Lecture 1 - Introduction to Anatomy and Integument System
1/277
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANAT 305 - Cross-Sectional Anatomy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
278 Terms
Anatomy Definition
The study of body structure, examining the relationship between structures in the body
Gross Anatomy
Structures that can be examined without a microscope
Histology
Microscopic anatomy
structures of tissues and their organization into organs
Levels of body organization, from smallest —> largest
Atoms in combination —> complex protein molecules —> protein filaments (chemical/molecular level) —> Muscle cells (cellular level) —> Muscle tissue (tissue level) —> Organ level
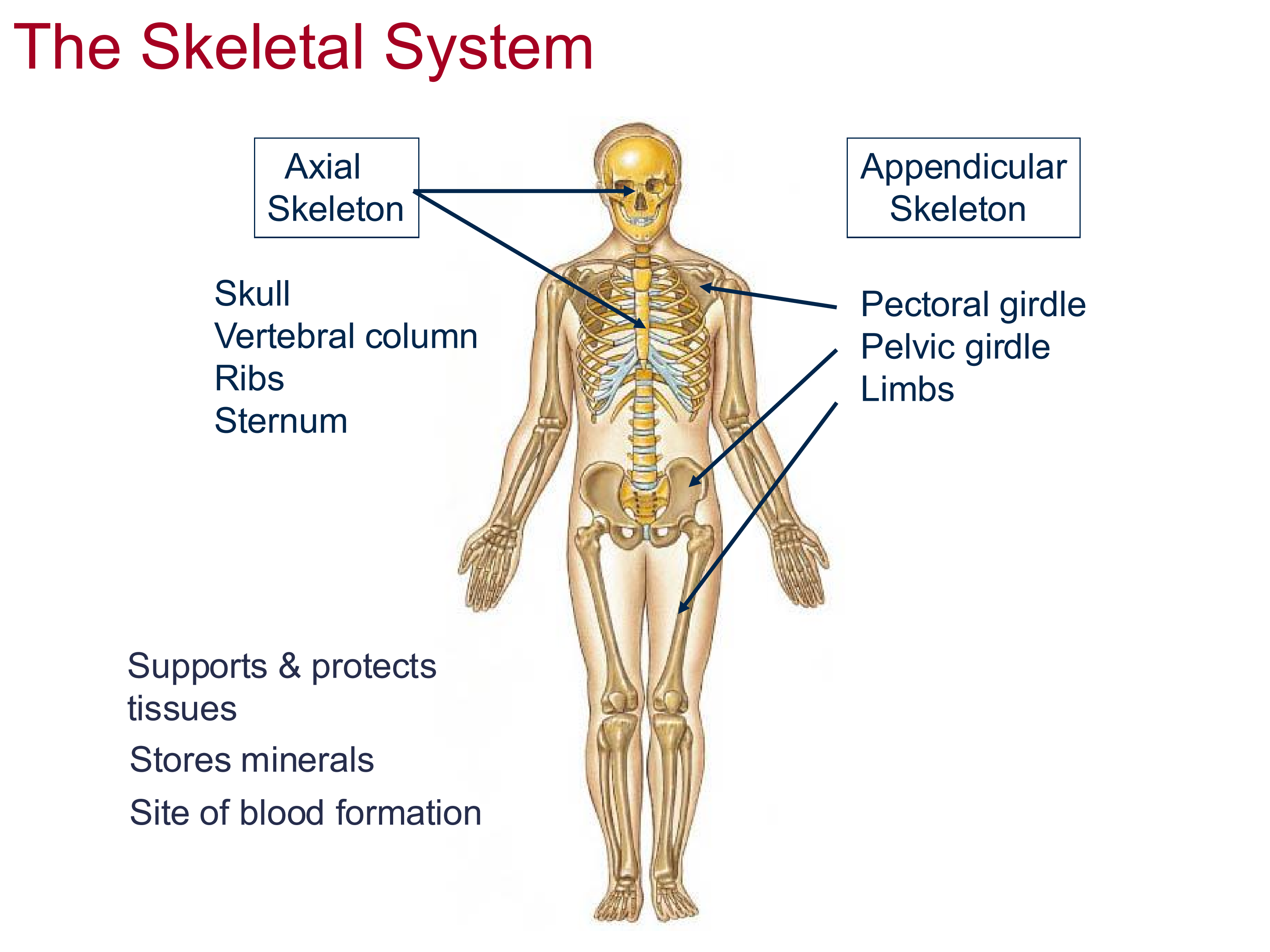
Three functions of the skeletal system
support and protect tissues of the body, providing a structure for the tissue to attach to
store and release minerals
blood formation
Two components of the skeletal system
Axial Skeleton: the core of the body
Appendicular Skeleton: supports the movement of the 4 appendages
5 Components of the Axial Skeleton
Skull, vertebral column, ribs, sternum, pelvis
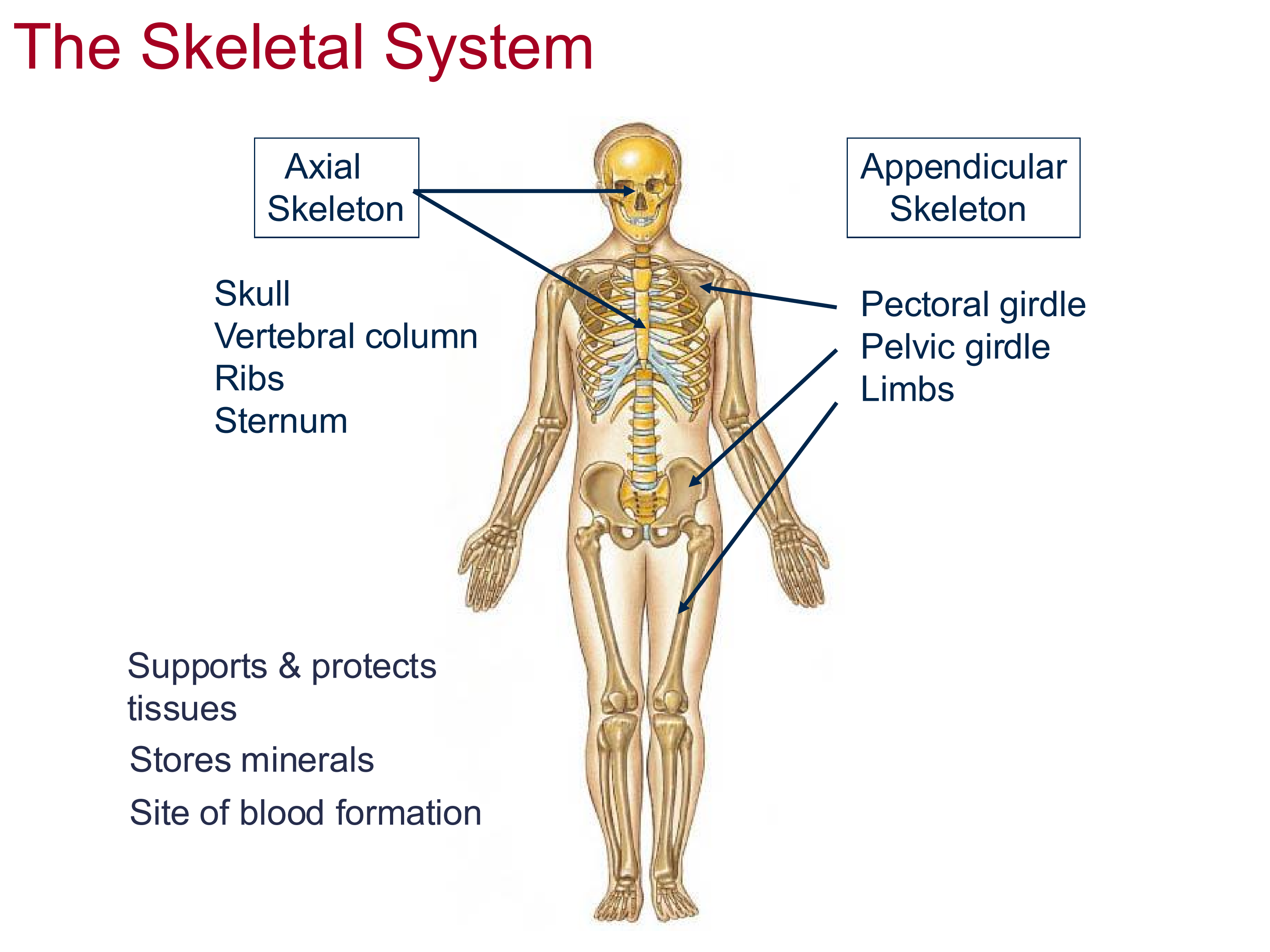
Components of the Appendicular Skeleton
Pectoral and pelvic girdle, limbs
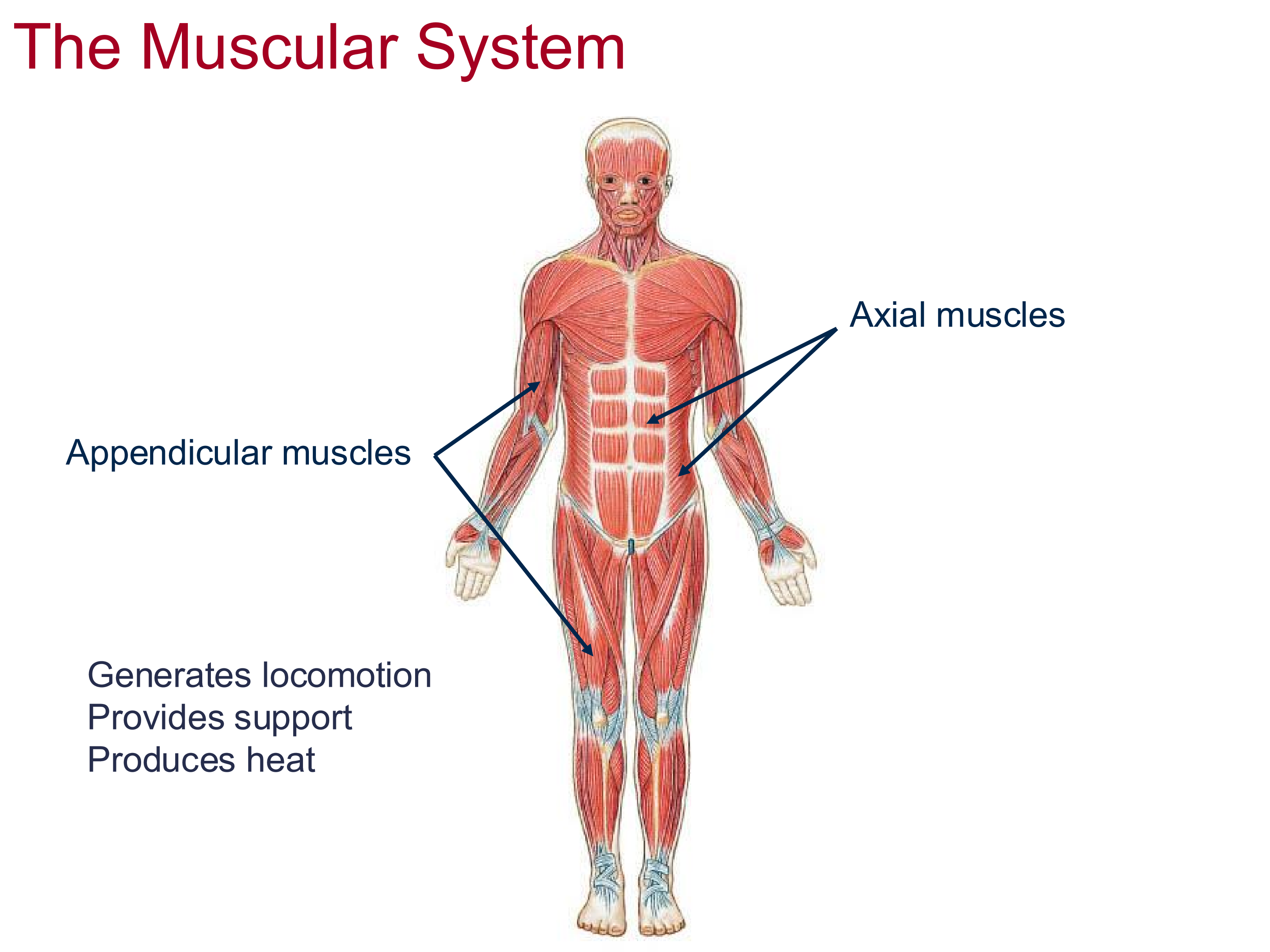
3 Functions of the Muscular System
Generates locomotion
Provides additional support to organs/body
Generates heat energy through movement
Components and functions of Muscular System
Axial muscles = core muscles
Appendicular Muscles = move the appendages
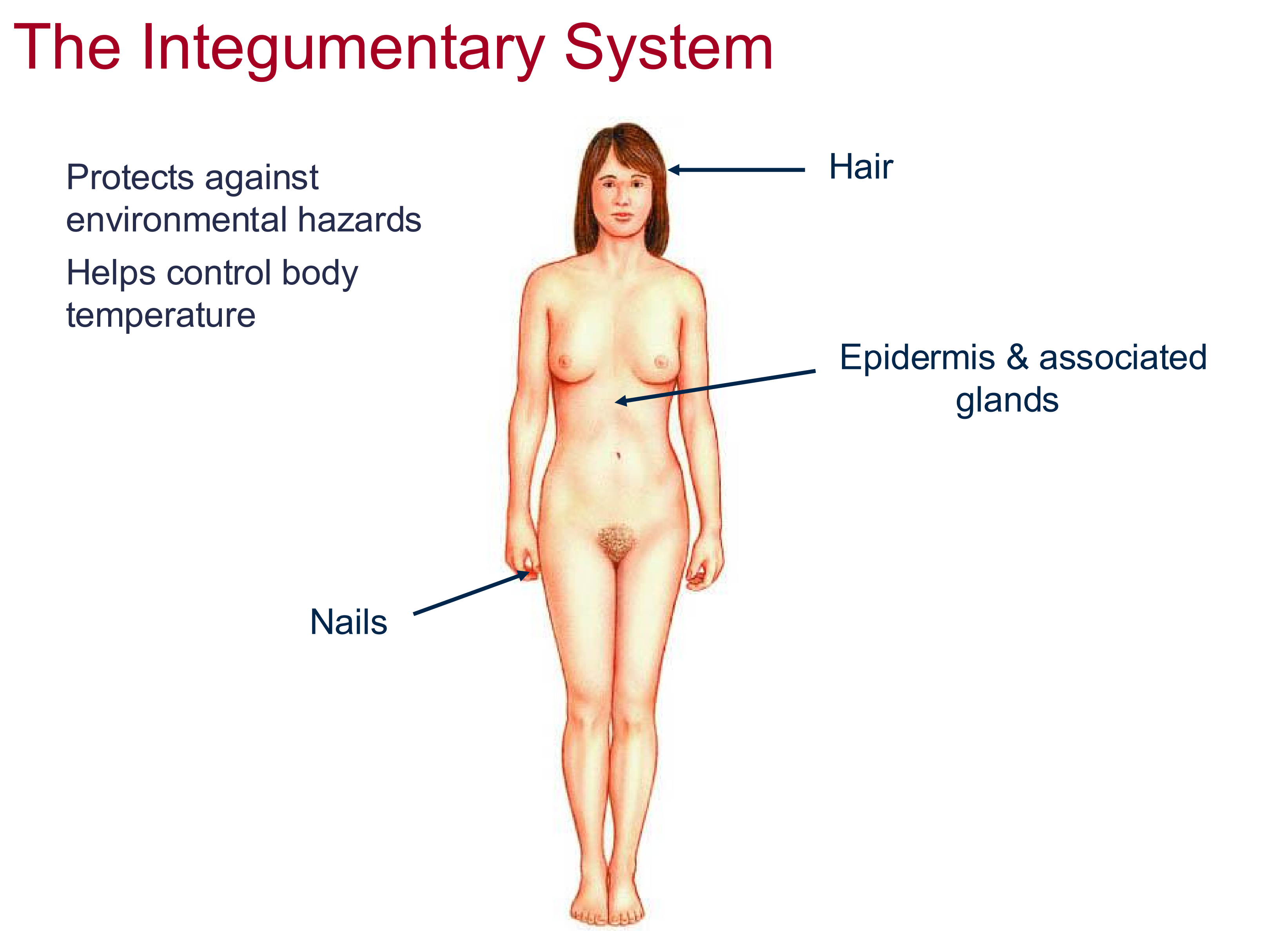
2 Functions of the Integumentary System
protects against environmental hazards
helps control body temperature
Structures of the integumentary system
hair, nails, epidermis, and associated glands
Outer layer of integument system
epidermis
what layer of integumentary system contains sweat glands?
inner dermis
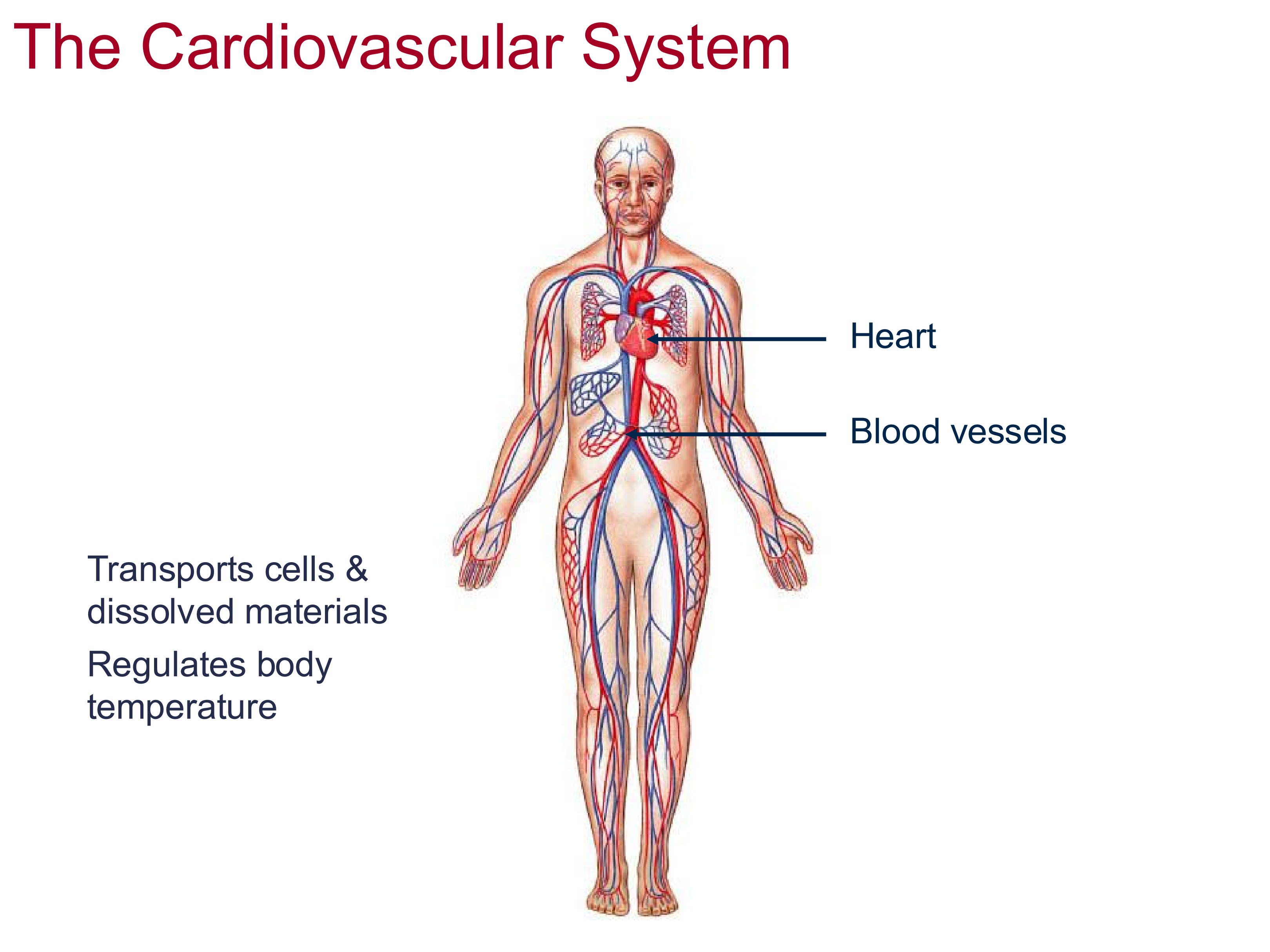
2 Functions of the Cardiovascular System
transports cells and dissolved materials,
regulates body temperature
Interacts with integument system
Structures of the CV system
heart and blood vessels
2 Functions of the Lymphatic System
defends against infection and disease
returns tissue fluid from blood stream
Structures of the lymphatic system
thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, vessels
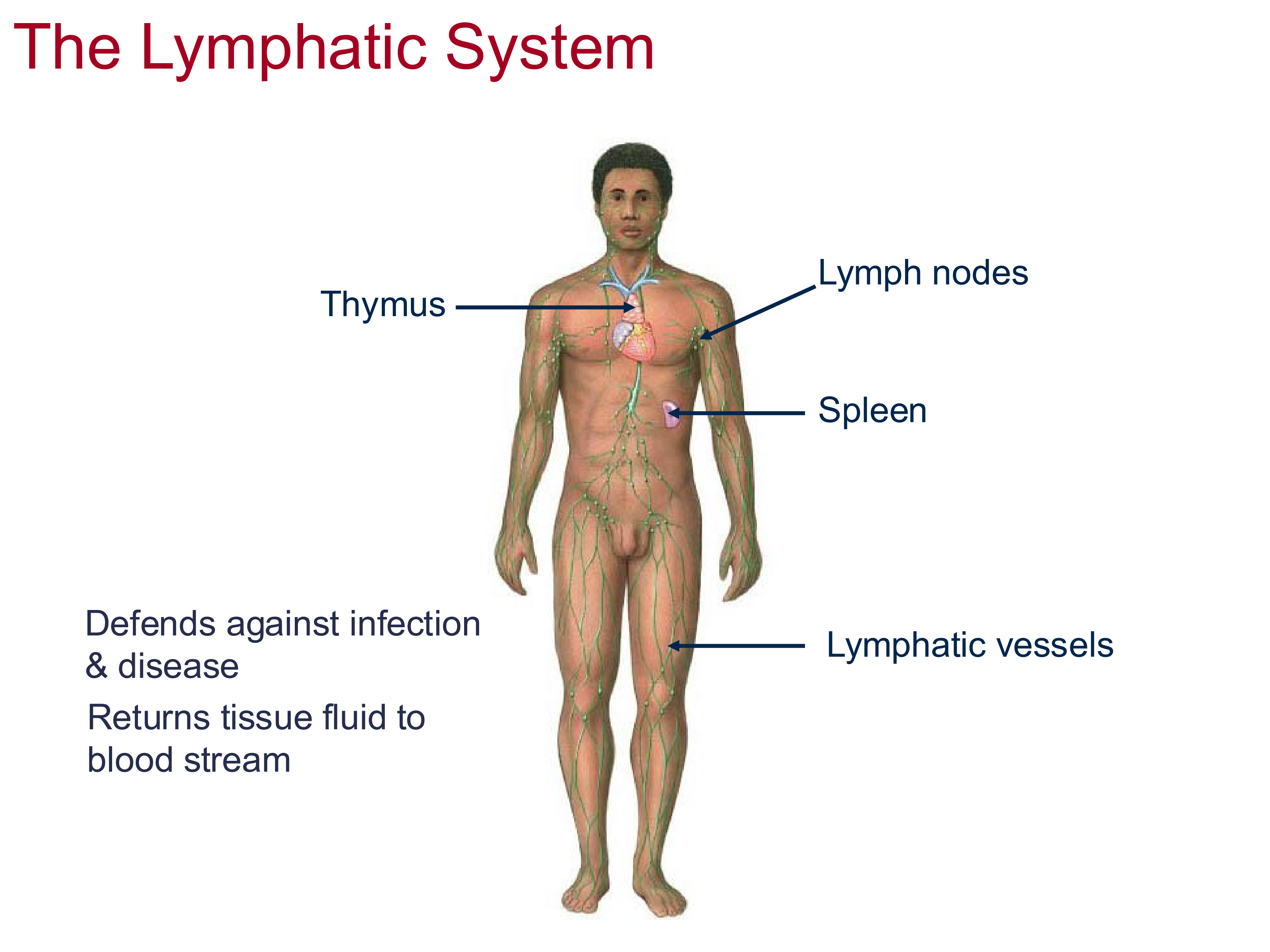
Thymus
Matures and develops T-cells
Spleen
sits posterior to midline axilla, filters metabolic waste products
Lymph Nodes
contain antibodies, which attack pathogens flowing through lymph system
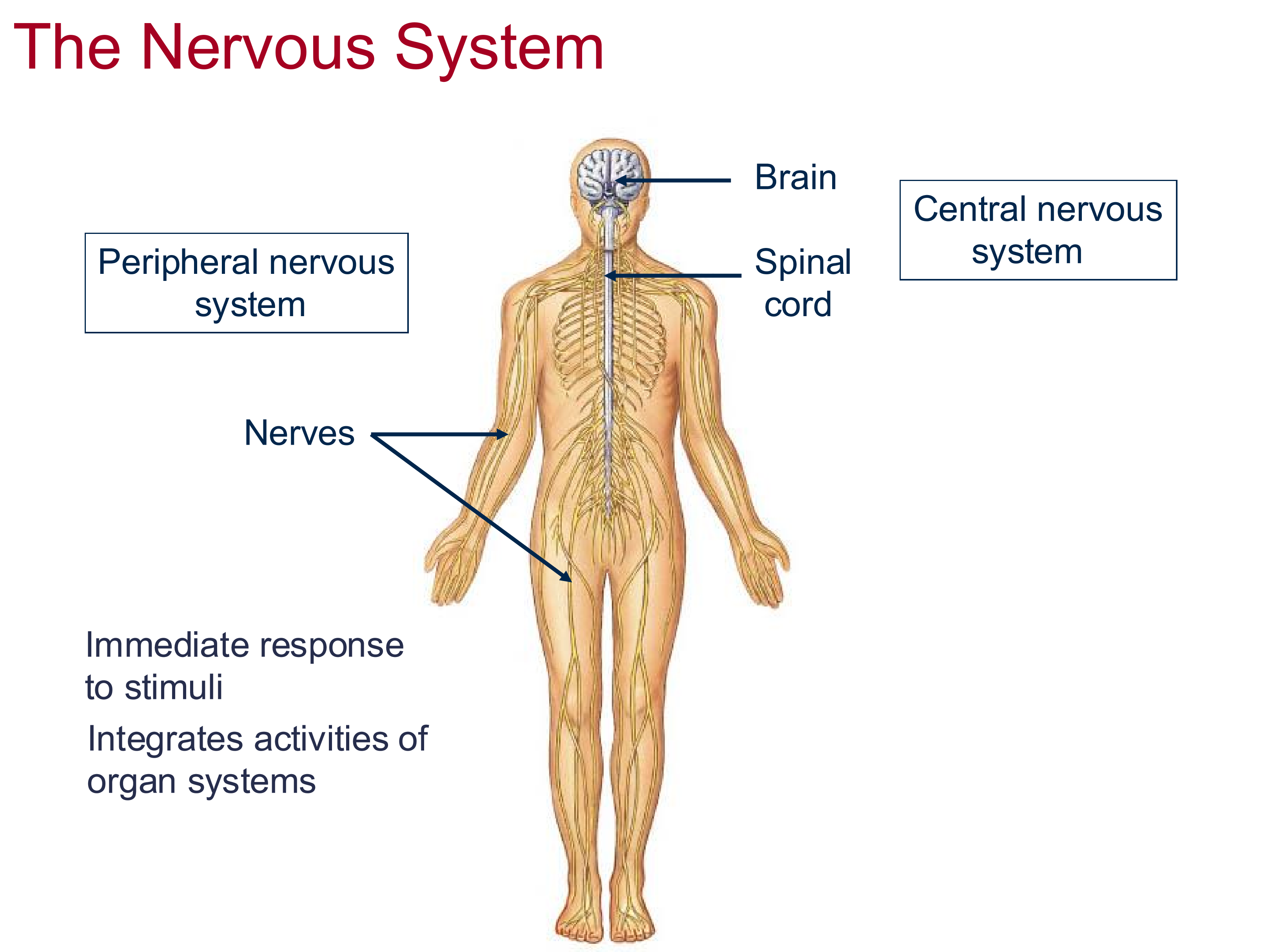
Nervous System Function
Immediate response to stimuli
integrates activities of organs
Two components of the nervous system
CNS: Brain + spinal cord
PNS: neurons going towards regions of body
Endocrine System Function
Long term regulation of organ system
similar to CNS but longer lasting effects
Structures of the endocrine system
Pituitary (master) , thyroid/parathyroid, thymus, pancreas, adrenal, gonad glands
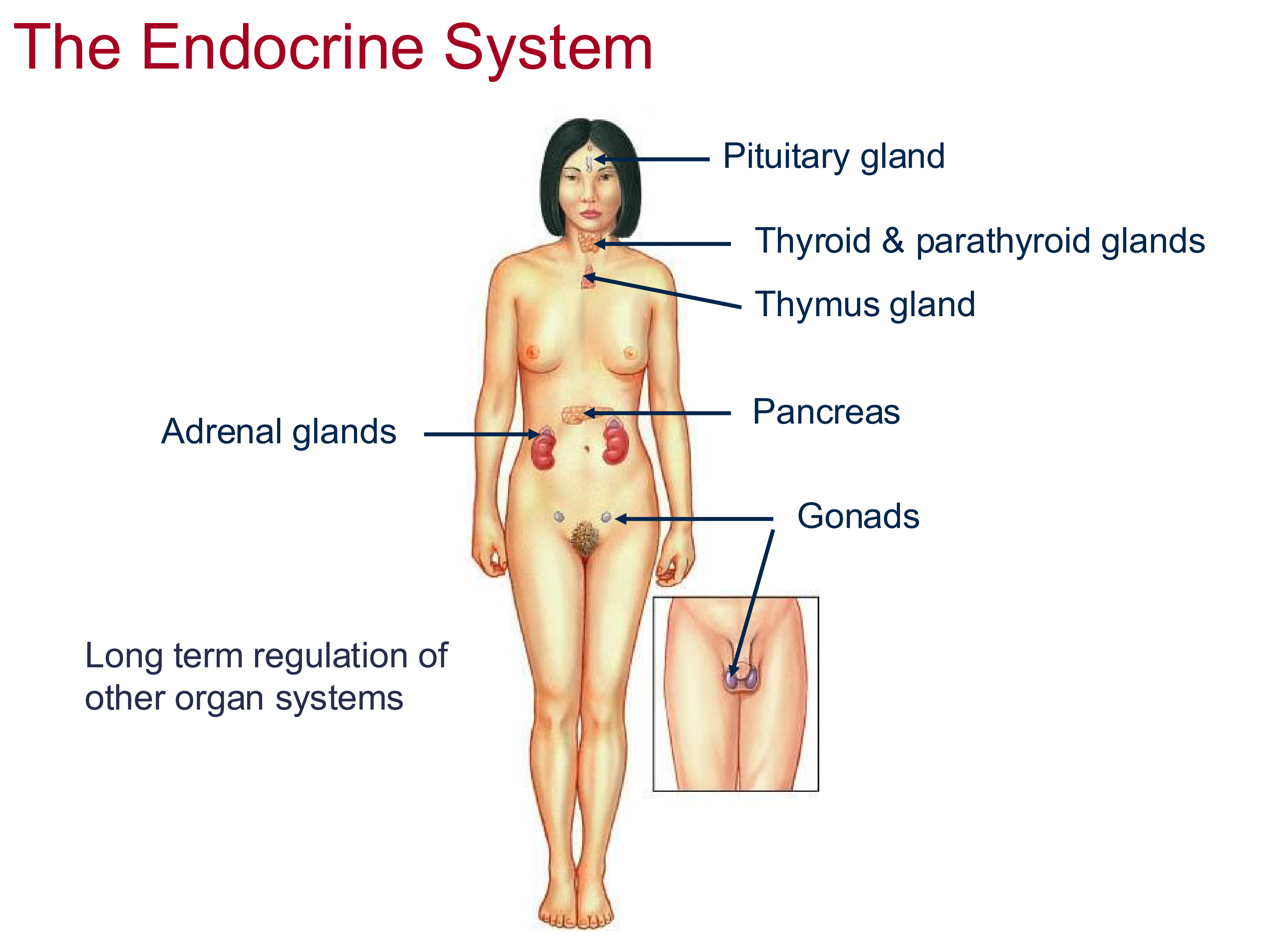
How do male and female gonads differ anatomically
male gonads sit outside the body in the scrotum, female gonads sit within the body in the pelvic cavity
Respiratory System Function
Exchange gas between air and circulating blood
exchange between internal and external environment
Structures of the respiratory system
Nasal Cavity + Sinuses, airways, larynx, lungs, diaphragm
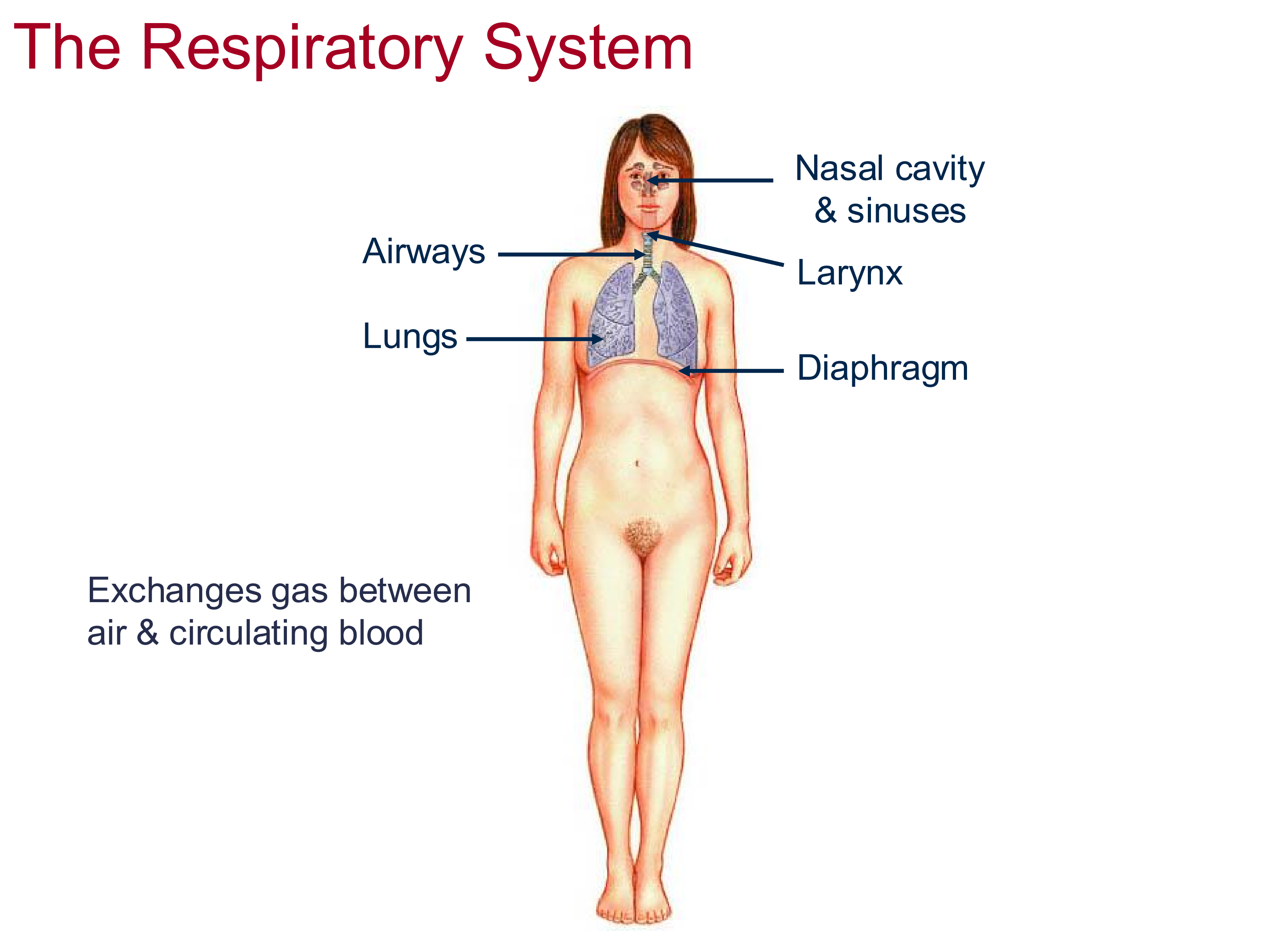
Diaphragm
located across costal (rib) margin, creates negative pressure in lungs to force air from environment to go into lungs
Digestive System Function
process and absorb nutrients
Two components of the Digestive System
Digestive Tube
Digestive Glands
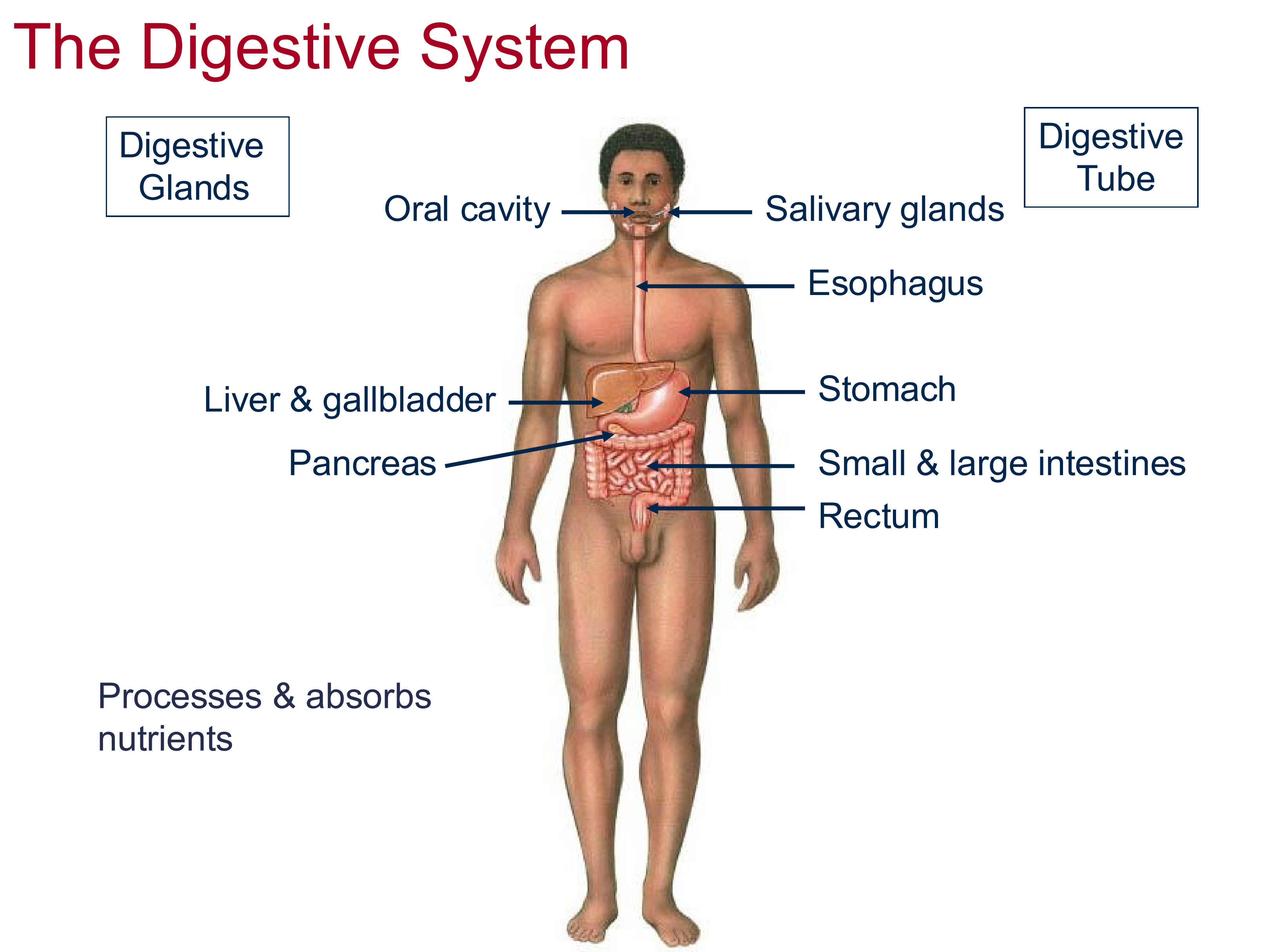
Structures within the digestive tube
oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small + large intestines, rectum
Structures of the digestive glands
Salivary glands, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, stomach as well
Salivary glands
release amylase to break down carbs in oral cavity
Liver + Gall Bladder
release bile to break down fats
Pancreas
release proteases and lipases to break down fats
Why is the digestive system considered part of the outside world
it is a tube that begins at the mouth and ends with the rectum, we have to pull nutrients out of this tube into the body
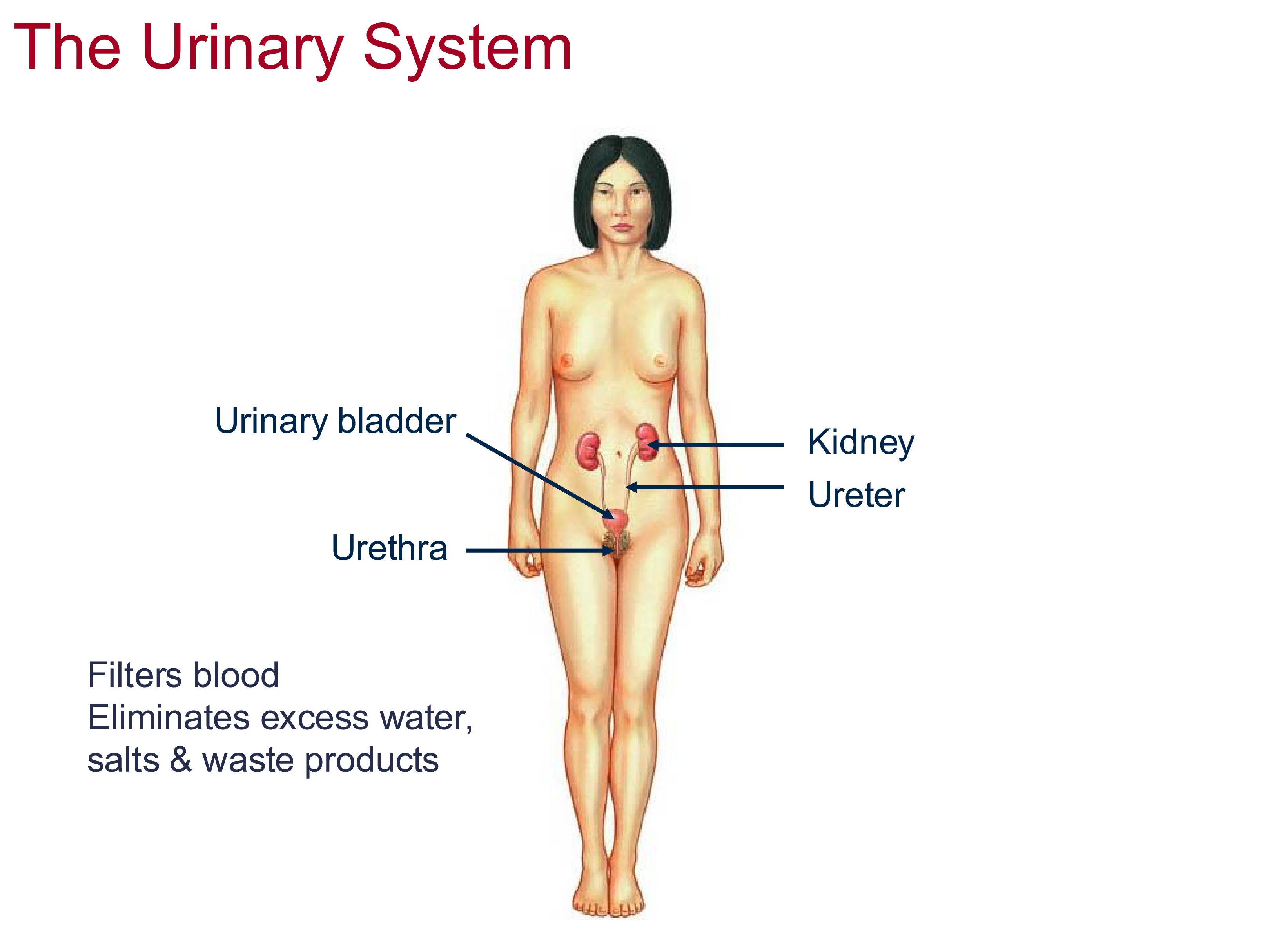
Urinary System Function
Filters blood and eliminates water, salts & waste products
Structures of the urinary system
Kidneys: filter blood
Ureter: A tube that connects the kidneys to bladder
Bladder: storage unit of urine
Urethra: tube that connects the bladder to the external environment to release waste
Function of Reproductive Systems
Produce gametes and sex hormones
Gametes
reproductive cell (sperm or egg)
Sex Hormones
support reproductive activity
Superior/Cranial
Upper, towards the skull
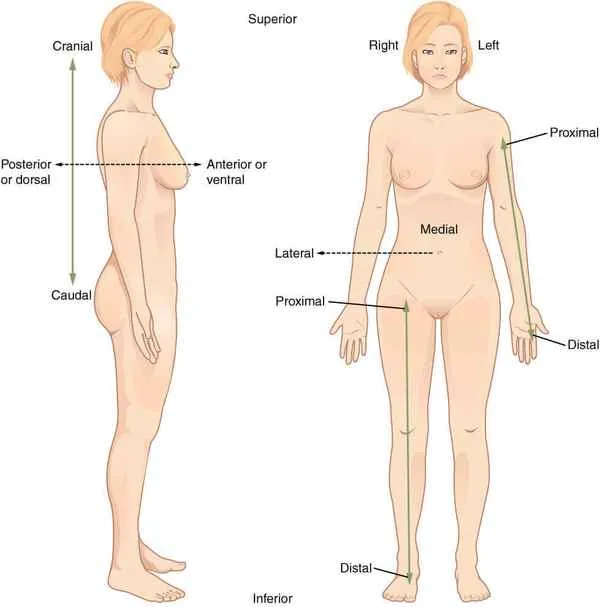
Inferior/Caudal
Below, towards the tail
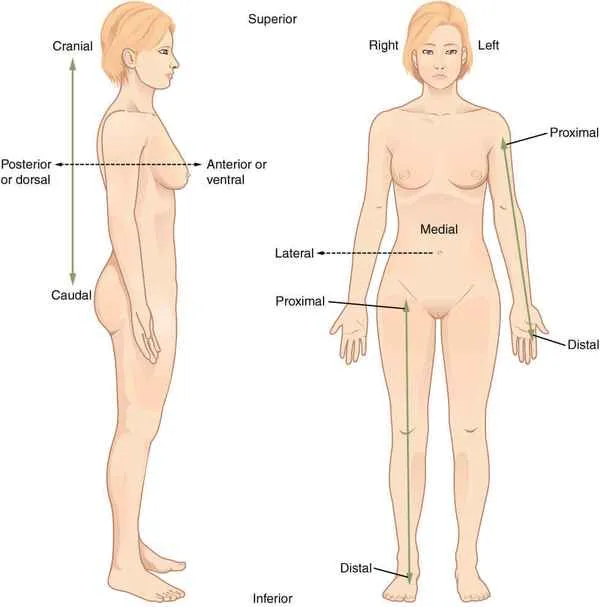
Posterior/Dorsal
Towards the back
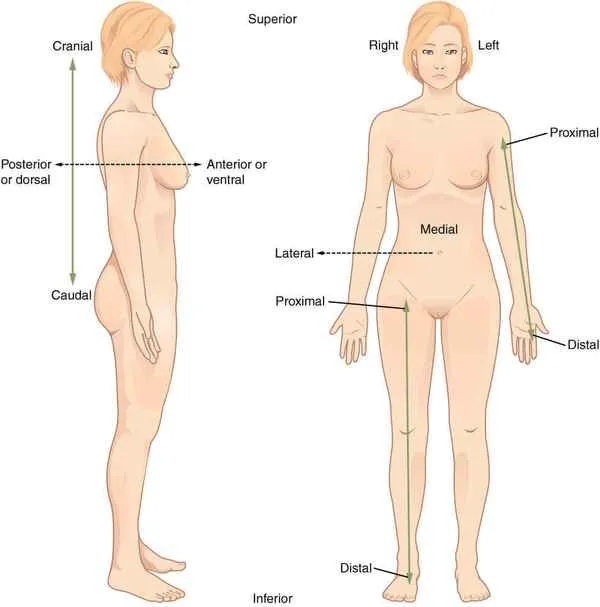
Anterior/Ventral
Towards the front
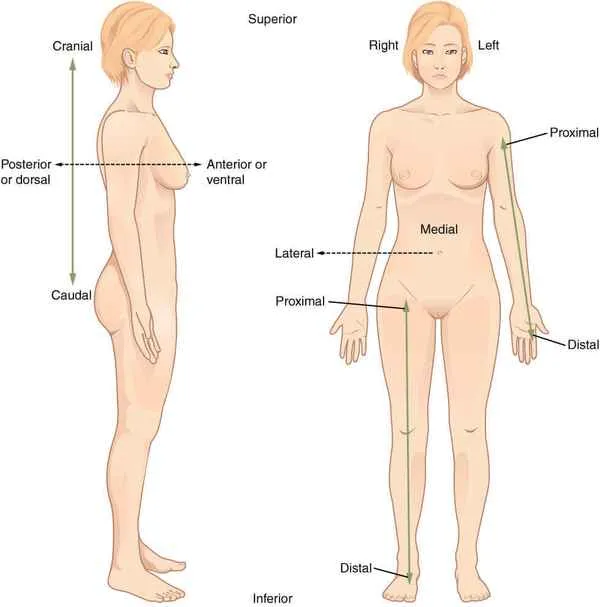
Proximal
toward or nearest the core/trunk or the point of origin of a part
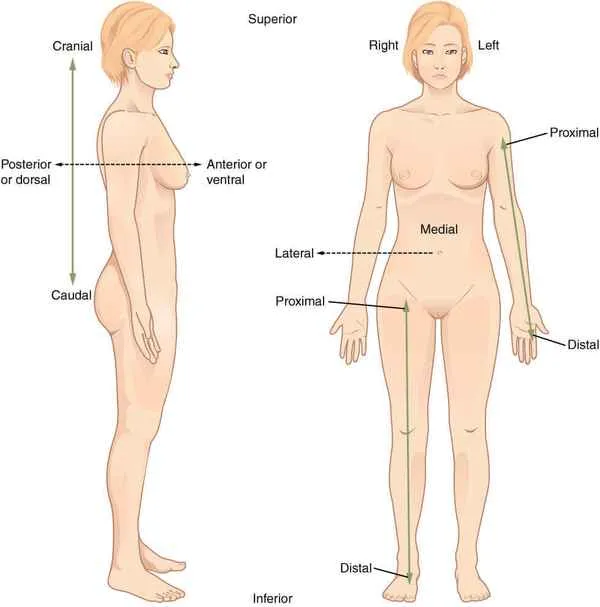
Distal
away from or farthest from the core/trunk or point of origin of a part
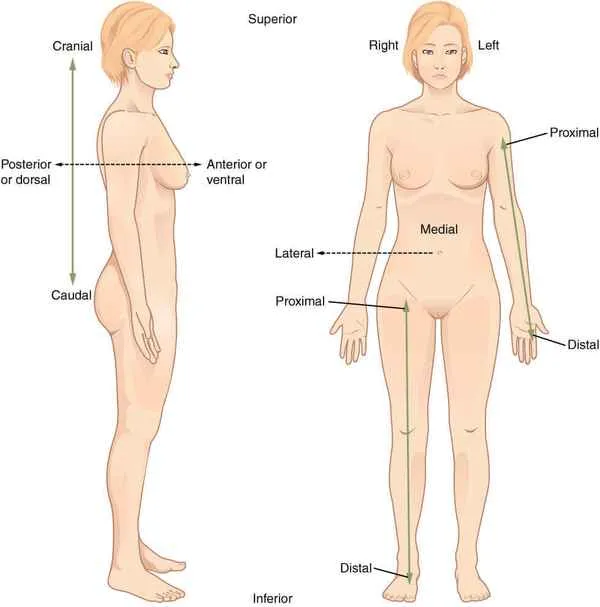
Is the wrist distal or proximal to the elbow
distal
is the shoulder distal or proximal to the elbow
proximal
Lateral
farther away from the middle
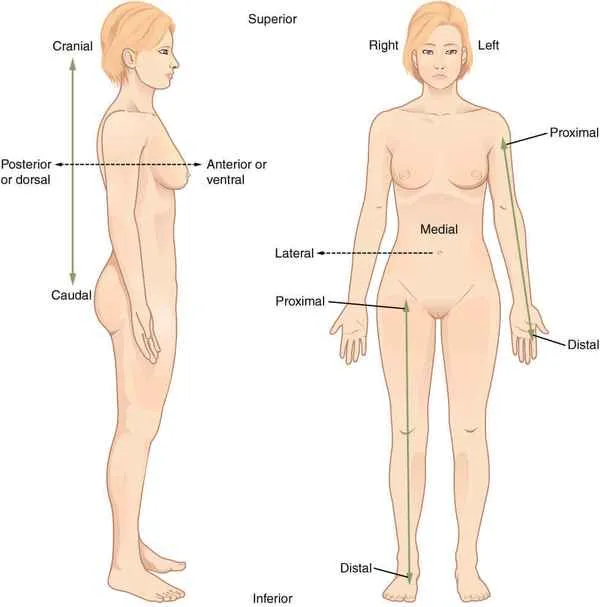
Medial
closer to the middle
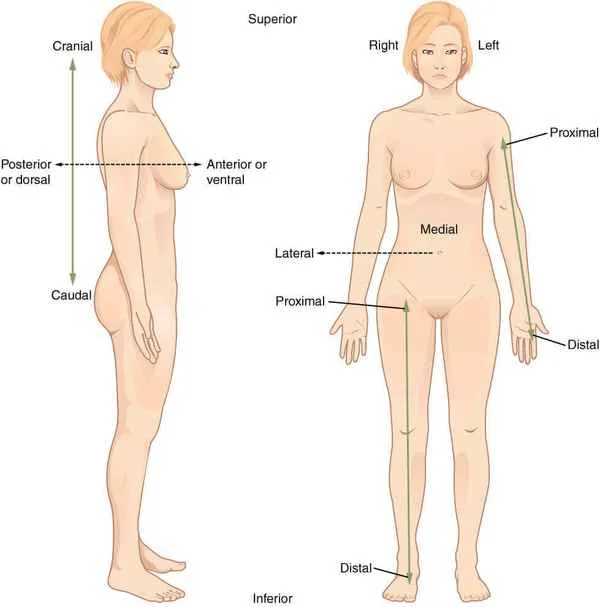
Is the nipple medial or lateral to the belly button
lateral (and caudal)
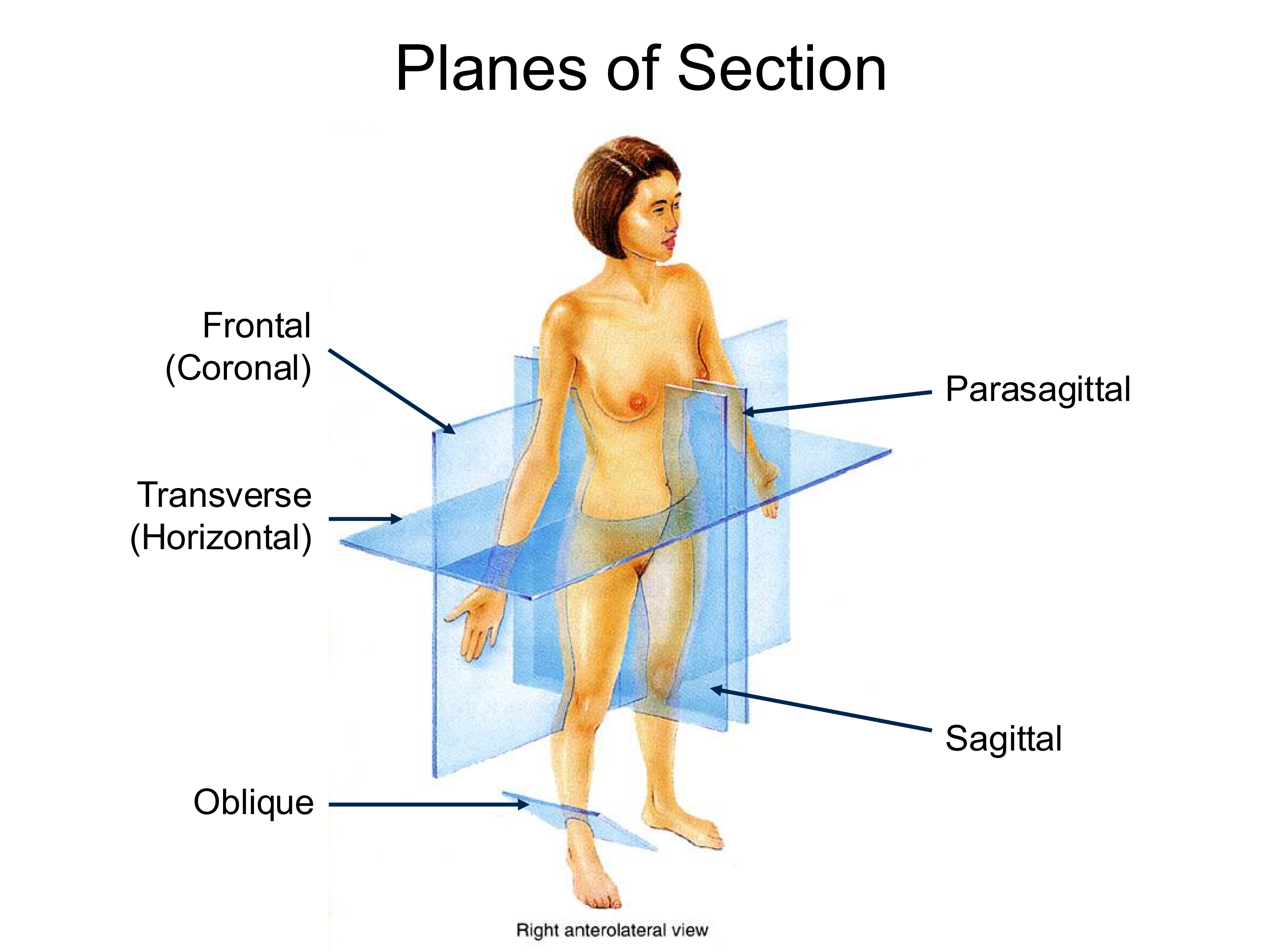
Sagittal Plane
splits the body into left and right sides
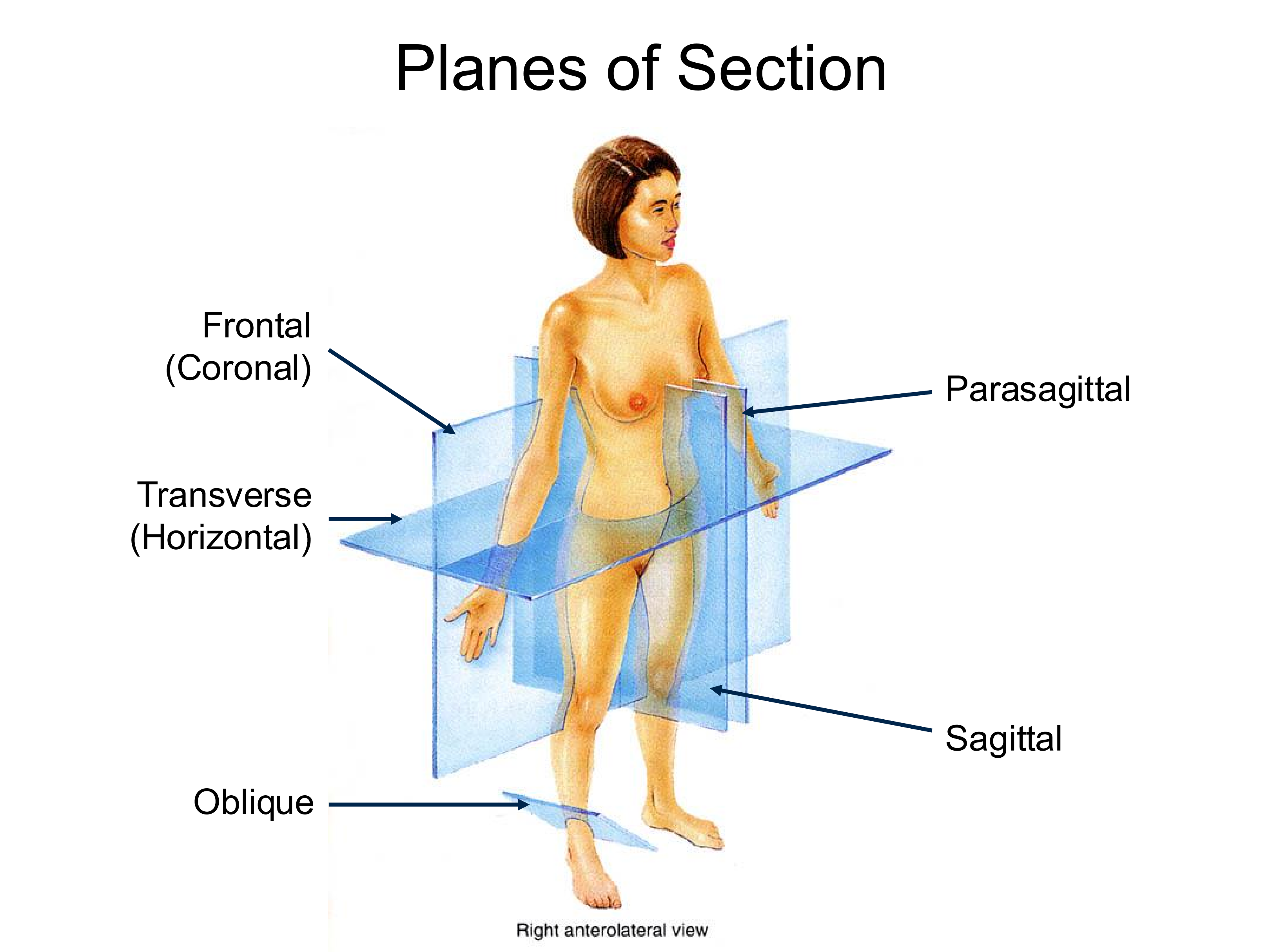
Transverse Plane
Splits the body into superior and inferior sections
perpendicular to the long axis of the body
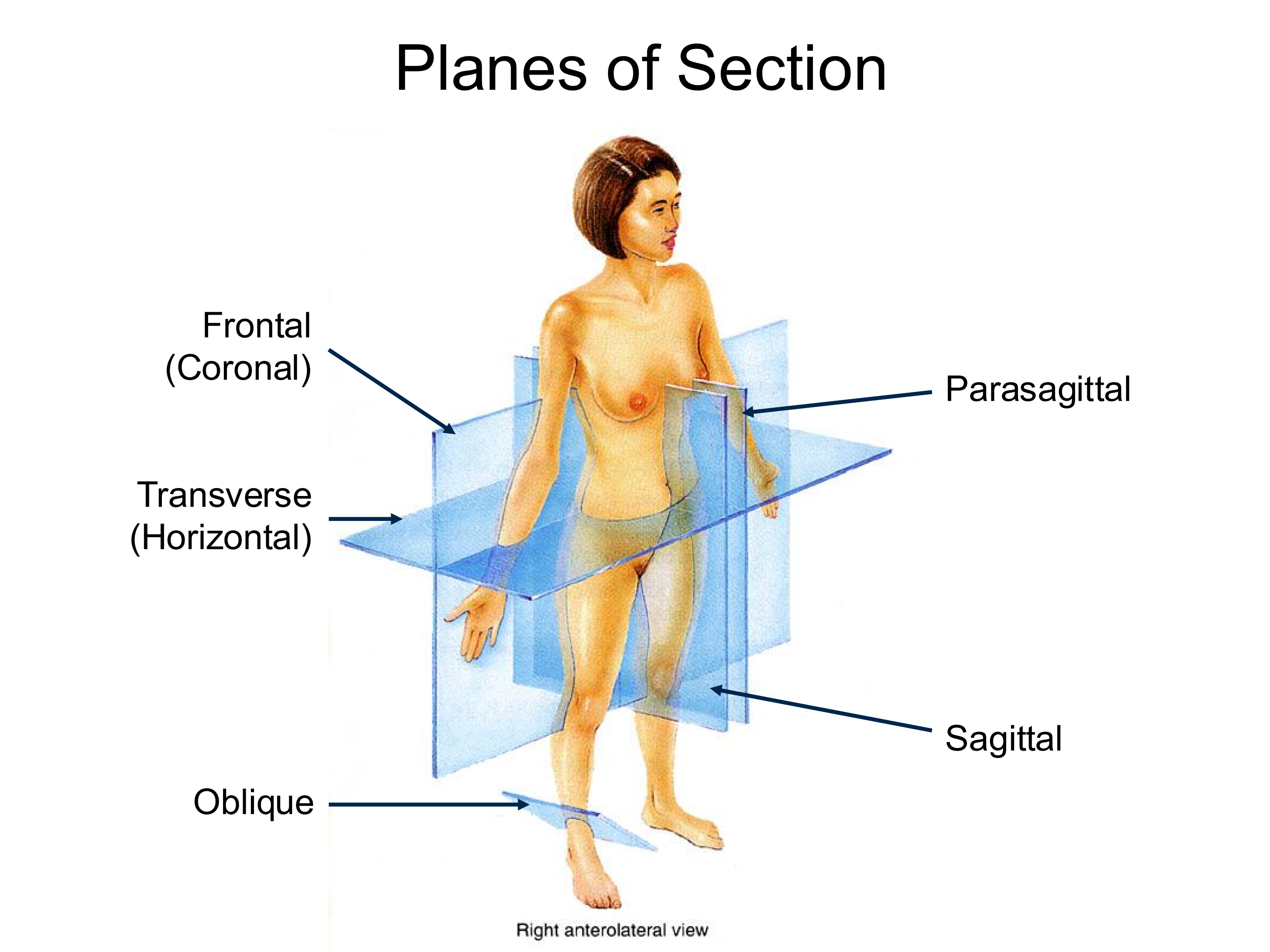
Coronal (Frontal) Plane
Splits the body into anterior and posterior sections
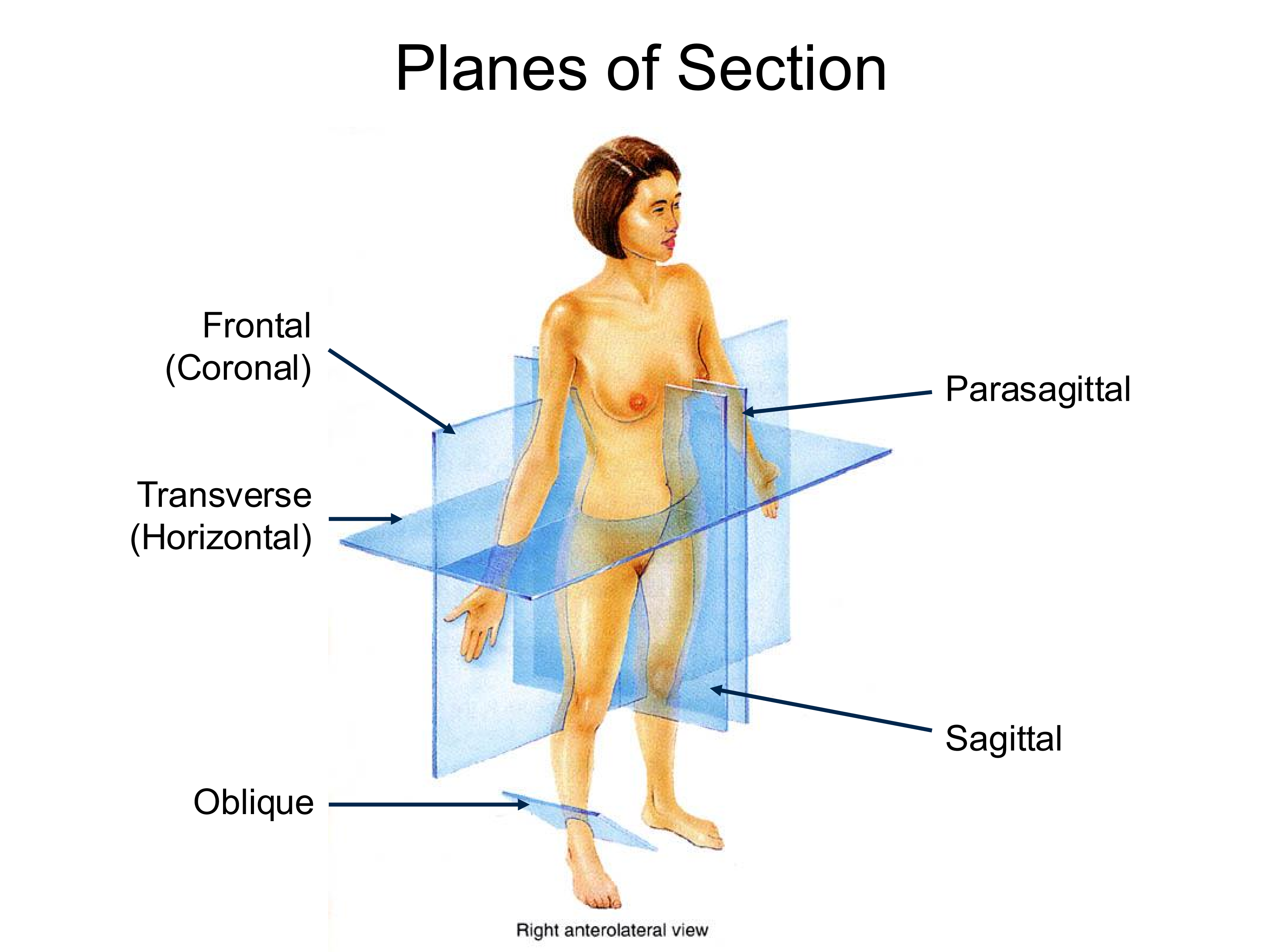
Parasagittal Plane
Same direction as saggital plane, but off midline
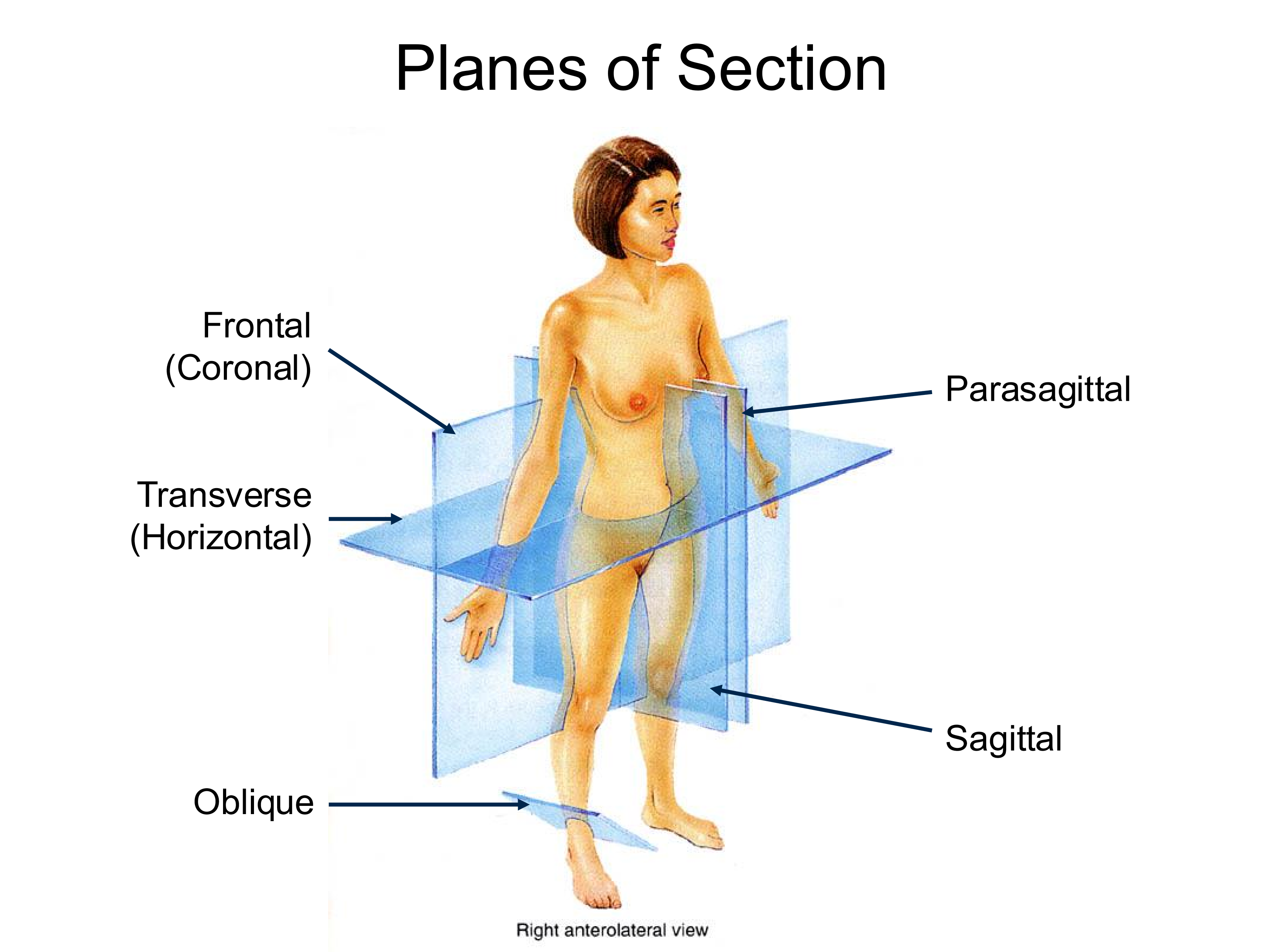
Oblique Plane
Any plane that does not fall into the category of the others
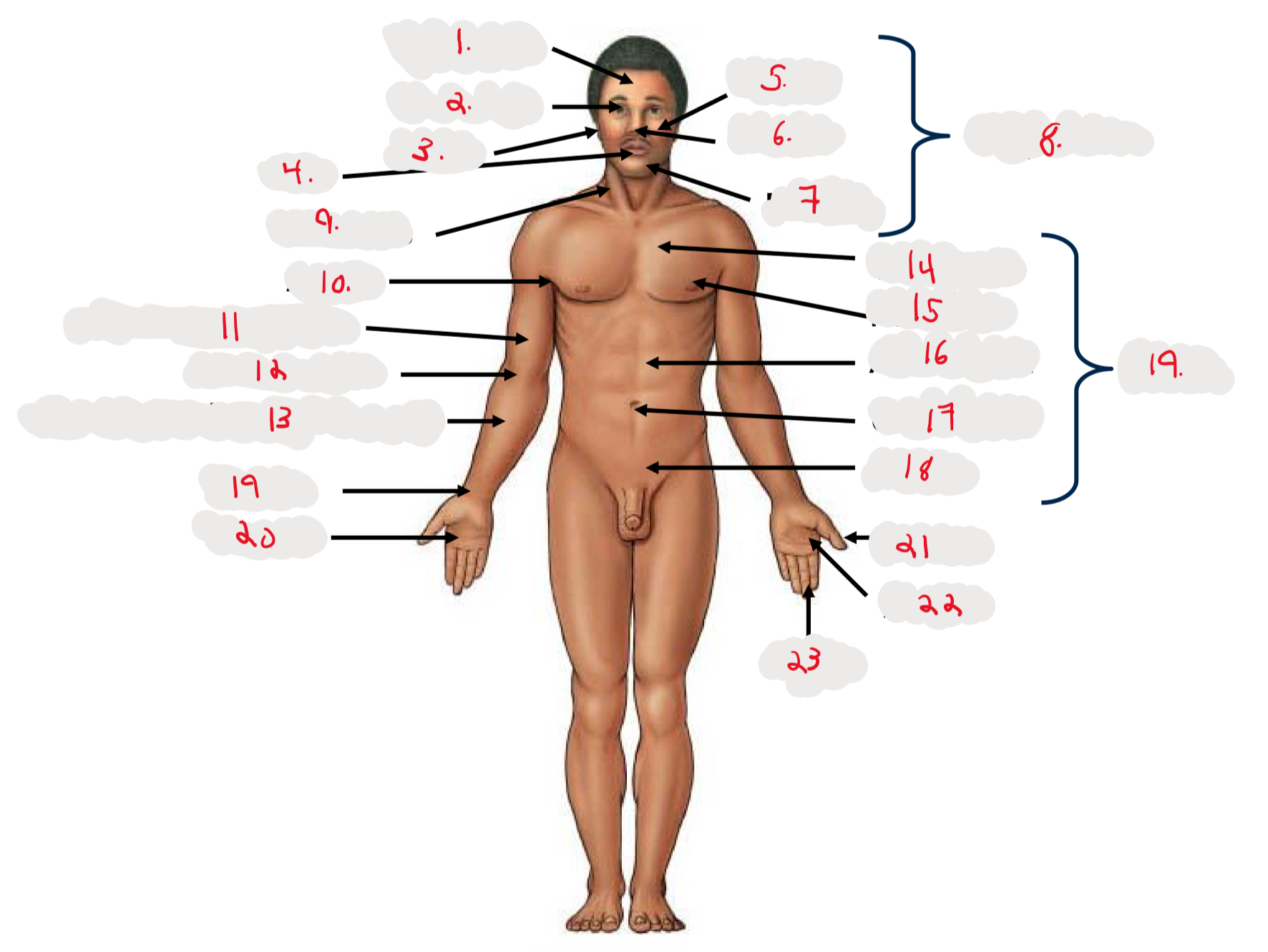
1.
Cranium
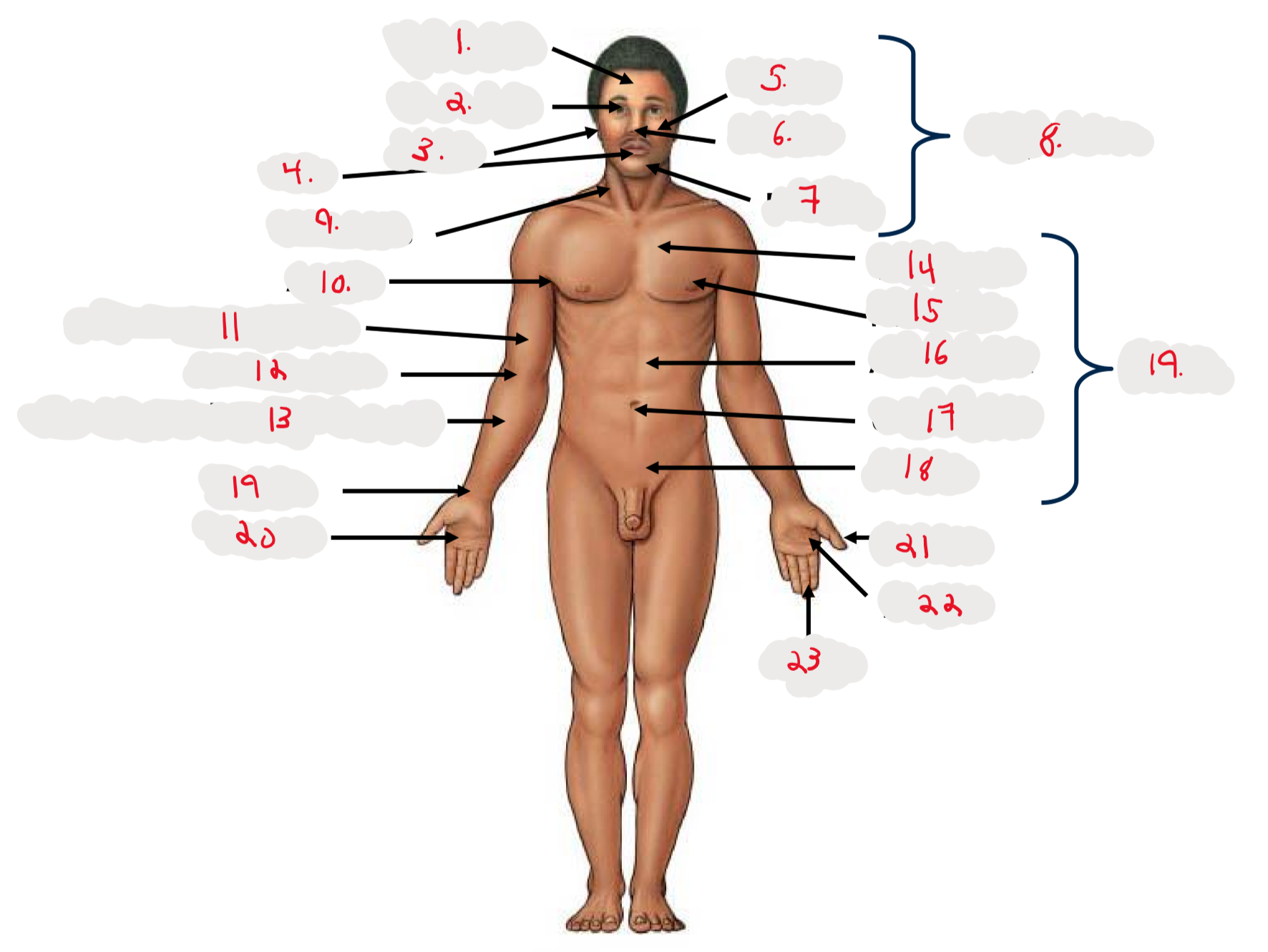
2.
Occulus (eye)
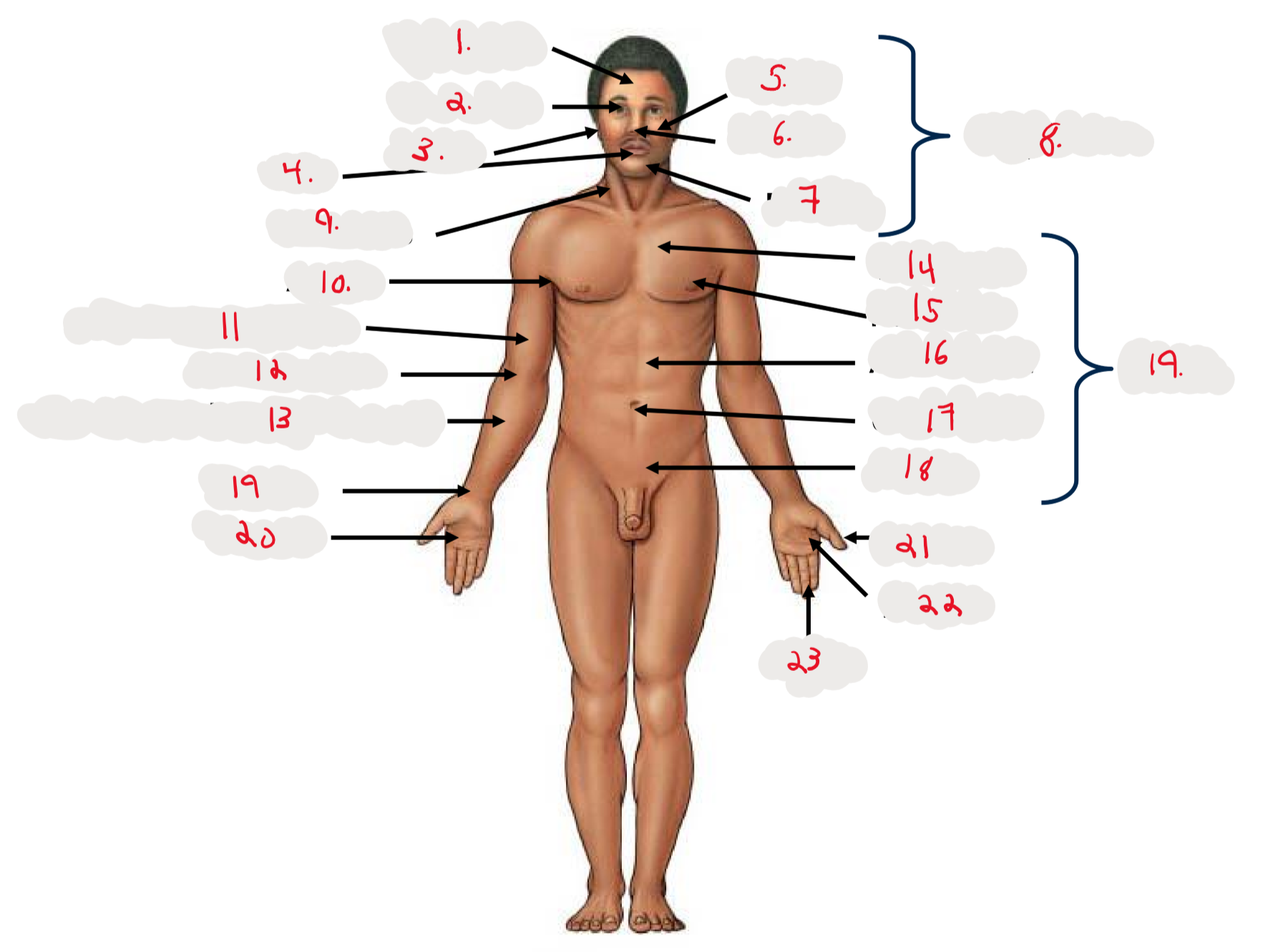
3.
Auris (ear)
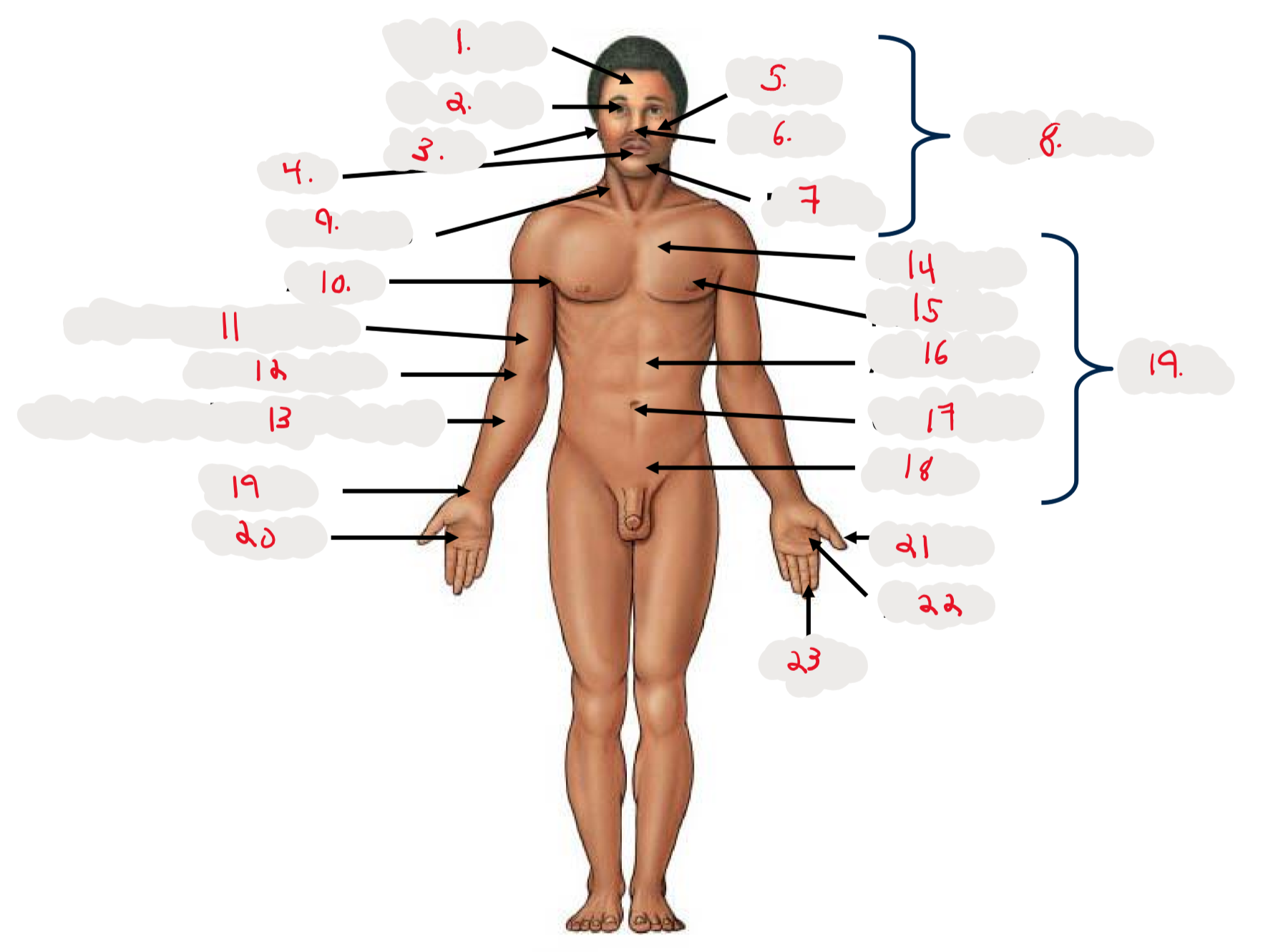
4
Oris (mouth)
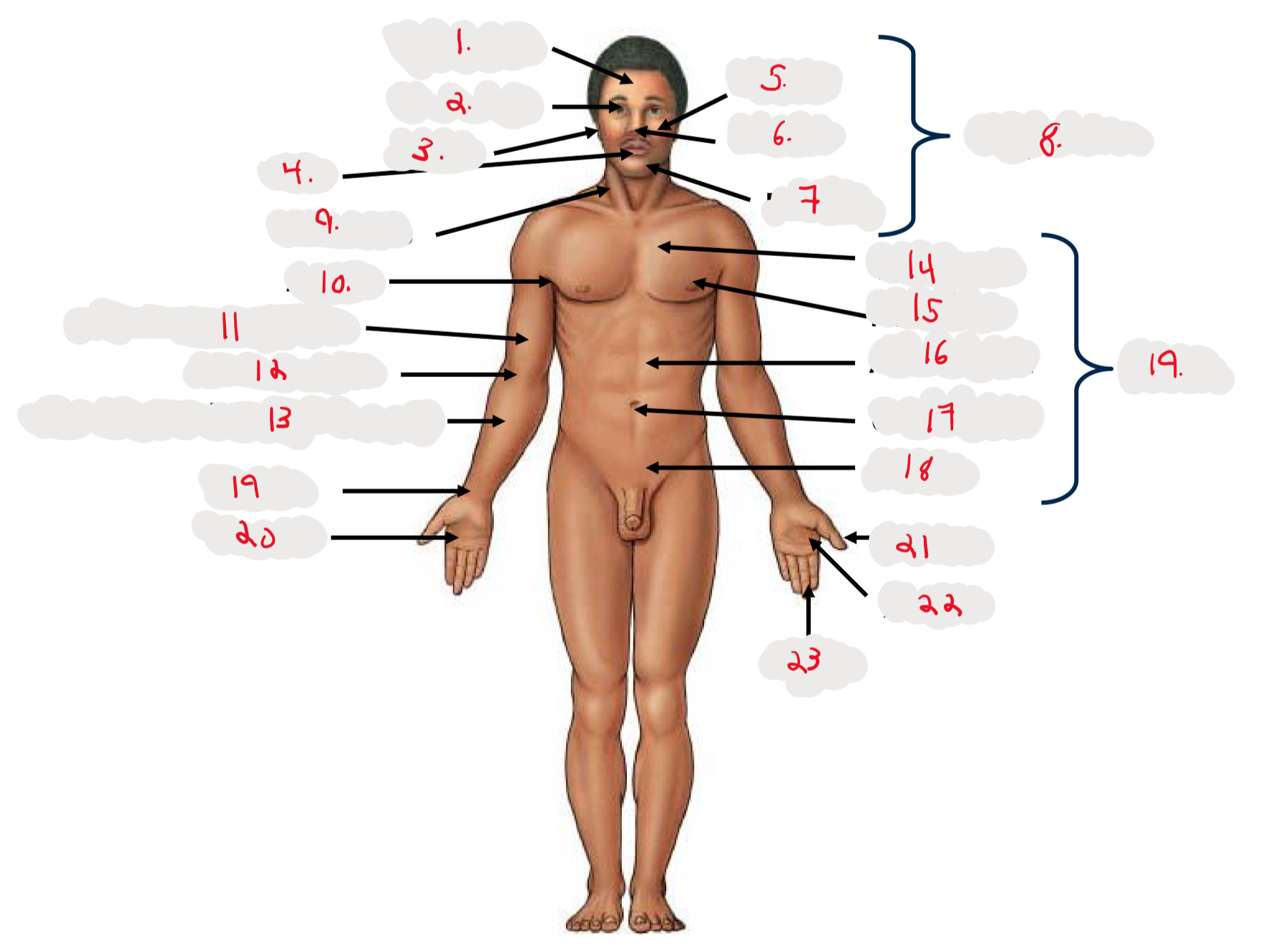
5
Bucca (cheek)
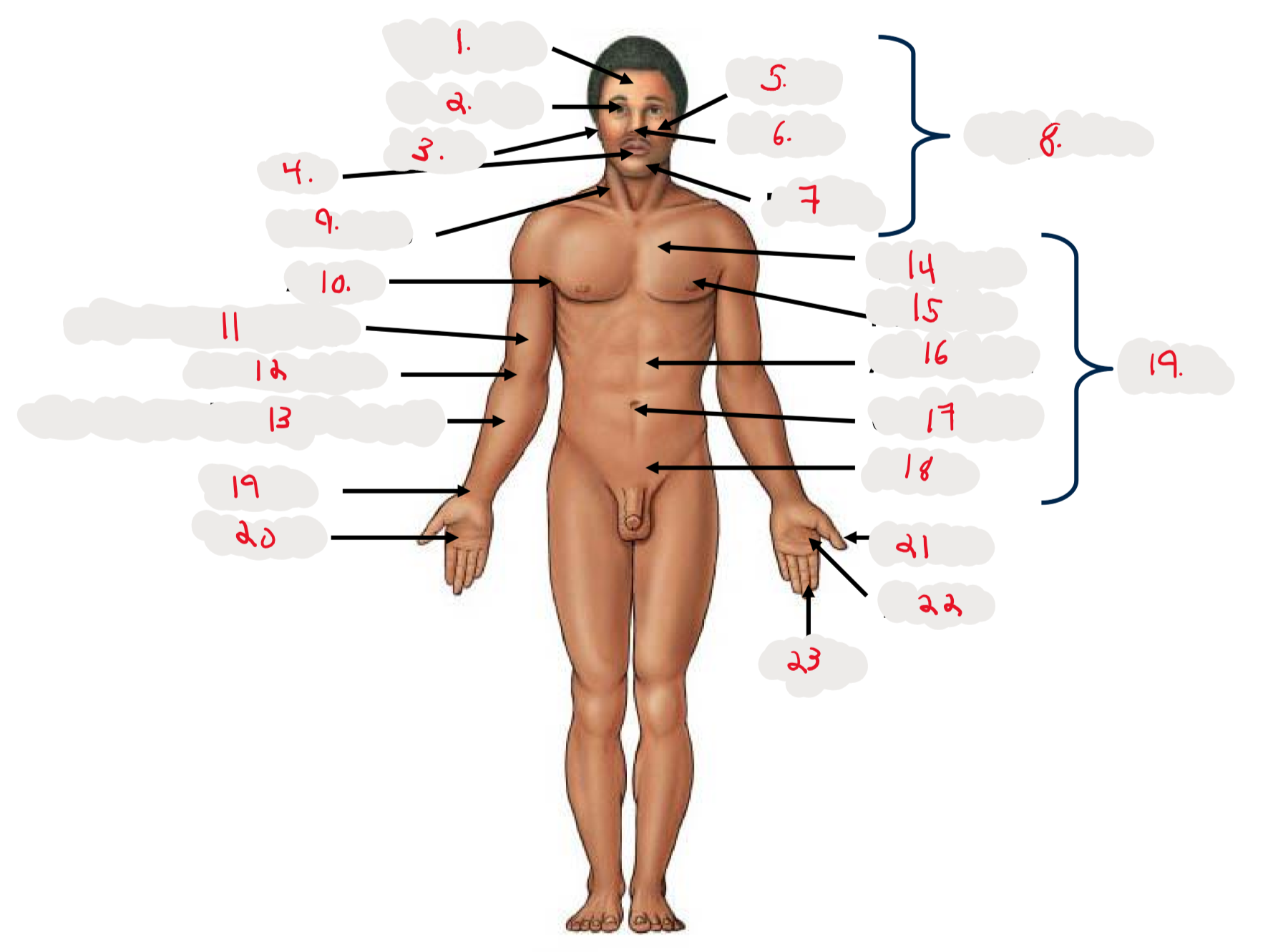
6
Nasus (nose)
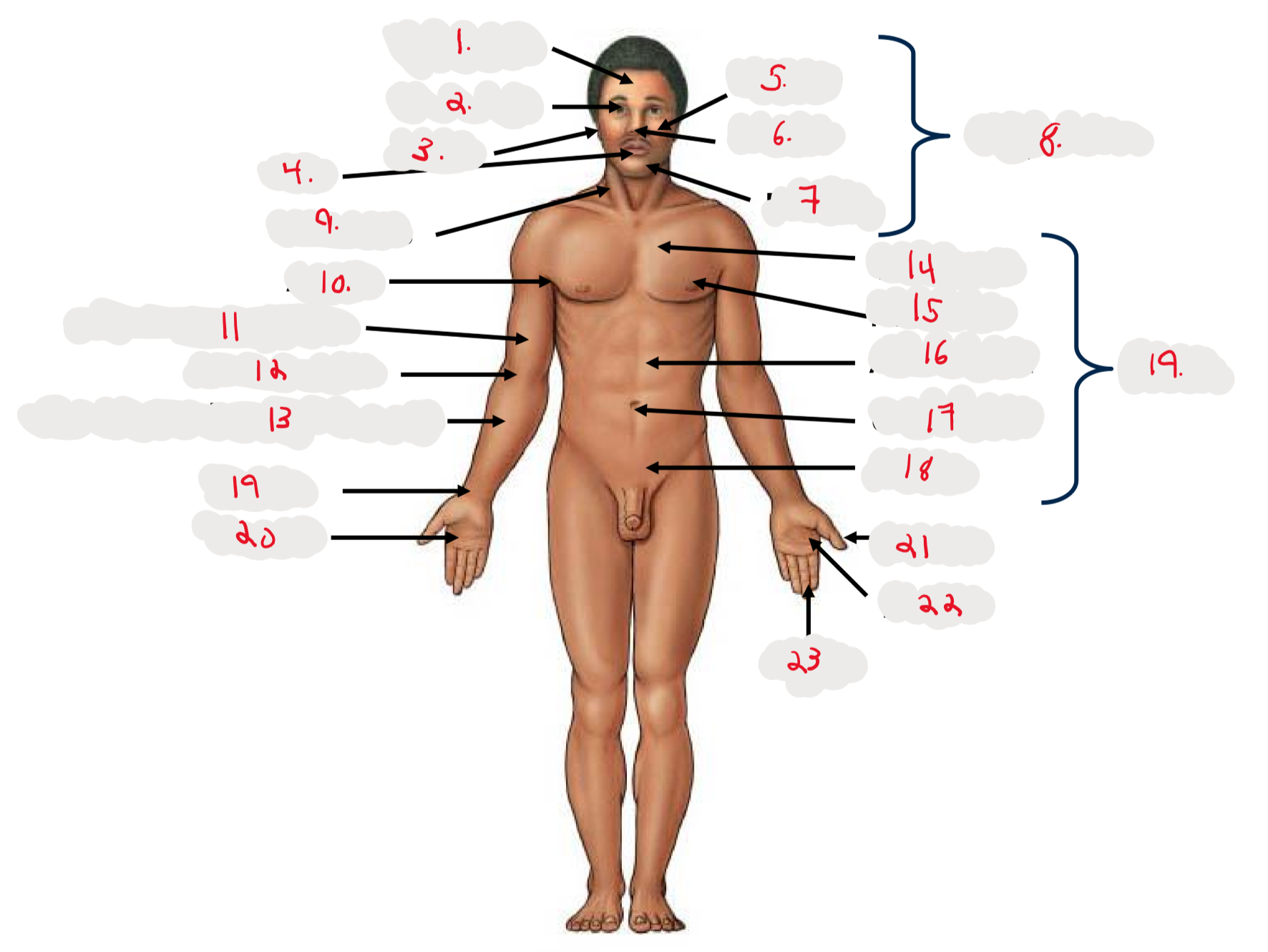
7
Mentis (chin)
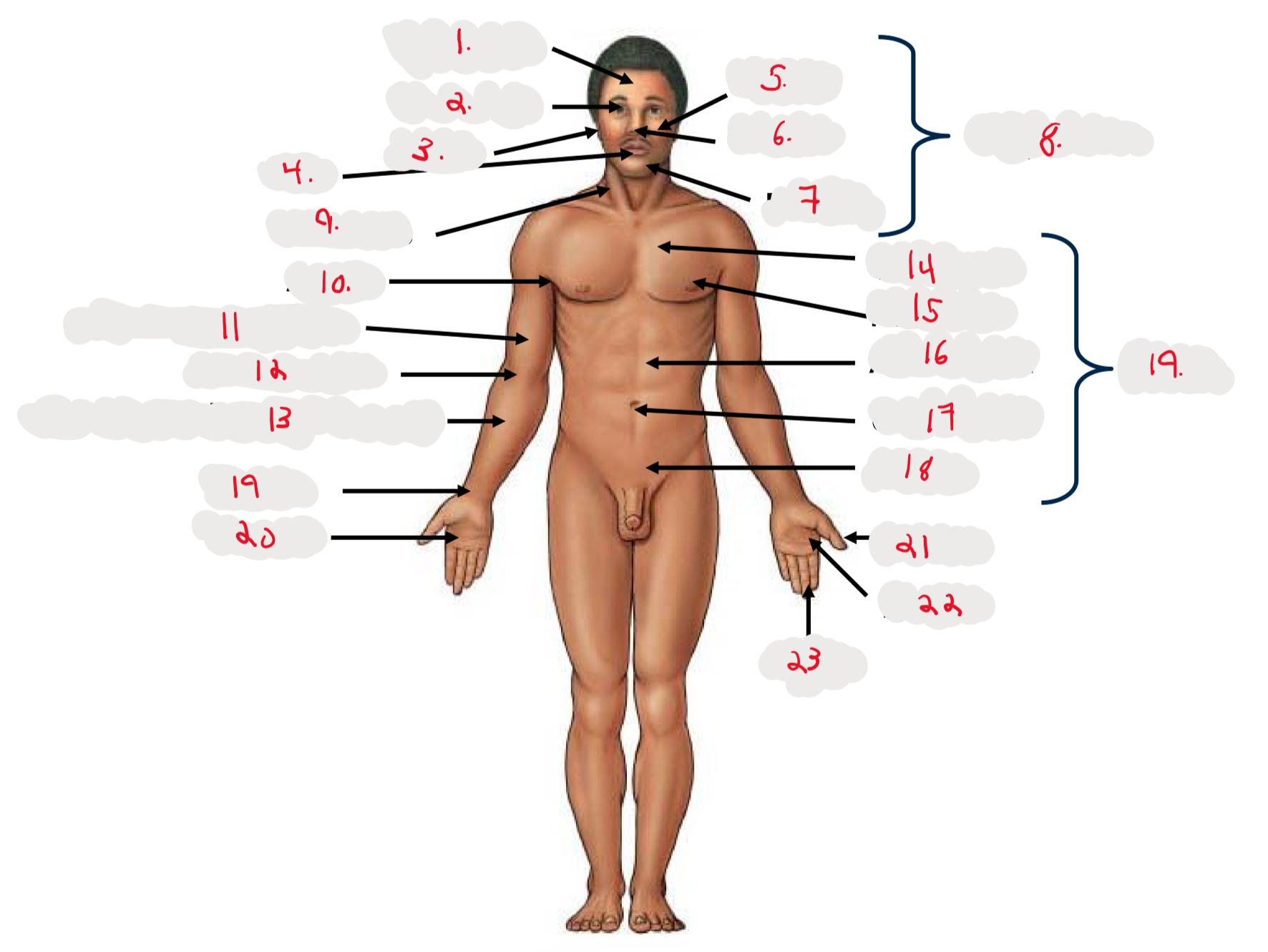
8
Cephalon
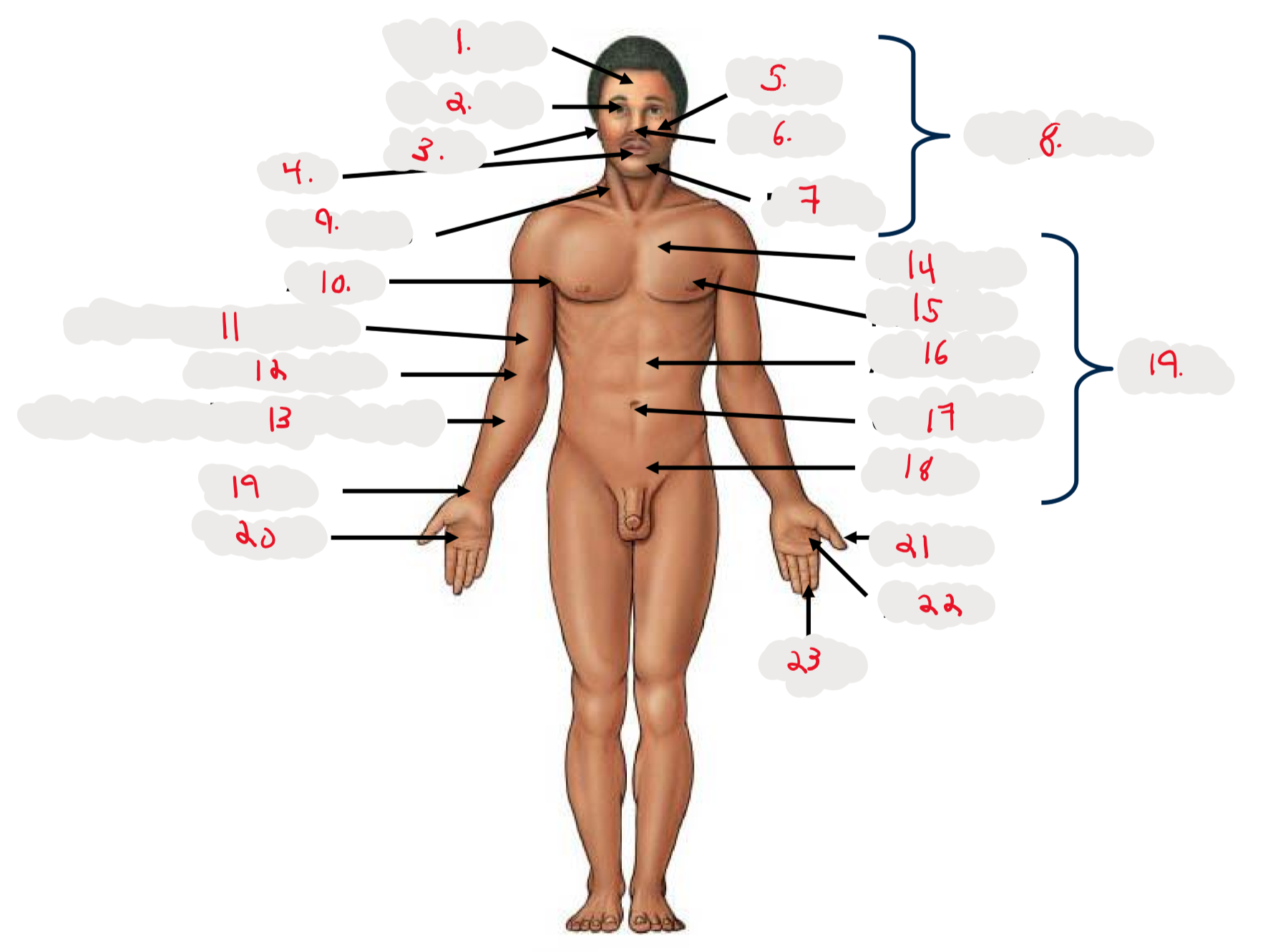
9
Cervicis (neck)
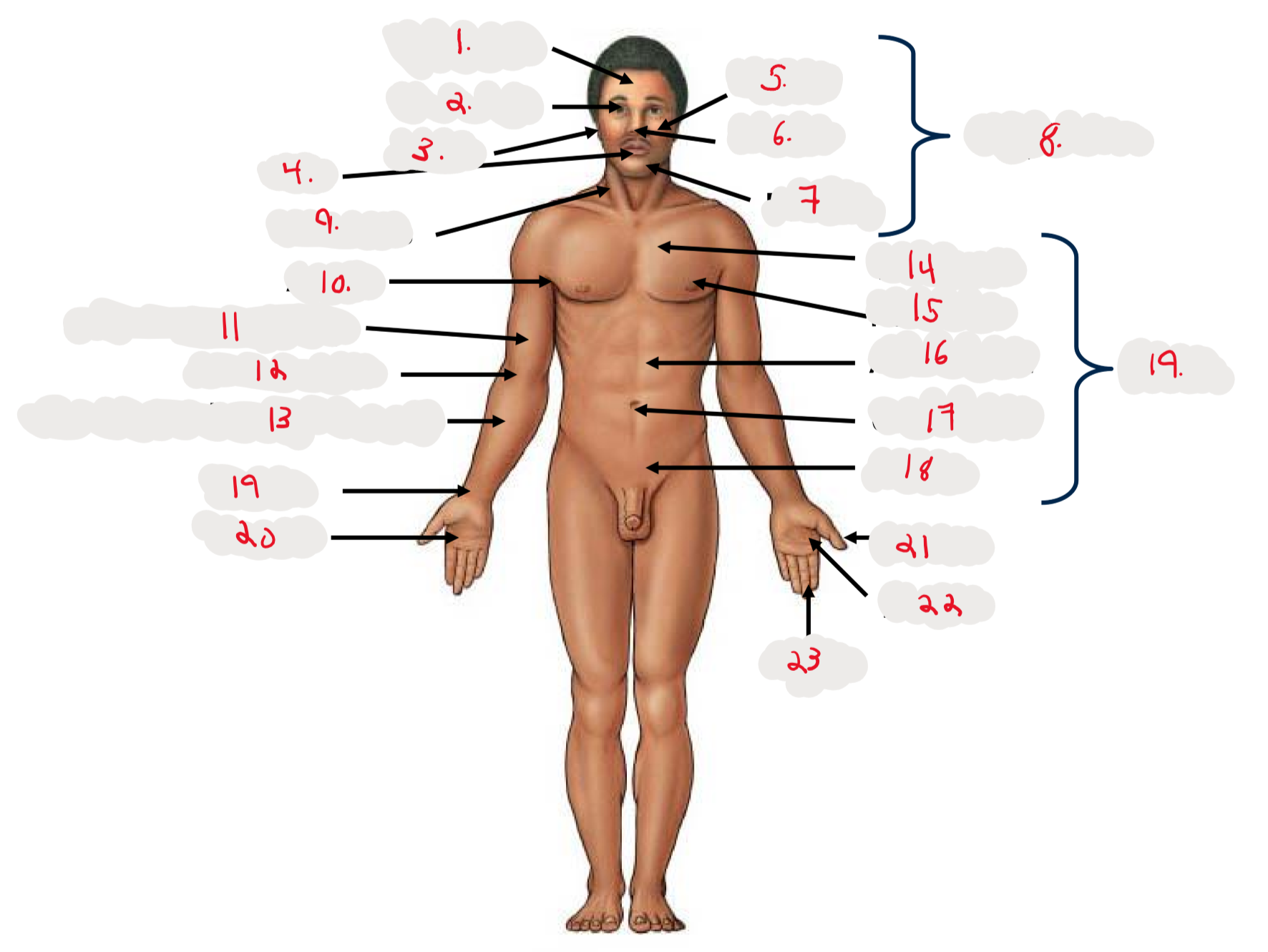
10
Axilla (armpit)
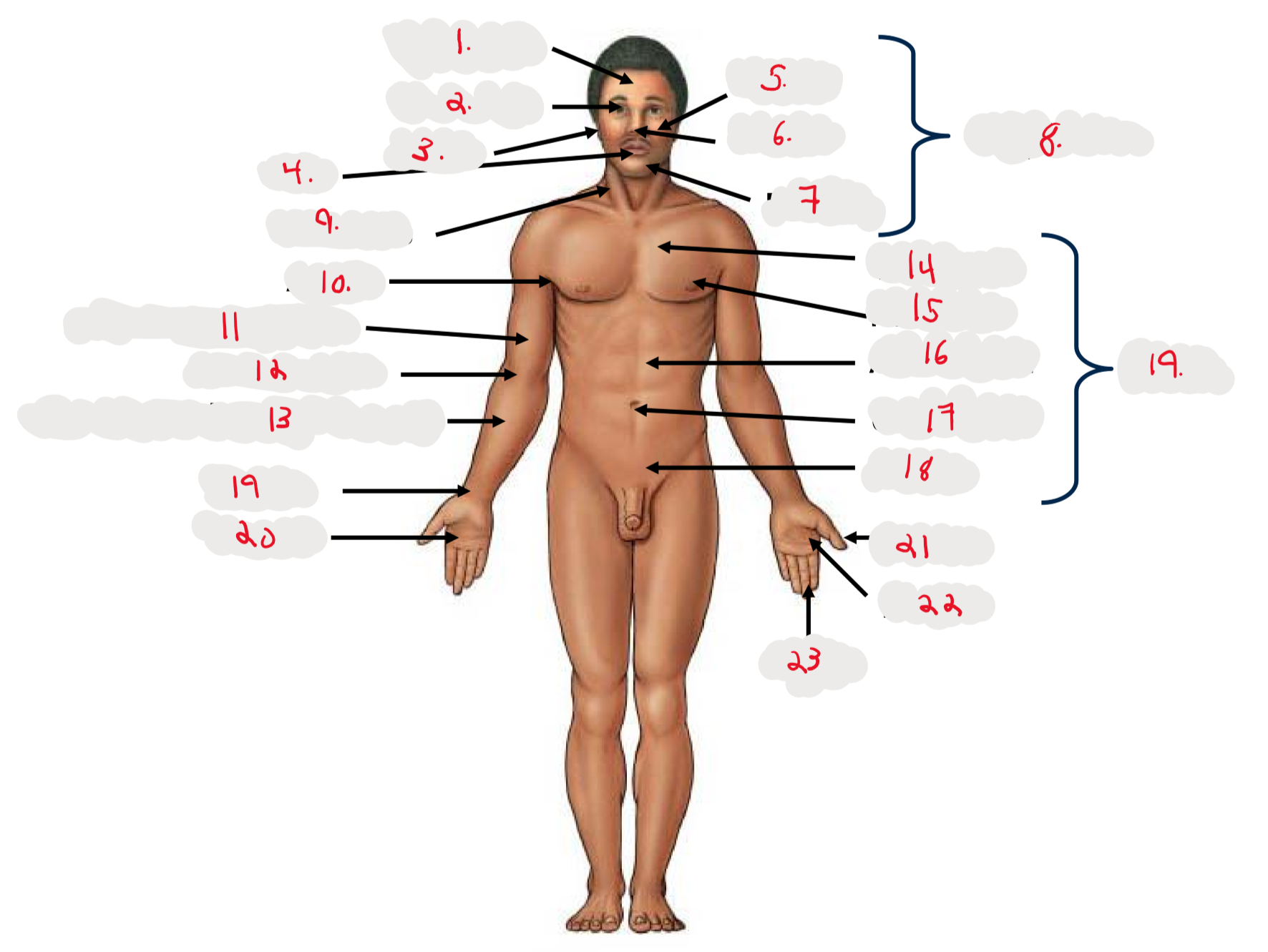
11
Brachium (arm)
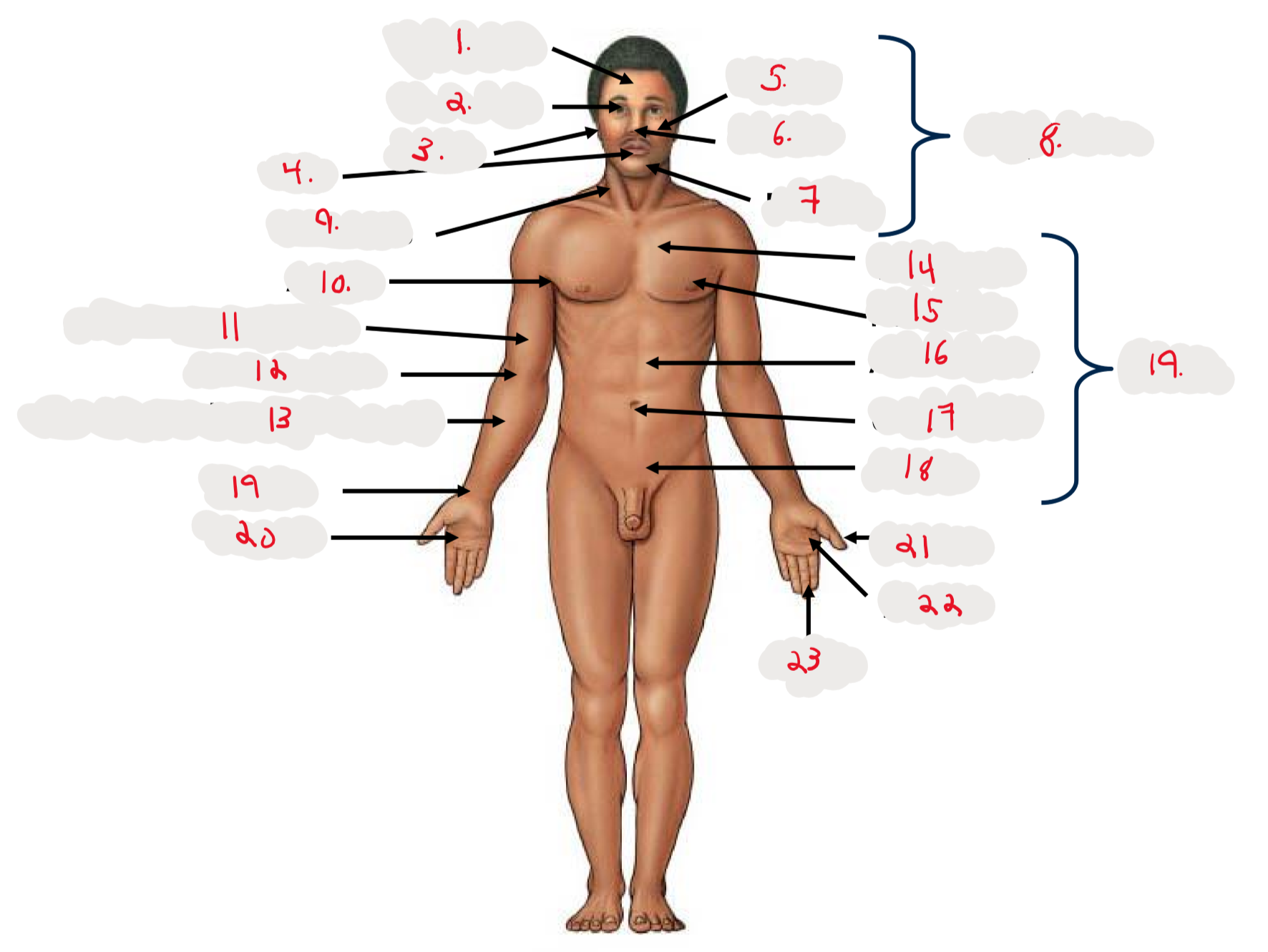
12
Antecubitis (anterior portion of elbow)
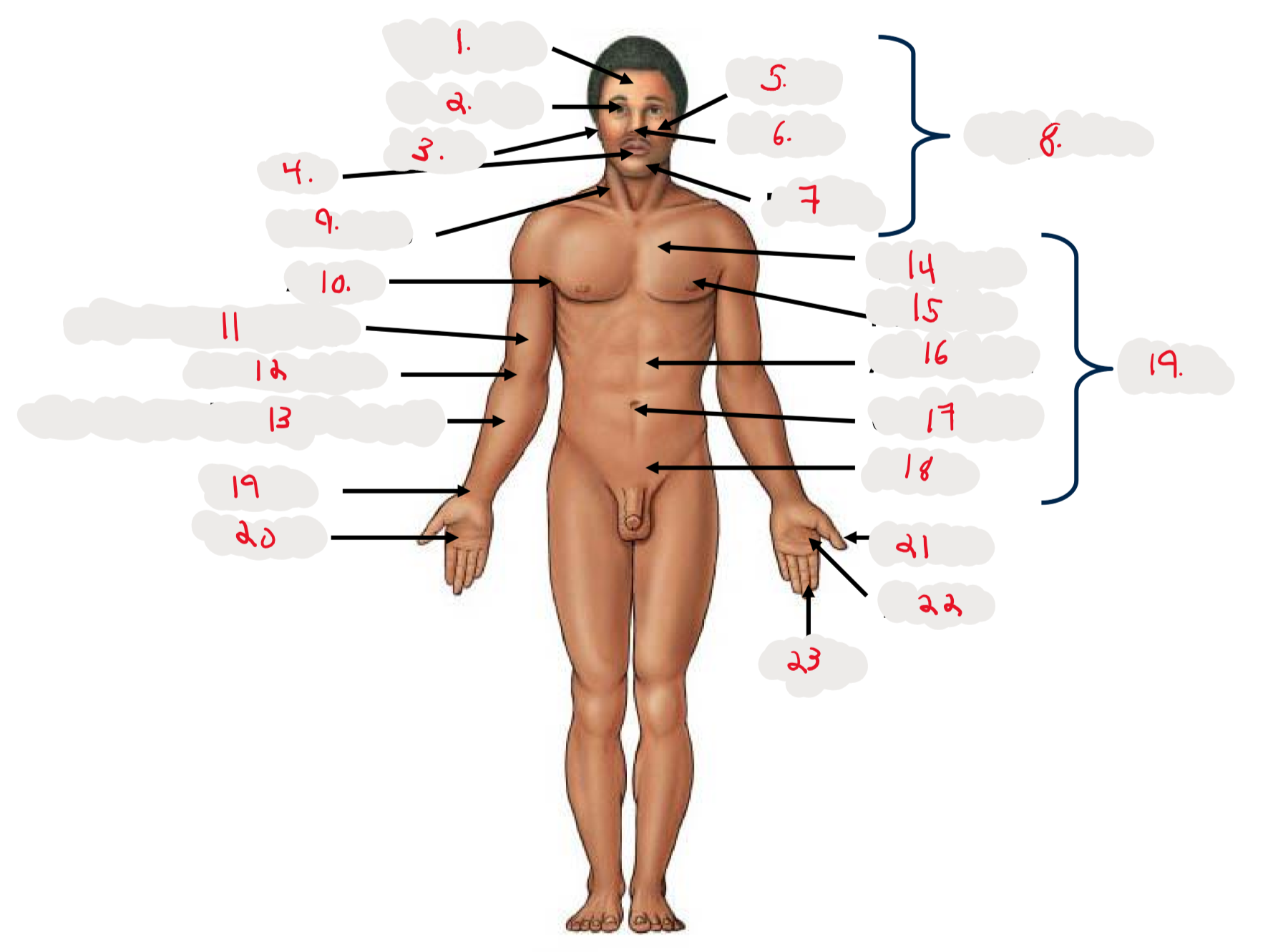
13
Antebrachium (anterior forearm)
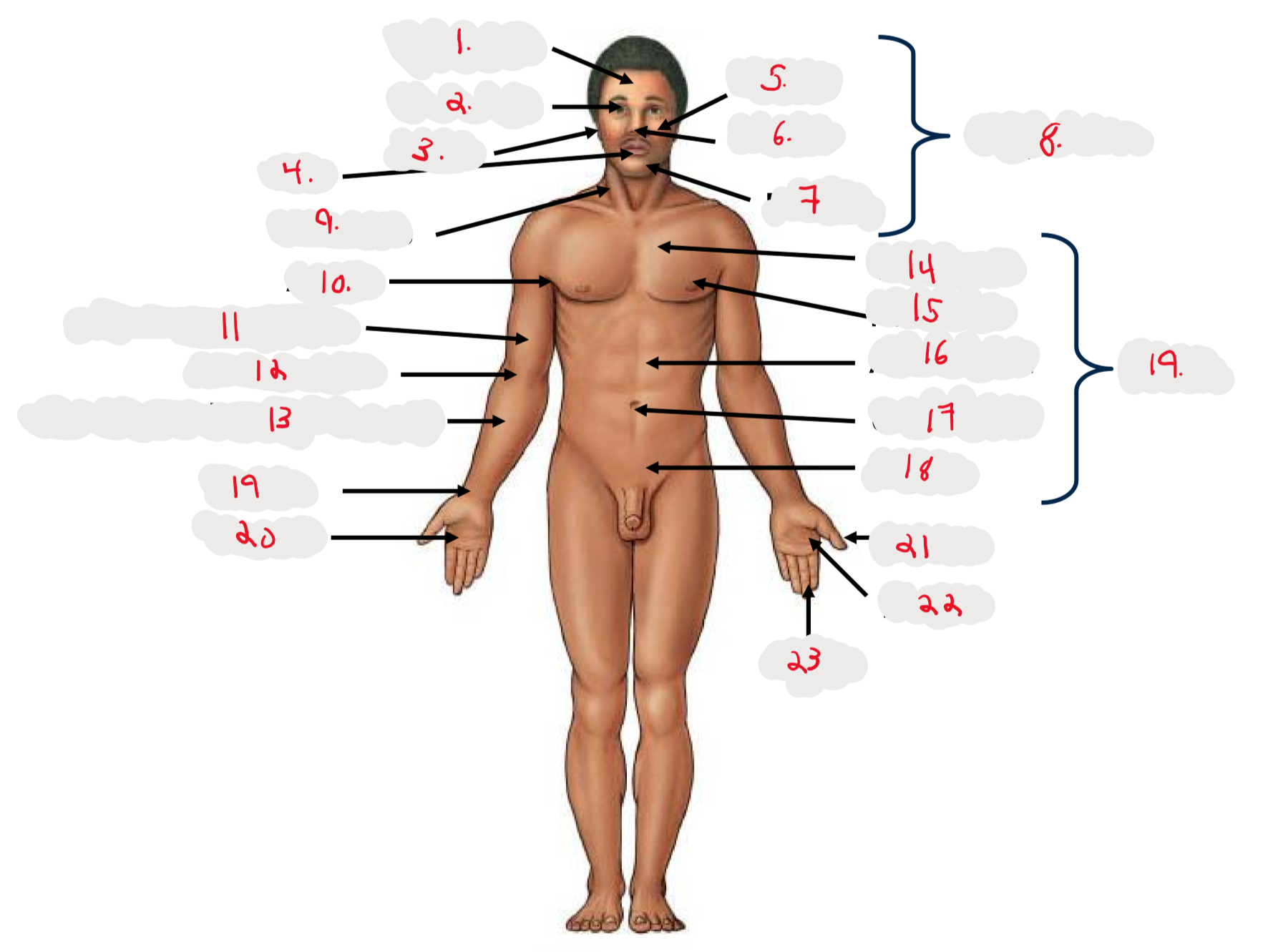
14
Thoracis (chest)
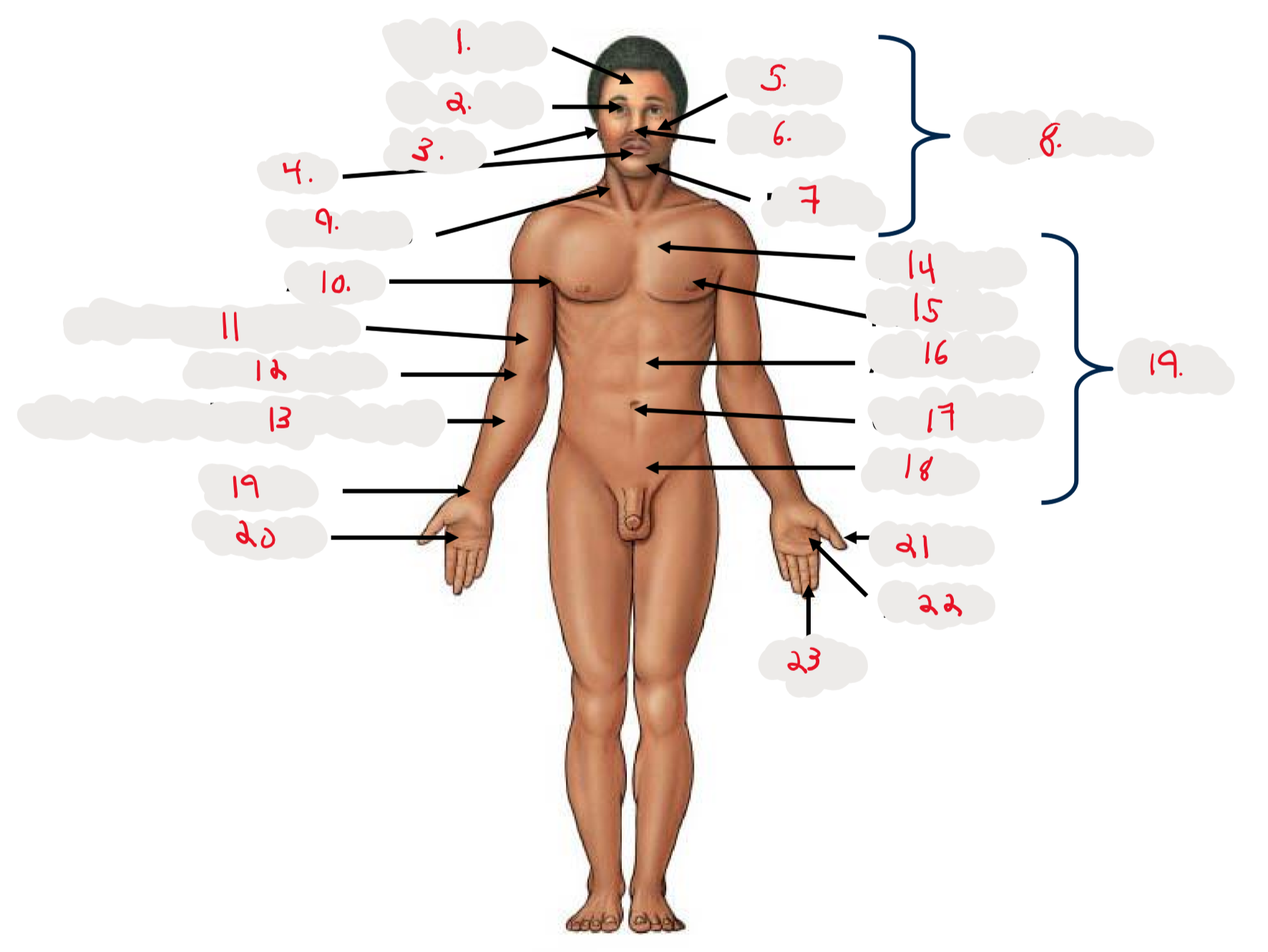
15
Mamma (breast)
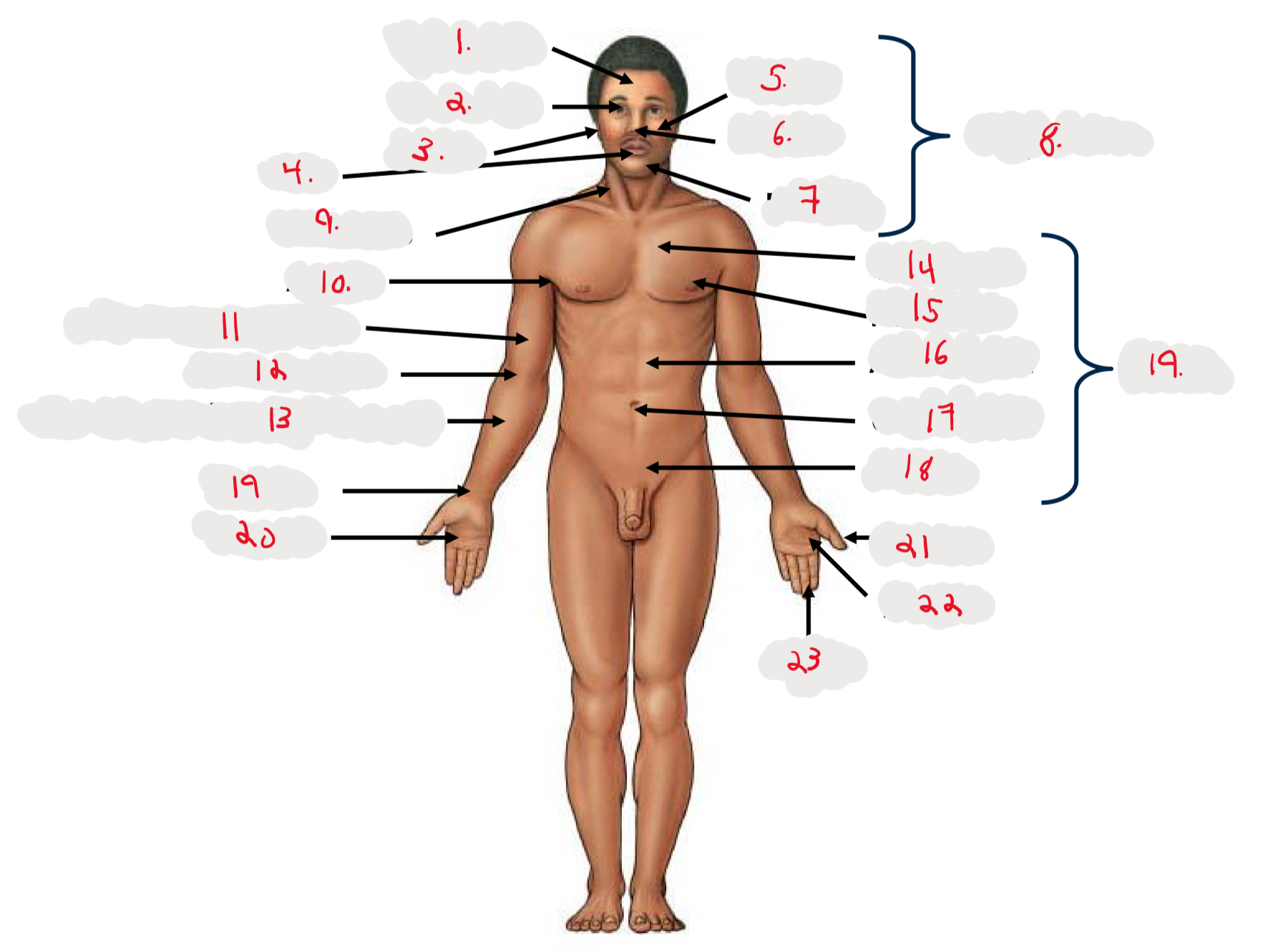
16
abdomen
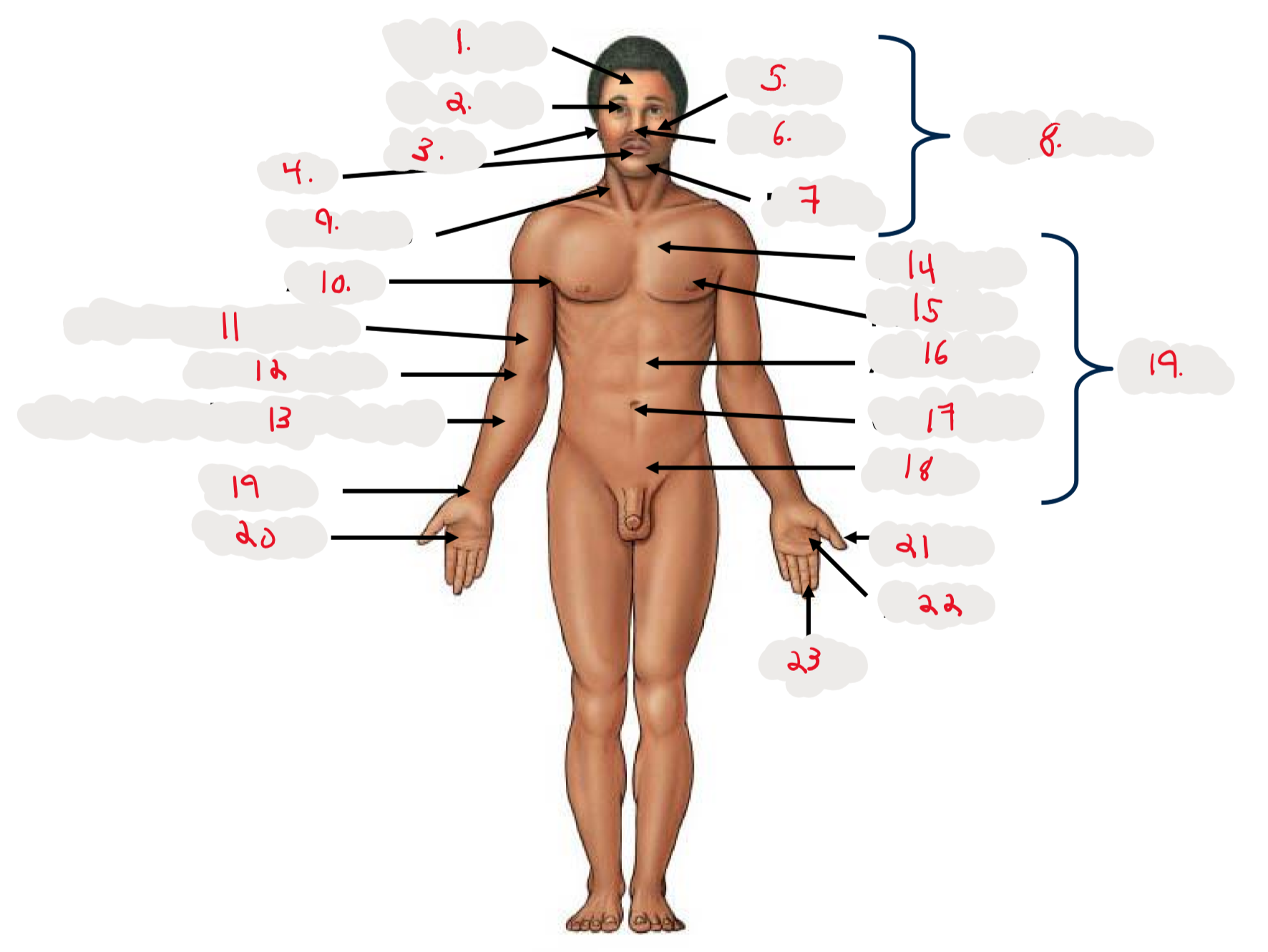
17
Umbilicus (belly button)
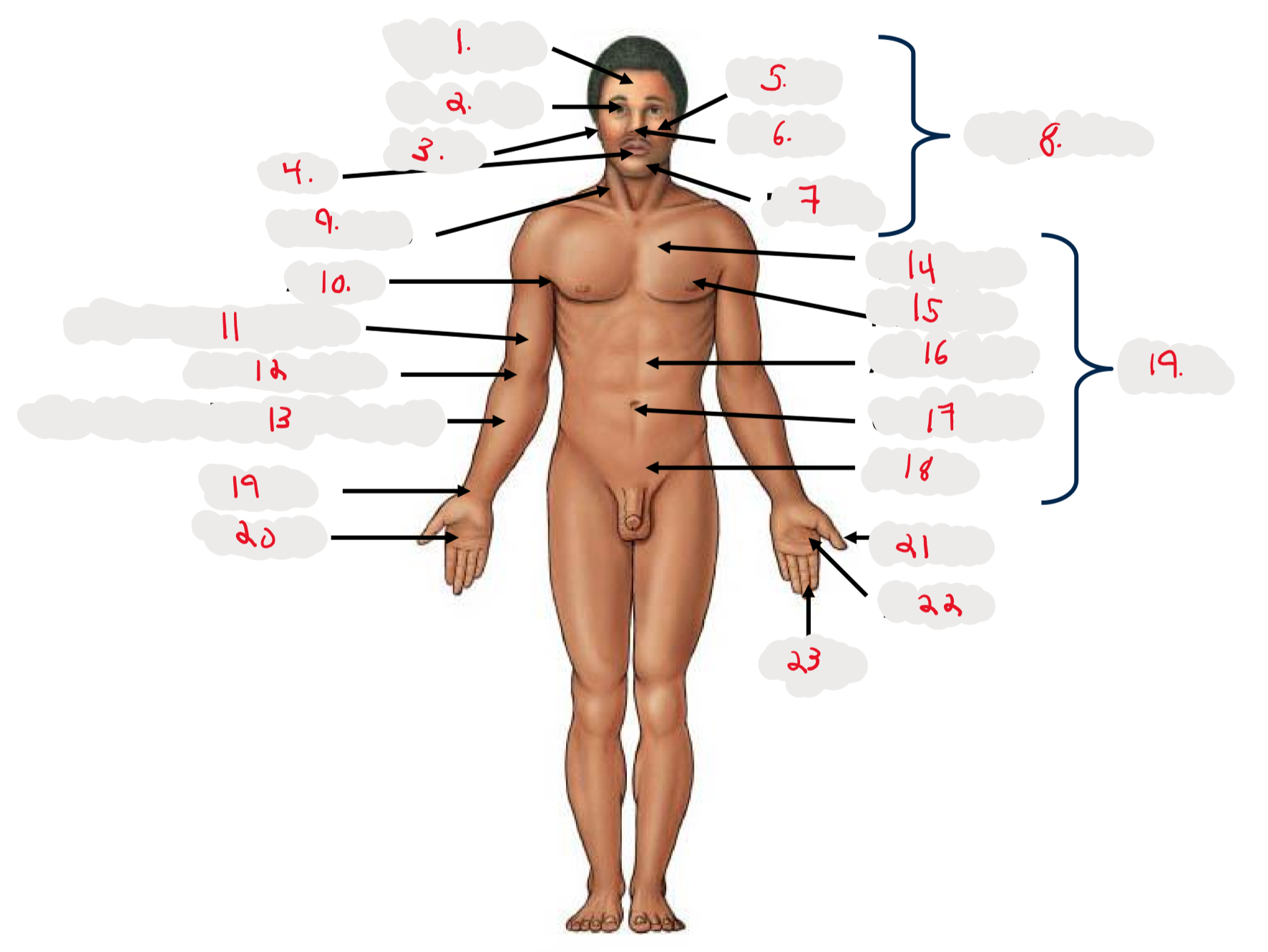
18
Pelvis
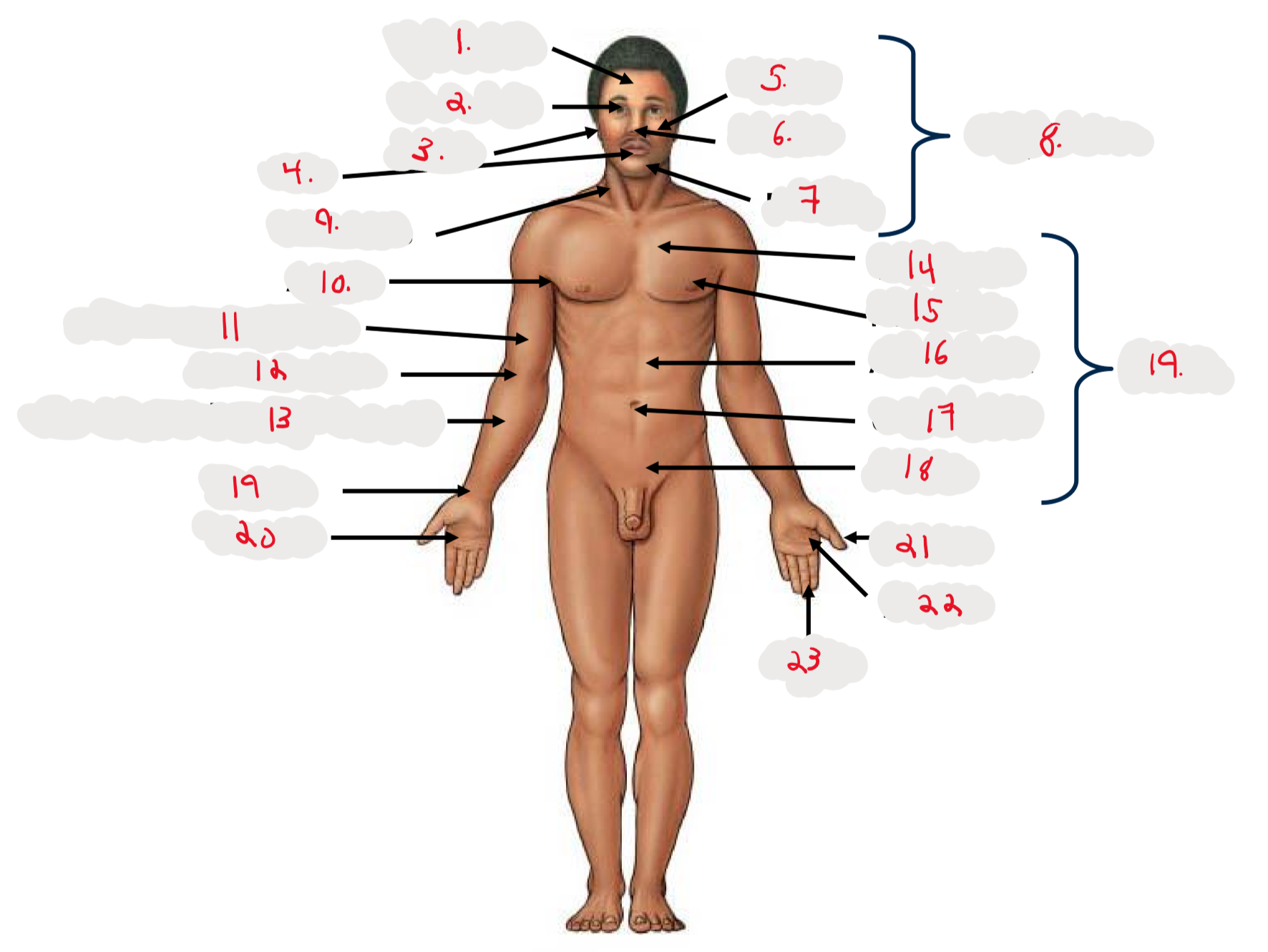
19
Trunk
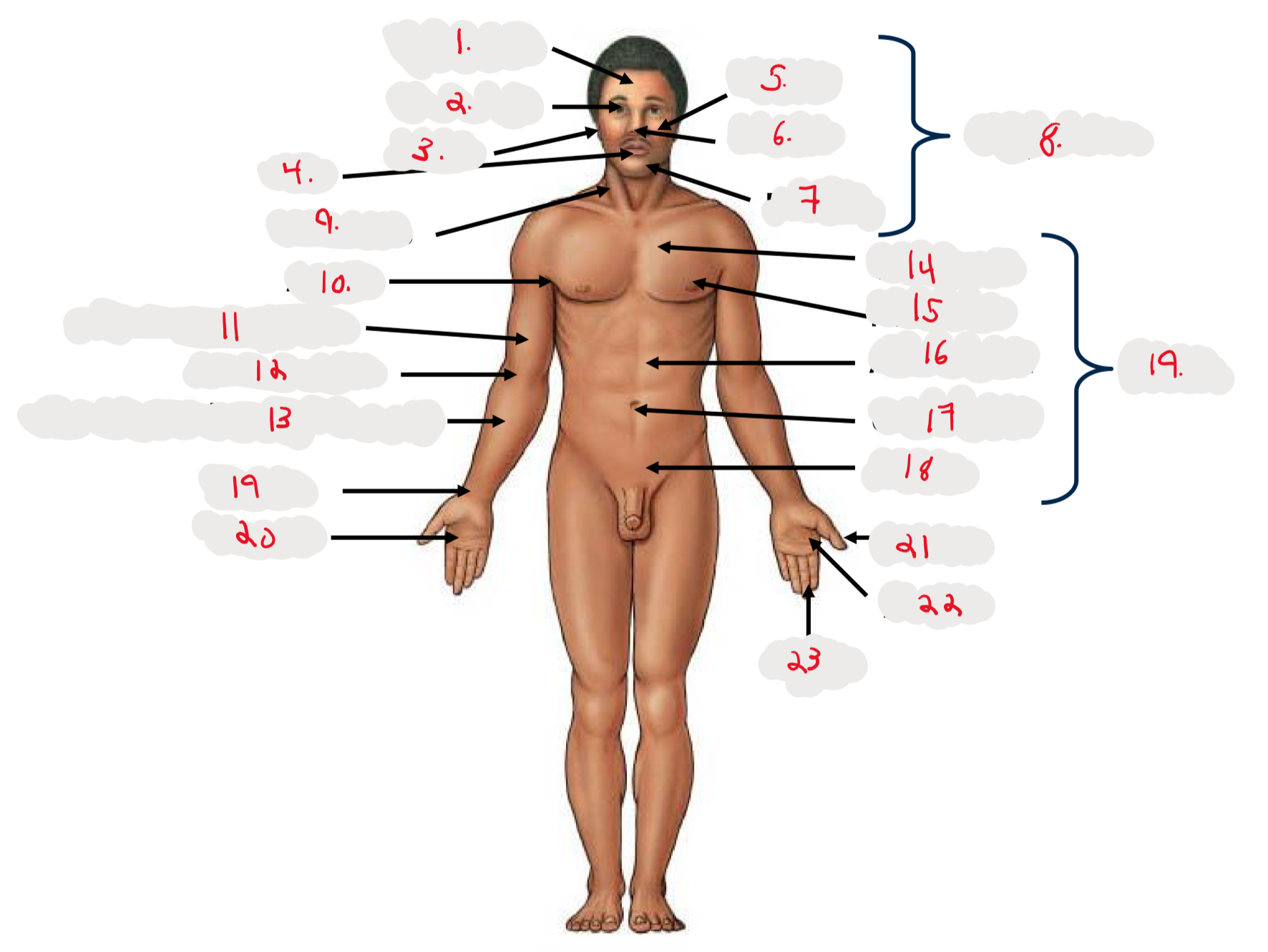
19 (on right hand)
Carpis (wrist)
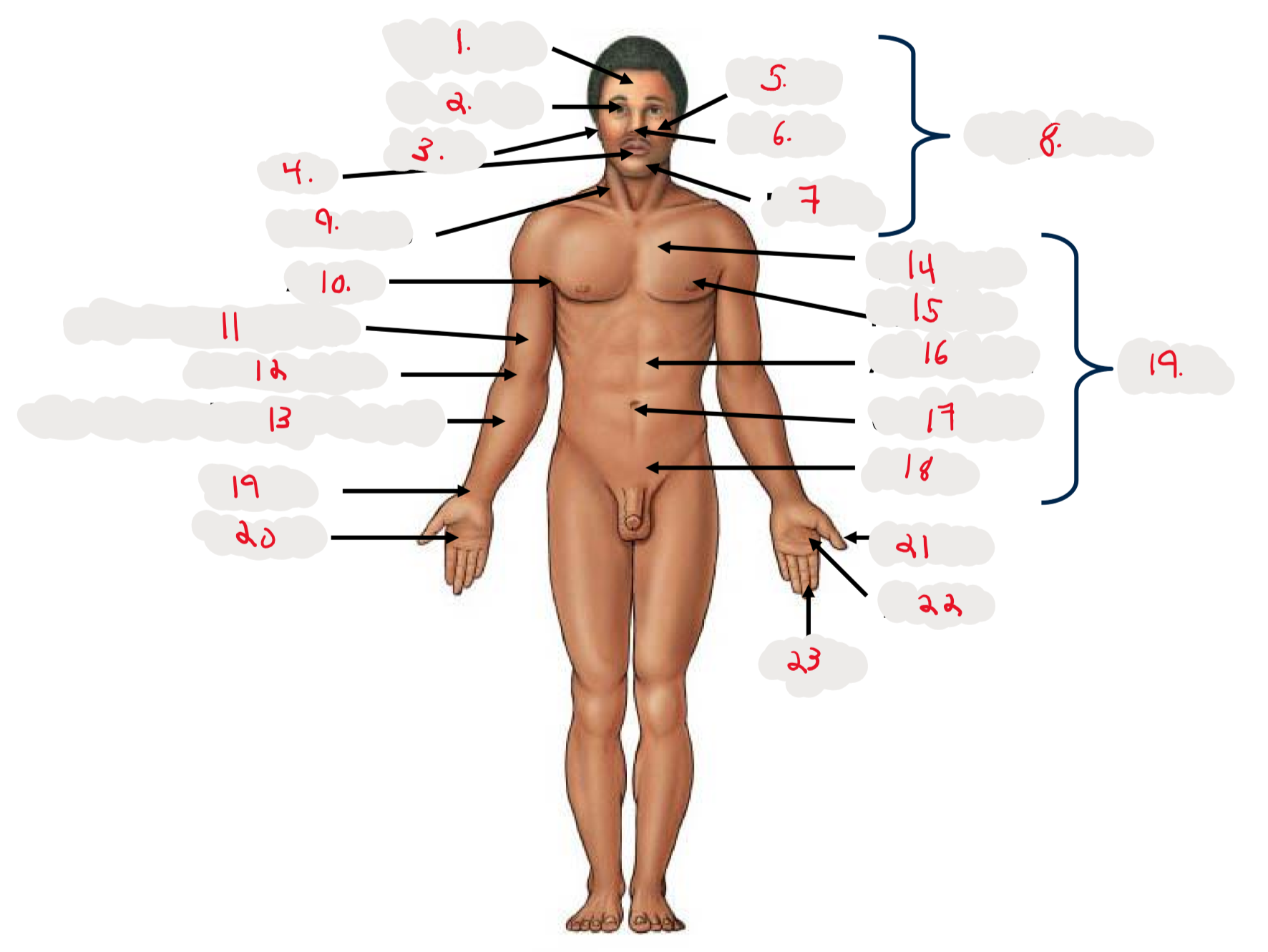
20
Manus (hand)
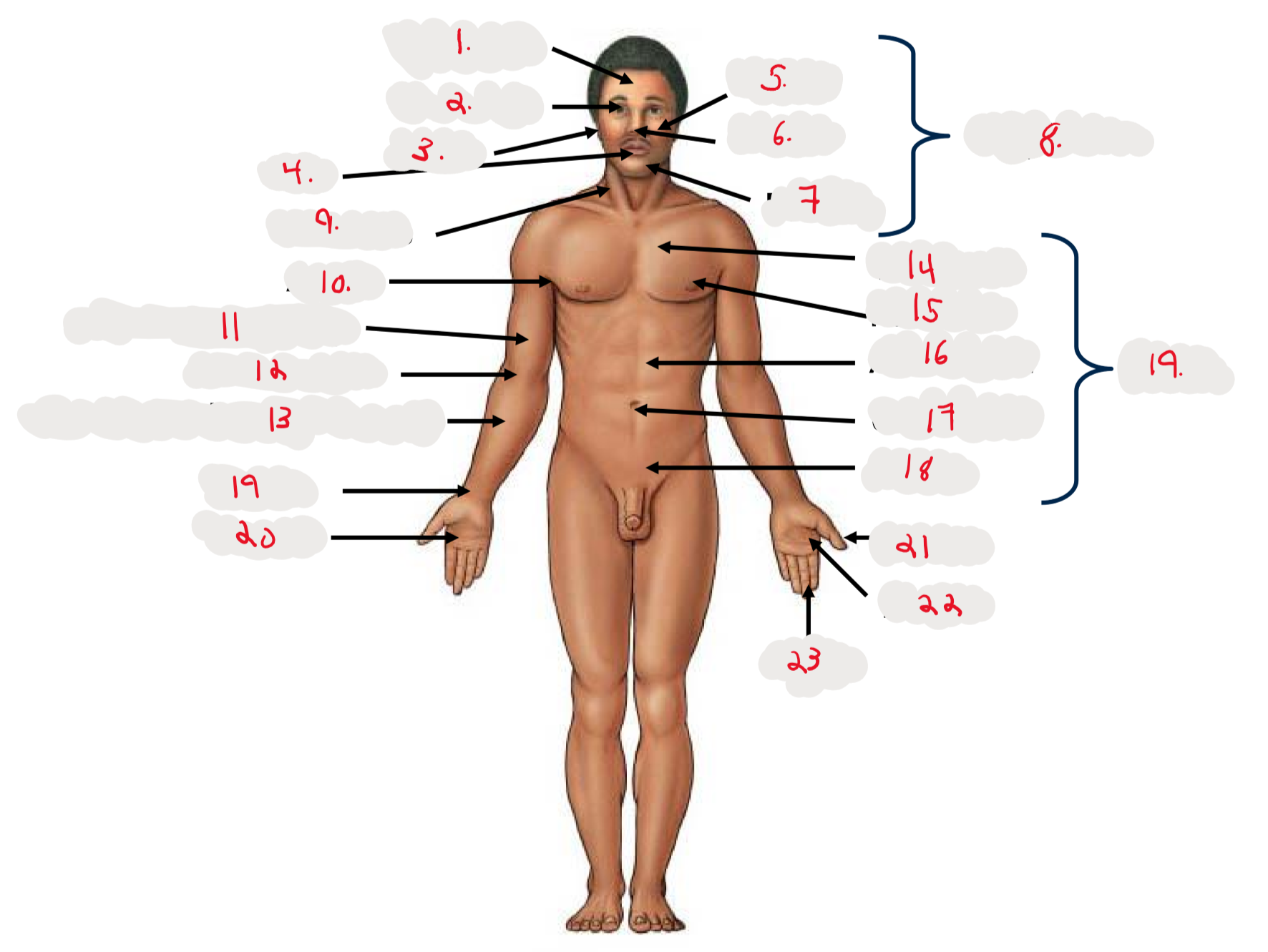
21
Pollex (thumb)
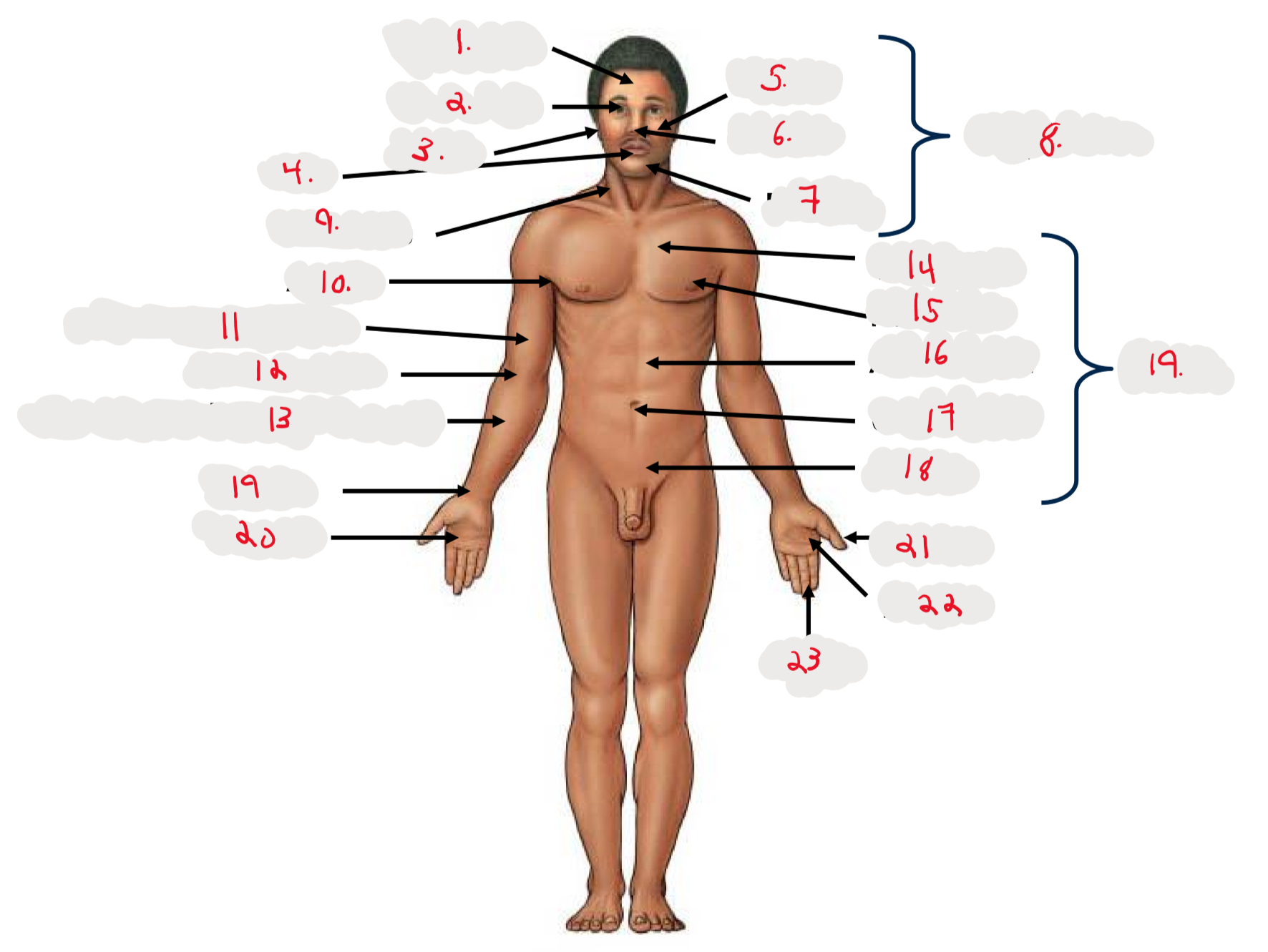
22
Palma (palm, anterior surface of hand)
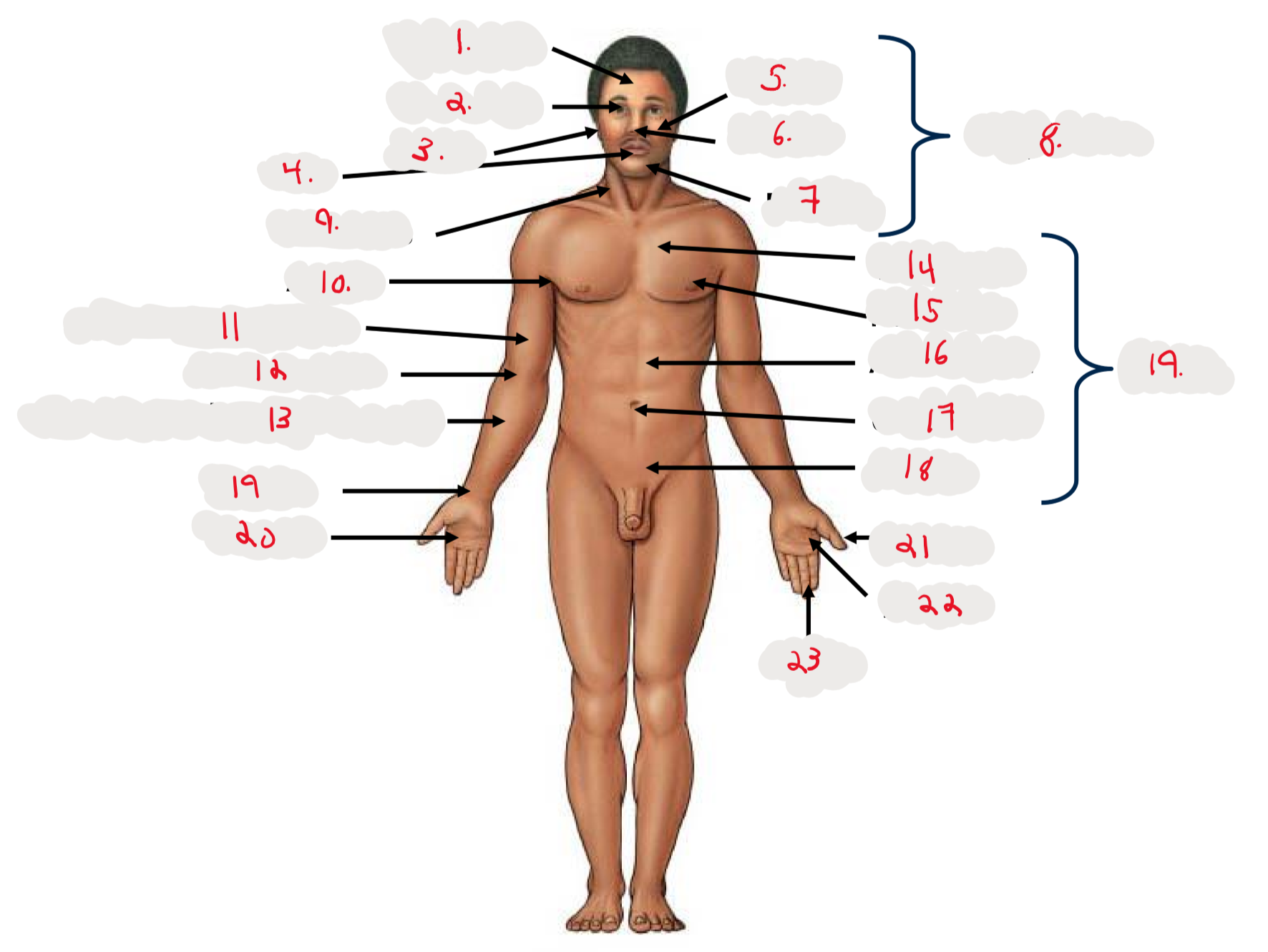
23
Digits (fingers)
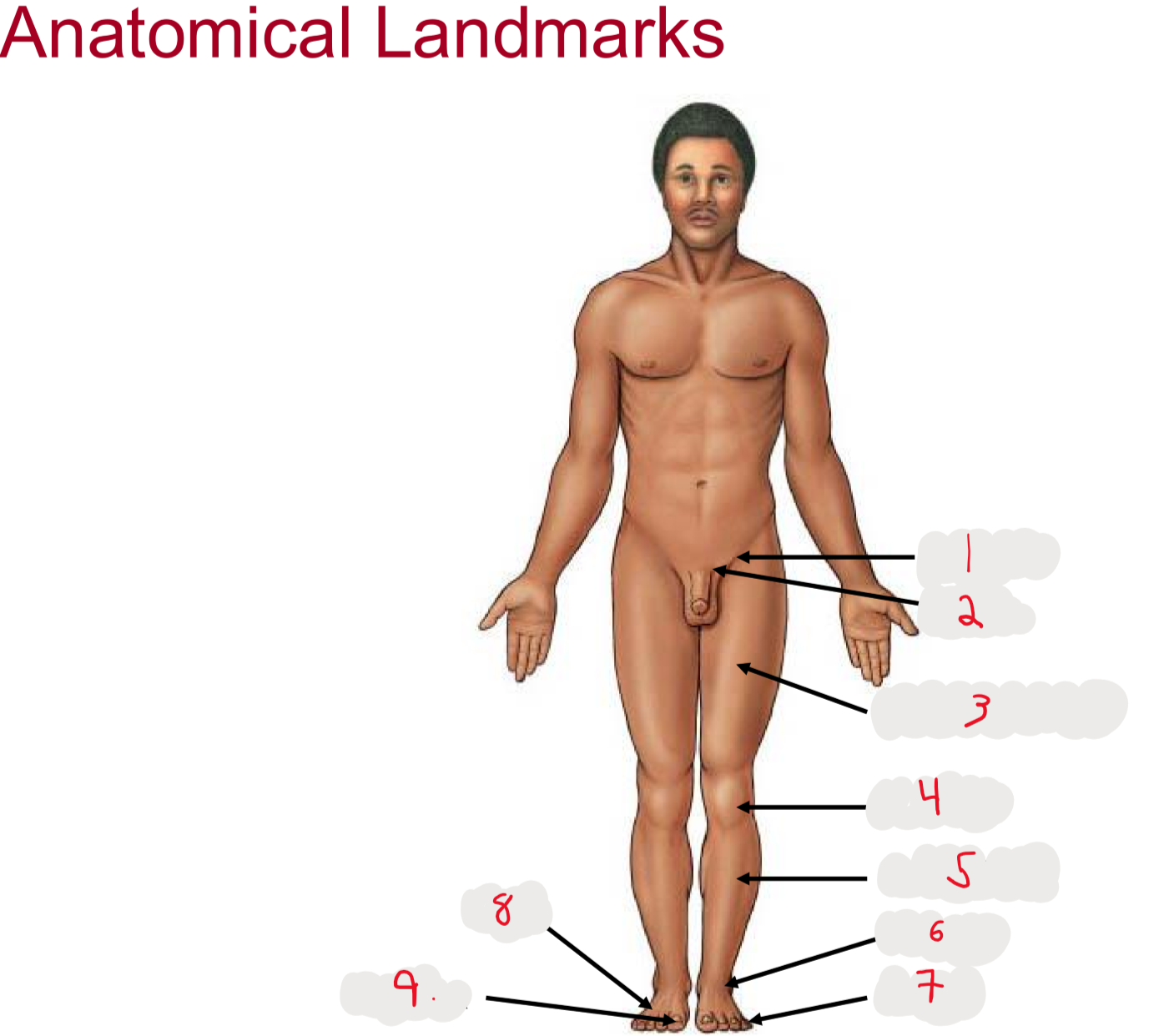
1
inguen (groin)
seperation from abdomen to thigh
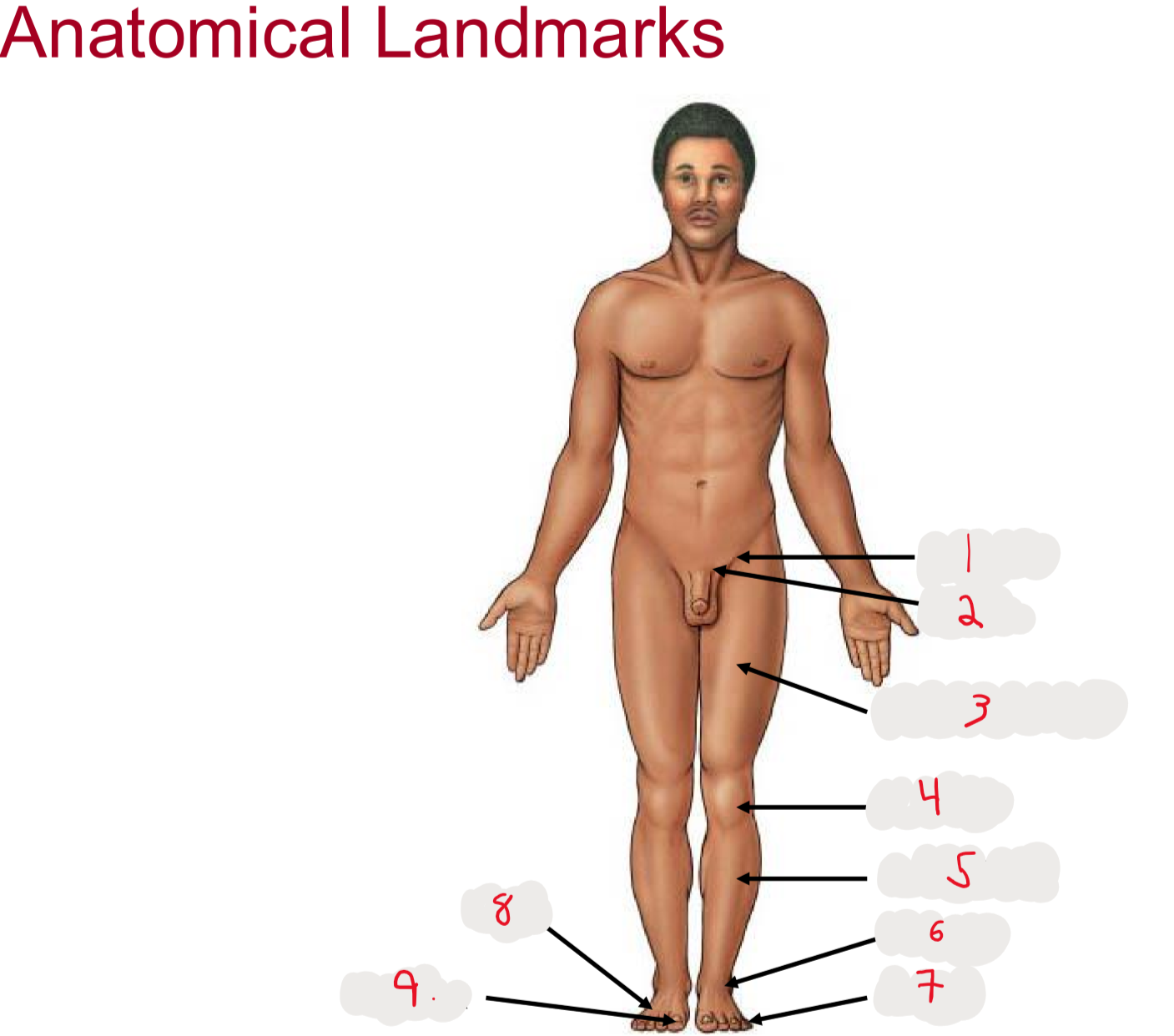
2
Pubis (pubic bone)
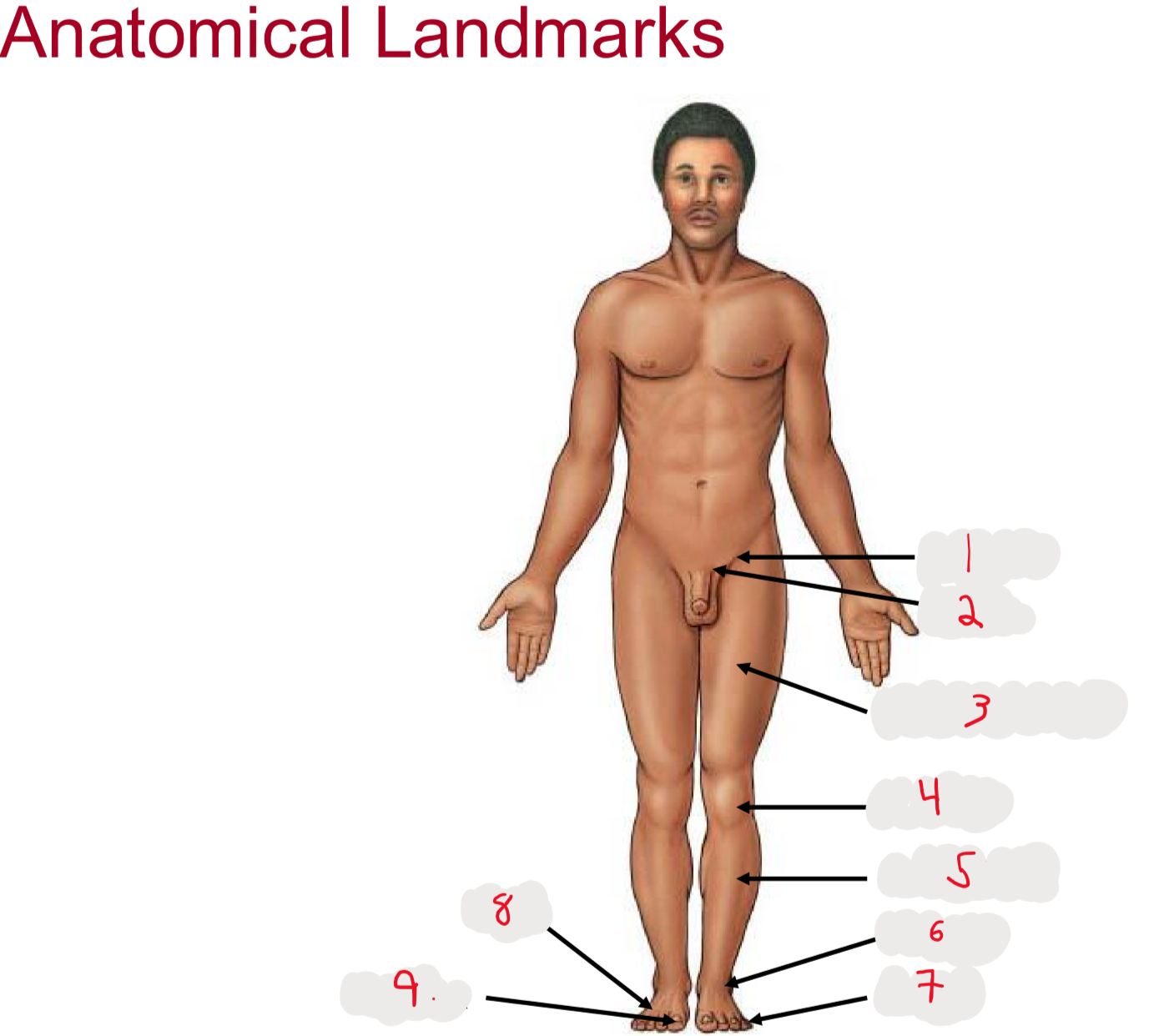
3
Femur (thigh)
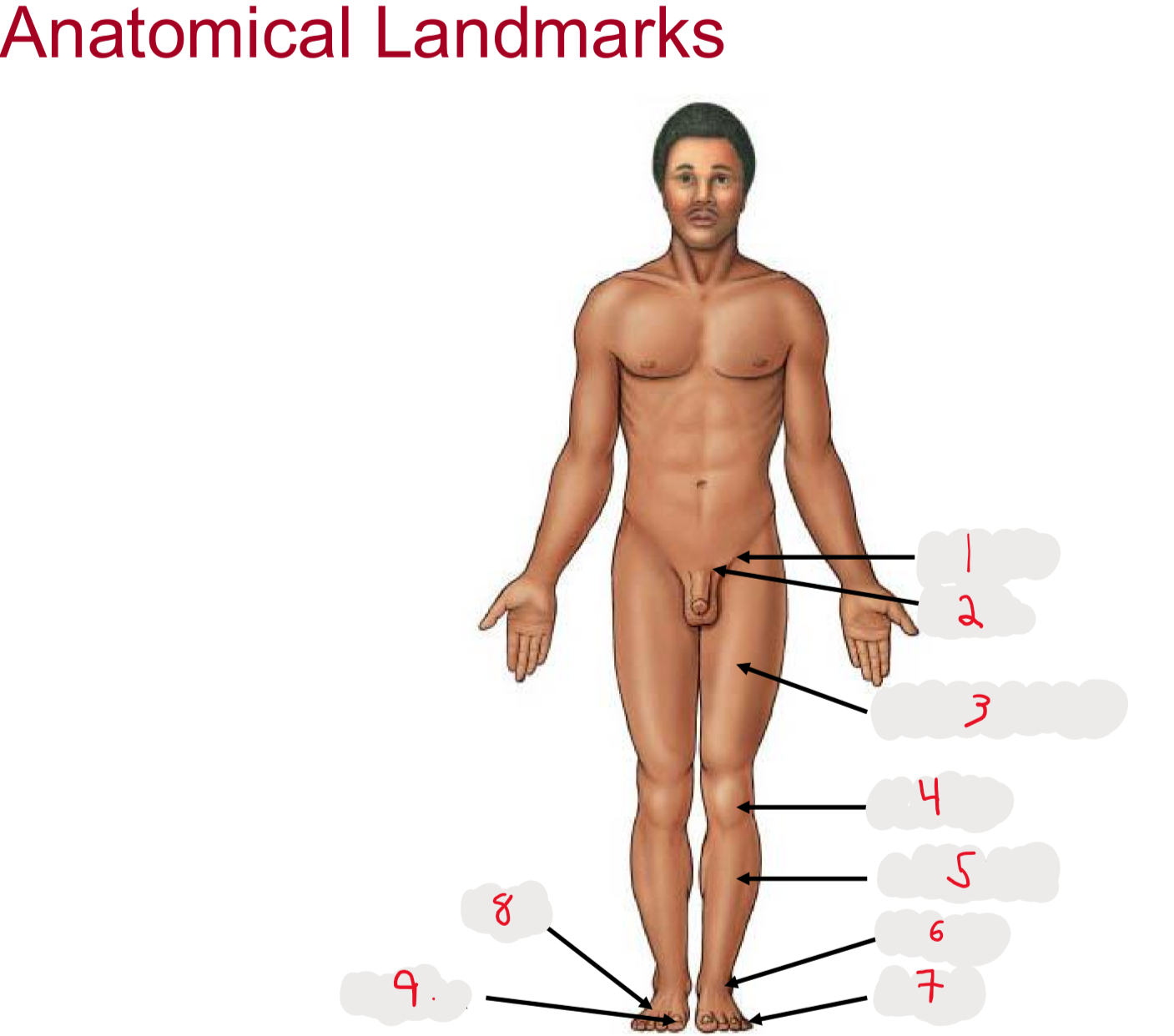
4
Patella (kneecap)
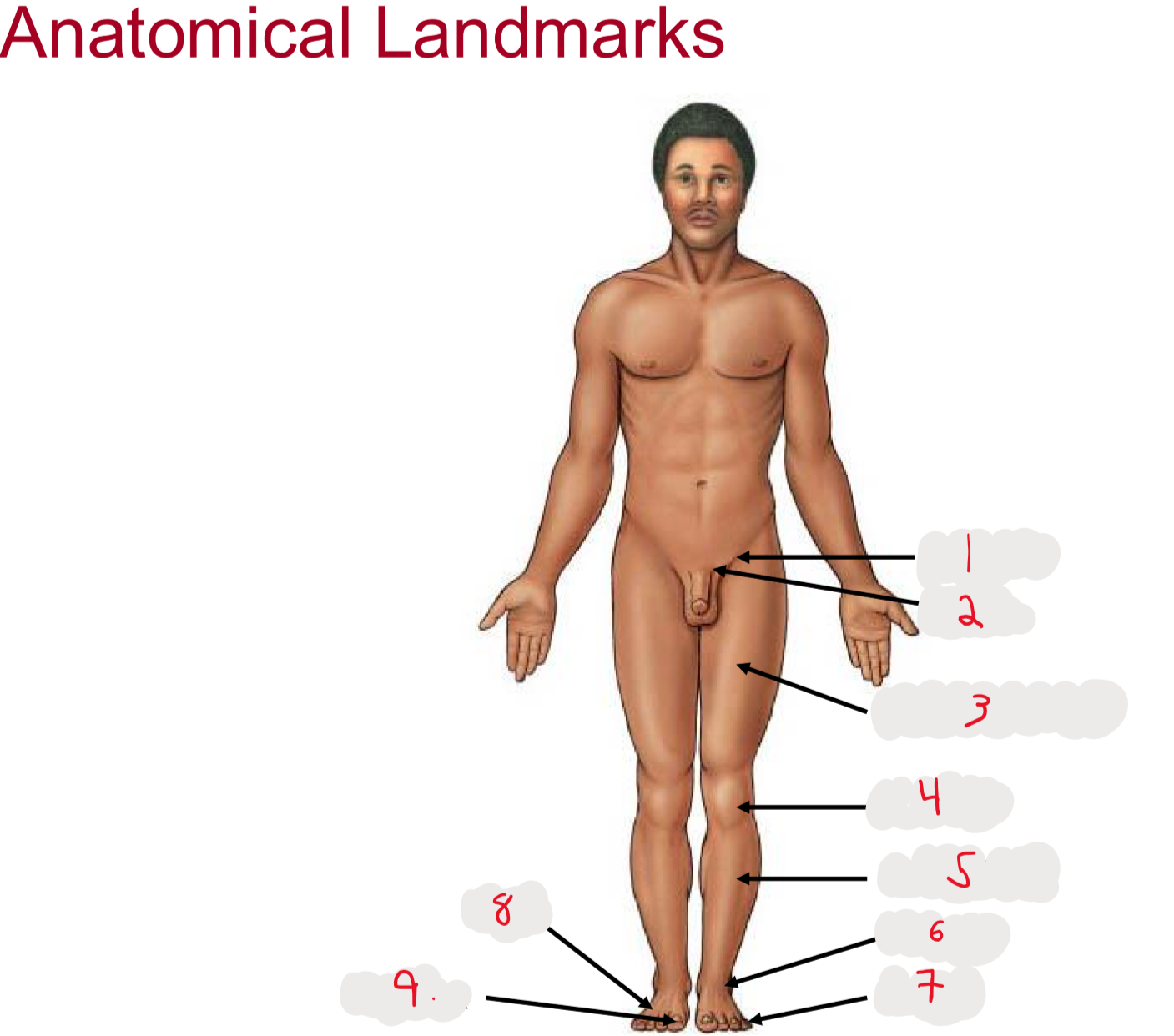
5
Crus (leg)
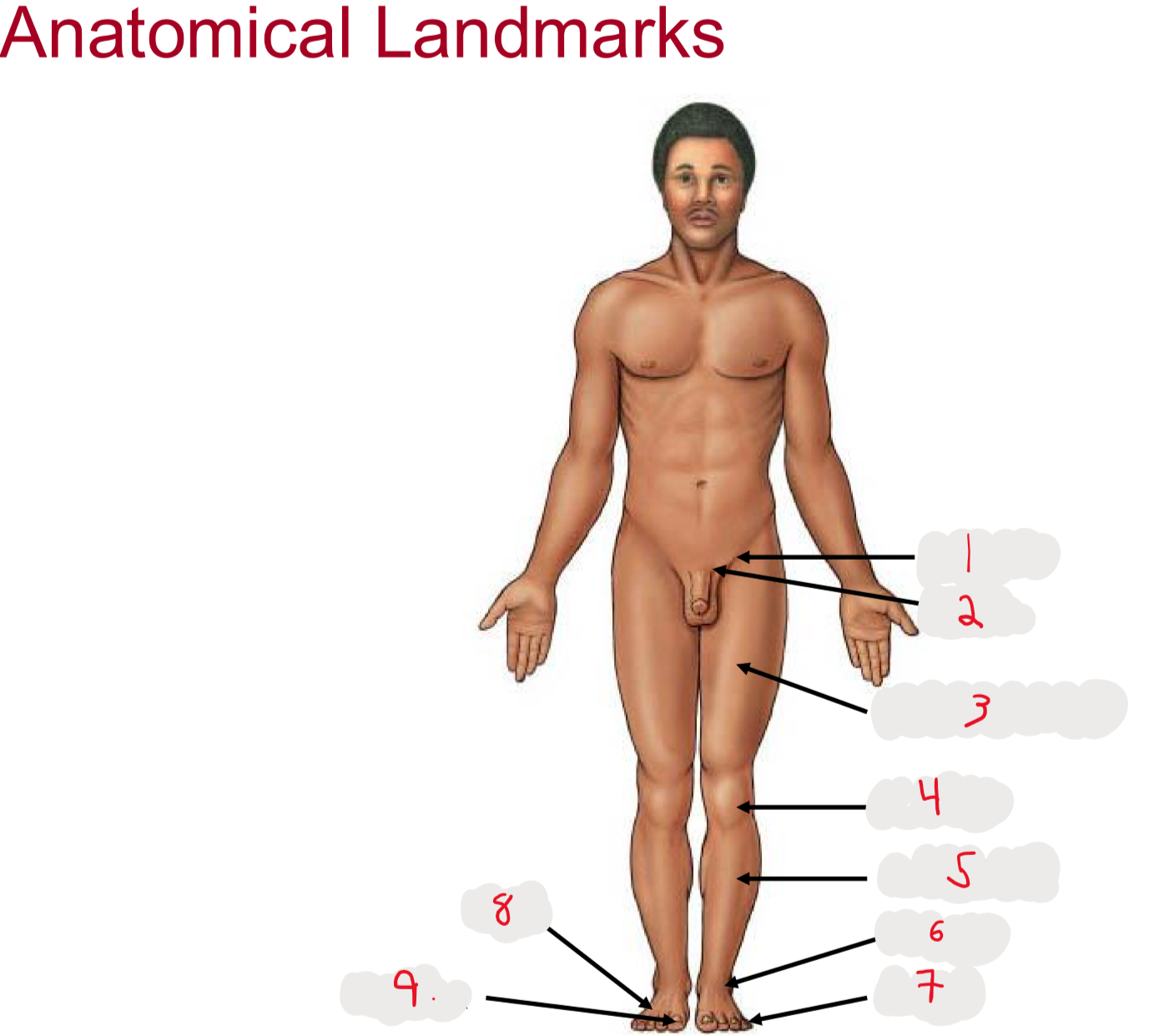
6.
Tarsus (ankle)
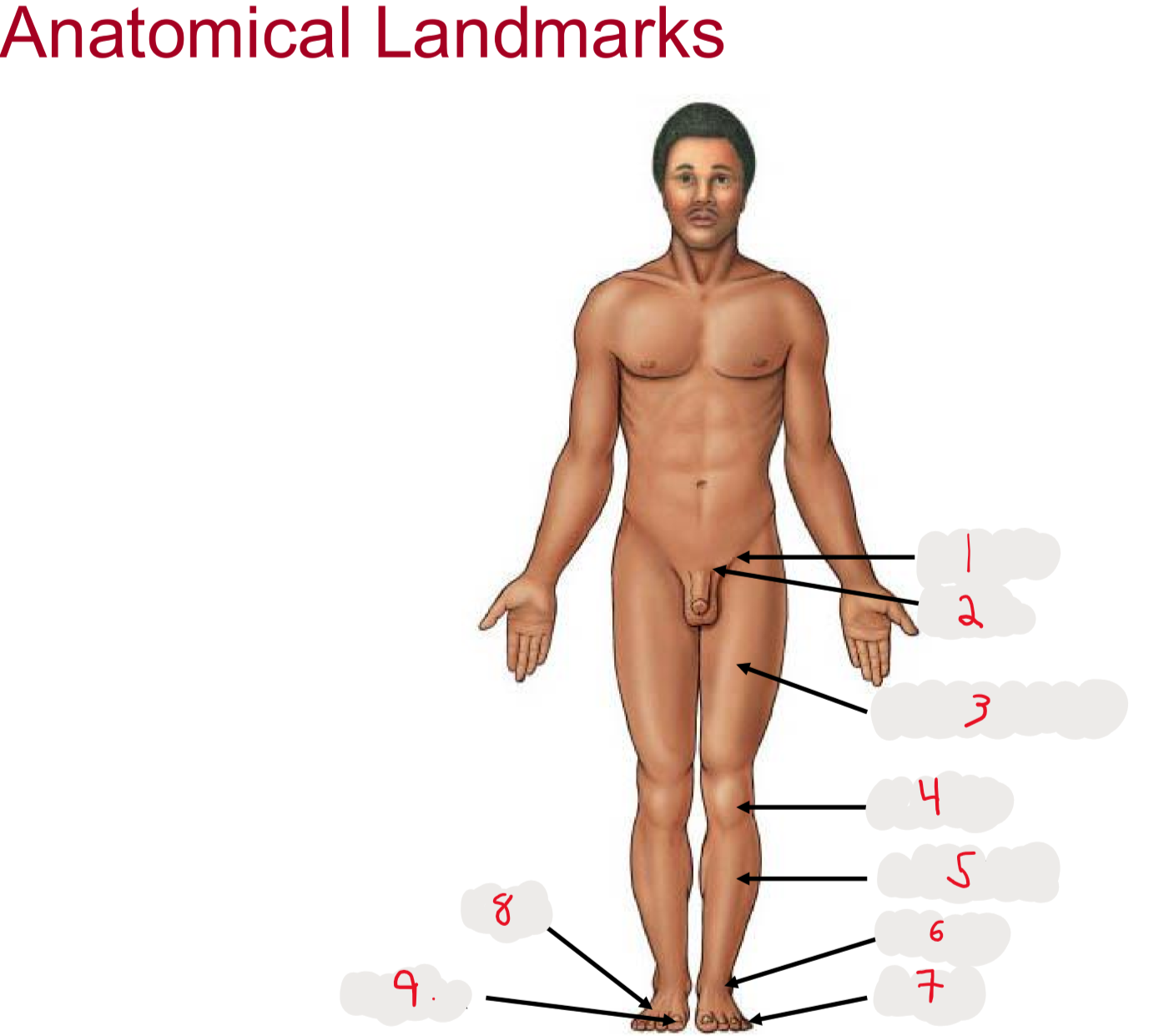
7
Digits (toes)
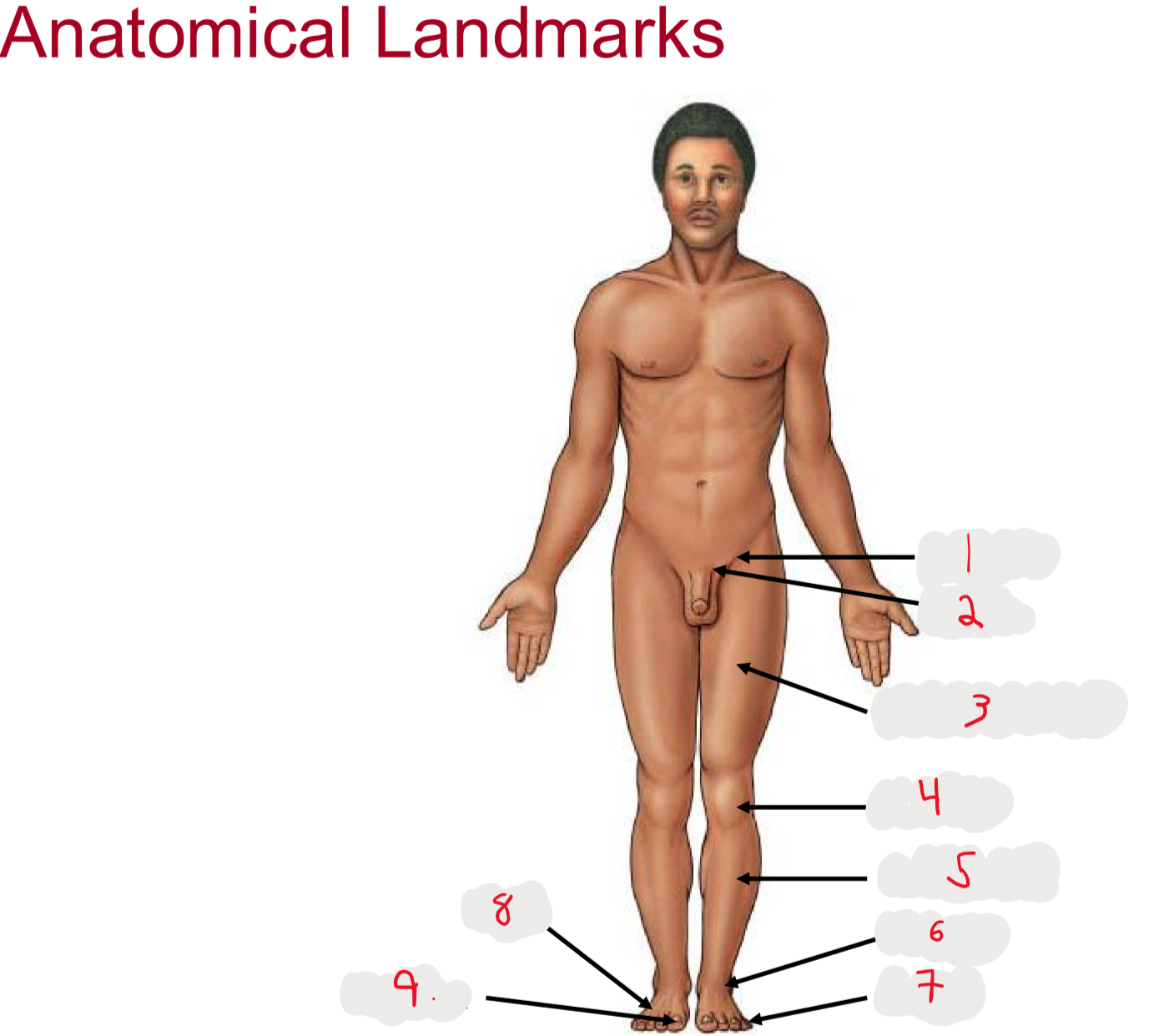
8
Pes (general term for foot)
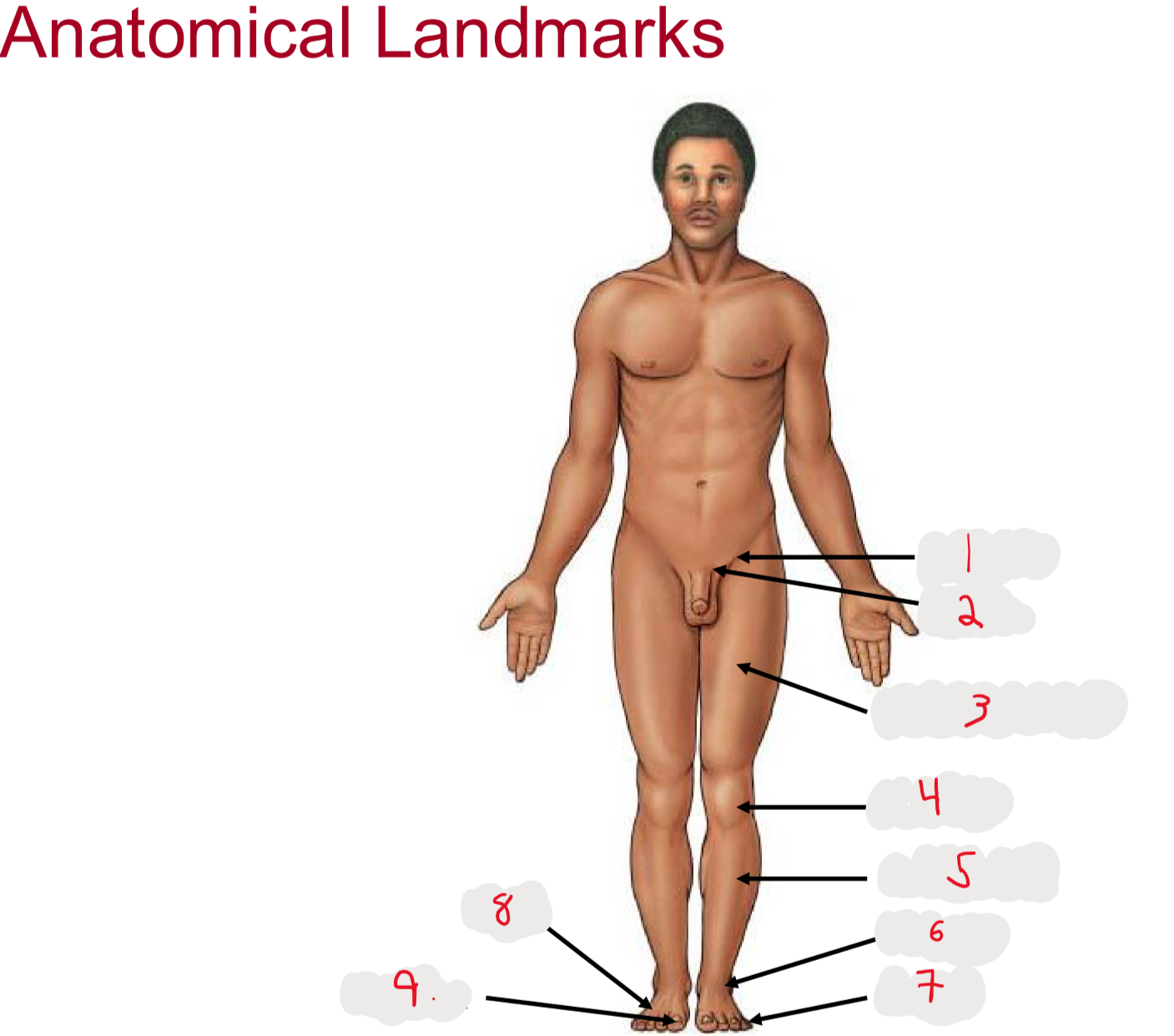
9
Hallux (big toe)
Anatomical Landmarks of Posterior Body
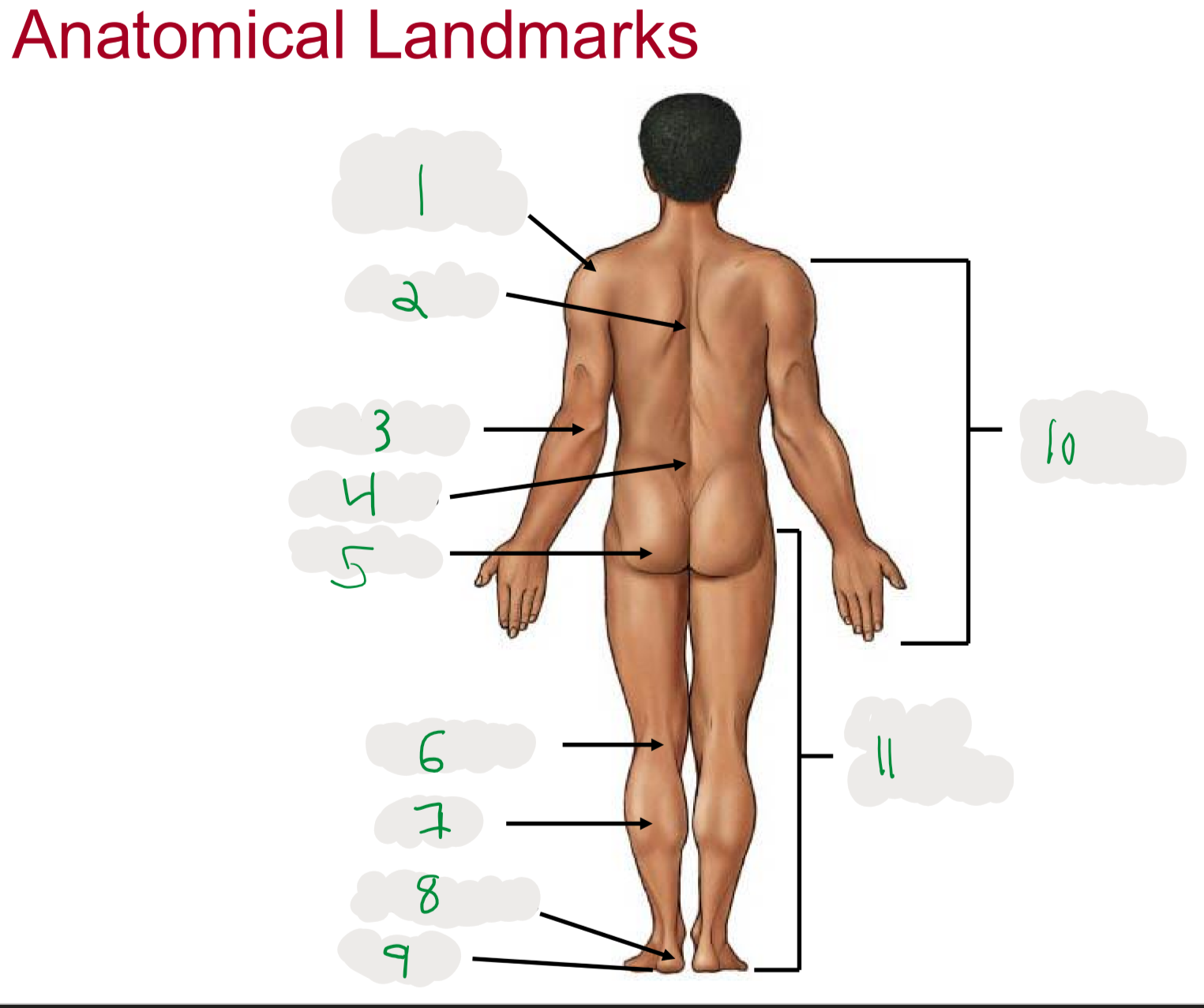
1
Shoulder (acromion)
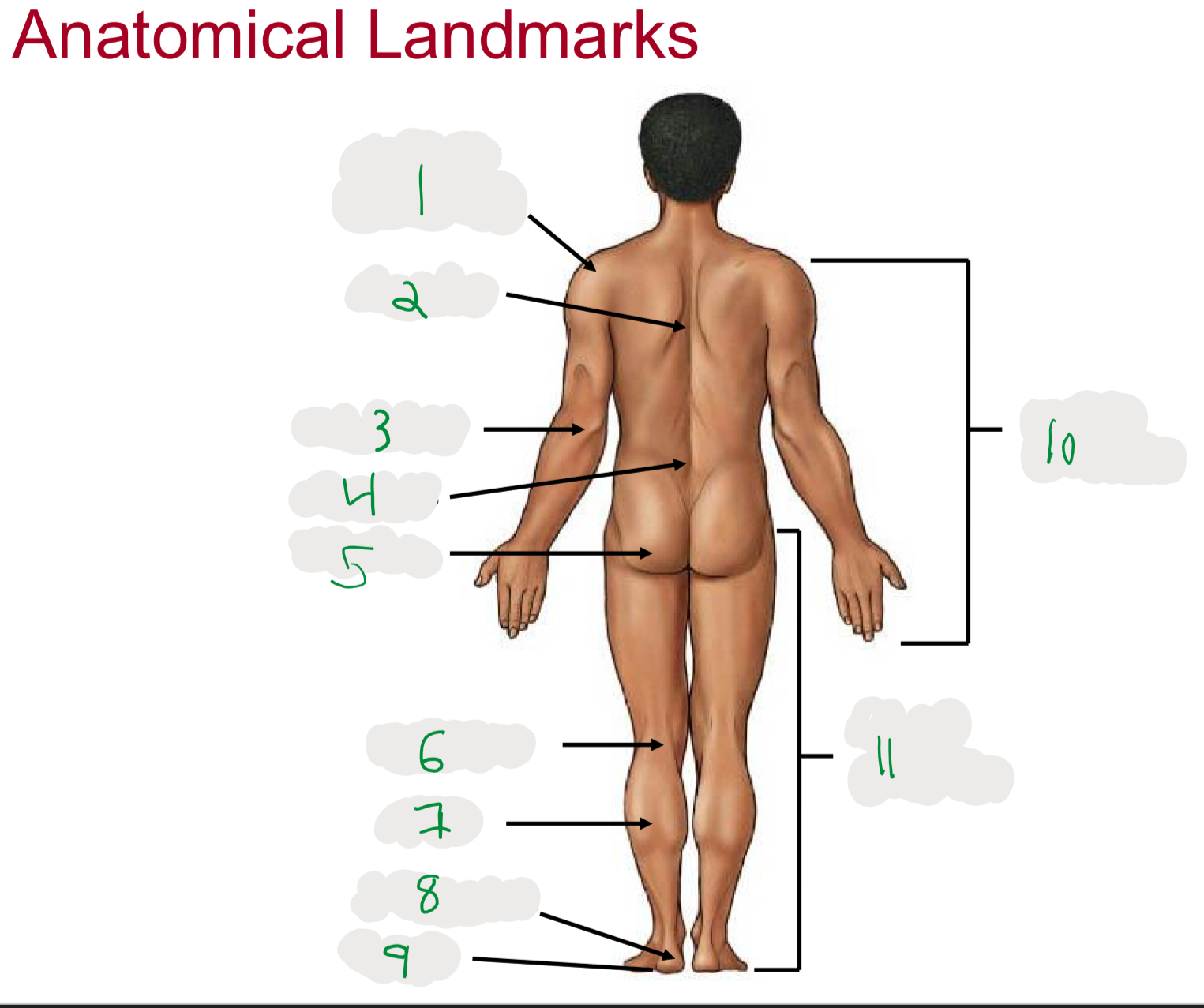
2
Dorsum (cord of upper back)
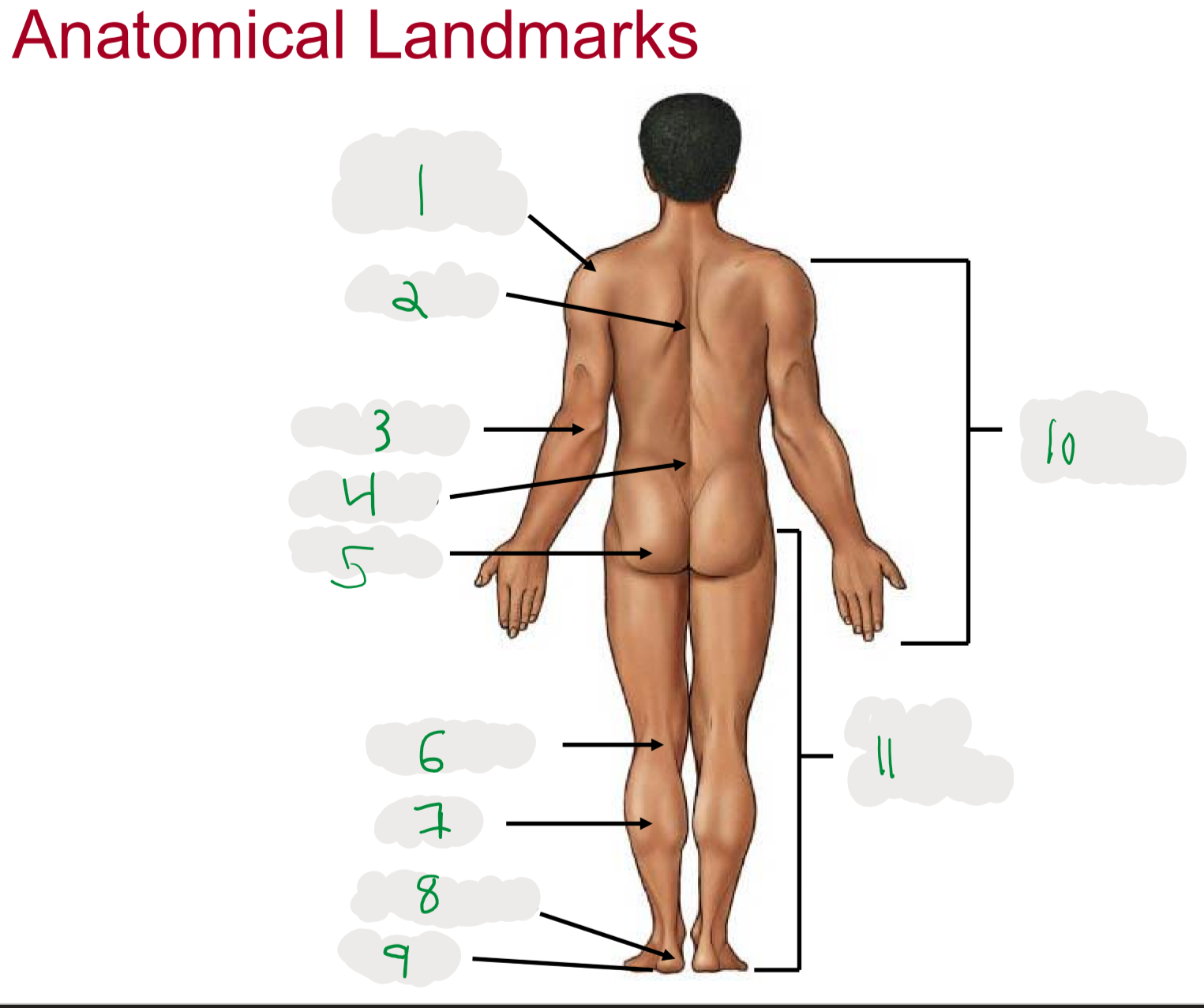
3
Olecranon (posterior portion of elbow)
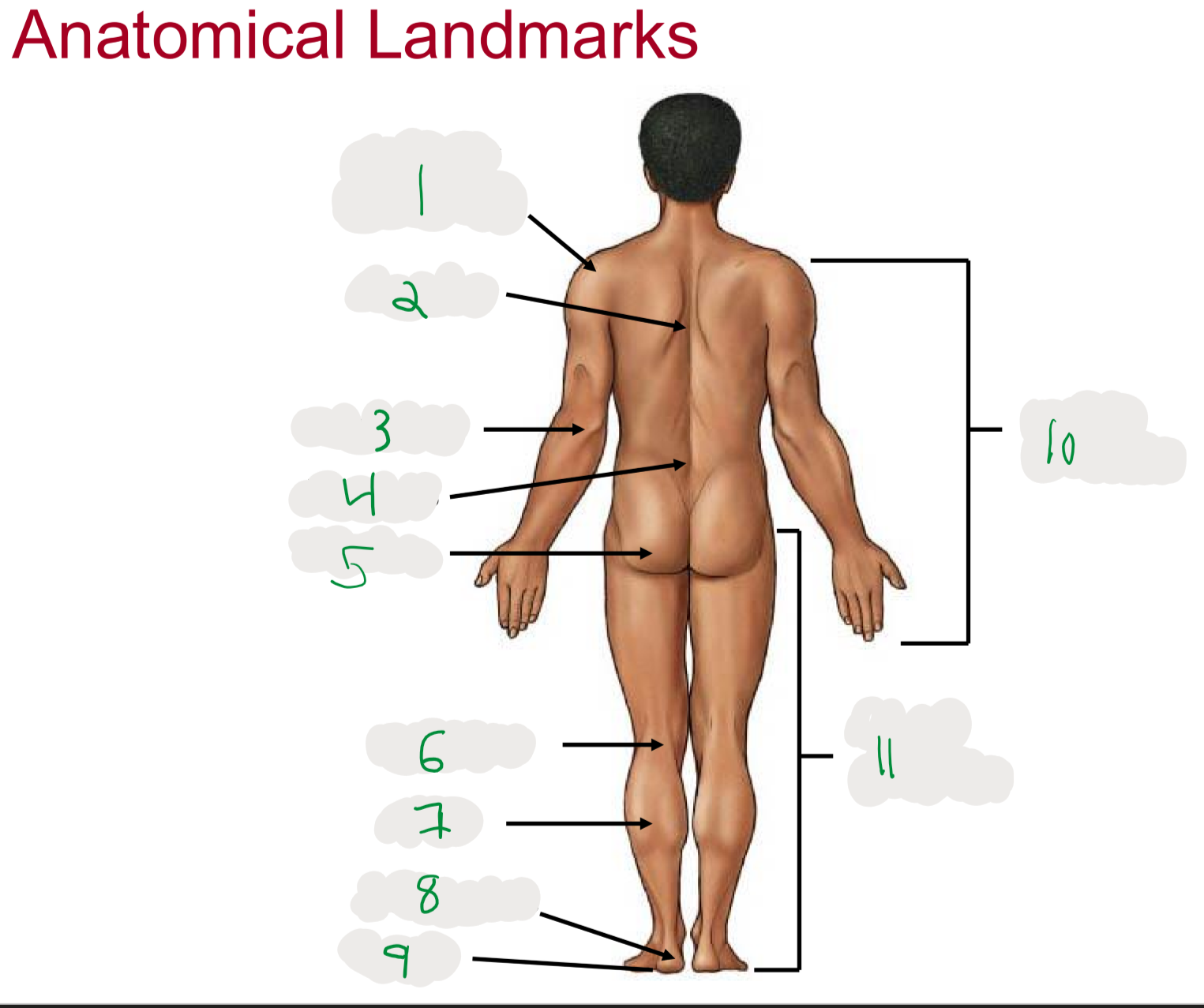
4
Lumbus (lower back)
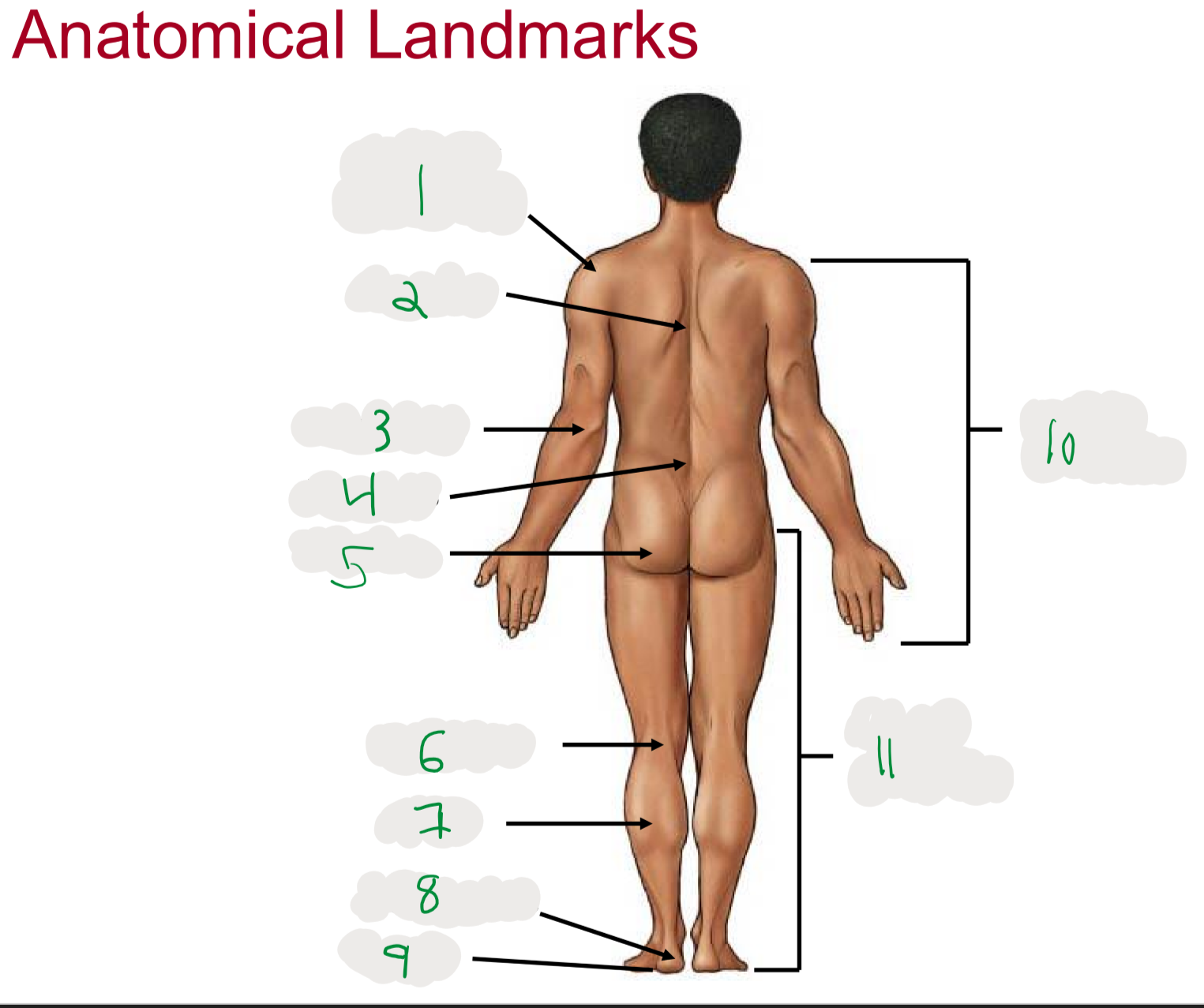
5
Gluteus (butt)
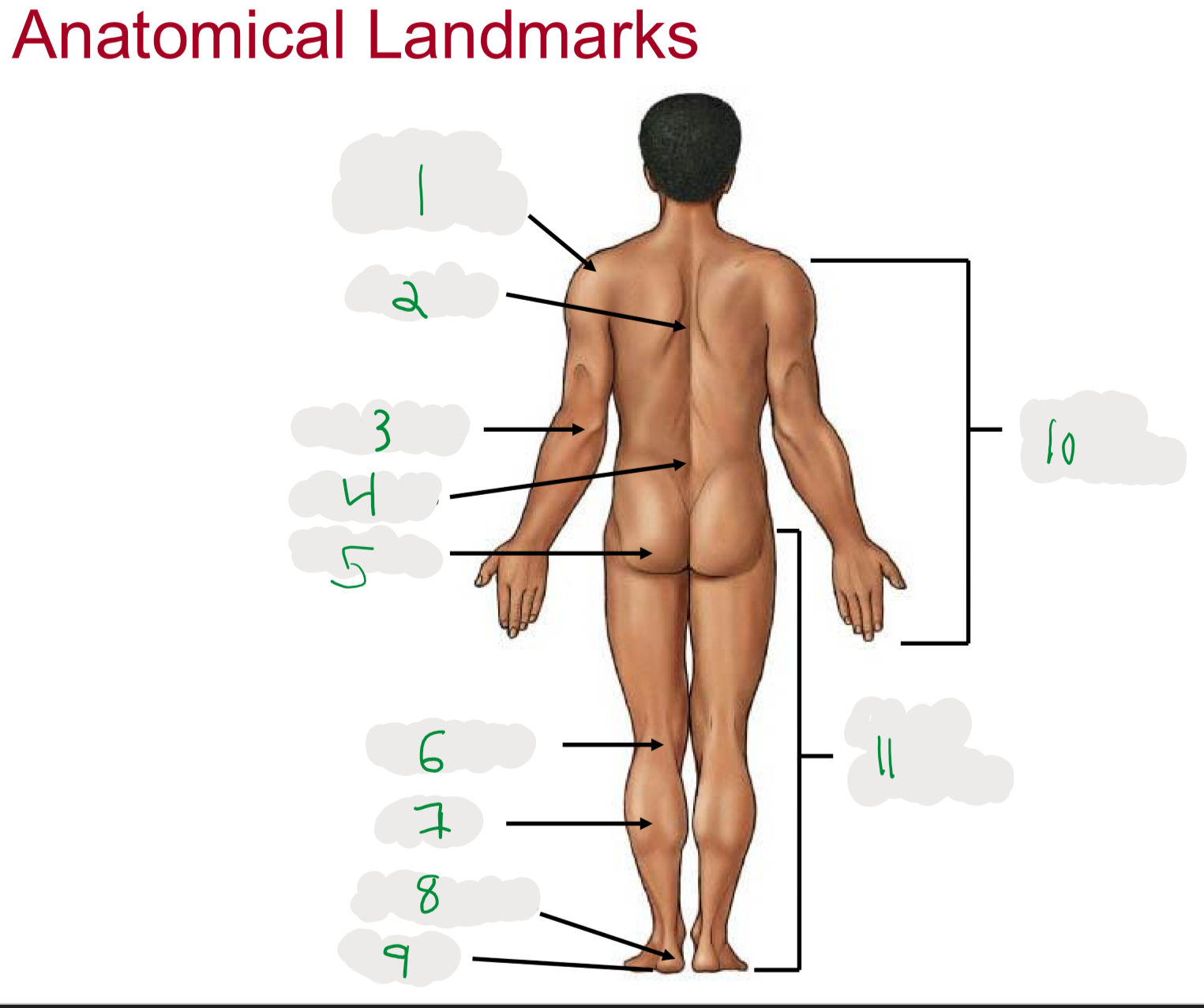
6
Popliteus (posterior portion of knee)
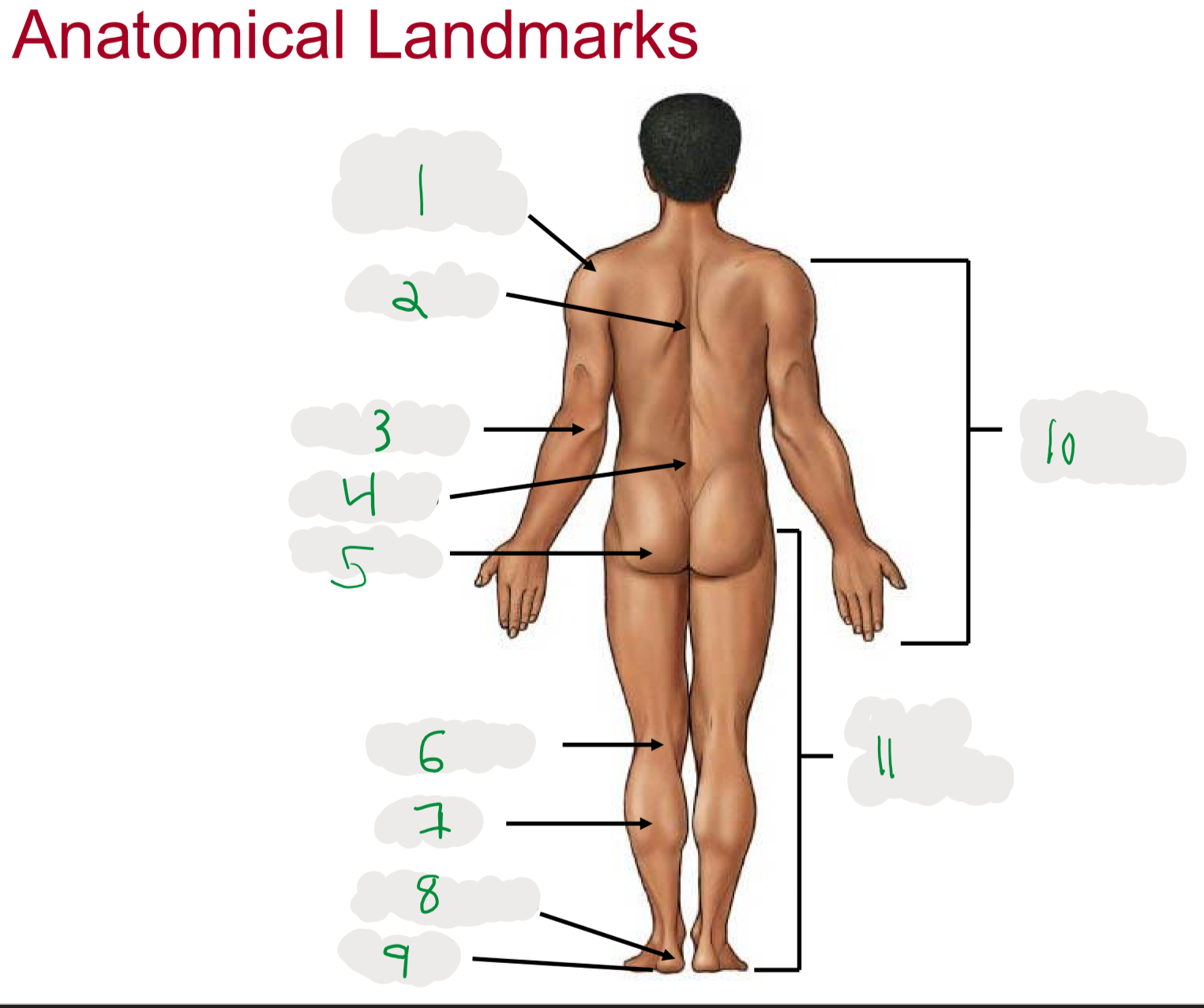
7
Sura (posterior aspect of leg)
not thigh
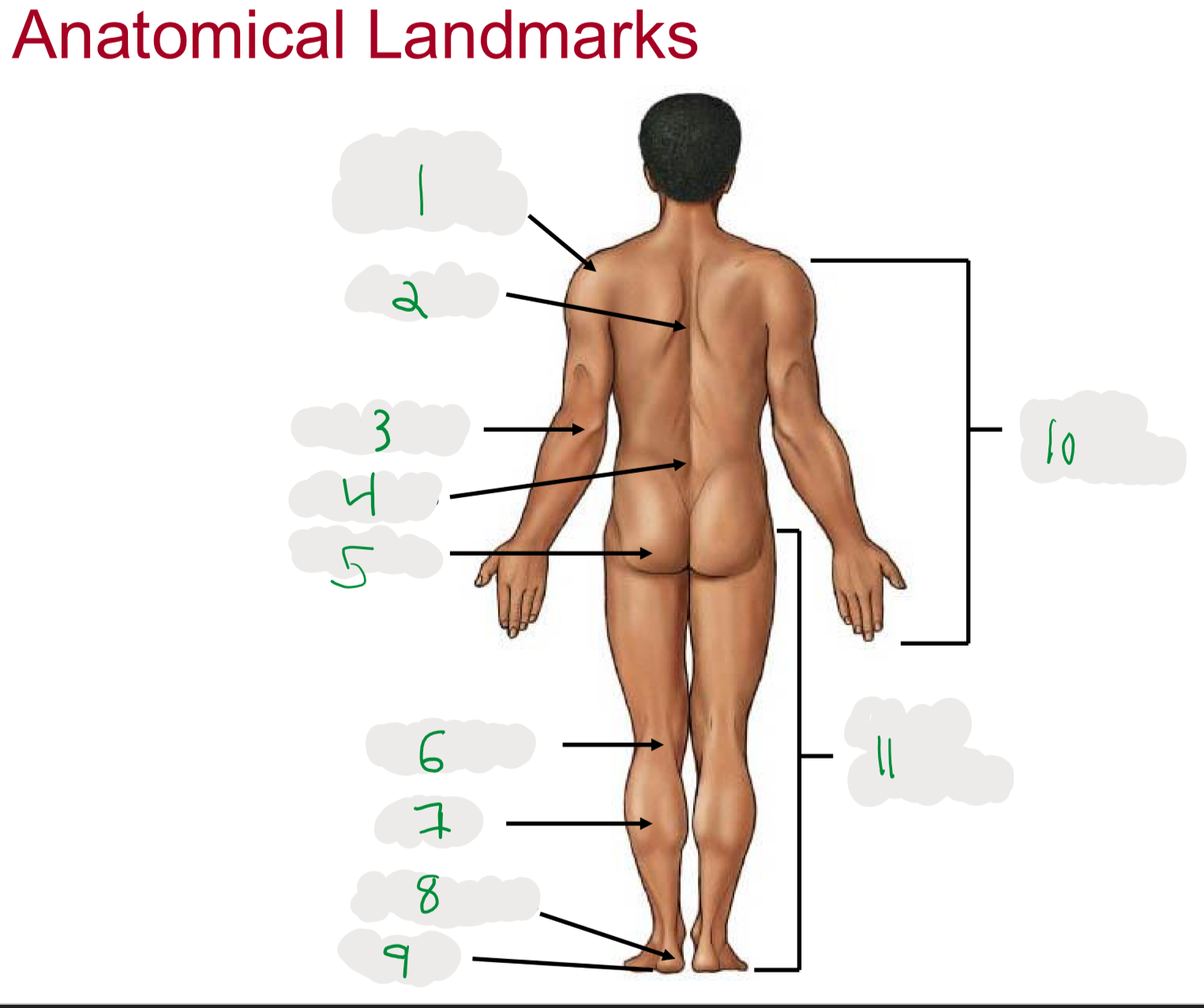
8
Calcaneus (heel)