Abdominal cavity: contents and peritoneal spaces (Cavities L4)
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
abdominal cavity boundaries
-above: diaphragm (thoracic outlet)
-below: pelvic inlet
-anterior/lateral/posterior abdominal walls
abdominal cavity
-broken into 4 quadrants defined by vertical line through midsagittal plane and a horizontal line through umbilicus (~L4)
pelvic inlet
-pubic symphysis
-pectin pubis
-arcuate line (pelvic brim)
-sacral promontory
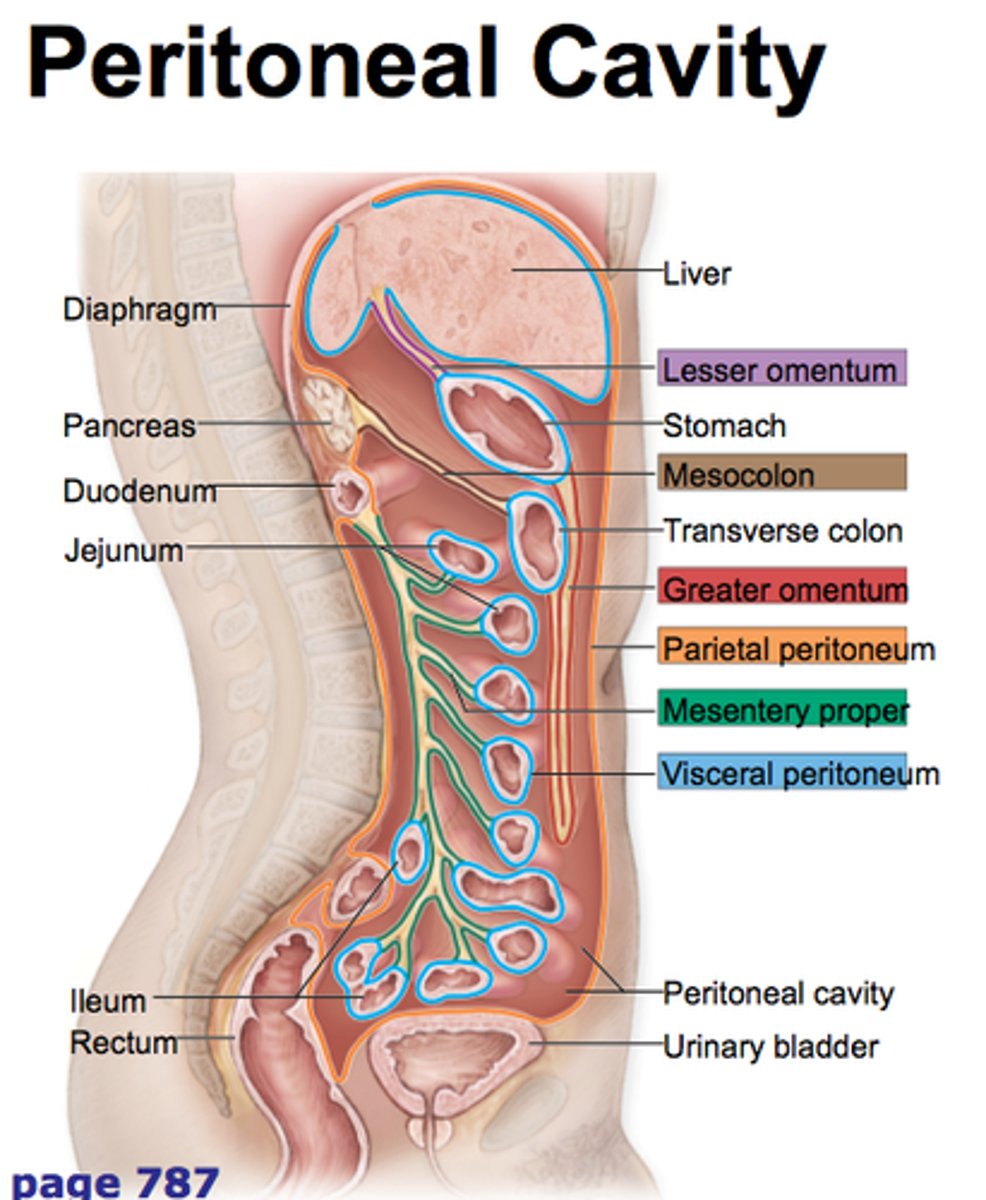
Lining of the peritoneum
-parietal: lines abdominal cavity
-visceral: covers the viscera
Development of the peritoneum
-in fetus peritoneum lines the abdominal cavity like a large sac that before organs develops
-many organs push into the sac as they grow and are surrounded
vessels and nerves to organs
-often run btwn peritoneal layers surround the organ
intraperitoneal organs
-grow into the peritoneal sac and get covered by it
retroperitoneal organs
-organs that don't grow into the peritoneal sac
visceral and parietal peritoneum
-as organs grow into the peritoneal sac the peritoneal cavity disappears and small potential and/or real spaces are left behind
peritoneal ligaments
-falciform ligament attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall
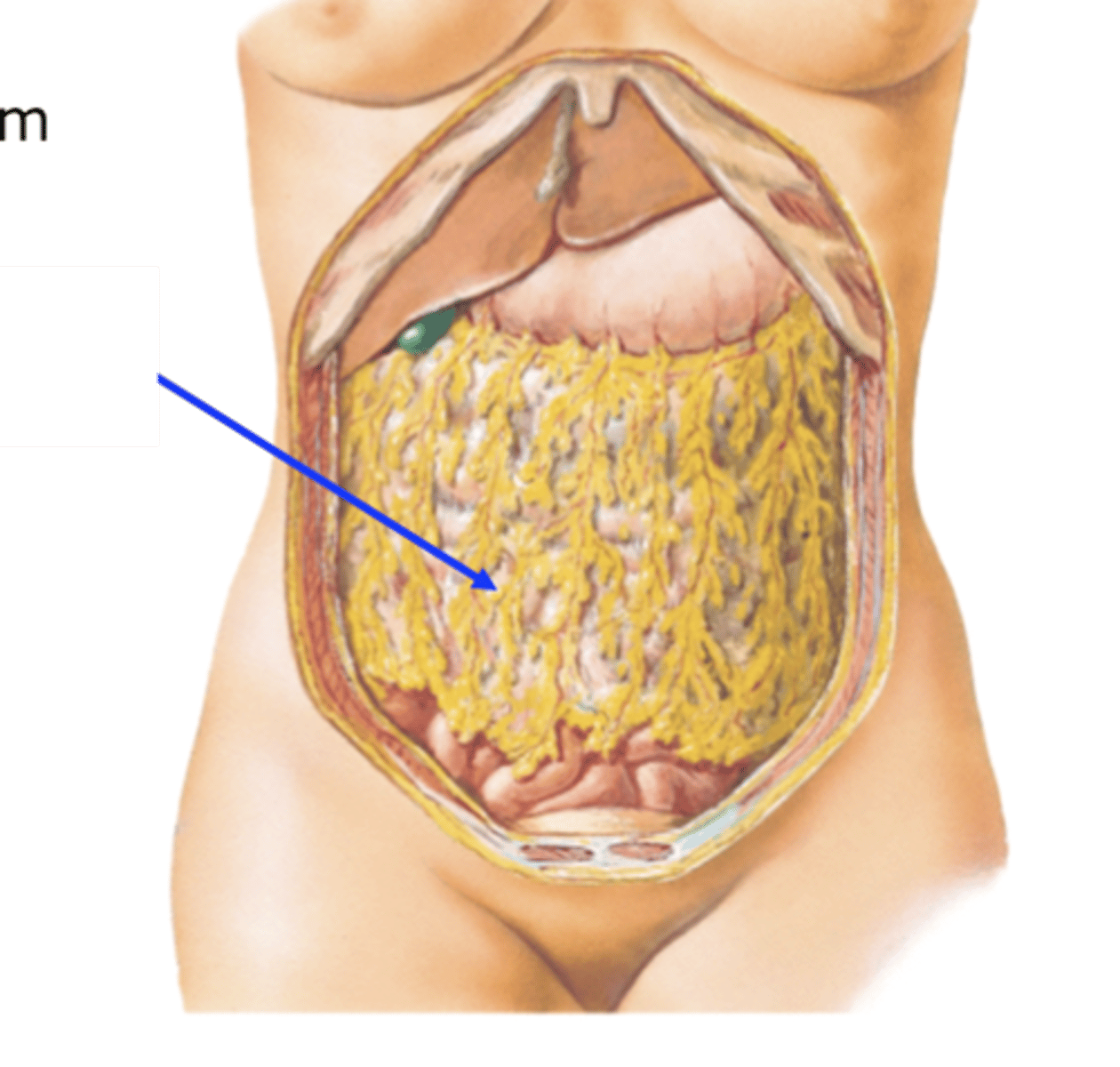
greater omentum
-attached to greater curvature of the stomach and transverse colon.
-usually covers small intestine
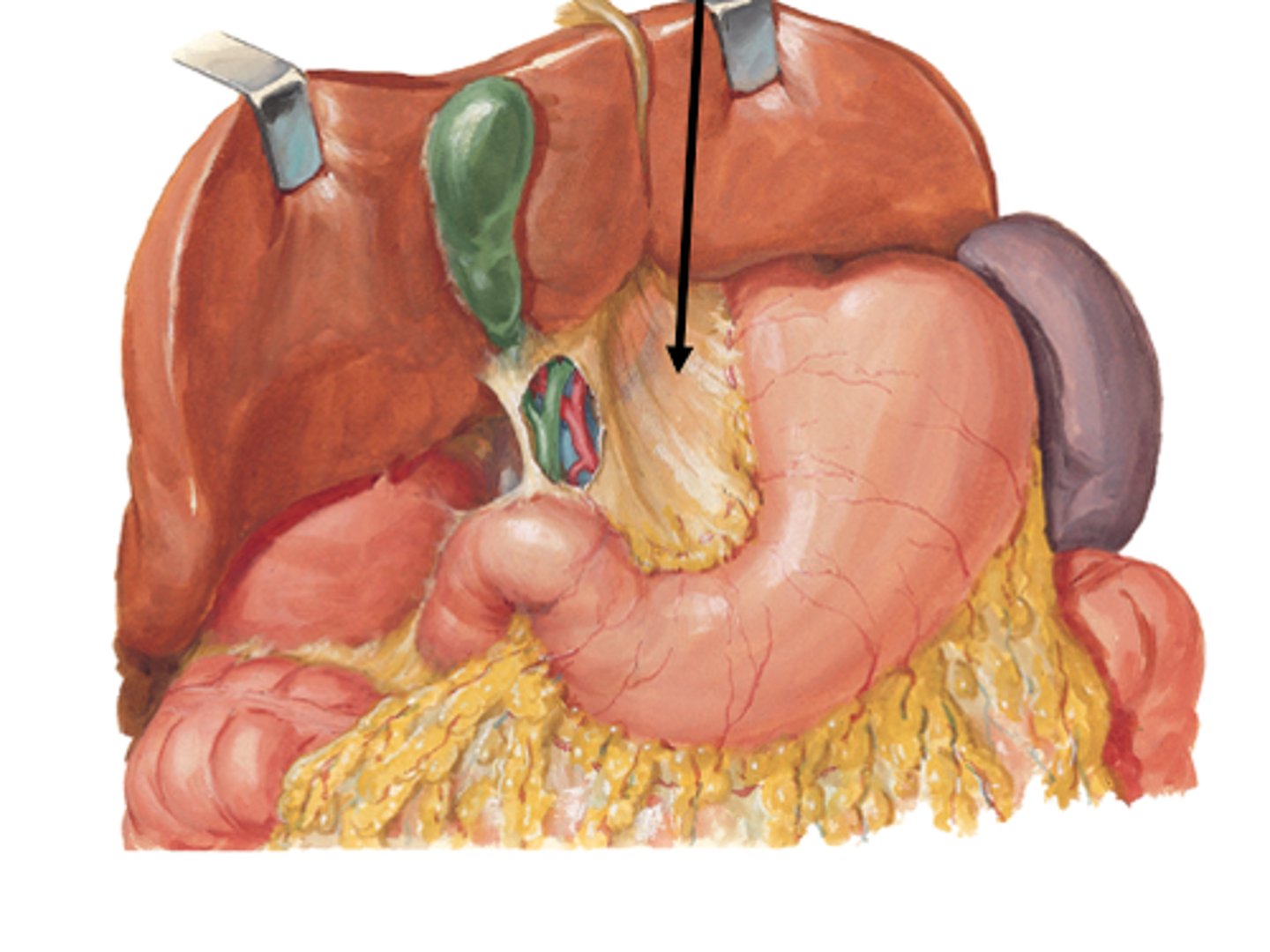
lesser omentum
-attached to lesser curvature of the stomach, to the liver and from the liver to the duodenum
peritonitis
-inflammation of the peritoneum (membrane lining the abdominal cavity and surrounding the organs within it)
-can lead to fluid buildup
ascites
accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity
mesentery
-attaches the small intestine to the posterior abdominal wall
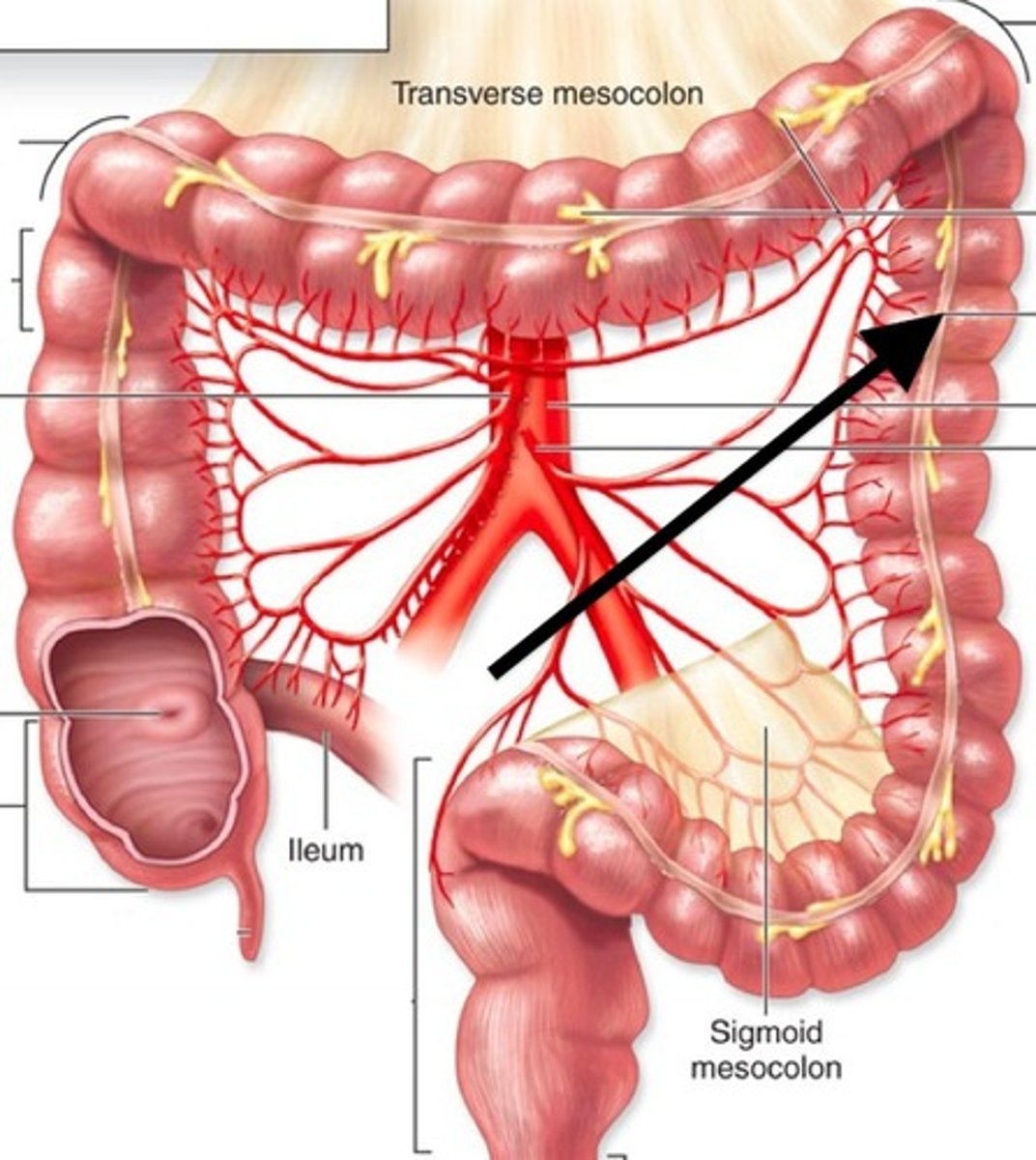
transverse mesocolon
-mesentery that attaches the transverse colon to the posterior abdominal wall
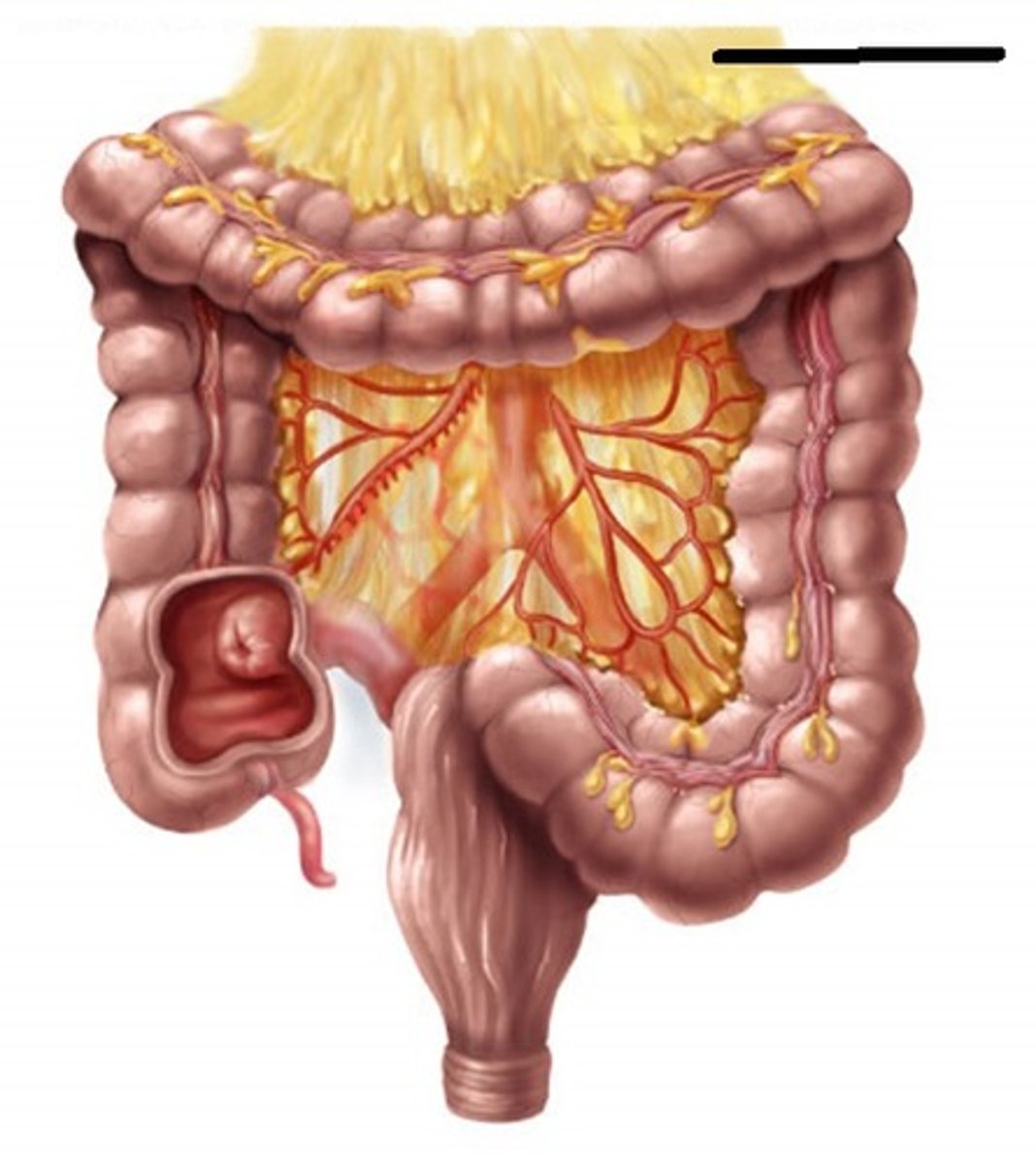
sigmoid mesocolon
-Mesentery that attaches the sigmoid colon to the posterior abdominal wall
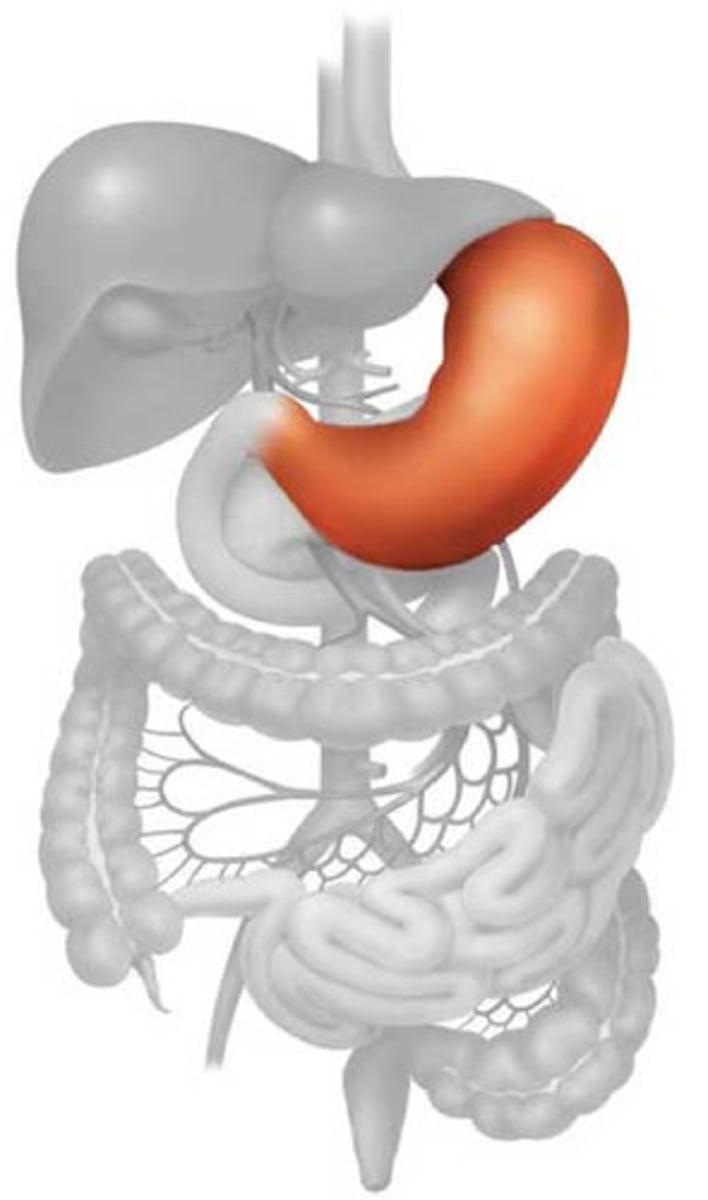
Stomach
-intraperitoneal
-found mostly in upper left quadrant
-attached to lesser omentum (lesser curvature) and greater omentum (greater curvature)
-has 4 regions: cardia, fundus, body, pyloric
-functions as a reservoir of food, mechanical blender, chemical breakdown of food
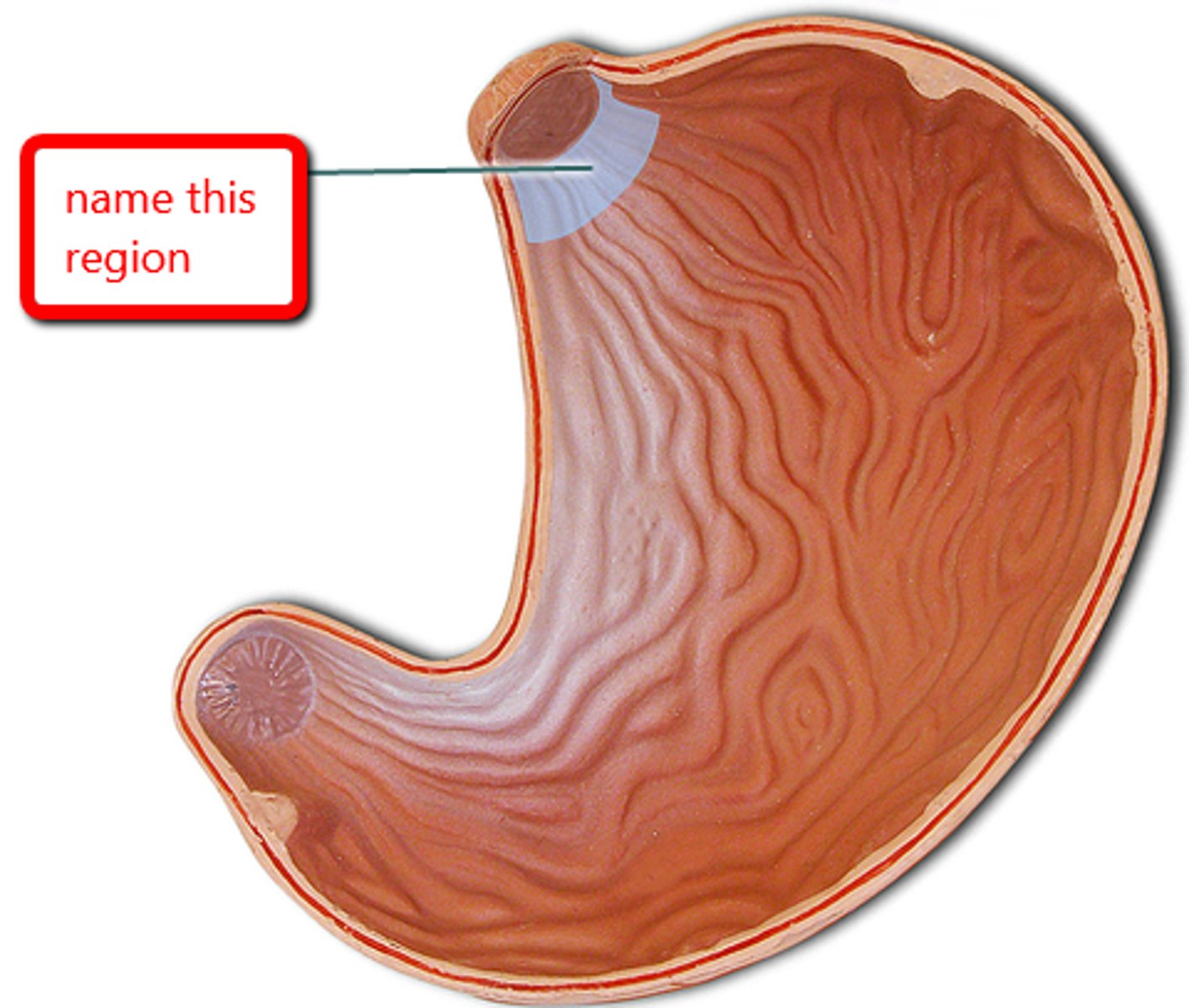
stomach cardia
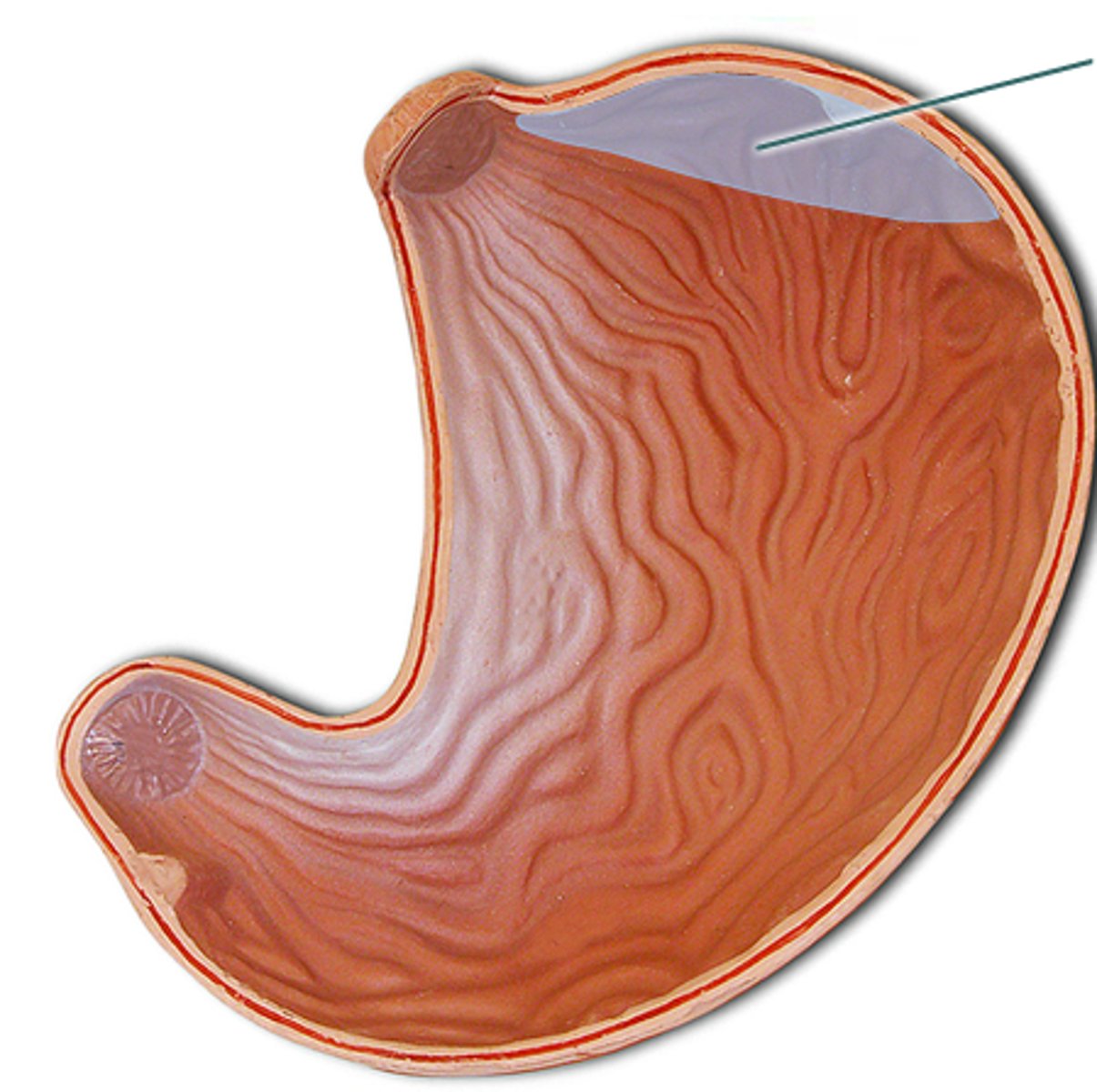
stomach fundus
dome-shaped region beneath diaphragm
stomach body
largest region; functions as a mixing tank; contains gastric glands
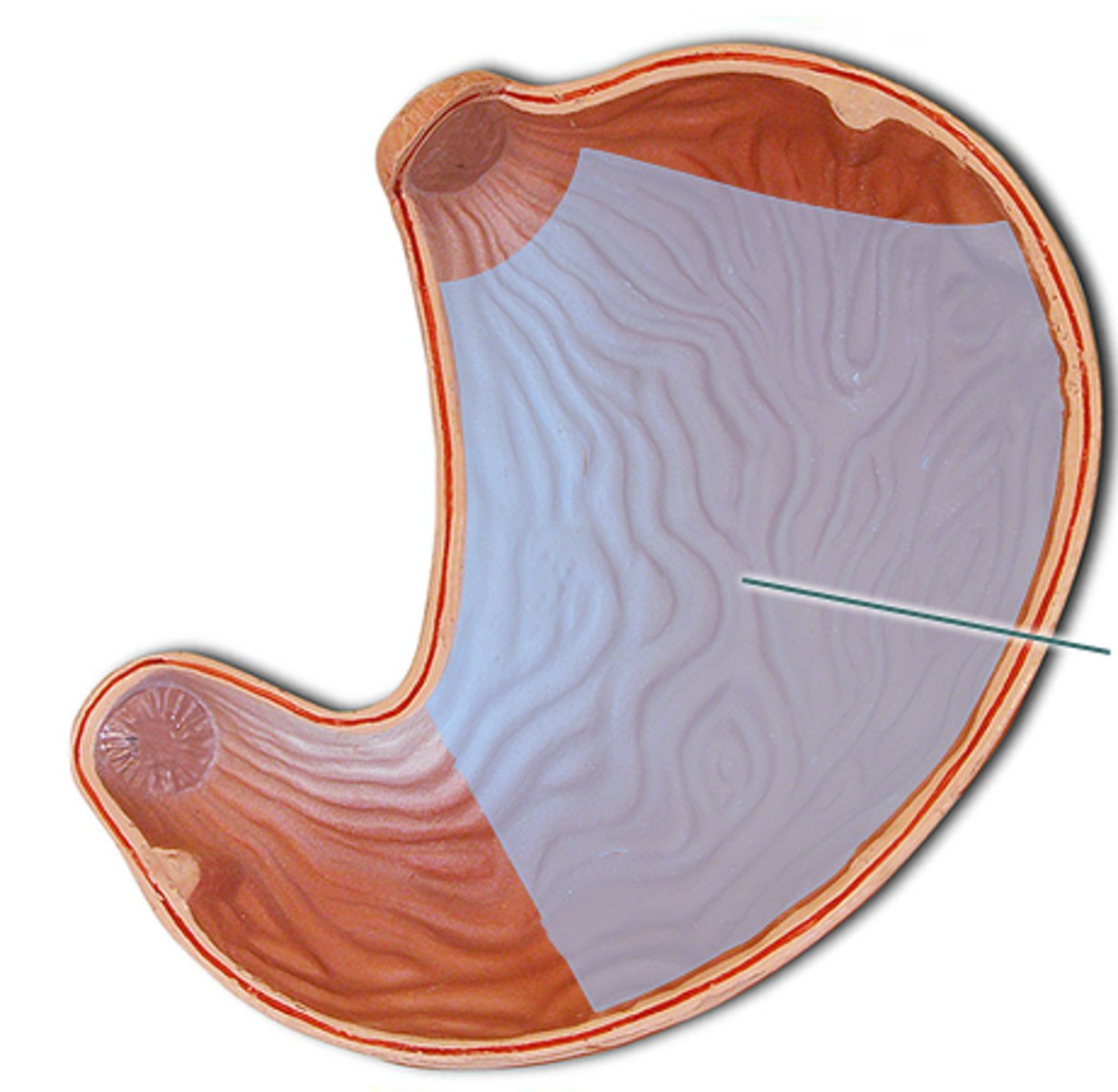
stomach pylorus
region of the stomach leading to small intestine, connects to small intestine
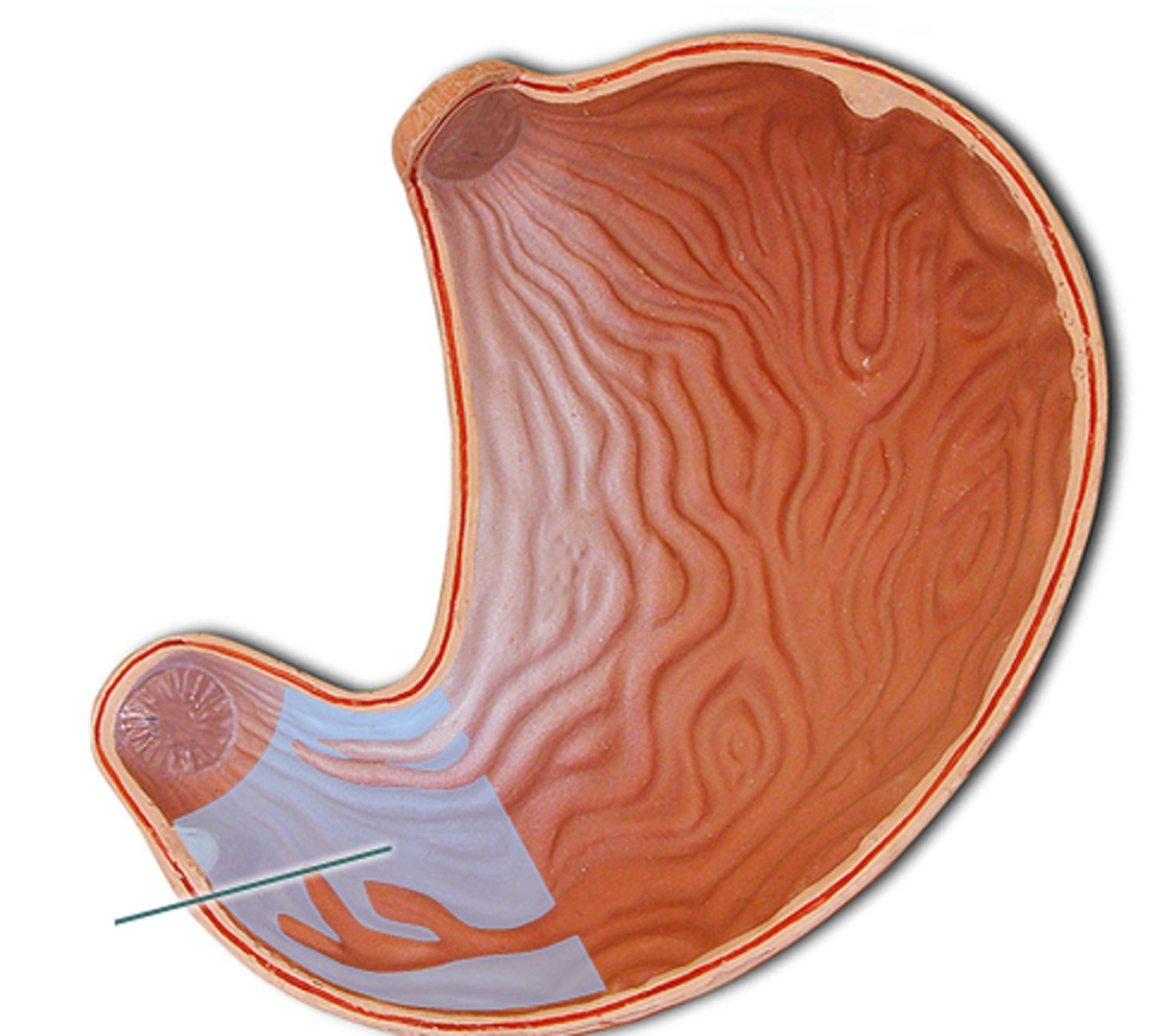
What attaches to the cardiac region of the stomach?
-esophagus
What attaches to the pyloric region of the stomach
-duodenum
What is the function of the esophageal sphincter?
-to prevent acid reflux from stomach back to esophagus
-if it doesn't work you get GERD, regurg, which can mimic MI
What is the function of the pyloric sphincter?
-control flow from stomach to small intestine
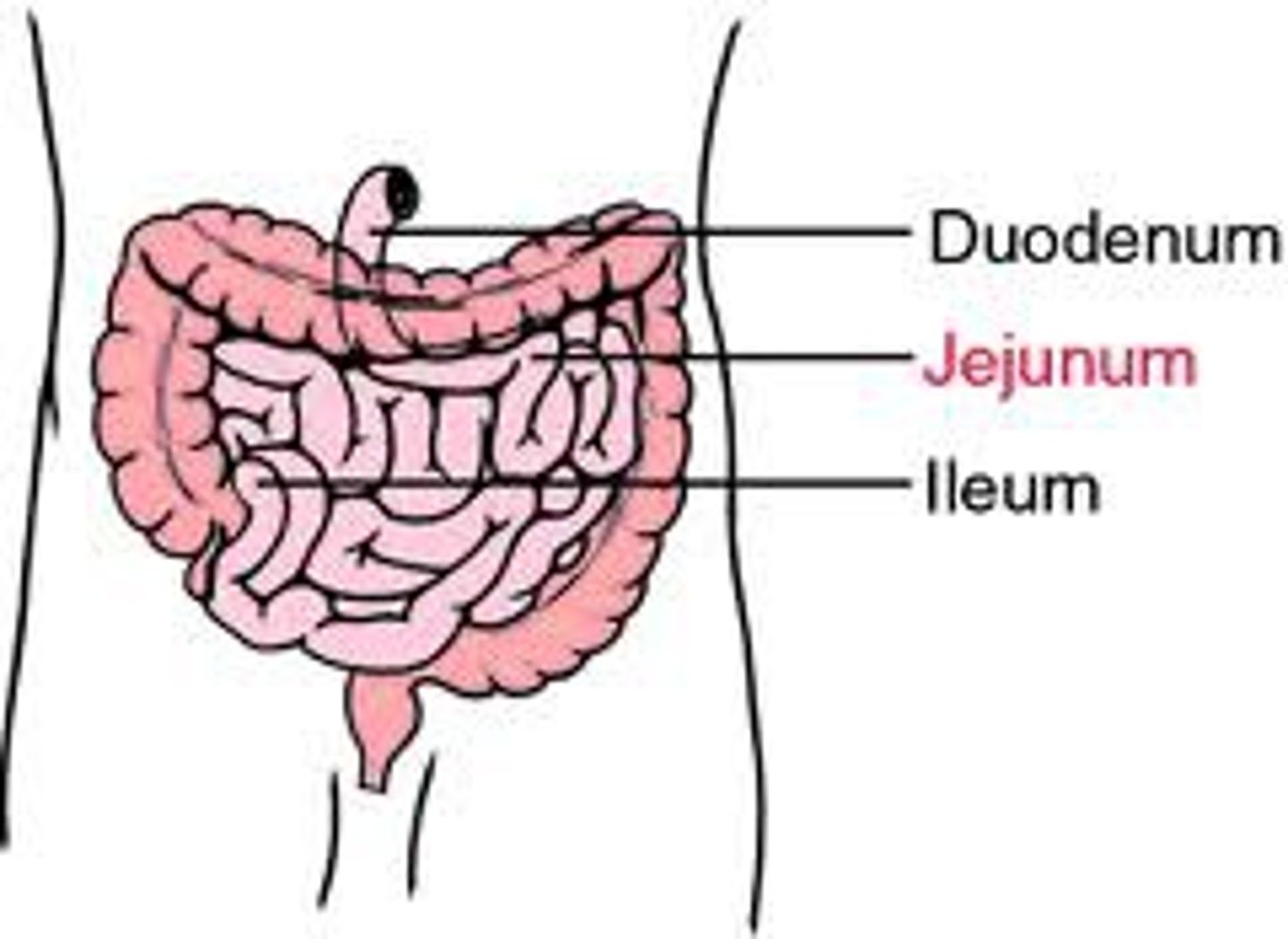
Small intestine
-made of duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
-takes up most of anterior abdominal cavity
-function is absorption and secretion of food and water
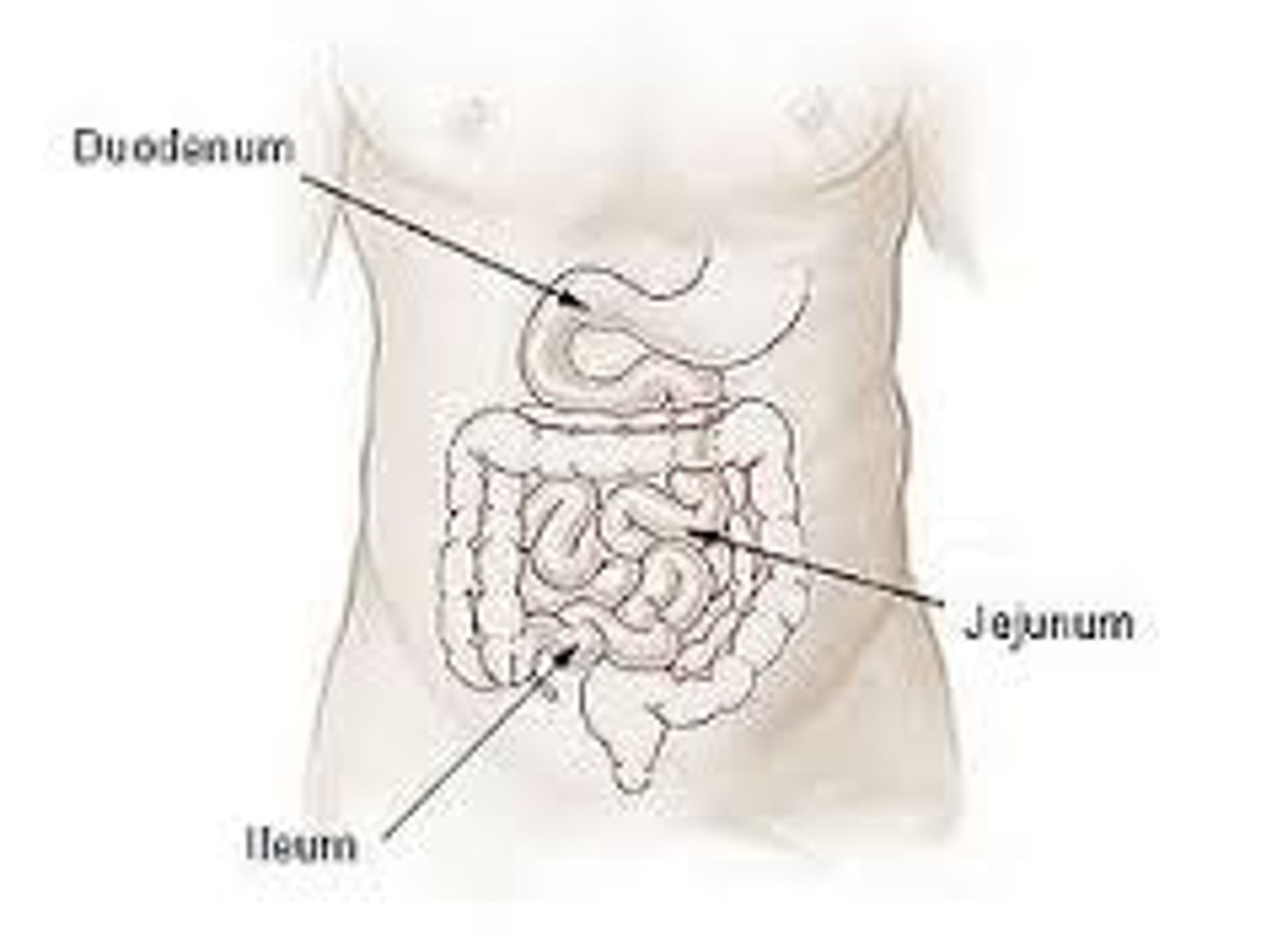
duodenum
-retroperitoneal
-upper right quadrant
-short
-C shaped
-pancreas sits in concavity attached to duodenum
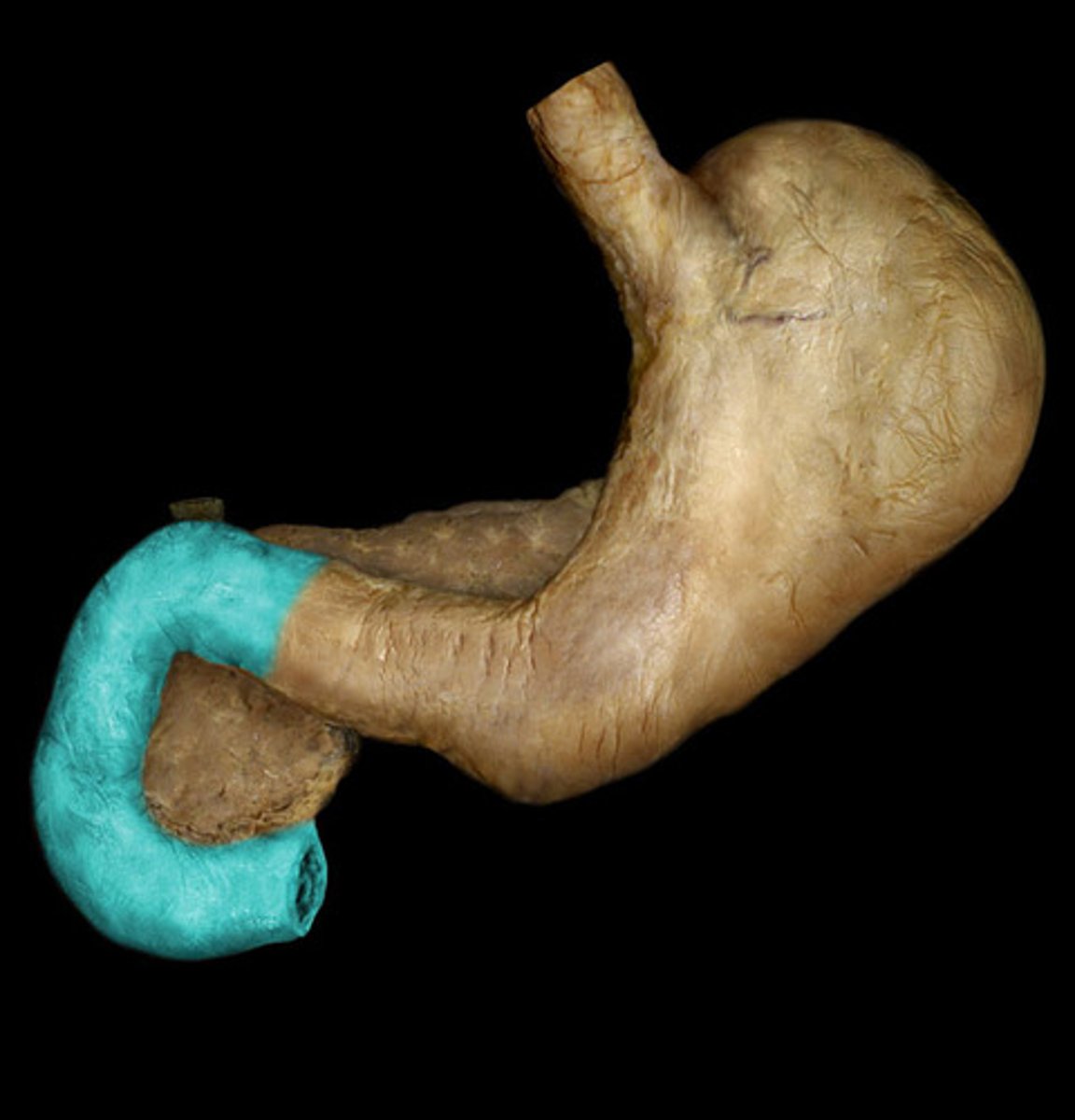
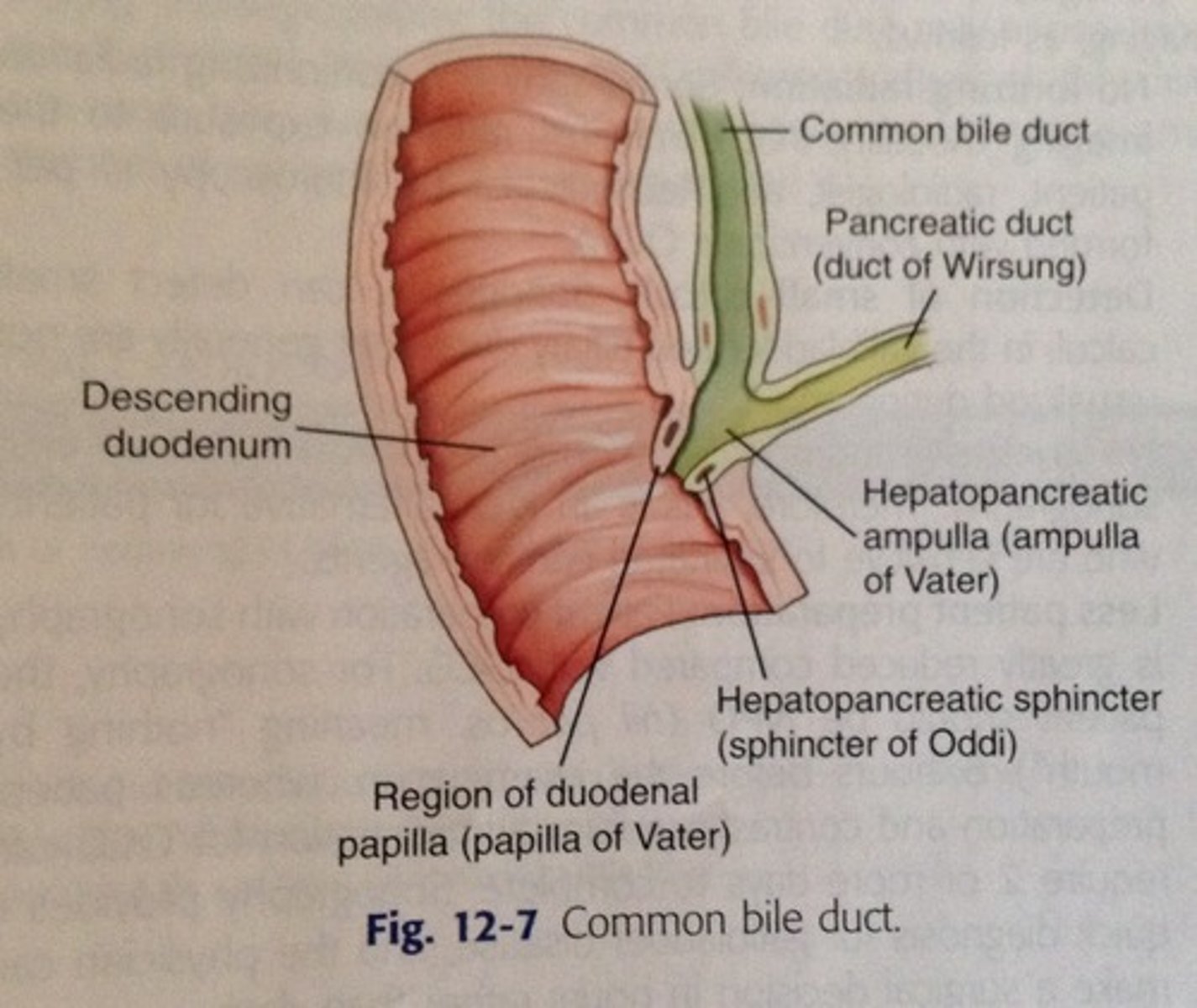
pancreatic duct
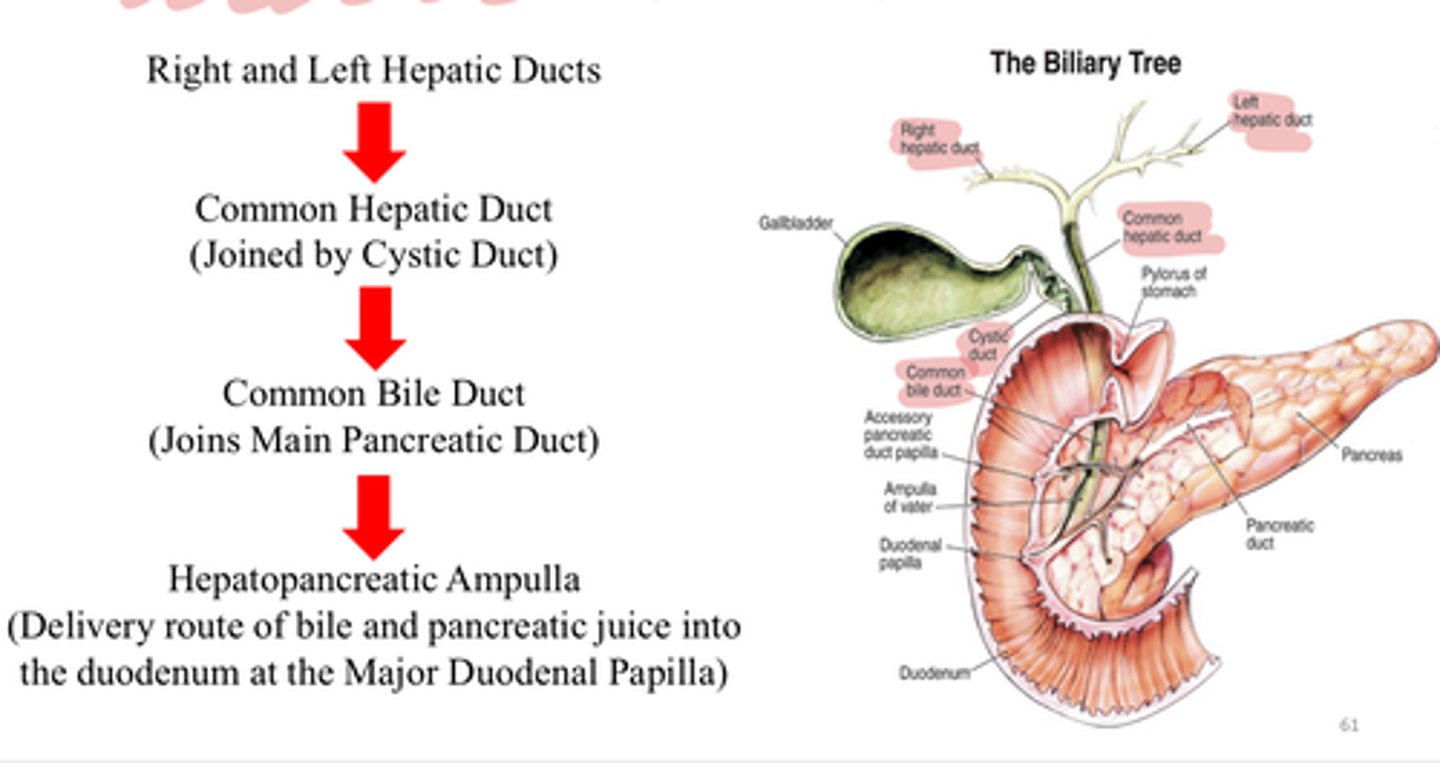
-merges with common bile duct (common hepatic duct+cystic duct) and forms hepatopancreatic ampulla
-allows enzymes, hormones, etc from pancreas to be released into duodenum at the hepatopancreatic sphincter (sphincter of Oddi)
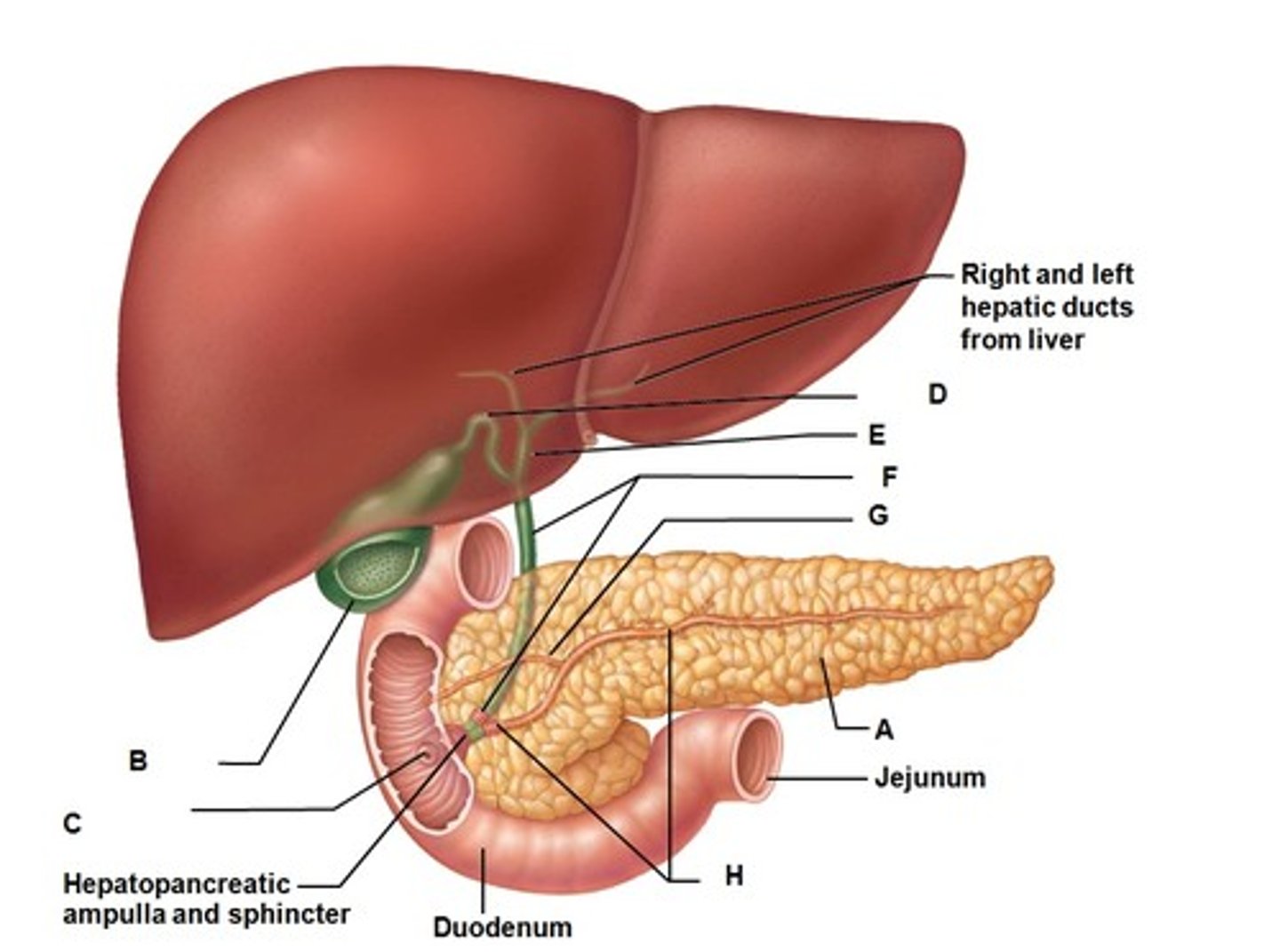
hepatopancreatic sphincter
controls entry of bile and pancreatic juice into duodenum
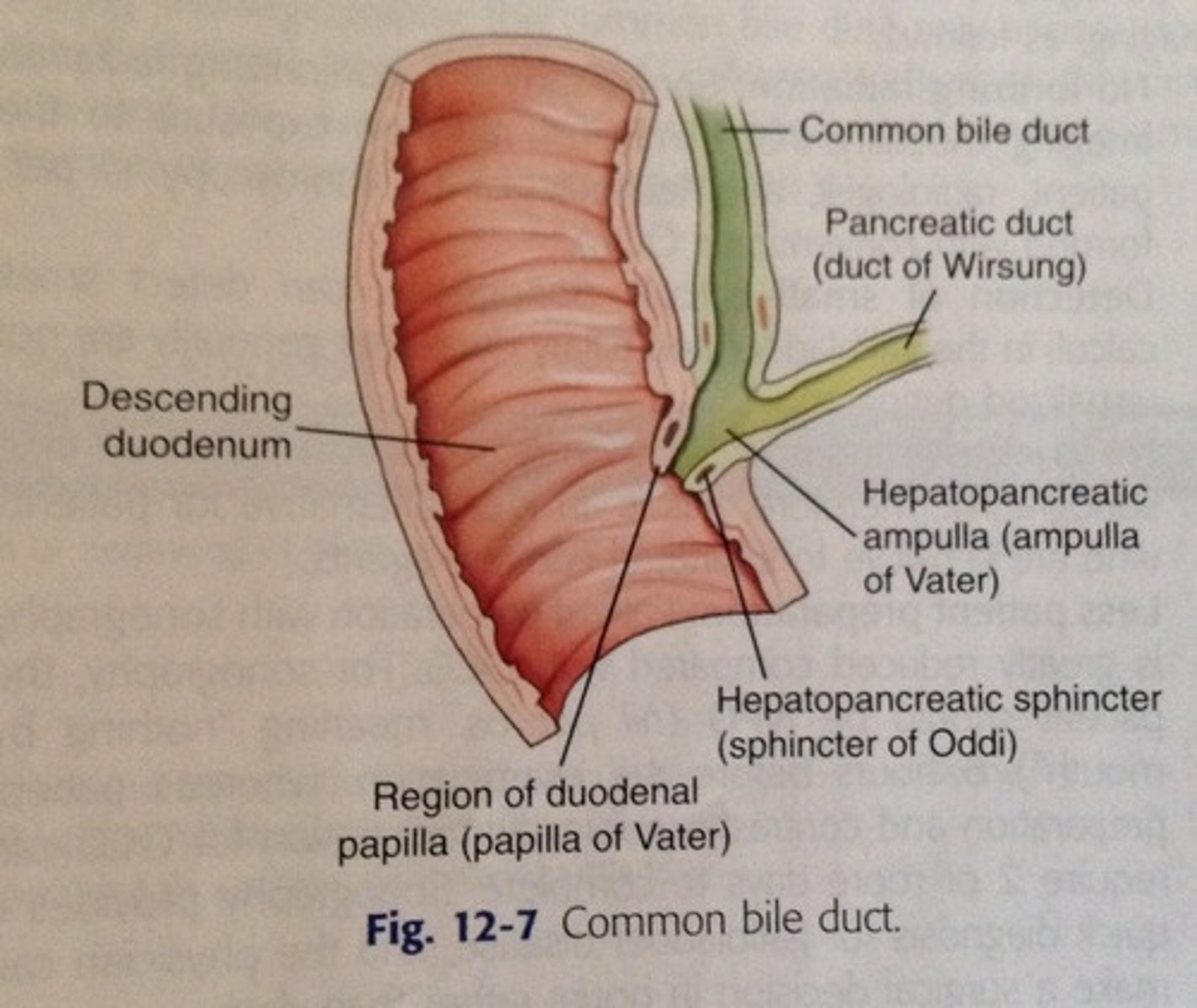
hepatopancreatic ampulla
Connection of the common bile duct (brings in bile) and the pancreatic duct (brings enzymes & juices) to the duodenum
jejunum
-intraperitoneal
-upper left quadrant (but mostly in lower right&left)
-start where small intestine becomes intraperitoneal
-roughly 6-7 m long
-shorter than the ileum
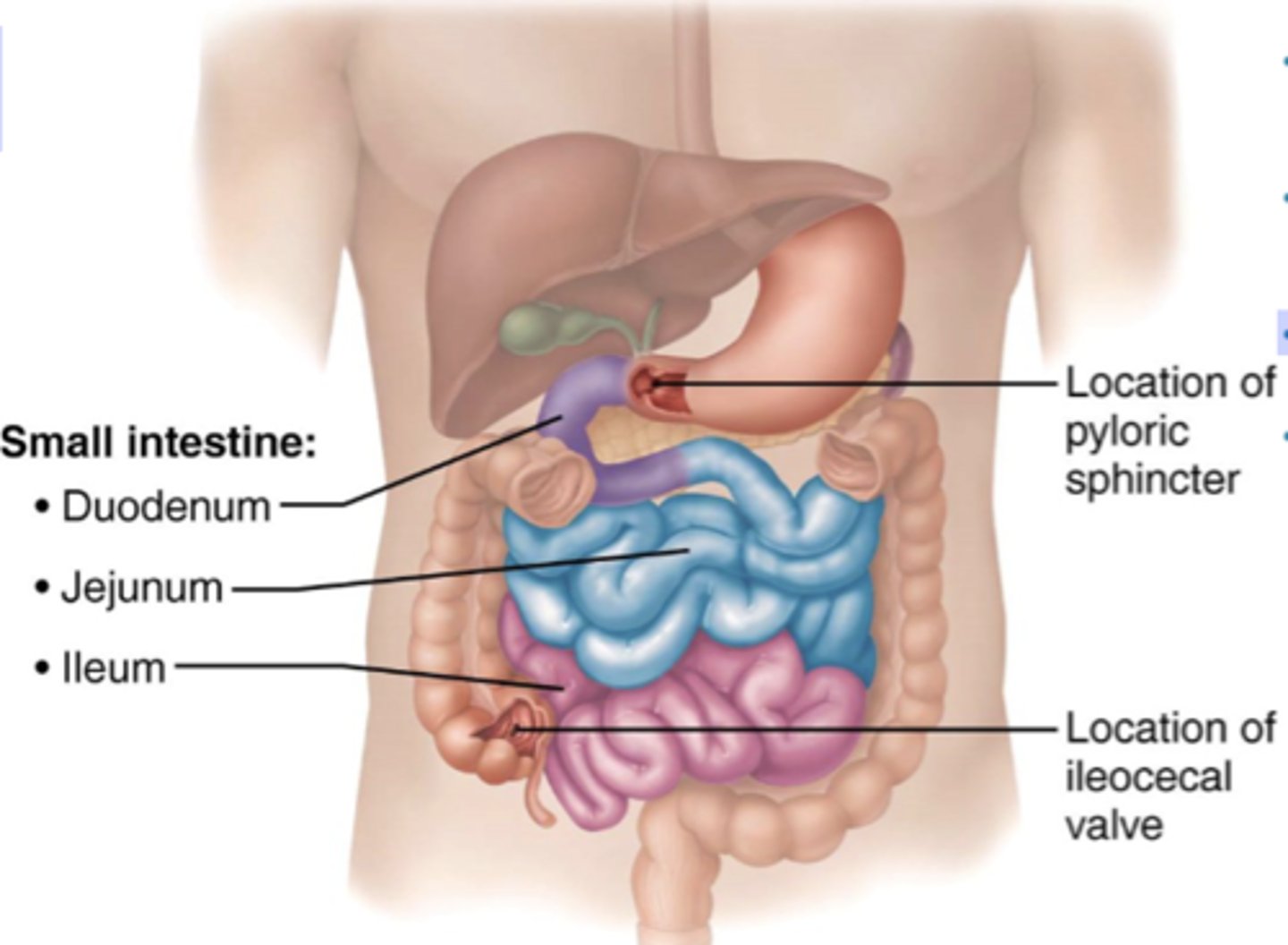
ileum
-intraperitoneal
-lower right and left quadrants
-start where small intestine becomes intraperitoneal
-roughly 6-7 m long
-longer than the ileum (60%)
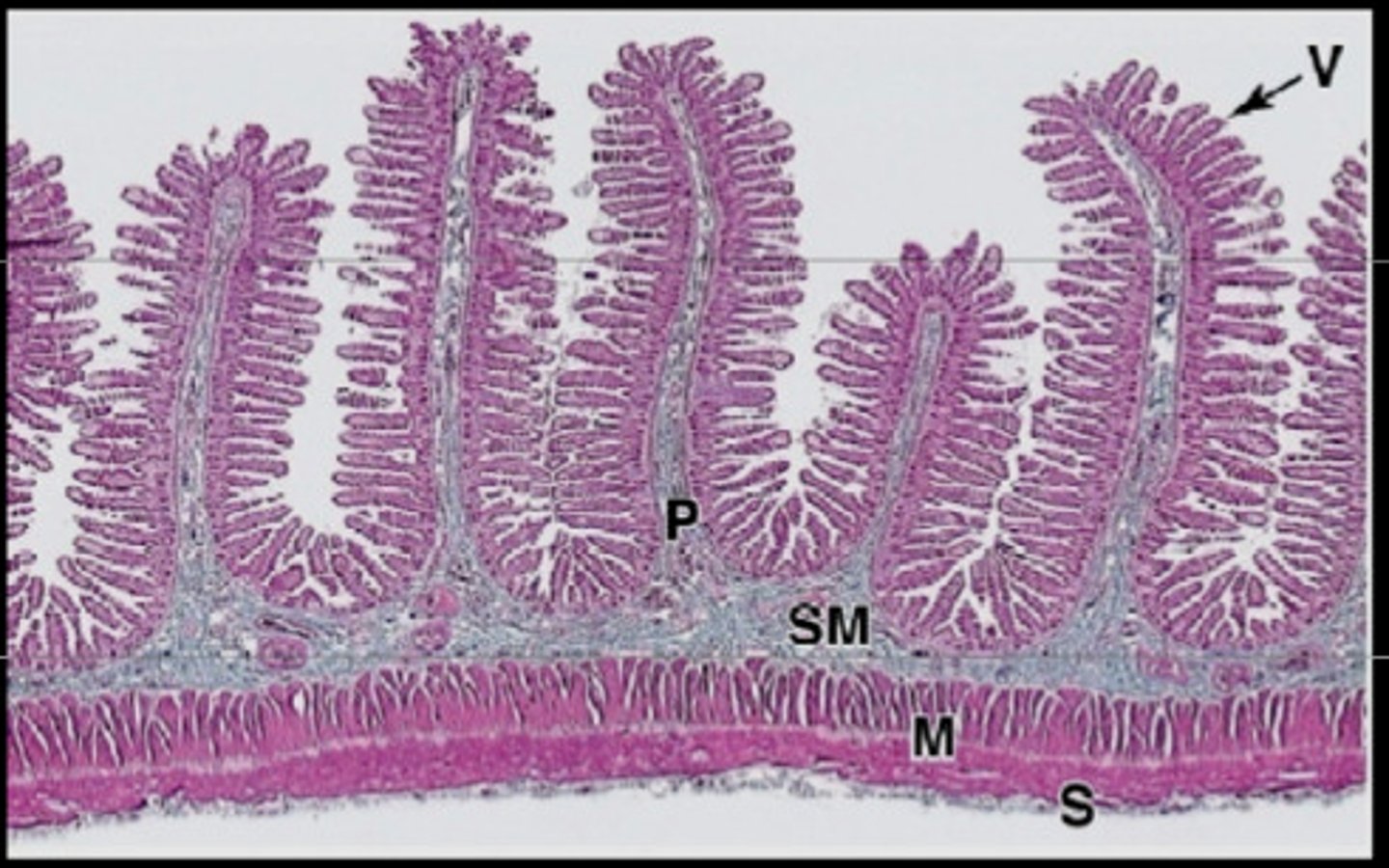
histology of the small intestine
-plicae circularis
-villi
-microvilli
-all increase surface area of small intestine
plicae circulares
circular folds in small intestine
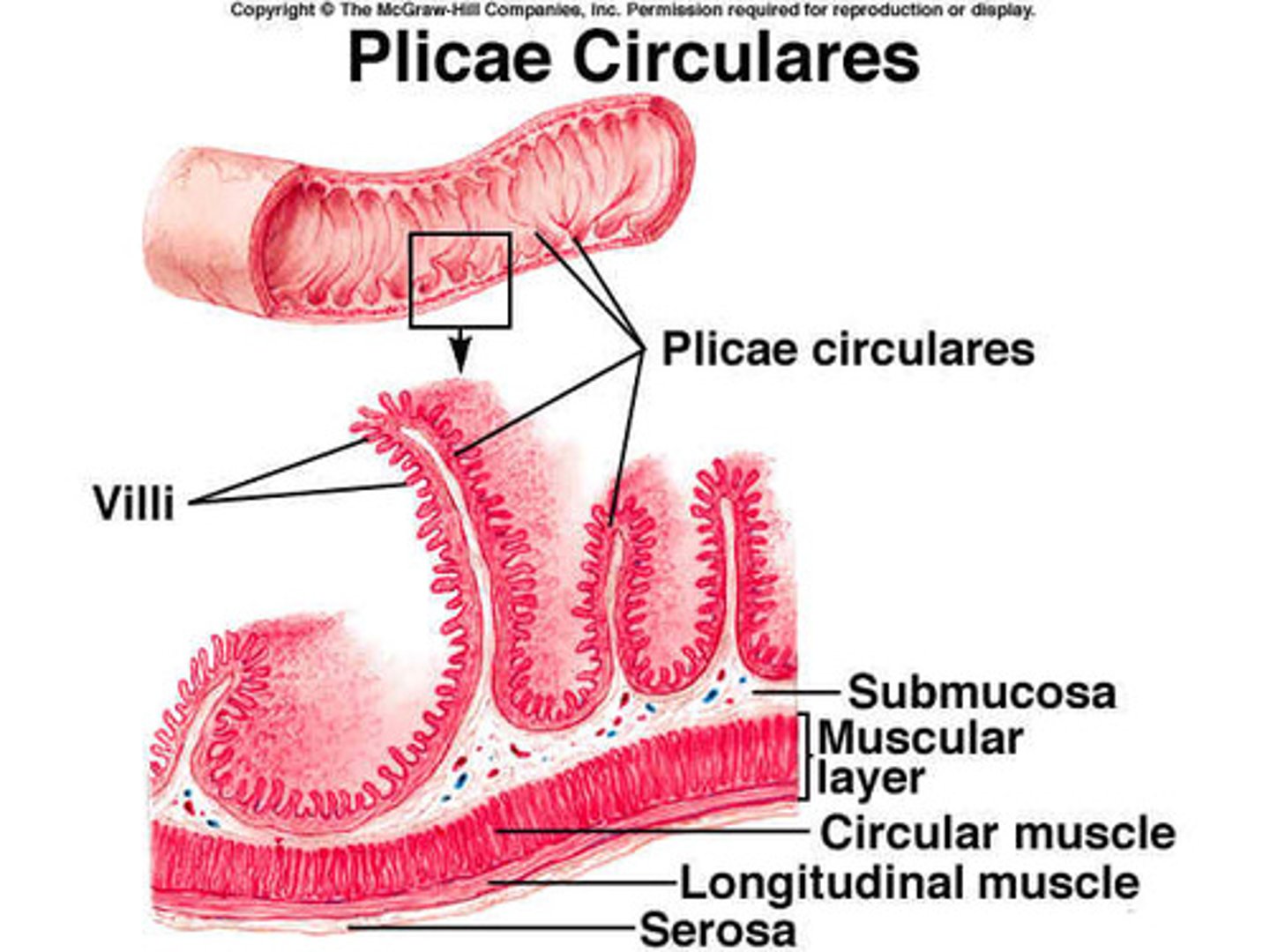
villi of small intestine
provide an enormous surface area that facilitates absorption.
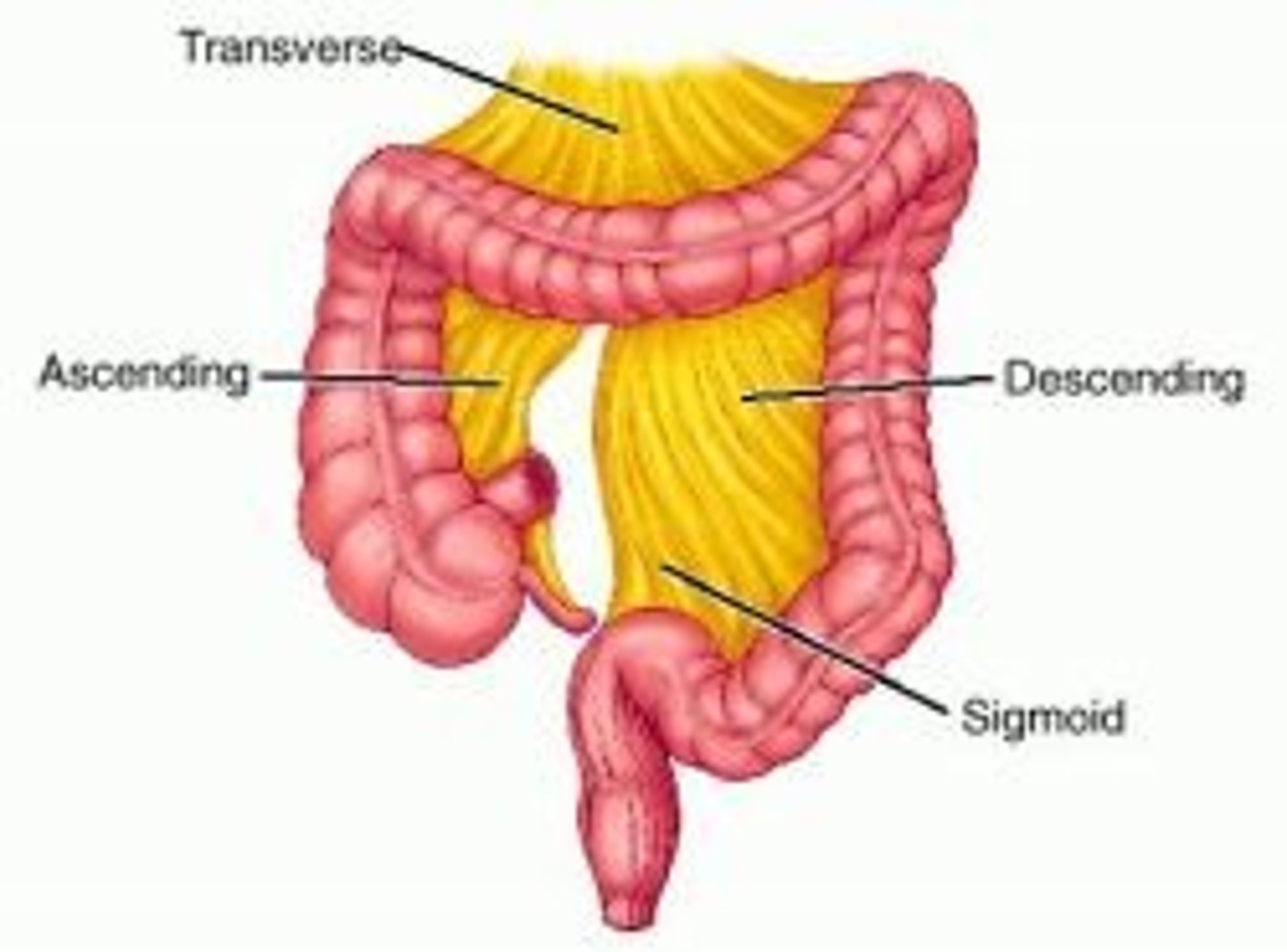
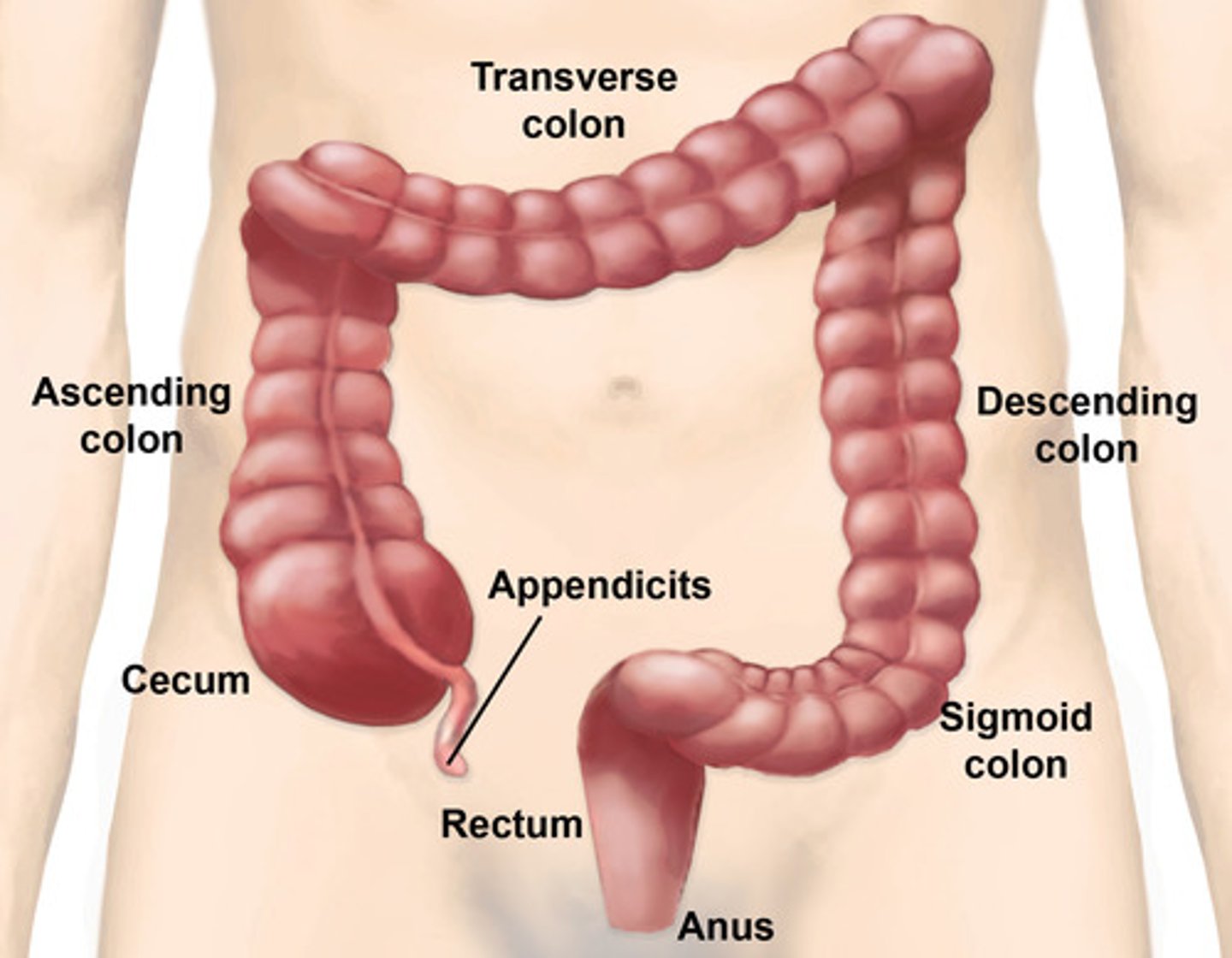
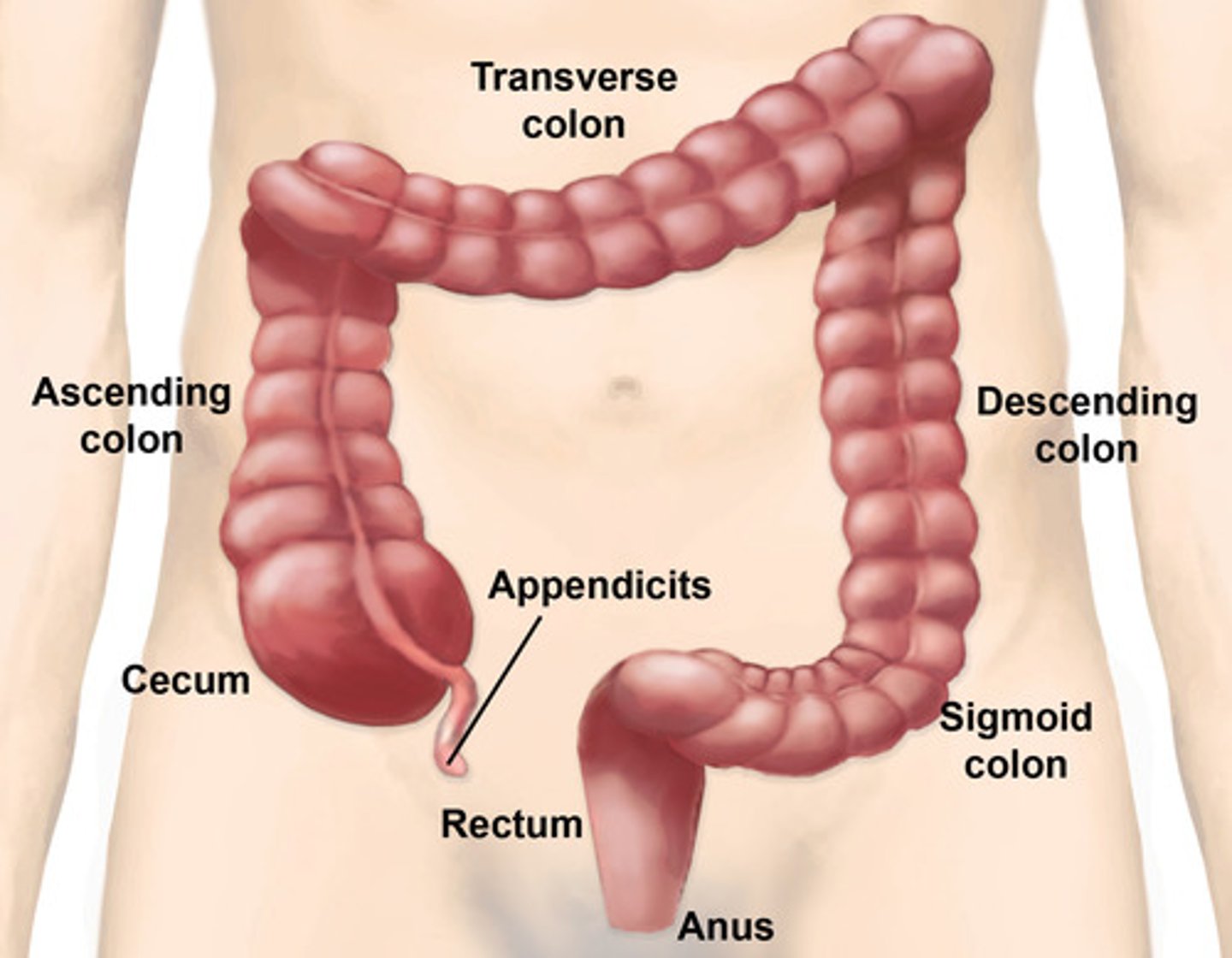
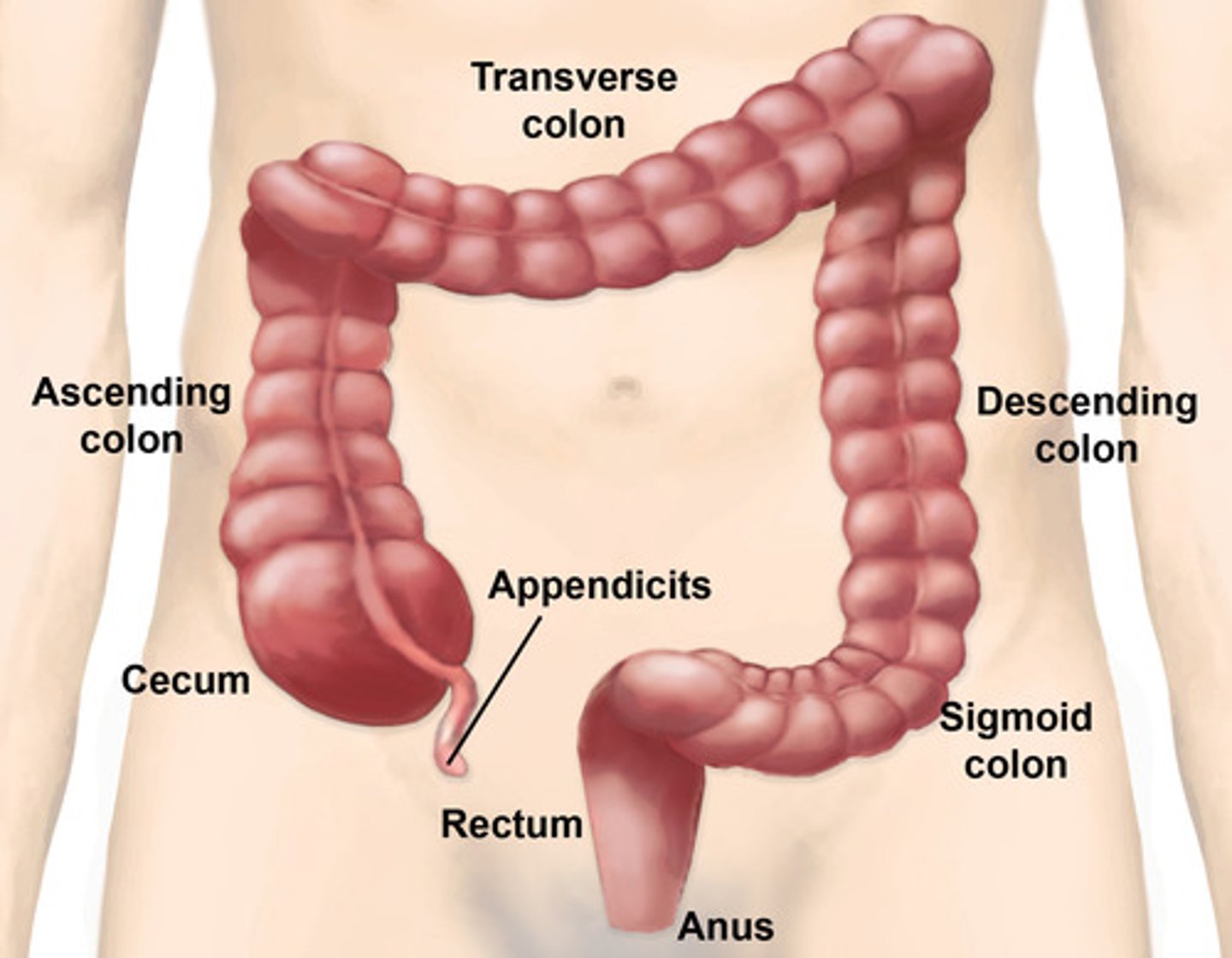
Large intestine (colon)
-cecum
-ascending colon
-right colic flexure
-descending colon
-sigmoid colon
-rectum
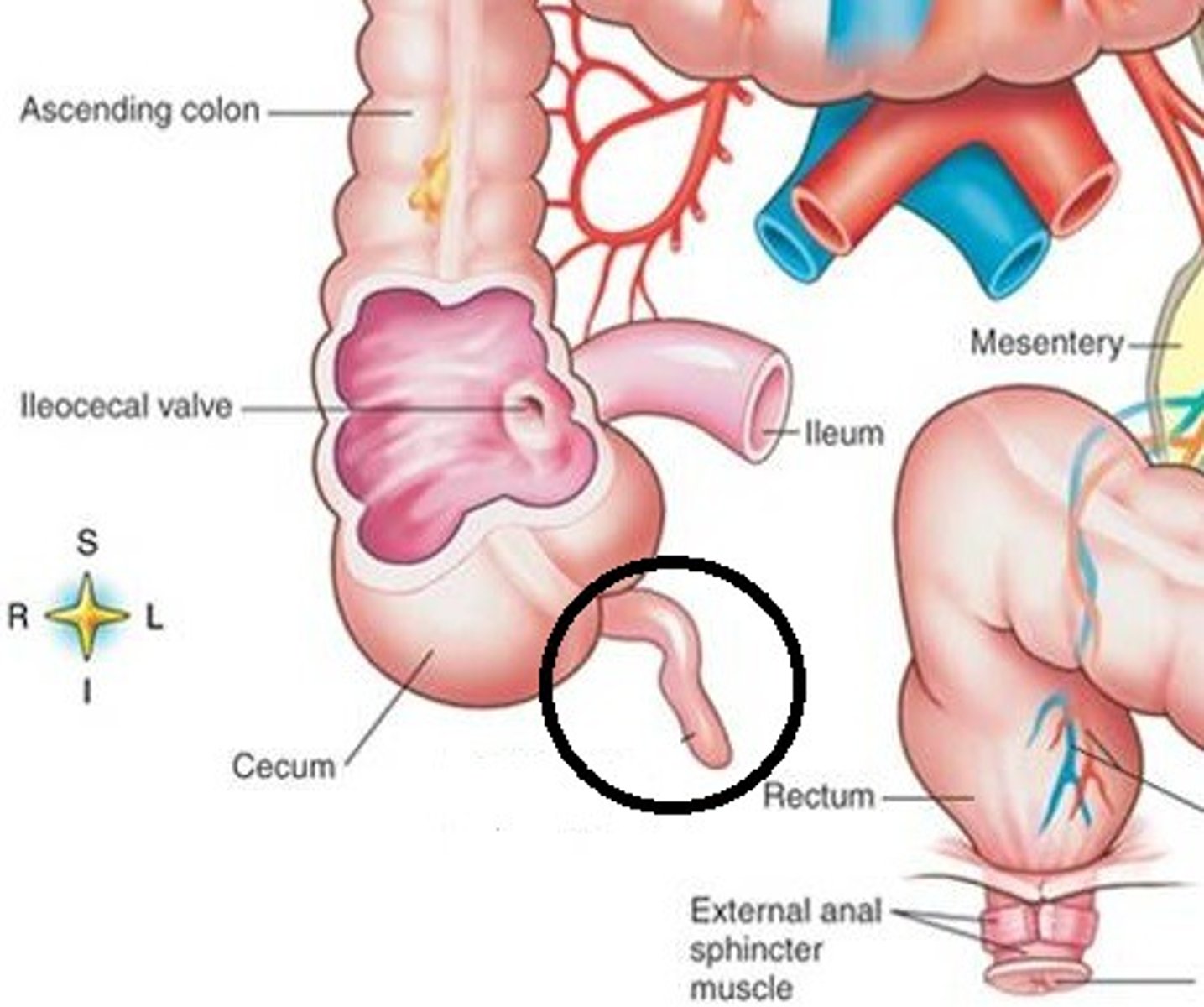
cecum
-first part of the large intestine
-intraperitoneal
-lower right quadrant
ileocecal junction
where the ileum joins the cecum of the large intestine
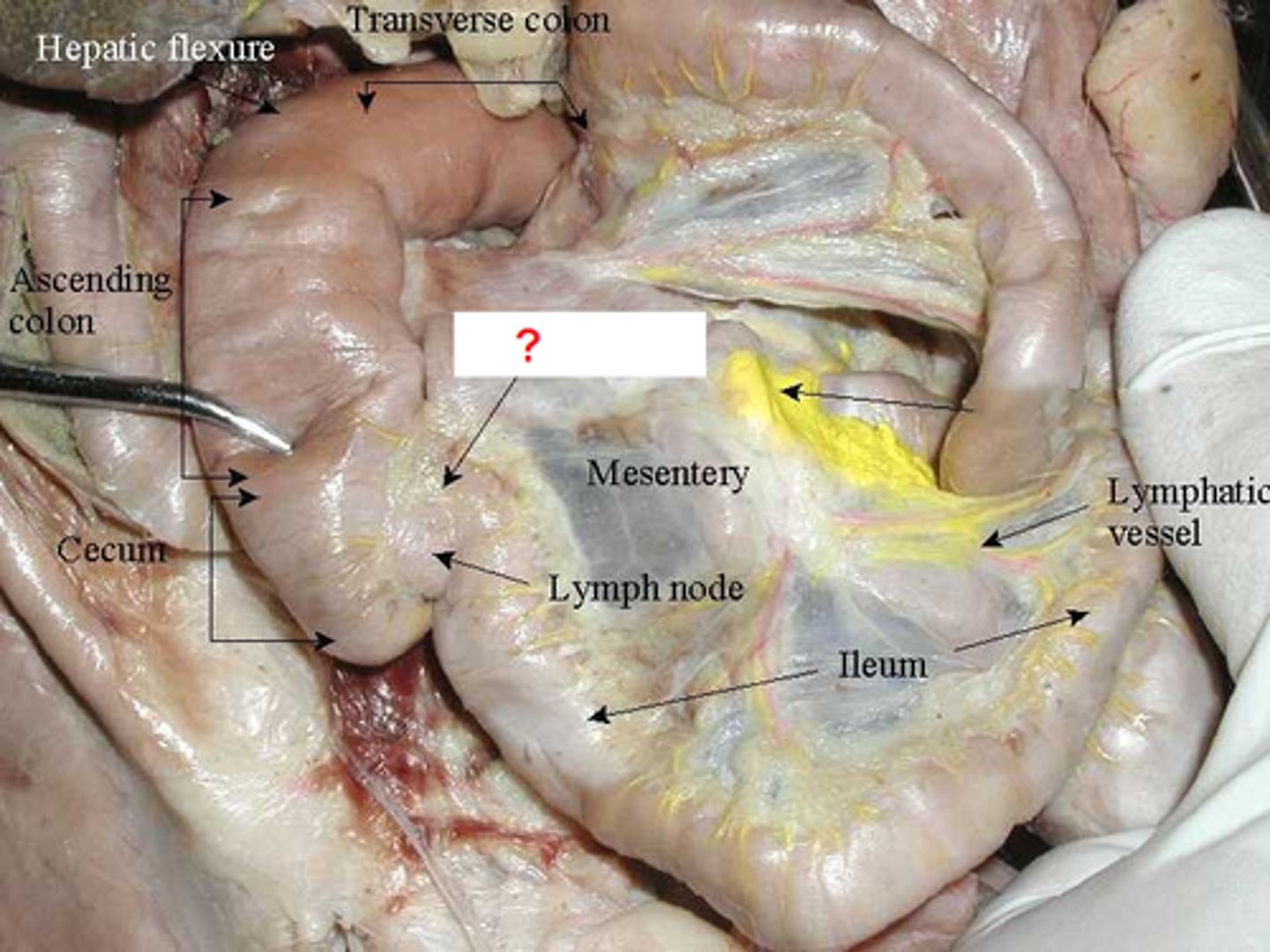
vermiform appendix
hangs from the lower portion of the cecum
-vestige of some organ
-appendicitis can happen here
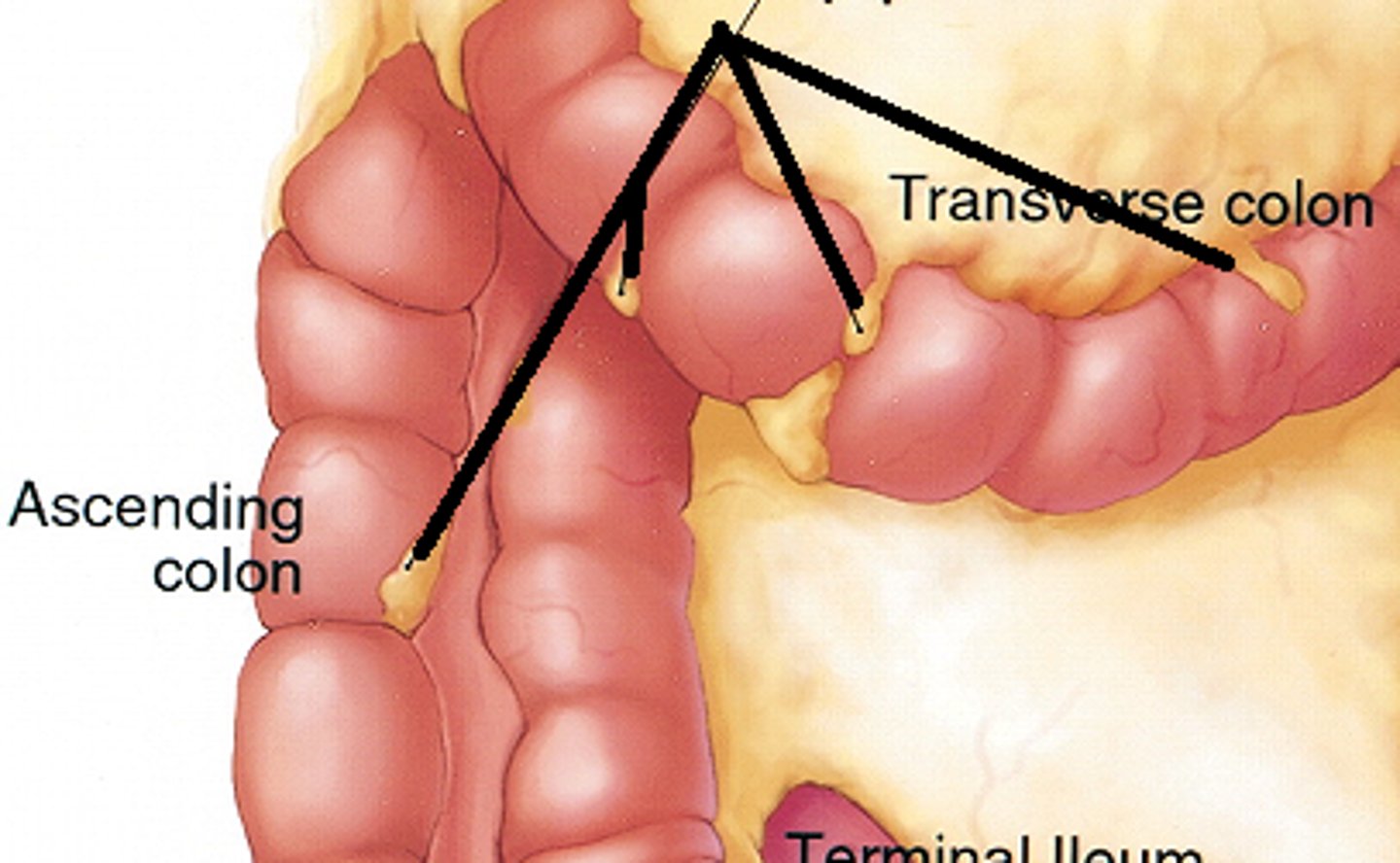
ascending colon
-retroperitoneal
-upper and lower right quadrants
-10-20cm along right side of posterior abdominal wall
-turns left (medially) at right colic flexure
-has no mesentery
-function: absorb food and water
transverse colon
-intraperitoneal
-upper right and left quadrants
-attached to posterior abdominal wall by transverse mesocolon
-turns down (inferiorly) at left colic flexure
-function: absorb food and water
descending colon
-retroperitoneal
-upper/lower quadrants
-descends from left colic flexure to sigmoid colon
-lies along left posterior abdominal wall
-has no mesentery
-function: absorb food and water
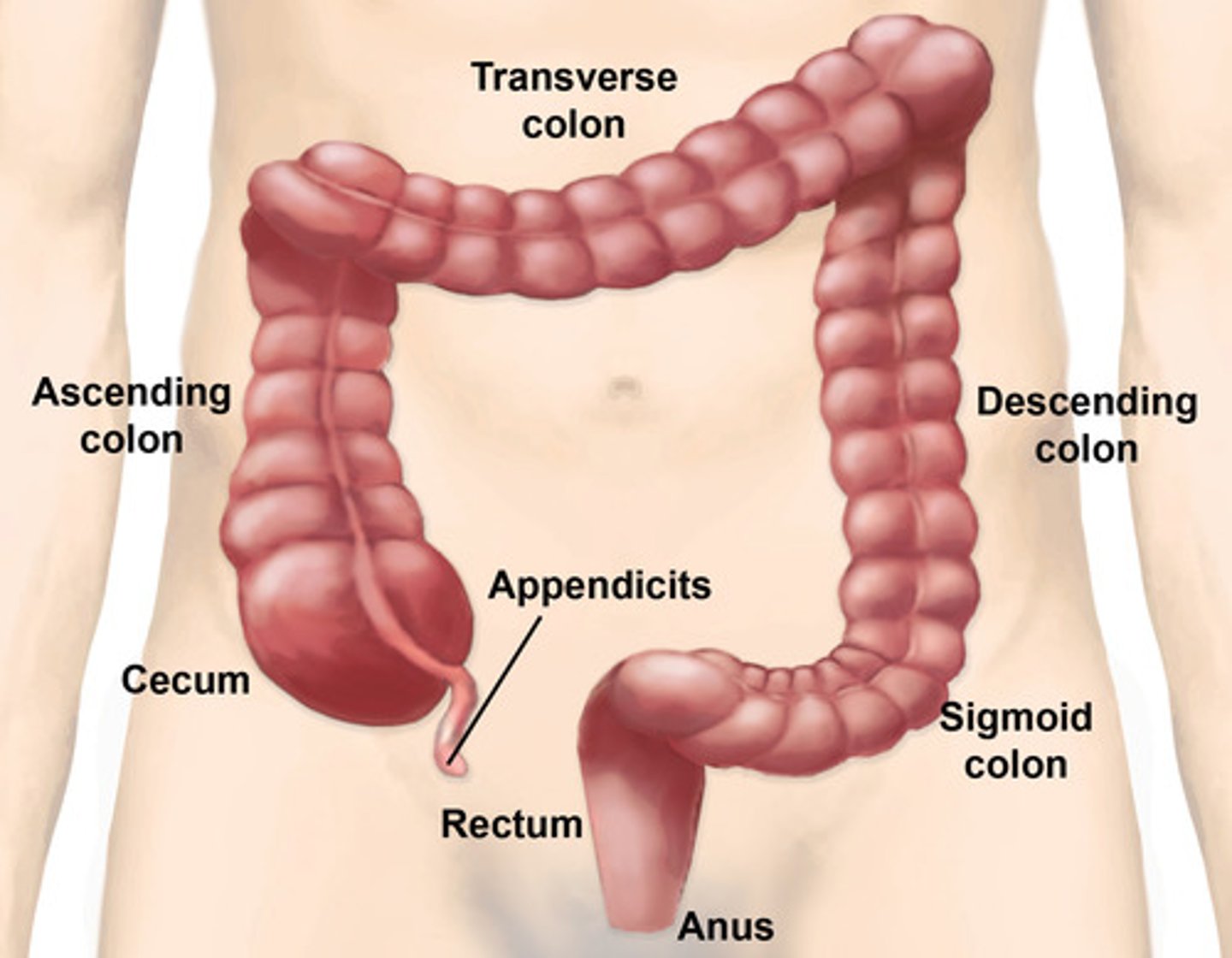
sigmoid colon
-intraperitoneal
-lower left quadrant
-s shaped
-leads to rectum
-attached to posterior abdominal wall by sigmoid mesocolon
-function: storage of feces
diverticulitis
-herniations of muscular wall of sigmoid colon
-cause: pressure build up from lack of fiber
left colic flexure
(also, splenic flexure) point where the transverse colon curves below the inferior end of the spleen
right colic flexure
aka the hepatic flexure, the right-angle turn that continues from the ascending colon
other structures of the colon
-tenia coli
-haustra
-epiploic appendices
tenia coli
-bands of smooth muscle running the length of the large intestine which produces the bunching of the colon
haustra
pouches that form in the large intestine when the longitudinal muscles are shorter than the colon
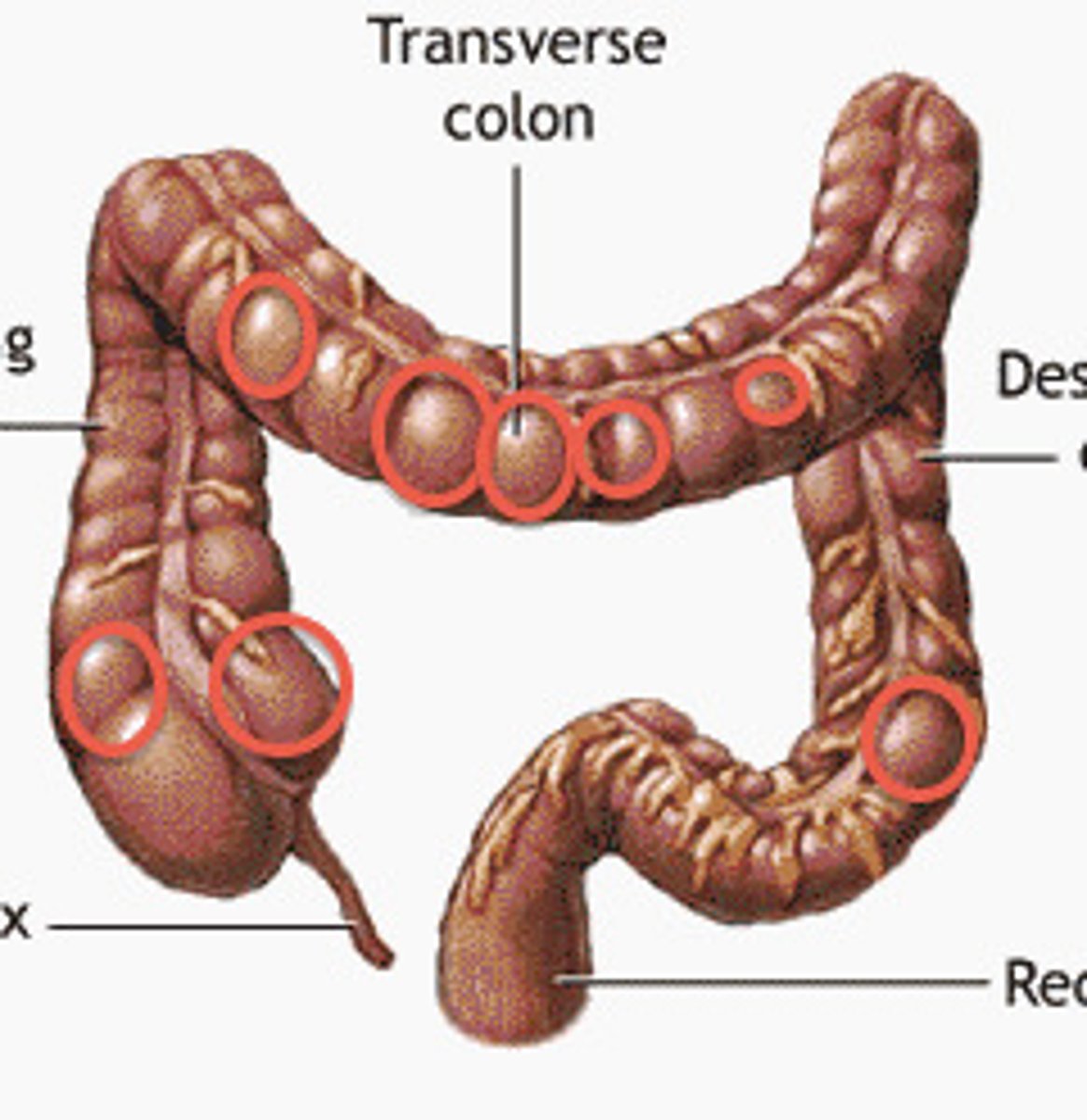
epiploic appendices
small pouches of the peritoneum filled with fat and situated along the colon
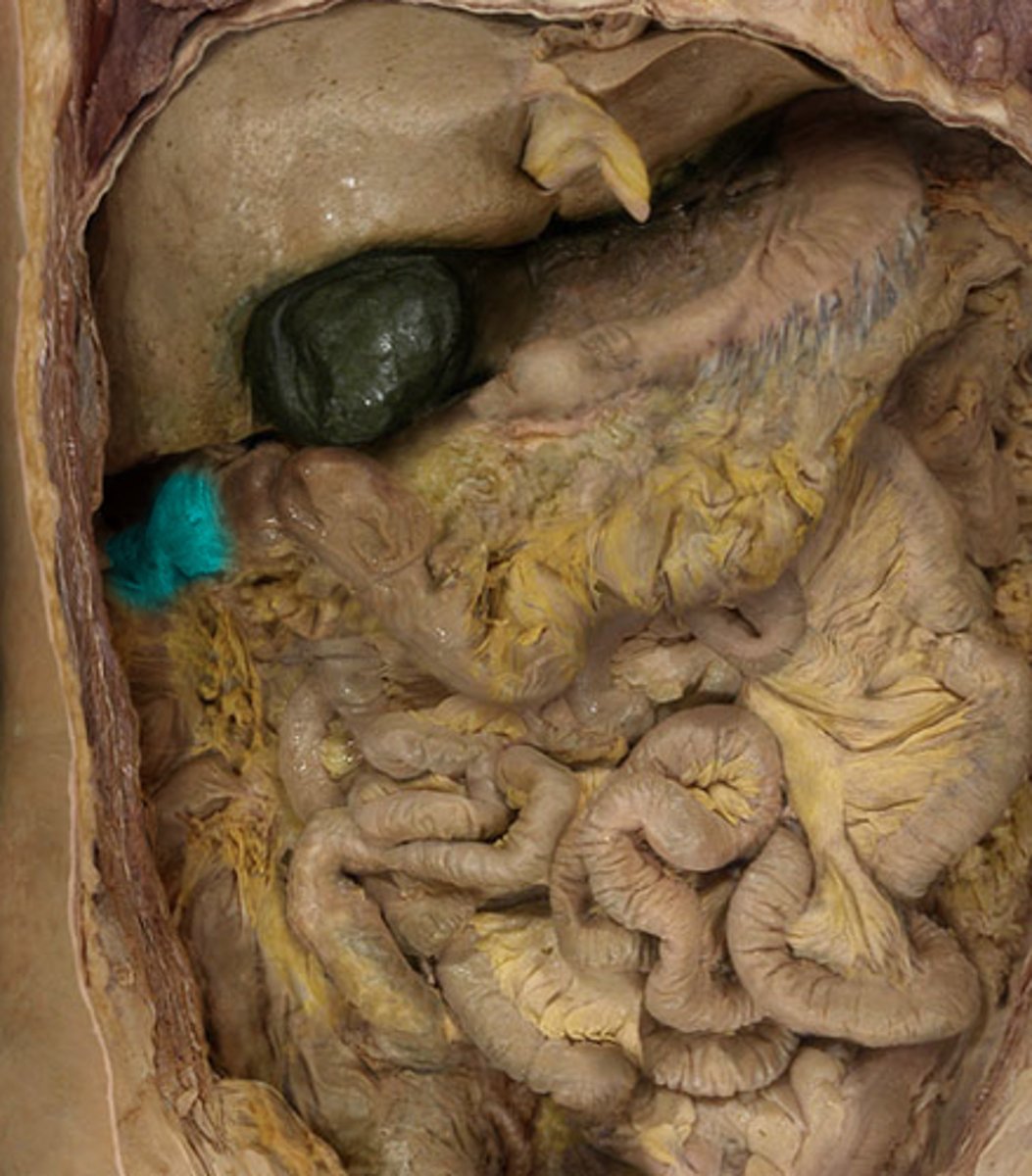
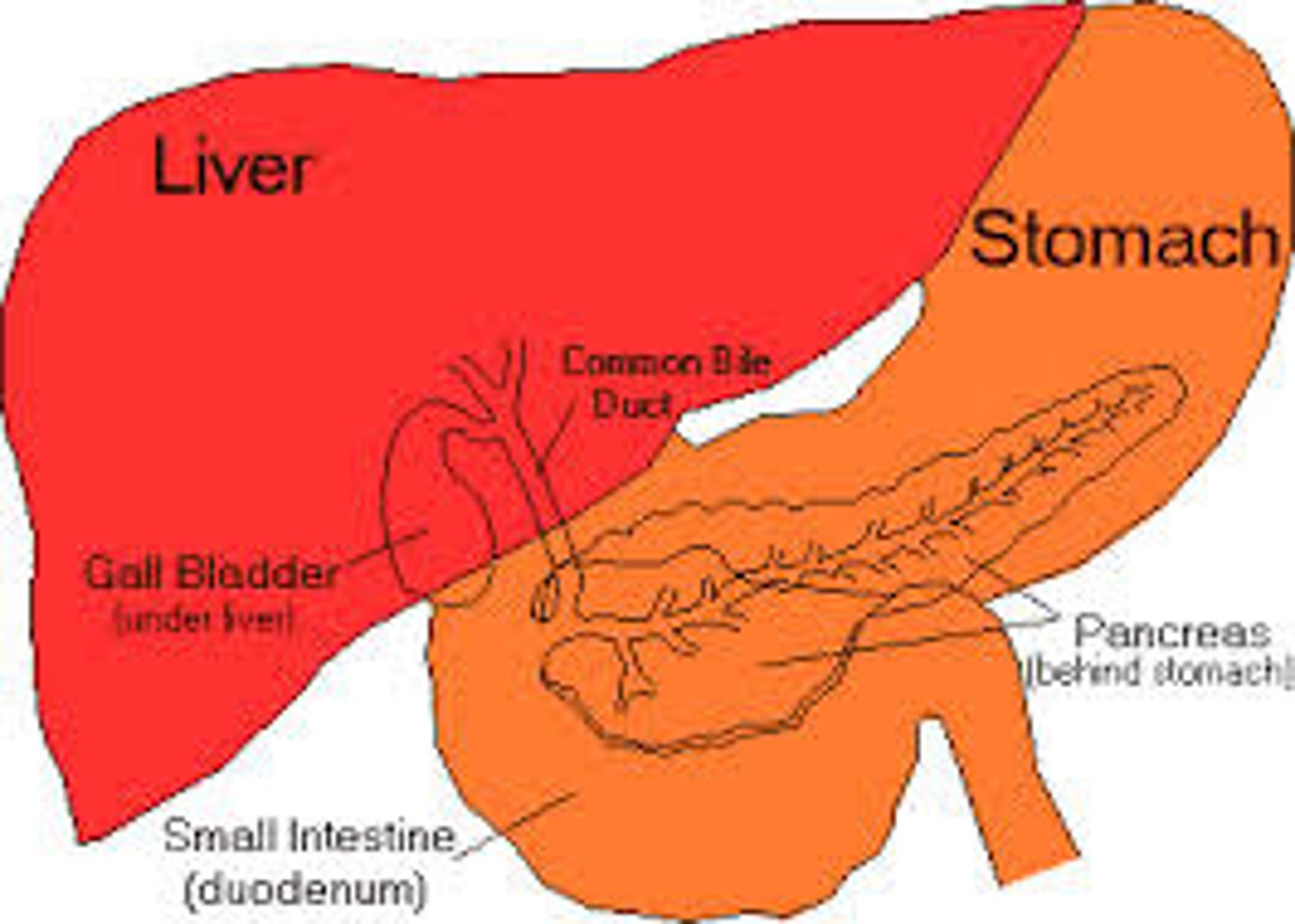
The liver
-largest gland in the body
-intraperitoneal
-upper right quadrant
-just below hemi-diaphragm
-covered by ribcage
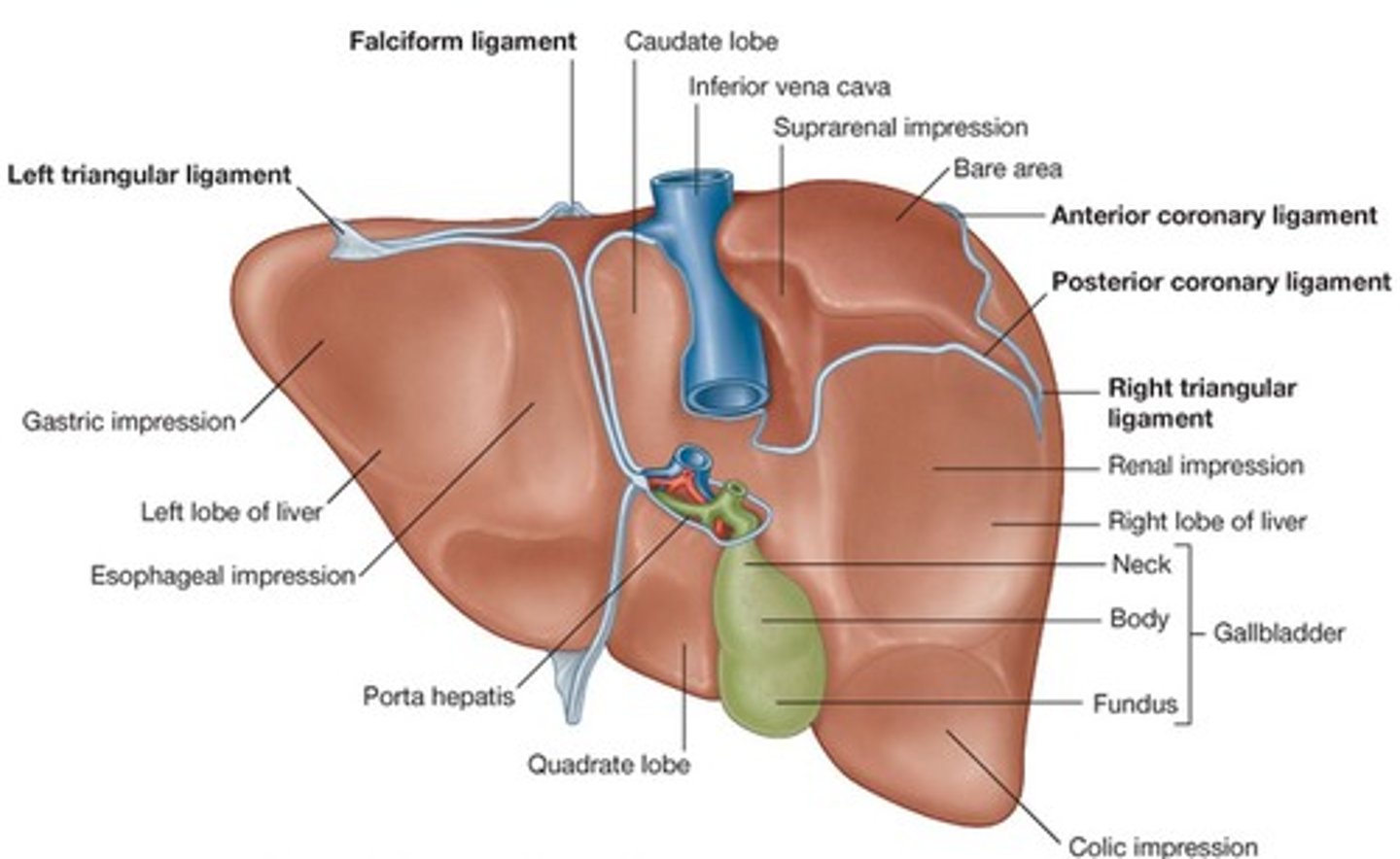
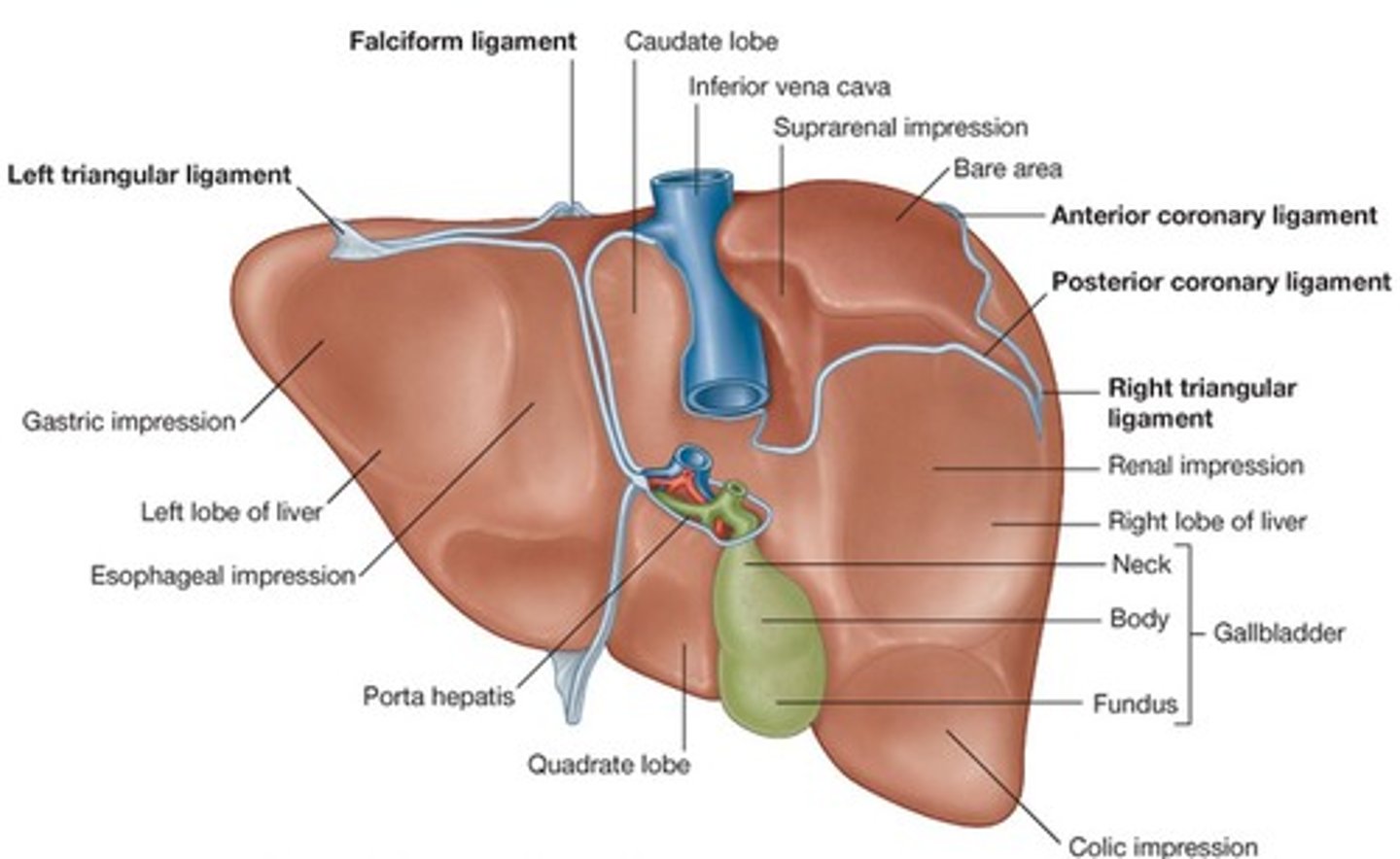
-split into lobes (4)
-function: process material from GI tract, controls blood glucose levels, stores glycogen and converts lactic acid to glucose, metabolizes drugs, produces bile etc
lobes of the liver
-right, left, caudate, quadrate
-split into lobules
-each lobule has its own blood supply and bile duct (portal triad)
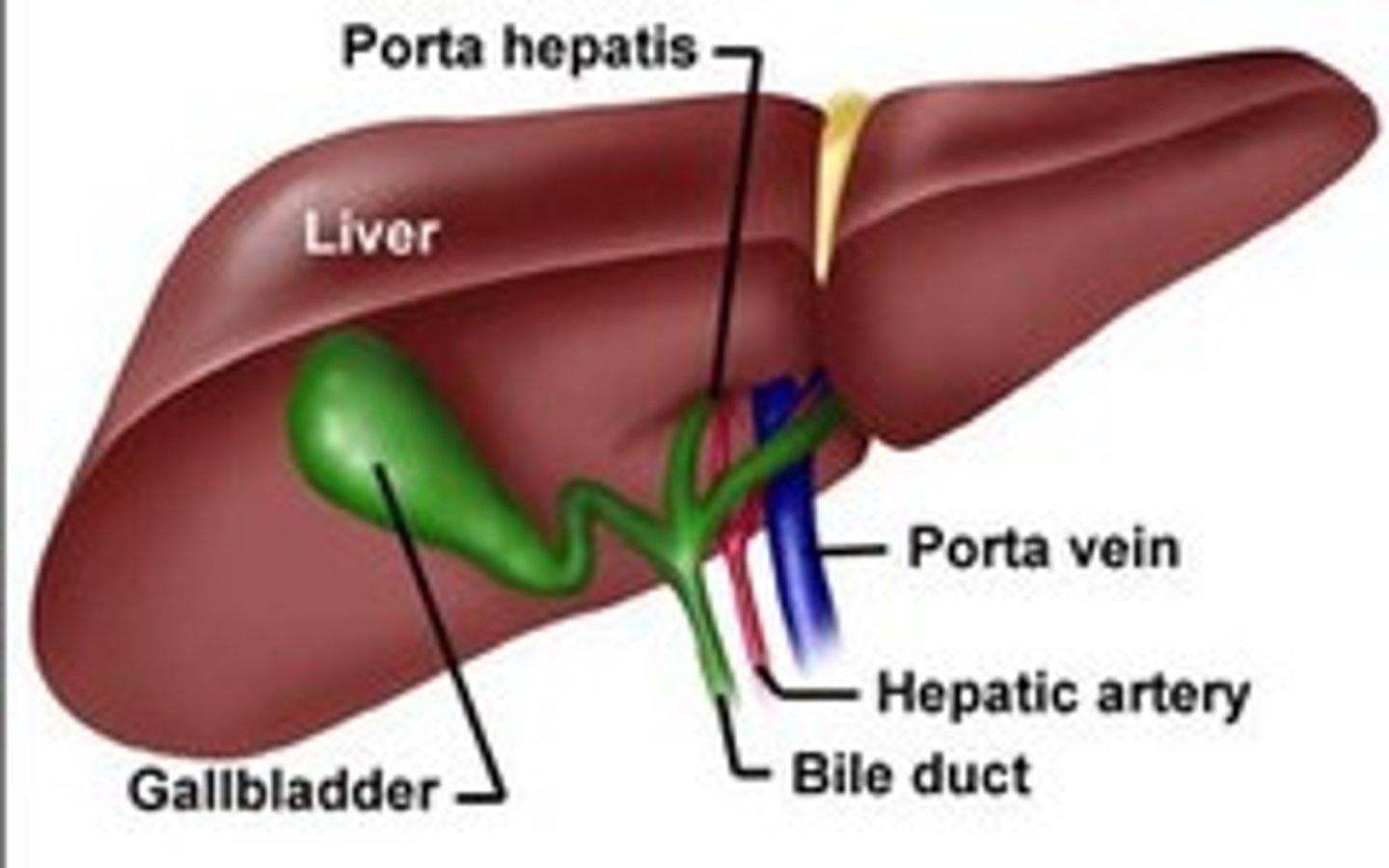
portal triad
-portal vein, hepatic artery, bile duct
-found throughout liver at each lobule
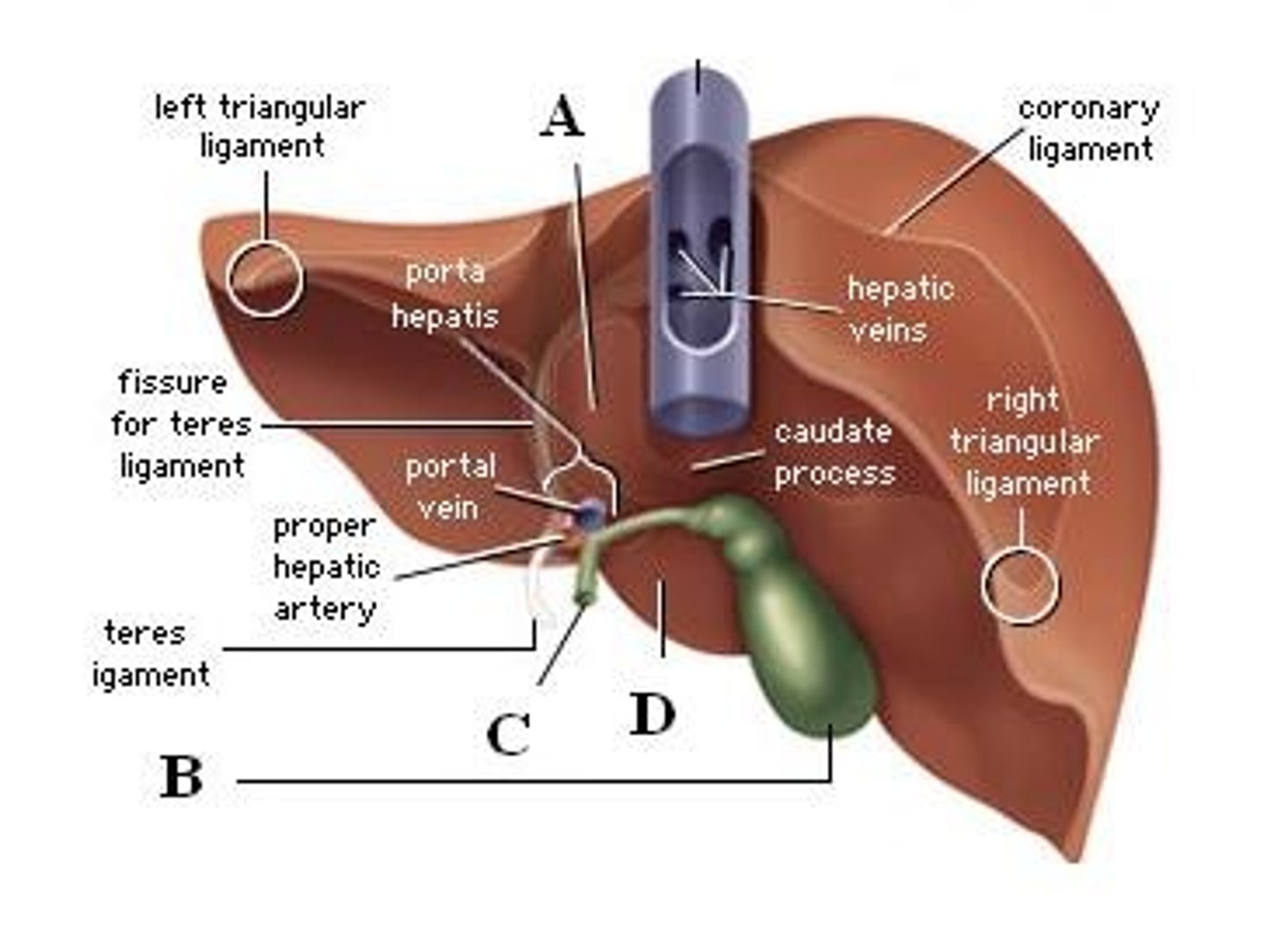
falciform ligament of liver
-attaches liver to anterior abdominal wall
-lower part is ligamentum teres (round ligament)
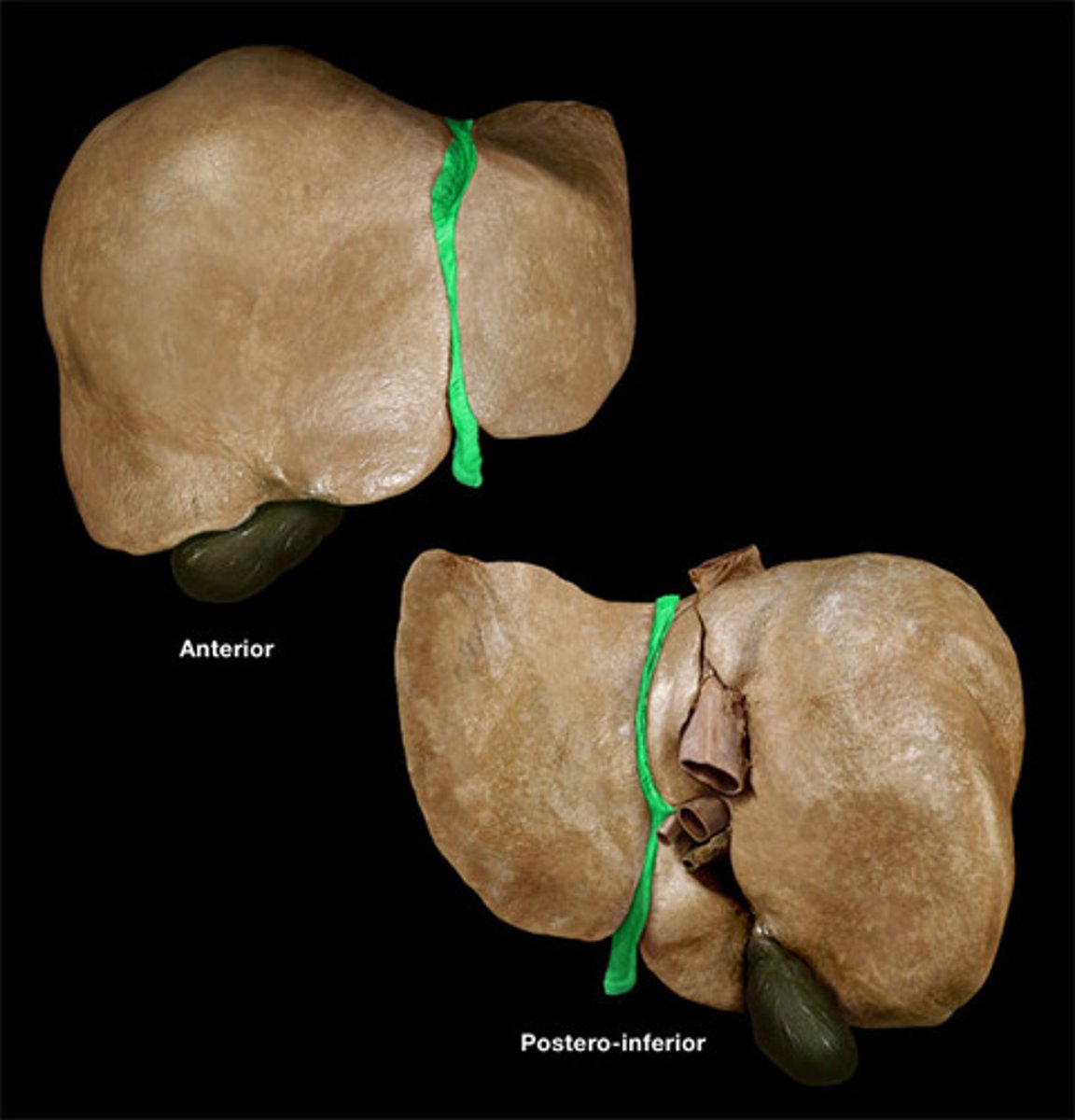
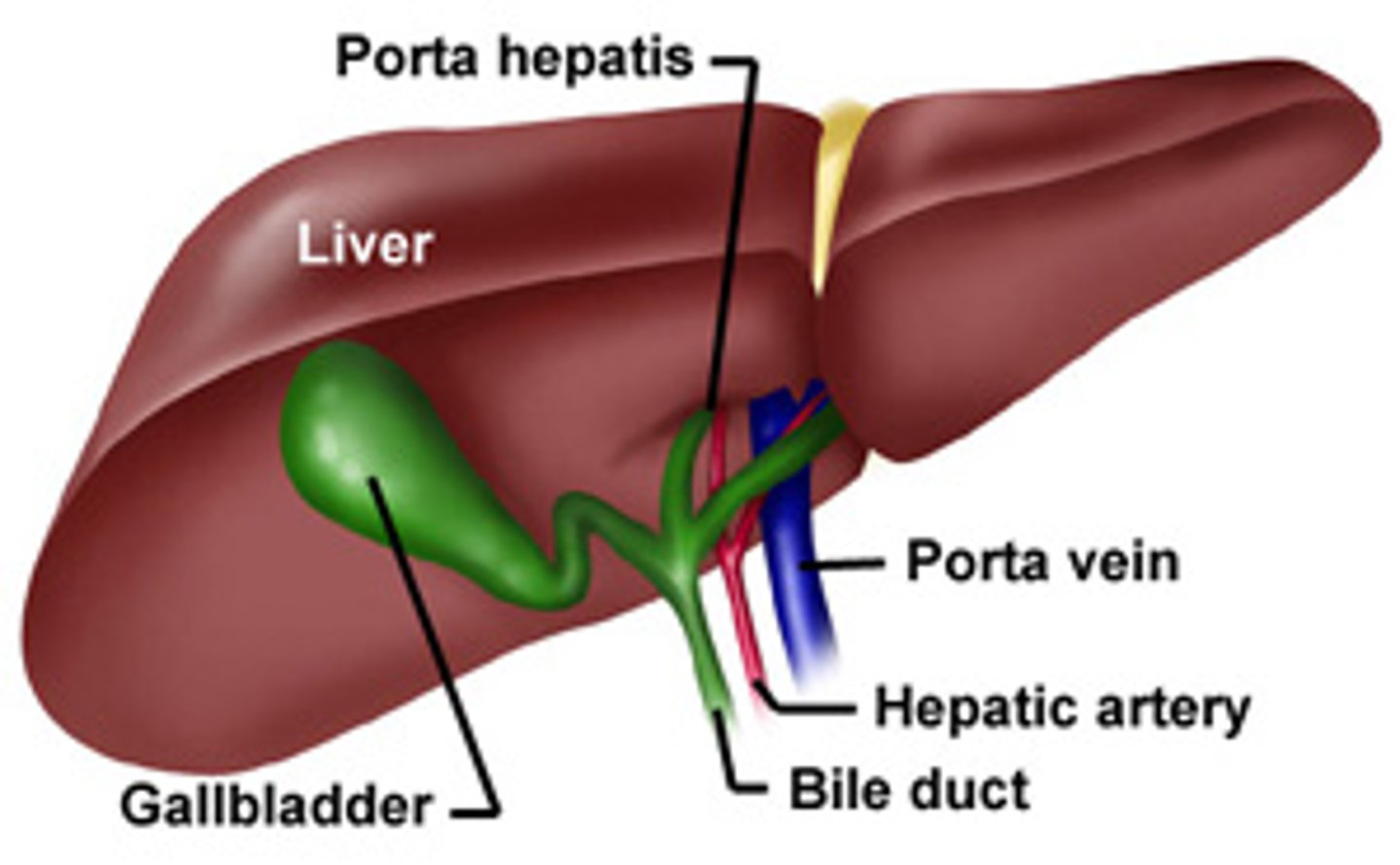
porta hepatis
-entryway into liver for proper hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, and common hepatic duct
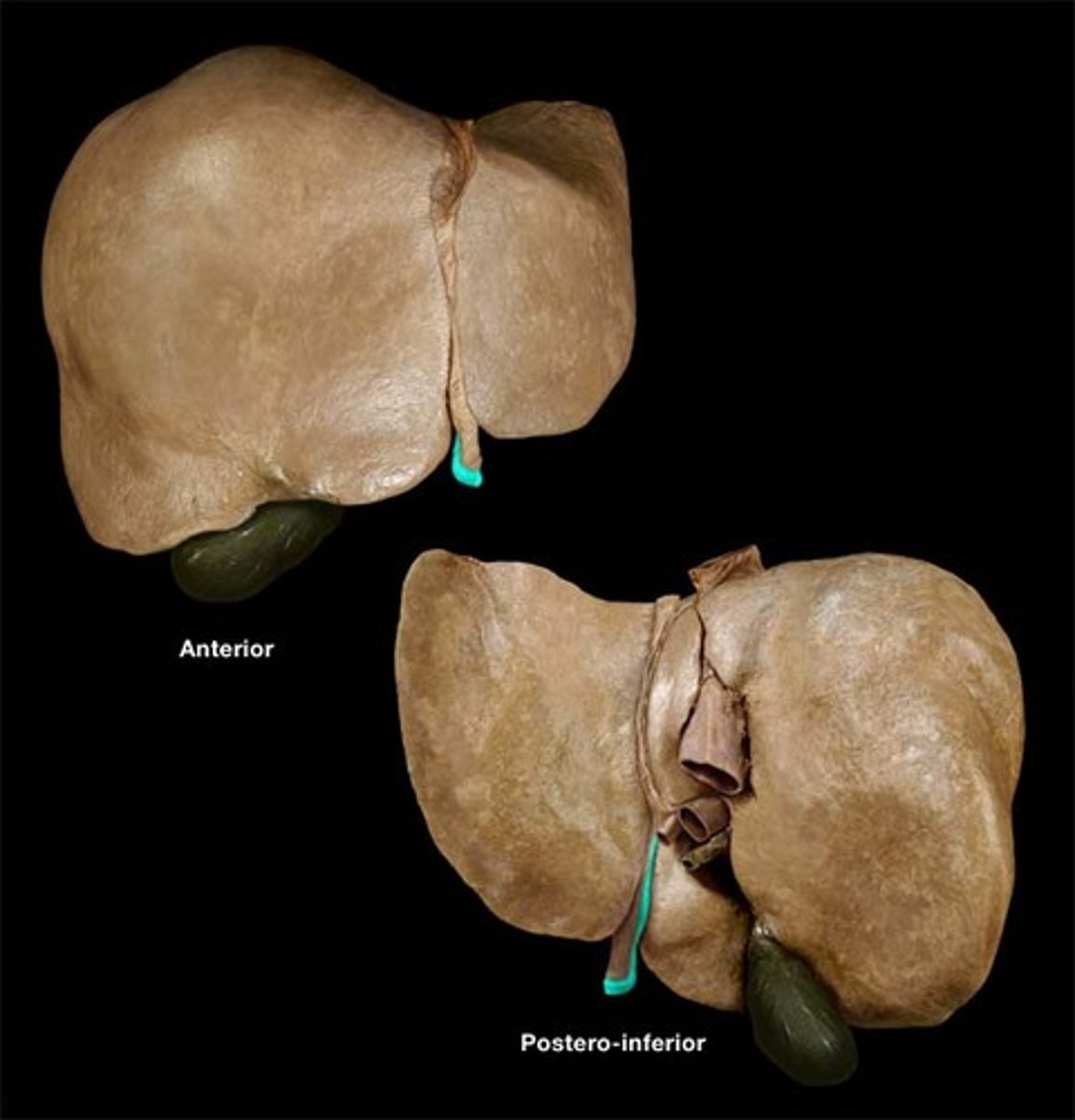
ligamentum teres (round ligament)
-remnant of fetal umbilical vein
-last fetal bypass
coronary ligament of liver
-attaches liver to diaphragm
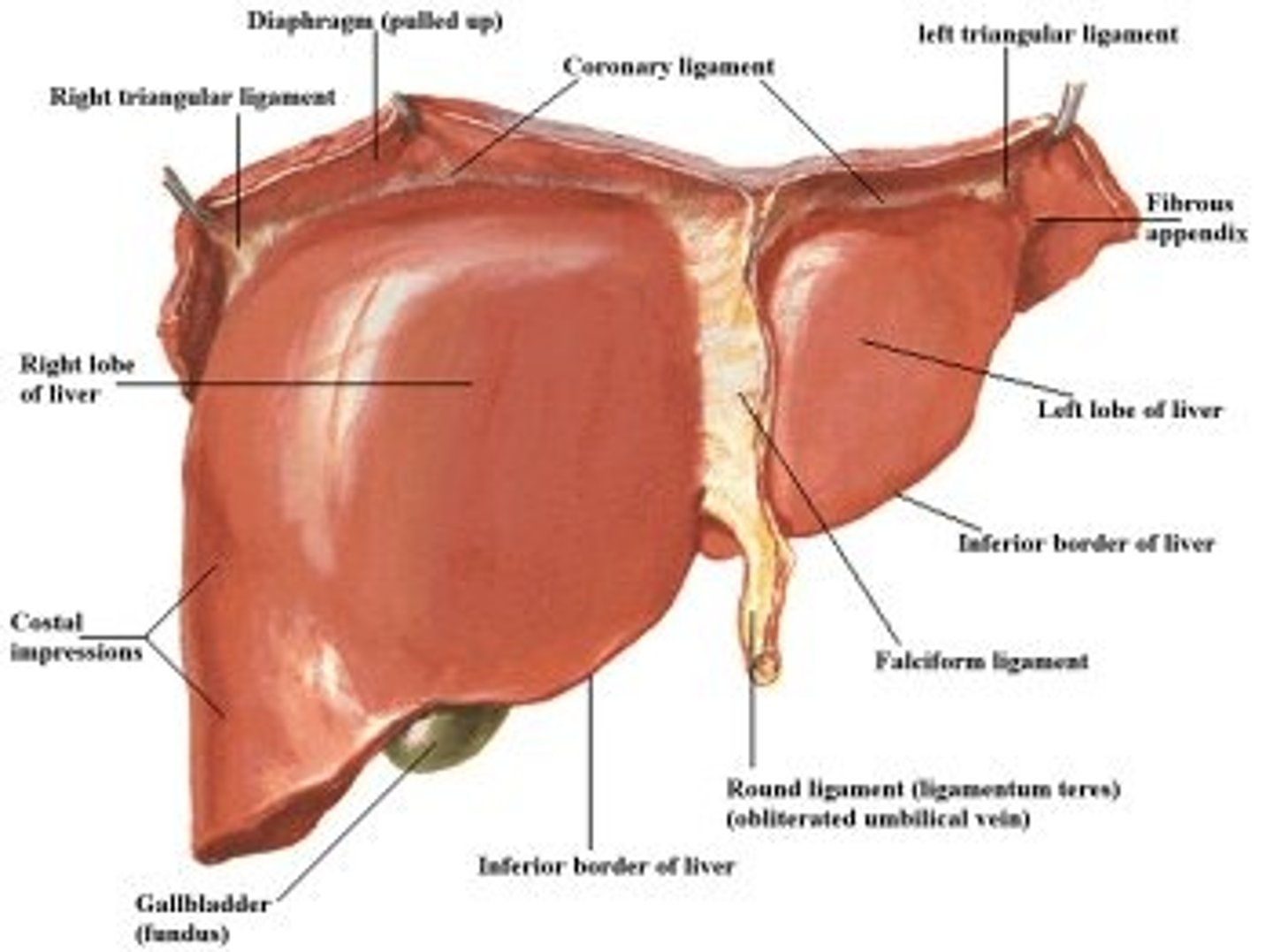
gallbladder
-attached inferiorly to liver btwn right and quadrate lobes
inferior vena cava (liver)
-is posterior to liver btwn right and caudate lobes
blood supply to liver
-common hepatic artery
-hepatic portal vein
-liver drains into IVC via right, middle and left hepatic veins
common hepatic artery
-from celiac trunk
-breaks into gastroduodenal artery and proper hepatic artery before entering liver
-supplies ~30% of total blood to liver (fully oxygenated)
-50% of O2
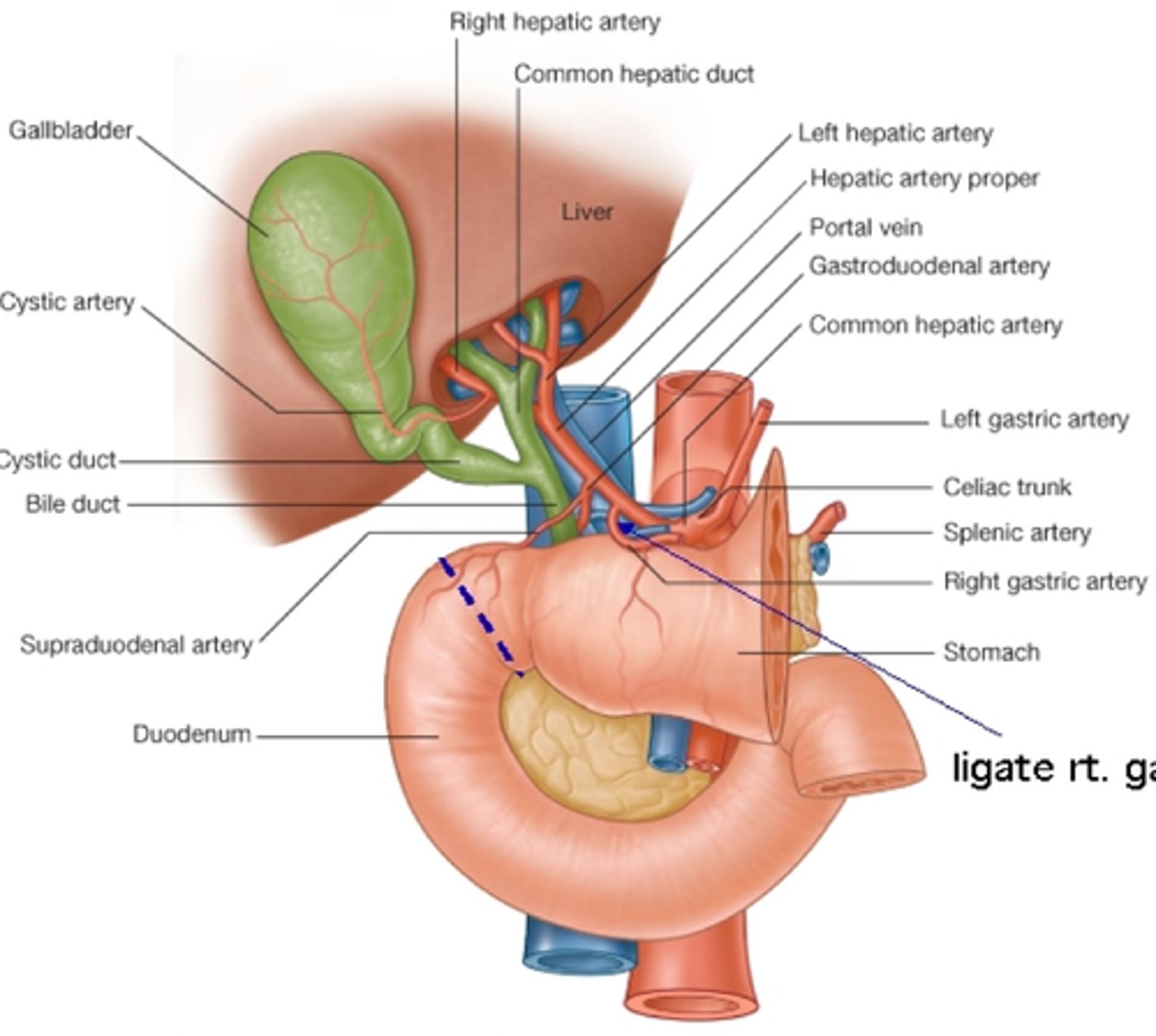
hepatic portal vein
-drains blood from GI tract (stomach, small and lrg intestines etc) and transports it to the liver
-supplies ~70% of blood to liver
-50% of O2
gastroduodenal artery
-gives off branches to supply gallbladder, duodenum, pancreas and stomach
right, middle and left hepatic veins
Drains blood from the liver into the IVC just inferior the diaphragm
bile
-produced by hepatocytes from bilirubin (comes from breakdown of RBCs)
-used by body to emulsify fats in GI tract
bile flow from liver
-hepatocytes produce bile-->
-common hepatic duct joins with cystic duct to become common bile duct-->
-common bile duct joins with pancreatic duct to form hepatopancreatic ampulla near duodenum-->
-hepatopancreatic ampulla is where bile and pancreatic secretions mix-->
-they dump into duodenum at major duodenal papillae which is controlled by the hepatopancreatic sphincter
Diseases of the liver
-portal HTN
-cirrhosis
-caput medusa
-jaundice
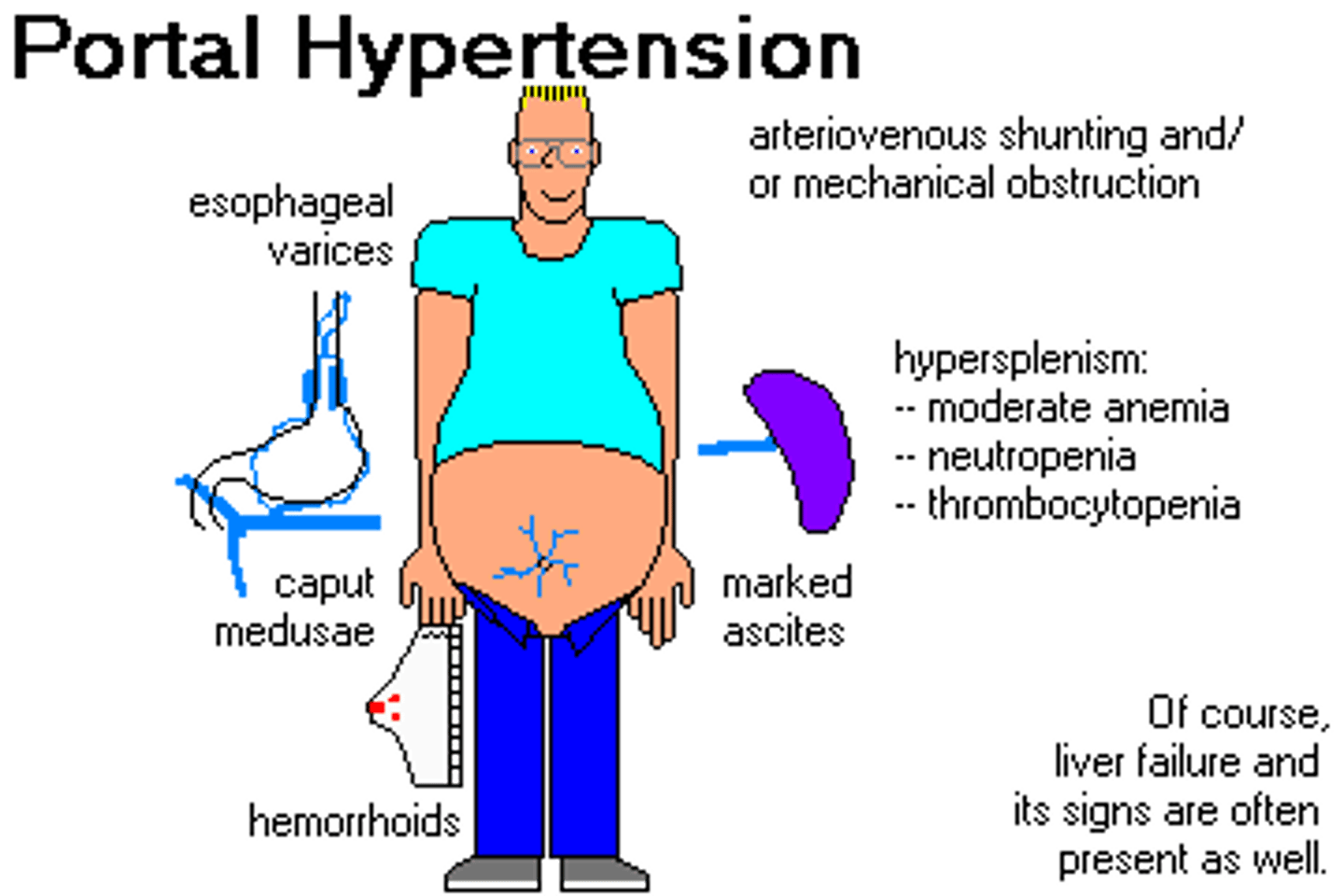
portal HTN
-CHF causes back up of blood
-increased pressure backs up to veins
-causes hemorrhoids, esophageal varices, caput medusa
cirrhosis
-chronic degenerative disease of the liver
-scarring
-damage to hepatocytes
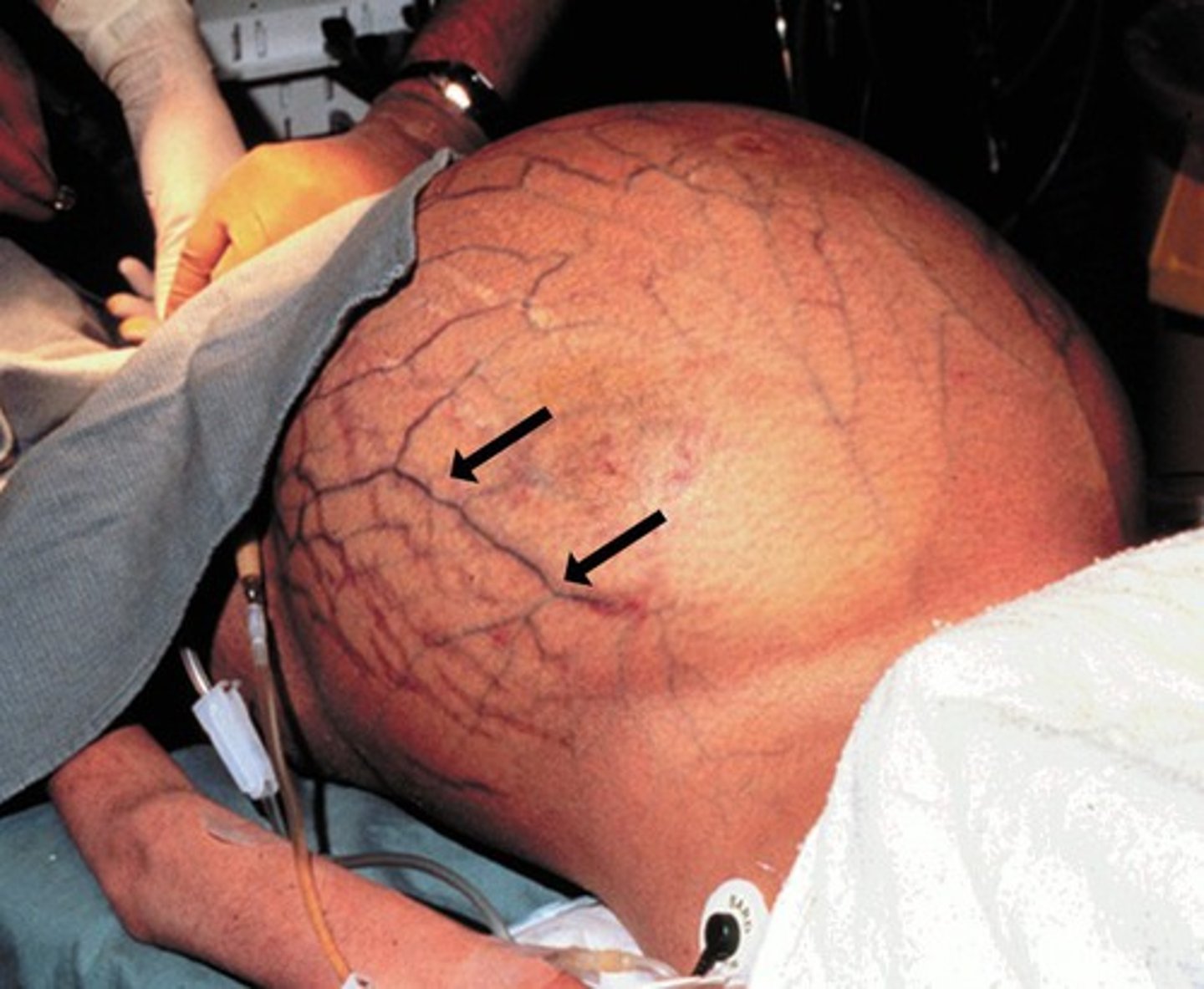
caput medusa
-varicose veins radiating from the umbilicus due to portal hypertension
jaundice
-back up of bilirubin
-yellow: low level
-brown: high level
Gallbladder
-intraperitoneal
-upper right quadrant
-under liver btwn right and quadrate lobes
-cystic duct meets with common hepatic duct to flow to duodenum via common bile duct
-function: stores and concentrates (absorbs water) bile from liver
Pancreas
-retroperitoneal
-upper right and left quadrants
-has exocrine and endocrine function
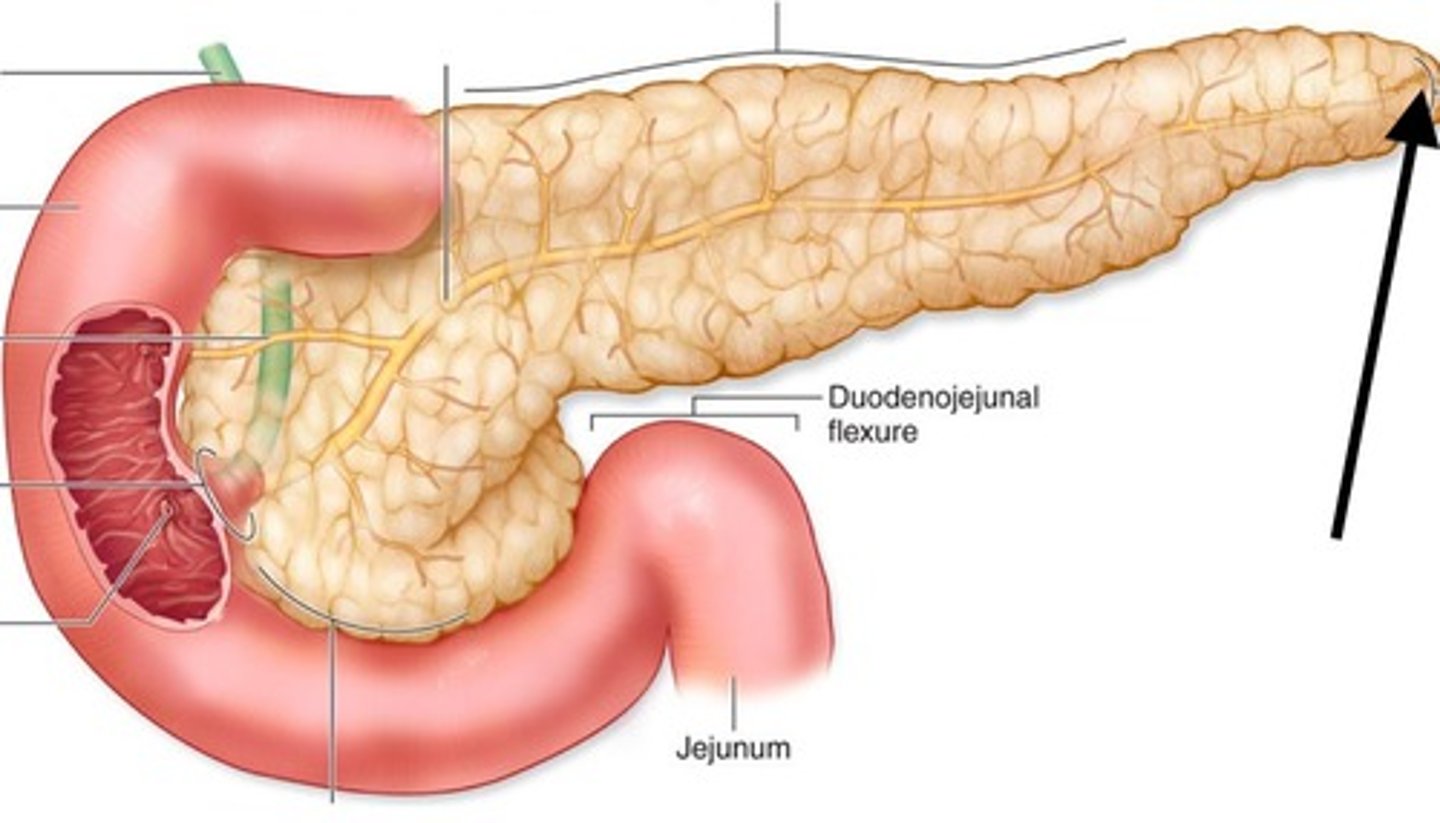
Pancreas endocrine function
-secretes insulin (beta cells) and glucagon (alpha cells) into blood to help regulate blood glucose levels
Pancreas exocrine function
-secretes digestive enzymes via pancreatic duct secreting into duodenum
Pancreatic rupture
-pancreatic juices can eat nearby organs
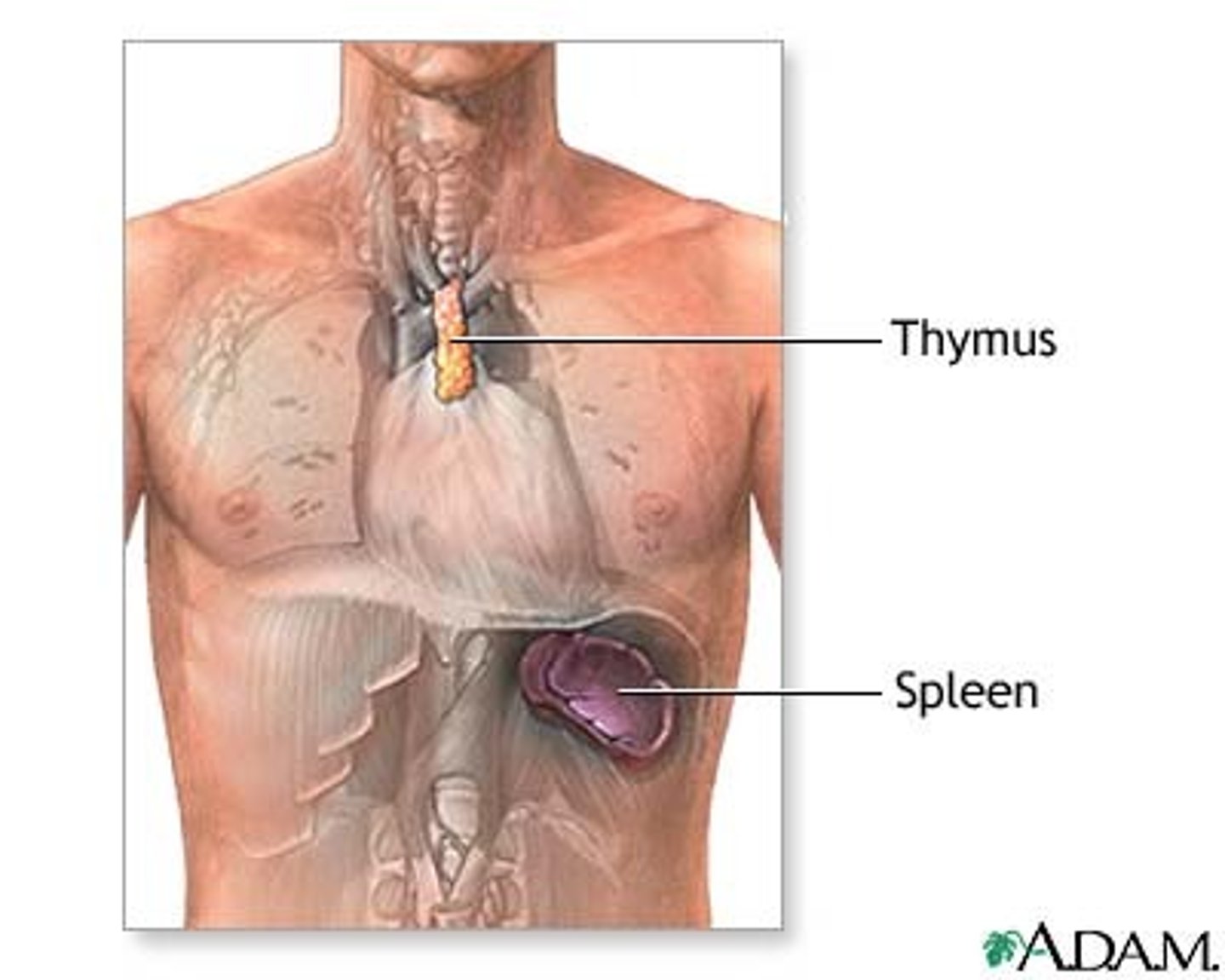
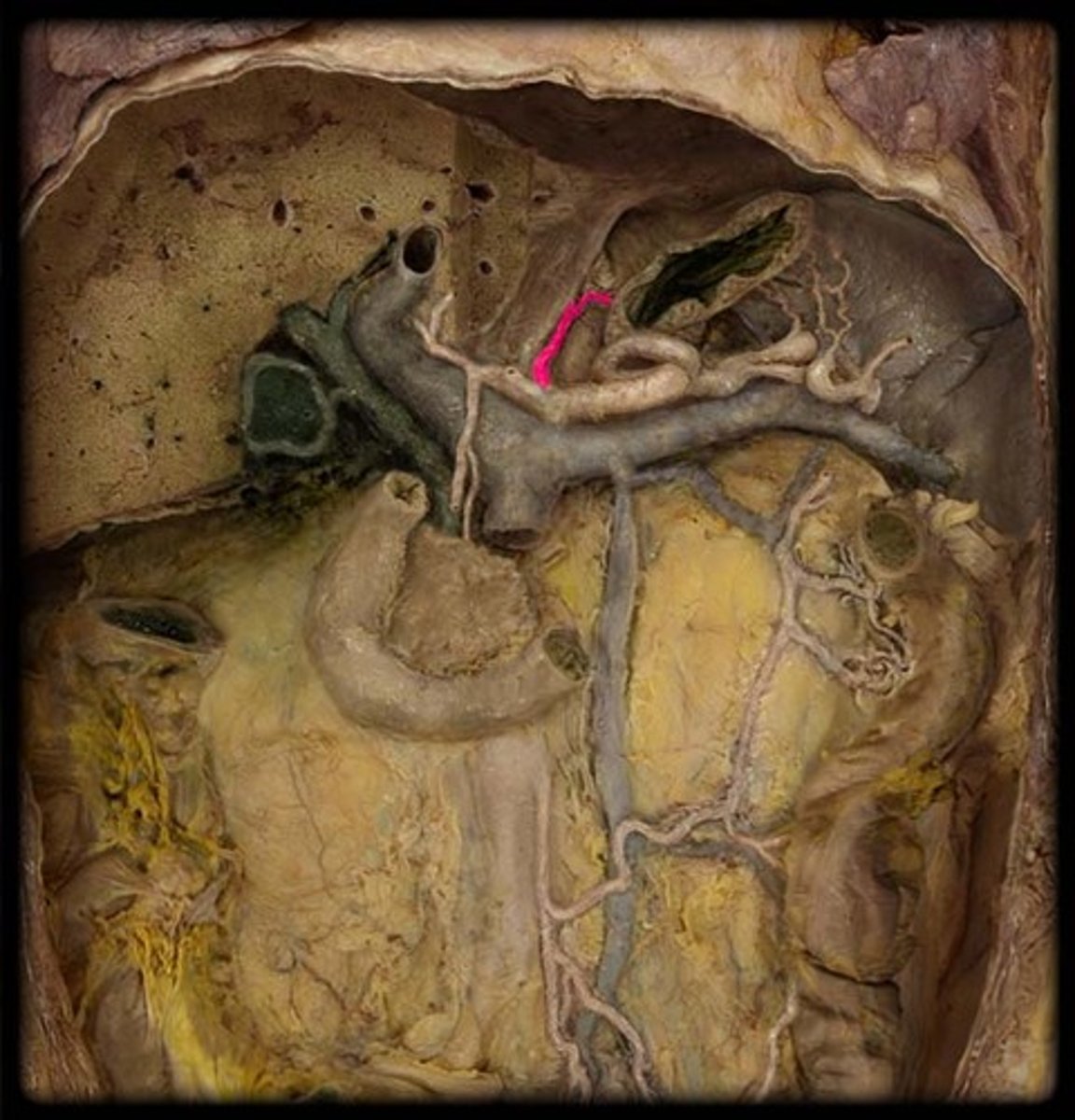
Spleen
-protected by lower ribs
-intraperitoneal
-upper left quadrant (above left kidney)
-vascularized by splenic artery (comes off celiac trunk)
-function: process lymph fluid as an immune gland, scavenges RBCs
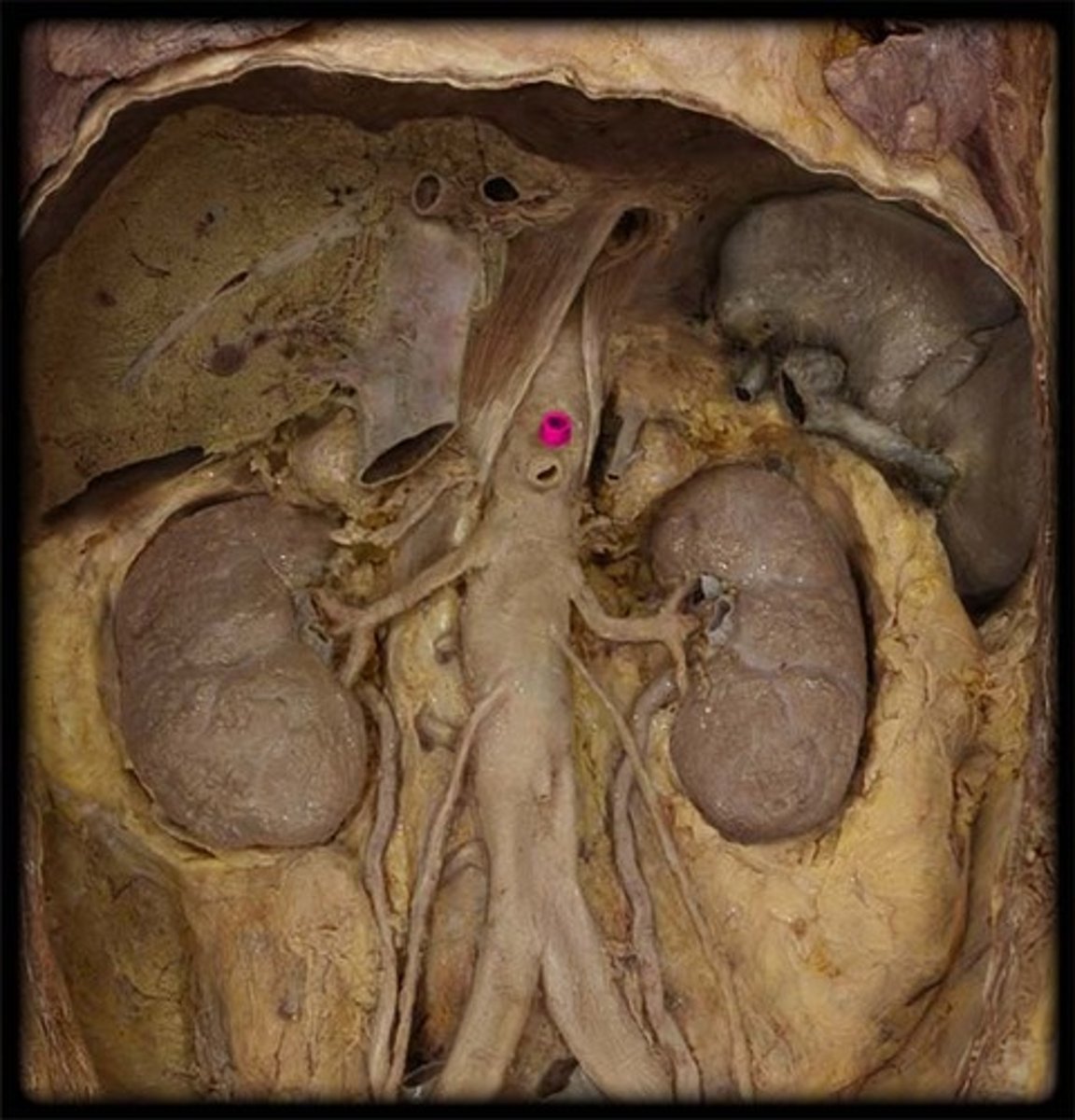
kidney vascularization
left and right renal aa.
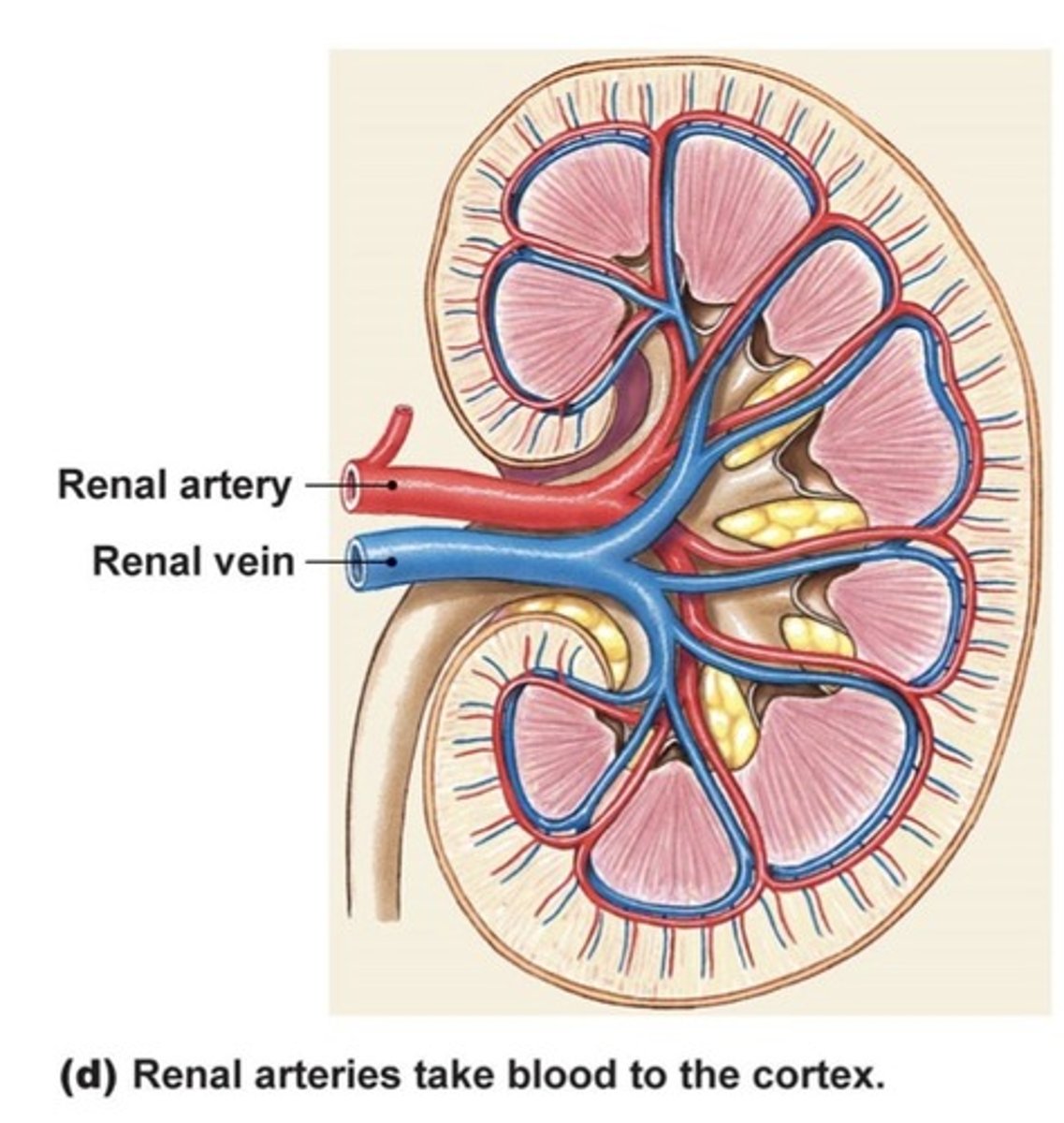
Kidneys
-retroperitoneal
-upper right/left quadrants
-vascularized by renal arteries coming off abdominal aorta
-covered by renal fascia (tough fibrous outer layer)
-take 25% of cardiac output at rest
-function: long term acid/base balance, fluid balance (BP), electrolyte balance, and RBC levels (hematocrit) controlled by EPO
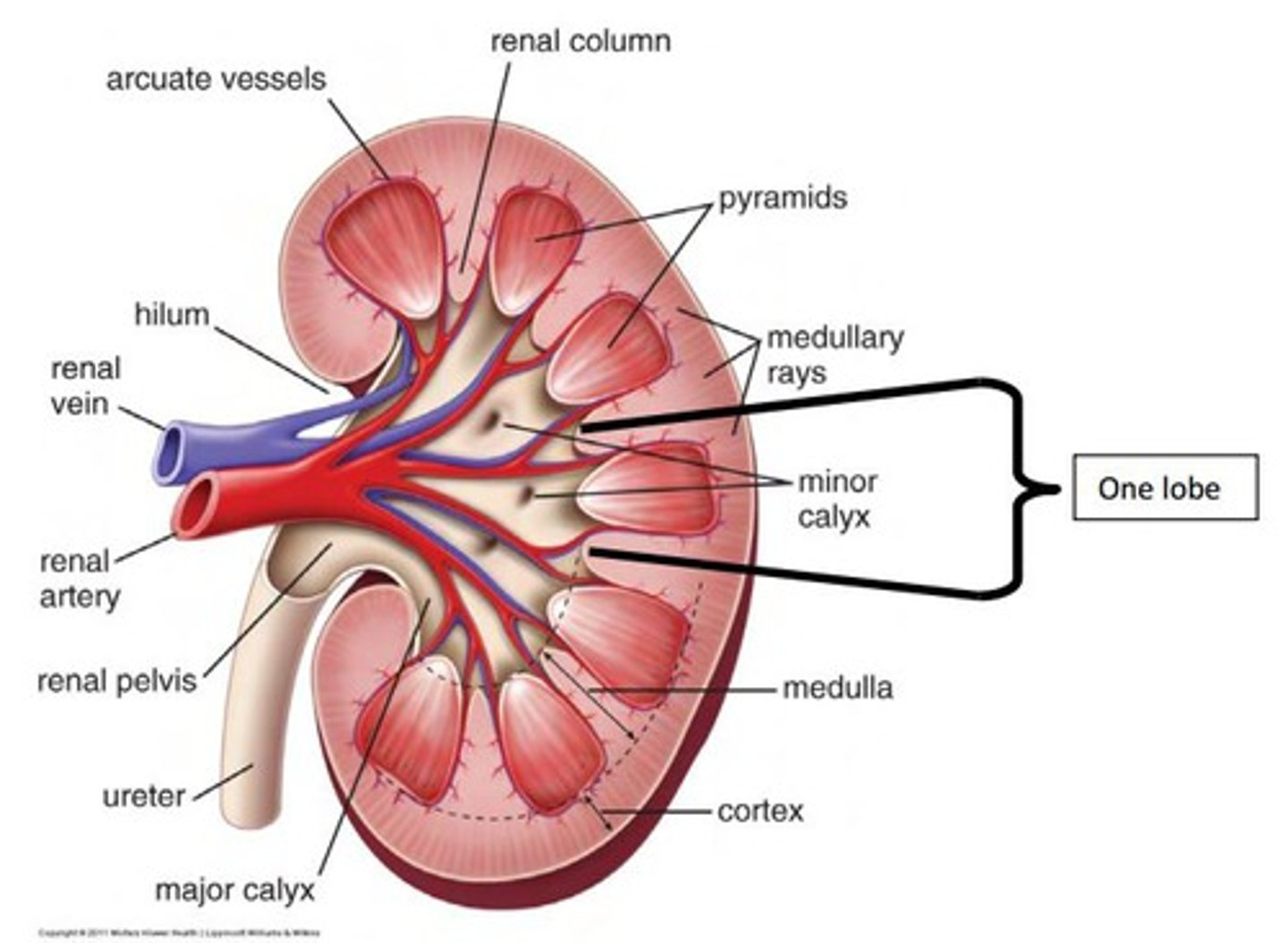
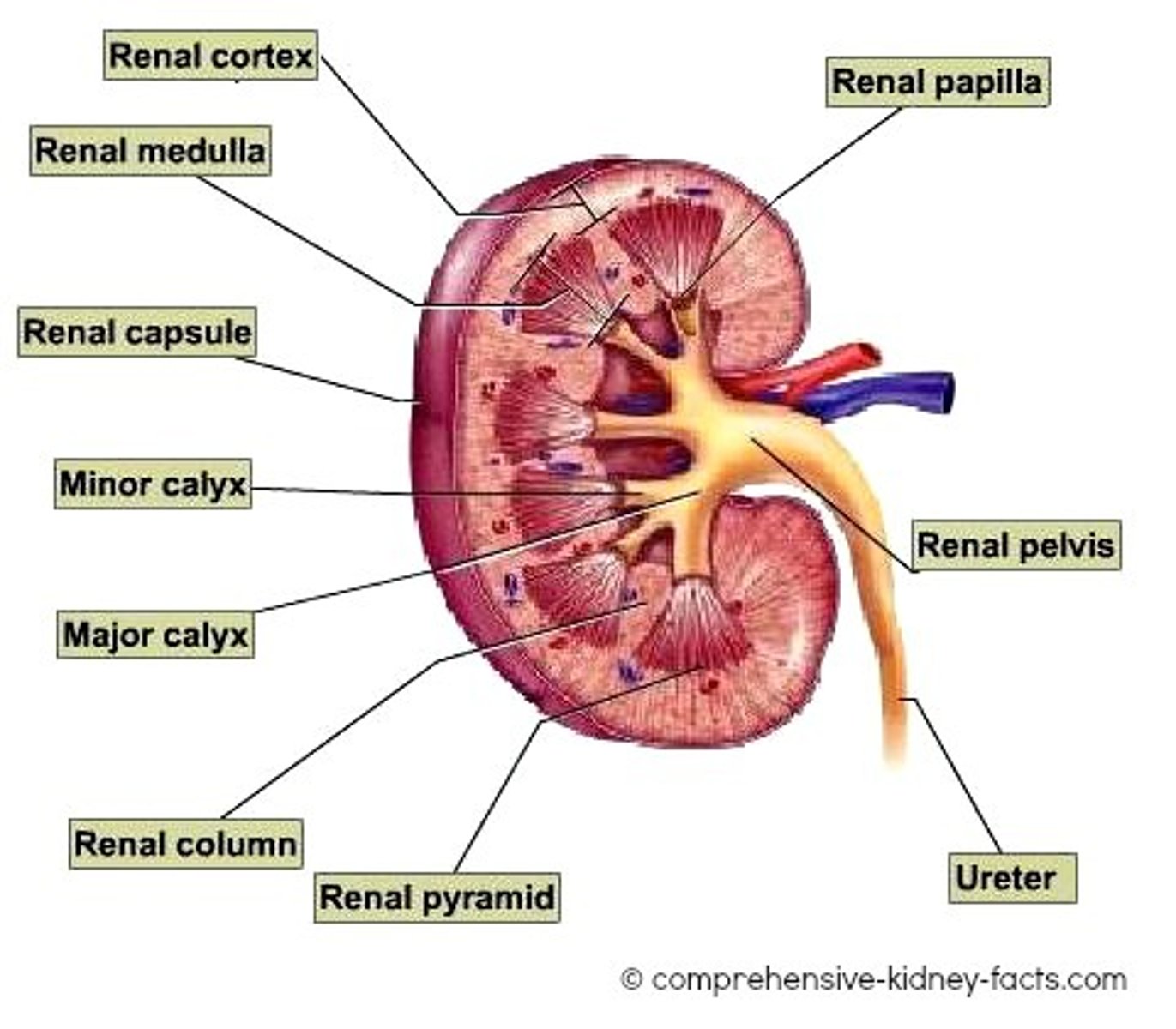
Kidney composition (internal)
-renal cortex consisting of glomeruli and tubules of nephrons (functional unit of the kidney)
-central renal medulla consisting of medullary pyramids (grps of loops of henle, vasa recta and collecting ducts which lead into minor and major calices, renal pelvis, ureter, and bladder)
ureters
-run from kidneys (renal pelvis) to urinary bladder down posterior abdominal wall and cross over bifurcation of common iliac aa
-transport urine from renal pelvis to urinary bladder
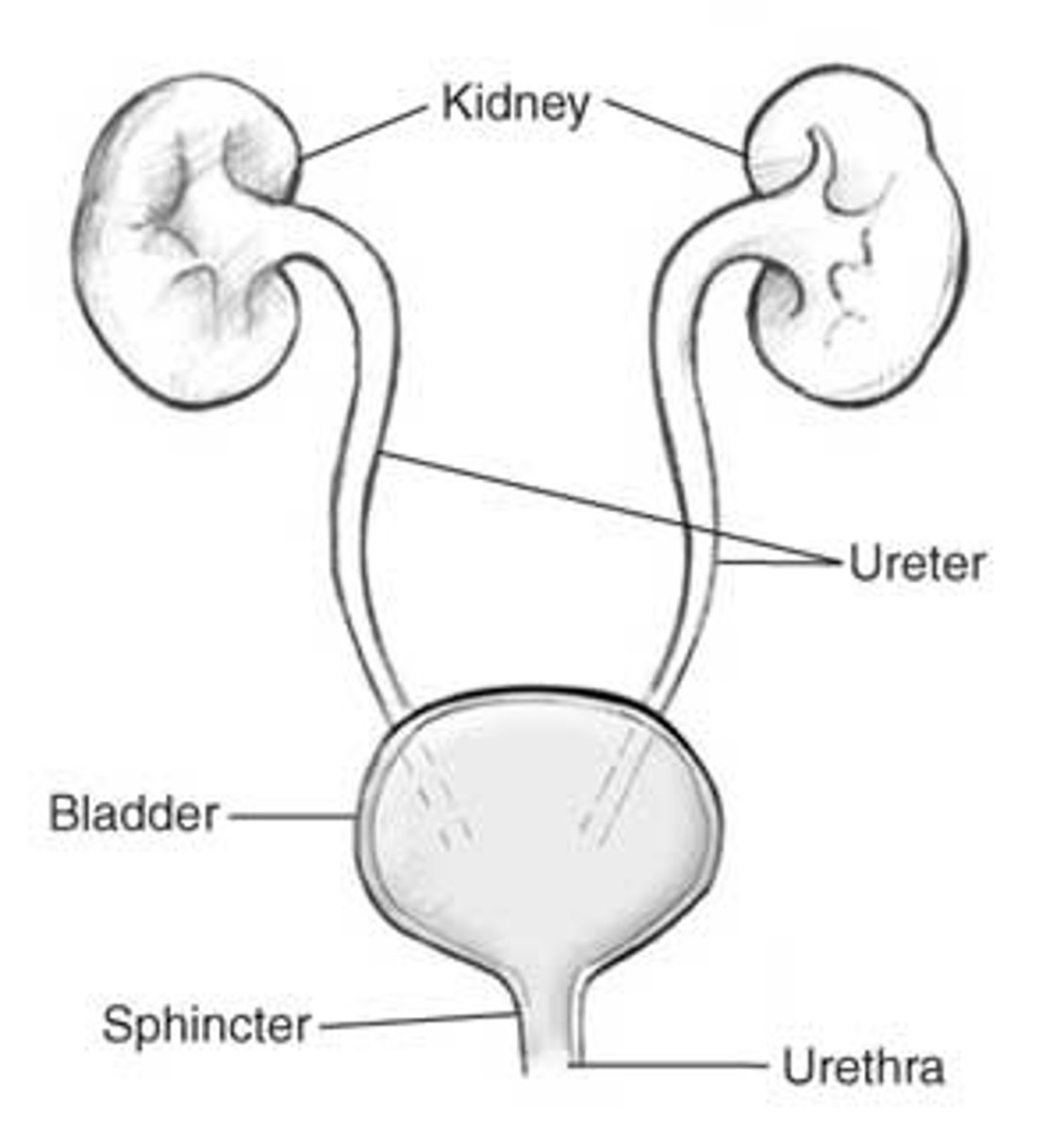
renal pelvis (of kidney)
suprarenal glands
-sit on top of kidneys
-secrete aldosterone, cortisol and androgens from the adrenal cortex
-secrete epinephrine from the adrenal medulla
-post ganglion for this glans is the release of epinephrine into blood
aldosterone
-increases reabsorption of Na+
cortisol
-stimulates gluconeogenesis/mobilizes fuels
-suppresses immune system
androgens
-secondary sex characteristics in males
-precursors to estrogens in males and females
What organs can be damaged by broken ribs?
-lung
-liver
-spleen
-kidney
Sympathetic innervation
-part of ANS
-thoracolumbar system
-shorter pre-ganglion
-longer post-ganglion
-4 pathways
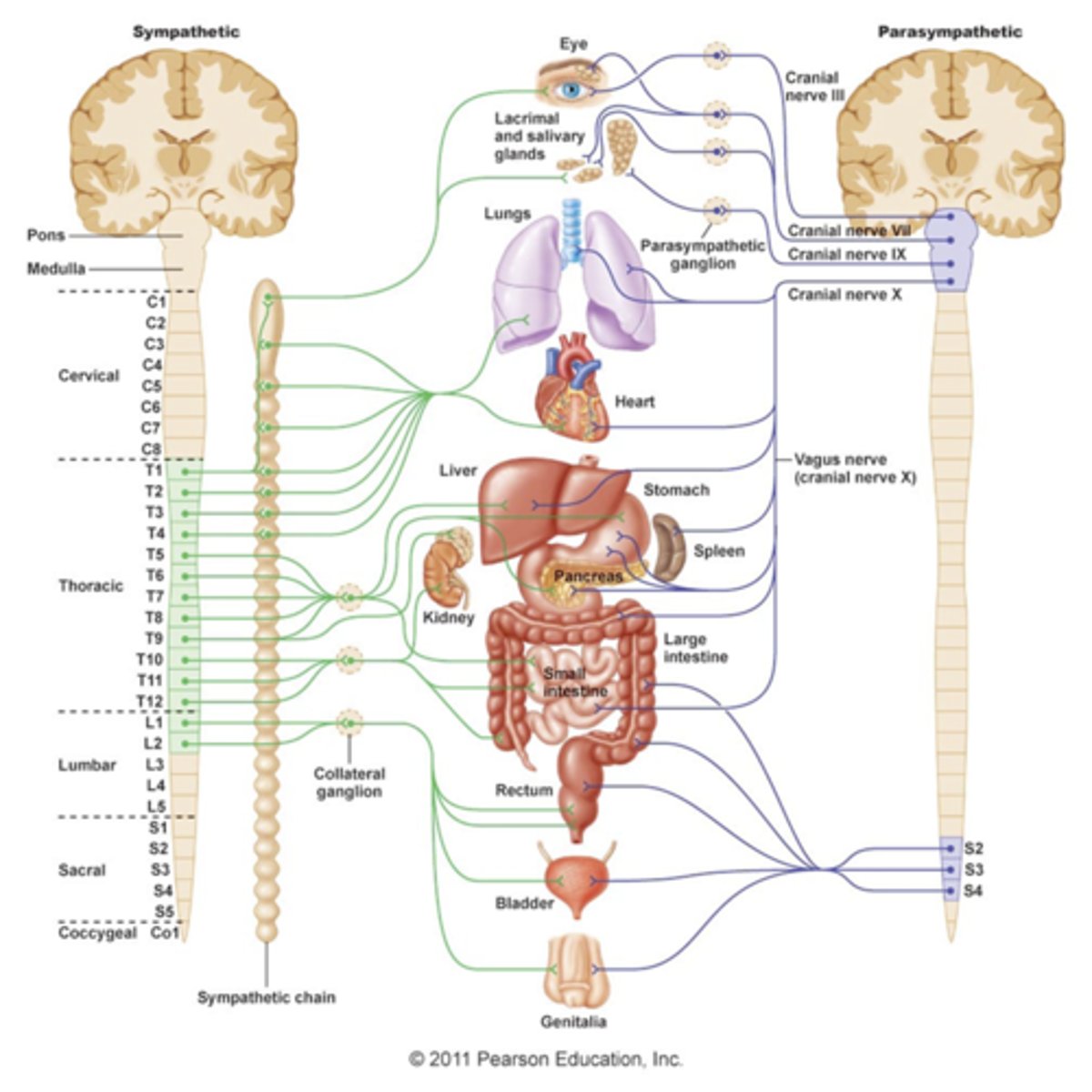
4 pathways of sympathetic innervation
-synapse in sympathetic chain ganglia at same spinal level
-go up or down sympathetic chain before synapsing at different spinal level
-go straight thru sympathetic ganglia w/o synapsing and travel to celiac, superior and inferior mesenteric ganglia via greater (T5-T9), lesser (T10-T11) or least (T12) splanchnic nn.
-go straight through sympathetic ganglia w/o synapsing and go to suprarenal glands to secrete epinephrine directly into blood
sympathetic post ganglionic neurons
-tend to be long
-innervate effector organs like smooth muscle of blood vessels
Parasympathetic innervation
-craniosacral system
-pre-ganglion are long and come from the brain (vagus n, CNX) and sacral vertebrae
-synapse with post-ganglionic neuron (shorter) in a given effector organ (ex: vagus n. travelling thru esophageal hiatus to synapse with a post-ganglionic neuron in the GI tract to cause peristalsis)
Blood supply to the abdominal cavity
-inferior phrenic aa.
-celiac trunk
-sup/inf mesenteric aa
-renal aa
-testicular and ovarian aa
-lumbar aa
-common iliac aa
inferior phrenic aa
-come off abdominal aorta above celiac trunk
-feed diaphragm from below
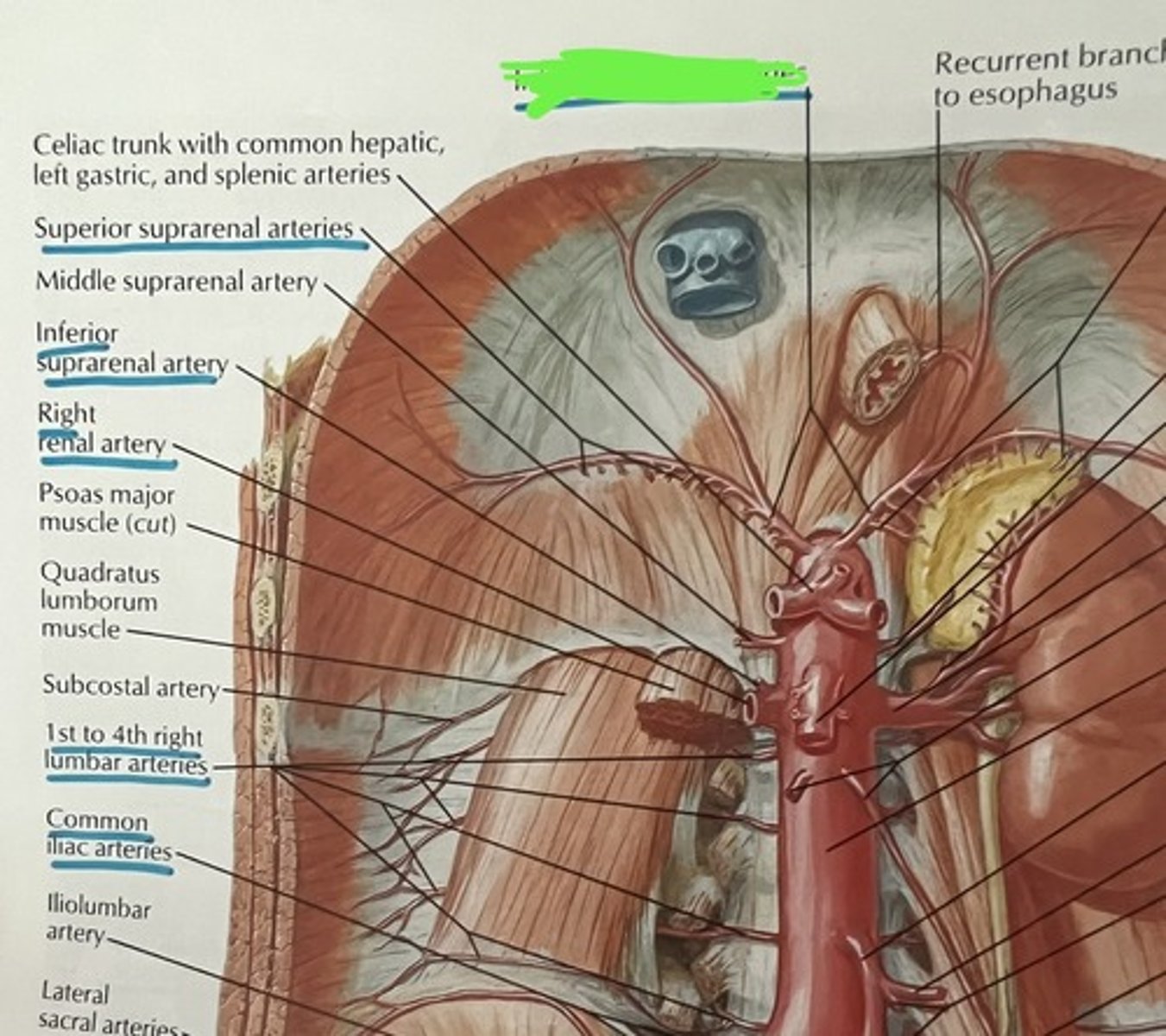
celiac trunk
-comes off abdominal aorta
-gives off: common hepatic a., left gastric a., splenic a.
common hepatic artery (2)
-gives off proper hepatic artery which supplies liver
-gastroduodenal which gives off branches that supply gallbladder, duodenum, pancreas and stomach
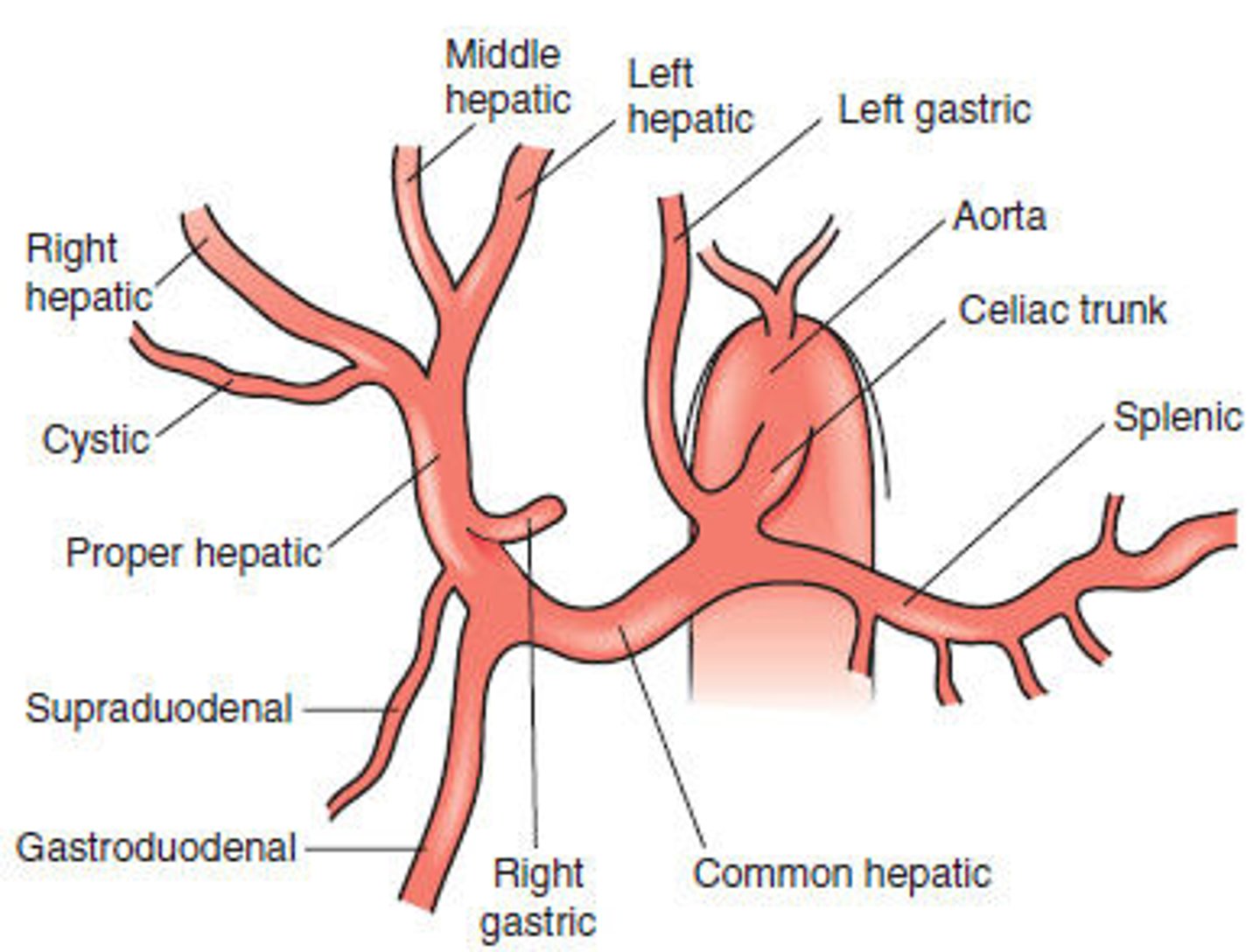
left gastric artery
-supplies stomach and esophagus
splenic artery
-supplies spleen, stomach, and pancreas
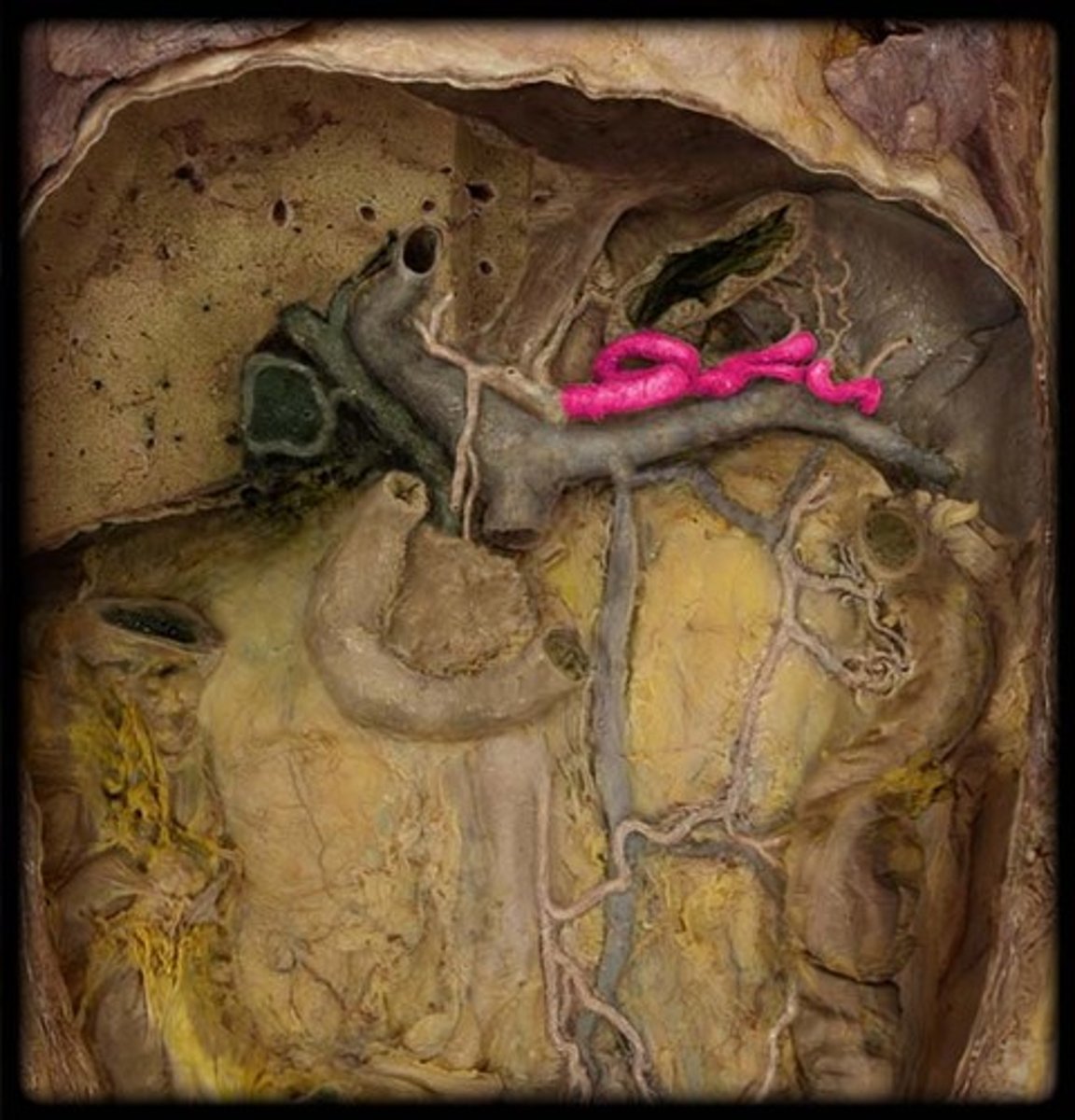
Superior mesenteric artery
-supplies small intestine, cecum, ascending colon and 1/2 of the transverse colon
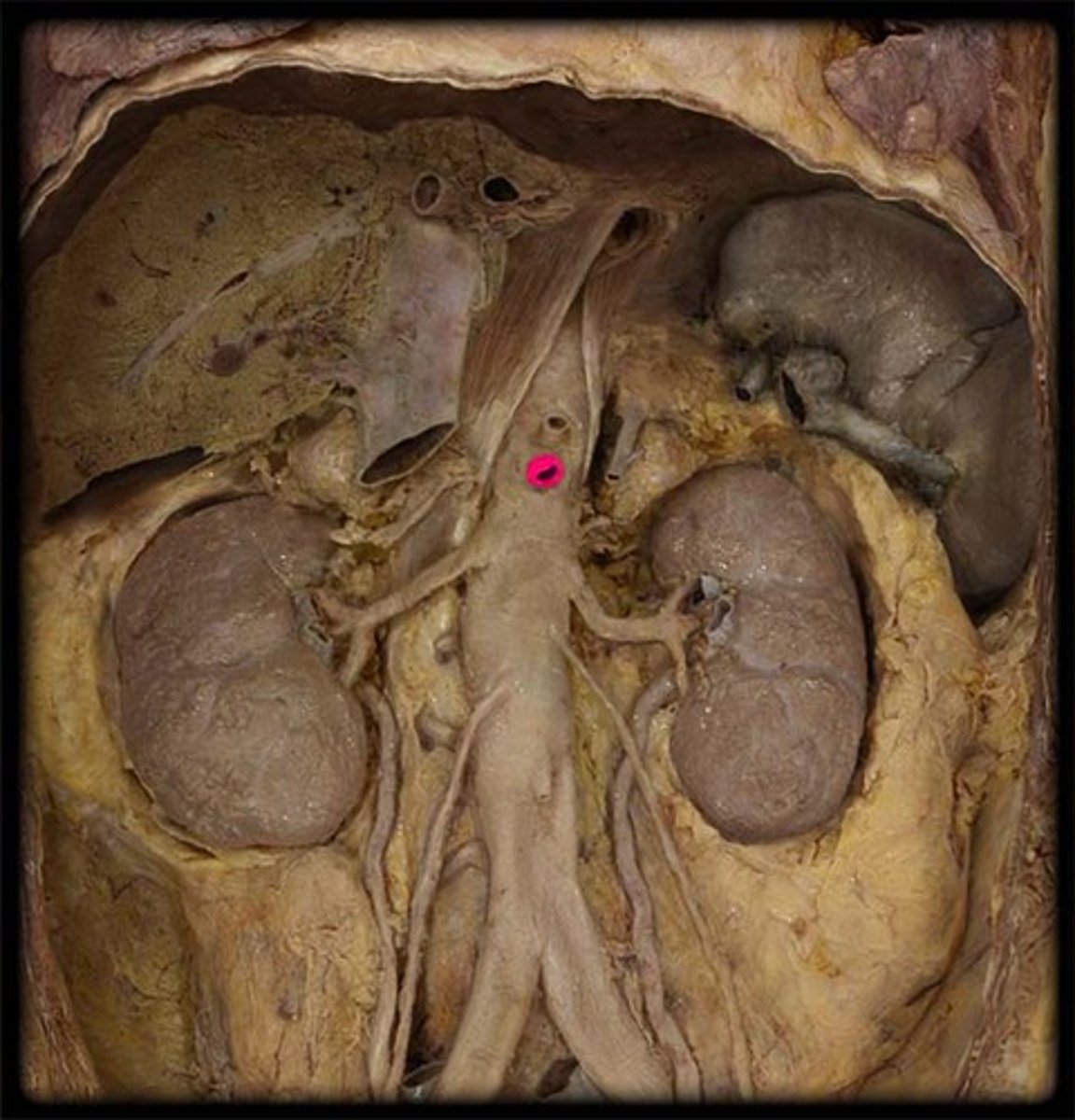
inferior mesenteric artery
-supplies 1/2 of transvers colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum