Lecture 12 Viridiplantae and Rhodophytae
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What category includes Rhodophytae and Viridiplantae?
What are they?
What is their relationship?
Super kingdom Archaeplastida
Kingdoms
Sisters
Synapomorphies for Rhodophytae? Traits? How did they acquire chloroplast?
*Possess ability to produce carrageenan
(carbohydrate used as food additive)
*Possess ability to produce floridean
starch (polymer of glucose used for
energy storage)
Traits: phycoerythrin + phycocyanin, lack flagella
Acquired chloroplast through primary endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria to contain photosynthetic pigments
Synapomorphies for Viridiplantae?
Possesses chlorophyll A and B (in thylakoids)
Possess beta carotene
Starch storage in chloroplasts
Possess chloroplasts with stacks of thylakoids called grana
What does Viridiplantae include? What is an important sister group?
Green Algae (Chlorophyceae) and Embryophytes
Charophytes
What algae forms lichen?
Trebouxiophyceae
What are coenobia? What is a thallus?
When a colonial form of algae has a colony with a specific number and arrangement of cells.
A flat sheet
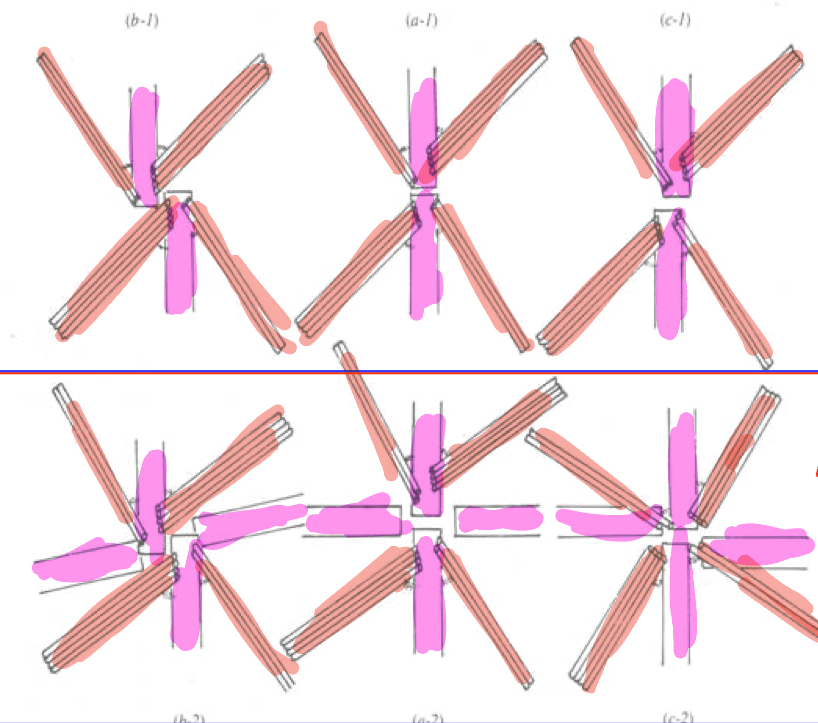
Describe the flagellar ultrastructure in this image
Top - Biflagellate
Bottom: Quadriflagellate
Left: Counter Clockwise
Right: Clockwise
All: Cruciate
What is different about charophyceae (and embryophyta) flagellar ultrastructure compared to chlorophyceae?
They have asymmetric flagellar roots as opposed to cruciate
This means only one side of the cell has a microtubular band
Open vs closed mitosis?
In open, the nuclear membrane breaks down during prometaphase. In closed, it persists until after the anaphase.
Persistent vs non-persistent spindle
In non-persistent, spindle breaks down before new nuclear membrane forms in telophase. In persistent, spindle persists in telophase until wall starts to form.
Difference between phragmoplast and phycoplast?
Phragmoplast is when the golgi and microtubules are laying perpendicular to the plane of division
Phyco is when they are parallel to the plane of division
What do embryophytes and Charophyceae have in common?
Asymmetric flagella with MLS, open mitosis with persistent spindle, phragmoplast.