Micro 20 - Lab exam 2: Parasitic Protozoa and Helminths
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is the infective stage of protozoa?
Cysts
- resisting dormant stage that helps the organism surive the environment
What is the vegetative stage of protozoa?
Trophozoite
- actively feeding, metabolizing and reproducing stage
Entamoeba histolytica
pseudopodian parasite of class Sarcodina that causes amebic dysentery
infective, resistant cysts are released from the lumen of the itnestine through fececs and are deposited in water, soil, or on vegetation
upon digestion the mature quadrinucleated cyst wall disintegrates and the nuclei divide producing eight active trophozoites that move to the colon where they establish infection
Entamoeba histolytica cyst
Infection by ingestion of cysts in contaminated drinking water
- causes diarrhea, dysentery and liver abscess
- has chromatid bar
Dx: fexal exam/serological test
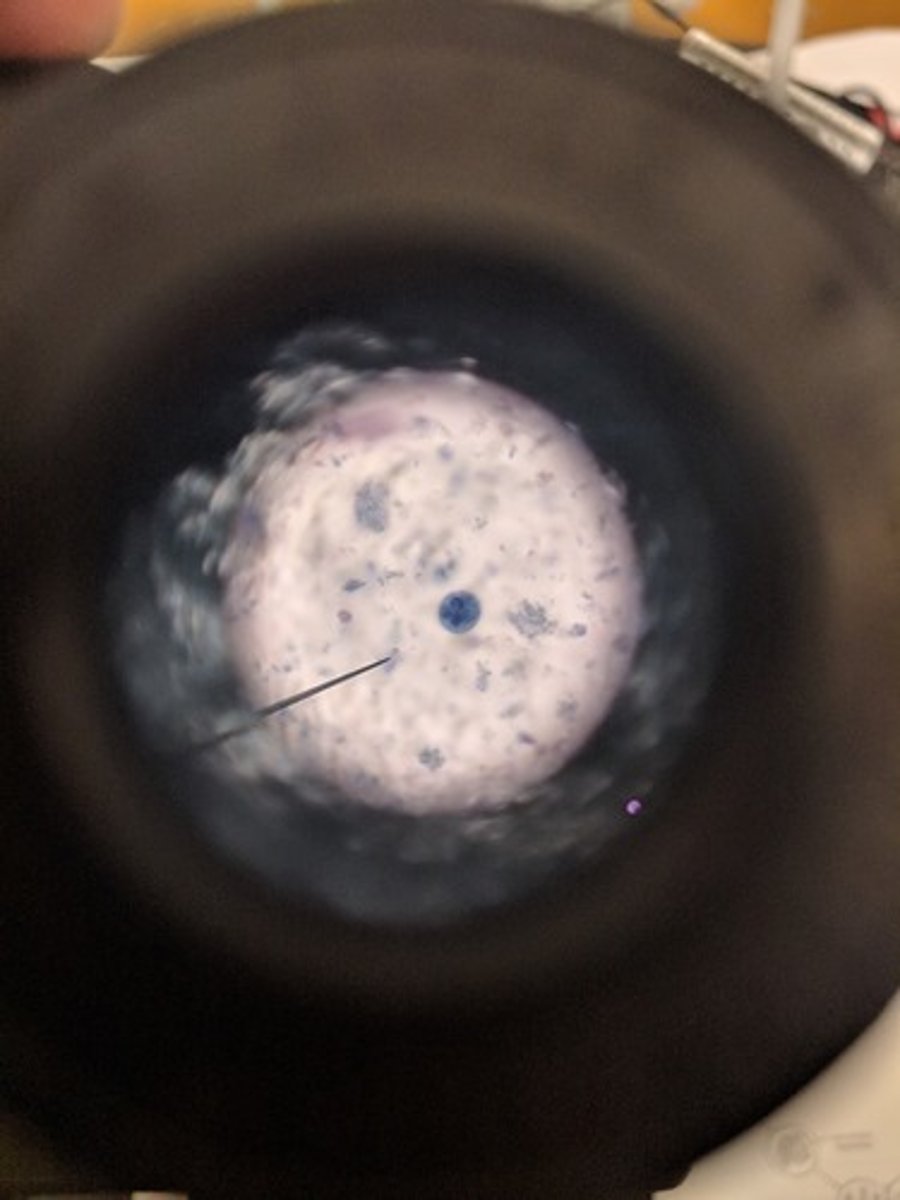
Entamoeba histolytica cyst pic2

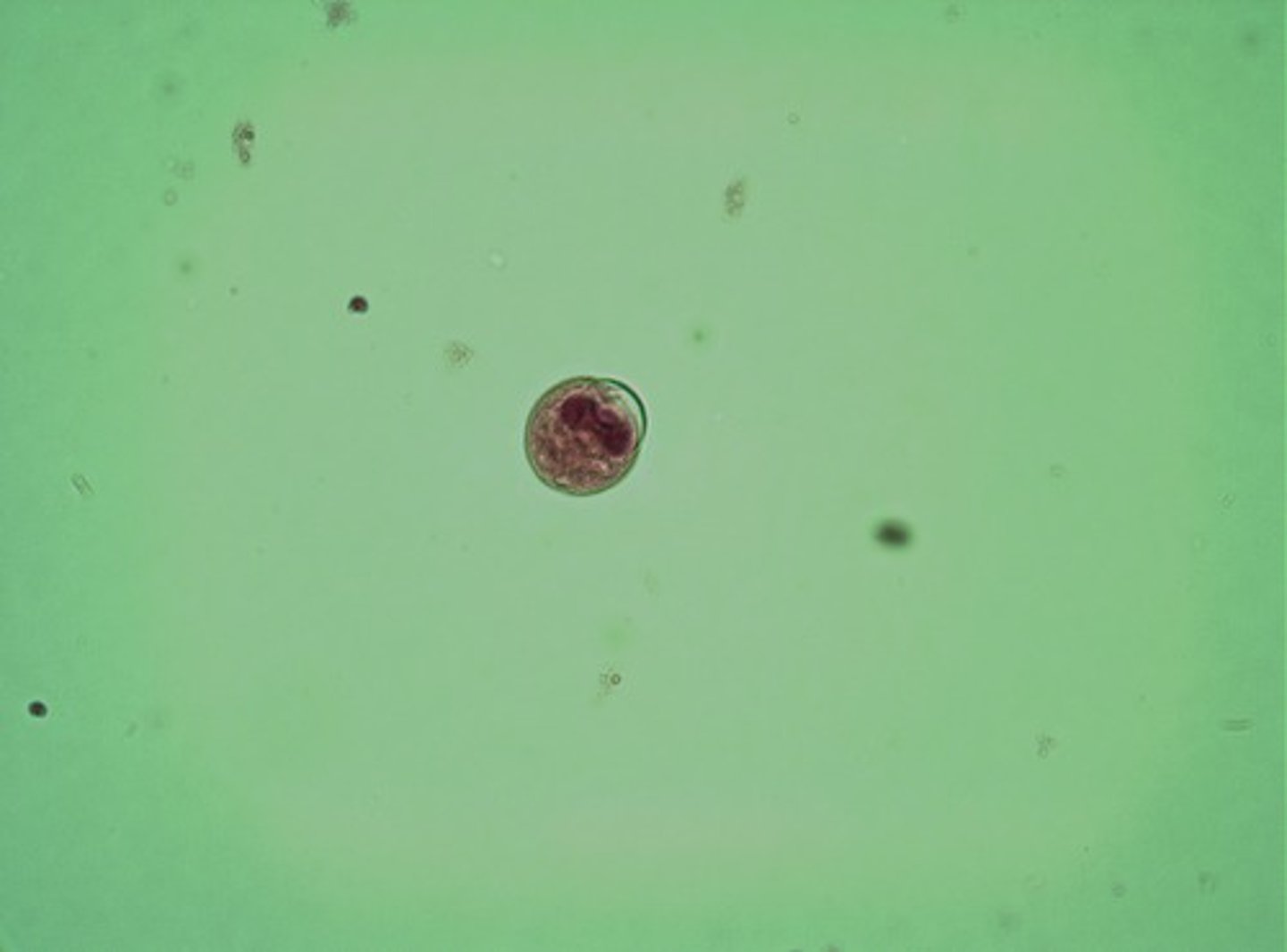
Balantidum coli
- ciliated parasitic protozoan similar to E.histolytic, but does not multiply within the cyst
- organism resides primarily in the lumen and submucosa of colon
- causes ulceration and alternating constipation and diarrhea
Balantidum coli cyst
Has double walled yeast cell
Balantidum coli trophozoite
Has cytostome (mouth) and micronucleus is outside of macronucleus
ciliated
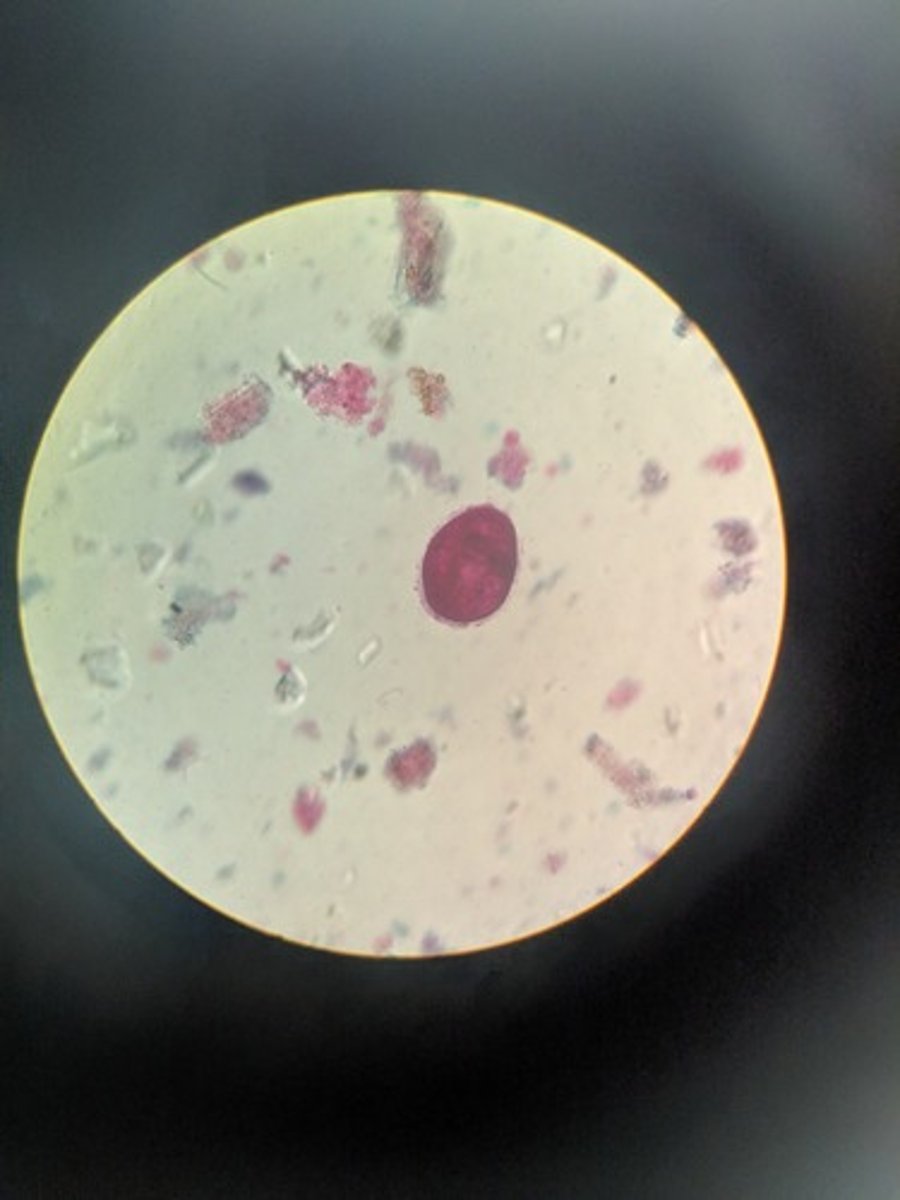
Giardia lamblia cyst
Ingestion of cysts in contaminated drinking water
- Oval with well defined cyst wall
- four nuclei present at one pole
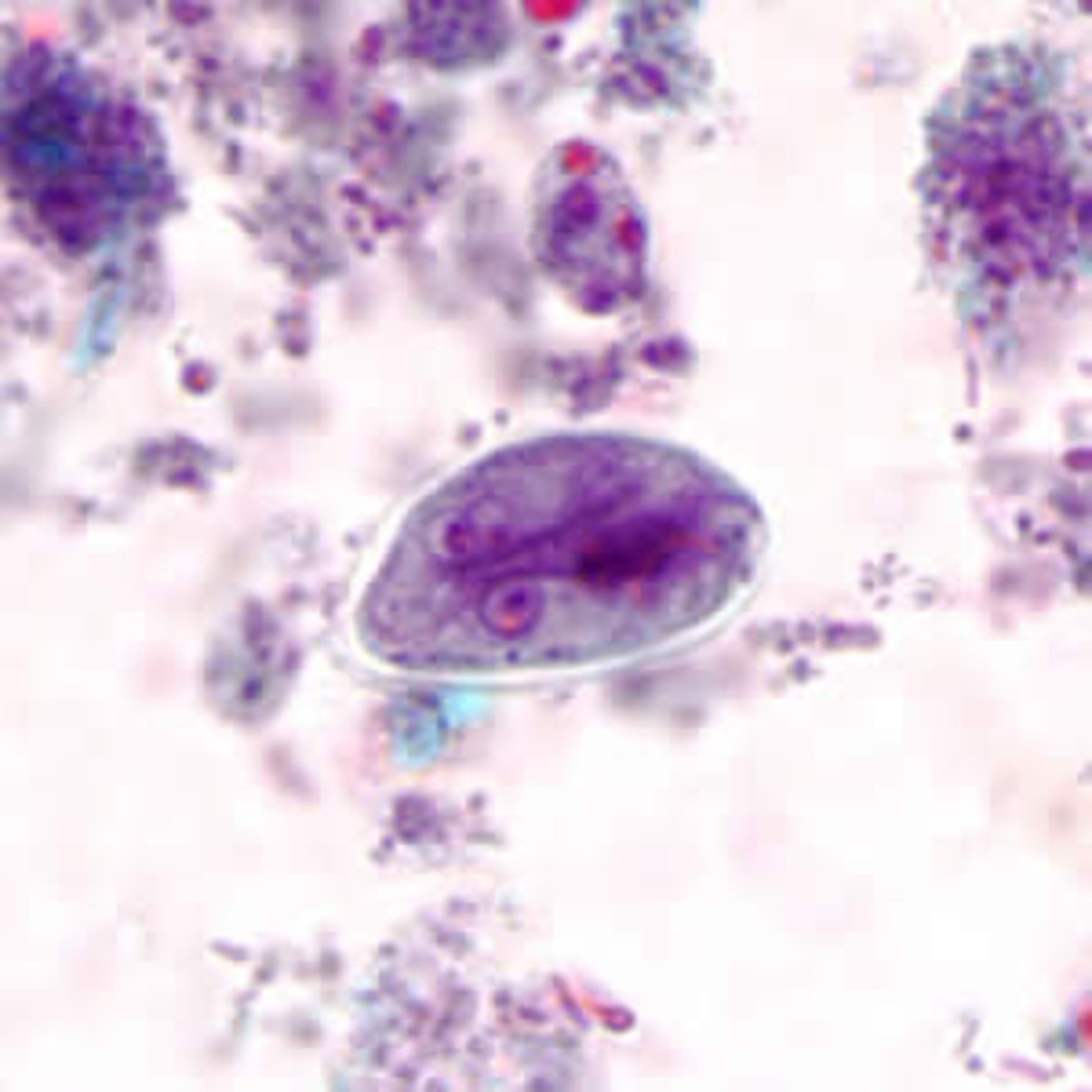
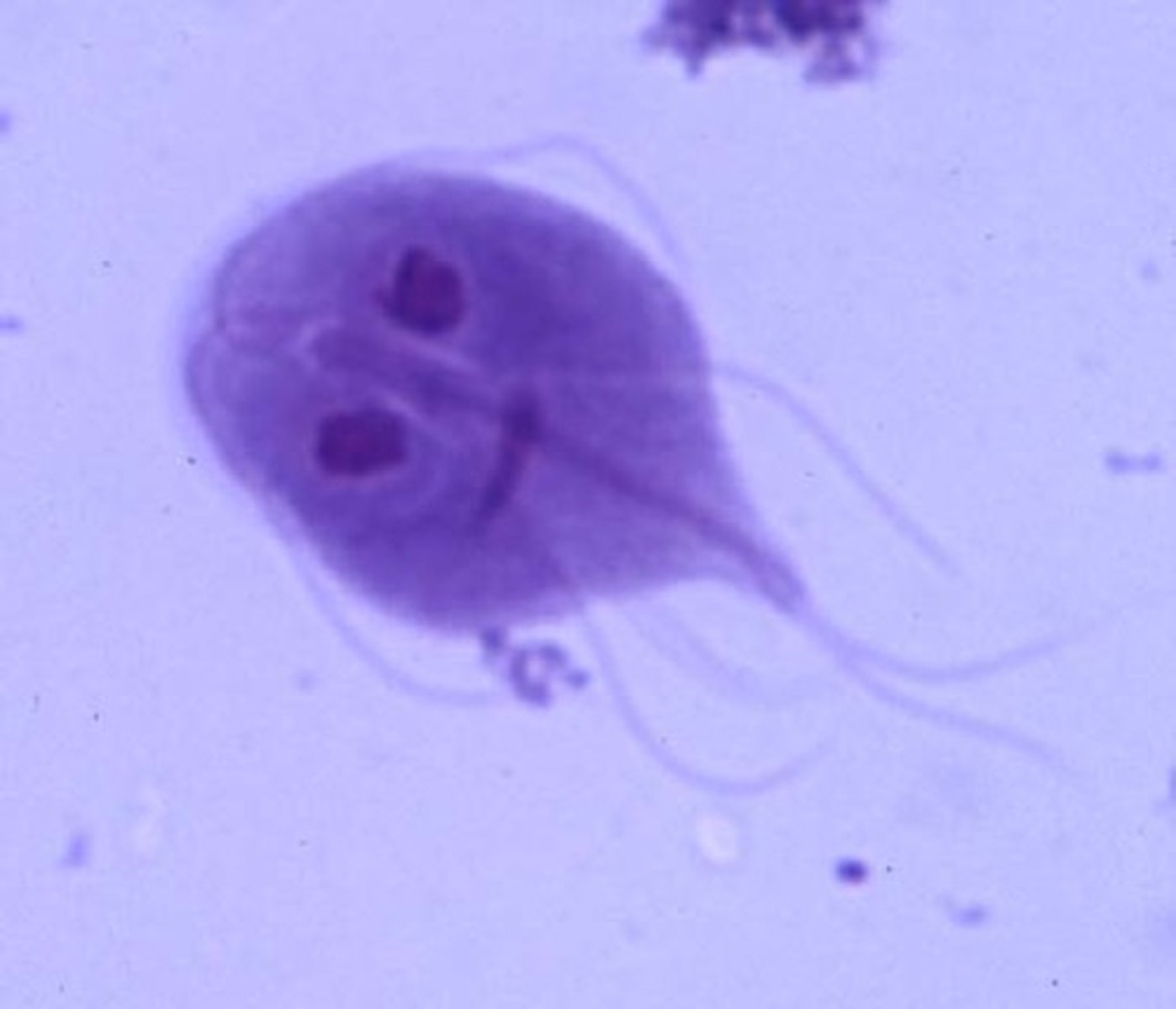
Giardia lamblia trophozoite
Has a kite shape, and flagella
Helminths
multicellular eukaryotic animals that generally possess digestive, circulatory, nervous, excretory, and reproductive systems
- some are free living in soil or water, and some are parasites of humans, animals, or plants
- cause infectious diseasesl disagnosed by microscopic examination of eggs or larvae
- eggs may have striations, a spine, or operculum (hatch where eggs leave)
Life cycle of parasitic helminths
- highly modified compared to free-living helminths
- lack sense organs and sometimes digestive systems
-reproductive system is complex w/ characteristics that promote infeciton of new hosts
Dioecious helminths
separate male and female
Monoecious (hermaphroditic)
male and female reproductive systems in one animal
Intermediate host
an organism that supports the immature or nonreproductive forms of a parasite
- some parasites have a different host for each larval stage
Ex. humans may be intermedaite host for dog tapeworm
Definitive host
Adult (reproductively mature) stage of parasitic helminth lives in the definitive host
-humans can serve as definitive host for beef, pork, and fish tapeworms
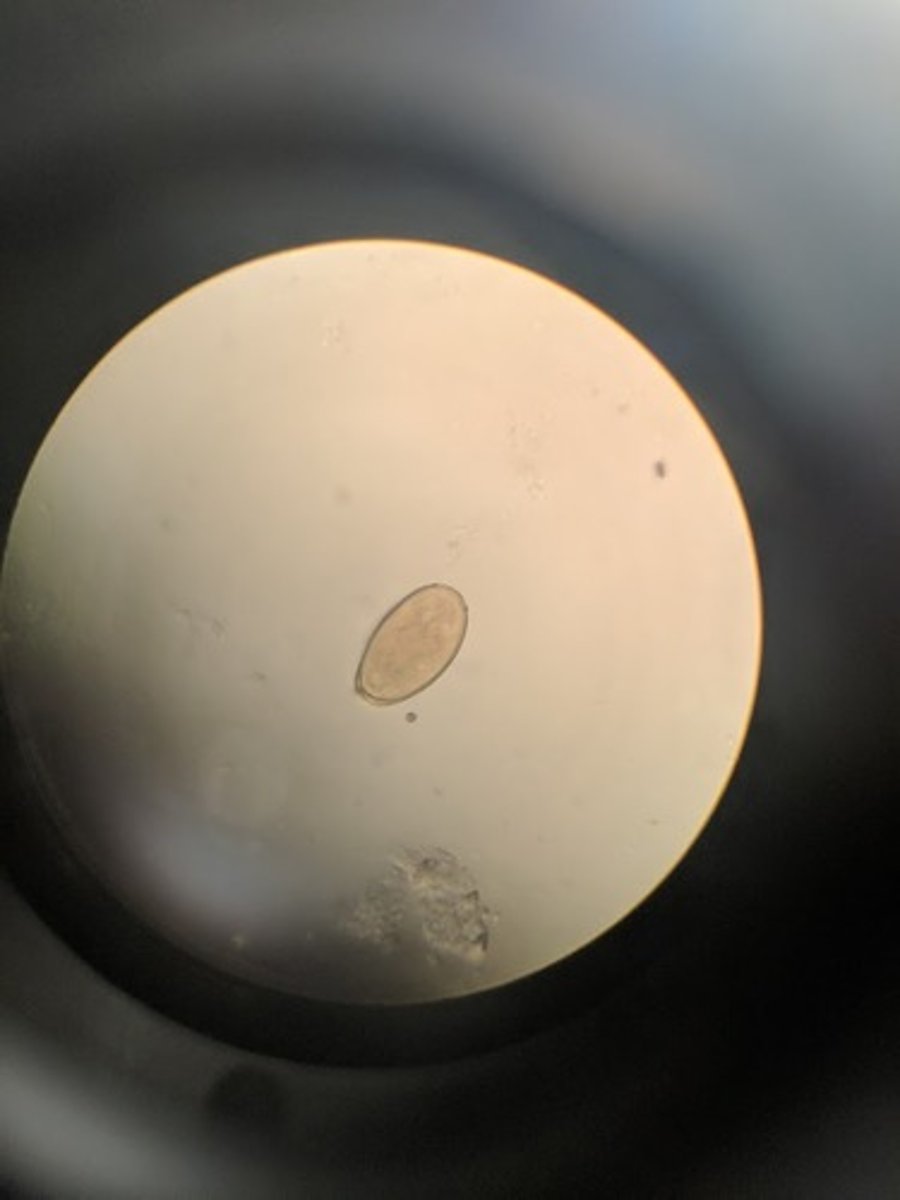
Paragonimus westermani
Lung fluke
- oval ova, have an operculum (lid)
- golden in color
-shell has unevne thickness
-snails and crayfish are intermediate host
man is definitive host
Schistosoma mansoni
- Penetration of skin by larva
-dx by fecal exam for eggs
- blood fluke / flatworm

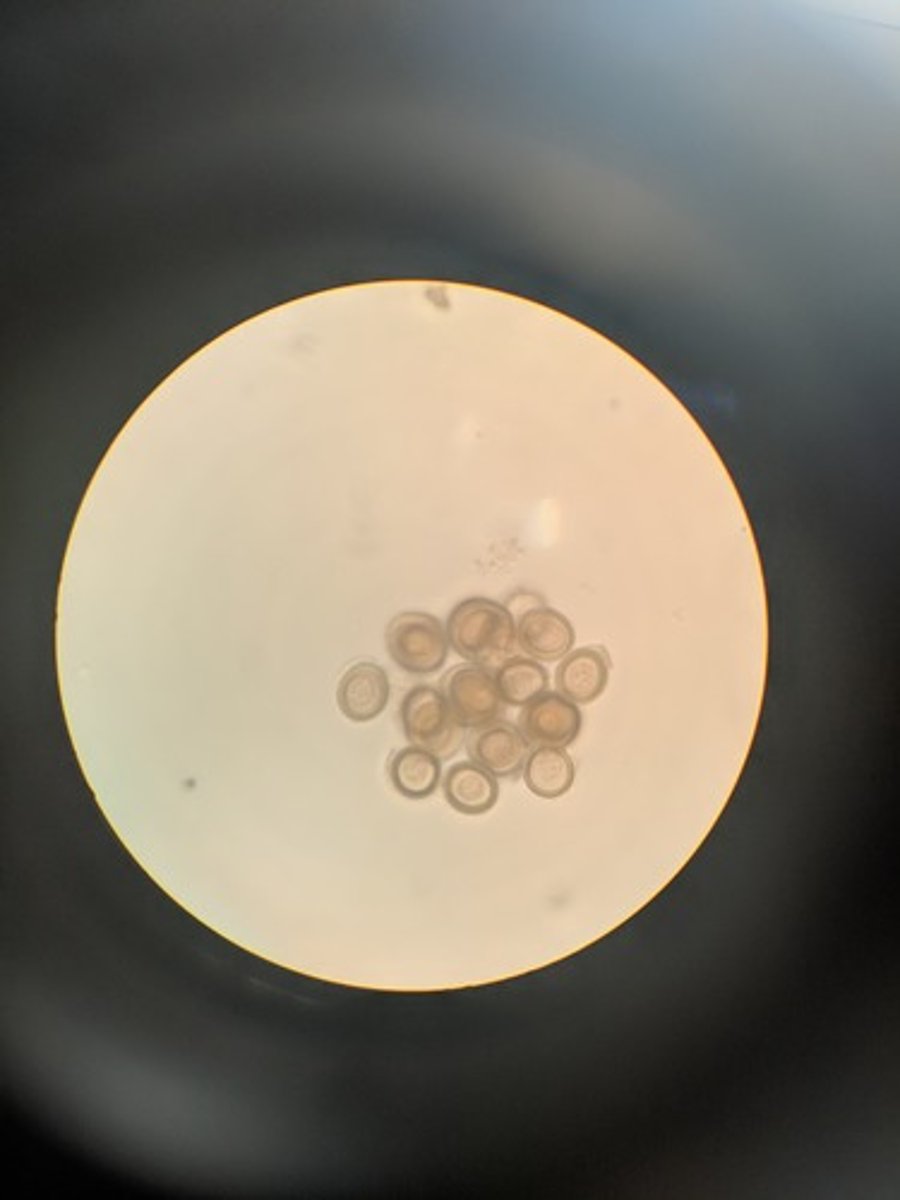
Taenia solium
Ingestion of Larvae or eggs, (if eggs, man is intermediate host, if larvae, pig is int. host.)
- pork tapeworm
- dx: fecal exam for tapeworm eggs or exam of affected tissues for larvae
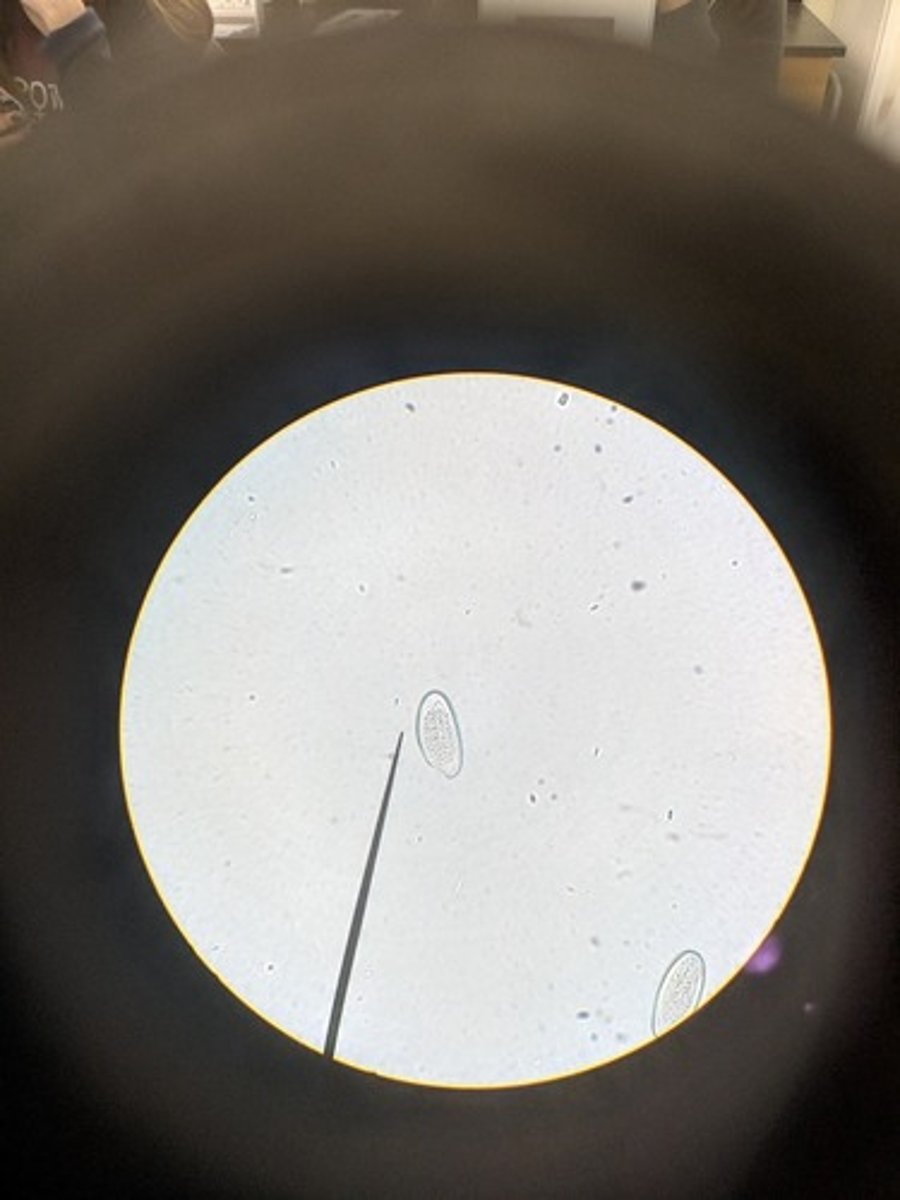
Enterobius vermicularis (roundworm)
- pinworm
- very abundant like grains of rice
- egg shape with one flat side
- larvae worm folded in half
-transparent shell
Eggs = infective form
dx: fecal exam for eggs / scotchtape method
Ascaris lumbricoides (roundworm)
Eggs = infective form
dx: fecal exam for eggs
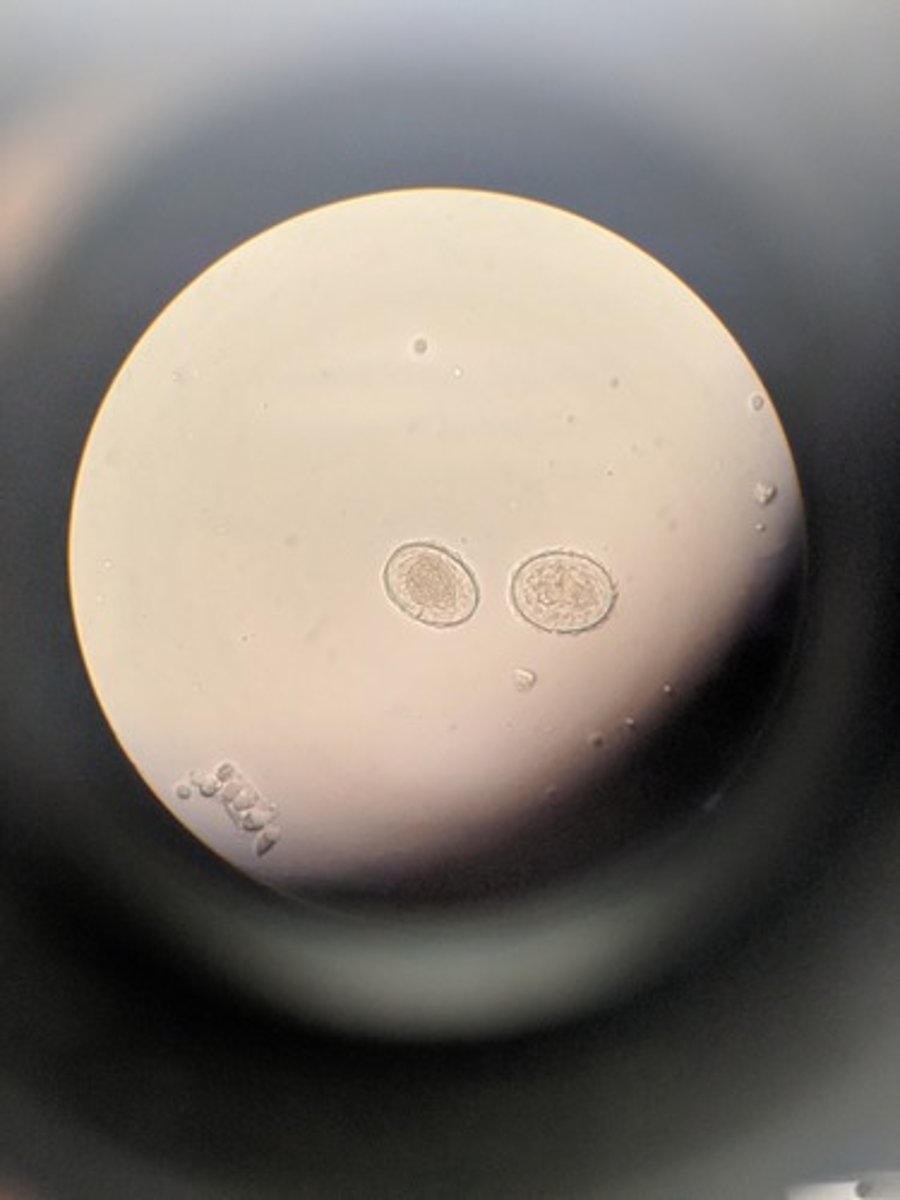
Trichuris trichuria (roundworm)
has two pinched ends
eggs = infective form
dx: fecal exam for eggs
"whipworm"
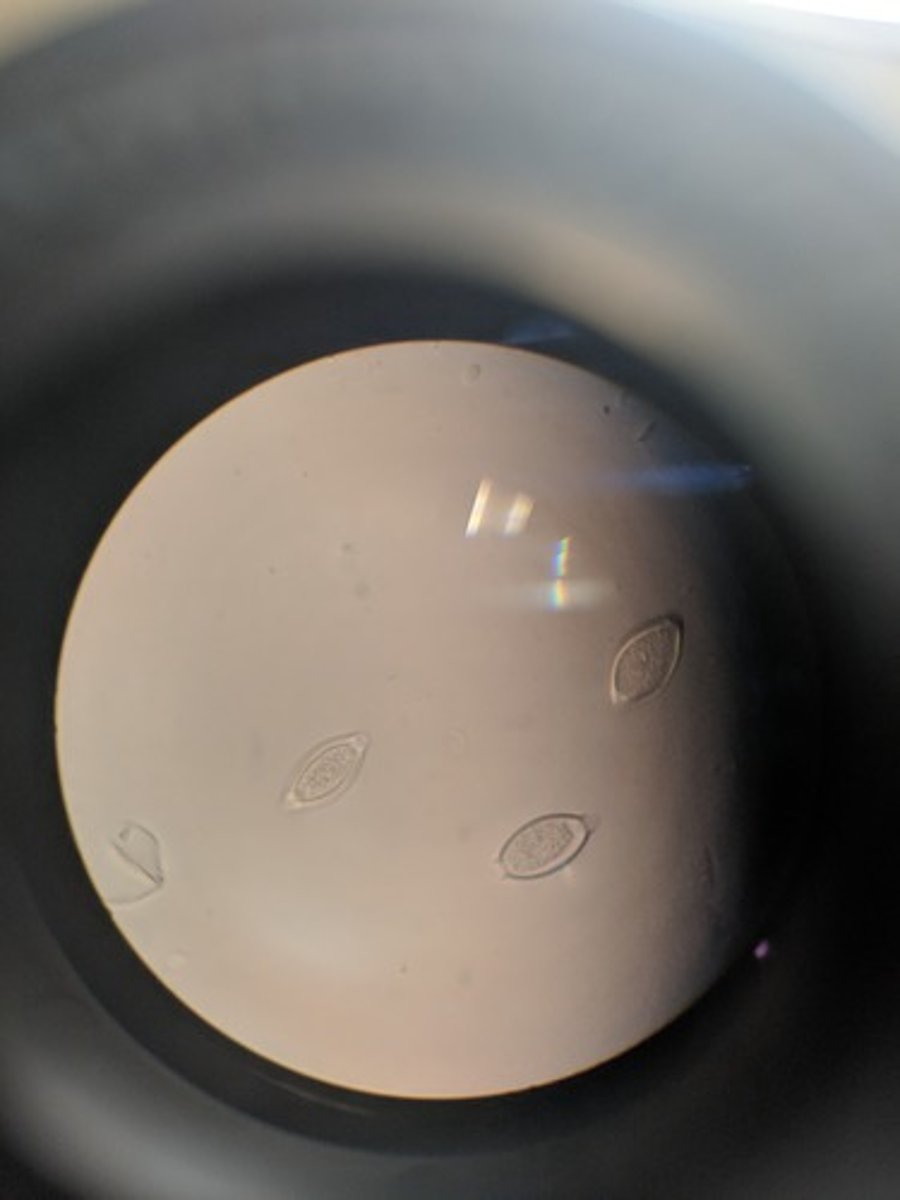
Necator americanus (hookworm&roundworm)
Larvae = infective form
dx: fecal exam for eggs
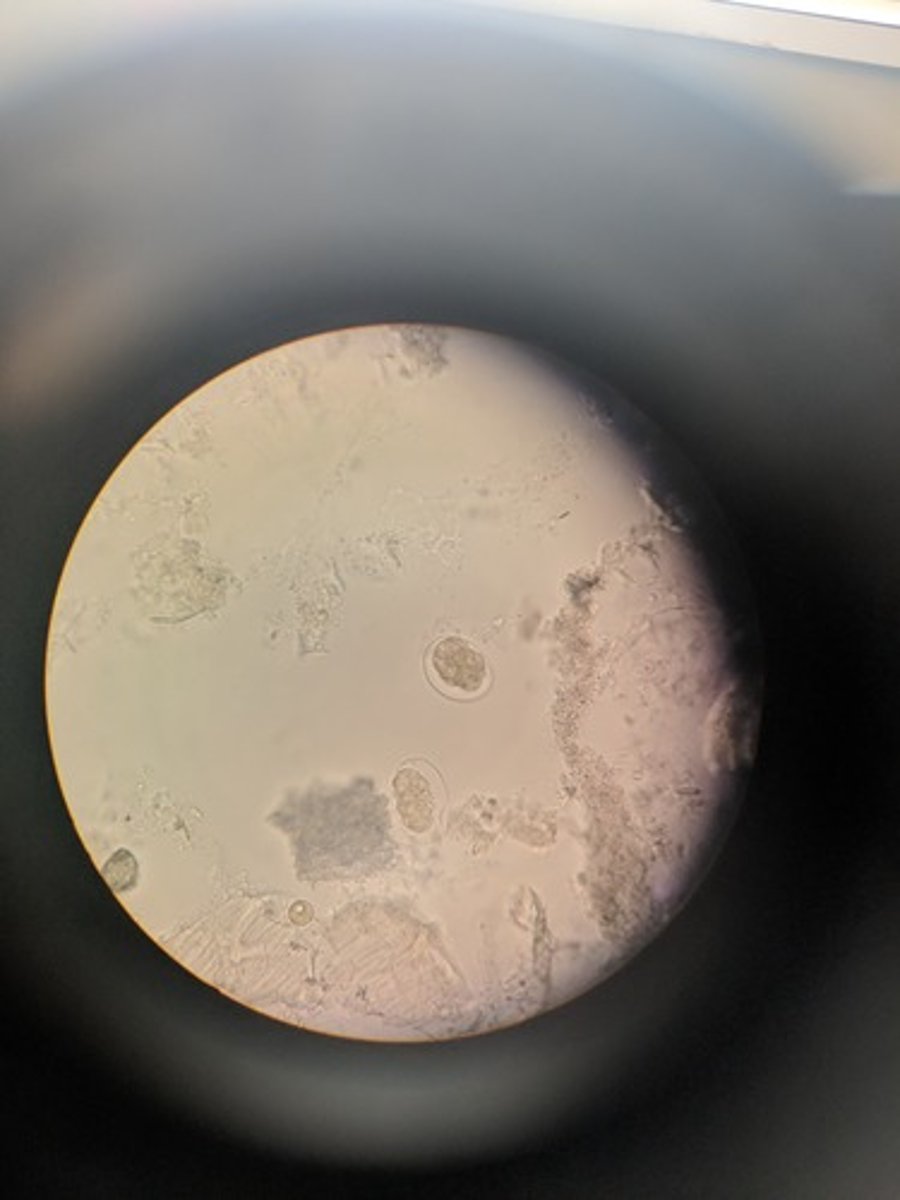
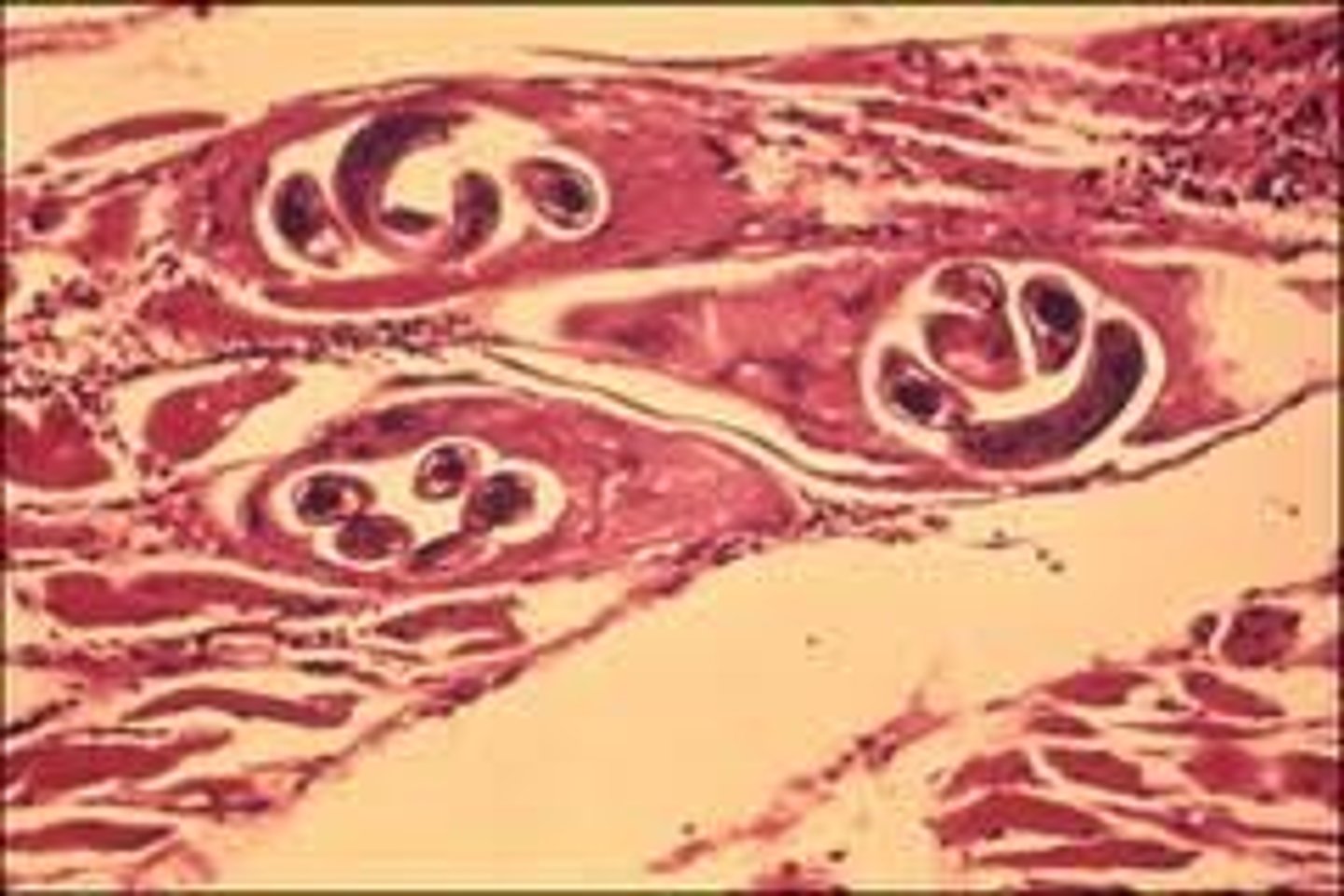
Trichenella spiralis (encysted larvae / roundworm)
Infective form: larvae
Man eats pork/bear meat containing larvae which then mature in man's intestine & reproduce; second generation larvae hatch and migrate through the body to become encysted in muscle tissue
Flatworms
Trematodes/flukes: flat, leaf shaped bodies with ventral and oral suckers
- obtain food by absorbing it through their "cuticle" outer covering
Cestodes/tapeworms - intestinal parasites
- has a scolex (head) which contains suckers for attaching to the intestinal mucosa of definitive host and some may have hooks
- Proglottids = body segments
Roundworms
Nematodes - cylindrical and taper at each end
- have complete digestive system (mouth, intestine, anus)
- Most are dioecious
- males have spicules to guide sperm
Ova
Eggs
Larvae
morphologically distinct juvenile forms