Anatomy of the Vertebral Column and Back Muscles
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
anterior/posterior
Terms used to describe the front (anterior) and back (posterior) of the body.
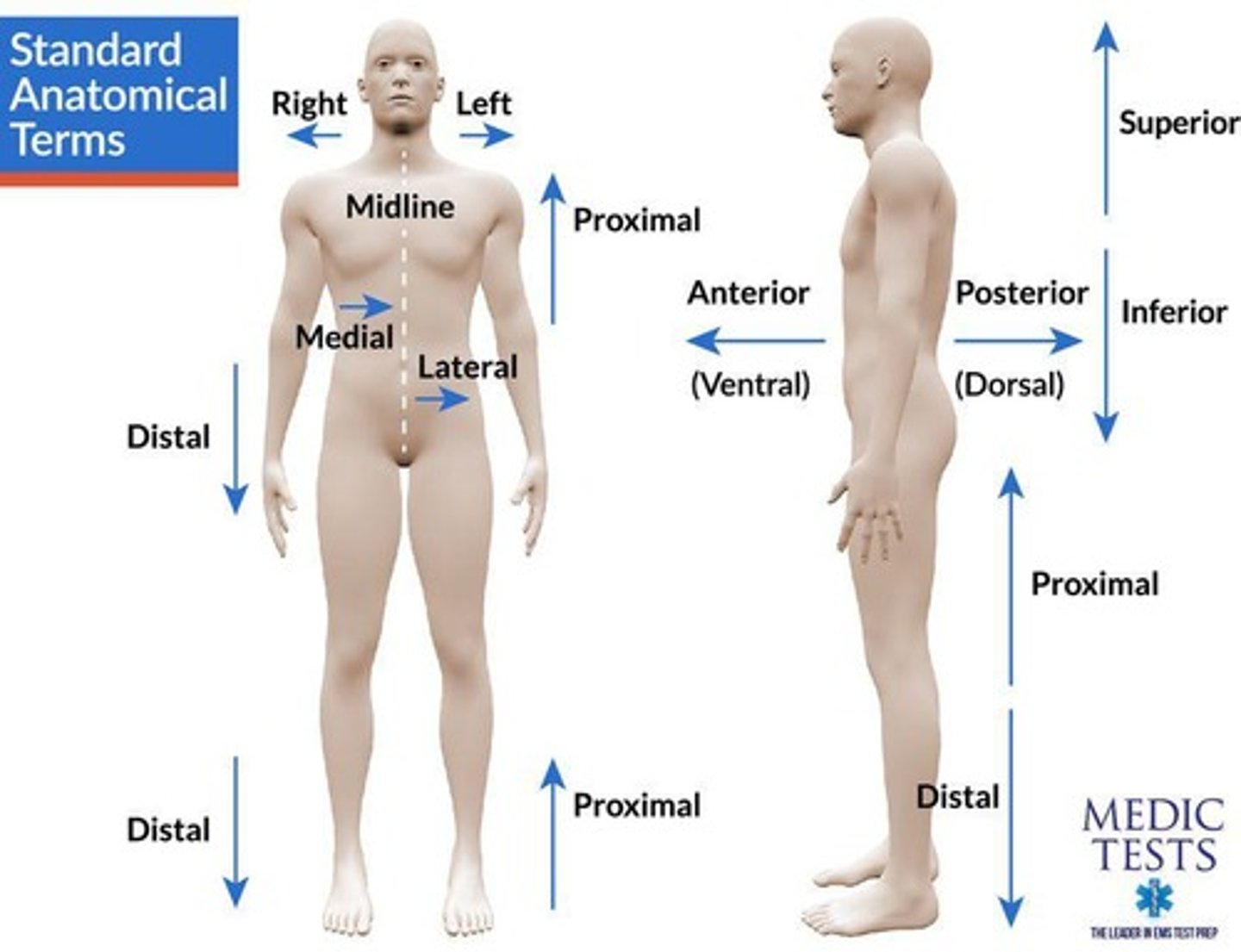
superior/inferior
Terms used to describe the position of structures relative to each other, with superior being above and inferior being below.
proximal/distal
Terms used to describe the location of body parts relative to their point of attachment, with proximal being closer and distal being farther.
medial/lateral
Terms used to describe the position of structures relative to the midline of the body, with medial being closer to the midline and lateral being farther away.
midline
An imaginary line that divides the body into equal left and right halves.
Proximal forearm
The region of the forearm that is closer to the elbow.
Medial collar bone
The part of the collar bone (clavicle) that is closer to the midline of the body.
Anterior thigh
The front part of the thigh.
Cervical vertebrae
The 7 vertebrae in the neck region of the vertebral column.
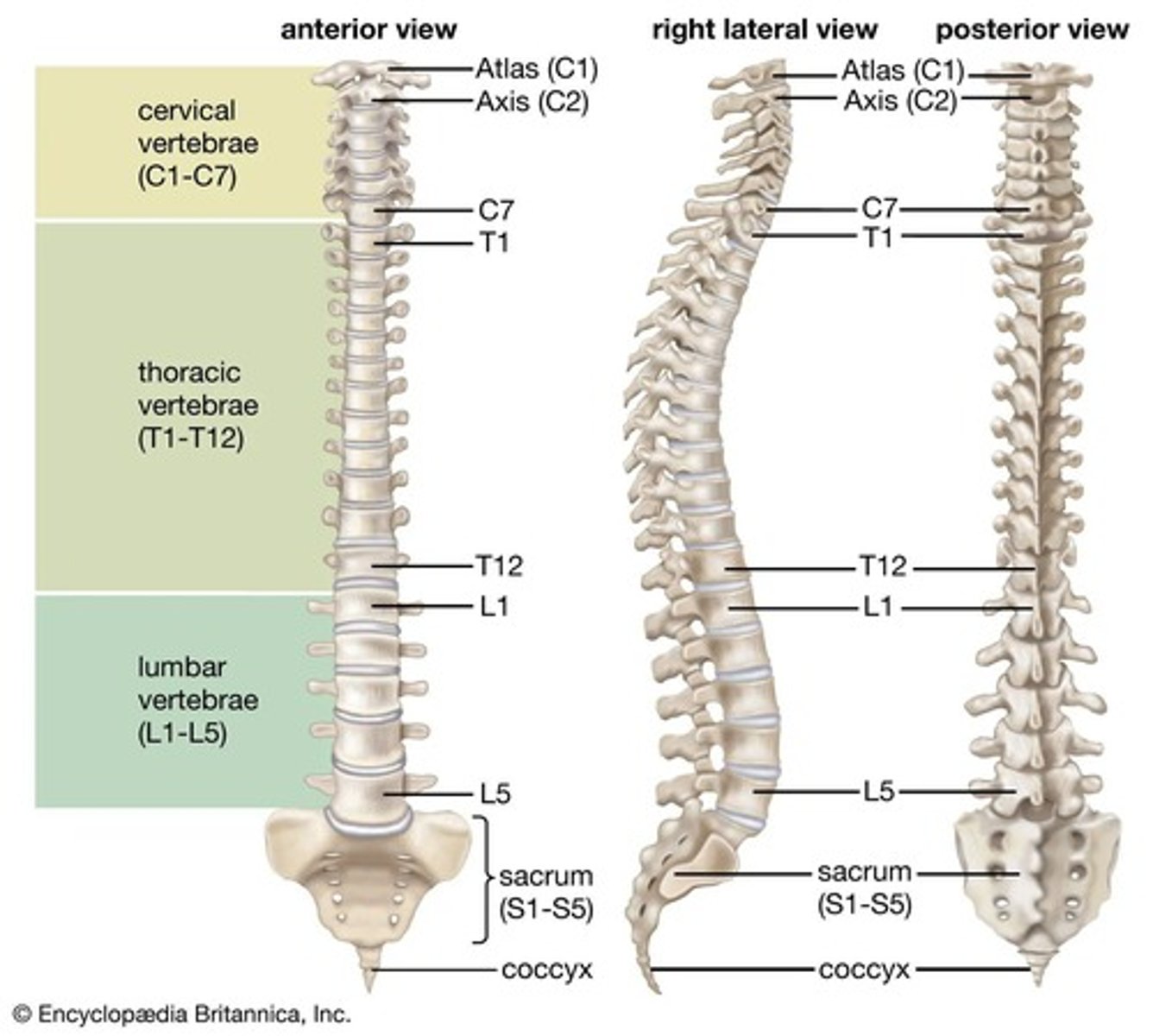
Thoracic vertebrae
The 12 vertebrae located in the upper and mid-back region of the vertebral column.
Lumbar vertebrae
The 5 vertebrae located in the lower back region of the vertebral column.
Herniated disc
A condition where the breakdown of the annulus fibrosus causes pain and increased risk of disc herniation, potentially leading to the escape of the nucleus pulposus.
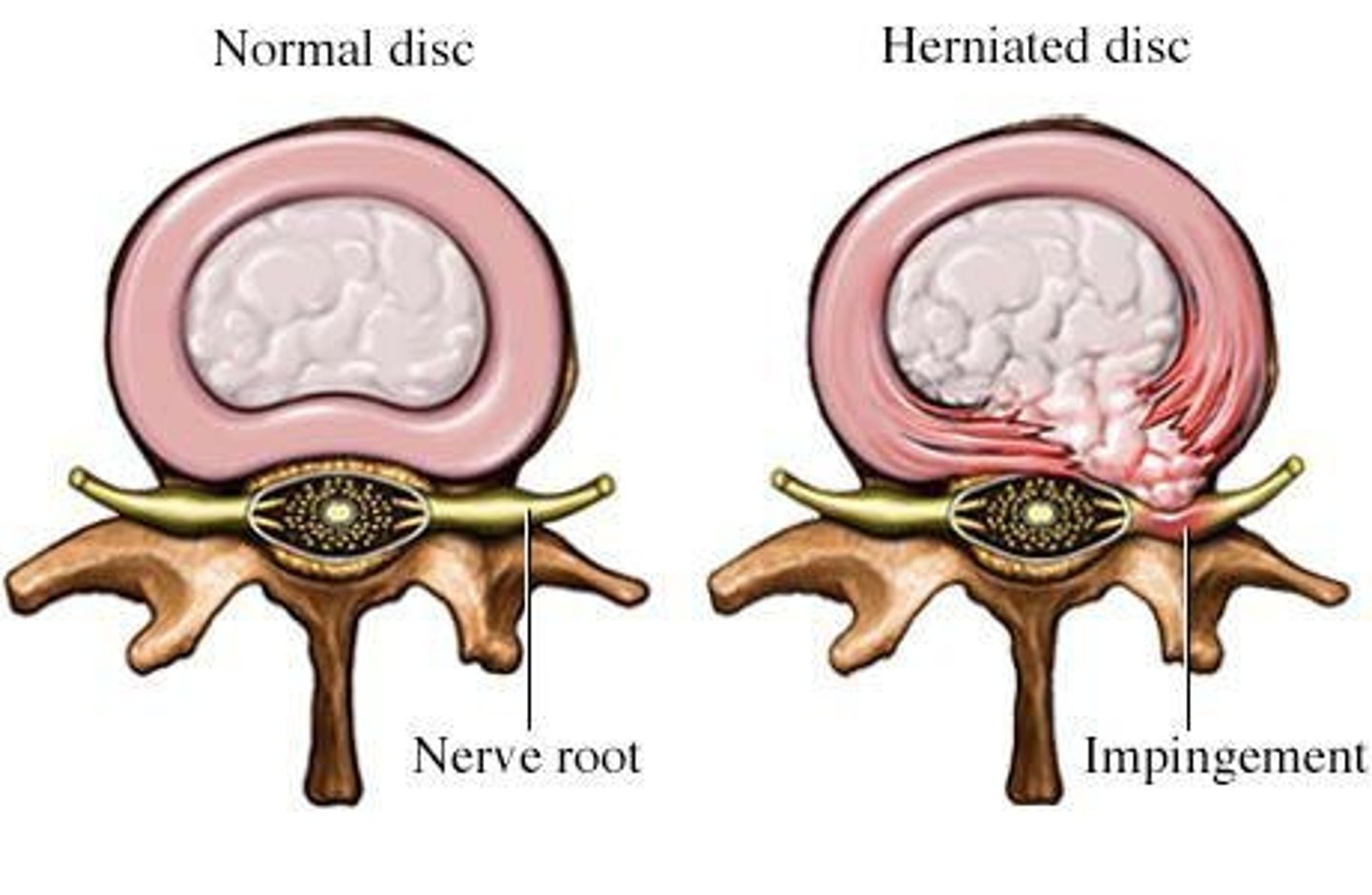
Nerve impingement
A condition where a nerve is compressed, leading to pain and decreased sensation or strength in the affected area.
Mnemonic for vertebral column
7/12/5 = breakfast/lunch/dinner, representing the number of cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae respectively.
Clinical correlate of herniated disc
Breakdown of the annulus fibrosus can lead to severe pain and neurological symptoms.
Decreased sensation
A reduction in the ability to feel stimuli, often observed in nerve impingement cases.
Decreased strength
A reduction in muscle power, which can occur in the affected leg due to nerve issues.
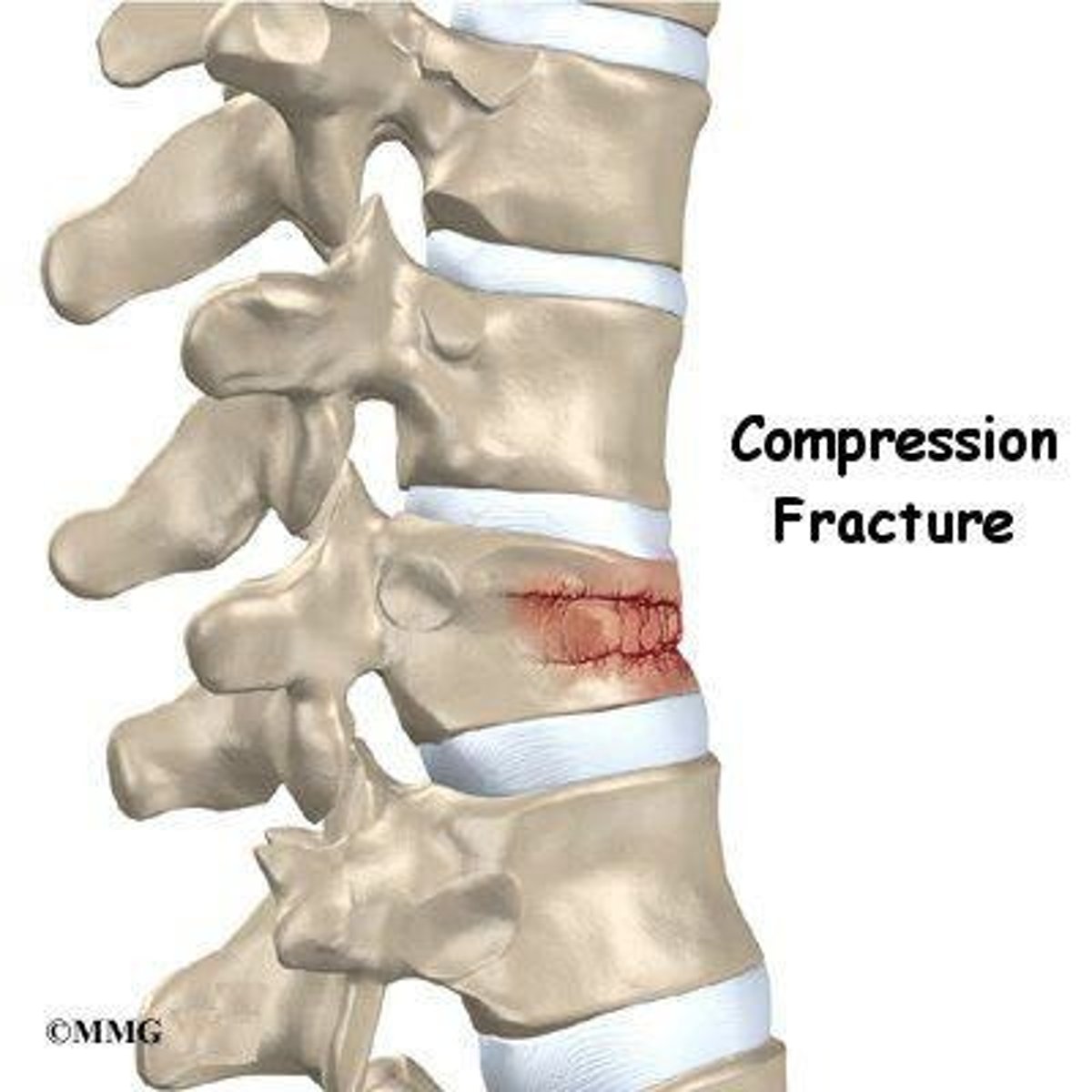
Compression Fracture
Compressive downward load on the spine, typically in elderly and caused from something as simple as sneezing or sitting down hard, usually in the thoracolumbar area.
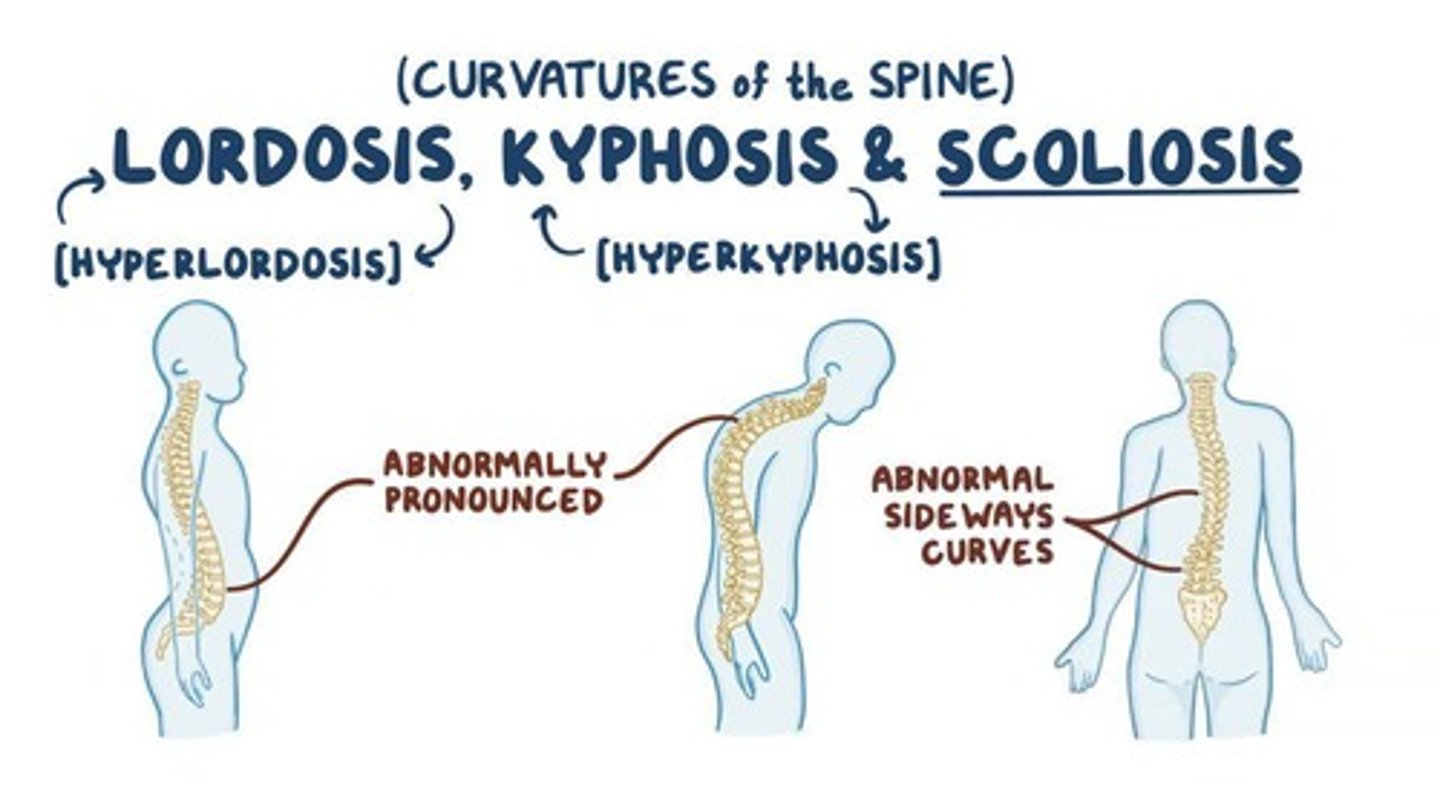
Scoliosis
Common in kids (especially girls), can lead to abnormalities in gait, and is corrected through bracing and physical therapy.
Adam's Forward Bend Test
A test used to assess scoliosis.
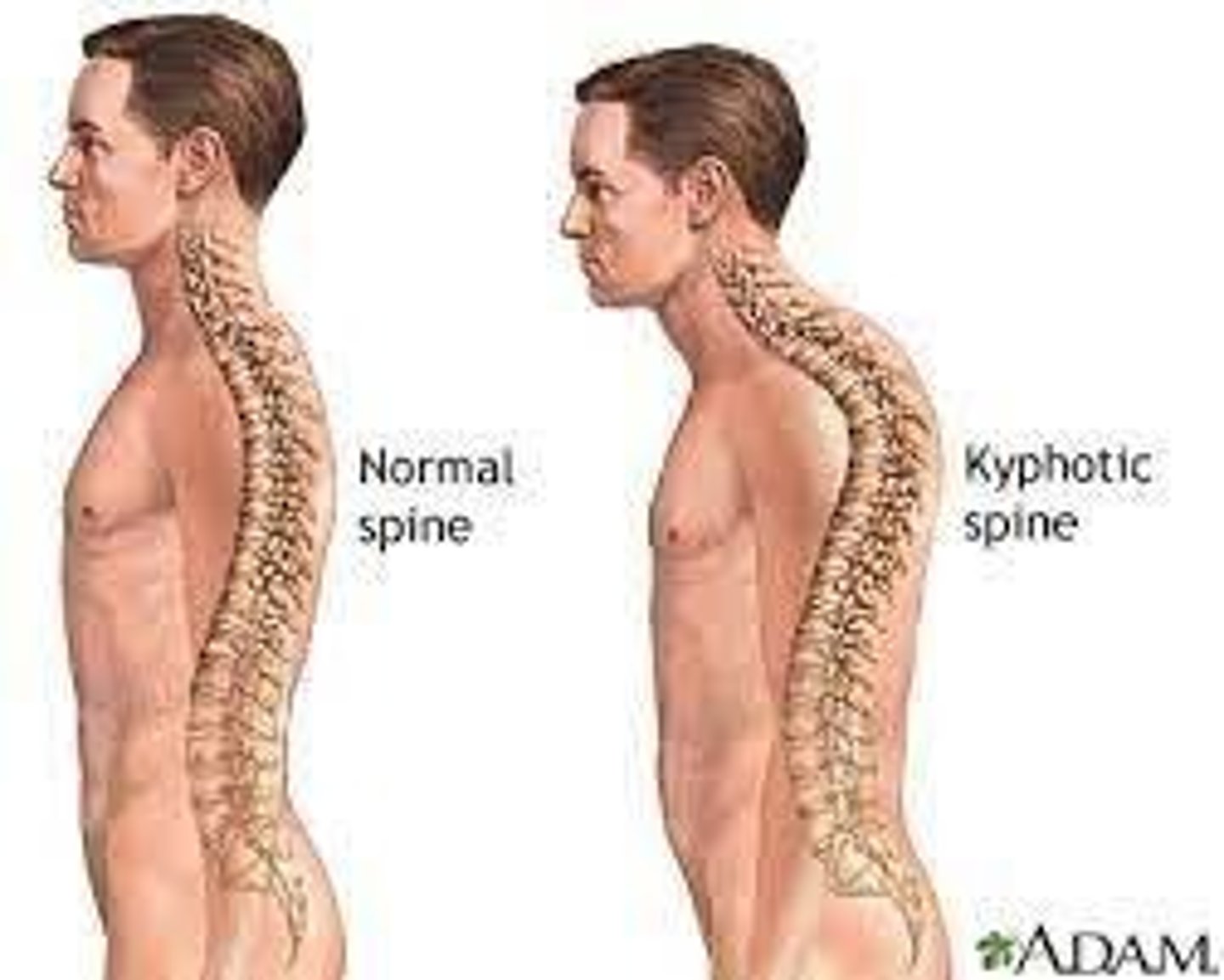
Kyphosis
Over-pronounced curvature of the thoracic spine, typically seen in older people, also known as 'Hunchback'.
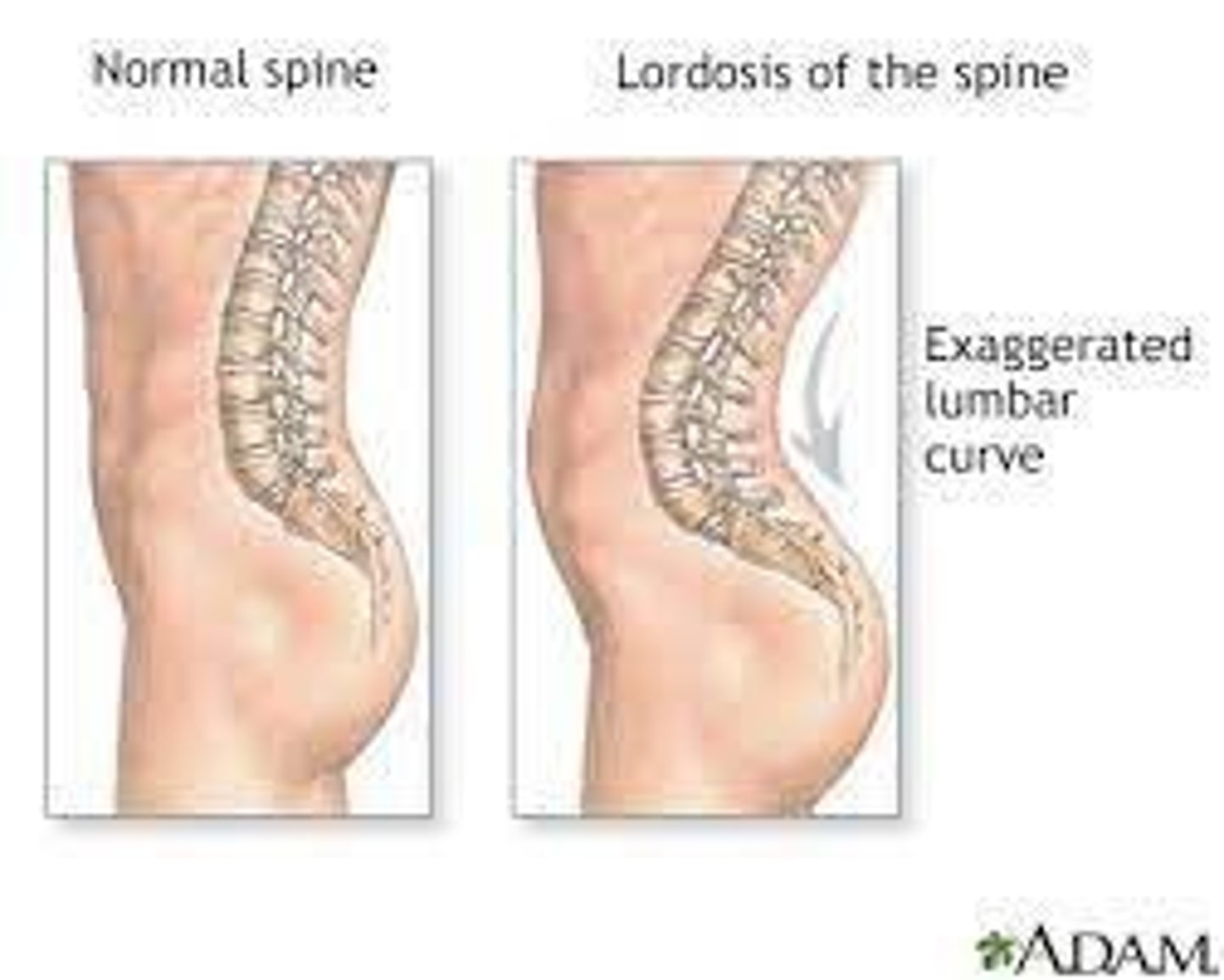
Lordosis
Over-pronounced curvature of the lumbar spine, frequently seen in pregnant women and obese people, also known as 'Swayback'.
Spinal Cord
Primary communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body, made up of nerve tissue that carries messages allowing for movement and sensation.
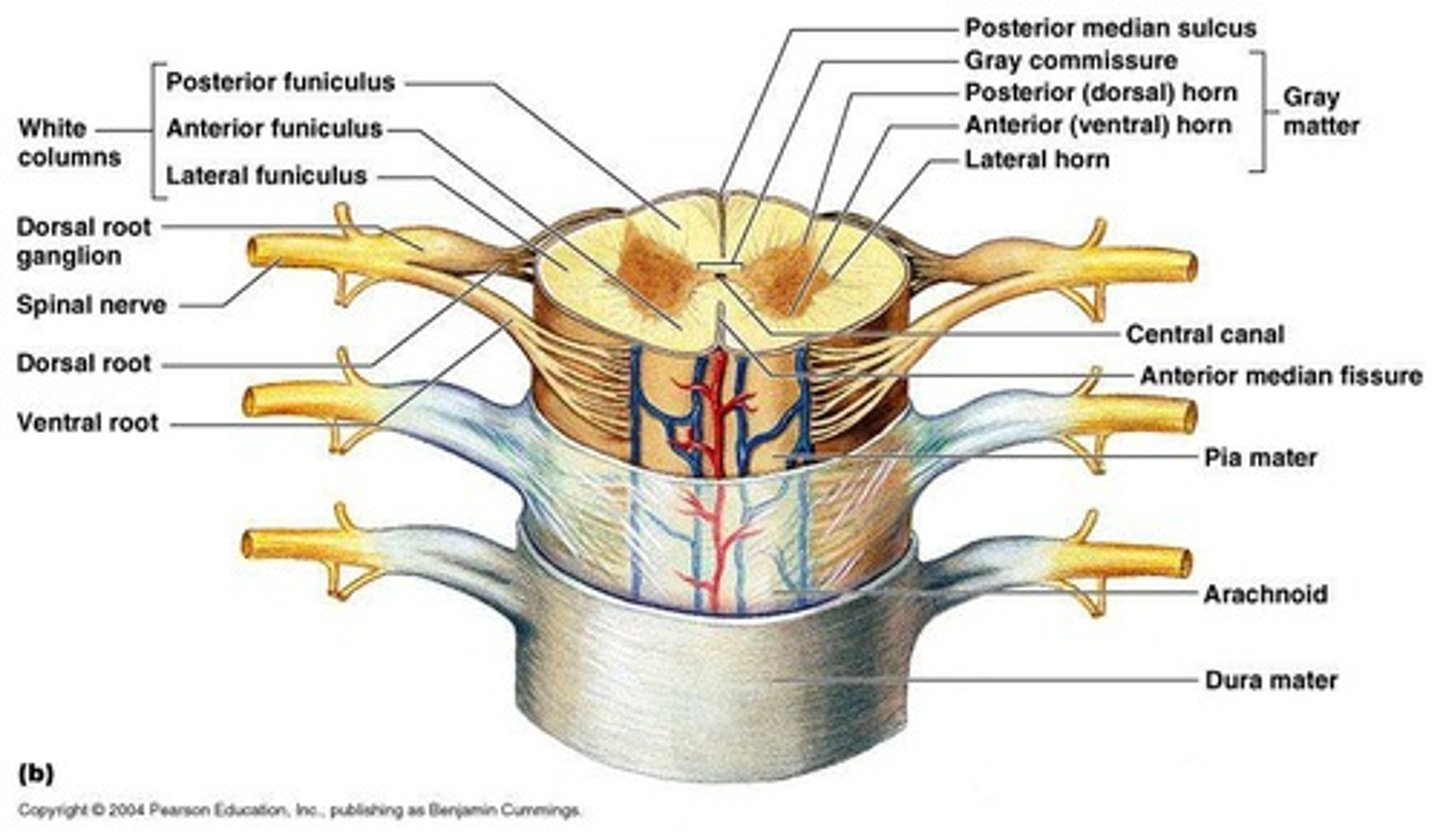
White matter
Part of the spinal cord that transmits outgoing information.
Gray matter
Part of the spinal cord that takes in incoming information.
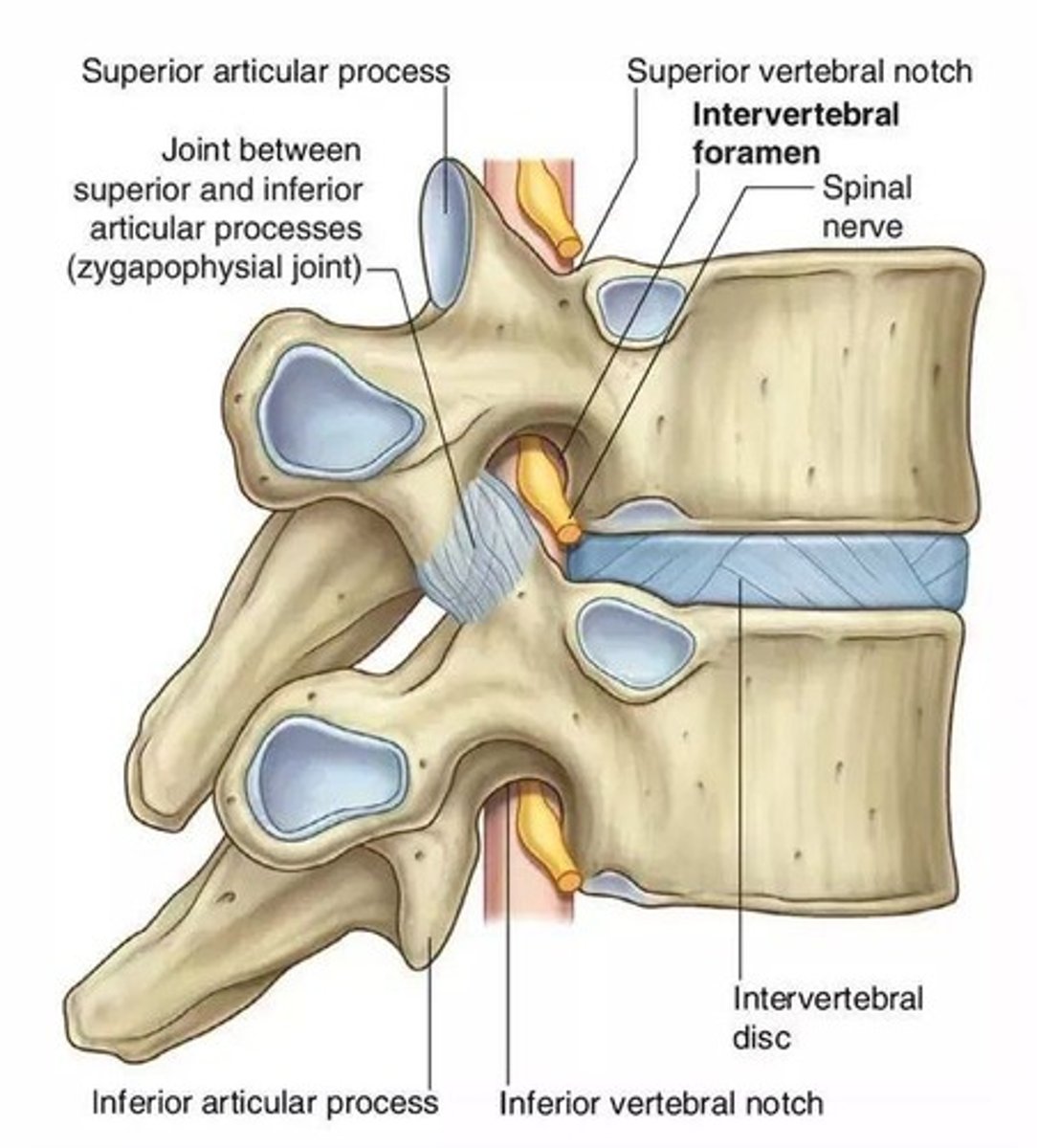
Foramen
Holes formed between vertebrae through which nerves from the spinal cord exit the spine.
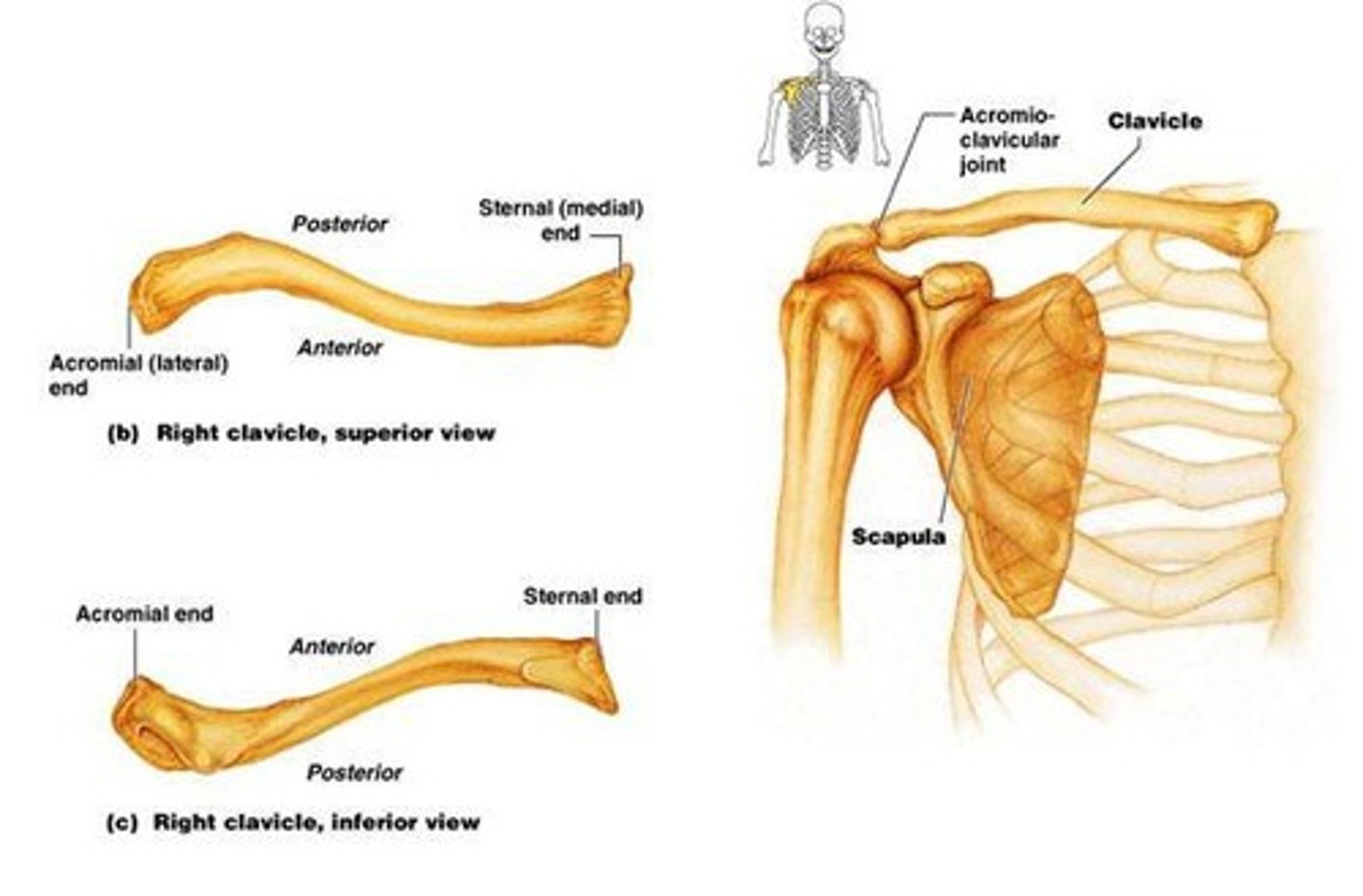
Pectoral girdle
Consists of the clavicle, scapula, and sternum.
Extrinsic (Superficial) Muscles
Muscles that move the upper limbs, including trapezius, latissimus dorsi, levator scapulae, and rhomboids (major and minor).
Intrinsic (Deep) Muscles
Muscles that help to maintain posture/stability and move the vertebral column, including splenius (capitis and cervicis) and erector spinae.
Trapezius
Muscle with functions including scapula elevation (upper), scapula retraction (middle), scapula depression (lower), and upward rotation of scapula (upper + lower).
Paralysis of Trapezius muscle
Loss of innervation to the trapezius muscle causes weakness and drooping of the shoulder, making it unable to elevate the shoulder on that side.
Latissimus Dorsi
Muscle that adducts, extends, and internally rotates the arm; helps with crawling, swimming, climbing, pushing off from a chair, and pull-ups.
Levator Scapulae
Muscle that elevates the scapula.
Rhomboids: Major/Minor
Muscles that retract the scapula and fix it to the thoracic wall.
Serratus Posterior Superior
Muscle that elevates upper ribs during inspiration.
Serratus Posterior Inferior
Muscle that depresses lower ribs during expiration.
Triangle of Auscultation
An anatomical region bordered medially by the trapezius, inferiorly by the latissimus dorsi, and laterally by the medial border of the scapula.
Intrinsic muscles of the back
Muscles that maintain posture and move the vertebral column.
Splenius Capitis and Splenius Cervicis
Superficial intrinsic muscles that extend/hyperextend the cervical spine, rotate the cervical spine, and allow lateral flexion of the cervical spine.
Erector Spinae Muscles
Intermediate intrinsic muscles that unilaterally flex the head and neck to the same side and bilaterally extend the vertebral column.
Mnemonic Device
From most lateral to medial = I Love Spine.
Compression fracture of spine
A likely diagnosis for a 73 year old woman with a history of osteoporosis who experiences increasing pain in the lumbar spine area after sitting down quickly into a hard wooden chair.
Rhomboid major
A muscle that assists in retracting the scapula.
Rhomboid minor
A muscle that assists in retracting the scapula.
Erector spinae muscles order laterally to medially
Longissmus, iliocostalis, spinalis.
Erector spinae muscles order distally to proximally
Iliocostalis, longissmus, spinalis (I Love Spine).
Torn rotator cuff surgery
A procedure that may lead to difficulty lifting the arm and inability to shrug the shoulder.