Optical Properties of teeth
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
translucent
not transparent but clear enough for light to pass
translucency in teeth increases from gingival towards incisal
the longer the wavelength of incident light, the more ____ is the enamel
translucent
light transmission of enamel is ___ and dentin is___
70.1%, 52.6%
refrective index
How fast the light propagates through a material.
determines also how much the path of the light is refracted (bent) when entering a material (Snell's law or law of refraction)
Describe the relationship between the angle of incidence and refraction, when light passes through a boundary between two different isotropic media (water, glass, or air).
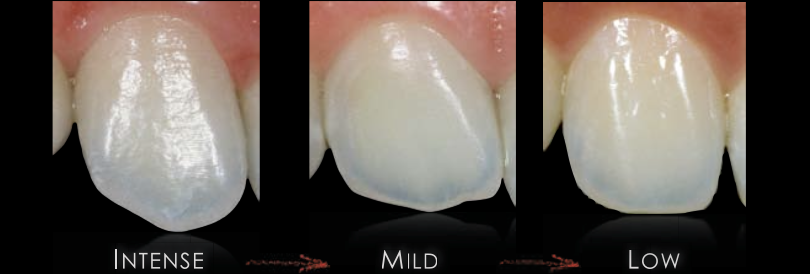
light reflection
The amount of light reflected by an object.
Reflection is highly dependent upon the texture of the surface
Specular Reflection: the incident light is reflected into a single outgoing direction on a smooth surface
Diffuse Reflection: the incident light is scattered at many angles in a rough surface
light scattering: OPALESCENCE
Is a phenomenon that occurs when light transmitted through a given object causes modification of wavelengths, which disperse and refract internally.
Incisal Opalescent Layer
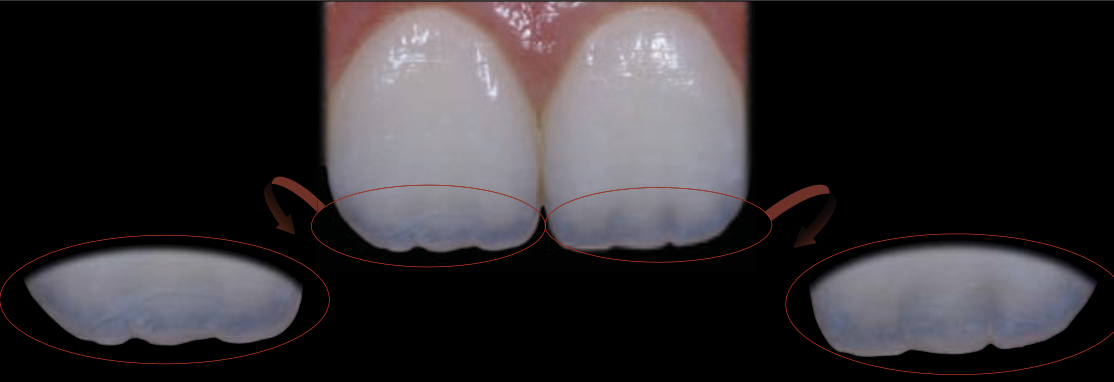
1. Type I - Mamelons
2. Type II - Straight
3. Type III - Diffused
4. Type IV - Mixed
TYPE I: mamelons
features an incisal opalescence that closely related to the dentin mamelons.
*53% of patients exhibit this
either continuous or intermittent, but it has an intimate relationship with the dentin mamelons.
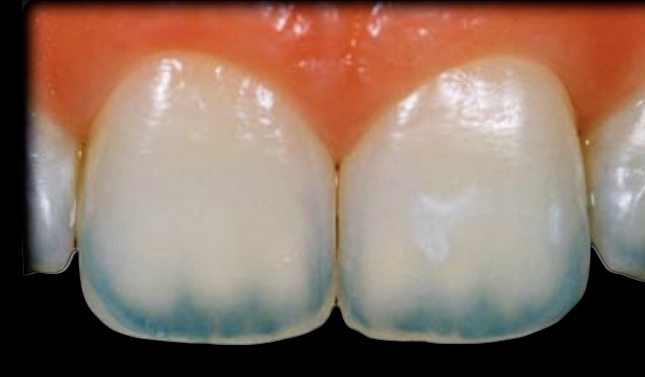
Type II: straight
does not penetrate into the dentin mamelons, instead it maintains a straight line parallel to the incisal border.
*17% of patients exhibit this
the mamelons appeared to fade away at the incised edge.
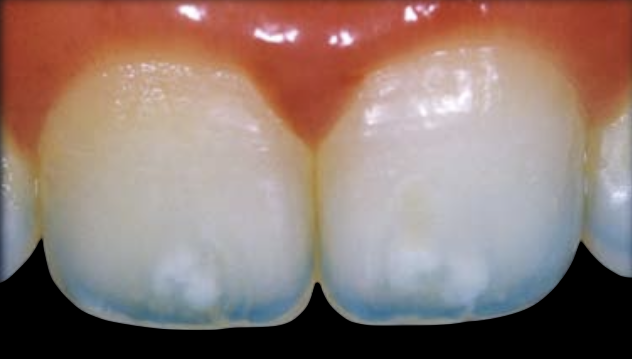
Type III: diffused
diffused type of opalescence that is randomly distributed at the incisal third.
4% of patients exhibit this
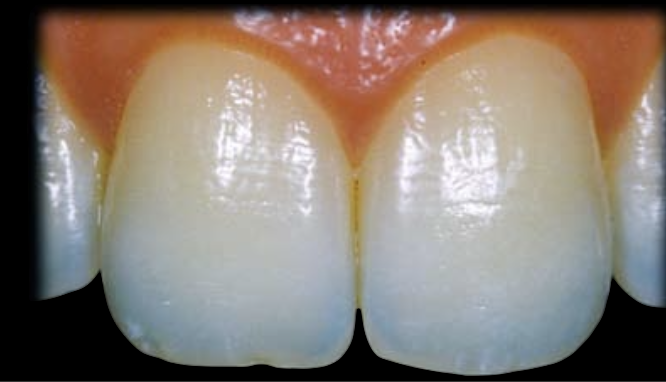
Type IV: Mixed
presents mixed opalescence patterns (1, 2, or 3) associated with some kind of pigmentation or characterization.
25% of patients exhibit this
*White spots, white cloudy pigmentation, or amber staining can be observed
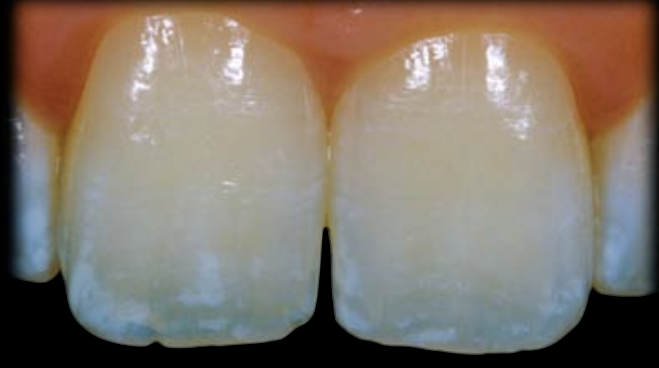
incisal halo
At the incisal third, the incisal border is more opaque than the remainder of the incisal third.
As the enamel prisms are larger than ____ all the visible wavelengths are scattered and deflected from their original path, which makes the border cloudy, opaque, and virtually white in the reflected light.
700 nm,
Fluorescence
Energy is absorbed and emitted at longer wavelength
Is a form of luminescence. In dentistry, it is defined as absorption of UV light by a substance and the spontaneous emission of visible light in the bluish spectrum.
more evident/ primary source in dentin than enamel
color space: HVC
Hue: The name of the color. For example, Red, Green, or Blue
Chroma: is the quality or purity of the color, independent of value.
Value (Brightness, Lightness): This defines the amount of black or white in a color, 'and it is based on the amount of light emanating from the color.
The brighter the color, the closer it is to white and the higher its value.
gingival/ middle have LOWER value (darker) than incisal
select first: Value, chroma then hue
CIE L*a* b
The lightness value, L", represents the darkest black at L = 0, and the brightest white at L 100.
The color channels, a" and b", represent true neutral gray values at a = 0 and b* = 0.
The a* axis represents the green-red component, with green in the negative direction and red in the positive direction.
The b" axis represents the blue-yellow component, with blue in the negative direction and yellow in the positive direction.
shade selection:
A shade: reddish brown
B shade: reddish yellow
C shade: grayish
D shade: reddish gray
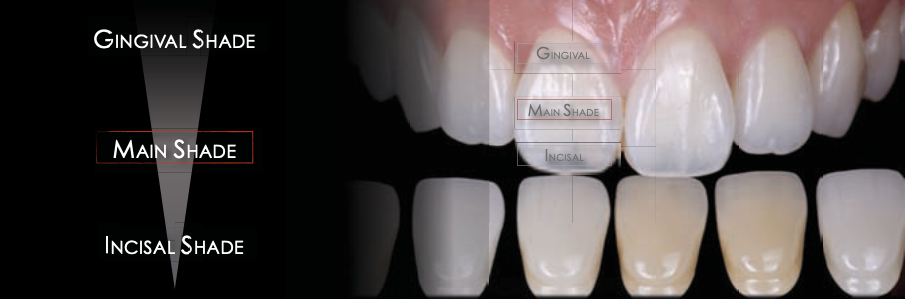
The shade tab must be positioned:
Parallel to the long axis of the Tooth
important to remember that
gingival 1/3 higher in chroma
incisal 1/3 more translucent
middle 1/3 provides main shade
The maximum thickness for the facial enamel composite layer should be ____ in
order to obtain the best translucency, chroma, and value
1.0mm
Enamel: opitcal facts
Highly translucent
High value (bright)
Opalescent
Low chroma
Dentin: Optical Facts
More opaque
Lower value than enamel
Higher chroma
Controls overall tooth color