into the dermis and occasionally into the hypodermis
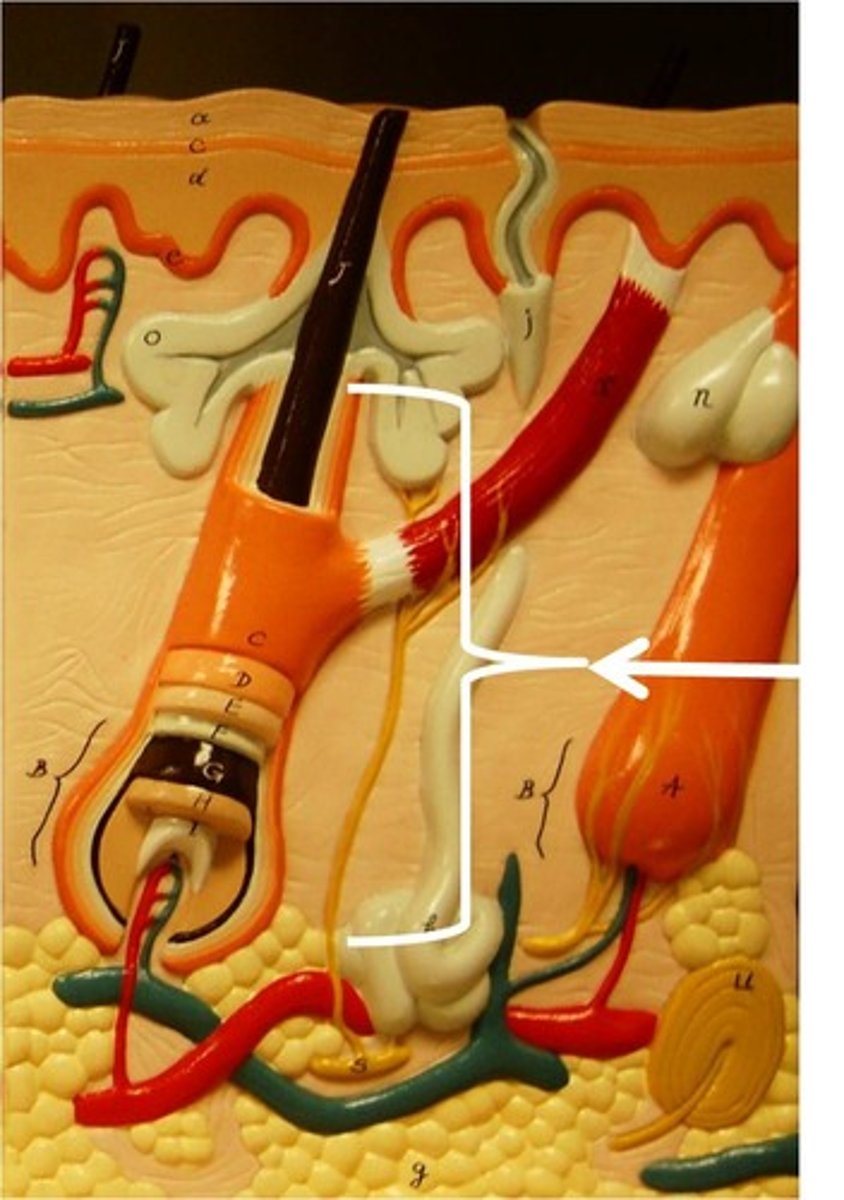
Hair bulb
the deep, expanded end of a hair follicle surrounded by sensory nerve endings
Peripheral connective tissue sheath
component of the hair follicle with a thickened basement membrane from the dermis
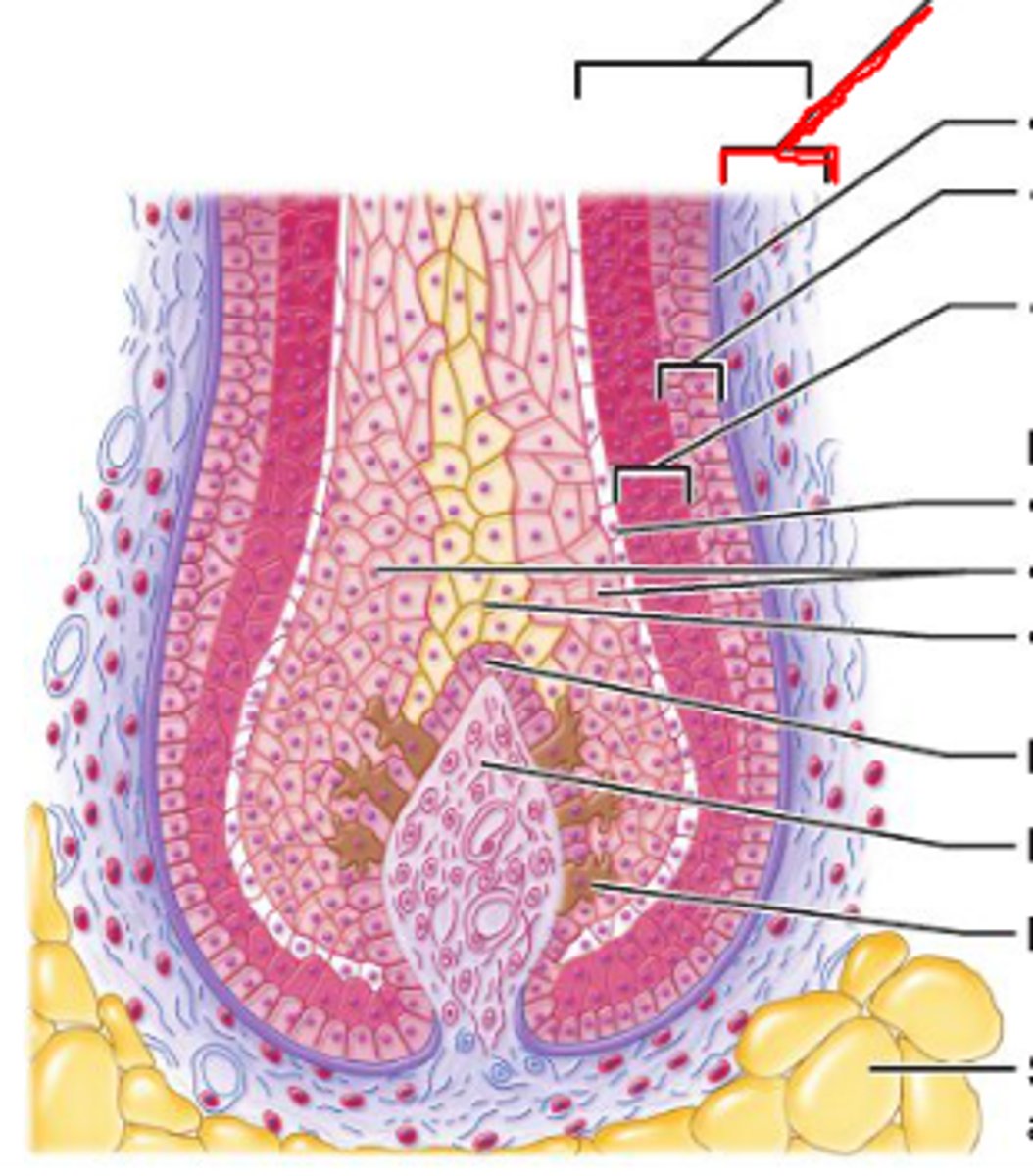
Epithelial root sheath
inner component of the hair follicle derived from the epidermis

Hair matrix
actively dividing cells that produce the hair within the hair bulb
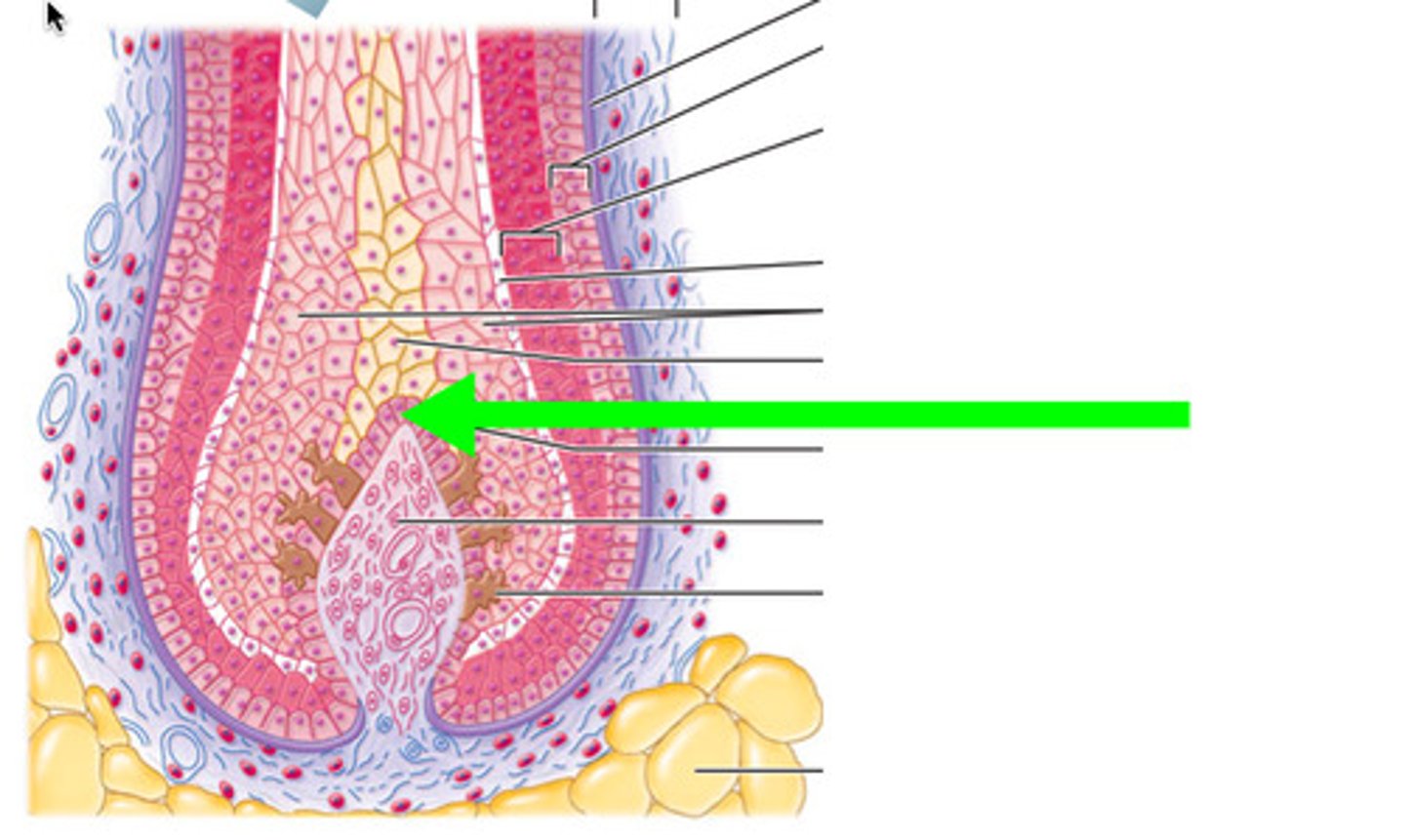
Arrector pili
a bundle of smooth muscle cells which causes the hair to stand upright with contraction
Hair papilla
dermal tissue containing a knot of capillaries that supplies nutrients to growing hair

Vellus hairs
pale fine hair

Terminal hairs
longer coarser hairs
Cycles
hair follicles grow in ______ and have a limited number of them
Alopecia
hair loss

Baldness
genetically determined, sex-influenced condition caused by a gene that changes the hair follicle in response to the hormone dihydrotestosterone

Alopecia areata
immune system attacks follicles
Sebum
an oily secretion that softens and lubricates the hair and skin, slows water loss, and is bactericidal

Sebaceous glands
function as holocrine glands that secrete sebum
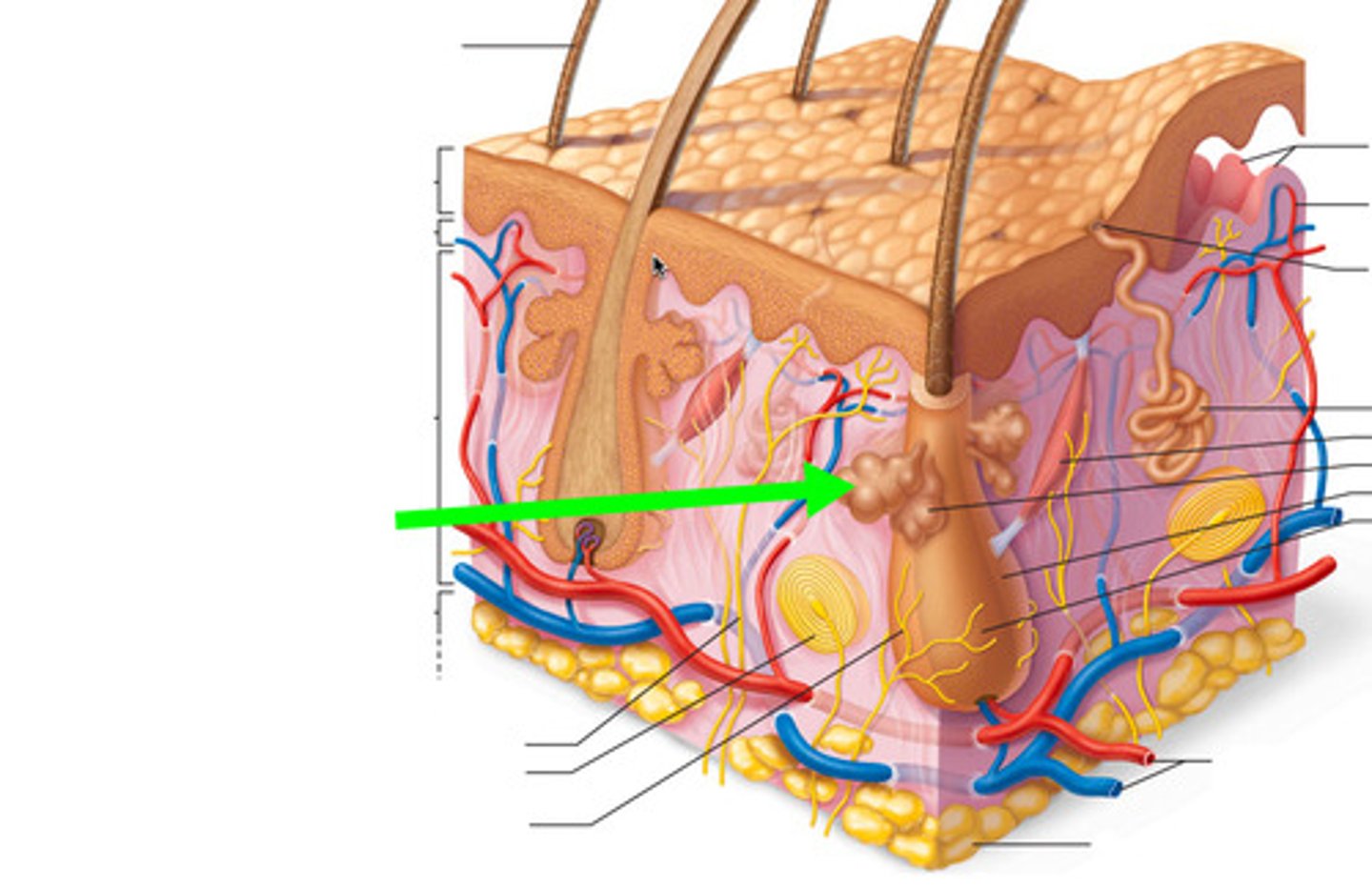
Eccrine/merocrine glands
sweat glands that produce true sweat and are abundant on the palms, soles, and forehead
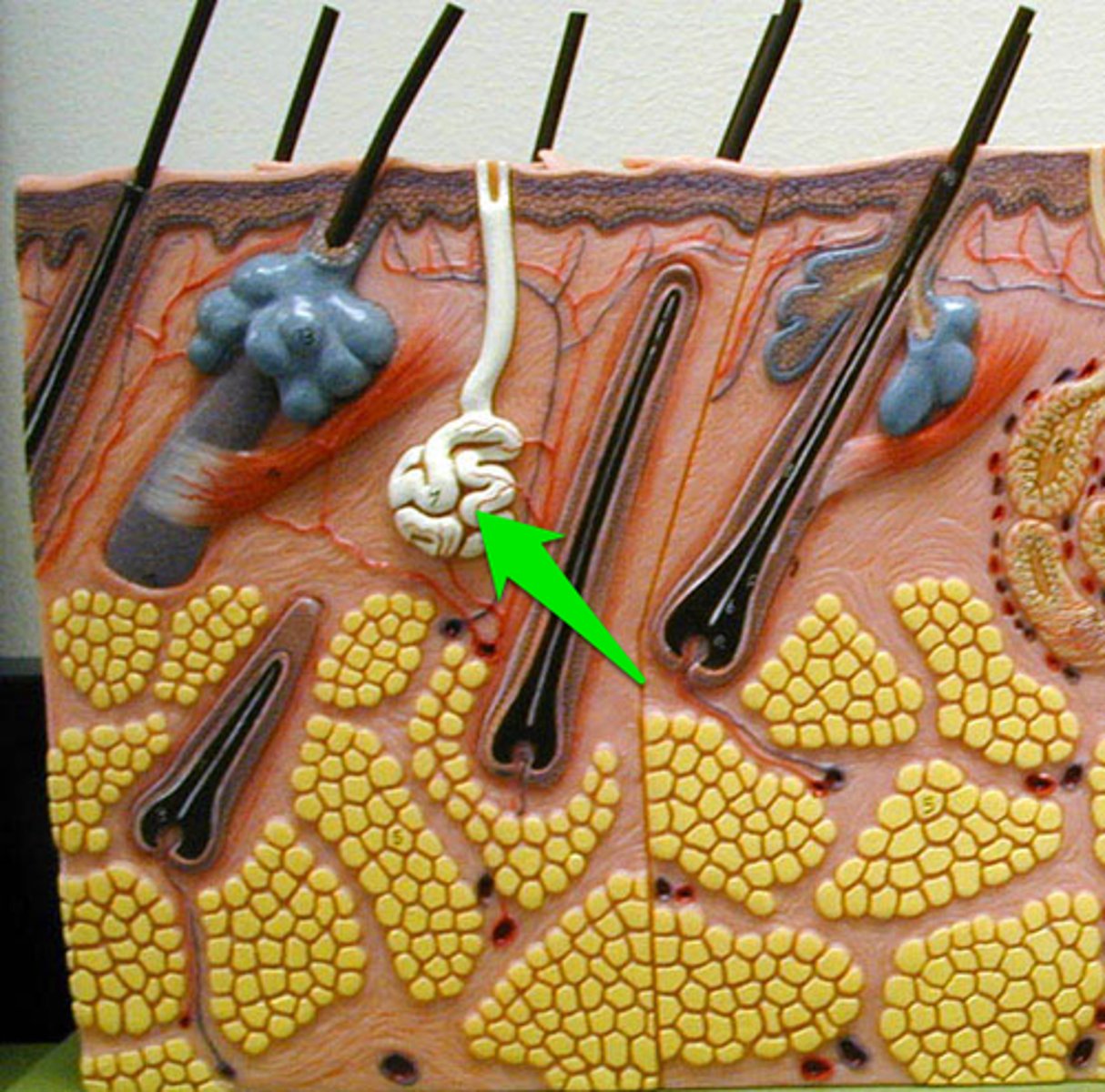
Secretion of eccrine glands
-99% water, salts, vitamin C, antibodies, dermcidin, metabolic wastes
-regulated by sympathetic nervous system and is used to prevent the body from over heating
Larger
apocrine sweat glands are _______ than eccrine sweat glands and have ducts emptying into hair follicles
Apocrine glands
-sweat glands confined to the armpit and anogenital areas
-produce fat and protein-rich sweat
-bacteria break down the sweat leading to body odour
-begin functioning during puberty

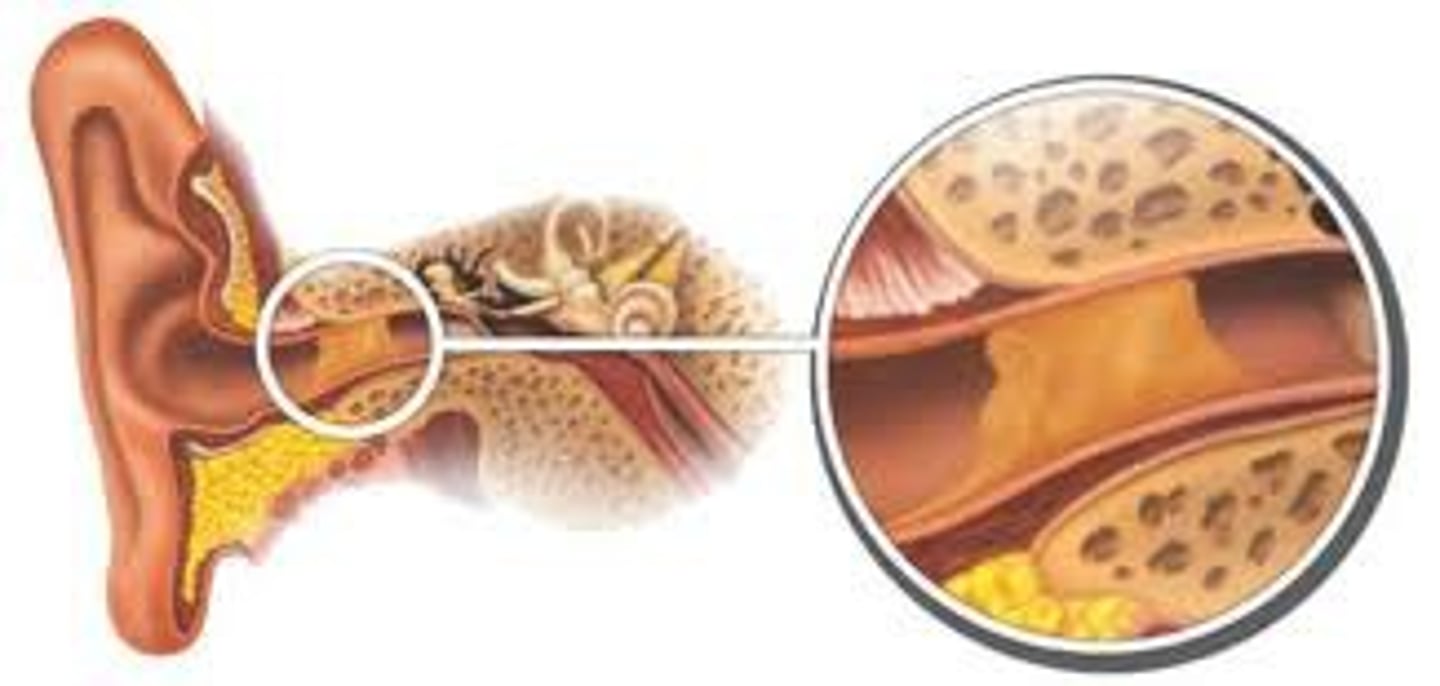
Ceruminous glands (cerumen)
modified apocrine glands found lining the ear canal that secrete earwax
Mammary glands
modified sweat glands that secrete milk

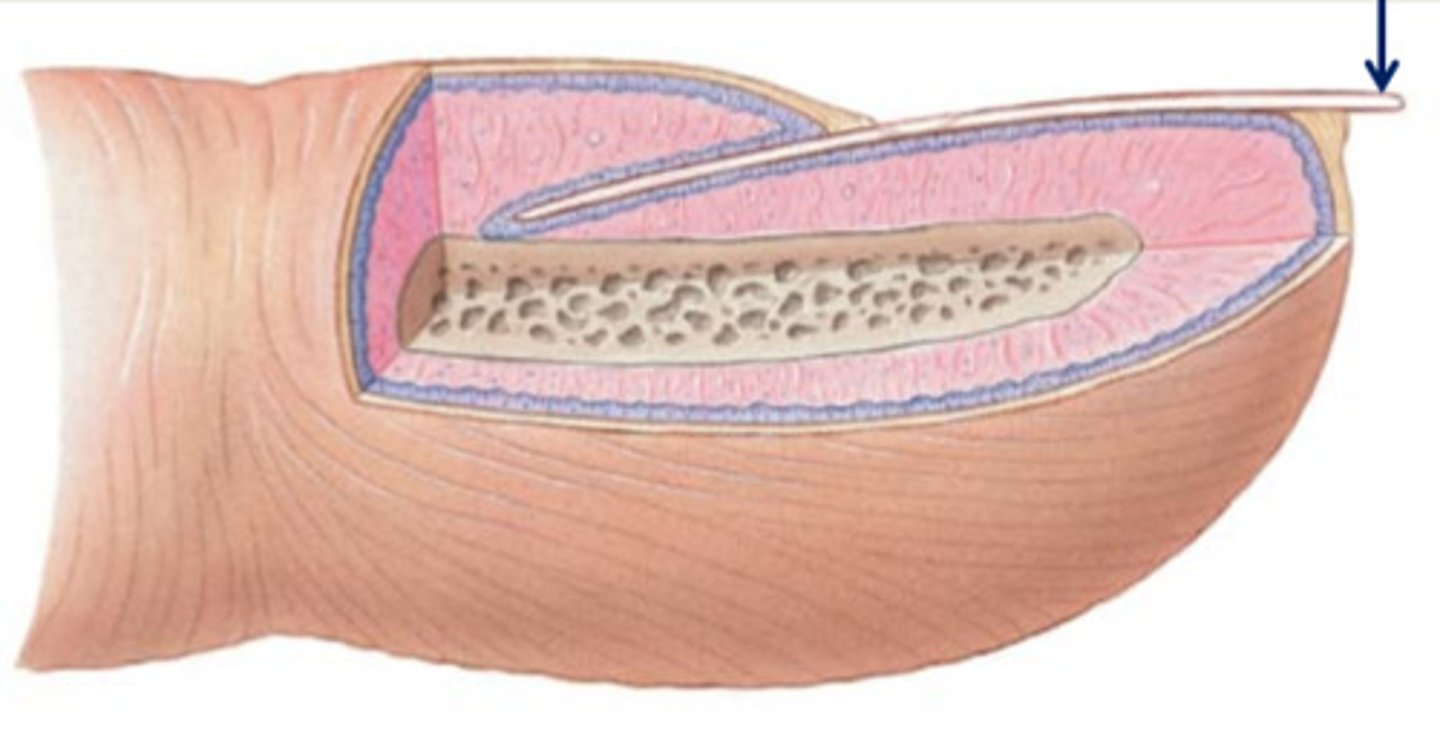
Nail
scale-like modification of the epidermis that forms a protective covering on the dorsal side of the distal finger or toe
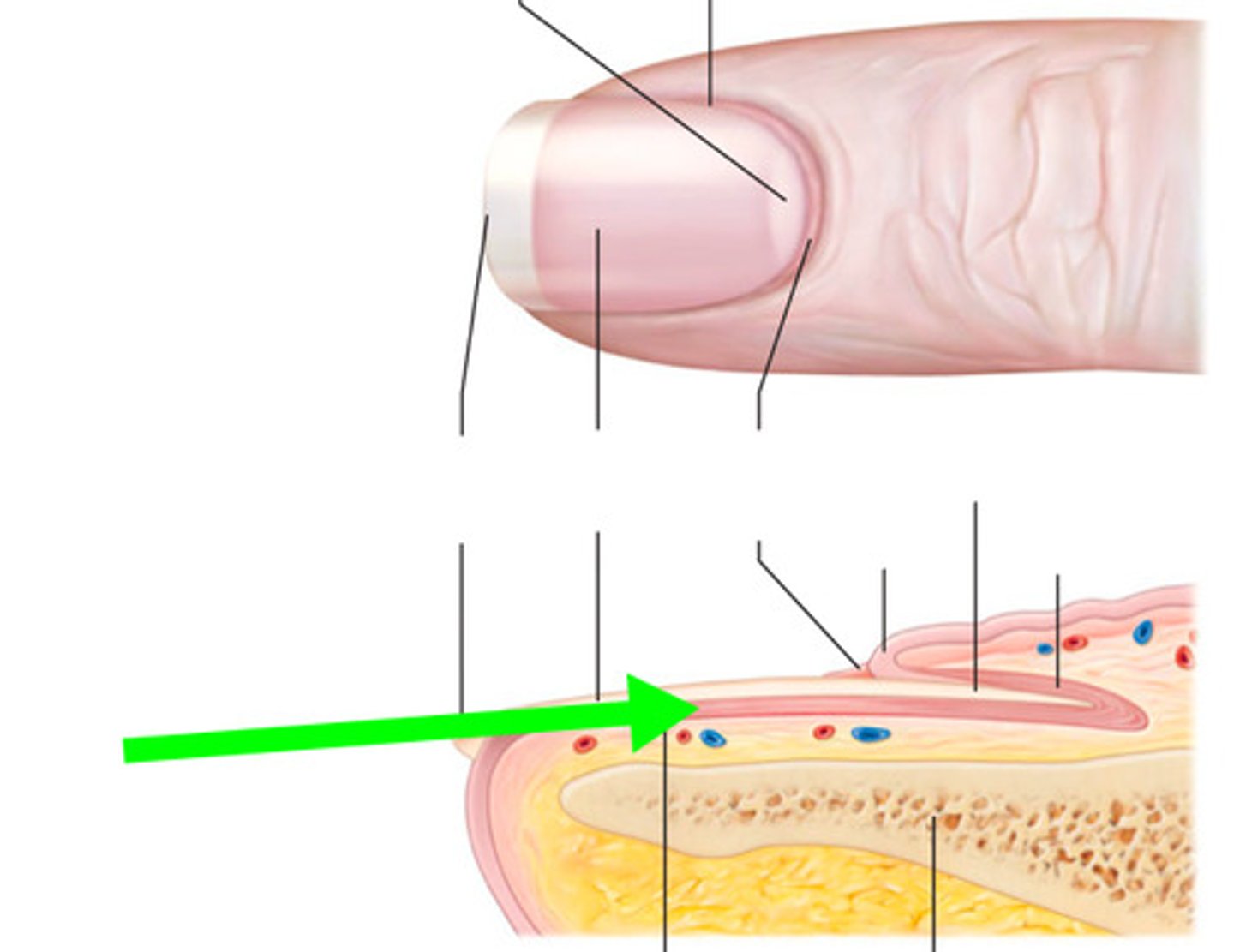
Nails are made up of
hard keratin and have a free edge, a nail body attached to the skin, and a root embedded in the skin
Nail matrix
epithelium responsible for nail growth in proximal part of the nail bed

Free Edge of Nail
extends past the finger or toe
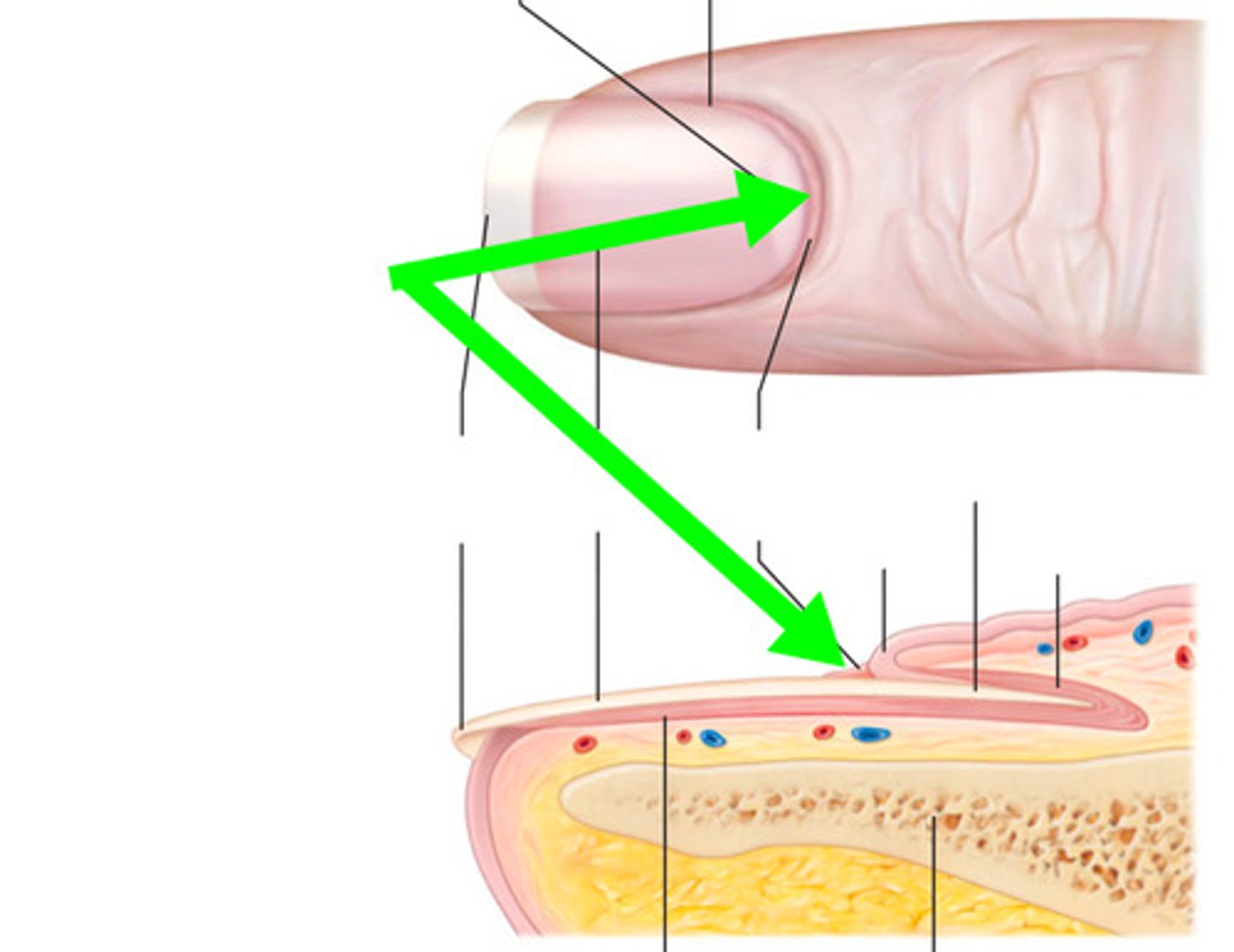
Proximal nail fold and lateral nail folds
where the skin covers over the edges of the nail
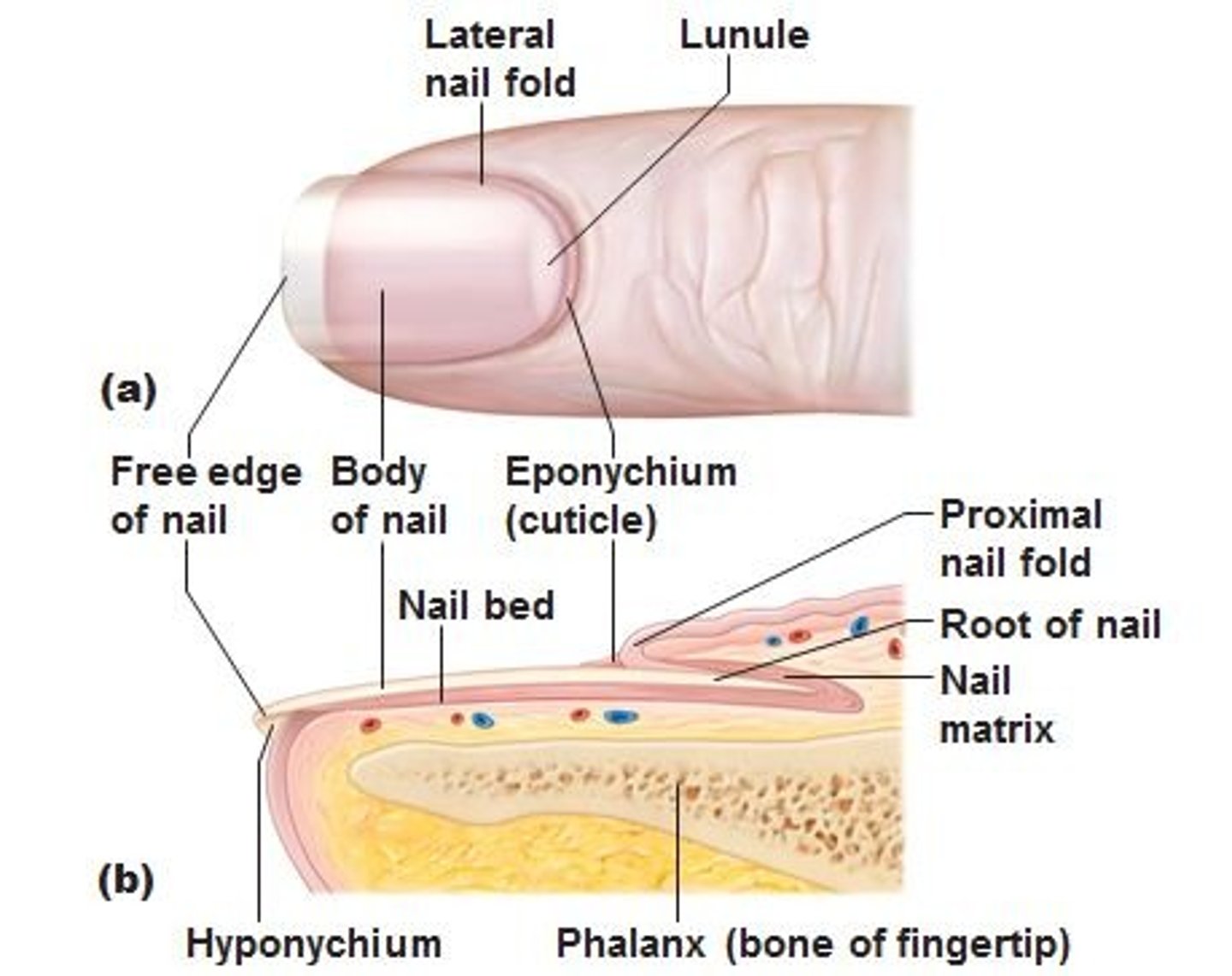
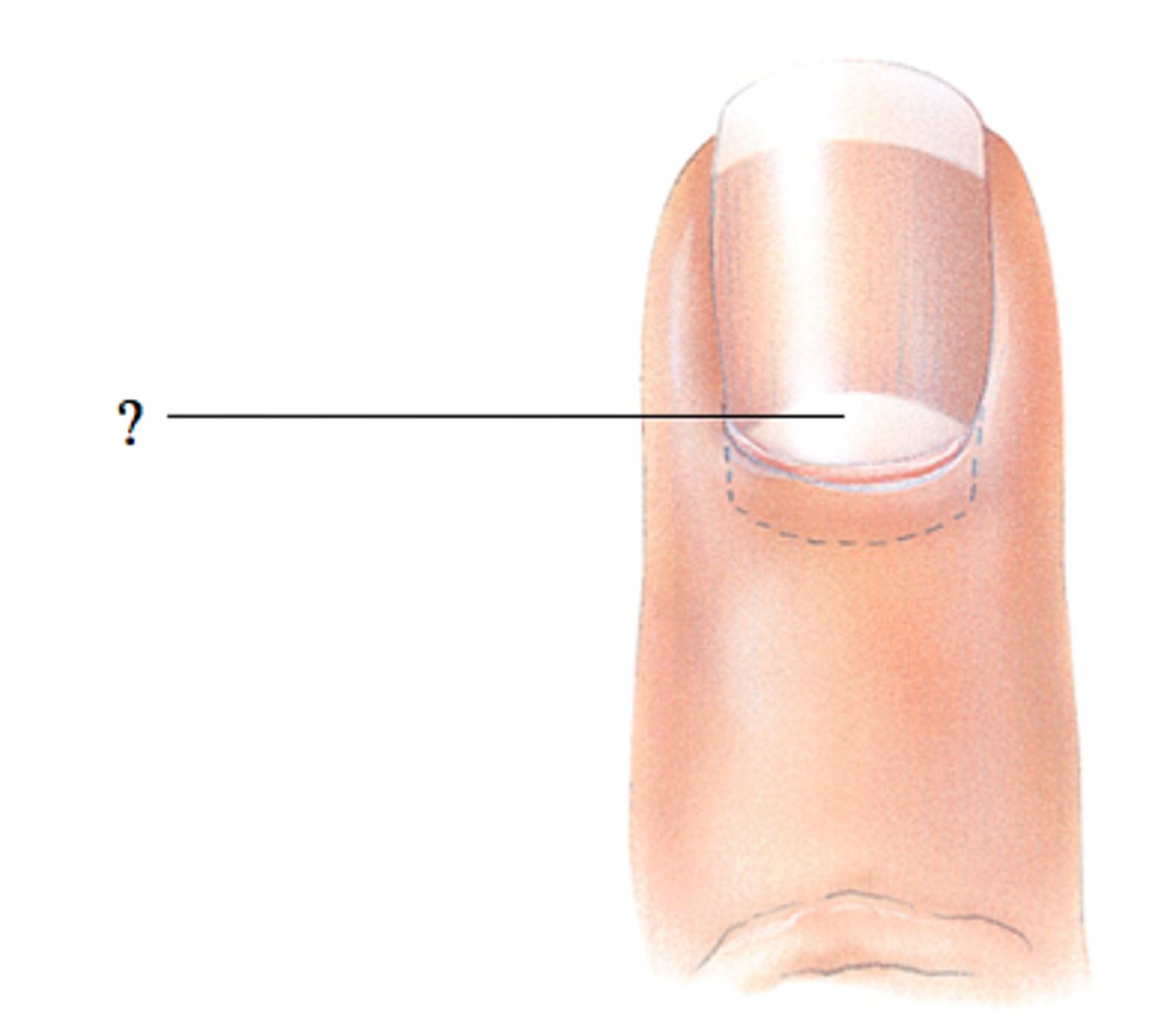
Lunula (little moon)
thick white part of the nail
Eponychium (cuticle)
stratum corneum of the epidermis at the proximal nail fold
Nail root
portion that isn't visible
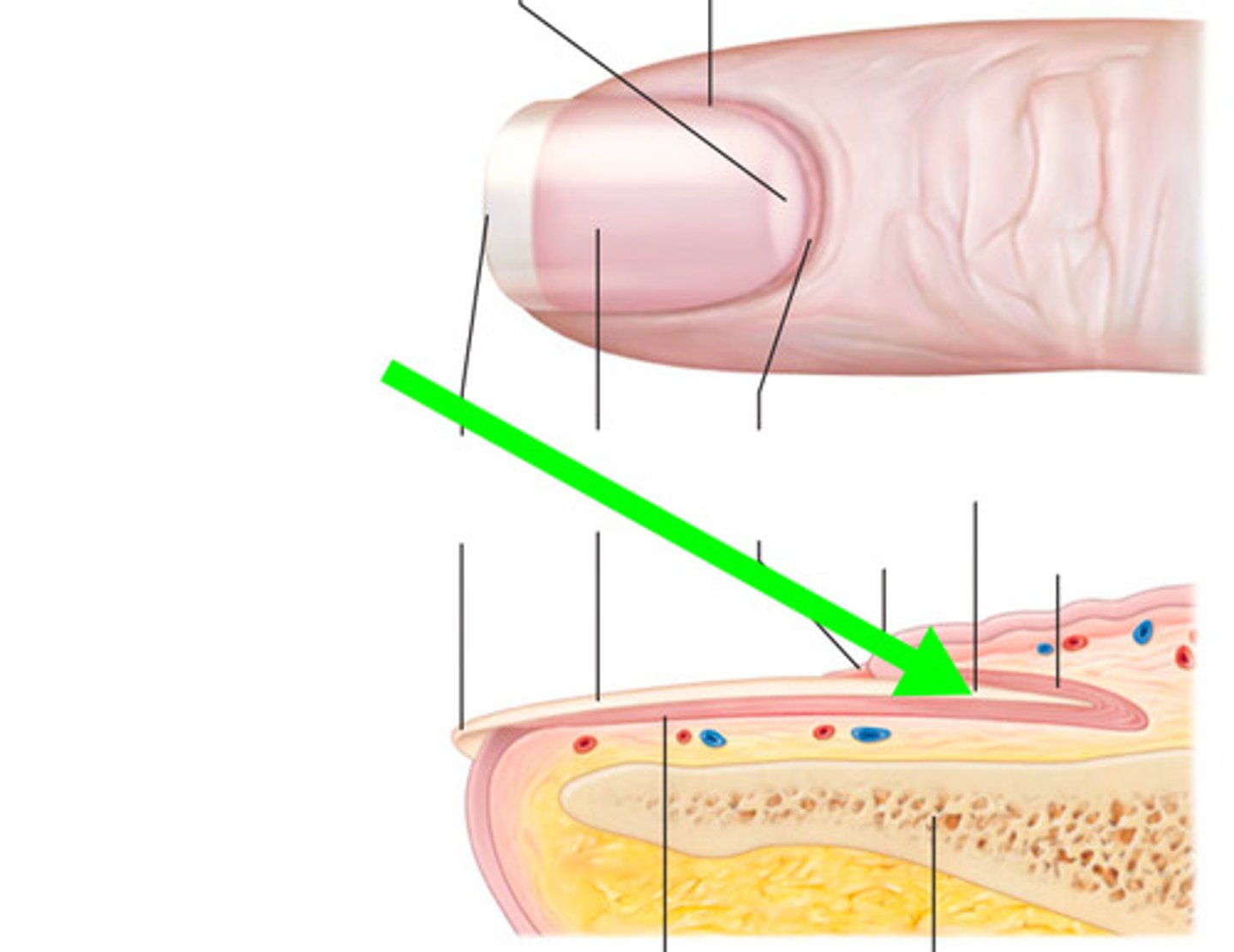
Nail body
visible portion of the nail

Nail bed
skin below the nail body

Hyponychium
secures the nail to the fingertip
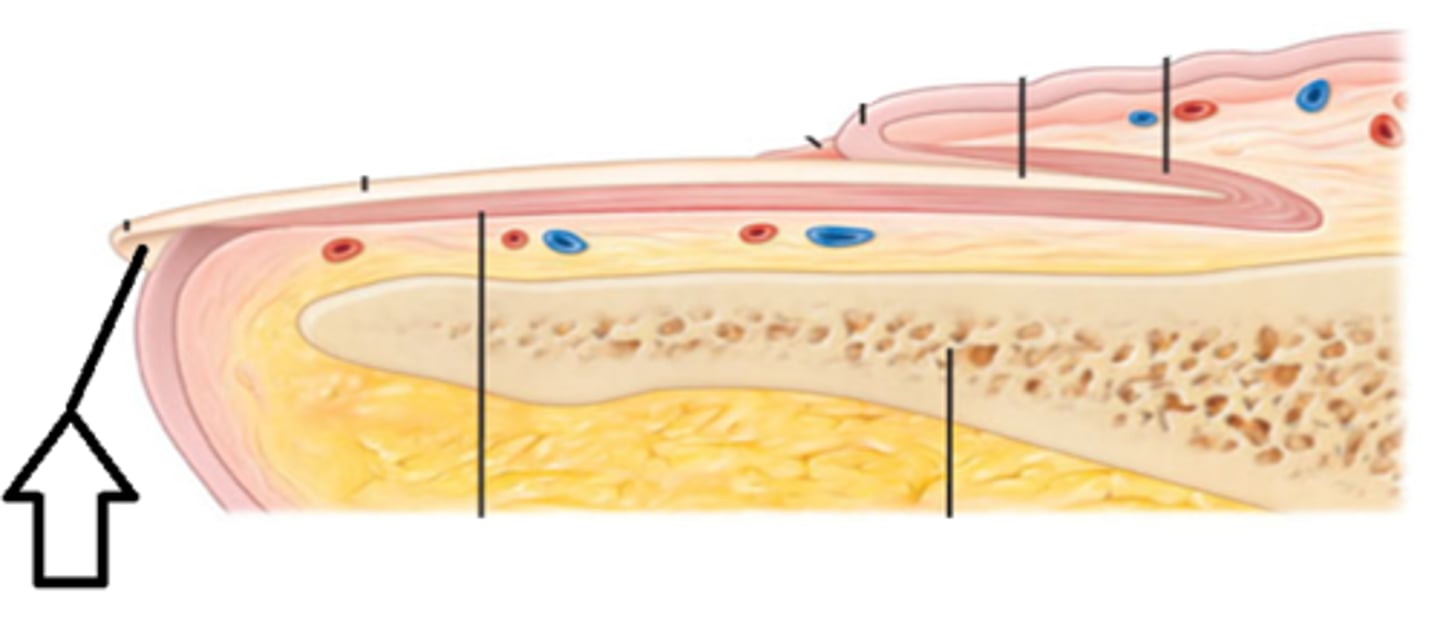
Distal phalanx
finger or toe bone under the nail
Chemical barriers of skin
skin secretions that are low in pH, inhibit bacterial growth, and melanin that protects the skin from UV damage
Physical barriers of skin
provided by the continuity of the skin and the hardness of keratinized cells
Biological barriers of skin
dendritic cells and the macrophages of the dermis
Skin's role in body temperature
manufacturing sweat to cool the body and causing constriction of dermal capillaries to prevent heat loss
Skin's role in sensation
cutaneous sensory receptors are a part of the nervous system in layers of the skin
Skin's role in metabolism
makes a vitamin D precursor when exposed to sunlight
Blood reservoir
skin may act as a _____________ by holding up to 5% of the body's blood supply which may be diverted to other areas of the body if needed
Shell
Core has higher temperature than the _____
Retained
Heat can be lost through increased flow to the skin or _______by bypassing vessels in the skin
Radiant flow of heat
heat exchange between our skin and the external environment occurs through
Conductive flow
flow of heat from warmer to cooler objects
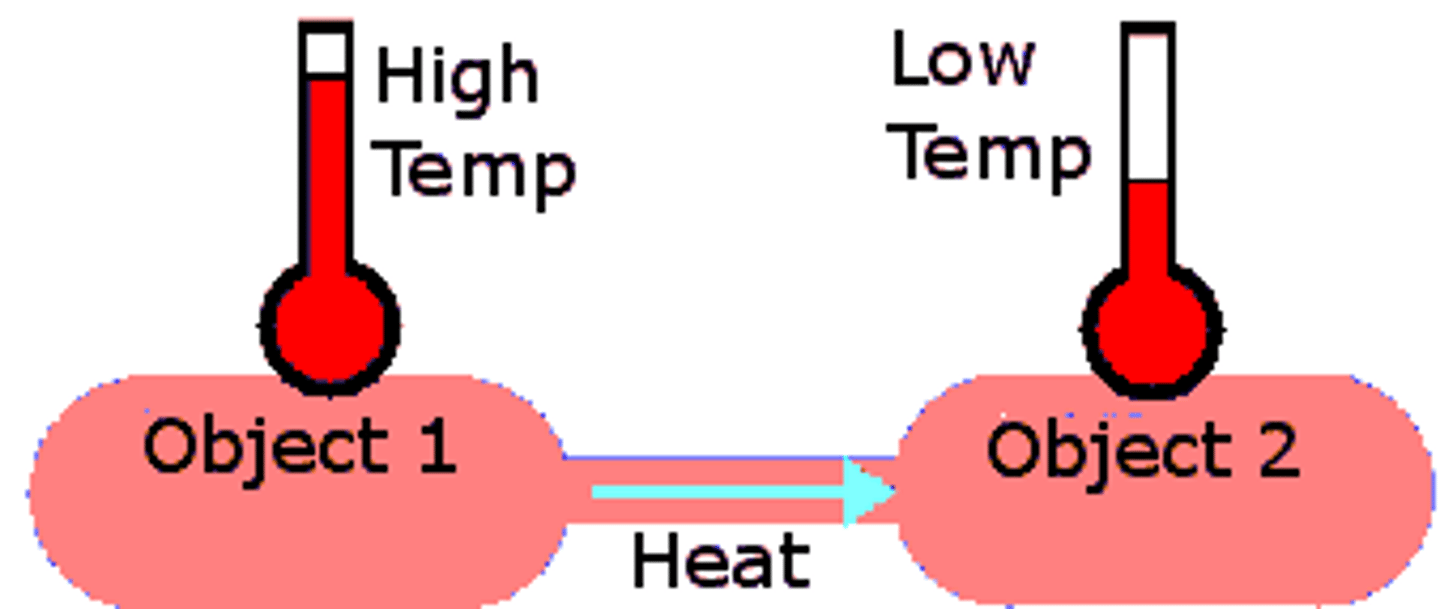
Convective flow
flow of heat of warm air away from the body
Evaporation
heat loss due to loss of fluids from the lungs, oral mucosa, and the skin
Insensible heat loss
accompanies insensible water loss from the lungs, oral mucosa, and skin and accounts for about 10% of basal heat production
Sensible heat loss
occurs when body temperature rises and sweating increases water vaporization
Heat cramps
when sweating is heavy and prolonged, losses of water and NaCl can cause painful muscle spasms
Hypothalamus
part of the brain that controls body temperature
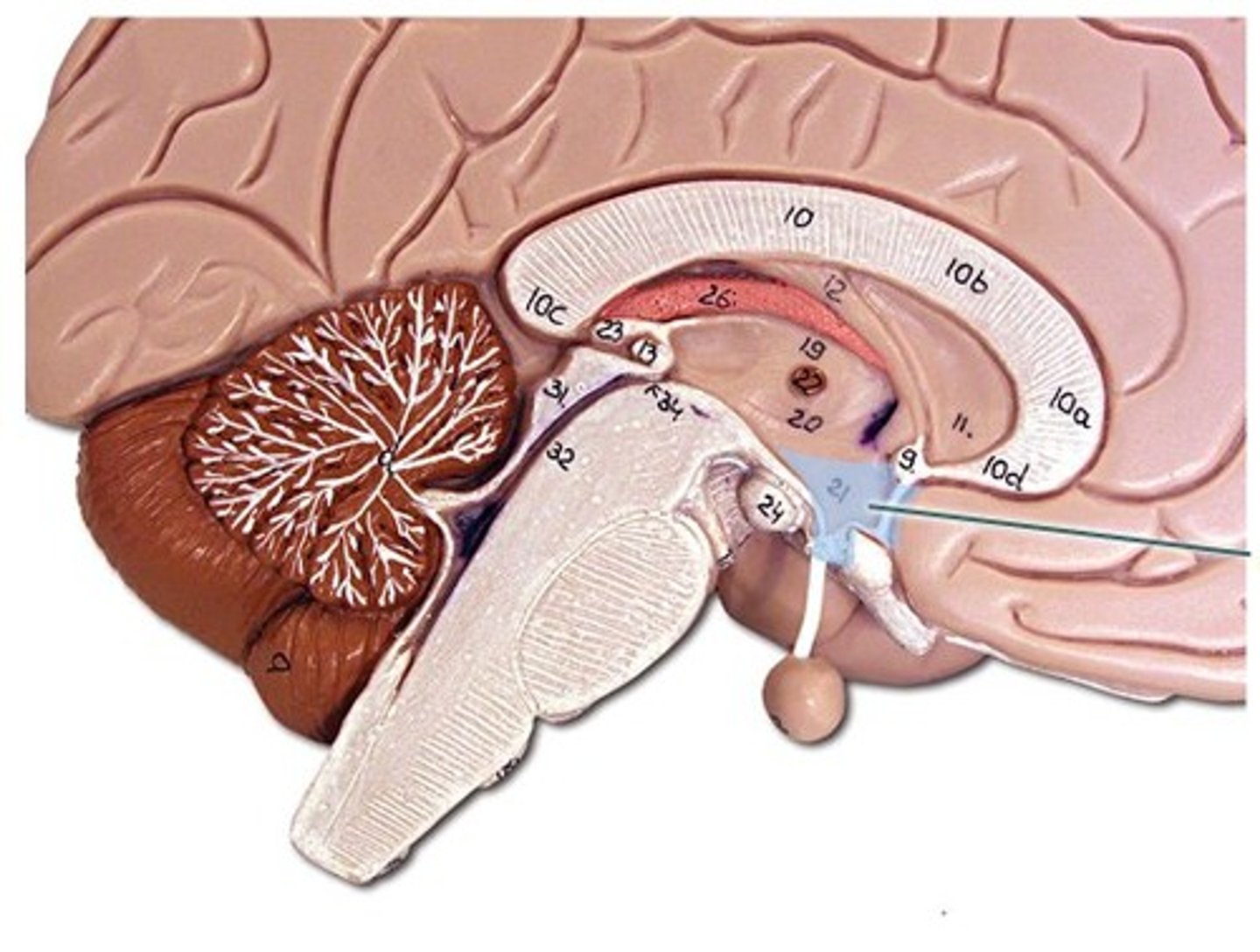
Heat promoting mechanisms
maintain or increase core body temperature and include constriction of cutaneous blood vessels, shivering, increase in metabolic rate, and increased release of thyroxine (in infants)
Heat loss mechanisms
protect the body from excessively high temperatures and include dilation of cutaneous blood vessels, sweating and behaviours that promote heat loss or reduce heat gain
Frostbite
occurs when blood flow to the skin is restricted due to extreme cold, causing skin cells to be deprived of oxygen and nutrients

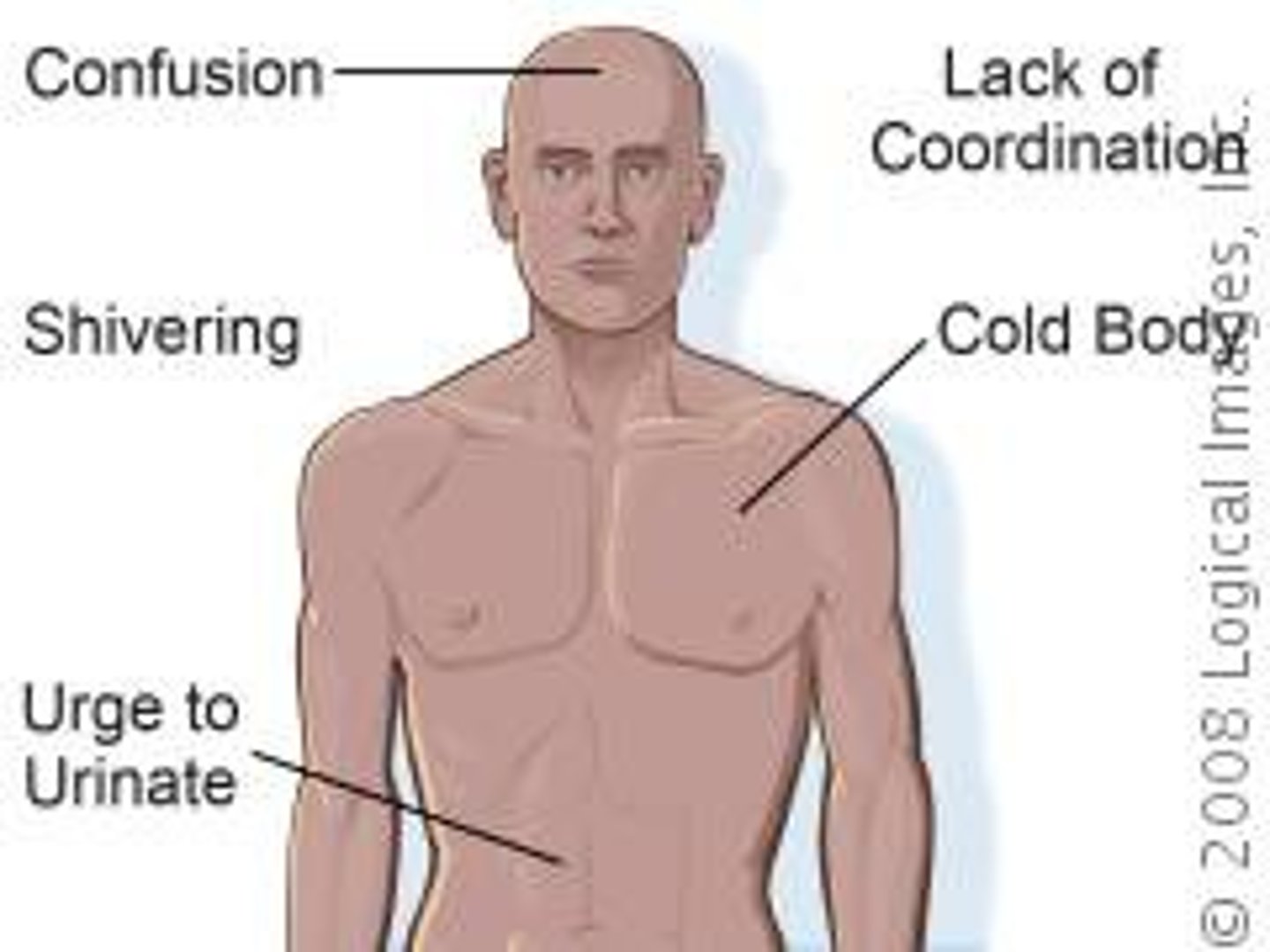
Hypothermia
-low core body temperature from cold exposure, leading to a decrease in vital signs
-shivering stops at core temp 30-32C and can progress to coma and death at 21C
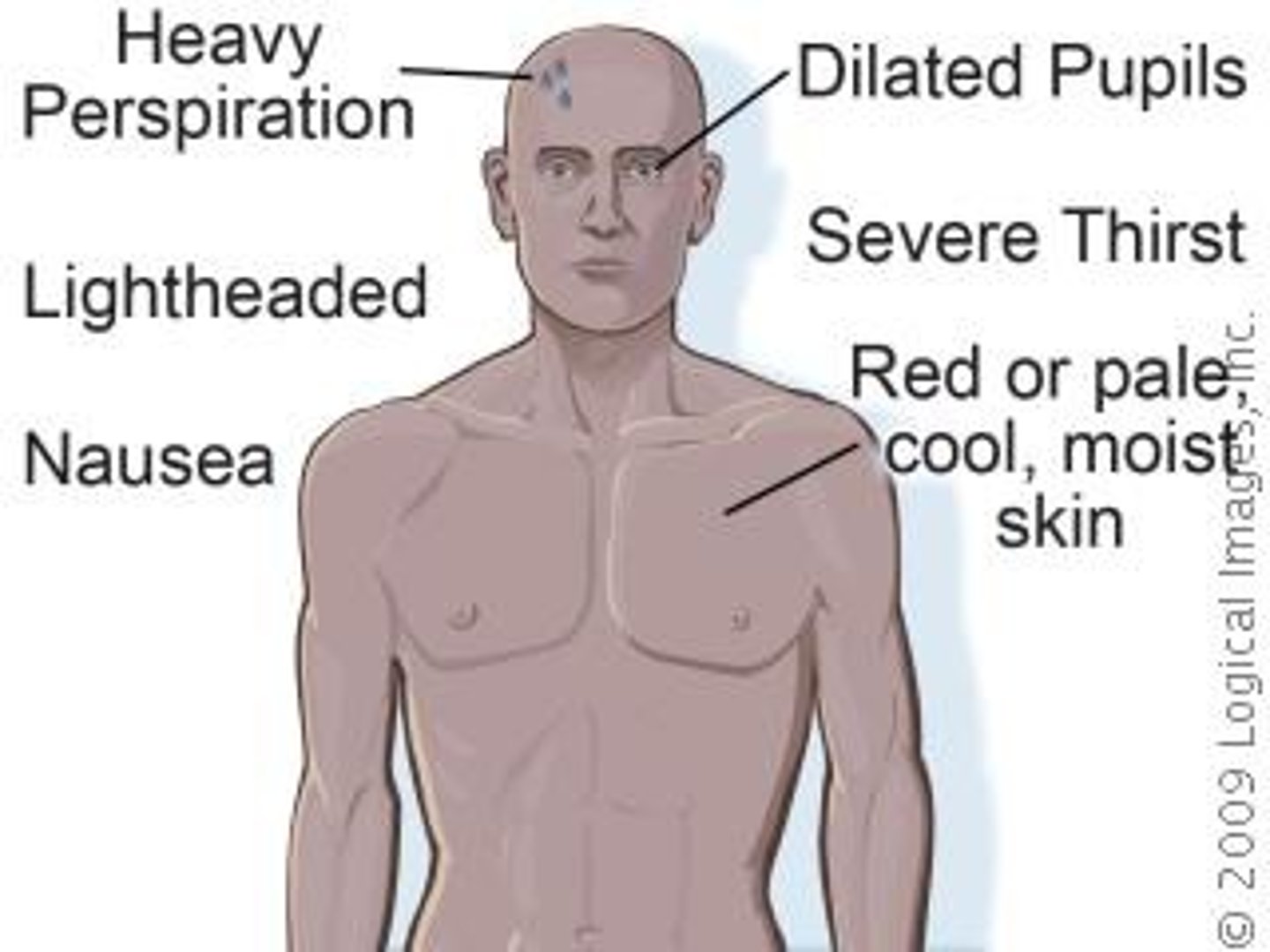
Hyperthermia
elevated body temperature that overwhelms the body's ability to cool down

Heat stroke
a positive-feedback loop begins at 41C core temperature which further increases body temperature and can be fatal

Heat exhaustion
heat associated collapse after vigorous exercise due to dehydration and low blood pressure
Fever
-controlled increase in body temperature that results when macrophages and other cells release cytokines that act as pyrogens
-causes the hypothalamus to reset to a higher than normal temperature
-cryogens reset the thermostat to normal

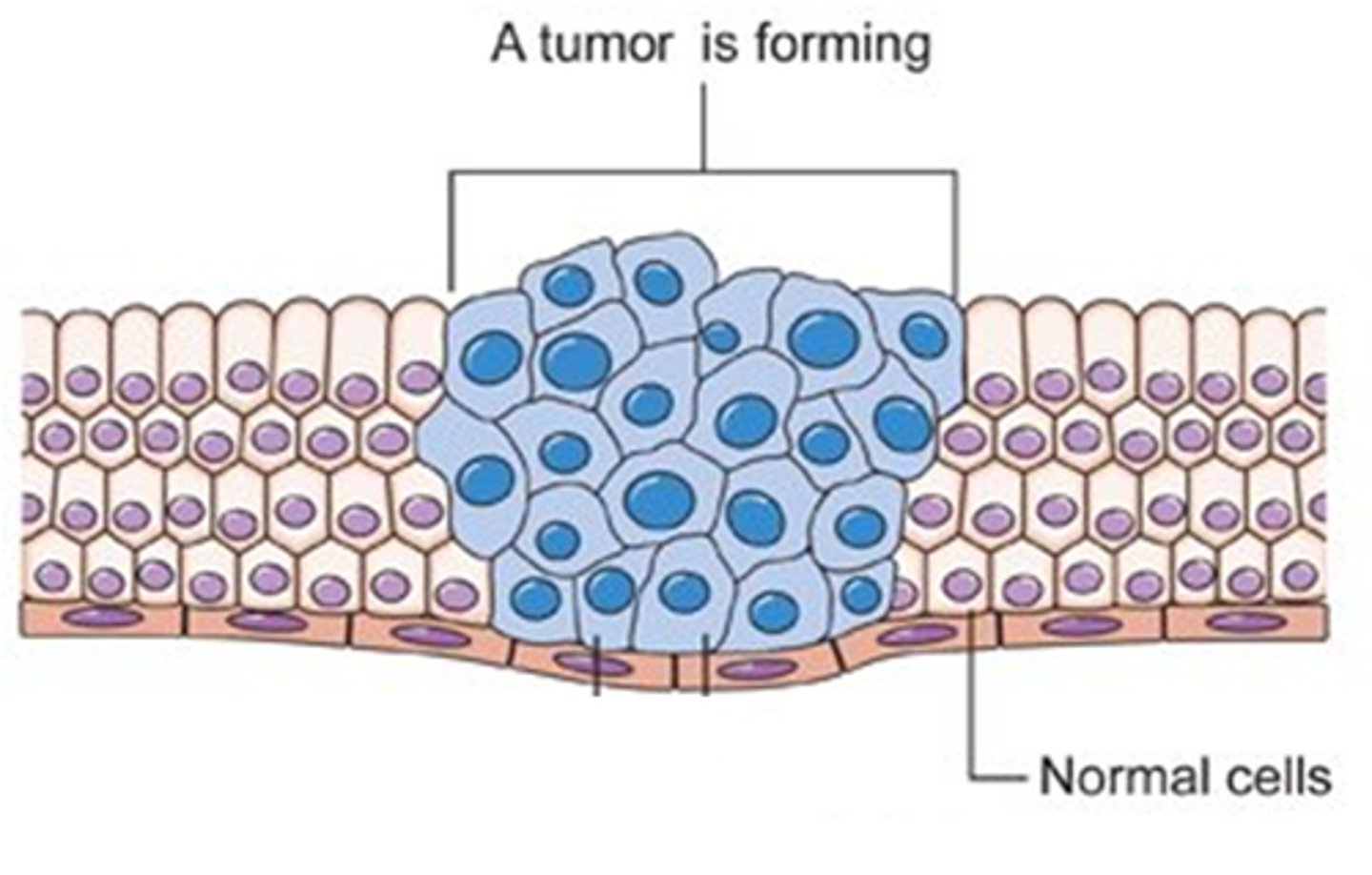
Cancer
occurs when the DNA of a cell is damaged or mutated and the cell begins to grow uncontrollably
Carcinoma
cancer that develops from the epithelial tissue
Adenocarcinoma
cancer from glandular epithelium
Sarcoma
cancer of the connective tissues other than blood
Leukemia and Lymphoma
cancers from blood-forming cells
Benign tumor
mass of cells that are not cancerous (malignant) because they lack the ability to invade neighboring tissues or spread throughout the body (metastasize)
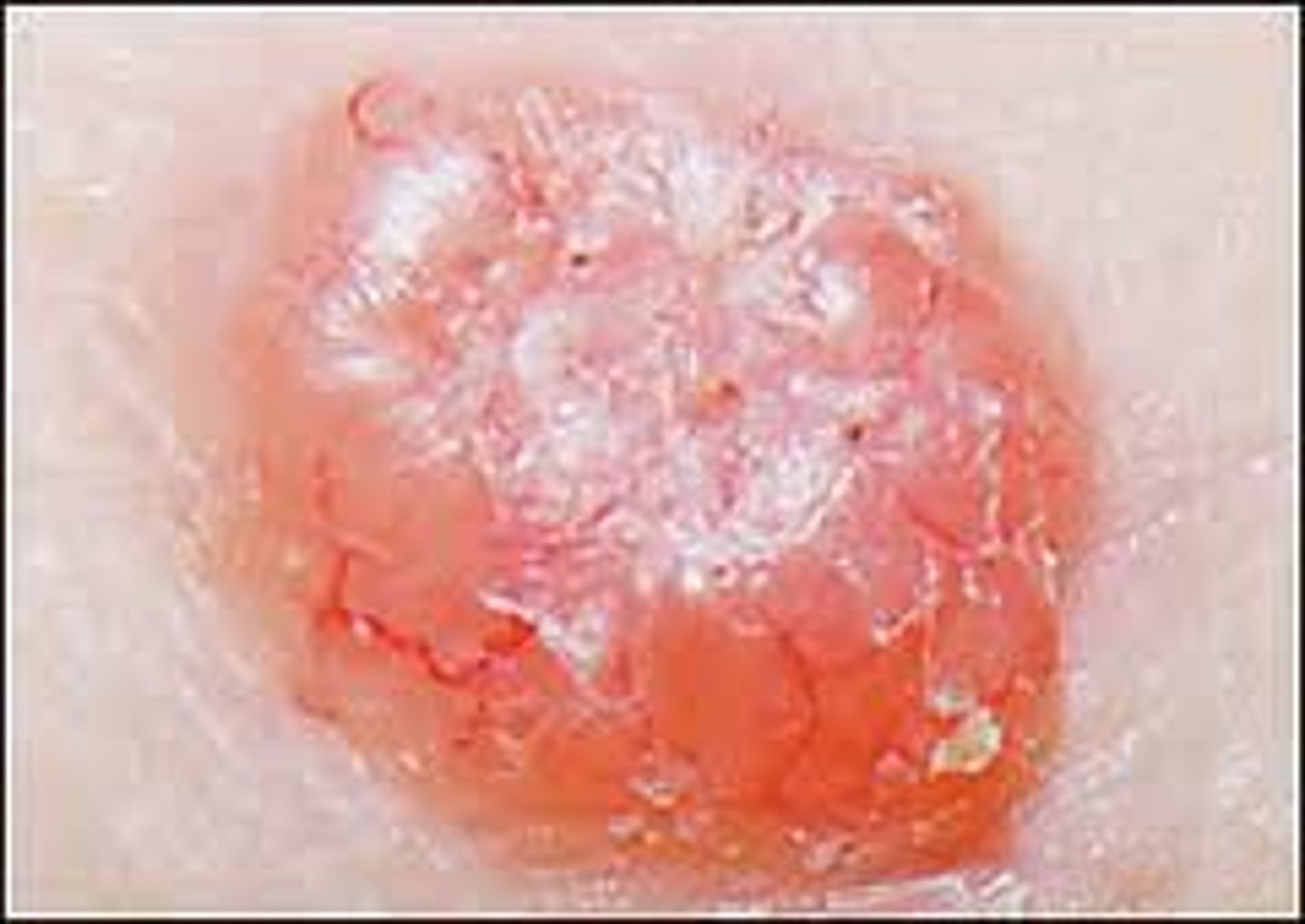
Basal cell carcinoma
-the least malignant and the most common skin cancer
-stratum basal cells proliferate and slowly invade dermis and hypodermis
-cured by surgical excision usually
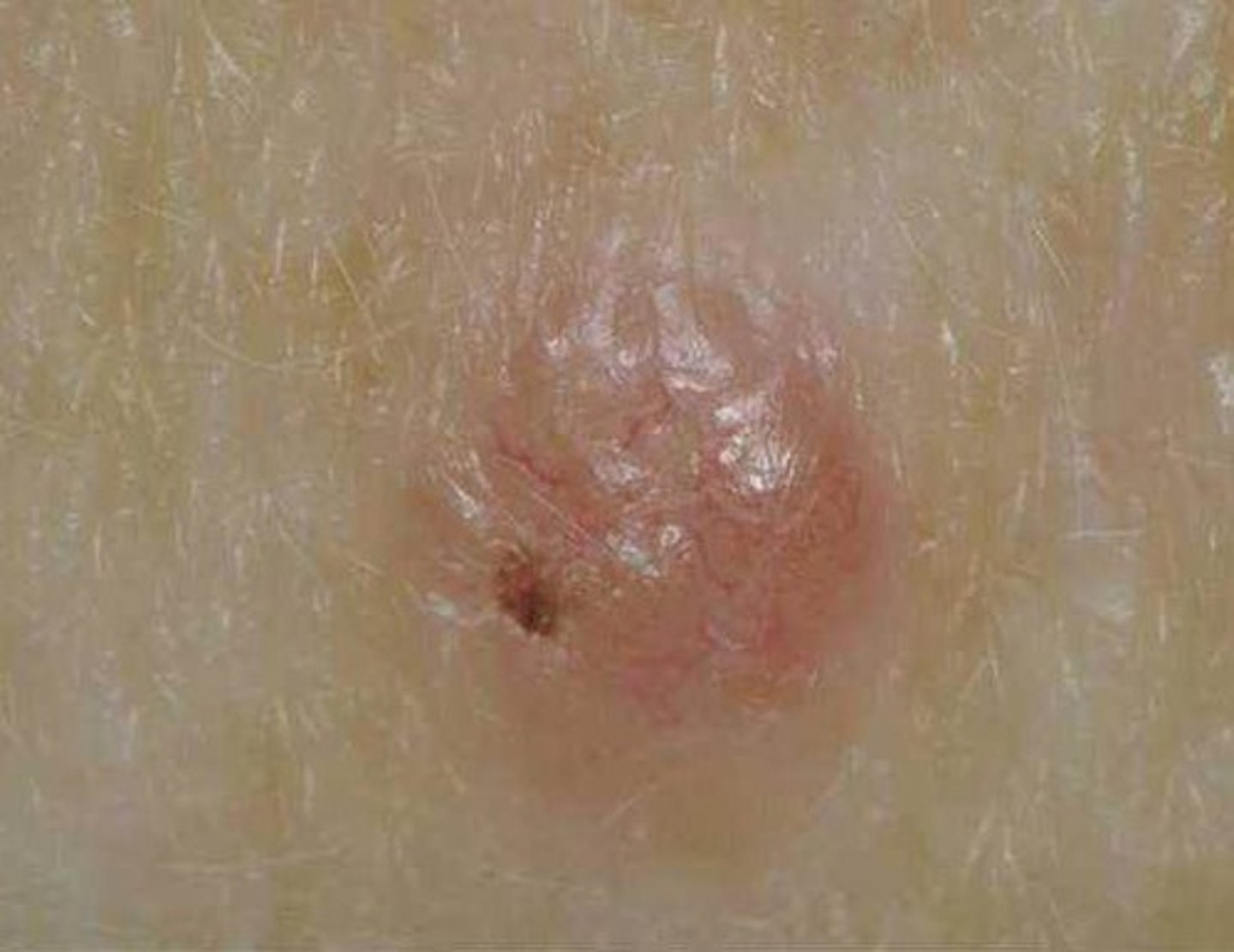
Squamous cell carcinoma
-the second most common type of skin cancer and can metastasize
-derives from keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum
-present as scaly reddened papule; grow rapidly
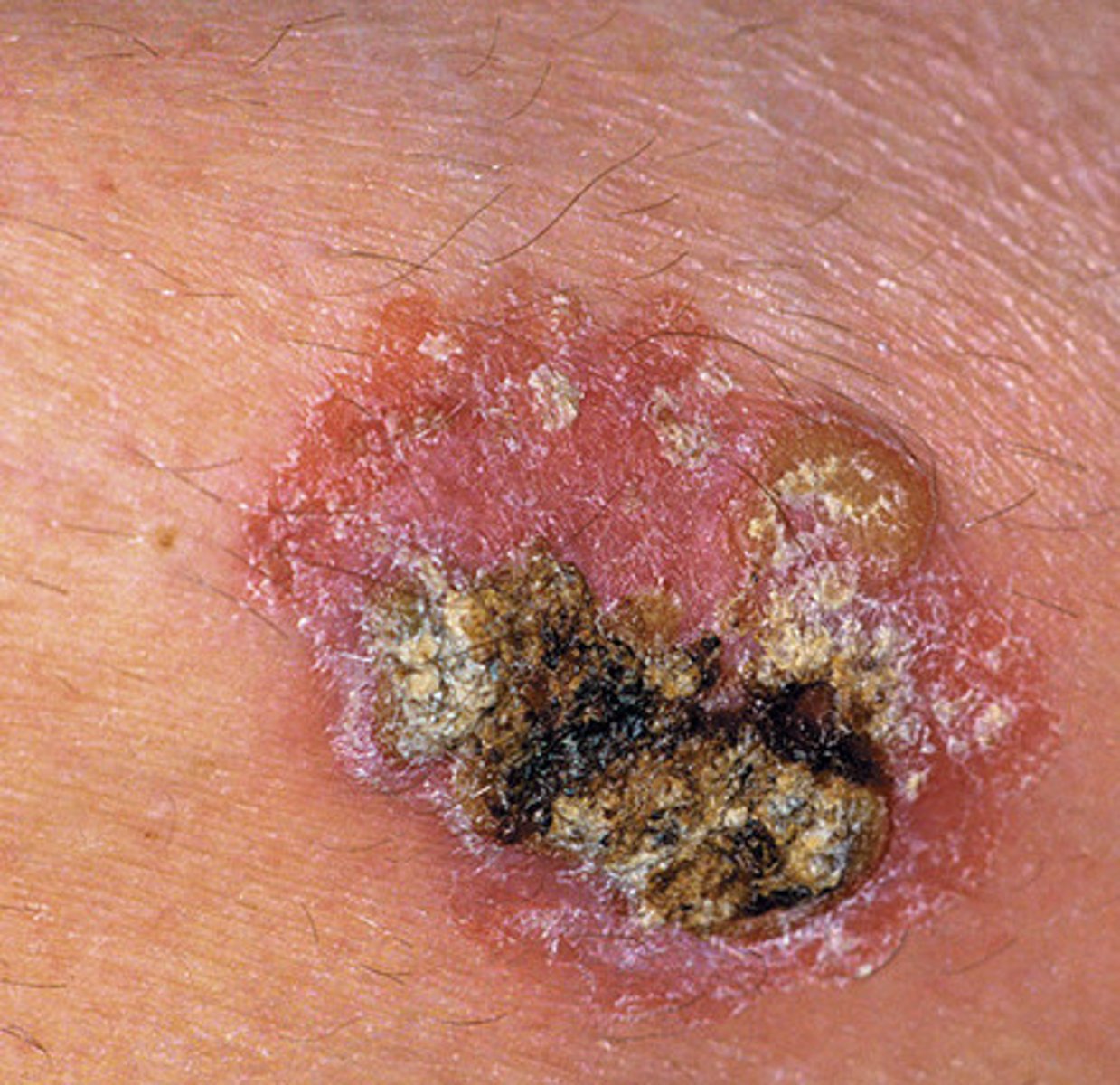
Melanoma
-cancer of melanocytes, most dangerous because it's highly metastatic and resistant to chemo
-treated by excision and immunotherapy
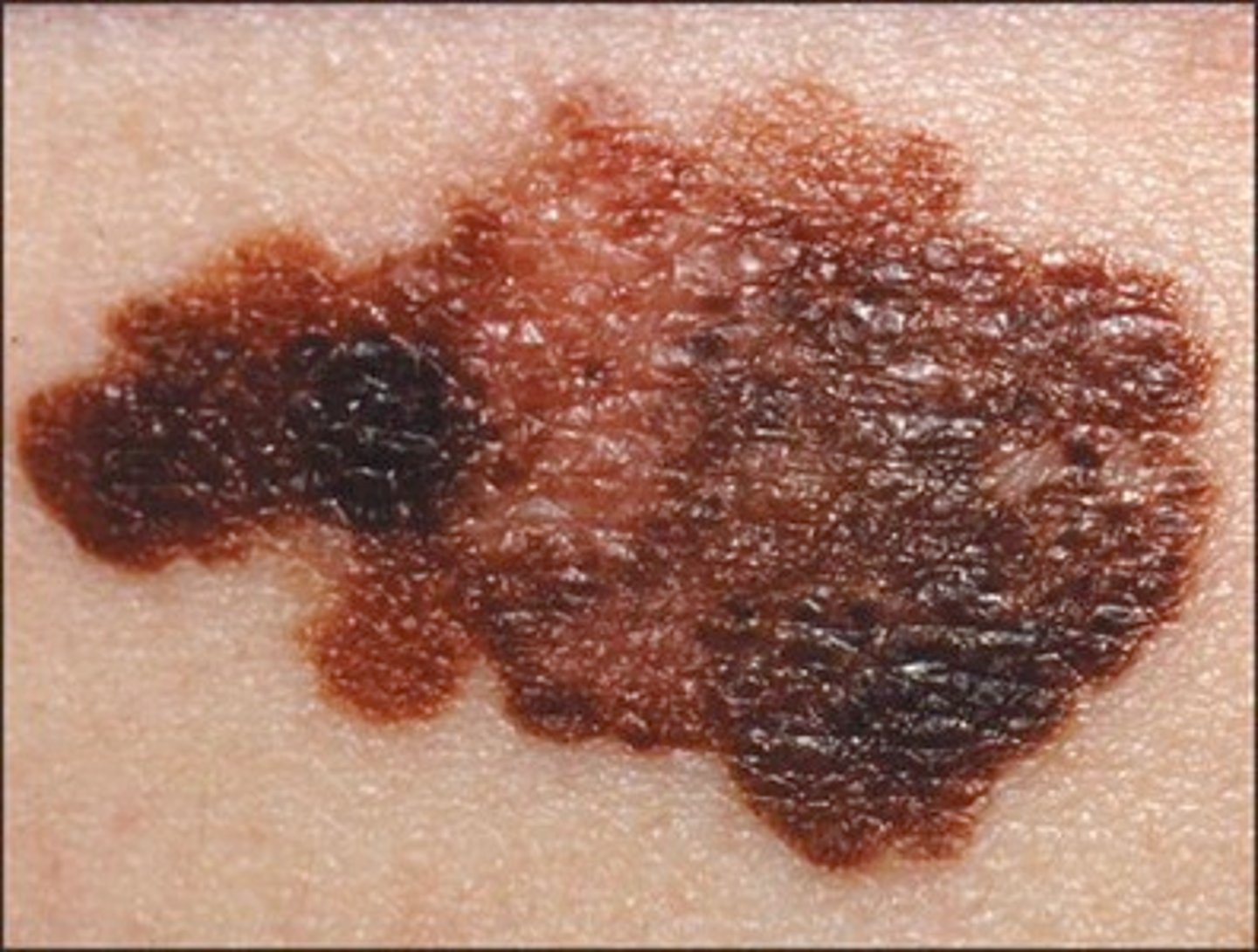
ABCDE of Melanoma
Asymmetry, Border Irregularity, Multiple Colors, Large Diameter, Evolution
Burn
tissue damage resulting from intense heat, electricity, radiation, or certain chemicals which denature cell proteins and cause cell death

Risks to a burn patient
dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, infection
Rule of Nines
-used to evaluate burns
-the body is broken to 11 sections with each section representing 9% except the genitals which account for 1%

First-degree burns
-epidermal damage only
-localized redness, swelling, and pain
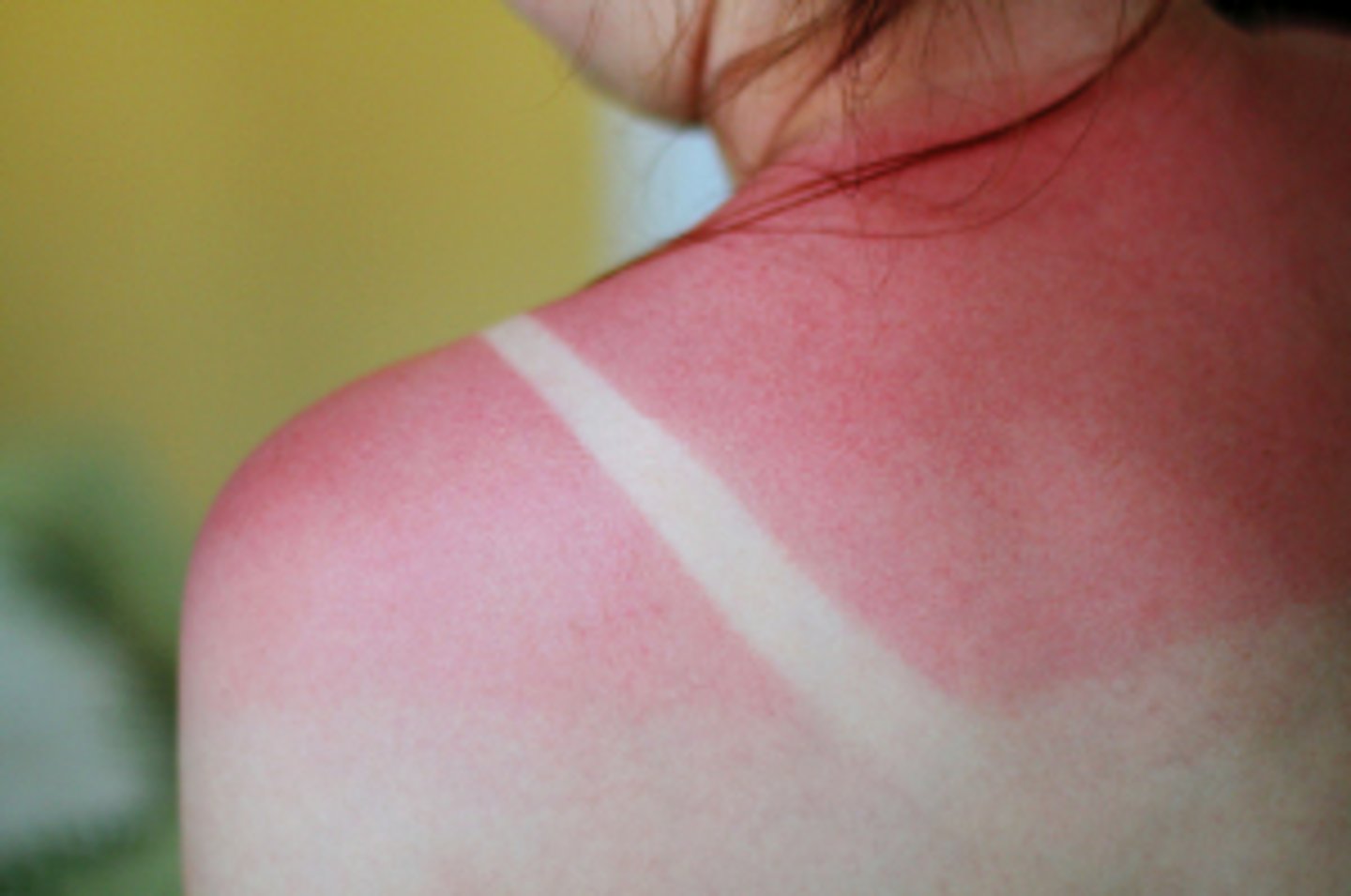

Second-degree burns
epidermal and upper dermal damage, blisters appear
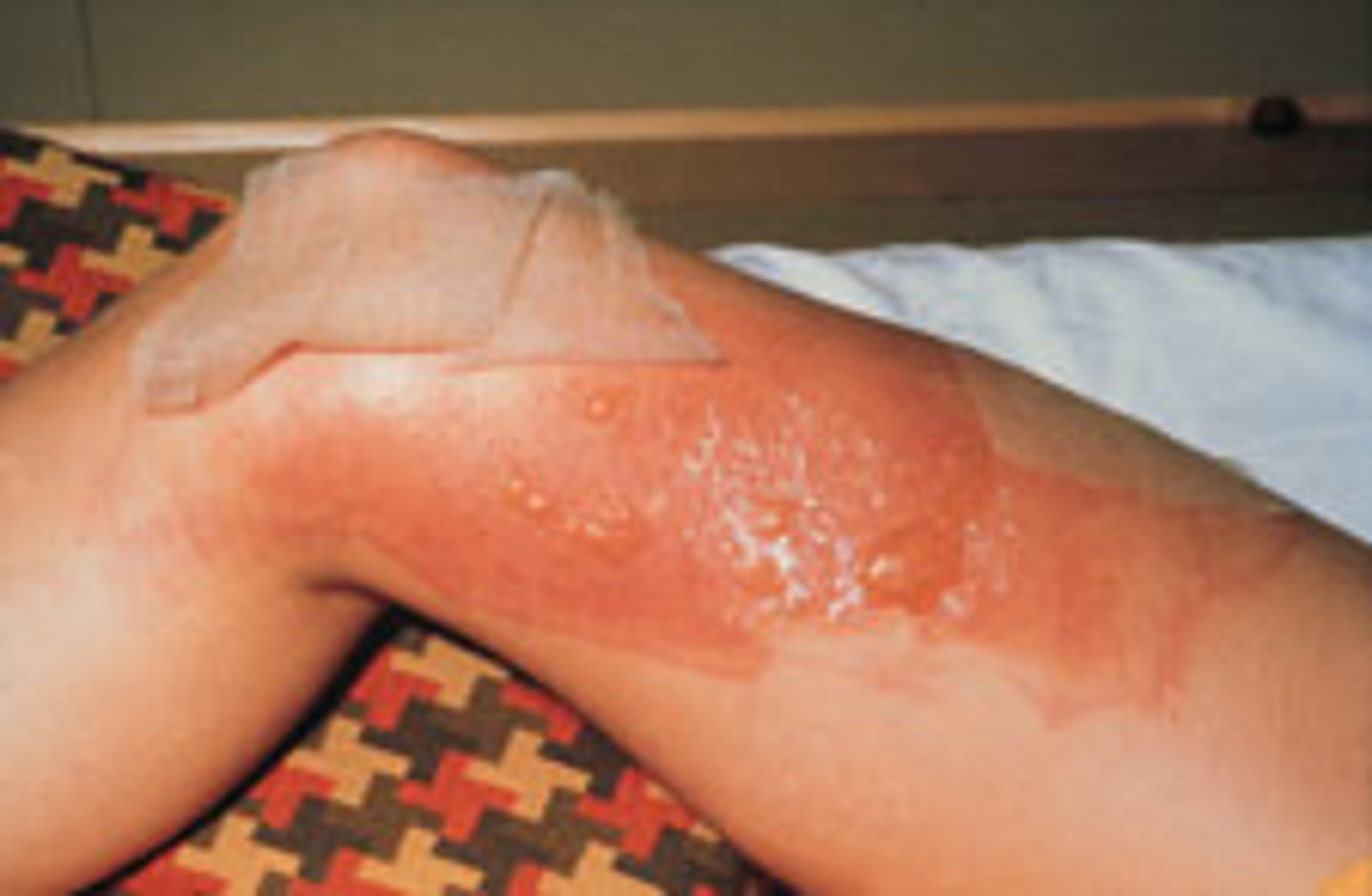
Partial thickness burns
First- and second-degree burns are referred to as ______________ because only the epidermis and upper dermis are involved
Third-degree burns
-involve the entire thickness of the skin
-skin turns grey-white, cherry red, or blackened
-typically not painful because nerve endings are destroyed
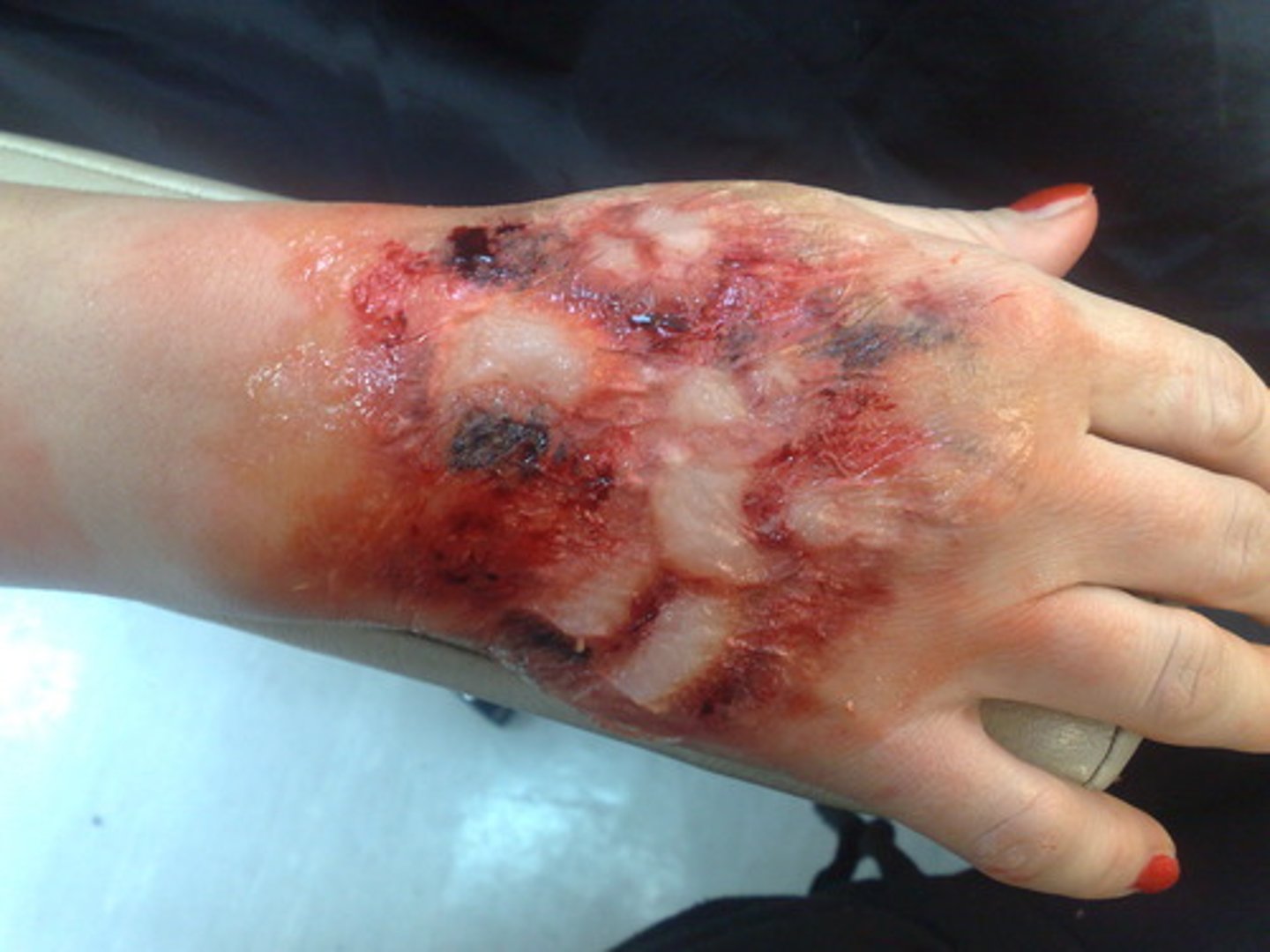
Critical burns
->25% of the body had 2nd-degree burns
->10% of the body has 3rd-degree burns
-face, hands or feet have 3rd-degree burns
Fourth degree burns
destroy all layers of skin and also burn into fat tissue
Fifth degree burns
burning into muscle
Sixth degree burns
burning into bone
Organs
bones are ______ because they contain different types of tissues; nervous tissue, cartilage, fibrous connective tissue, muscle cells, and epithelial cells
Osseous
bone connective tissue
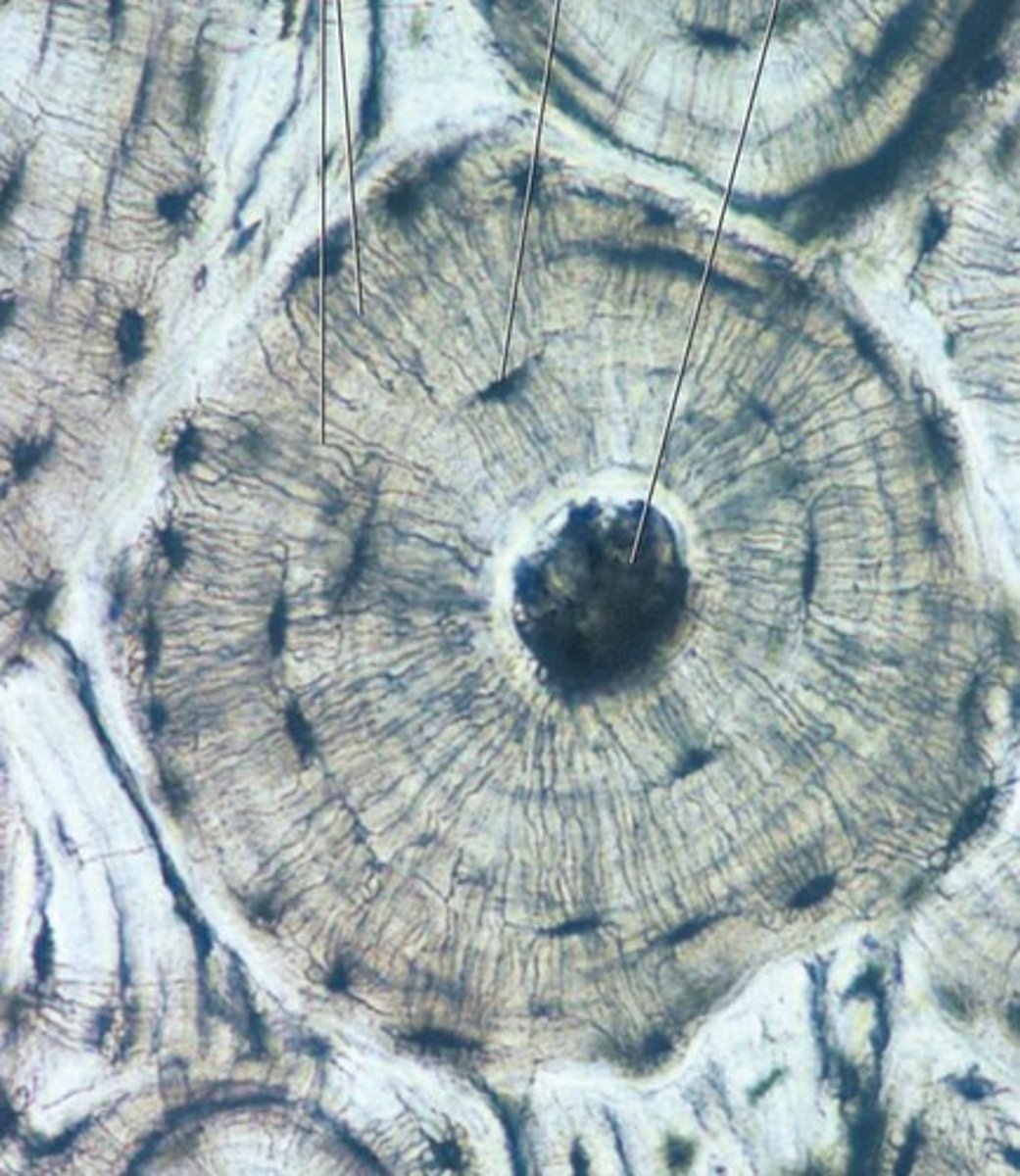
Compact bone
smooth and solid dense outer layer of bone
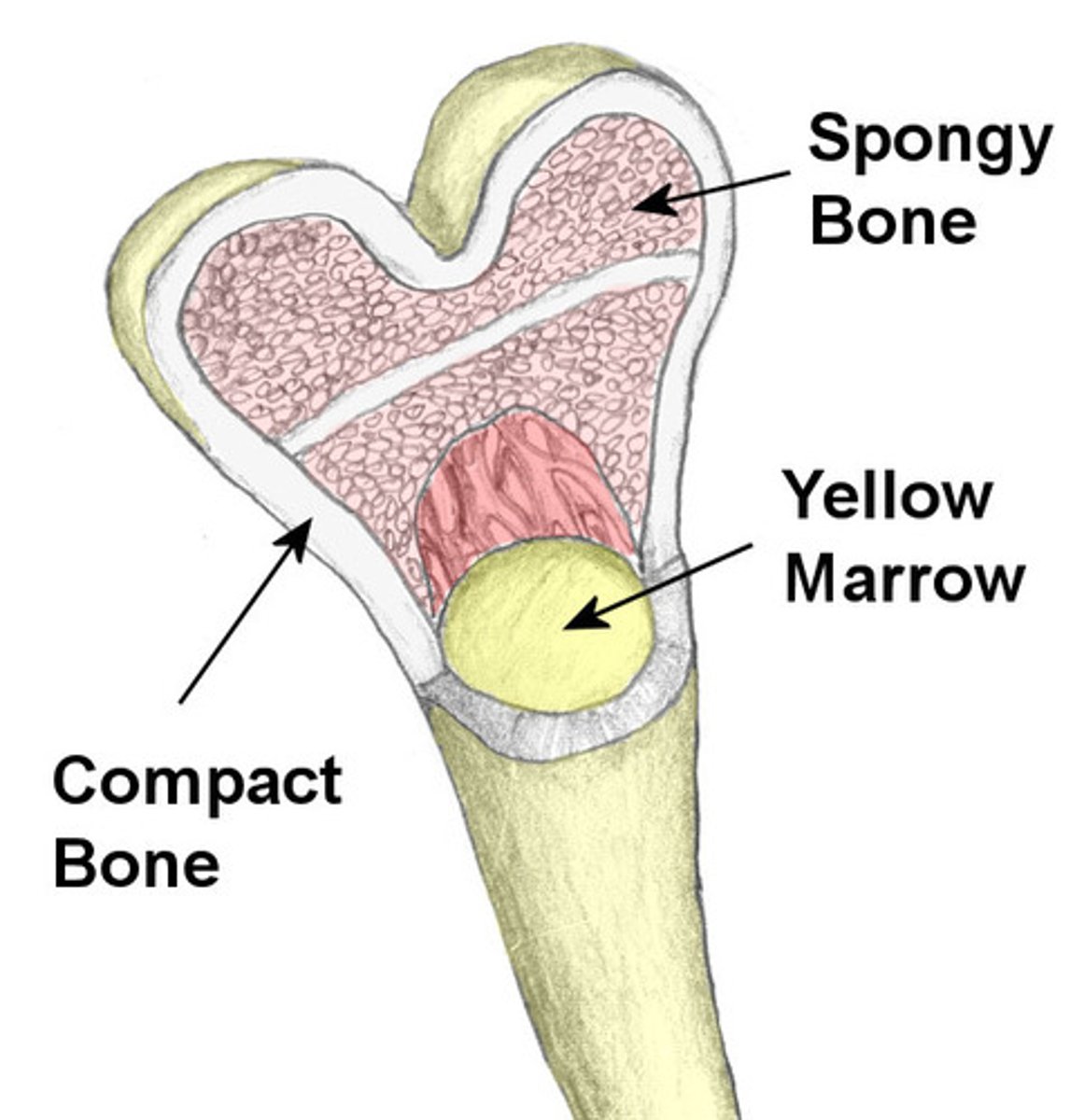
Spongy bone
inside compact bone which consists of honeycomb, needle-like, or flat pieces called trabeculae

Red bone marrow
full of red blood cells
Yellow bone marrow
full of adipose cells
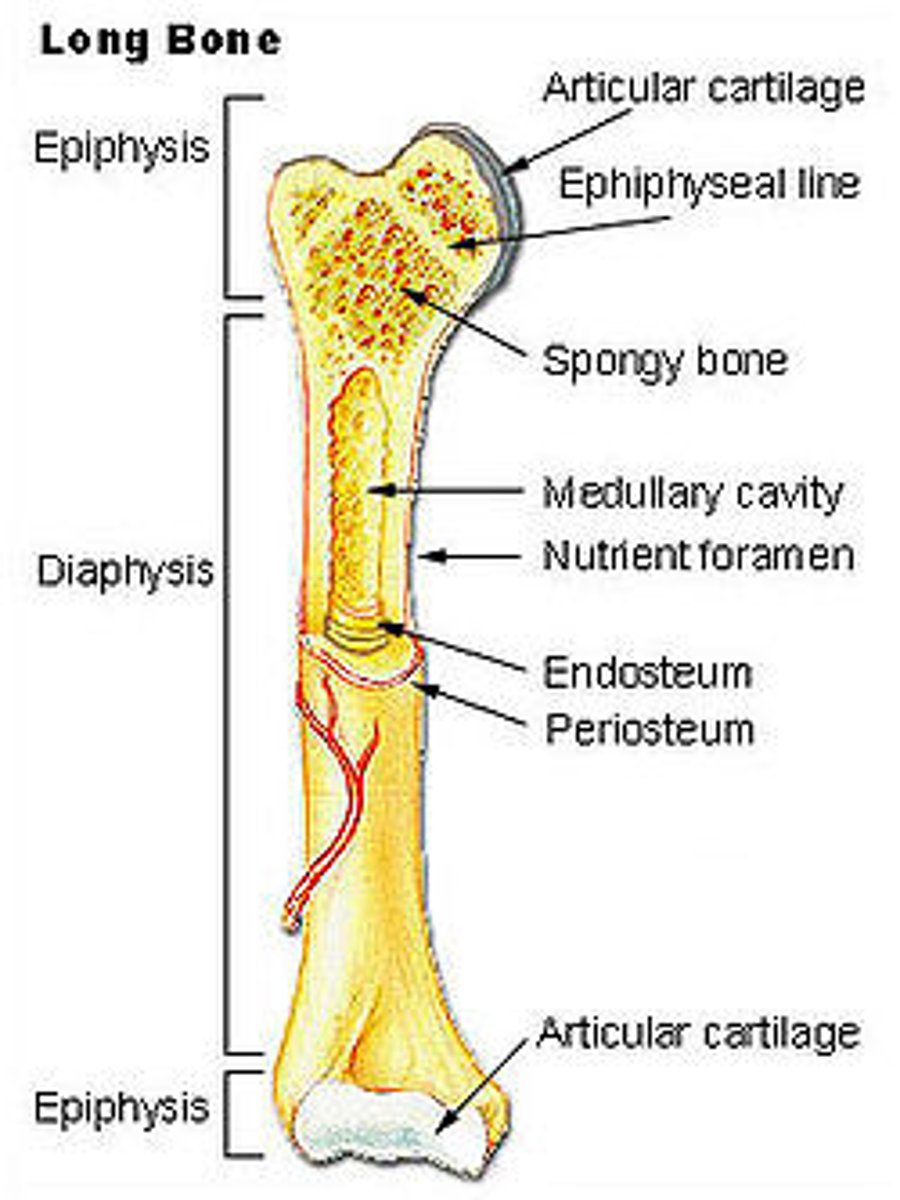
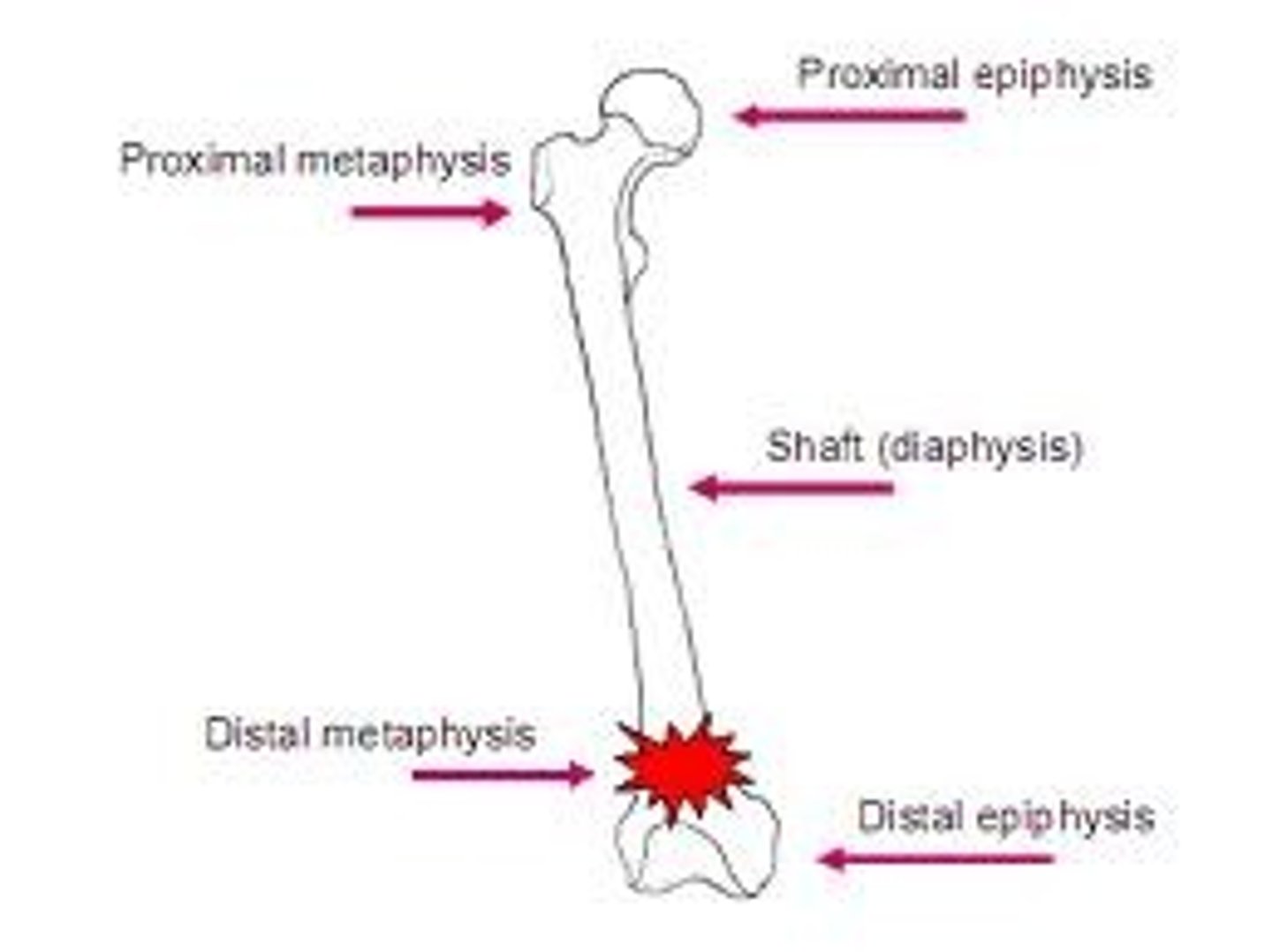
Diaphysis
long tubular shaft of bone made of outer layer of compact bone around a central medullary cavity filled with yellow bone marrow in adults

Epiphysis
ends of long bones that consist of compact bone around spongy bone filled with red marrow
Metaphysis
transition between the diaphysis and epiphysis
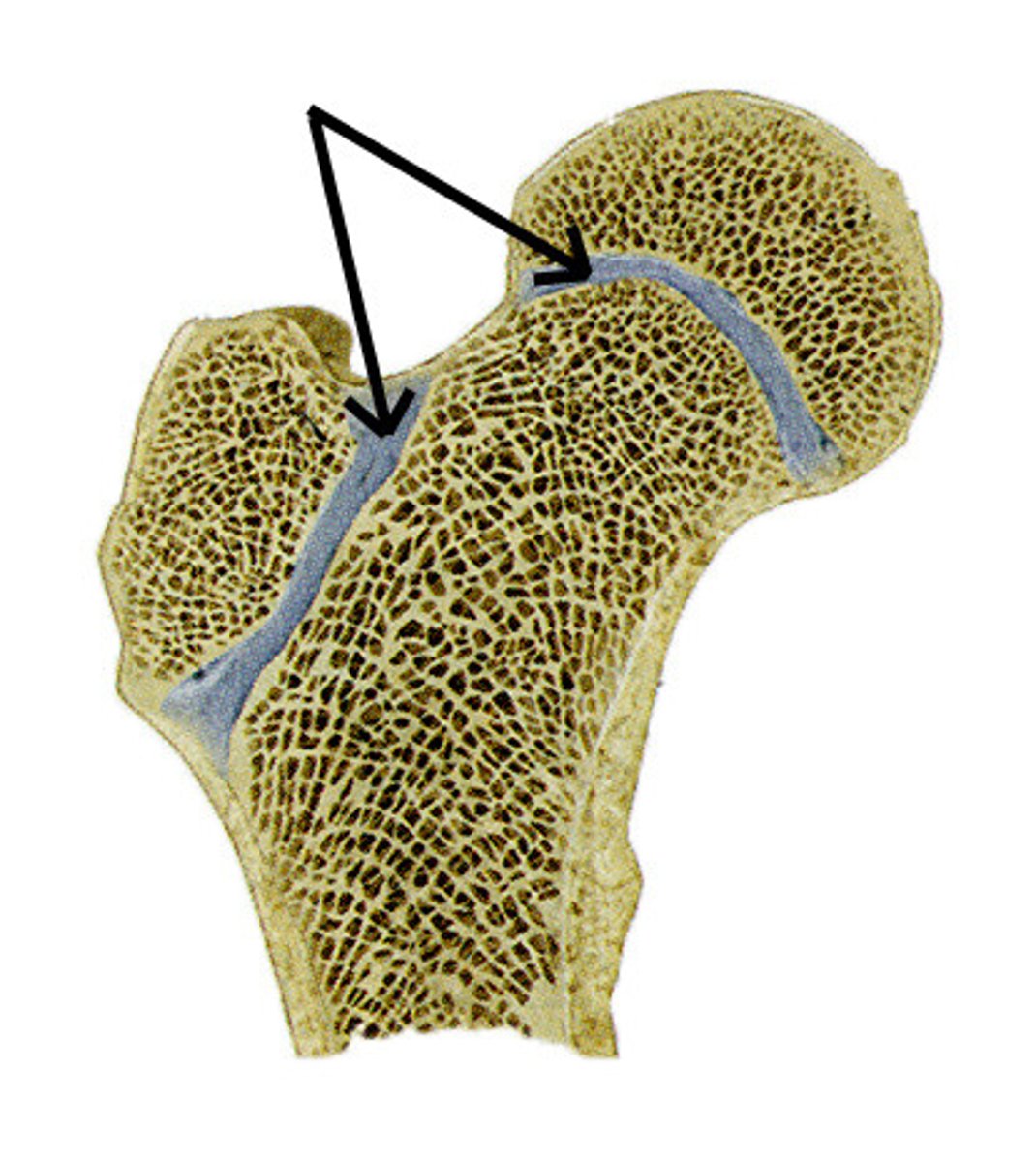
Epiphyseal line
-found in the metaphysis
-the remnant of the childhood epiphyseal plate where bone growth occurs
Articular cartilage
hyaline cartilage that covers ends of bones in synovial joints
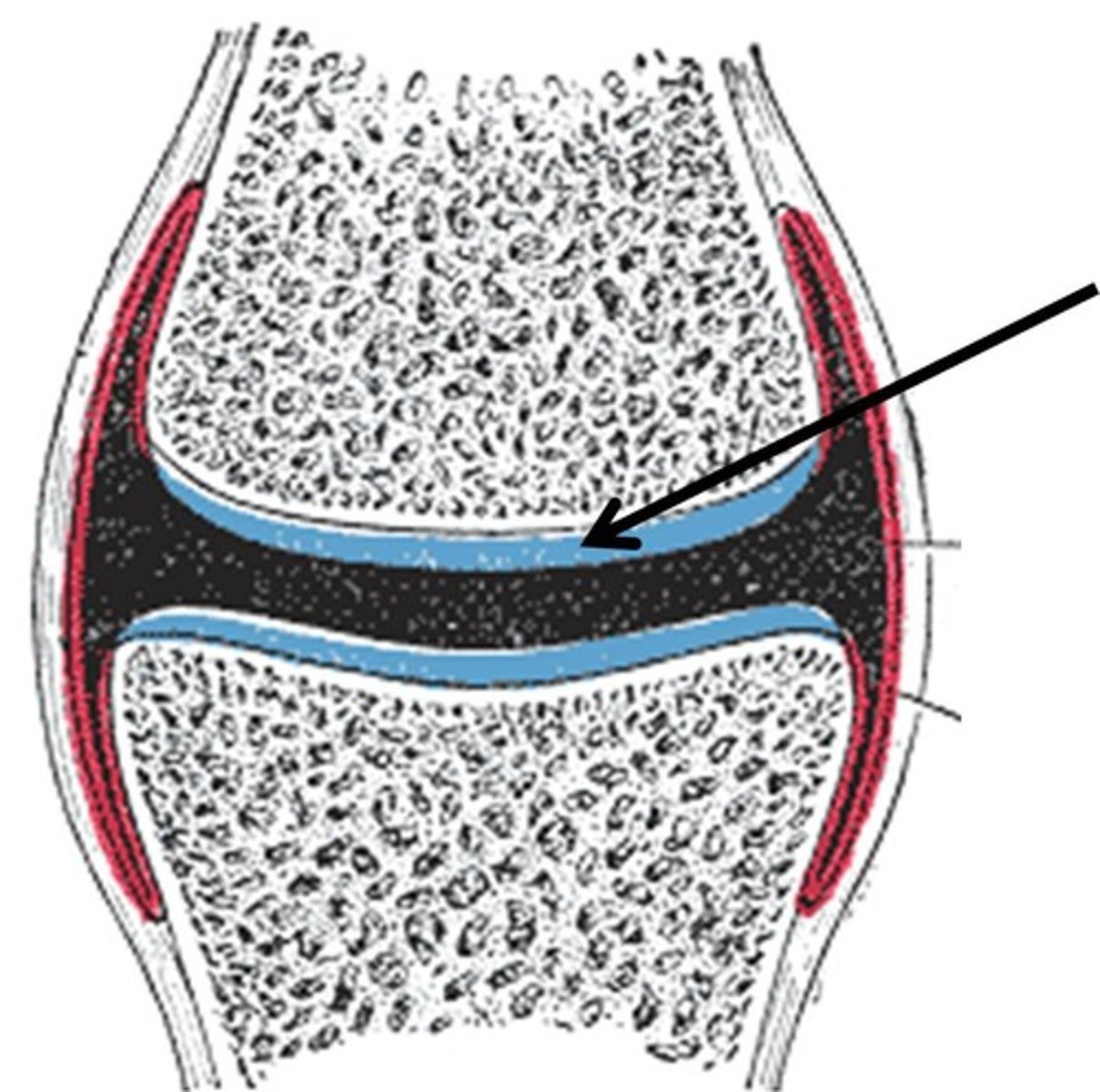
Osteogenic layer
inner layer in contact with bone that contains osteogenic stem cells that gives rise to most all bone cells
6 Functions of Bones
support, protection, movement, mineral and growth factor storage, blood cell formation, fat storage,