Alex's Bacteriology Lab Exam
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
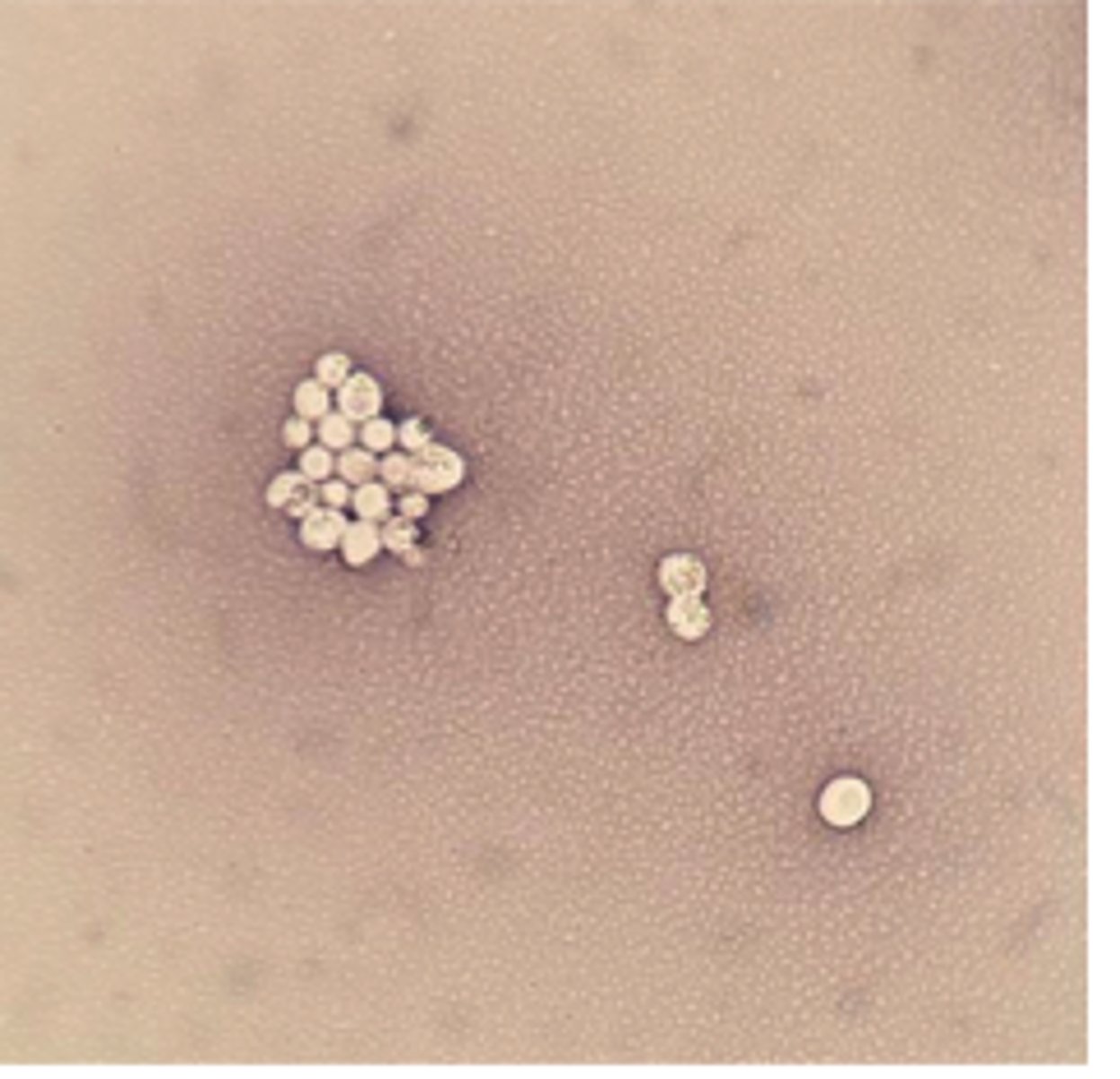
Staphylococcus aureus
A dairy cow develops sudden, severe mastitis in one quarter. Milk is watery with flakes and small blood clots . The quarter is swollen and painful.
Biochemical Tests
Catalase: Positive
Coagulase: Positive
No MAC Growth
Cytology Reveals Purple clusters of Cocci
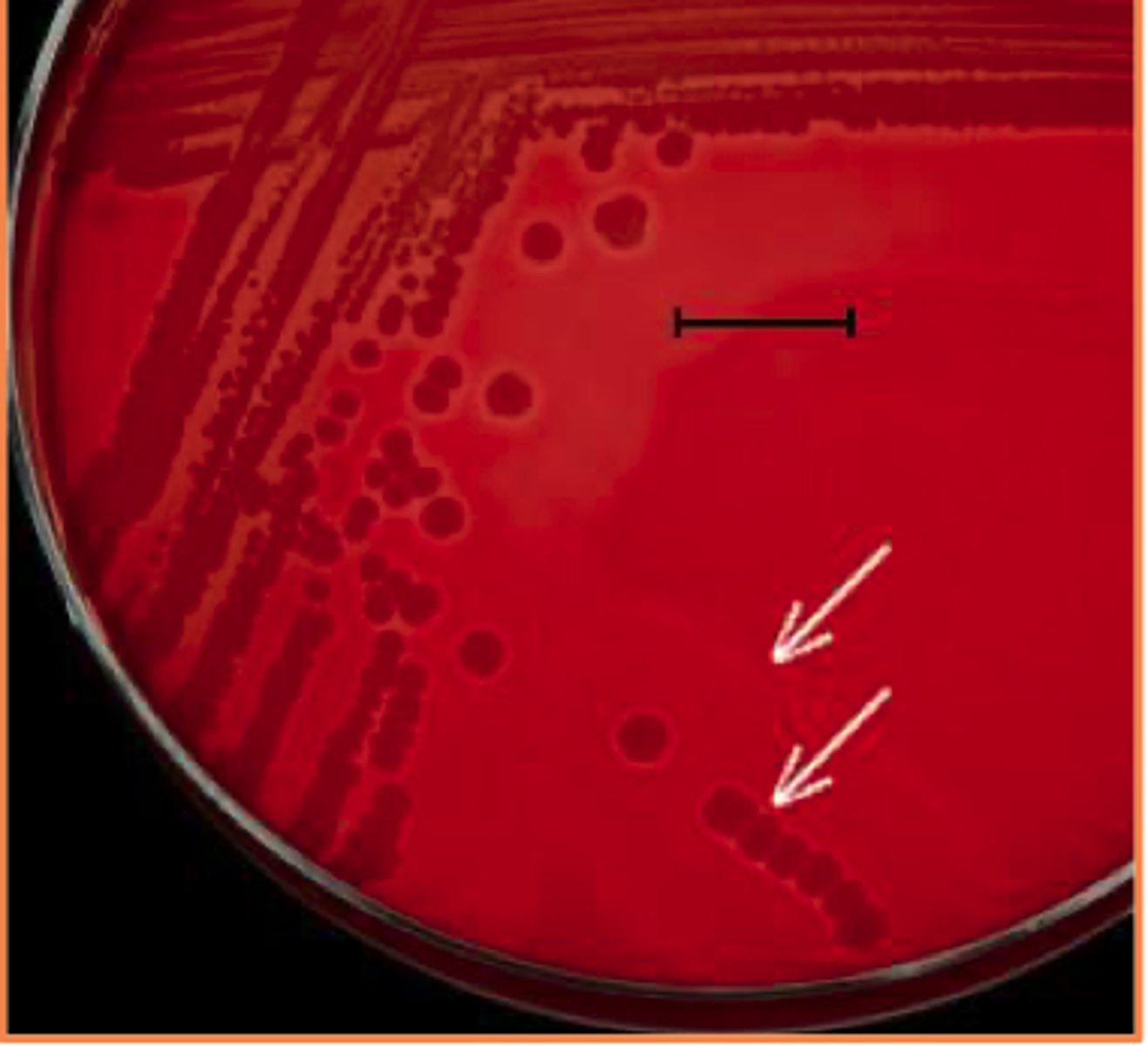
Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus
A Quarter horse presents with fever and thick mucopurulent nasal discharge.
Tests:
BA has Beta-hemolysis (NO MAC)
See Cytology
Escherichia coli
A dog shows dysuria, hematuria, and frequent urination. Urine cytology contains
Tests:
Cytology Gram-negative rods
Blood agar shows gray colonies;
See MacConkey Agar
Indole is positive.
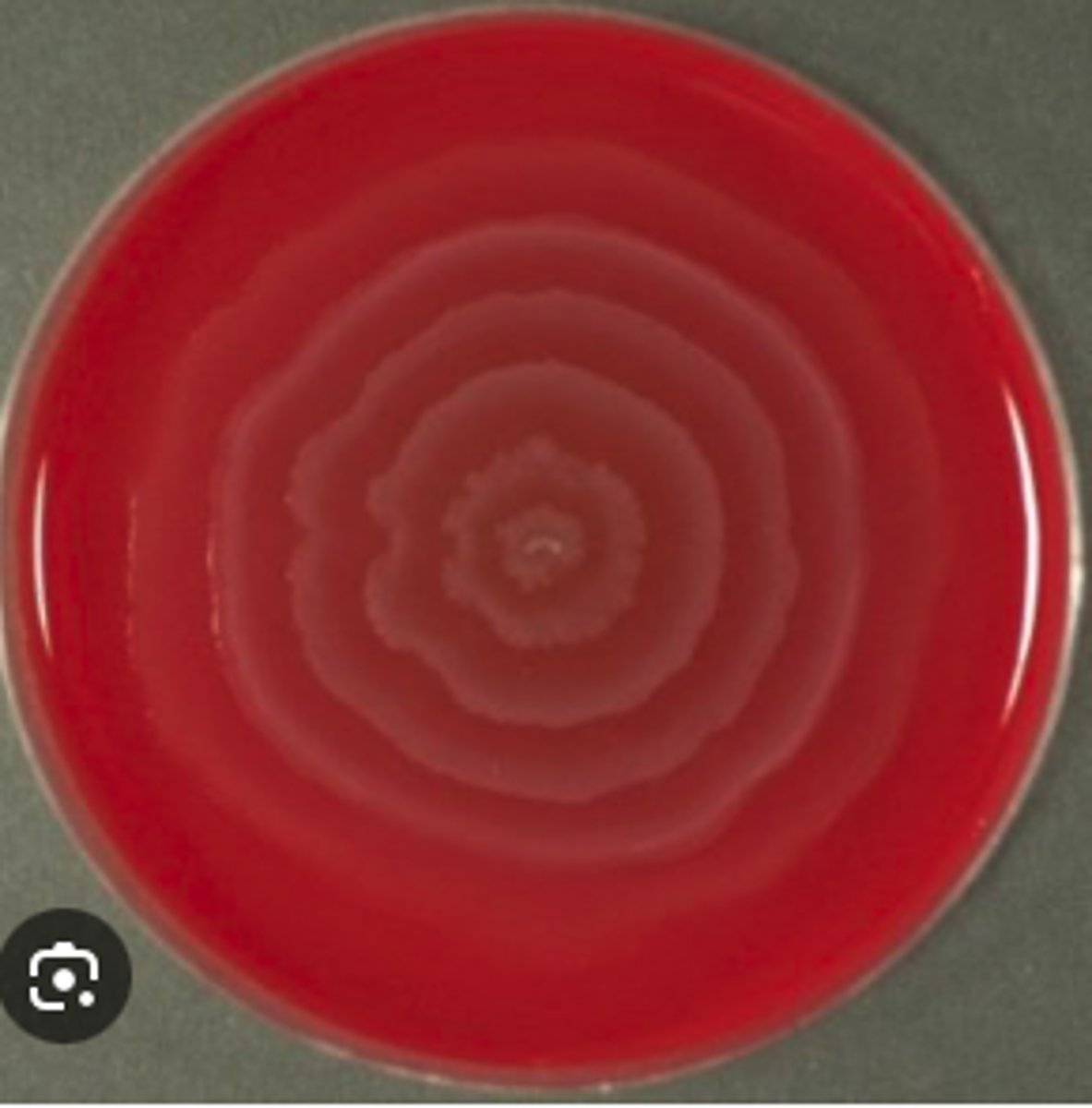
Proteus mirabilis
A dog with chronic otitis externa has foul-smelling brown discharge.
Tests:
Cytology :Gram-negative rods
MAC is non-lactose fermenting
Urease Positive
*See BA plate

Klebsiella
A mare develops post-foaling metritis with fever and purulent vulvar discharge. Uterine swab cytology shows Gram-negative rods.
See MAC culture
Double zone hemolysis
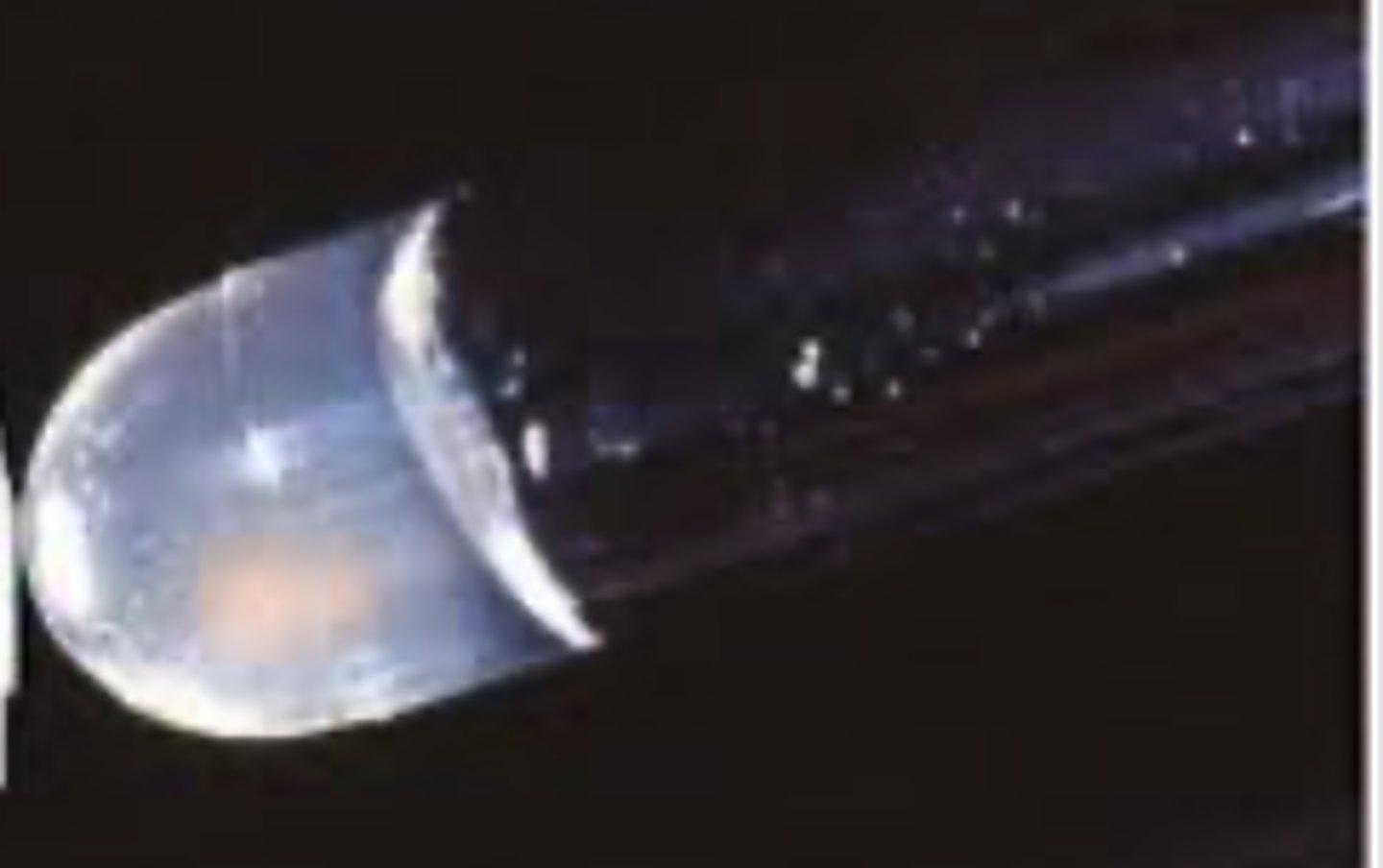
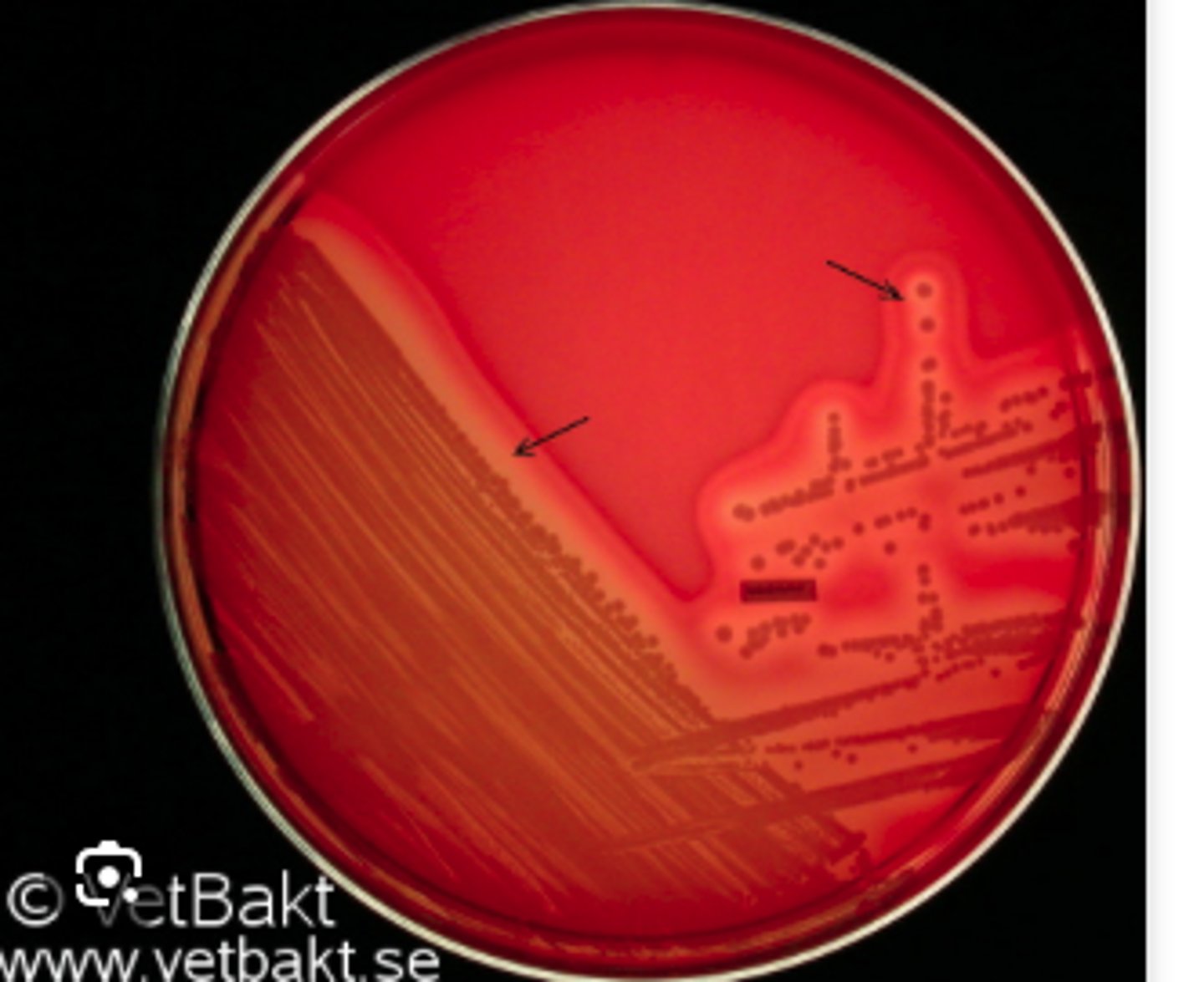
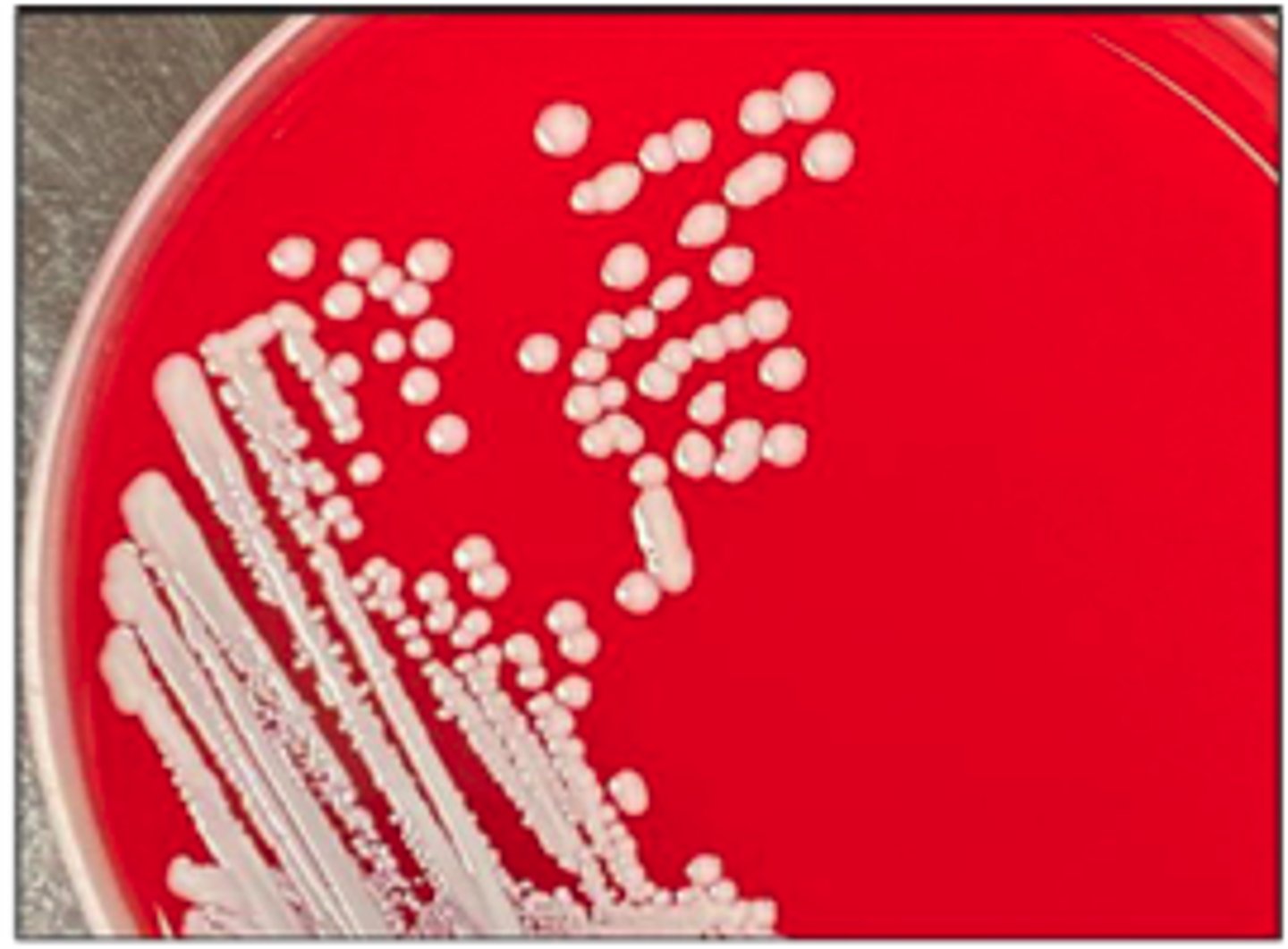
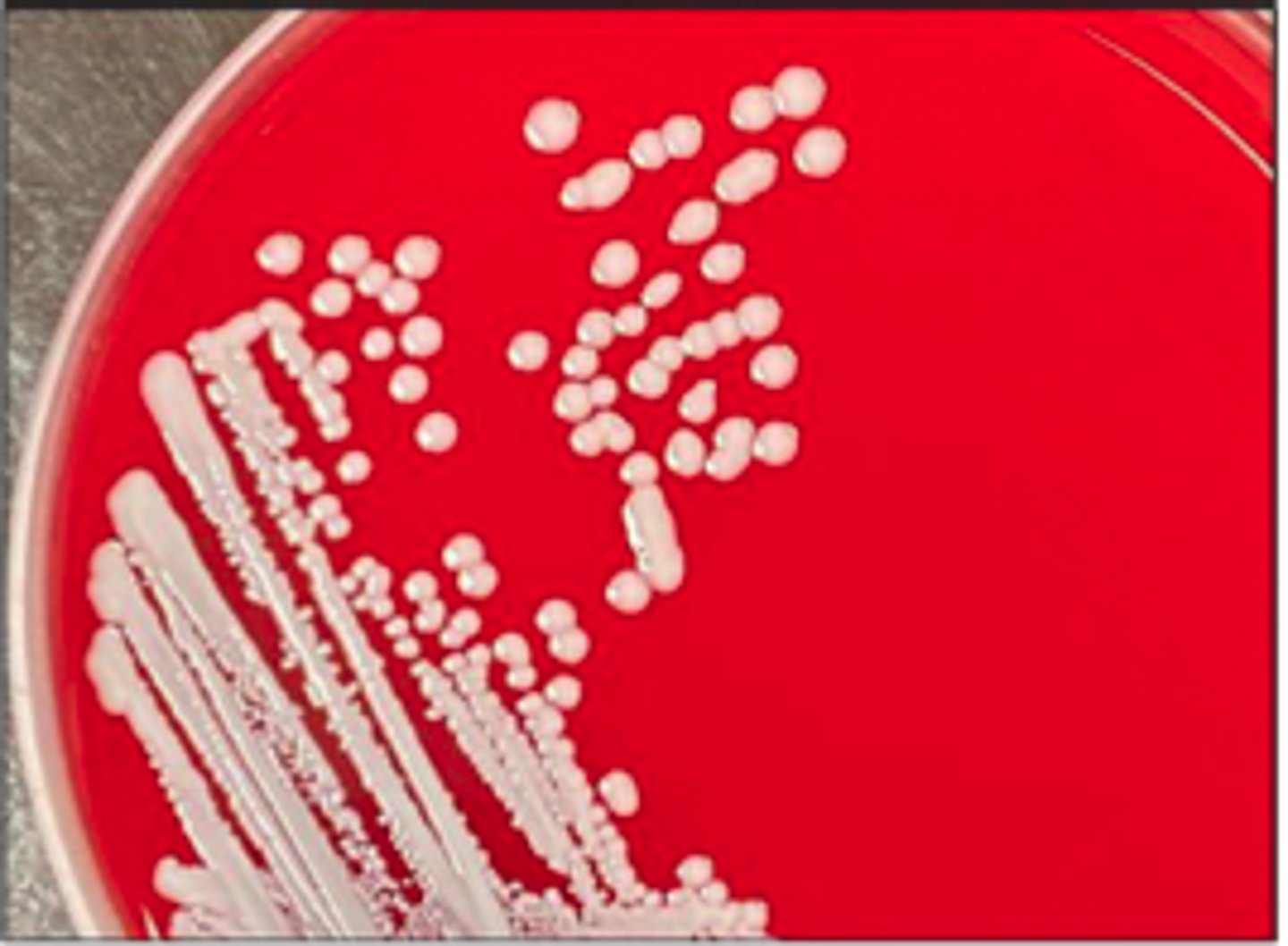
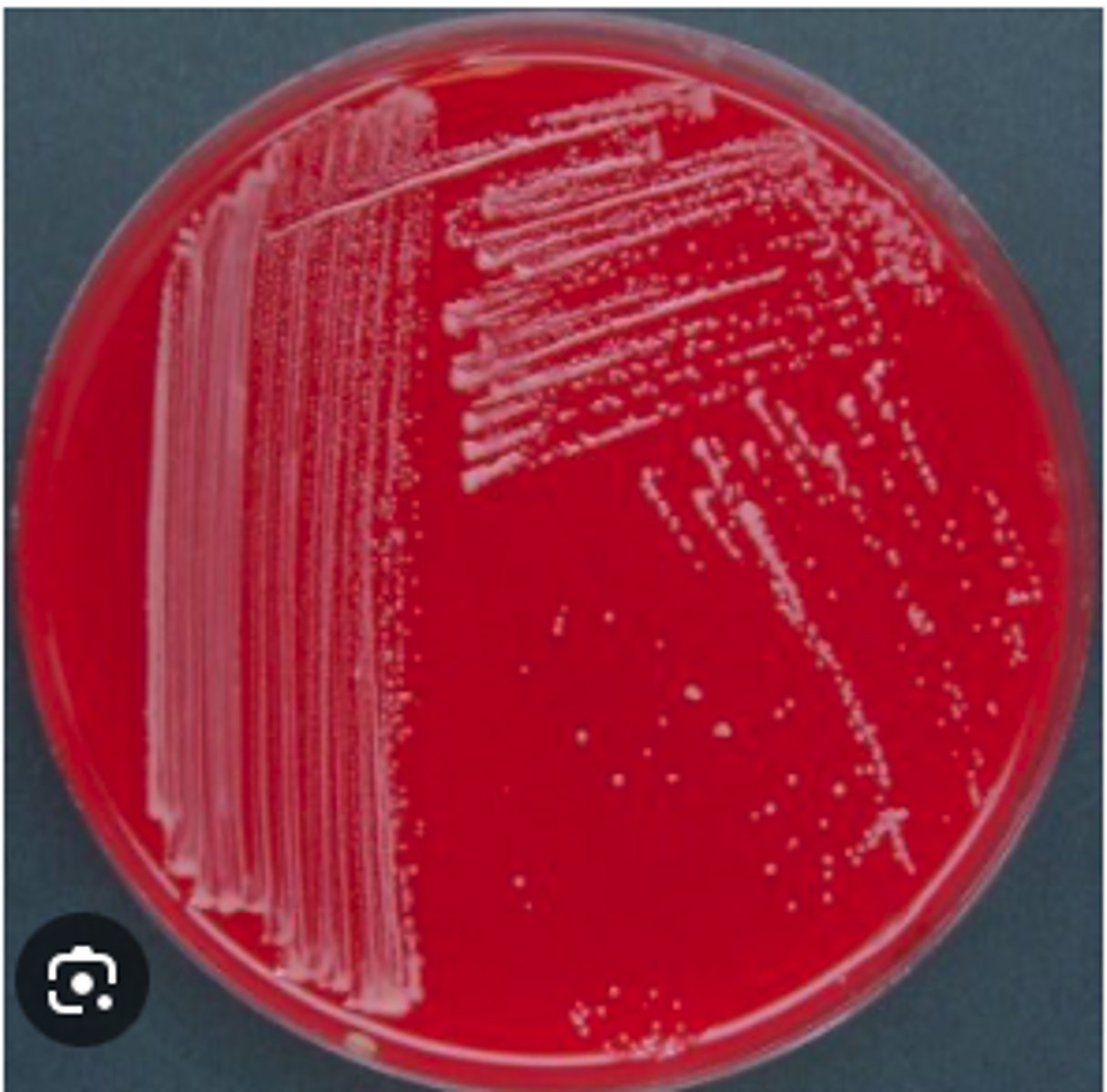
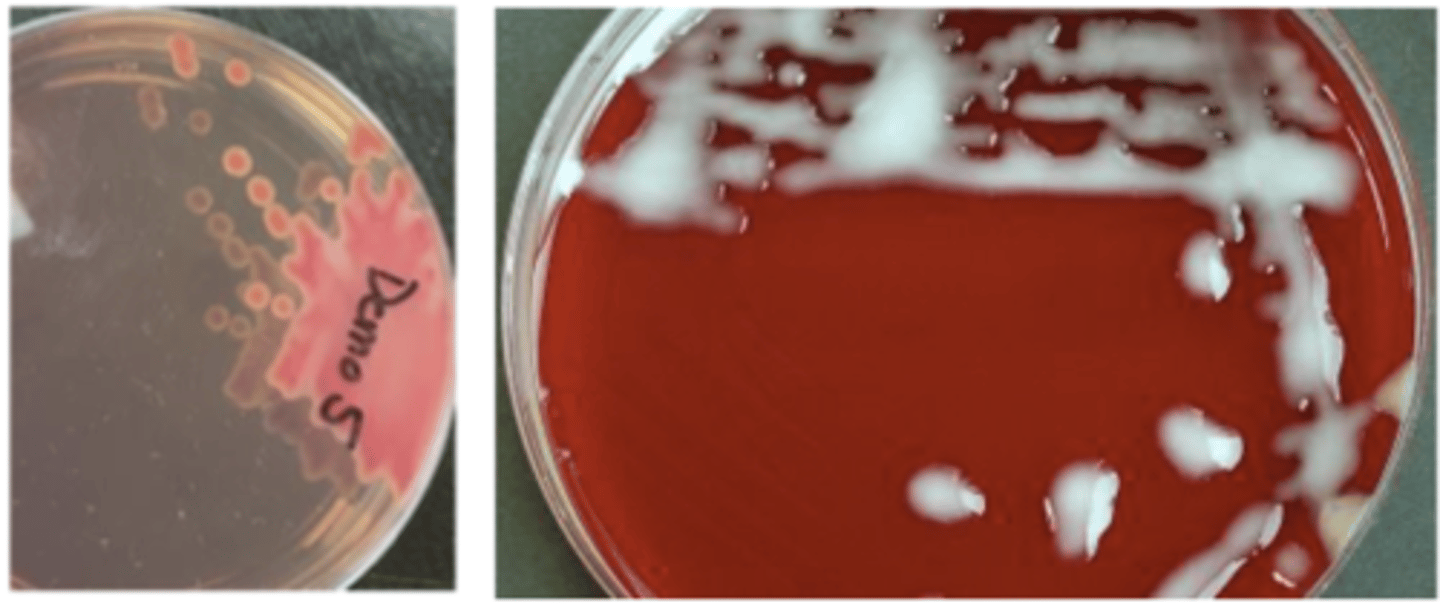
A dog presented with pyoderma of the face and limbs. Material from pustules was plated on Blood (BA) and MacConkey (MAC) agars and incubated overnight at 350C. BA plates are provided. There was no growth on MAC.
Is there an obvious hemolytic type or pattern?
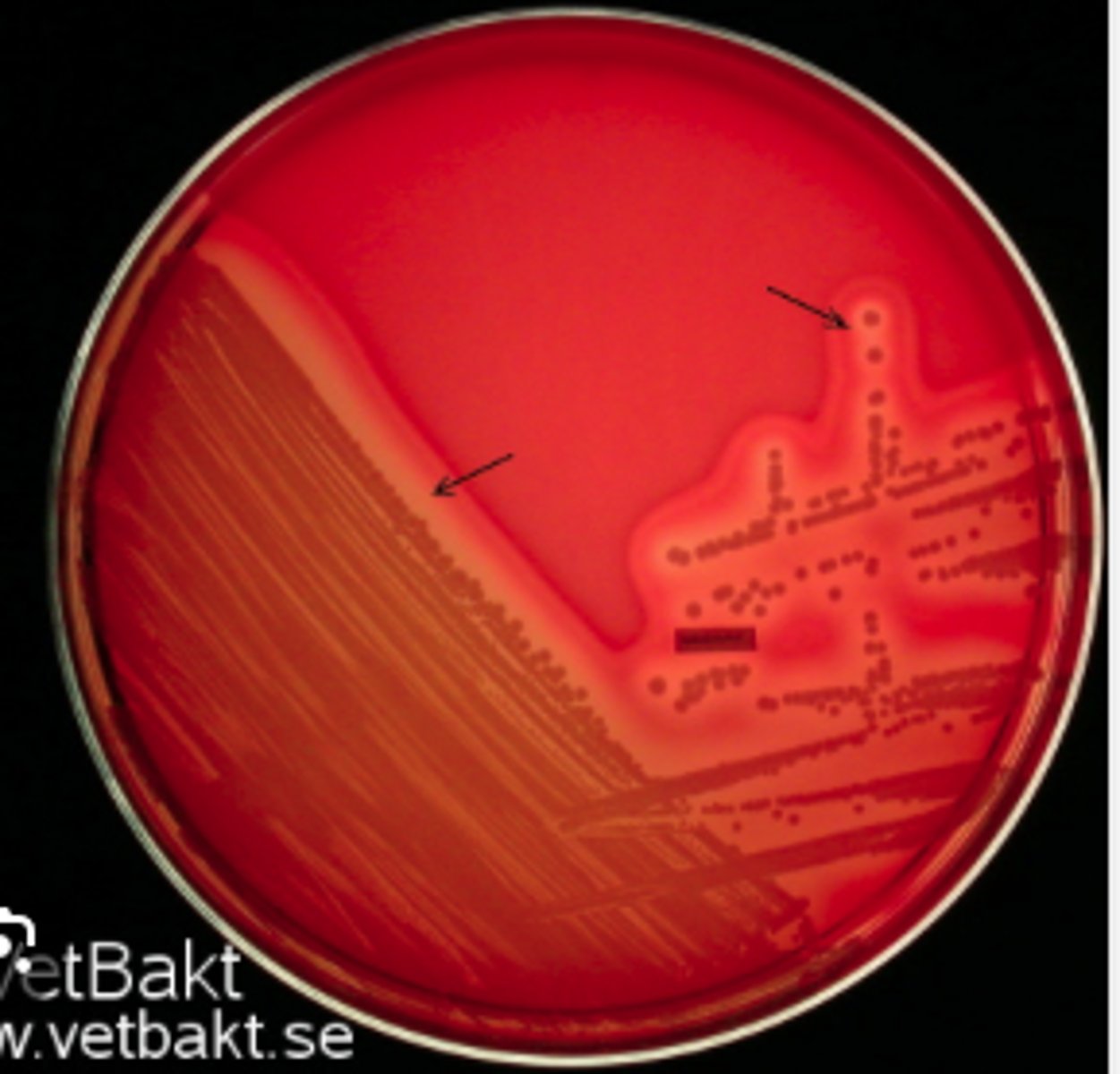
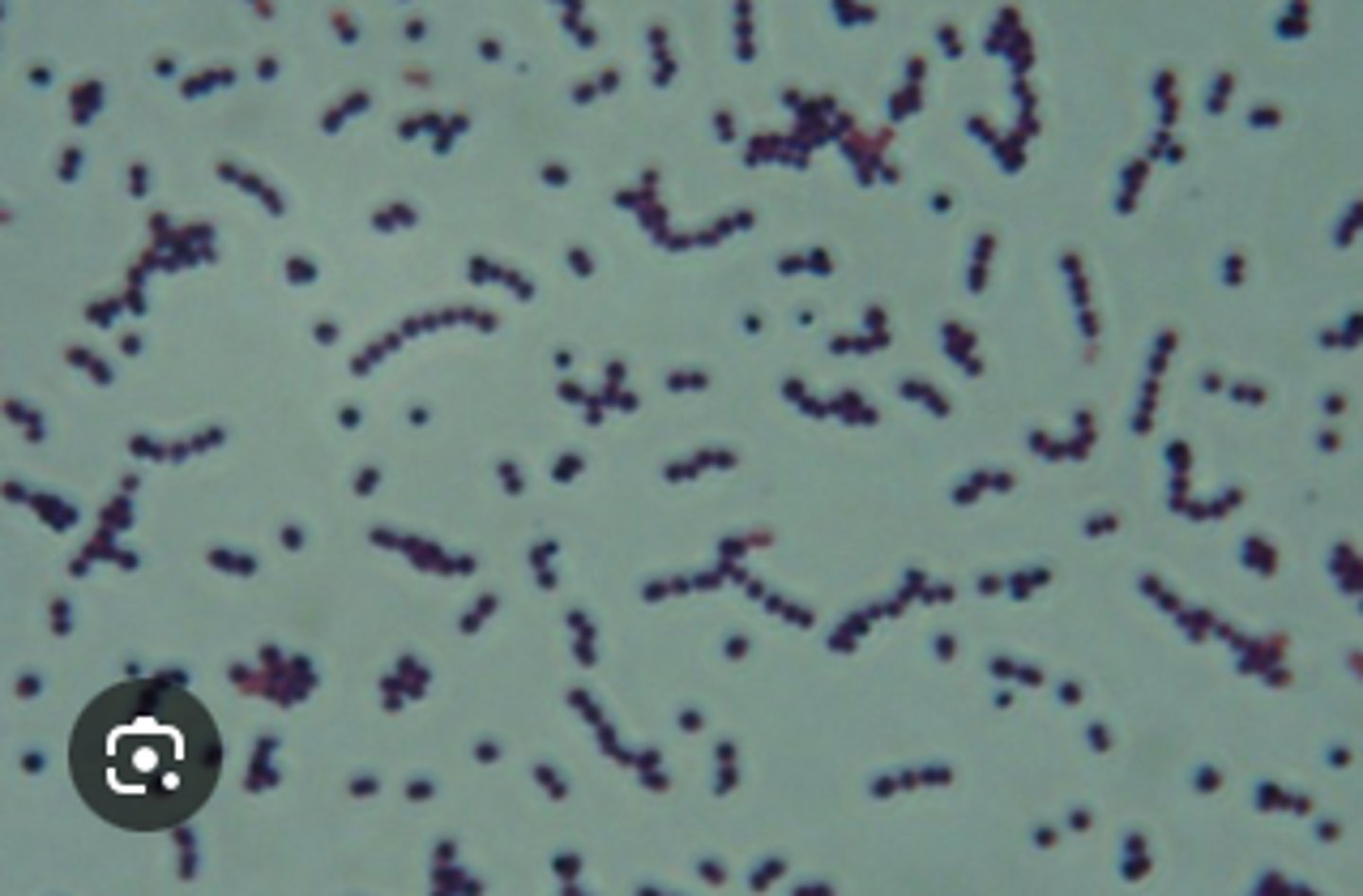
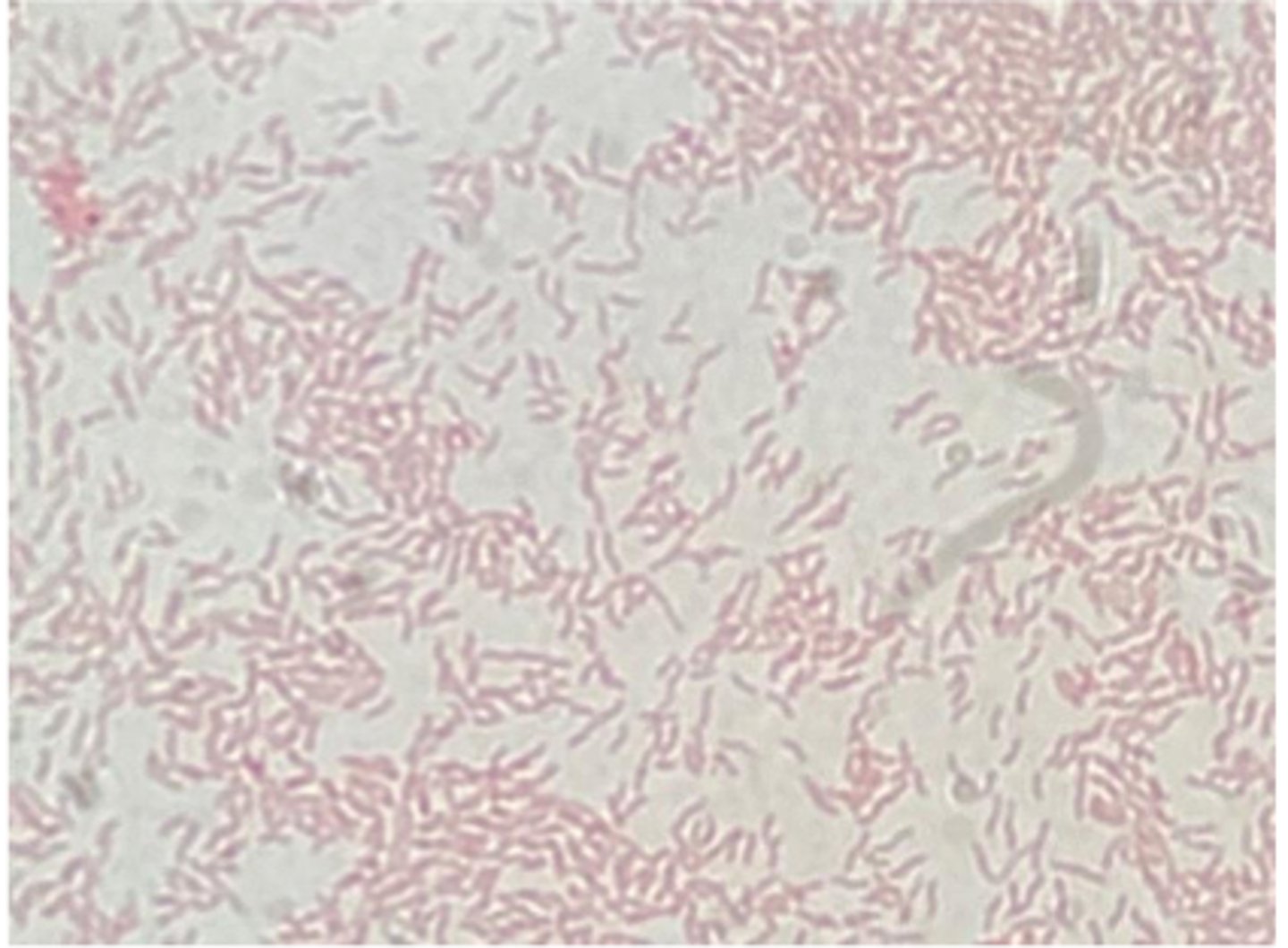
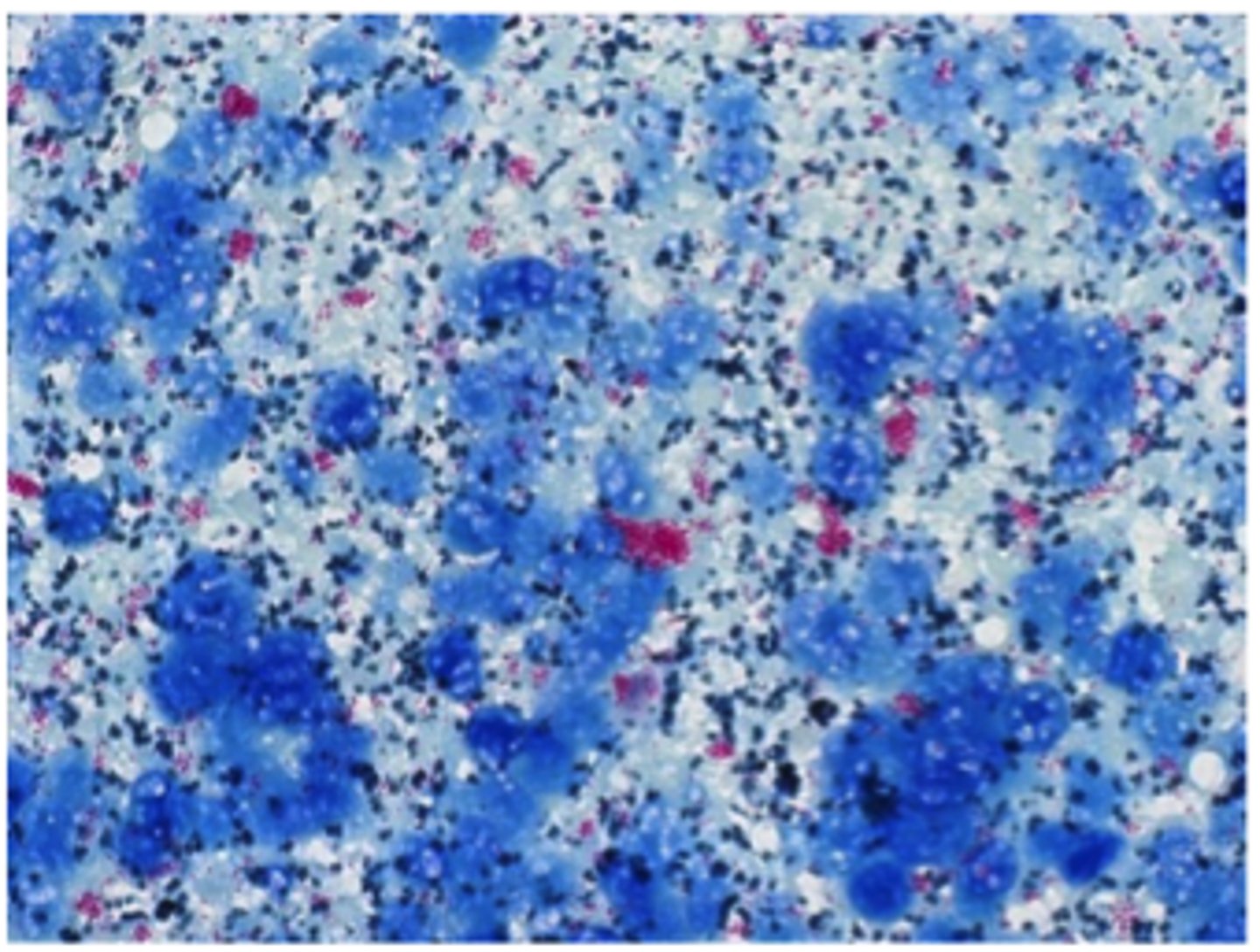
Gram positive cocci in clusters
A dog presented with pyoderma of the face and limbs. Material from pustules was plated on Blood (BA) and MacConkey (MAC) agars and incubated overnight at 350C. BA plates are provided. There was no growth on MAC.
Describe the cytology findings on your peep down the scope
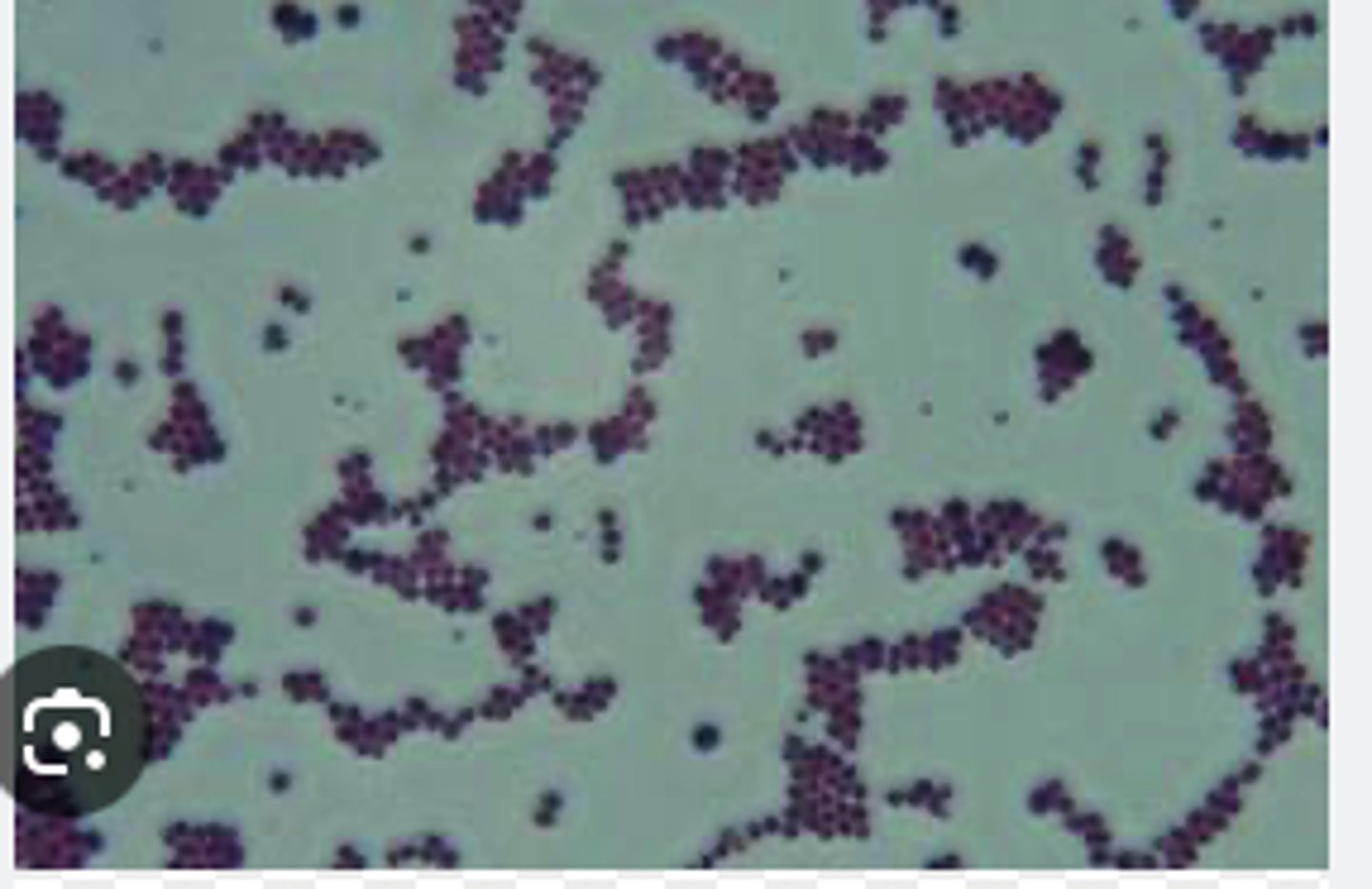
Catalase Positive
A dog presented with pyoderma of the face and limbs. Material from pustules was plated on Blood (BA) and MacConkey (MAC) agars and incubated overnight at 350C. BA plates are provided. There was no growth on MAC.
Do a catalase test by adding a drop of the hydrogen peroxide reagent to a colony on a glass slide. Is it
catalase-positive or negative?

Coagulase positive
A dog presented with pyoderma of the face and limbs. Material from pustules was plated on Blood (BA) and MacConkey (MAC) agars and incubated overnight at 350C. BA plates are provided. There was no growth on MAC.
The tube coagulase test for this exercise is set up in Demonstration 2 at the front. Is your colony
coagulase-positive or negative?

Staphylococcus pseudintermedius
A dog presented with pyoderma of the face and limbs. Material from pustules was plated on Blood (BA) and MacConkey (MAC) agars and incubated overnight at 350C. BA plates are provided. There was no growth on MAC.
Tests
Gram +ve cocci
Catalase and coagulase Pos
What is your presumptive identification?
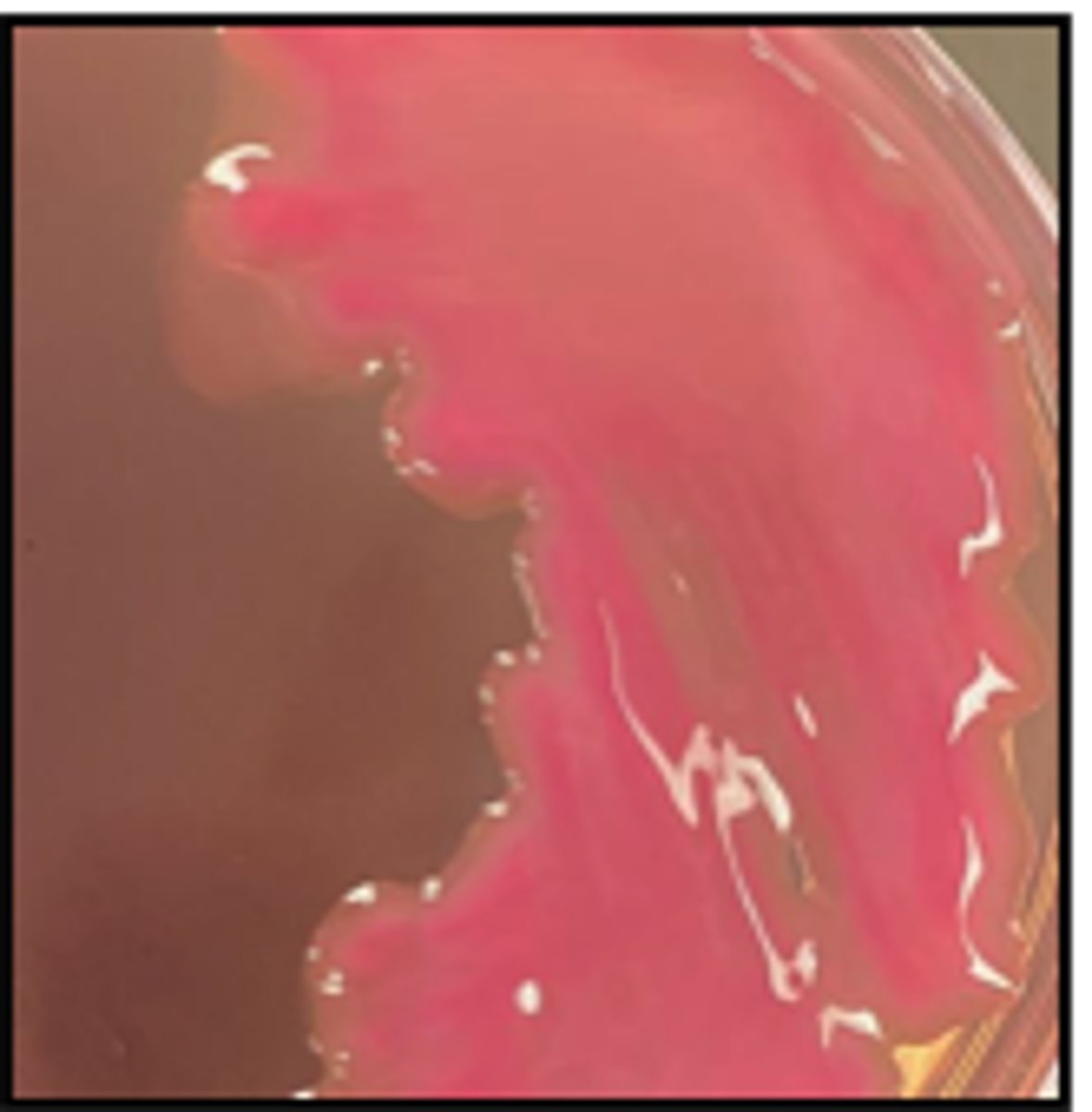
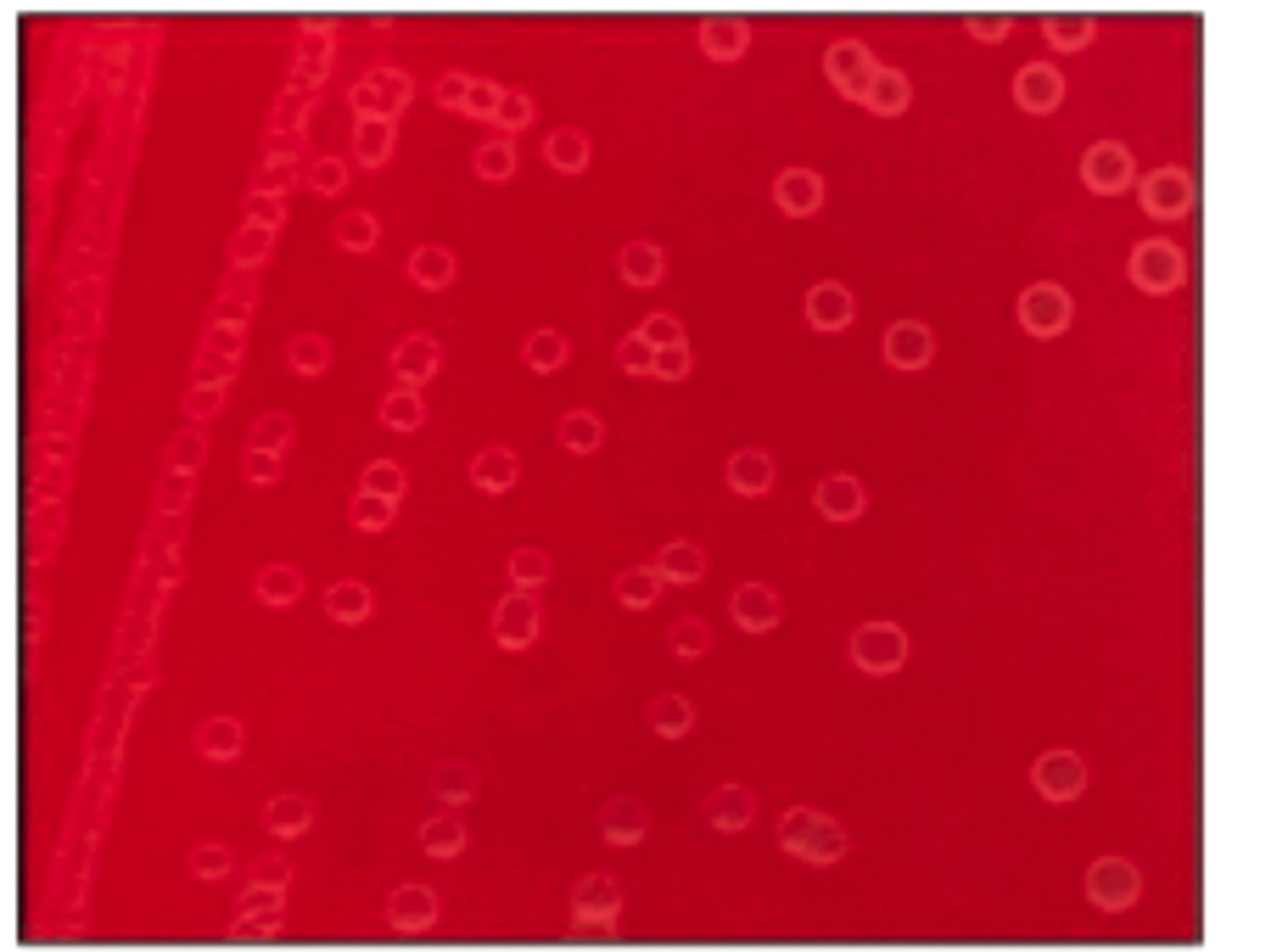
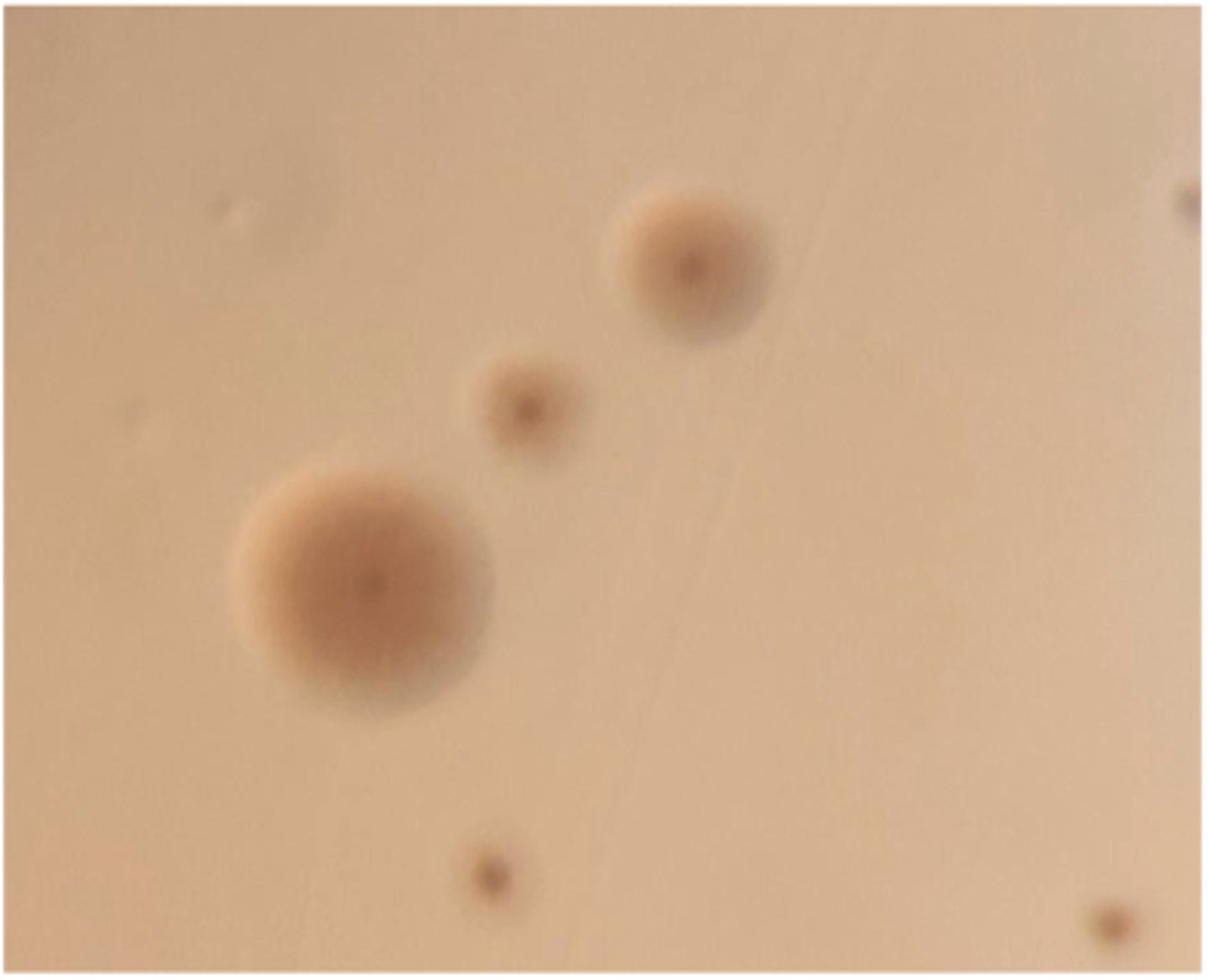
Narrow zone of β-hemolysis
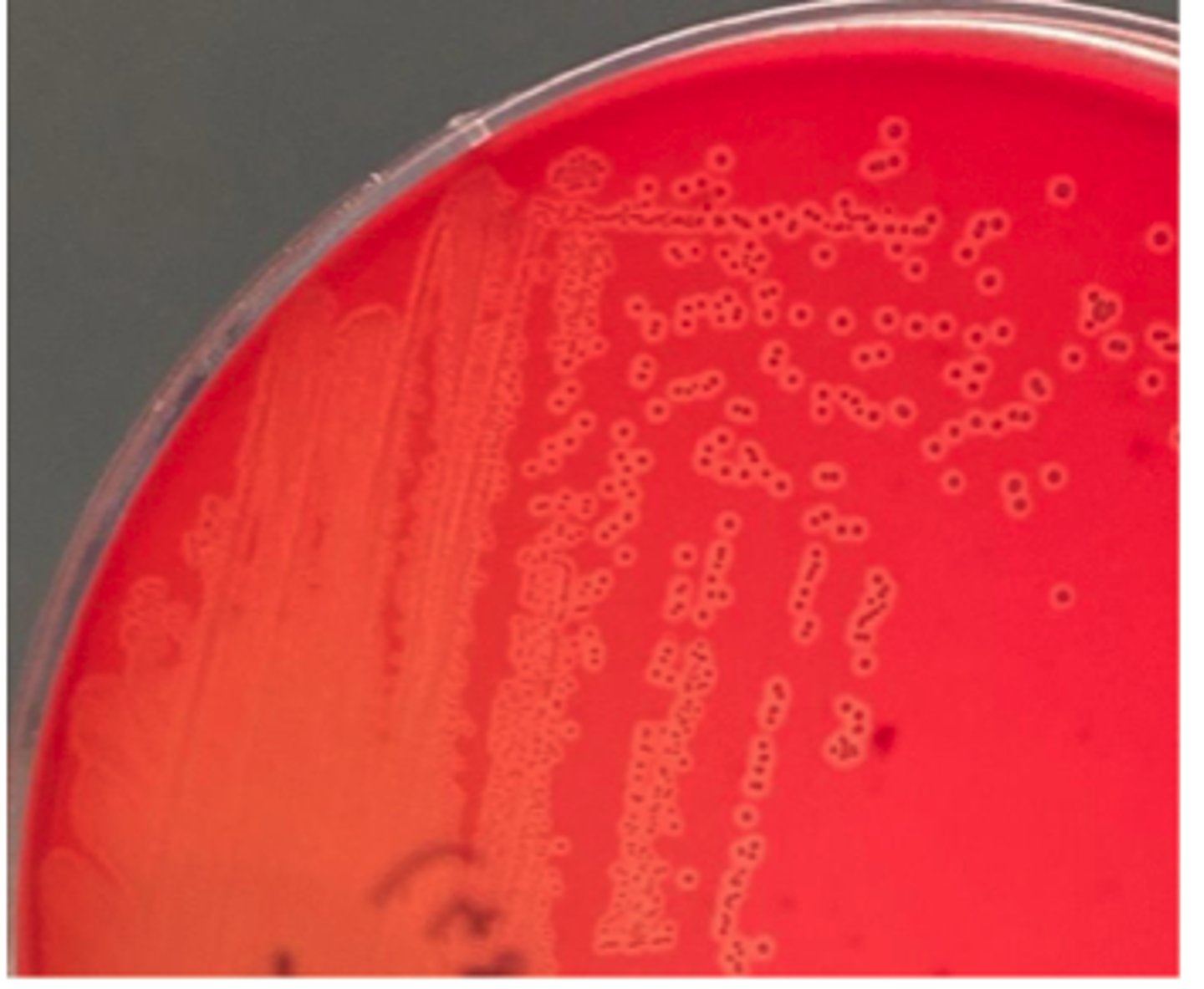
The organism on the BA plate provided was isolated from a milk specimen of a Holstein
cow with acute mastitis. The organism did not grow on MAC.
Is there hemolysis? If so, what type?
Weak, greenish alpha-hemolysis
The organism on the BA plate provided was isolated from a milk specimen of a Holstein
cow with acute mastitis. The organism did not grow on MAC.
No hemolysis
Staphylococcus hyicus
This IS a Staph species it has ________ hemolysis so must be ____________
No hemolysis
China white
BA plate culture from a case of acute exudative dermatitis in a recently weaned pig. The plates
were incubated at 37oC for 24 hrs. There was no growth on MAC. This organism is catalase-positive.
Is the organism hemolytic or not? _____
Colony colour: ________
Positive CAMP
With Arrow shape (Streptococcus Agalactiae)
The organisms on the BA plates provided were isolated from a milk specimen of a Holstein cow with acute mastitis. Interpret your CAMP Test
Presuptive diagnosis ?
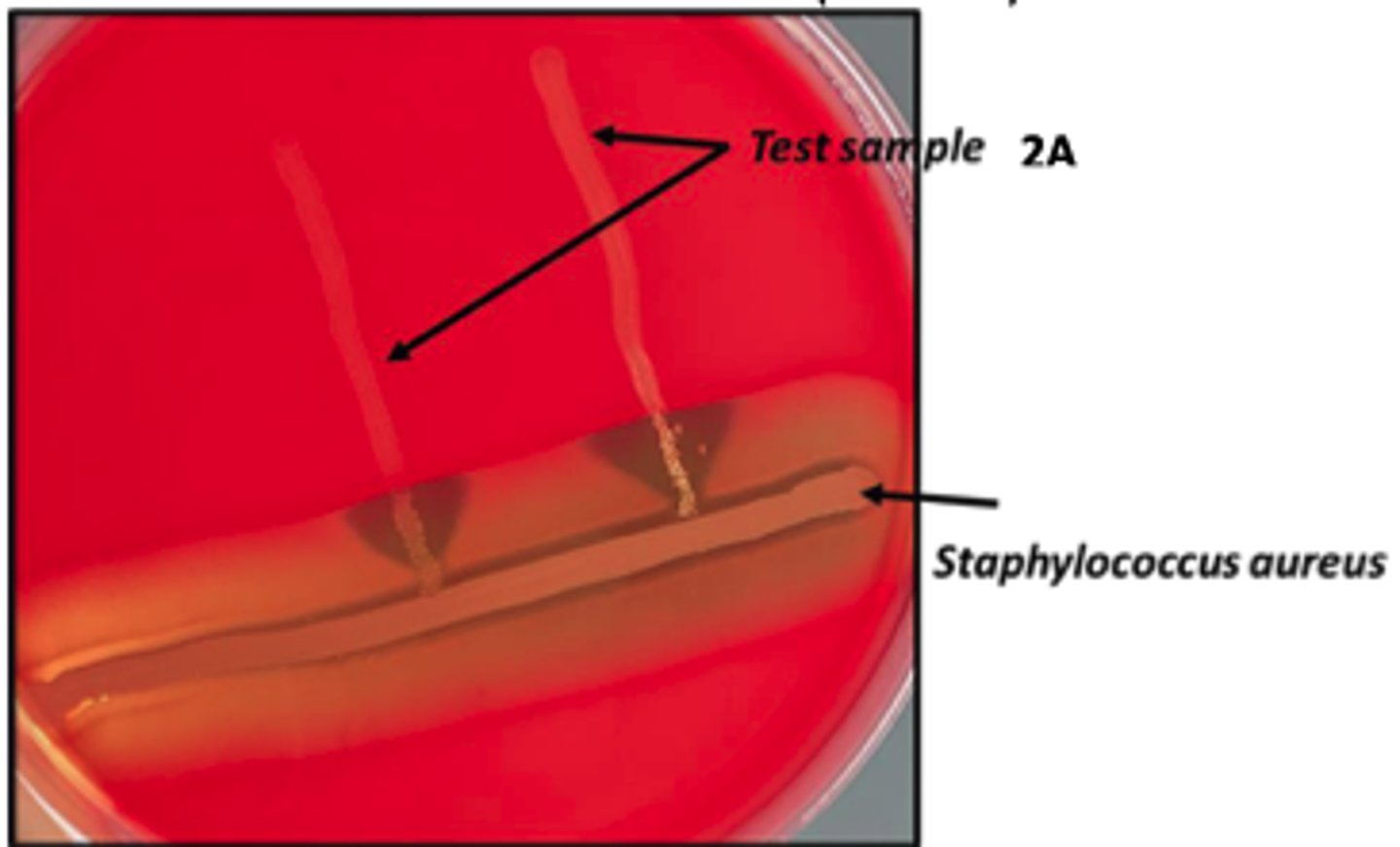
Beta-hemolysin
In positive reactions, a CAMP factor produced by a test organism will have a synergistic effect with
the _______ of Staphylococcus aureus and forms an enhanced beta hemolysis

Streptococcus equi subsp. equi - Beta hemolytic colonies
This organism was isolated from a horse that developed a high fever and swollen submandibular
lymph nodes several days after returning from a two-day riding event. The organism grew on BA
but did not grow on MAC. What is your presumptive identification and why?
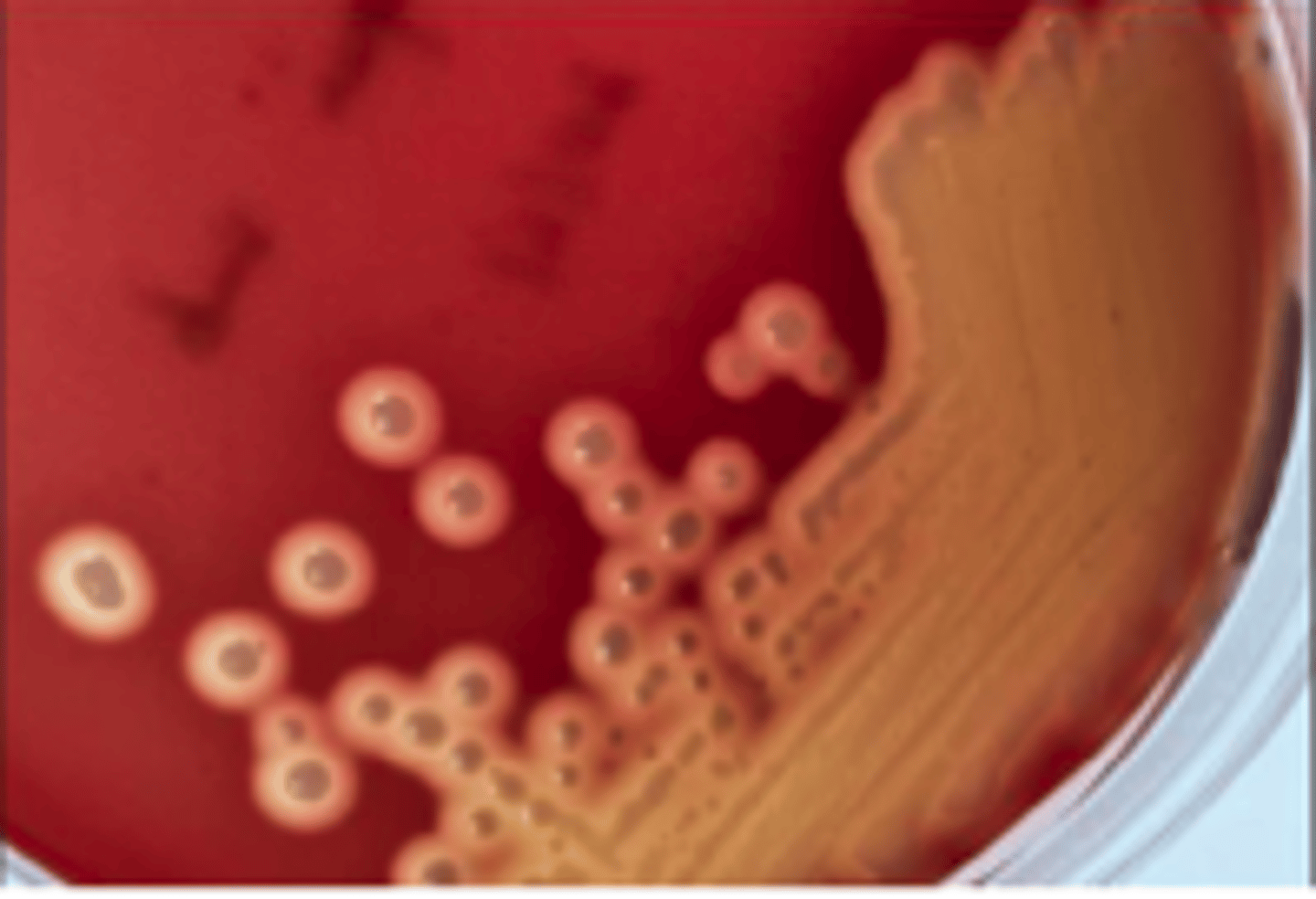
Streptococcus suis (alpha hemolystic)
Joint fluids from a few slaughter pigs showing signs of arthritis and/or valvular endocarditis were
collected using sterile swabs and submitted for standard aerobic culture. BA and MAC plates were
inoculated and grown overnight at 350C. There was no growth on MAC. What is your presumptive
identification and why?
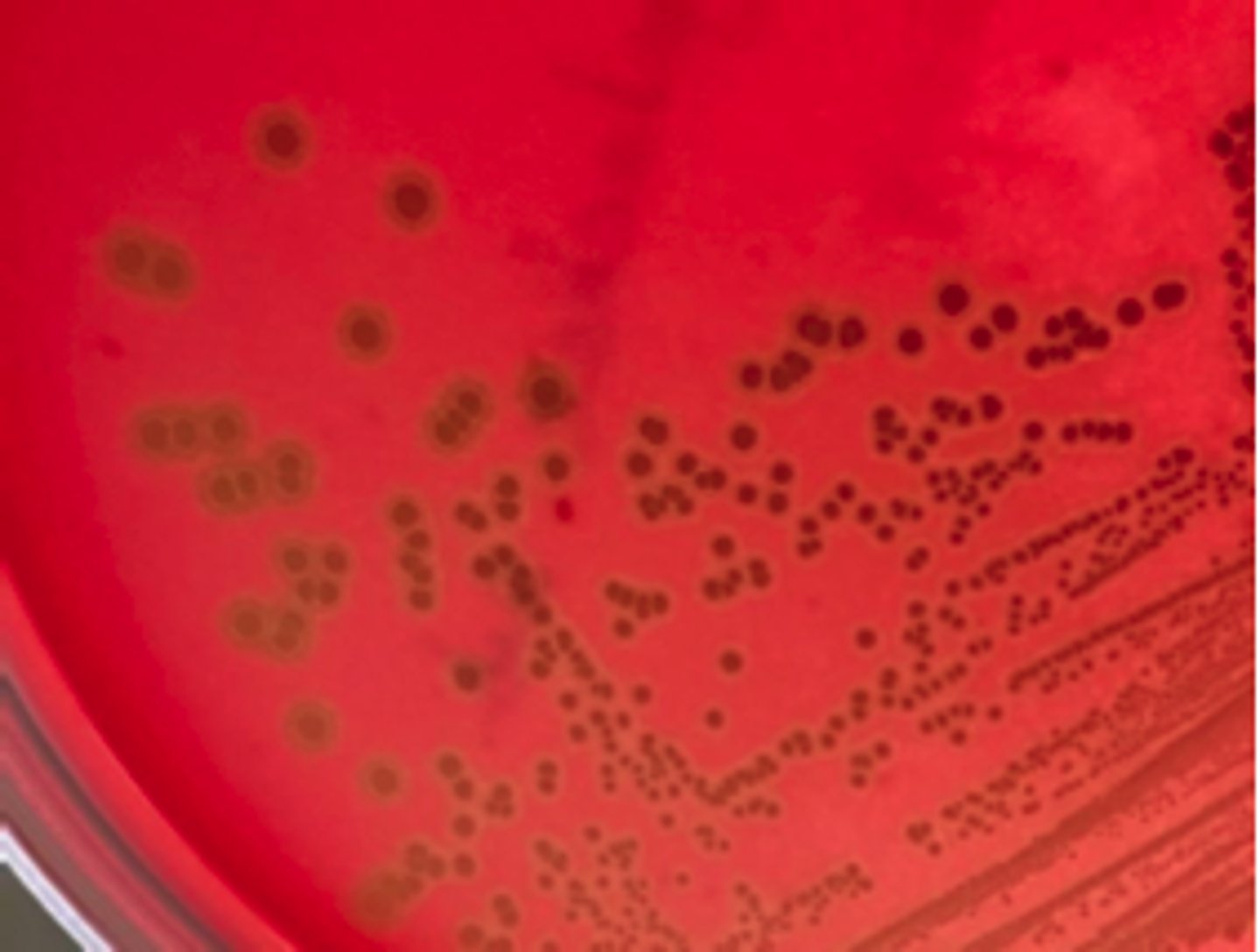
Diffuse β-type hemolysis
This organism was isolated from aspirates collected from several enlarged superficial lymph nodes from a number of sheep in a flock. You have been given a 48 hr BA
culture. There was no growth on MacConkey agar. A Gram-stained smear from the lymph node aspirates showed intracellular and extracellular small gram-positive bacilli and coccobacilli; coryneform morphology was observed.
Examine bacterial colonies and describe. Is hemolysis present?
Presence of lipids in the cell wall of Corynebacterium
You are trying to pick up a colony from the culture with your metal loop. You Struggle to scrape enough growth from a heavy streak area with the loop to get about a half loopful and flame the loop in the microincinerator. You will hear crackling noises as the colonies are incinerated.
What bacteria is this likely and why ?
Reverse/inhibitory CAMP reaction
Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
Examine a CAMP reaction.
Describe the result and what is the likely bacteria ?
No hemolysis
An organism was isolated from a transtracheal fluid collected from a 2 month old foal with fever, lethargy and cough. A thoracic ultrasound revealed multiple, large lung lesions. You are provided with a 48 hr BA plate. There was no growth on MacConkey agar. A Gram stain of a smear prepared from the fluid revealed intracellular and extracellular gram-positive coccobacilli.
Is hemolysis present?
Shovel shaped CAMP Positive
Rhodococcus equi
An organism was isolated from a transtracheal fluid collected from a 2 month old foal with fever, lethargy and cough. A thoracic ultrasound revealed multiple, large lung lesions. You are provided with a 48 hr BA plate. There was no growth on MacConkey agar. A Gram stain of a smear prepared from the fluid revealed intracellular and extracellular gram-positive coccobacilli.
Interpret the CAMP and presumptive ID

Positive sulfide rxn
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
This organism was isolated from joint aspirates of several feeder pigs that developed swelling and lameness. There is a recent history of "diamond-shaped skin lesions" in
this herd. A 48-72 hr blood agar plate, Gram stain and SIM tube results are provided. There was
no growth on MacConkey agar.
This organism is catalase negative. It is gram-positive, but can display a "gram-variable" stain
reaction. The organism can appear as rod-shaped and/or non-branching, short filaments when
viewed microscopically.
Interpret the Sulphide Rxn and presumptive diagnosis
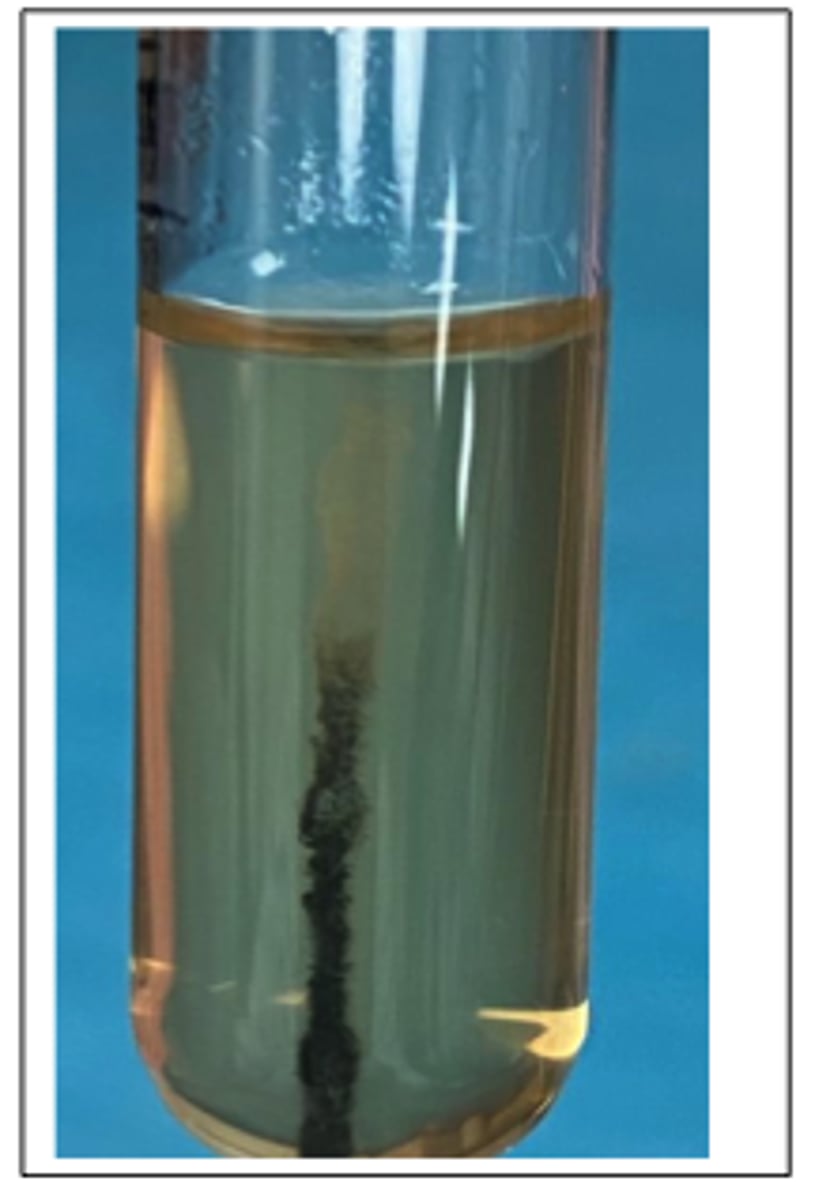

Weak β-type hemolysis
This pathogen was isolated from the brain stem of a cow with unilateral neurological signs. Presumptive diagnosis was "circling disease". A selective broth enrichment culture technique was used to isolate the pathogen provided. This organism is catalase-positive and CAMP-positive.
Examine the 24 hr BA agar culture. Describe the colony morphology. Is hemolysis present?
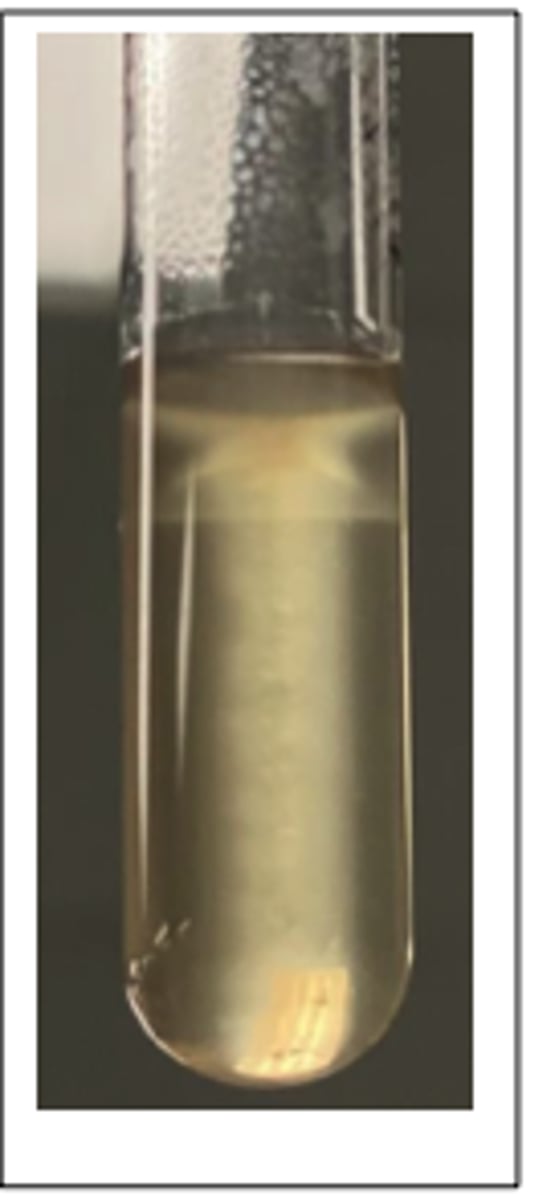
Sulphide - Negative
Motility: Note the characteristic motility = "umbrella-shaped" zone near top of agar.
This pathogen was isolated from the brain stem of a cow with unilateral neurological signs. Presumptive diagnosis was "circling disease". A selective broth enrichment culture technique was used to isolate the pathogen provided. This organism is catalase-positive and CAMP-positive.
Examine and Interpret the SIM (Sulphide-Indole-Motility medium test) reaction tube incubated at room
temperature (at 20-24⁰C). ** Indole reaction is not relevant for this.

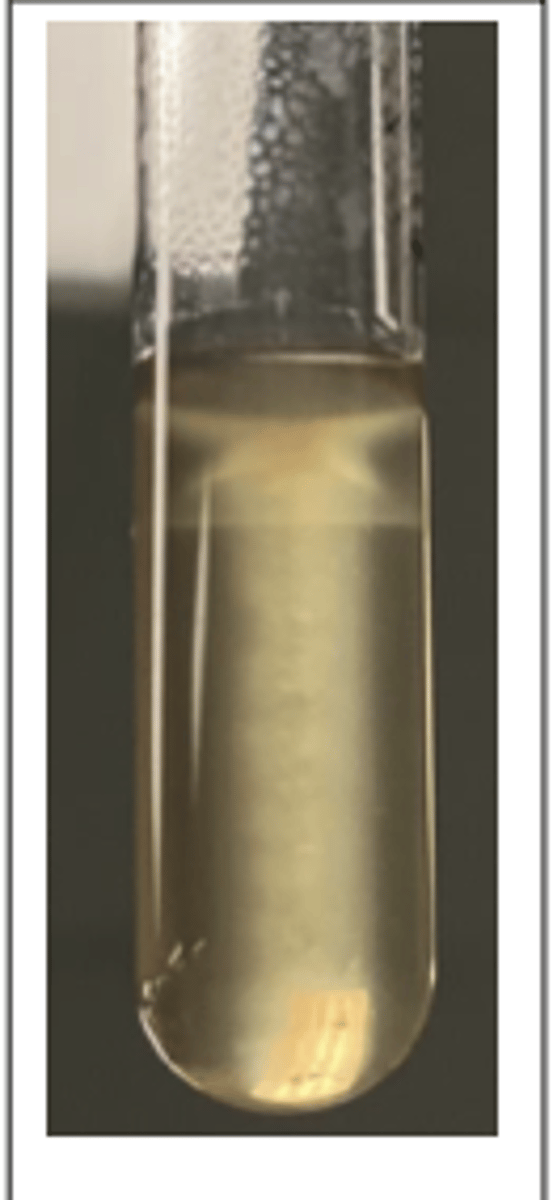
Listeria monocytogenes
This pathogen was isolated from the brain stem of a cow with unilateral neurological signs. Presumptive diagnosis was "circling disease". A selective broth enrichment culture technique was used to isolate the pathogen provided. This organism is catalase-positive and CAMP-positive.
See SIM test, what is diagnosis

Truperella pyogenes
A steer presented with a penetrating wound in the pectoral muscles. A swab of purulent material was collected during surgical management. 48 hr cultures on BA are provided. There was no growth on MacConkey agar. This pathogen is catalase-negative and
CAMP-positive (tests not shown).
Presumptive identification?
Positive
A swab of feces from a neonatal calf (< one week age) is provided. Examine your BA and MAC plates
Lactose positive or negative?
Salmonella
Selective enrichment isolation of _____*bacteria_______ from feces of an adult horse with diarrhoea using Rappaport brothand MSRV medium. MSRV is a soft semi-solid ___*bacteria___ selective agar which allows motile Salmonella bacteria to swim across it.
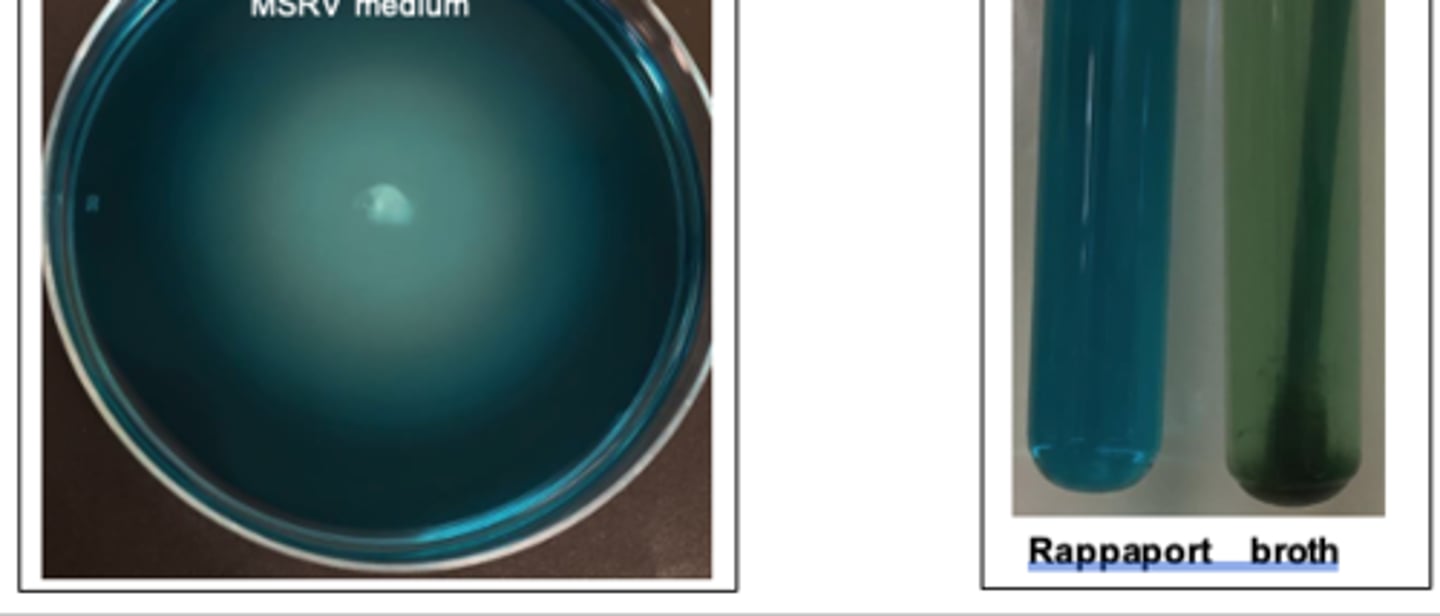
Campylobacter
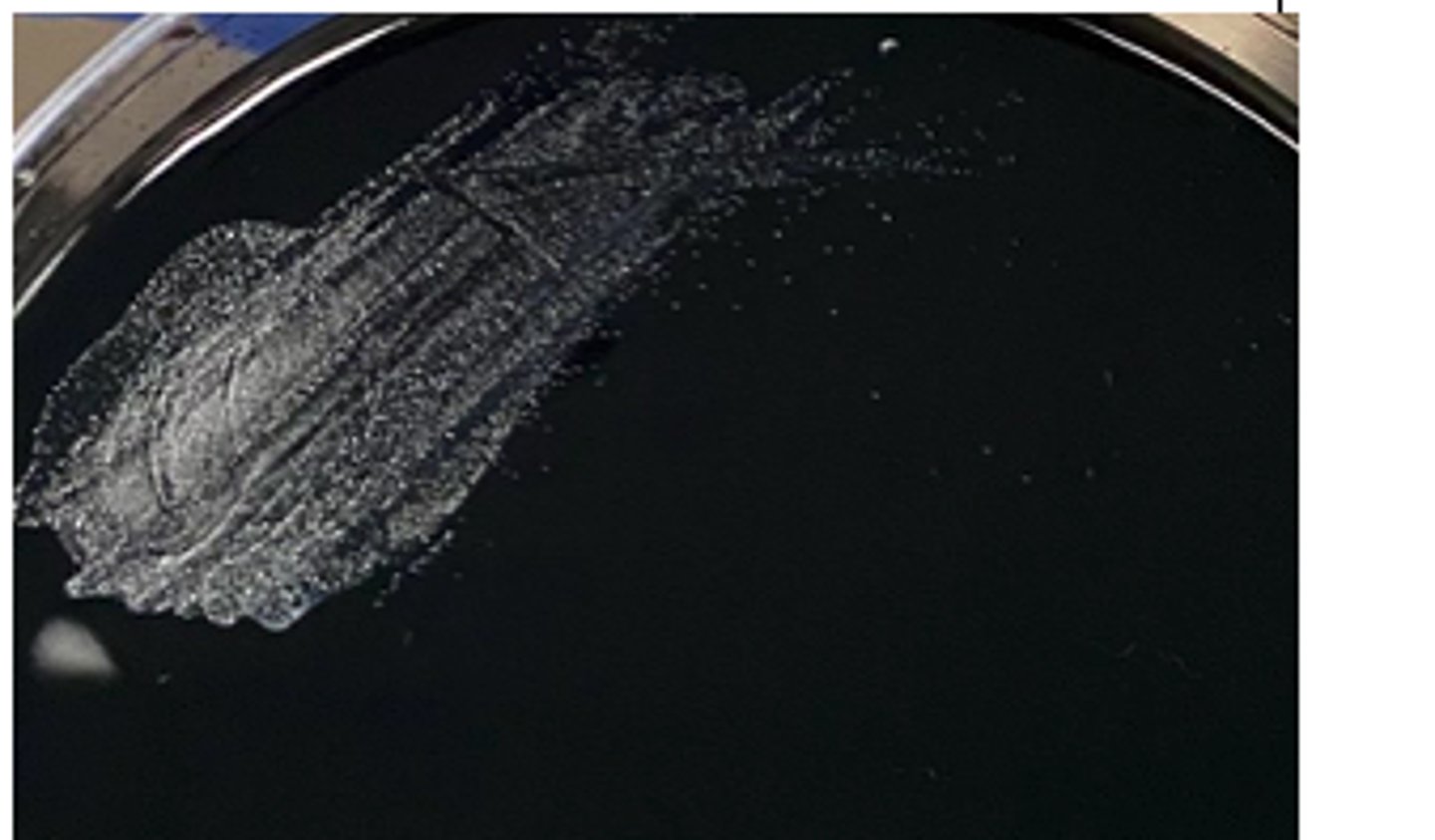
Campylobacter Cefoperozone Deoxycholate Agar ( CCDA): Selective mediaCampylobacter species
Campylobacter is grown on a ____ agar
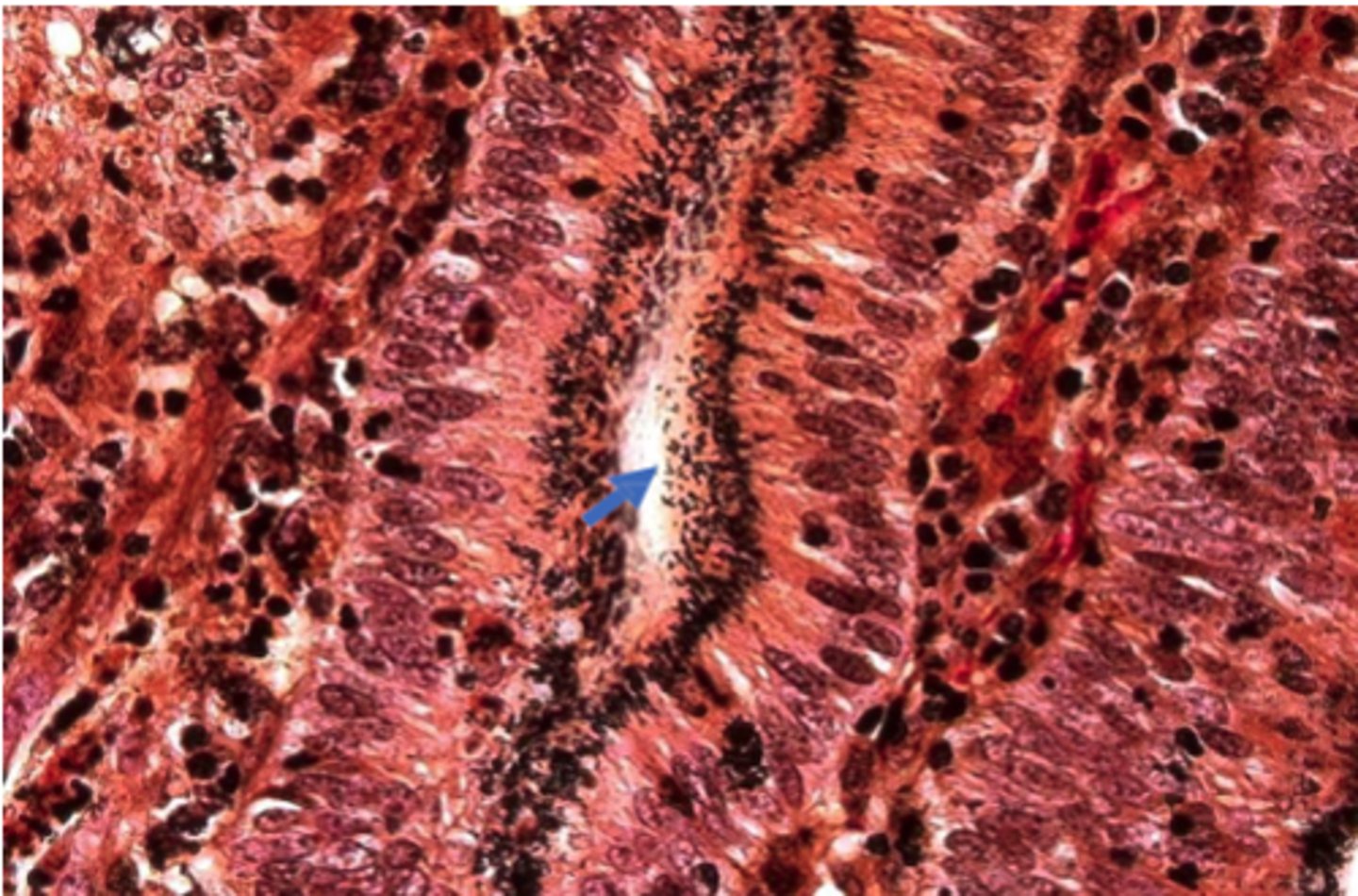
Lawsonia intracellularis.
A silver-stained histological section from the ileum of a pig with proliferative intestinal adenomatosis caused by _____________________ This pathogen can’t be grown on normal culture media; enterocyte tissue culture is required. Locate the darkly stained, thin, curved bacteria making up microcolonies within the apical cytoplasm of crypt epithelial cells.
Proteus + Klebsiella
Which of these bacteria are Urease positive
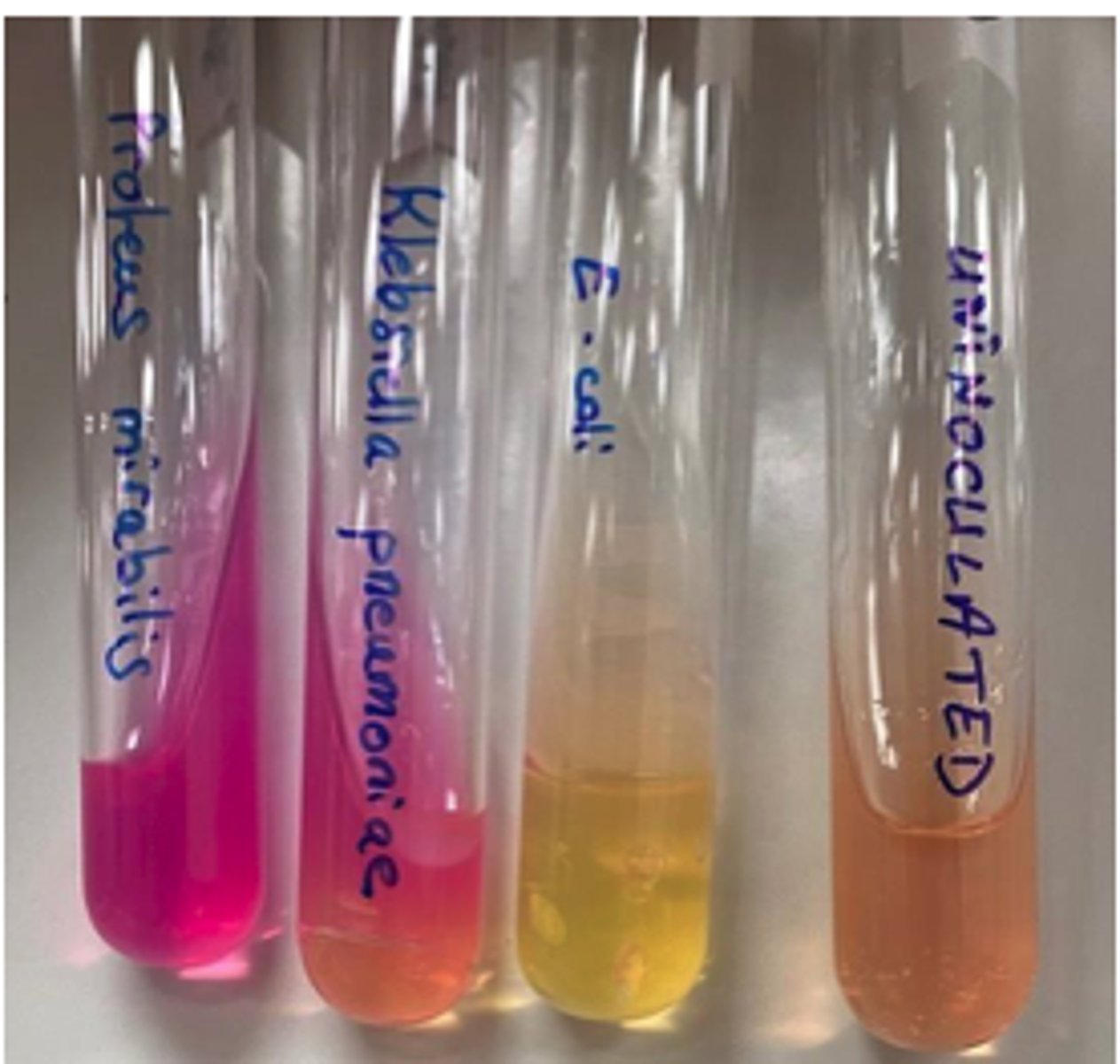

Klebsiella pneumoniae
Examine the photomicrograph and prepared slide of an India ink wet mount of____________demonstrating Rod-shaped bacteria with large white capsule
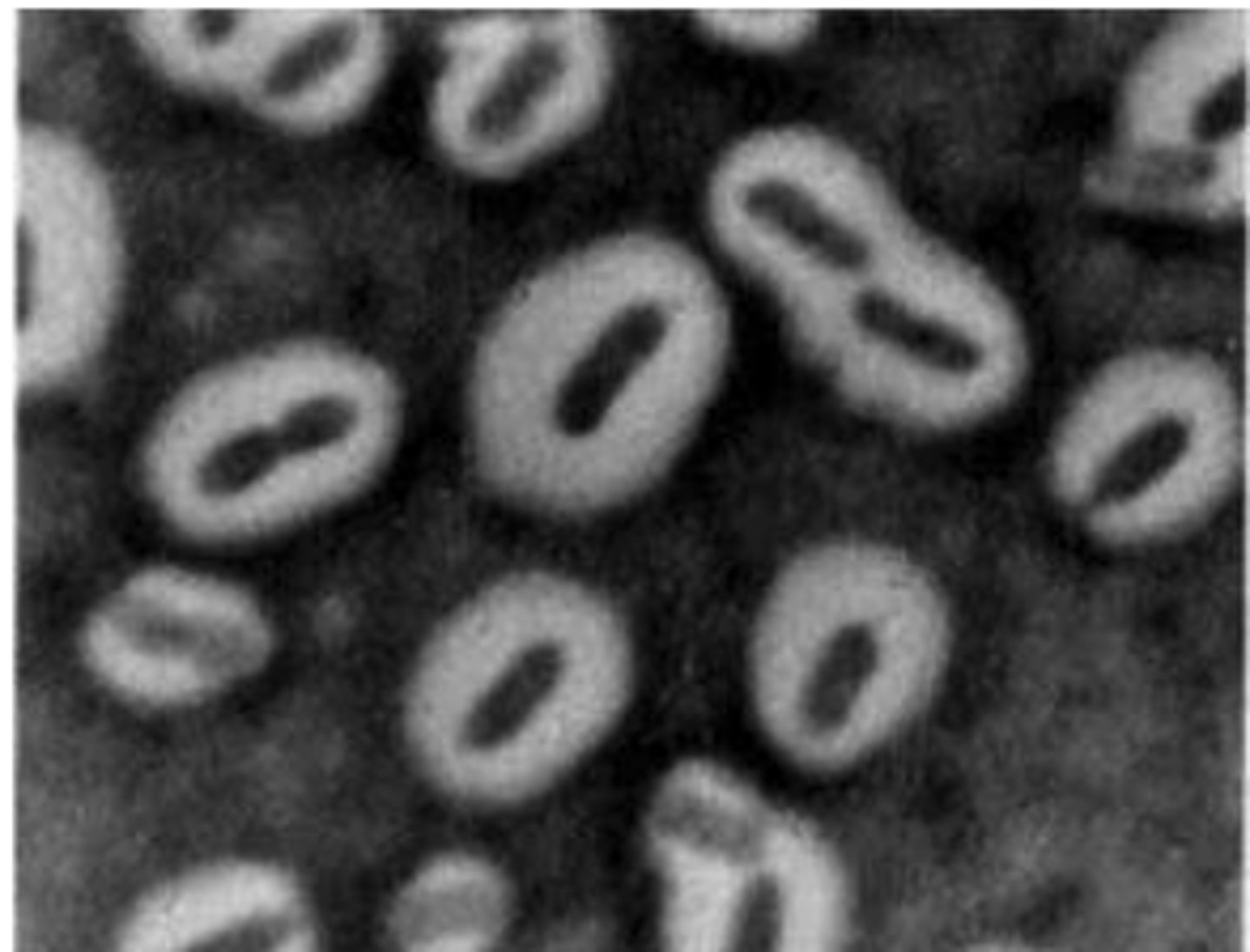
Staphylococcus spp. are catalase positive, Streptococcus spp. are catalase negative.
Helpful hints:
Staphylococcus spp. are catalase ______, Streptococcus spp. are catalase __________.
differentiates
l actose fermenters (pink colonies – such as E. coli & Klebsiella species) from n o n-l actose fermenters
(colorless colonies – such as Proteus spp. & Pseudomonas aeruginosa).
Helpful hint
MacConkey (MAC) agar is selective for Enterobacterales (and a few other Gram-negatives) & differentiates
l actose fermenters (pink colonies – such as _________ + __________) from n o n-l actose fermenters
(colorless colonies – such as _____________ + ___________).
esculin
Helpful hints
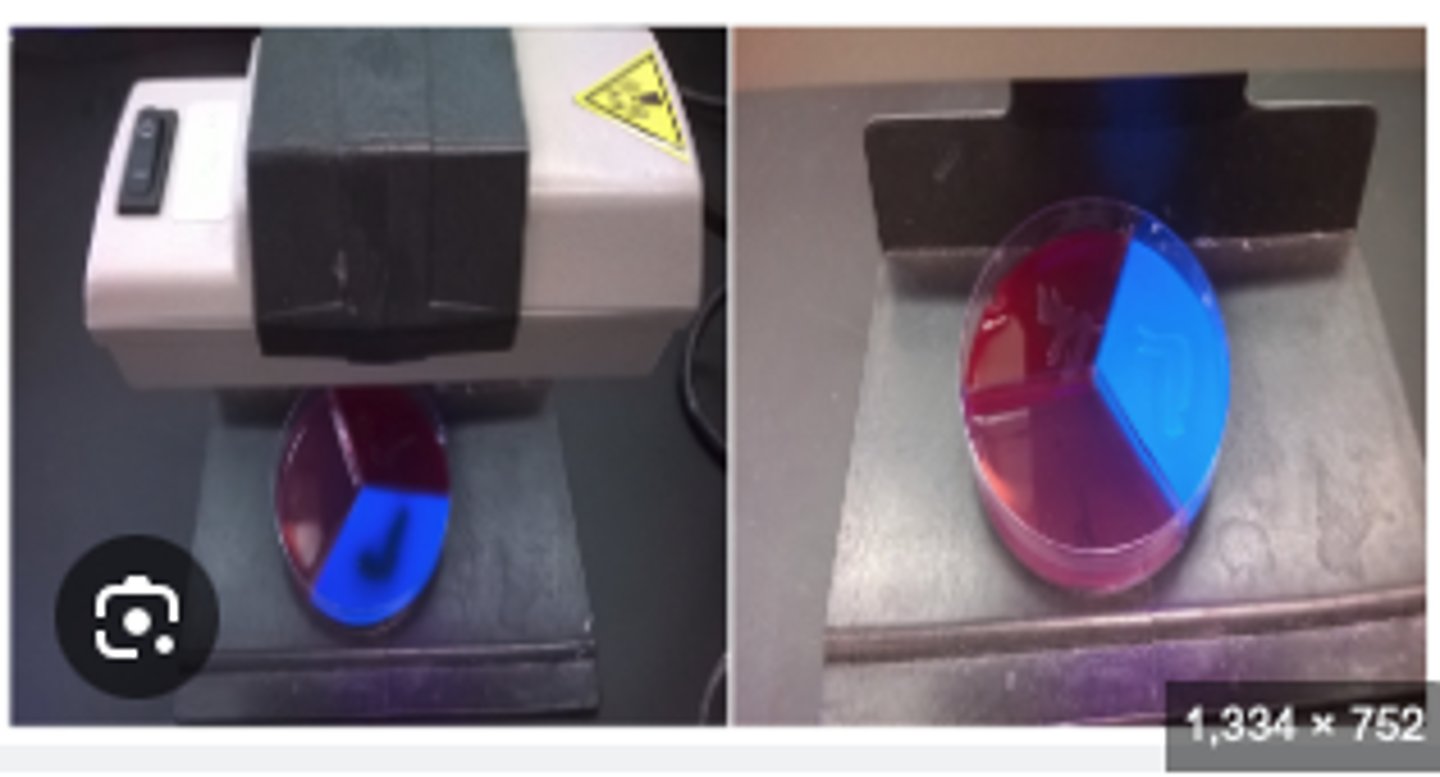
Edwards (Ed) agar is selective for s treptococci & enterococci a n d differentiates b e t w e e n _________________-positive (grey-black colonies) & _________-negative organisms
Absence of fluorescence indicating Aesculin hydrolysis
Streptococcus uberis
How to differ Streptococcus dysgalactiae and Streptococcus uberis
The will culture very similarly... BUT on Edwards there will be a difference. This is indicative of using A UV light and analyzing florescence. An Aesculin positive test has the ___________ of fluorescence indicating Aesculin hydrolysis.
______ is exculin positive
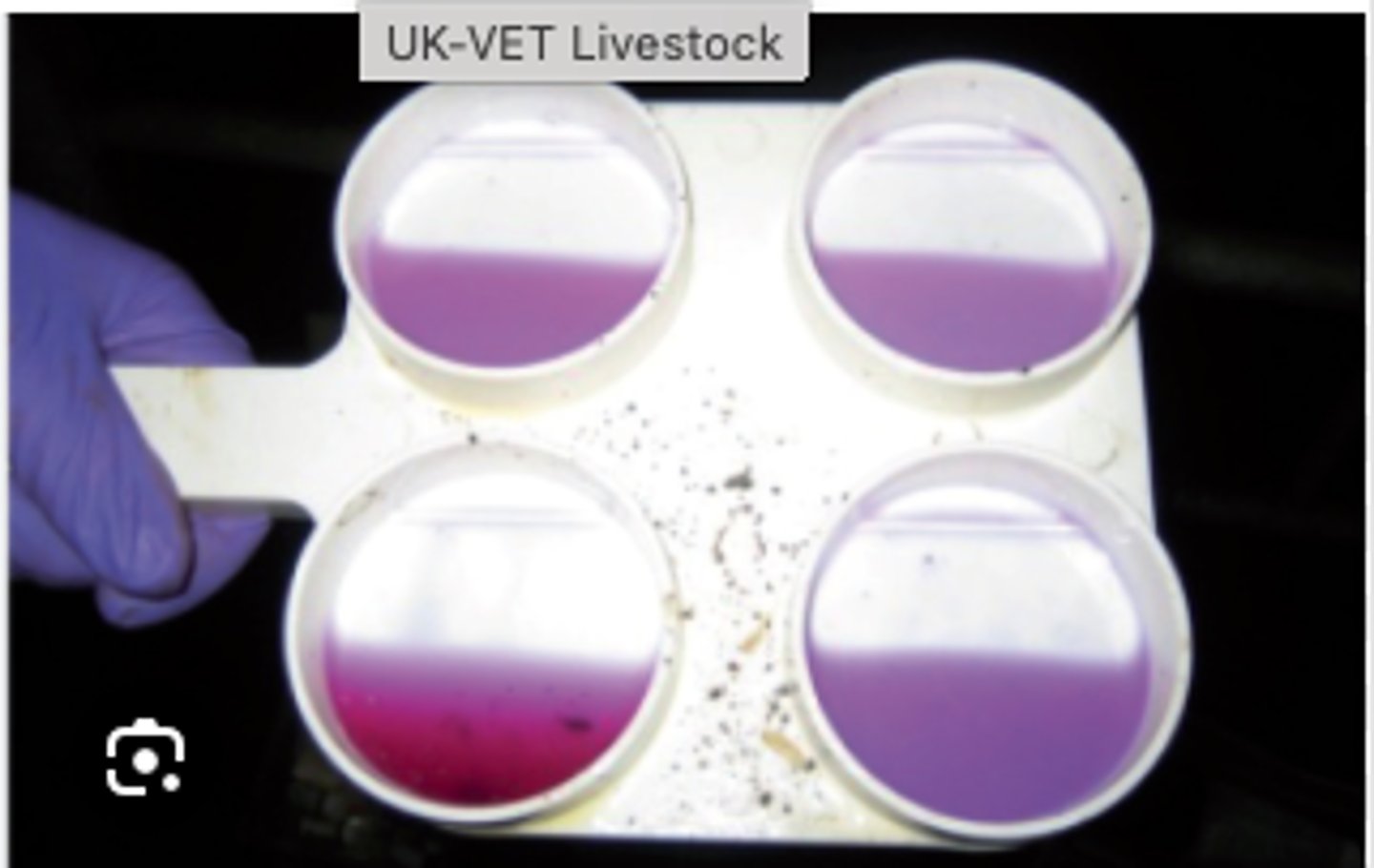
Somatic/ inflammatory cells
A california Mastits test that thickens is positive (it's on a grading scale too). this is indicative of higher ____ in the milk
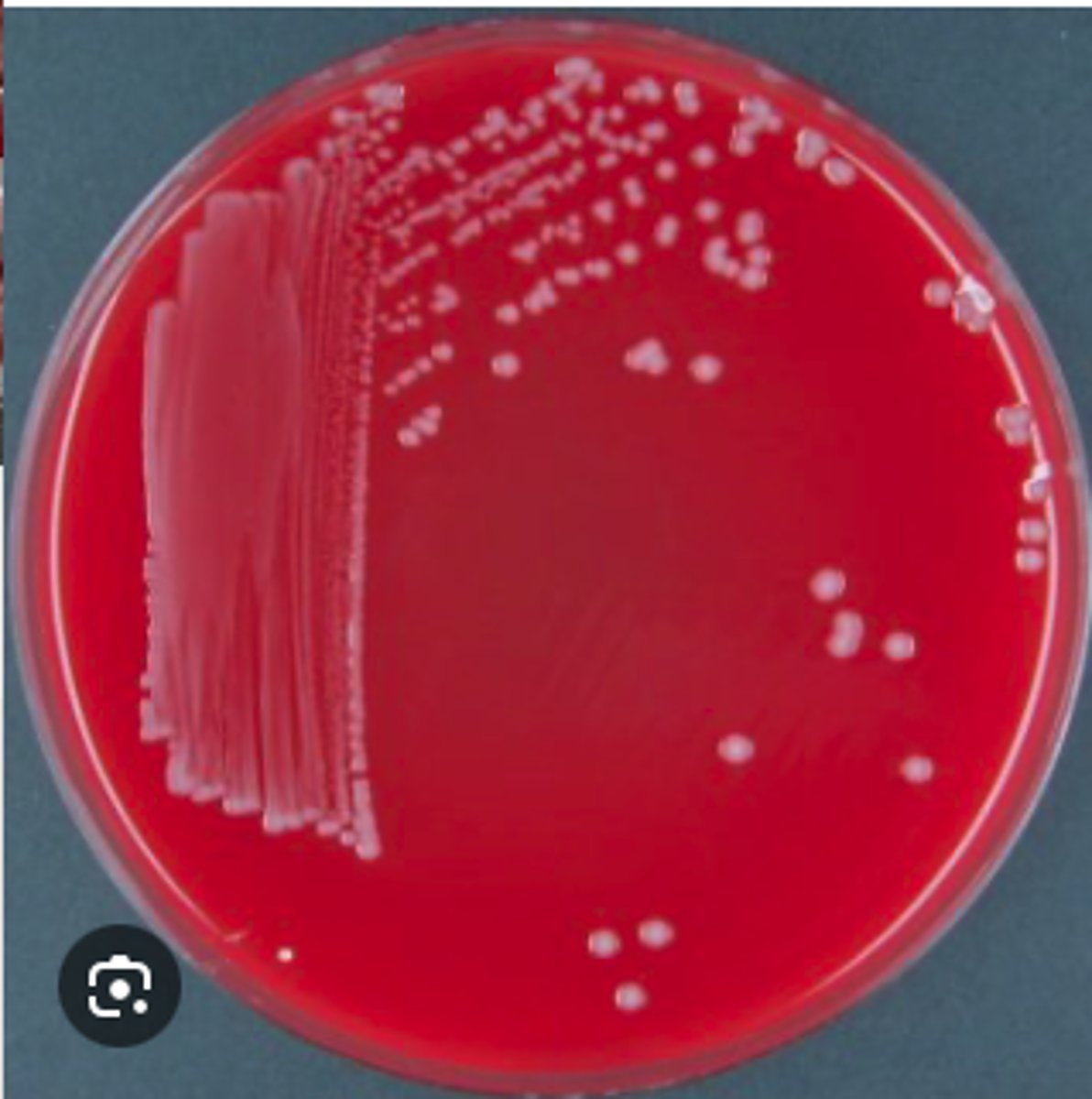
Pasteurella multocida
A young adult male cat was presented for clinical examination with a recent history of lethargy, inappetence, fever, and dyspnea. The cat also has a wound infection on his chest from a suspected cat fight a week ago. You are provided with a swab of the purulent exudate aspirated from the cat’s pleural cavity.
Tests:
Gram negative coccobacilli with bipolar staining
Non-hemolytic
Presumptive Diagnosis
Mannheimia haemolytica (hemolytic on BA)
Eight 12 month-old feedlot calves were quarantined with acute respiratory difficulties, one of which died despite treatment with a single dose long-acting antibiotic upon
arrival at the feedlot. Post mortem findings showed extensive haemorrhagic fibrinous bronchopneumonia in the cranioventral lung lobes.
Test:
Cytology: Medium sized greyish colonies
See BA and describe
Indole positive , Oxidase negative
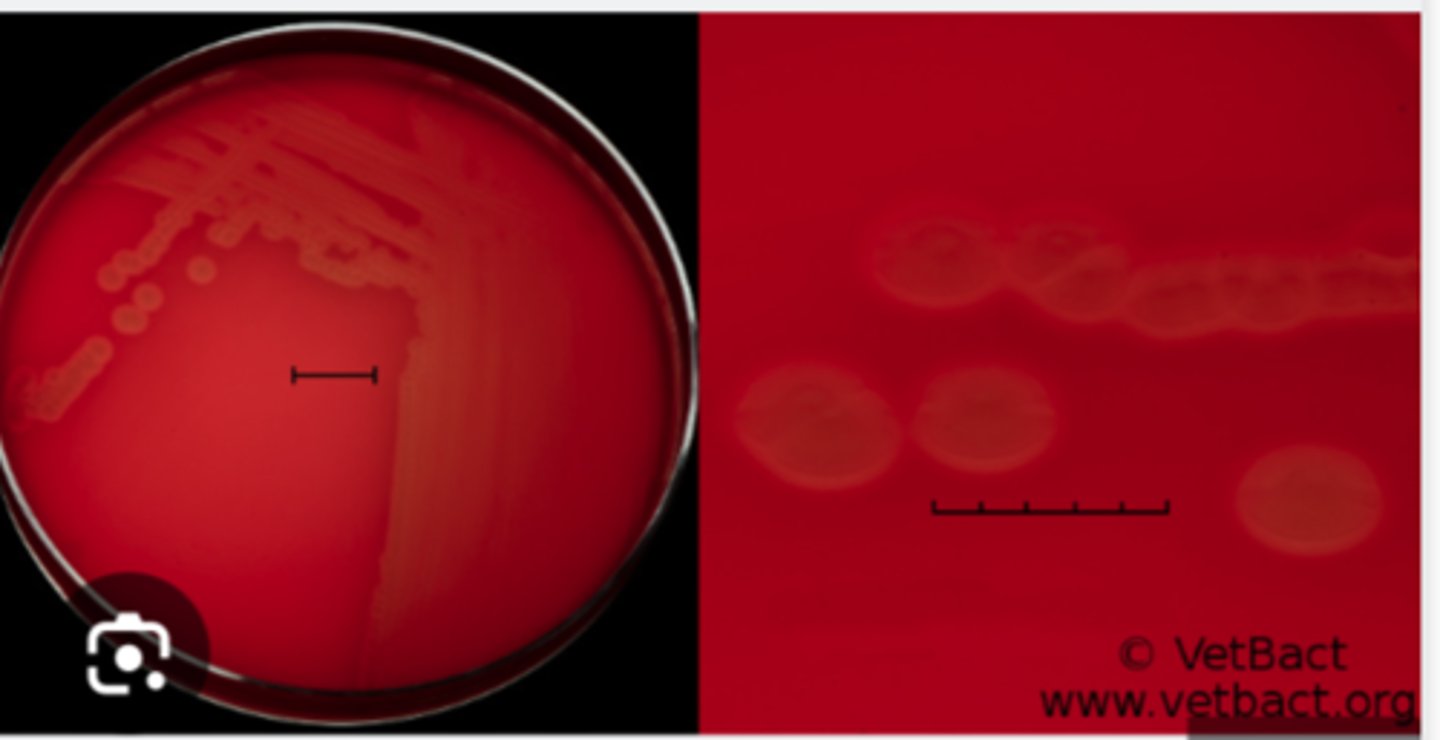
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
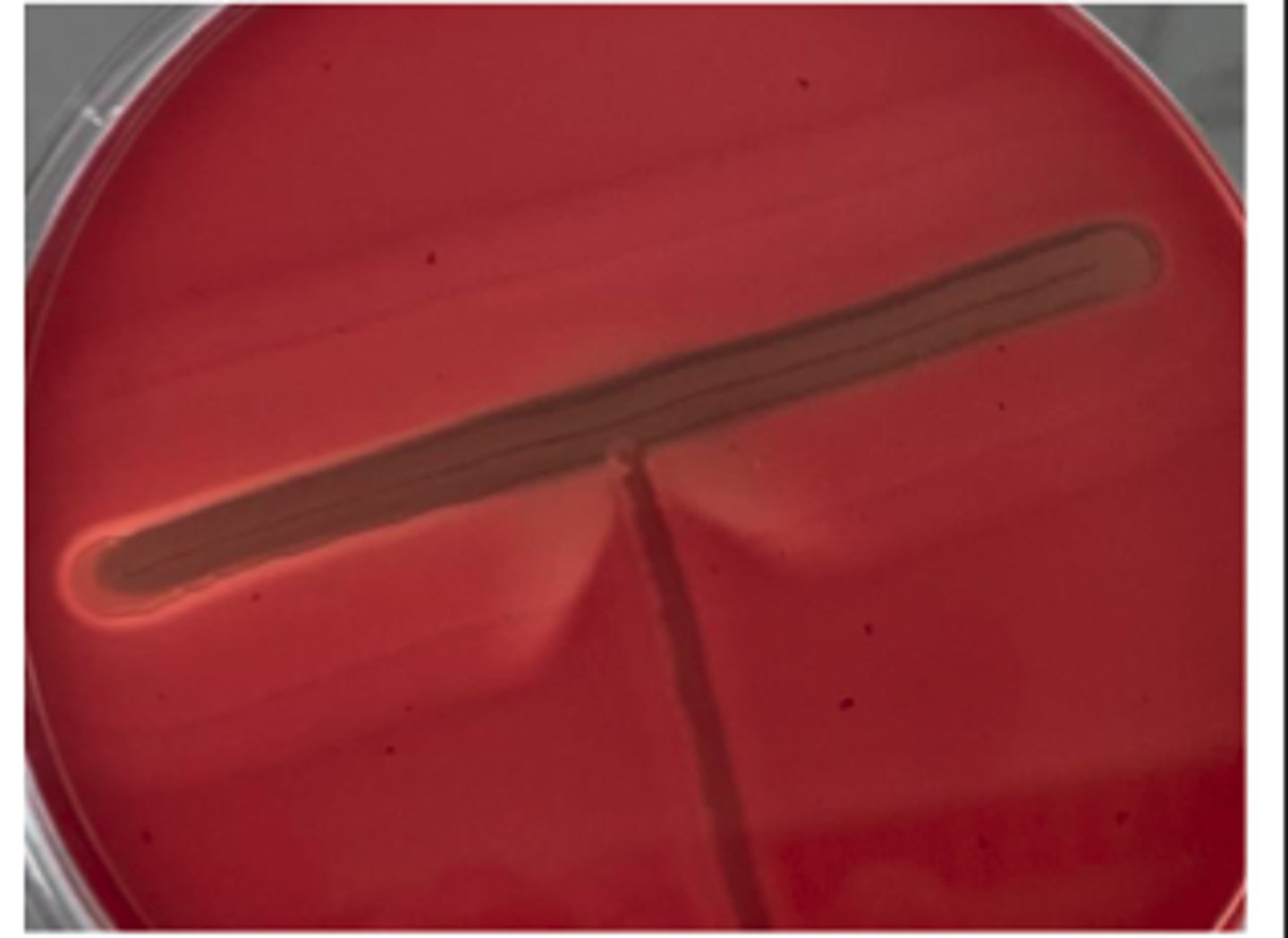
These will show “satellite-colony” growth adjacent to Staph streak.
Chocolate agar is blood agar with RBCs that have been lysed by heating to 80oC. This releases
haemoglobin containing hemin (Factor X) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) (Factor V),
which supports the growth of fastidious organisms
A group of previously healthy growing pigs suddenly develops severe respiratory distress with open-mouth breathing and cyanotic ears, several die within hours, and necropsy reveals dark, firm, caudodorsal pleuropneumonia.
Describe the pattern on the BA + chocolate
Presumptive diagnosis ?
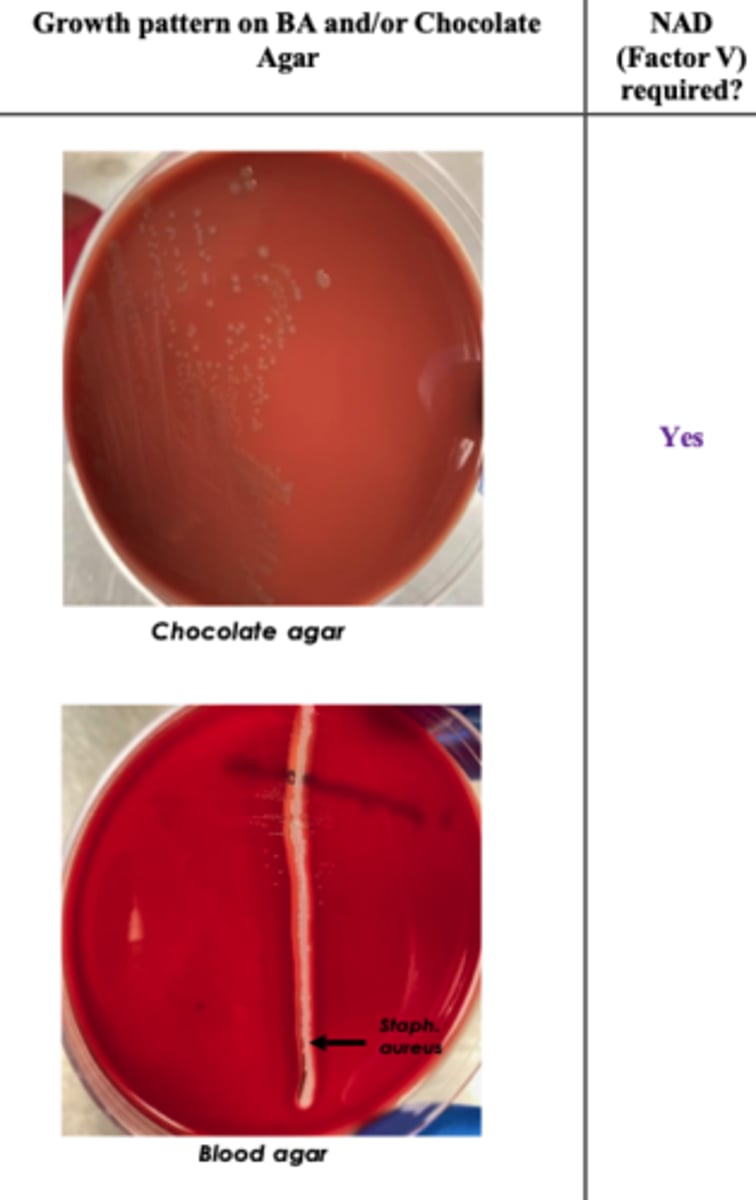
Histophilus somni
A feedlot steer is found depressed and febrile before suddenly becoming ataxic and recumbent
No NAD or X dependent
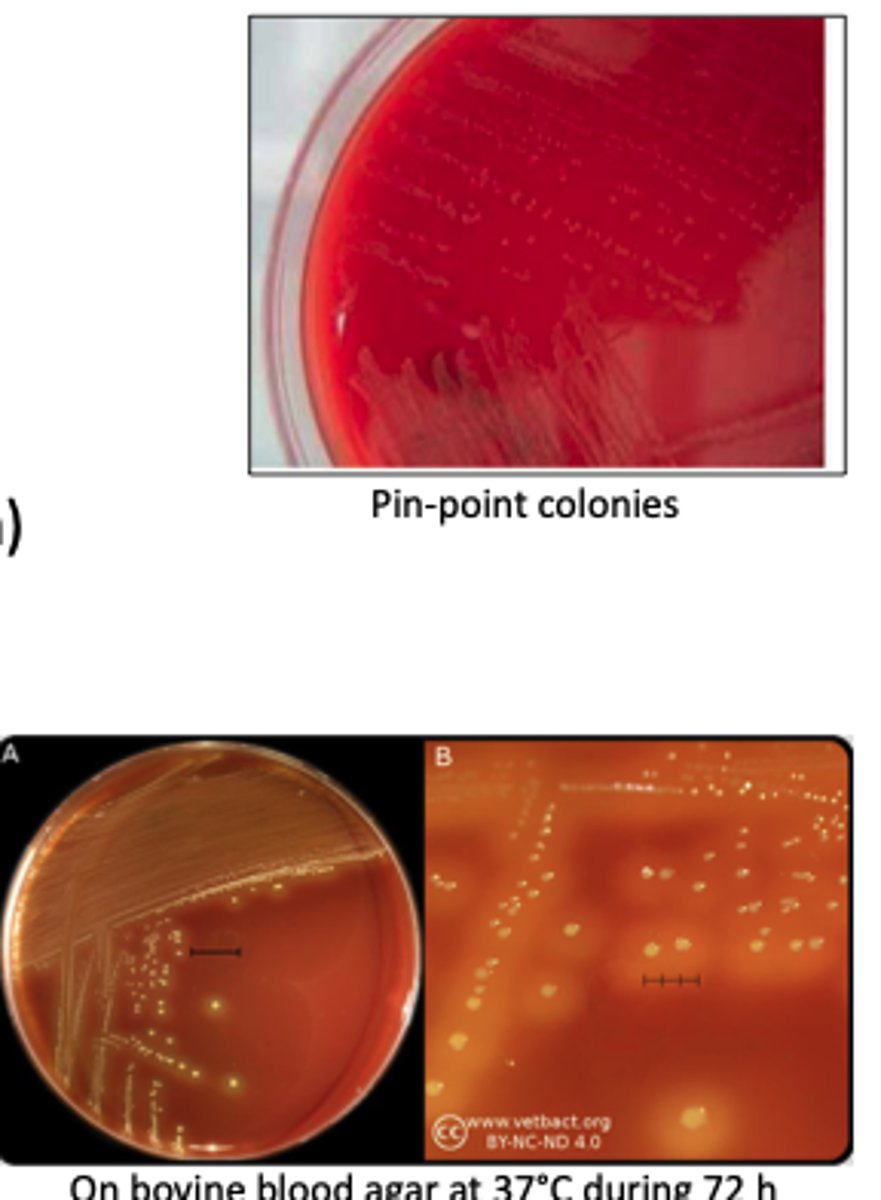
Beta hemolytic
Actinobacillus suis
A group of nursery pigs suddenly develops high fever, respiratory distress, and acute death, and survivors show multifocal skin hemorrhages and necrotic, embolic lesions in the lungs, liver, and spleen resembling septicemia.
It is not NAD dependent
Describe BA + Presumptive Identification
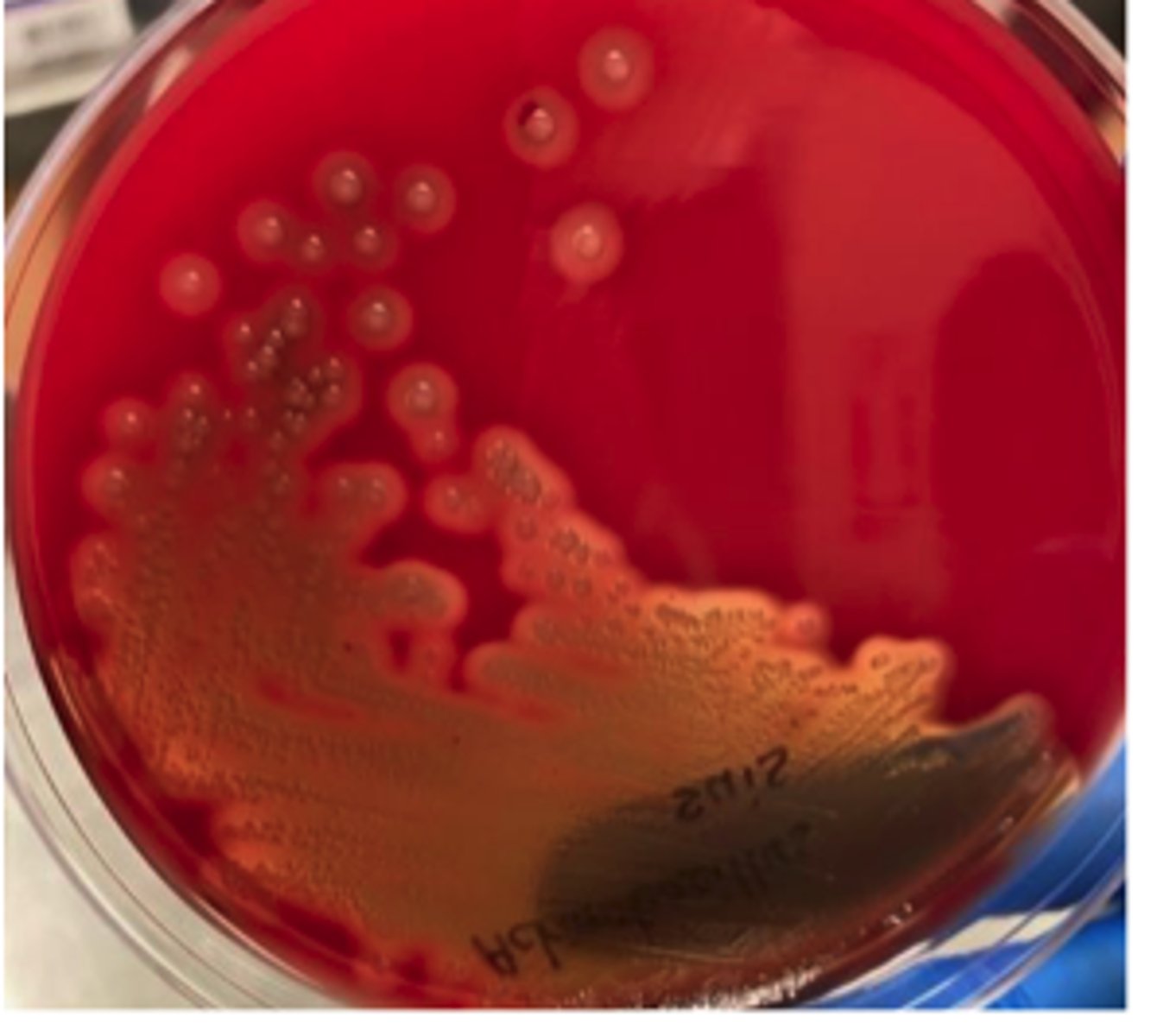
Bordetella bronchiseptica ( Kennel cough)
A one-year-old male Labrador retriever presented with mild depression and recent history of a harsh, dry "honking" cough that appears to be exercise-related. The dog has a mild fever and palpation of the trachea elicited the cough. Further questioning of the owners revealed that their dog had been in a boarding kennel two weeks prior to becoming ill. BA and MAC cultures from an oropharyngeal swab are provided. Examine the prepared
Gram stain. The isolate is oxidase-positive. Describe the colonial morphology. Use the history and culture results to determine a presumptive identification and disease
diagnosis.
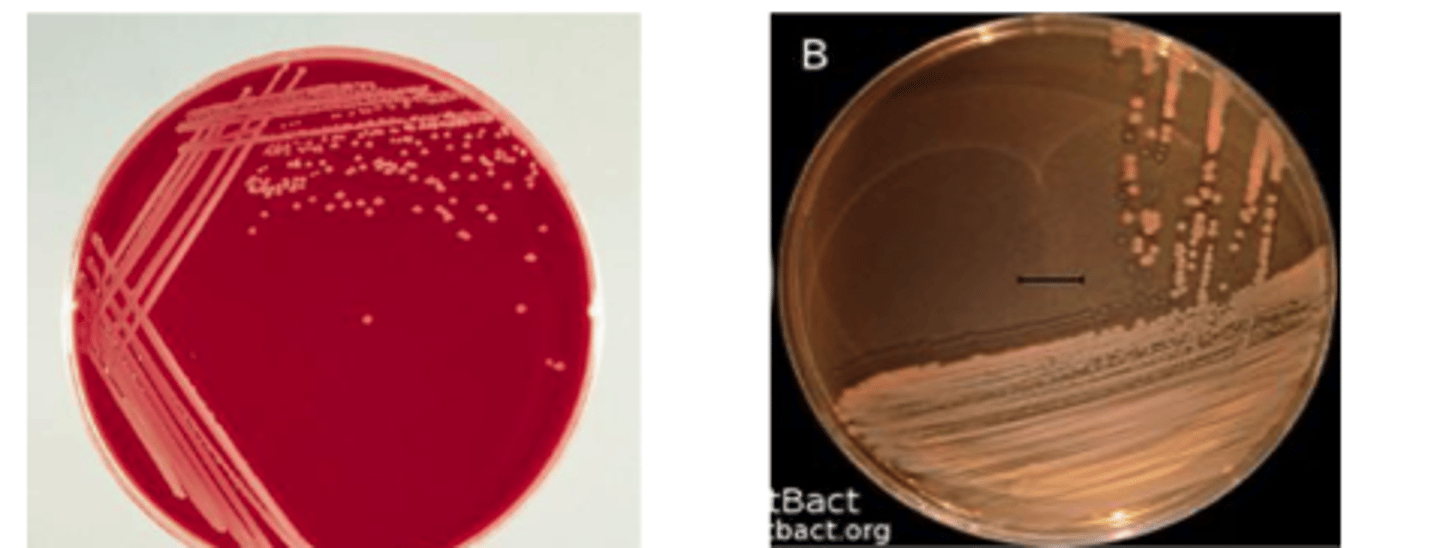
Non-hemolytic on blood agar
Gram negative rods with typical “Morse code” appearance
Actinobacillus equuli subsp. equuli
"Sleepy foal syndrome"
BA and MAC cultures from the kidney of a 4 day-old foal which died suddenly are provided. A Gram stained-smear prepared from colony material is also provided. On post- mortem examination, there were multiple microabscesses in the kidneys.
NO growth on MAC
Examine plates and Gram stain/microscopic morphology. Record the identification of this
equine pathogen.
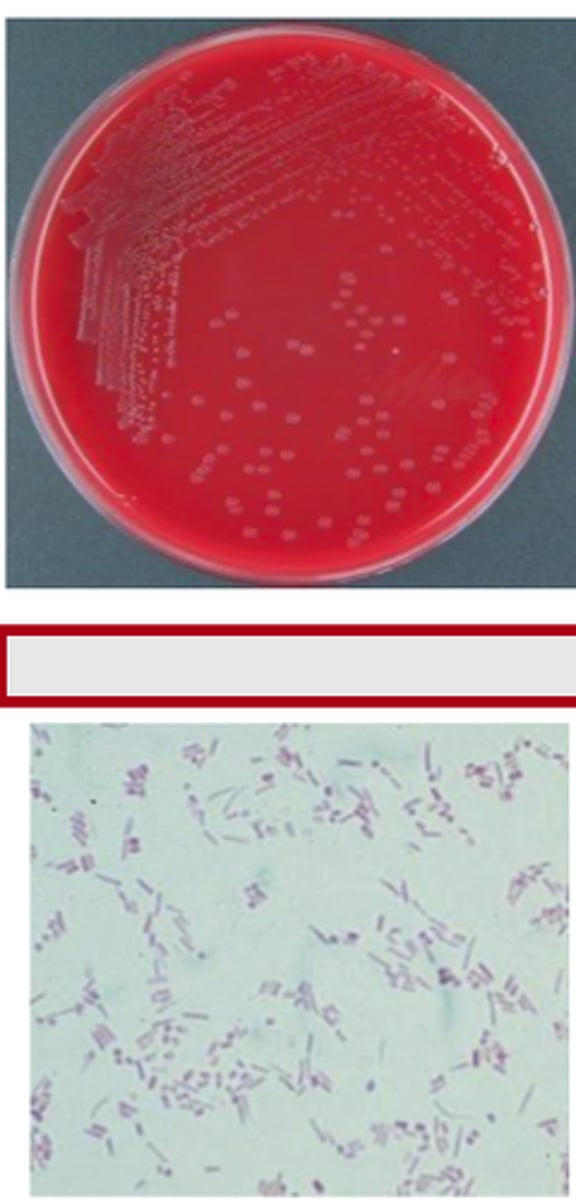
Corynebacterium renale
Pleomorphic (Coryneform) gram positive bacteria
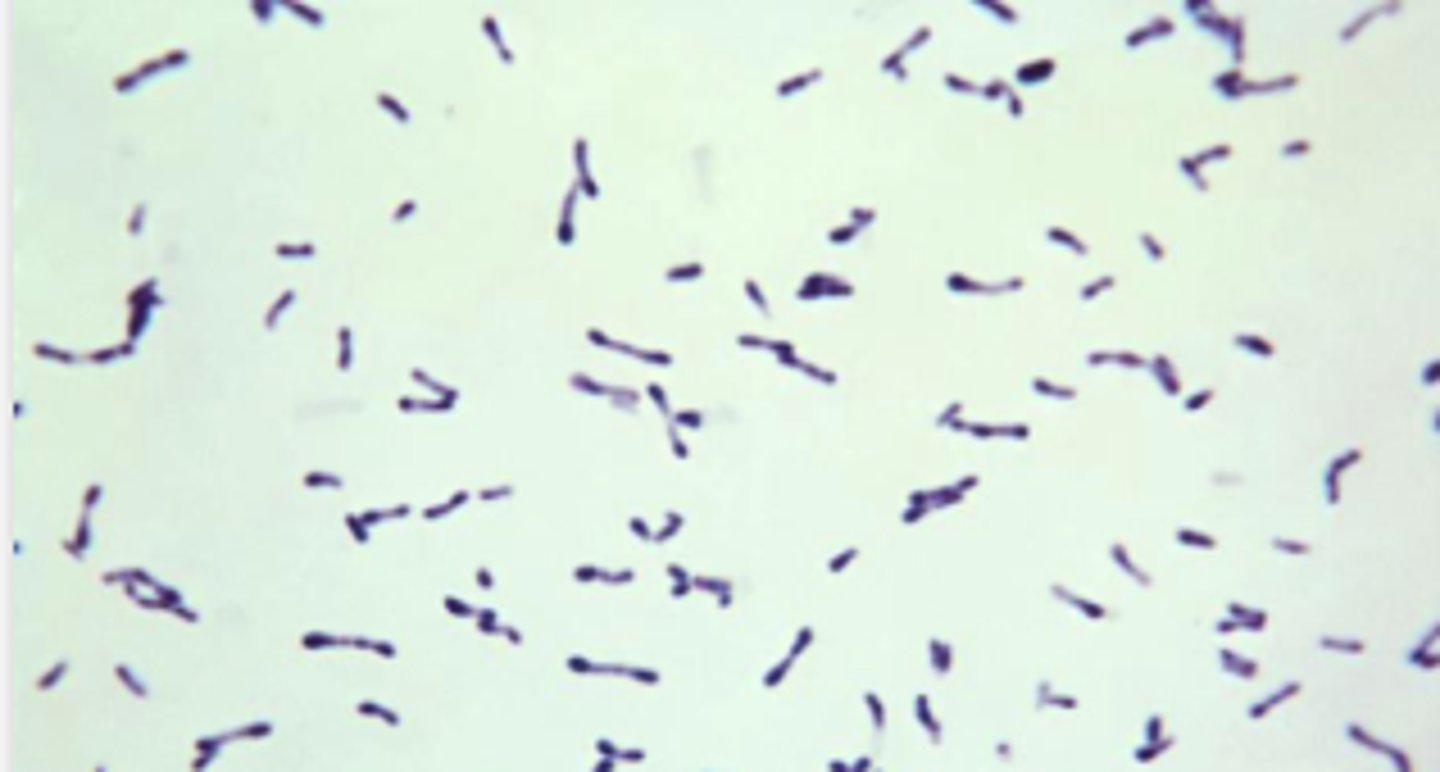
Urine sample from a cow with frequent urination, pyuria, hematuria and decreased milk production. Examine the Gram stain prepared from urine, a 48-hour BA culture, and a urease biochemical test.
Record the identification of this urinary pathogen.
Results:
*Urease positive
Non- hemolytic on BA
See Cytology
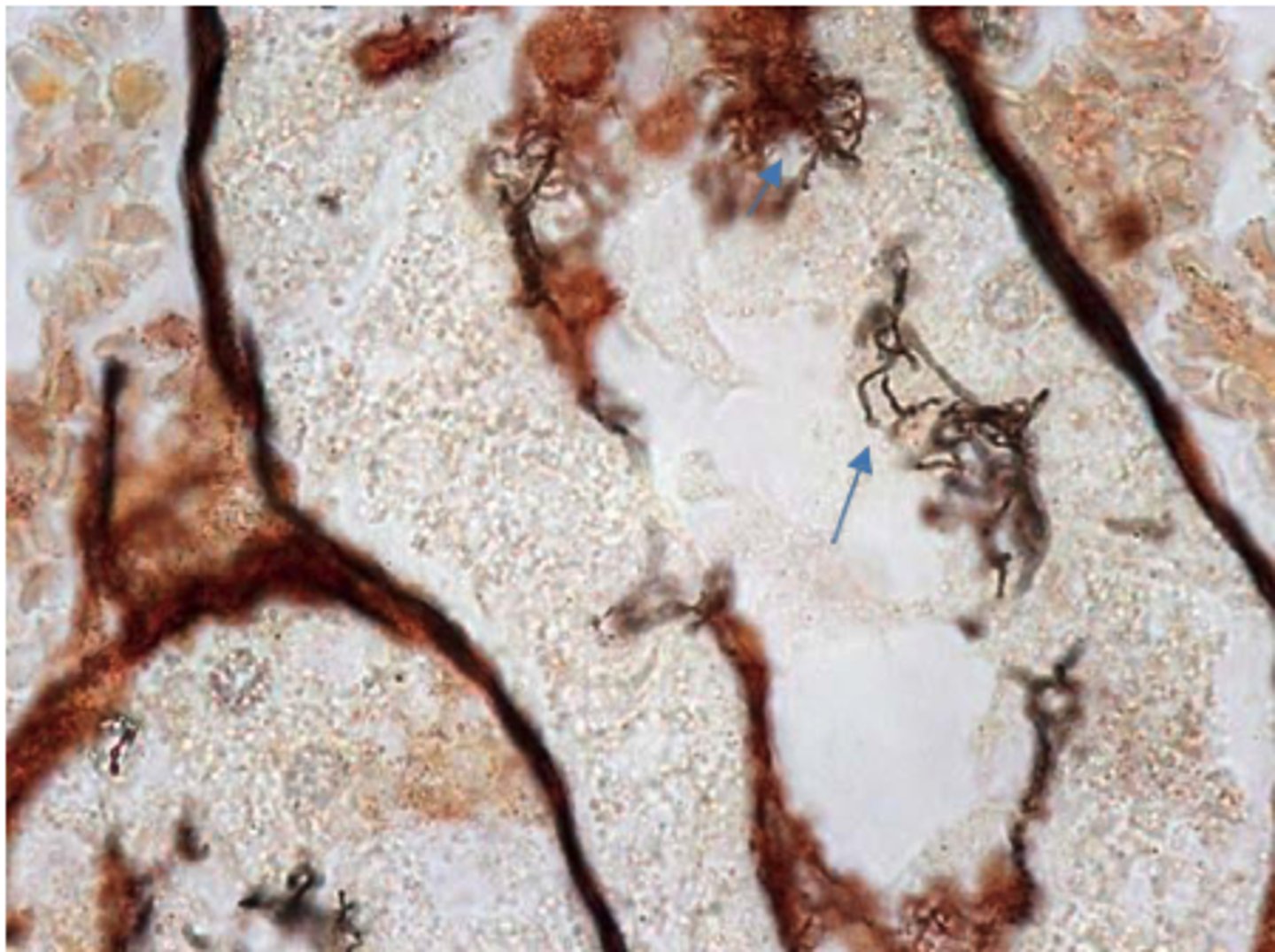
The Leptospira are present in the renal tubules, the bacteria are spiral in shape (arrows)
A silver-stained section of a kidney from a sow
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius
Note: E.coli is also common for UTI but is gram -ve
A canine urine specimen collected by cystocentesis for a UTI. Is B-hemolytic on BA. Describe the cytology (Gram positive or negative) and make a presumptive identification

Green coloration is due to pigment production (Pyocyanin) MAC agar
Metallic sheen appearance of on blood agar
--> Pseudomonas aeruginosa
A vet submitted swabs from sheep with exudative dermatitis (AKA "green wool disease", "fleece rot") for
culture and identification. A bluish-green discoloration of the wool next to the areas of inflammation was
noted. The organism isolated is gram-negative and oxidase-positive. It has several characteristic morphological features on culture, including a distinctive odour. Note the typical colony features on BA and MAC
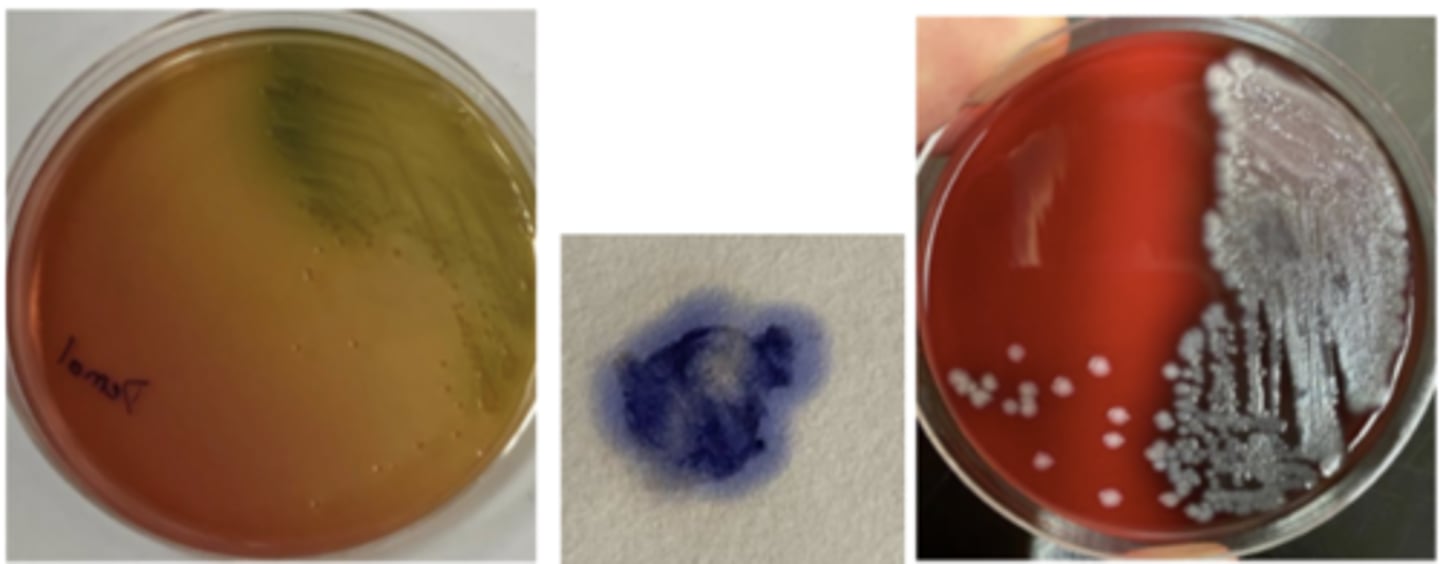
Dermatophilus congolensis
Cutaneous streptothrichosis (cattle), rain scald (on horses), lumpy wool (on sheep), and strawberry foot rot (sheep).
Several scabs were collected and submitted for examination from a Holstein cow with raised scabs covering 20 to 30% of the back. Examination revealed a mild-moderate exudative dermatitis beneath the scabs. The scabs are 1-2 cm in diameter and with the hair entrapped, resemble a paintbrush when viewed from the side.
Name the bacteria + names of the disease

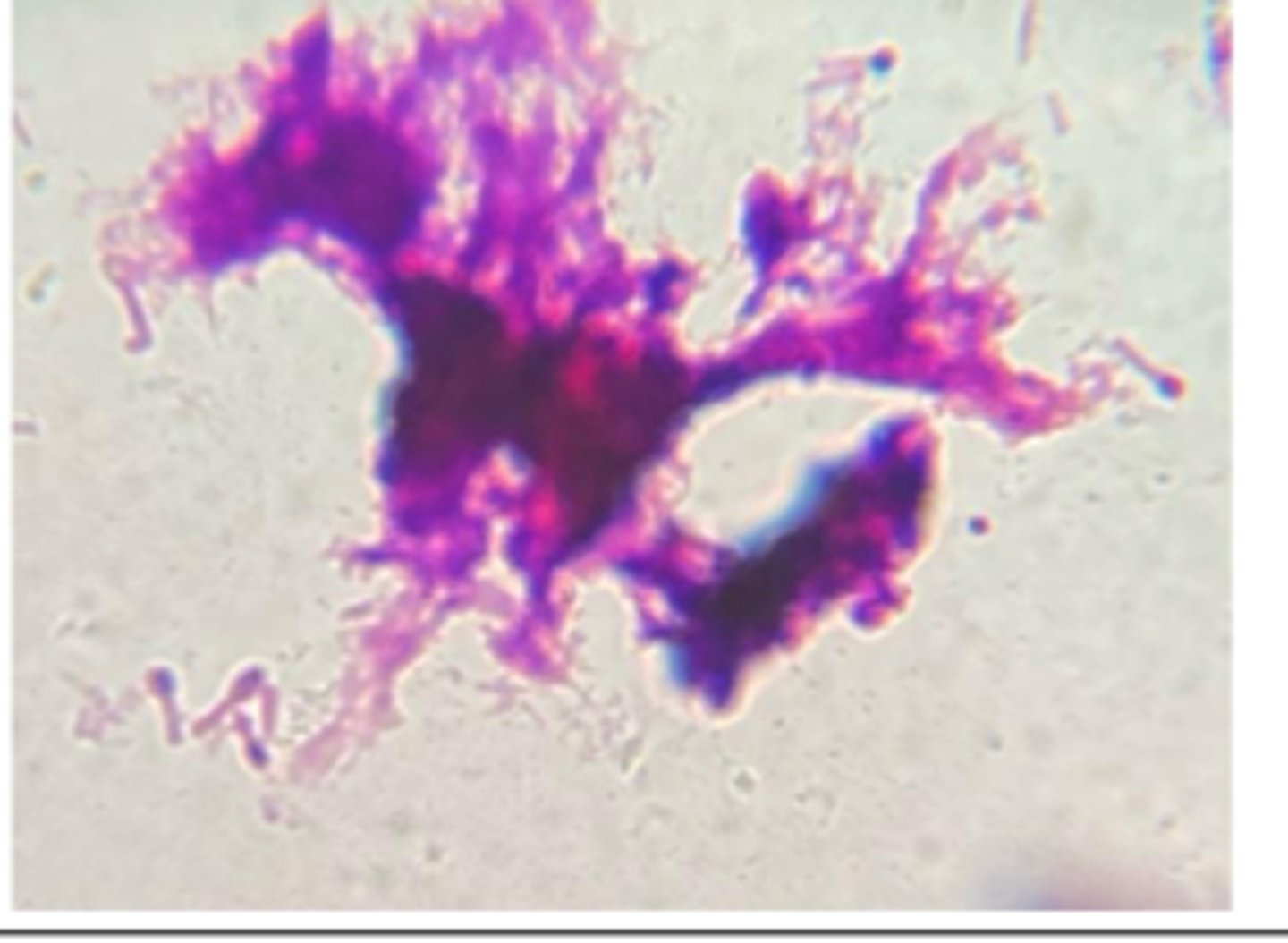
Clostridium tetani gram stain. Tennis racket or drumstick appearance
A horse developed rigid extension of neck, back and limbs and an elevated tail head ("sawhorse stance").
Examination revealed a puncture wound on the lower left hind foot. A direct Gram-stained smear prepared from a wound aspirate is provided.
Presumptive Diagnosis
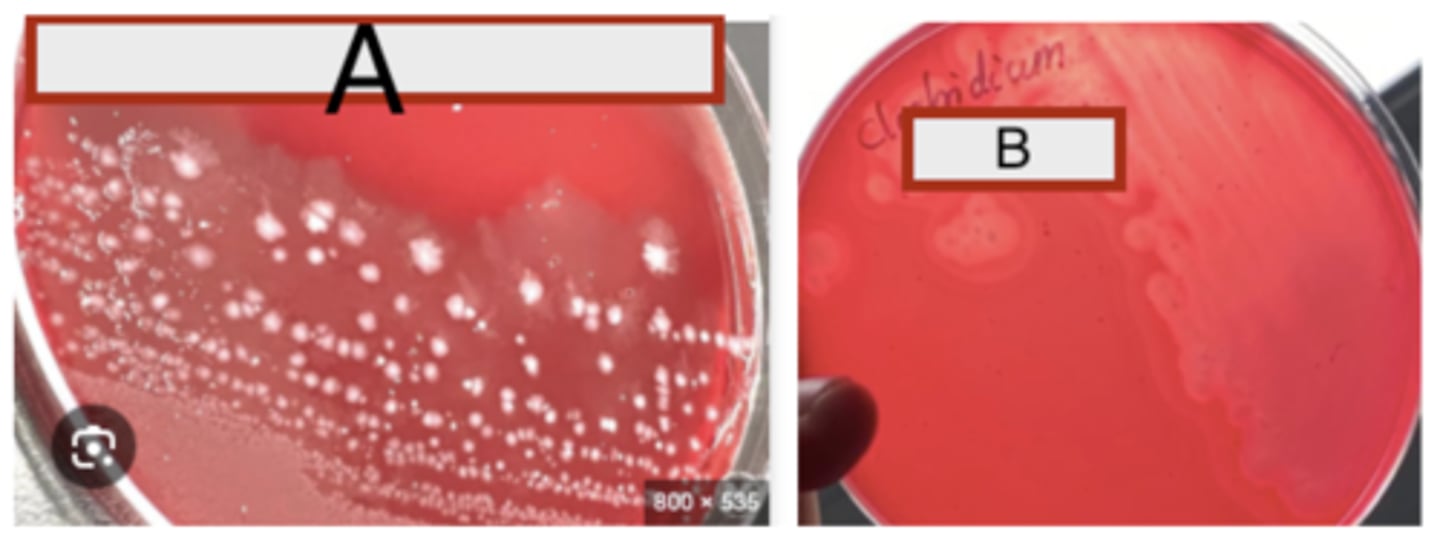
A- Clostridium septicum growth on blood agar, thick swarming non-hemolytic colonies
B- Double zone hemolysis, C. perfringens
Anaerobic BA cultures are provided of two Clostridium species causing histotoxic clostridial infections
(myonecrosis and gas gangrene) in animals and humans. Examine the plates provided and describe
What is you presumptive diagnosis of A + B and Why?
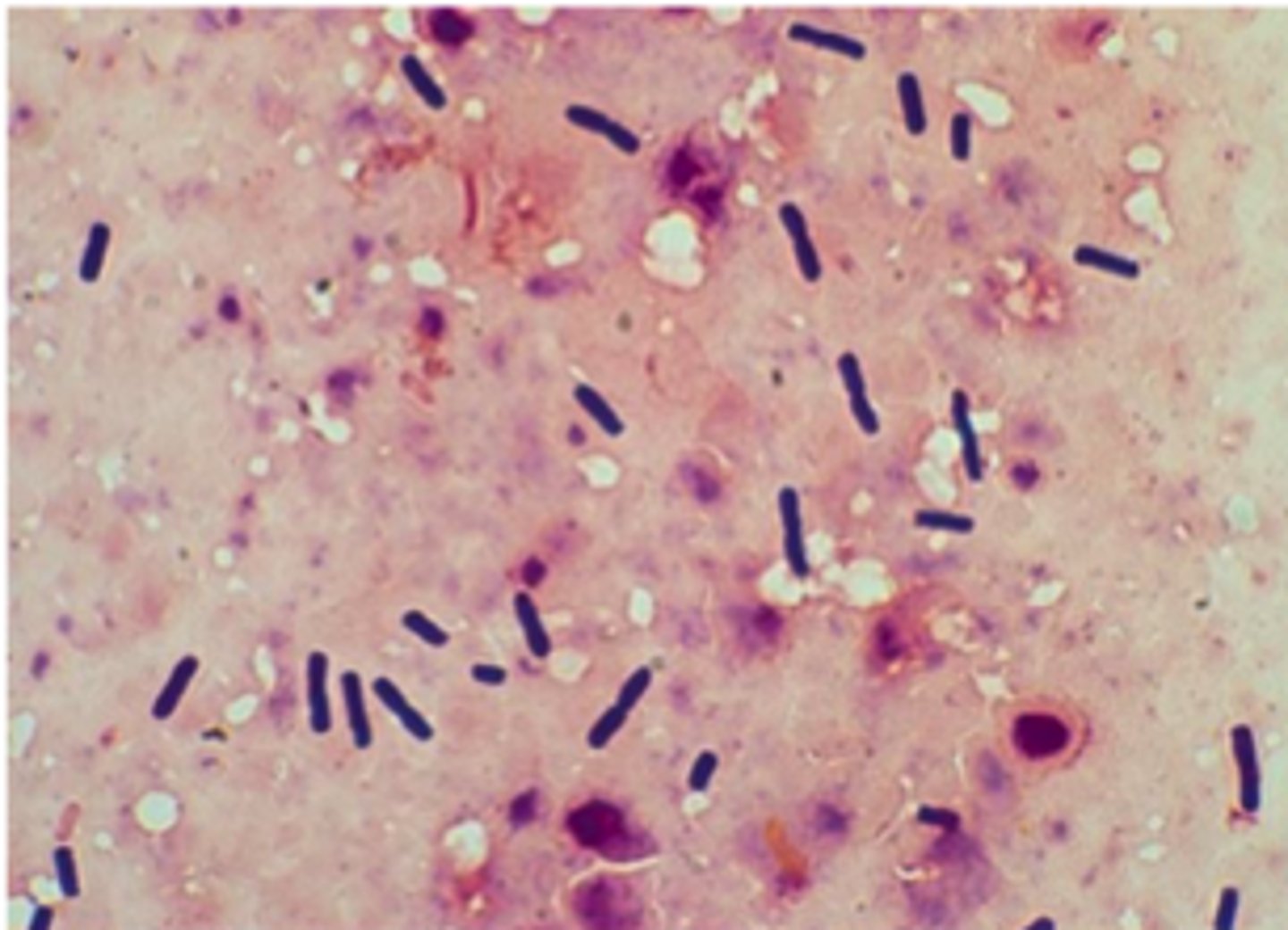
perfringens
Clostridium_____________gram stain large rectangular gram positive bacilli
--> Klebsiella pneumoniae
Other pathogens: Streptococcus zooepidemicus, Taylorella equigenitalis
A and MAC cultures of a uterine sample from a mare which developed metritis following natural breeding.
The isolate is an oxidase-negative gram-negative bacillus. What is your presumptive identification? What are other bacterial causes of equine metritis?
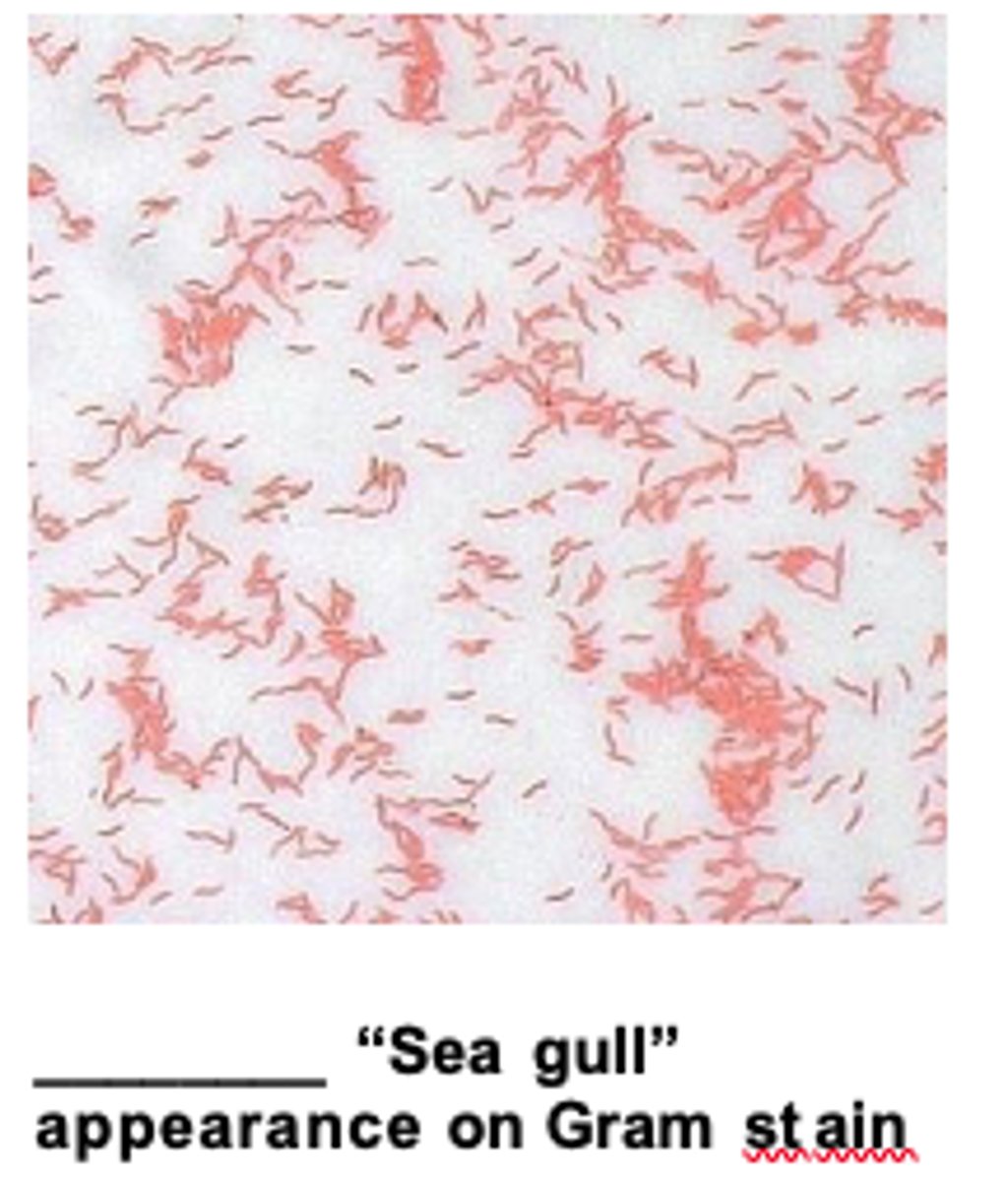
Note: the thin, curved, “seagull-shaped” gram-negative bacilli.
--> Campylobacter jejuni
Examine a gram-stained smear made from stomach contents of a sheep fetus which was aborted shortly before term. About 10% of the flock aborted. The fetal liver displayed multifocal, round "doughnut-like" necrotic
lesions.
Fried-egg” microcolonies of Mycoplasma species
Mycobacteria are intracellular bacteria with waxy/lipid cell wall which gives the bacteria hydrophobic properties as a result they tend to clump together
A Ziehl-Neelsen (ZN) stained histological preparation of ileum mucosa from a cow suspected of Johne's
disease. Note the clumped acid-fast (bright red/pink) bacilli. Why are they clumped?
Gram negative diplo coccobacilli
--> Moraxella bovis
BA & MAC plates were inoculated with swabs from cases of infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (IBK)
Growth on BA (no growth on MAC). Describe the morphologic features on cytology. What is the presumptive diagnosis
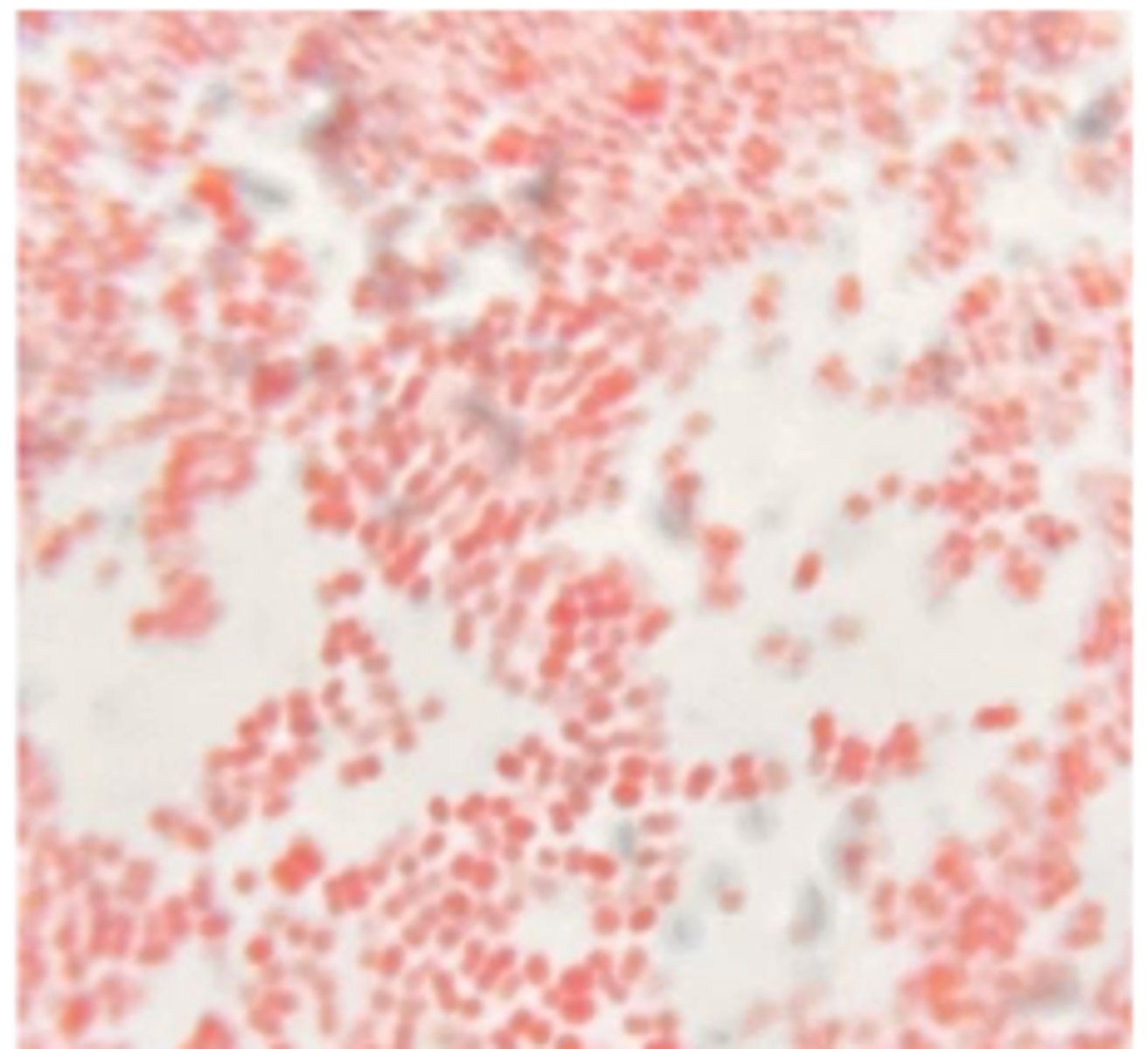
ZYGOMYCETES (Mucor spp., Rhizopus spp., and
Mortierella wolfii)
A dairy farmer notices one of his cows aborts in late gestation during a period of poor-quality, moist feed storage. At necropsy, the placenta appears thickened and necrotic.Histopathology of the placenta reveals broad, aseptate hyphae ------- spp.Cultures from the placenta grow rapidly on Sabouraud agar with fluffy, cotton-like colonies.
Lactophenol cotton blue (LPCB)-stained scotch tape lift slide mount of culture growth
DDX?
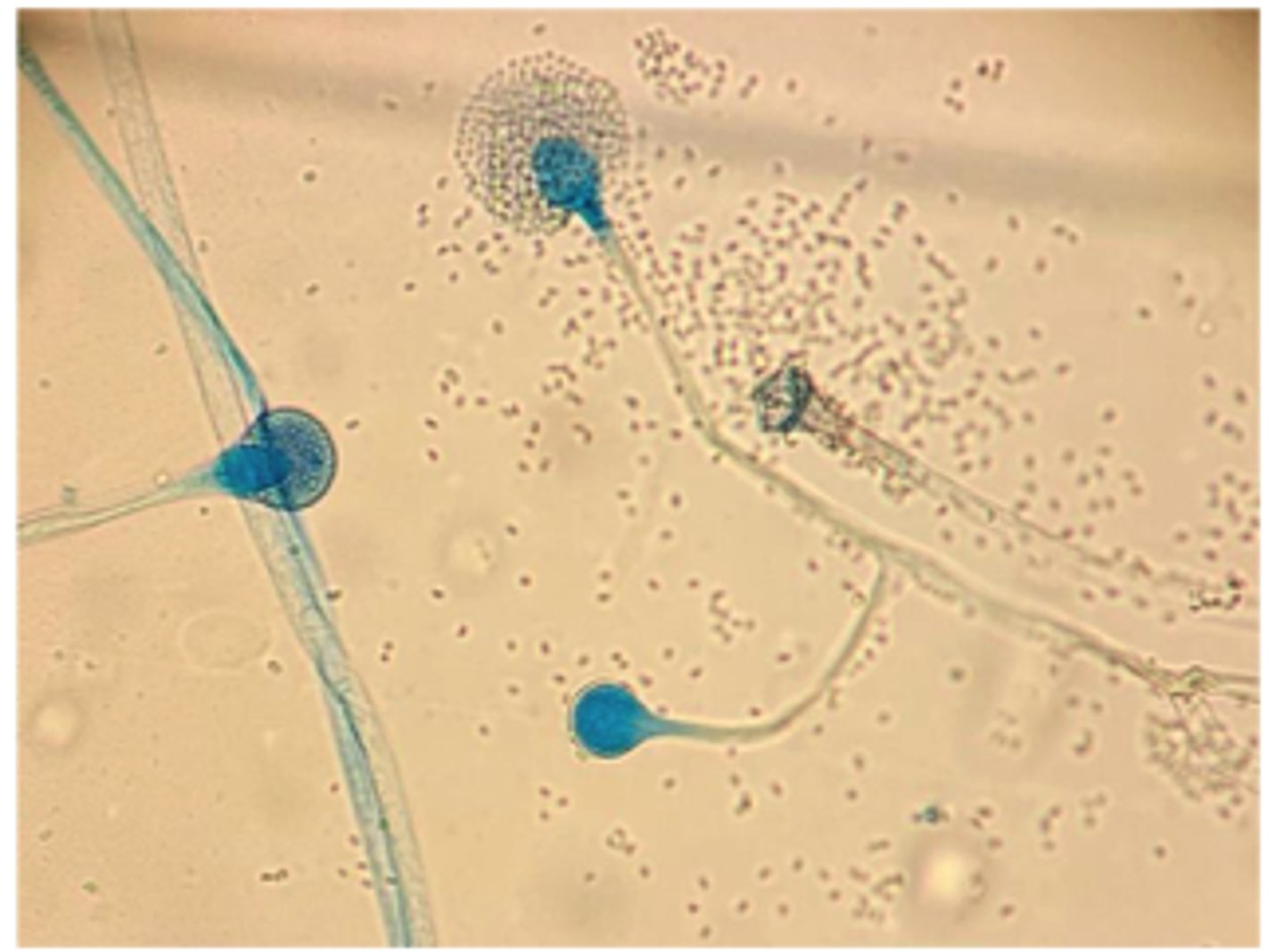
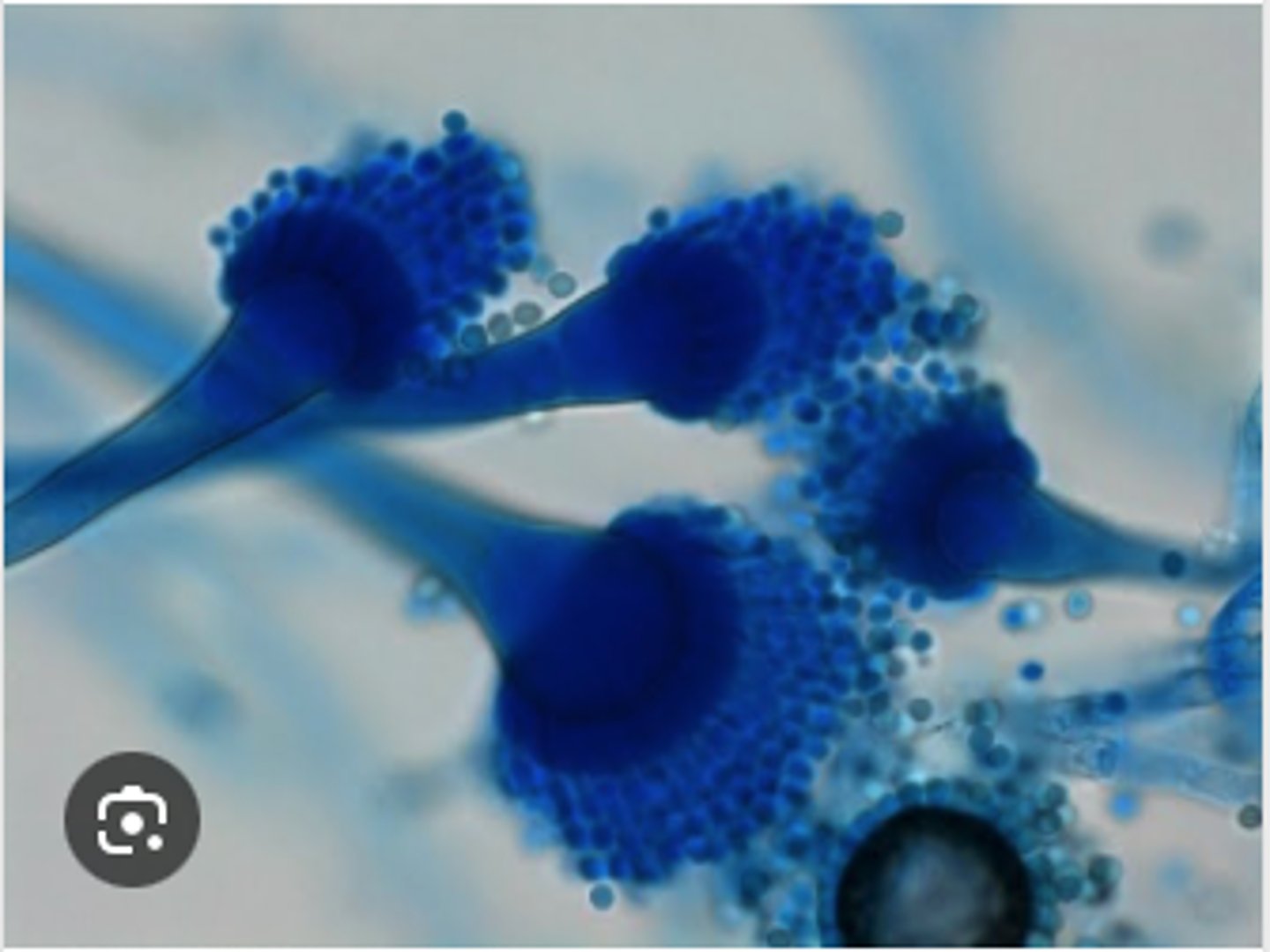
A. fumigatus.
During winter months, several cows abort in one herd. The farmer recently opened a moldy silage bale. Placental histopathology shows septate hyphae with parallel walls and dichotomous 45° branching, consistent with _____________________
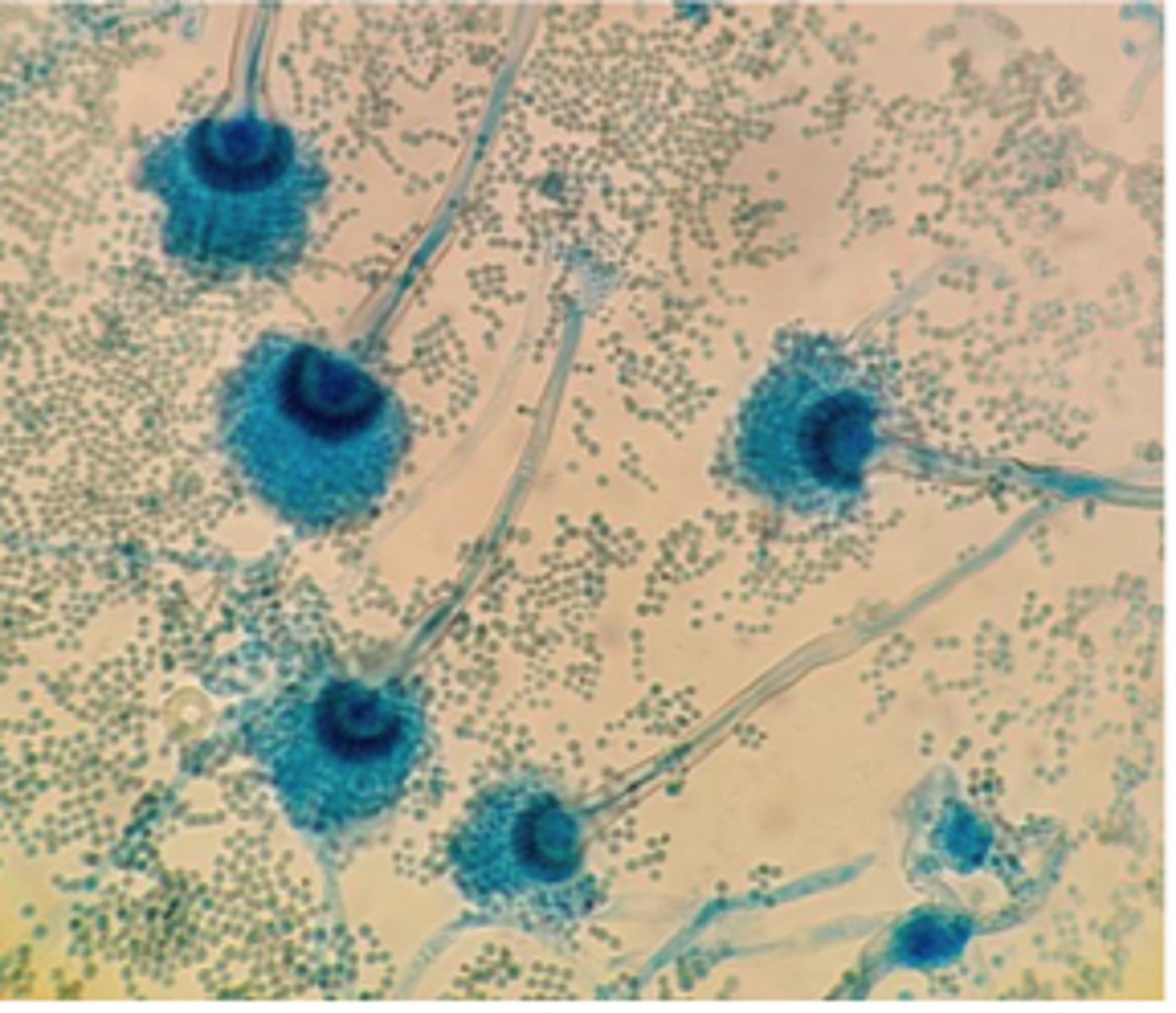
Aspergillosis fumigatus.
A 4-year-old German Shepherd presents with chronic unilateral nasal discharge and sneezing. Rhinoscopy reveals fungal plaques. Culture grows blue-green Aspergillus colonies, and a tape mount shows conidiophores with vesicles and phialides producing chains of conidia.
Dermatophytosis (Microsporum. canis).
A young cat fosterer develops skin lesions after handling a new stray kitten. The kitten has patchy alopecia. Skin scrapings show bright pink PAS-positive ectothrix arthroconidia surrounding hair shafts.
Ddx?
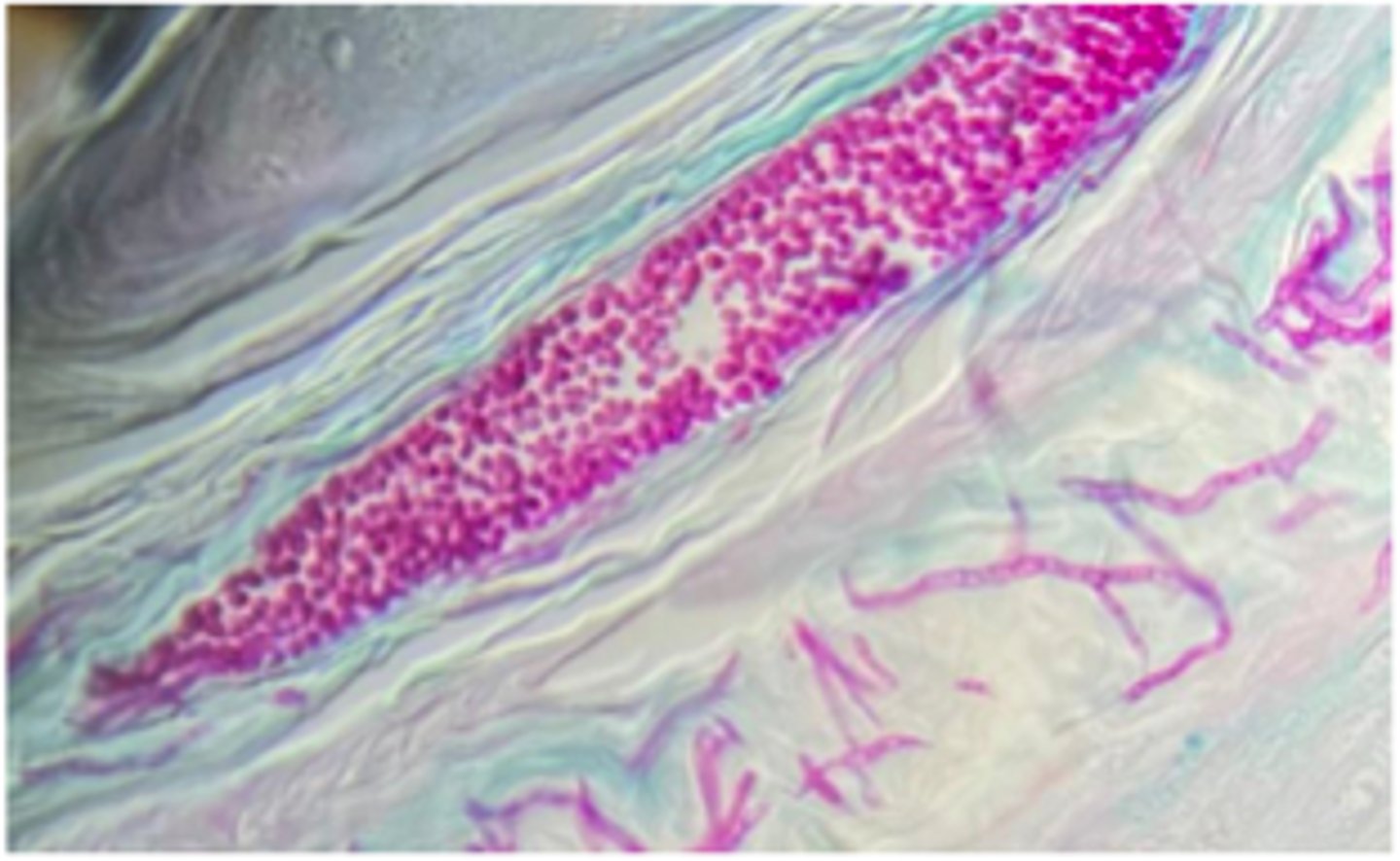
Trichophyton verrucosum.
Photomicrograph of a 10% KOH wet mount of an infected hair from a case of ringworm in a cow.
The most likely dermatophyte in cattle is ____________
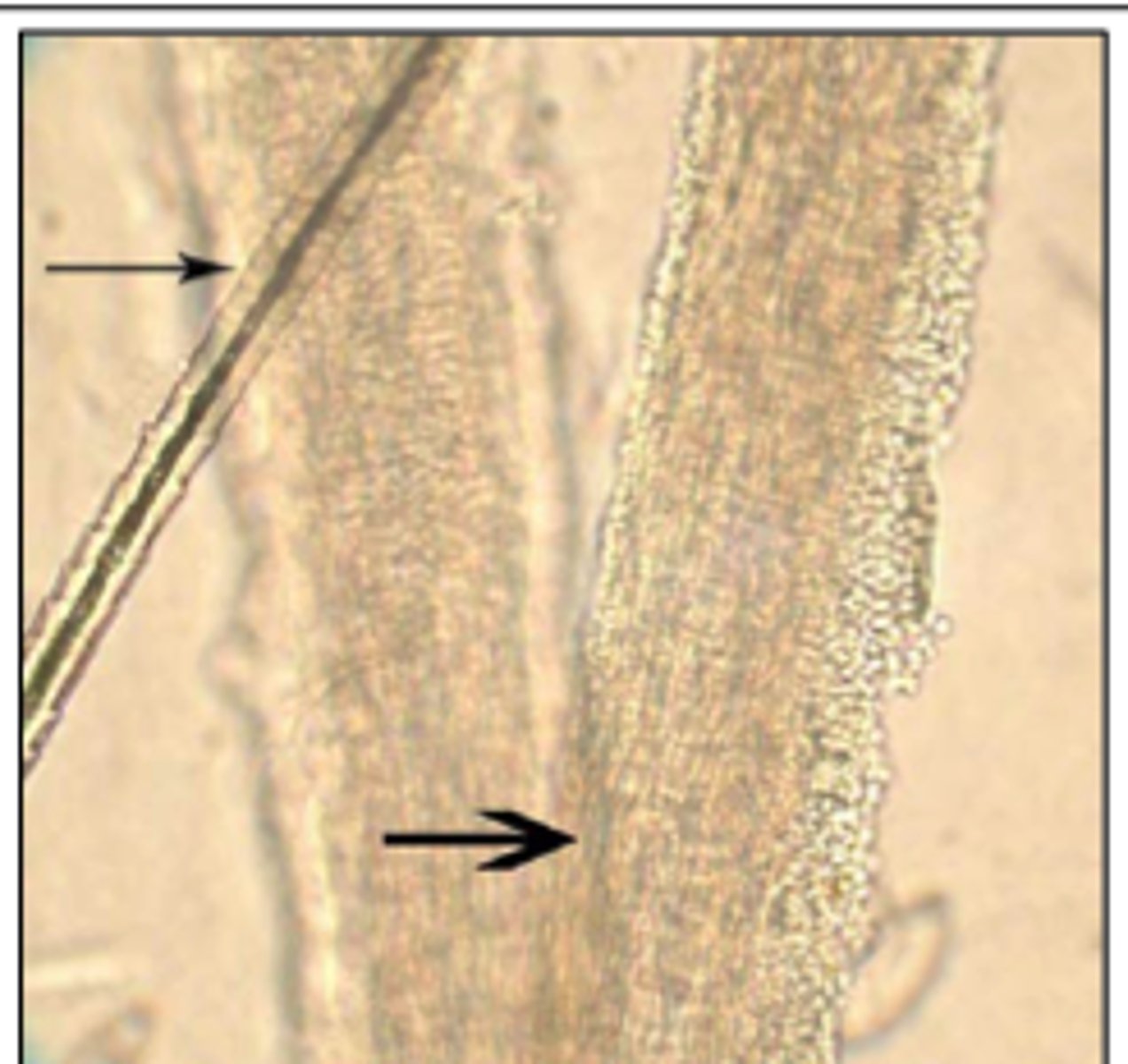
Microsporum canis
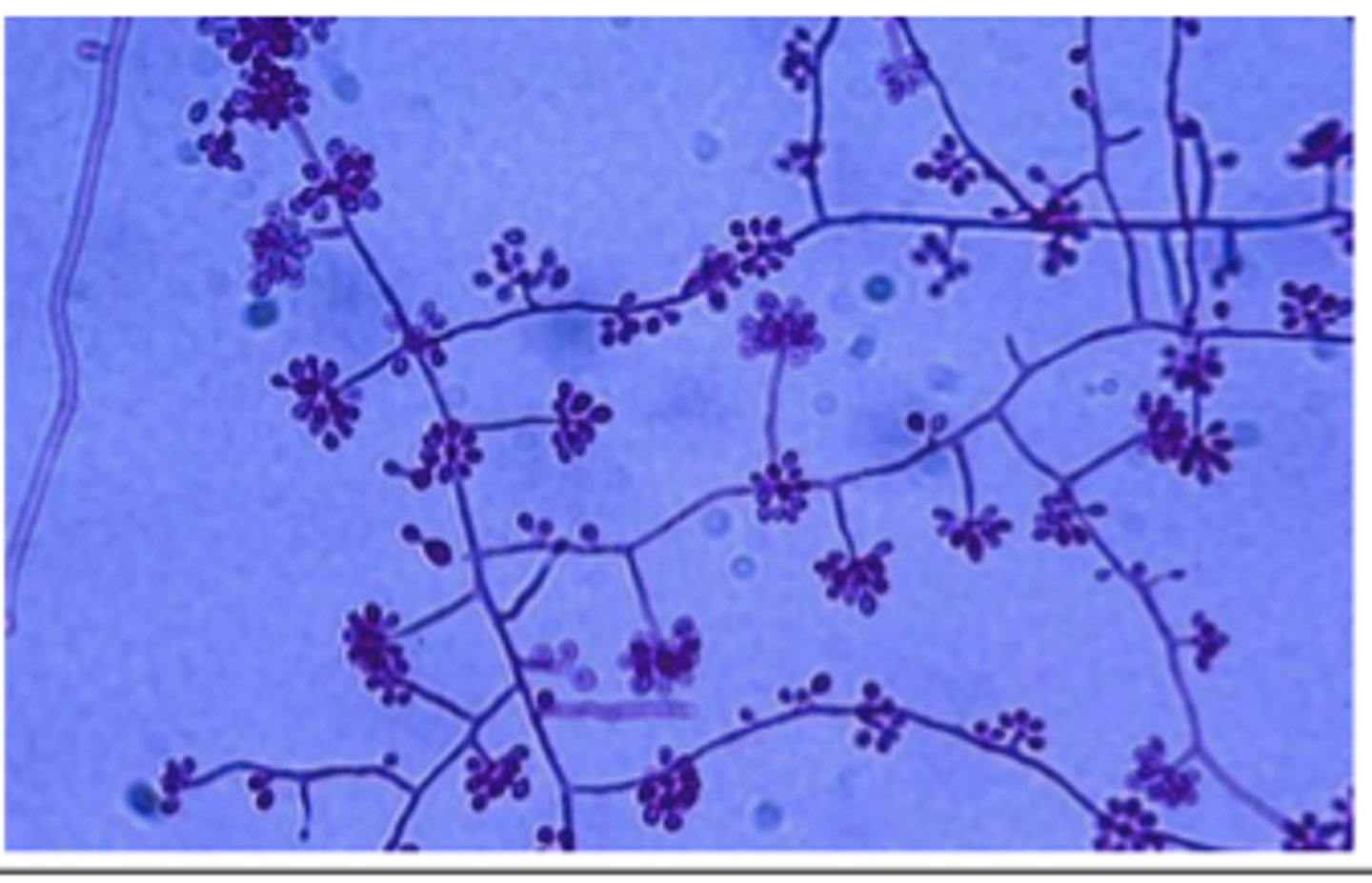
LPCB-stained slide mount of _________ culture showing macroconidia.
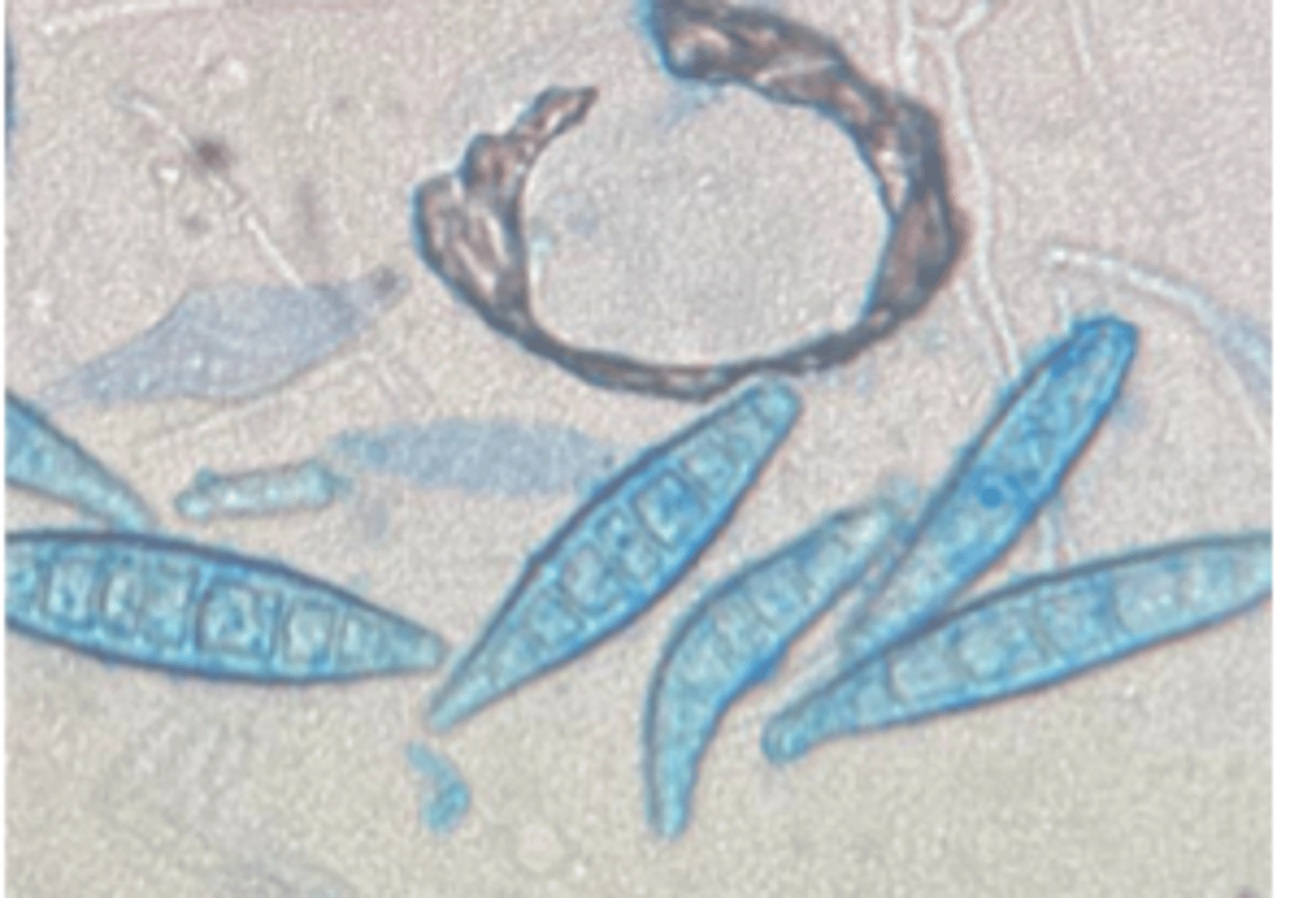
Candida albicans
A dog with chronic skin infection is sampled. Culture on BA yields cream-colored shiny colonies with a yeast odor. Gram stain shows budding yeast with occasional pseudohyphae.
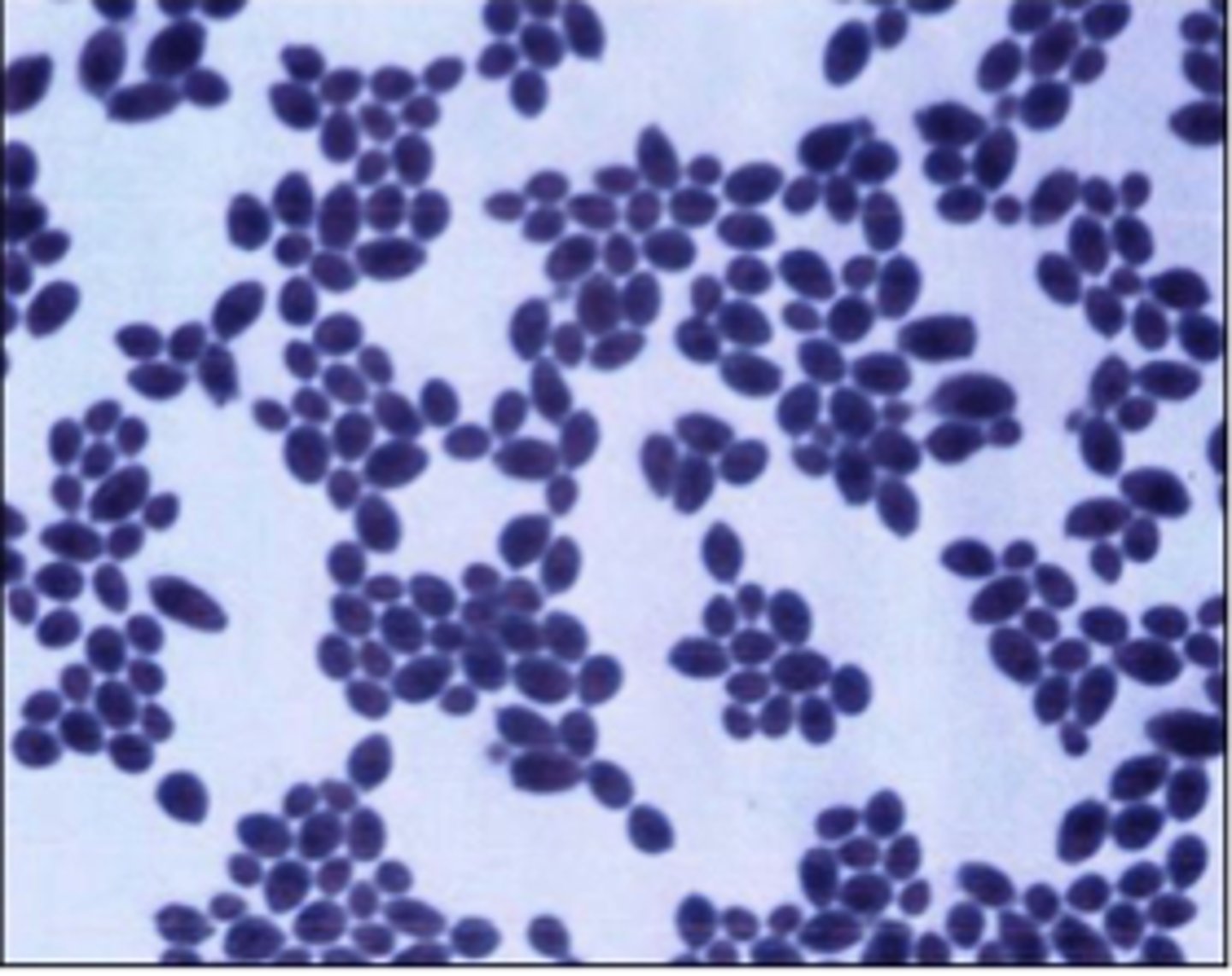
Malassezia pachydermatis
A Basset Hound presents with chronic smelly otitis
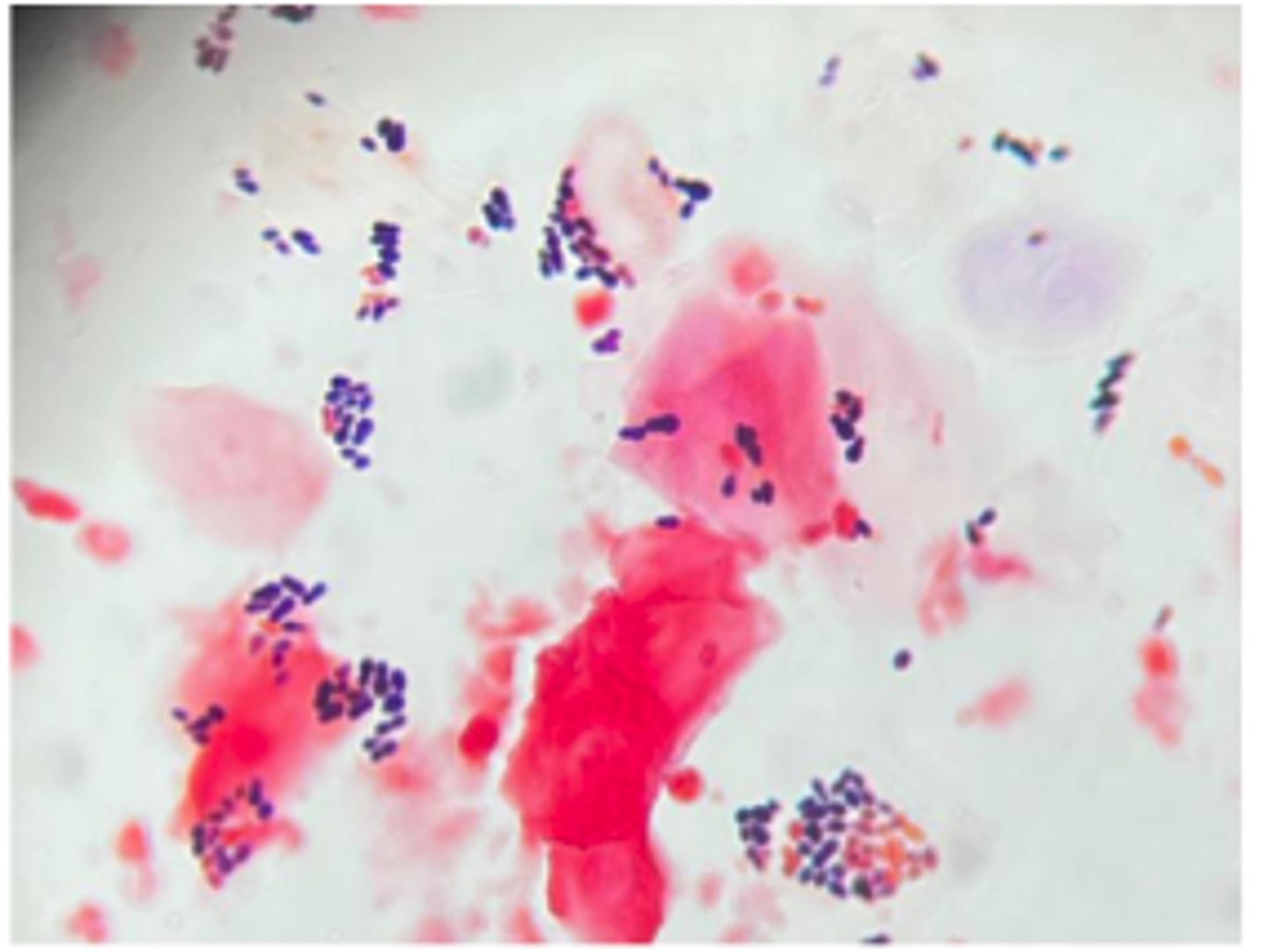
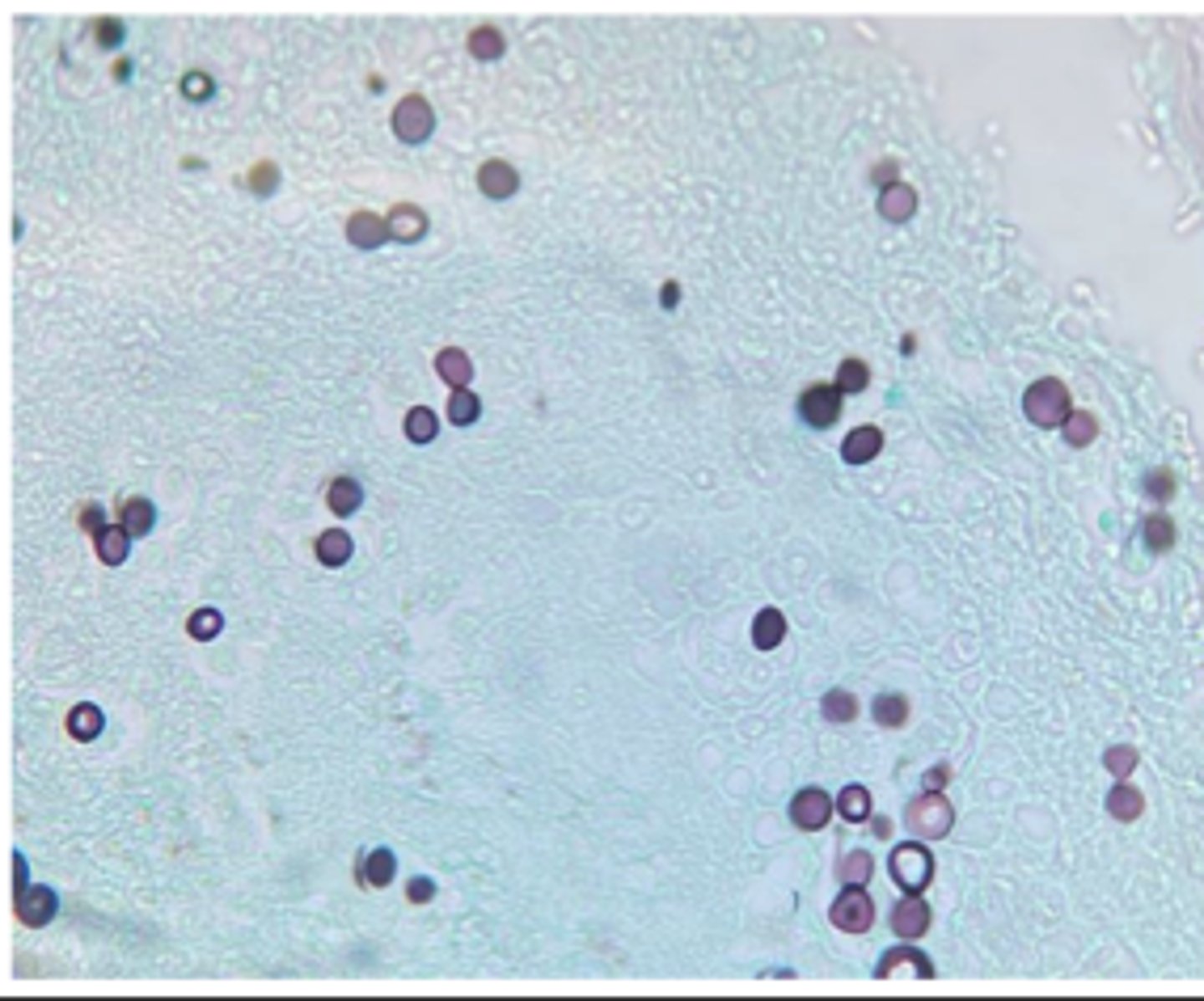
Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gatii
Thick capsule
A cat presents with chronic nasal discharge, polyp-like mass, and weight loss.
India ink stain
Ddx: and what feature of this yeast allows for repelling the ink ?
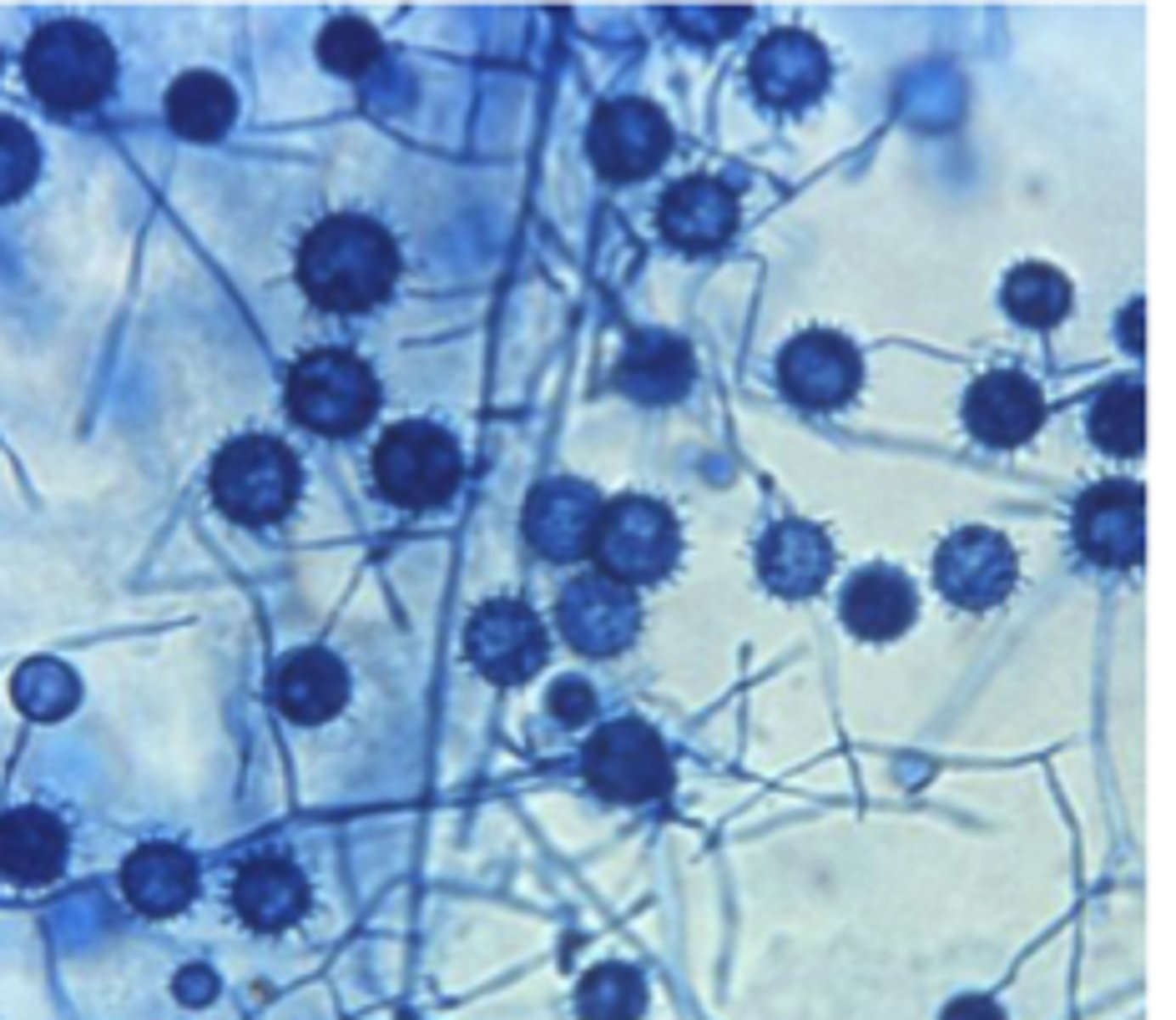
Histoplasma capsulatum
A cat presents with weight loss, diarrhea, and anemia. Rectal scrape cytology shows numerous intracellular 2–4 µm yeast with narrow-based budding.Culture at 25°C shows septate hyphae with tuberculate macroconidia.
Photomicrographs of LPCB-stained _________________ prepared from colonies grown at 200C and
350C.
Blastomyces dermatitidis
A dog with cough and draining skin lesions undergoes radiographs showing nodular lung disease. Lung aspirates show large (8–15 µm) thick-walled yeast with broad-based budding.
Coccidioides immitis
A dog with recent travel to Arizona (southern us) develops chronic cough and lameness. Lung biopsy reveals large spherules (20–200 µm) filled with endospores.

Sporothrix schenckii
A cat presents with ulcerated nodules along lymphatic tracts on the forelimb. Cytology reveals cigar-shaped yeast. Culture at 25°C produces fuzzy mold, while 35°C yields yeast-like colonies.Tape prep from mold shows flowerette arrangements of pyriform conidia.
Define PCR
PCR is a technique used for the rapid amplification of billions of copies of a specific region of
DNA
Denaturation, annealing, Extension
What are the 3 cycles of PCR
16S rRNA gene
What is the universal gene used for bacteria identification
See antimicrobial susceptibility testing
See antimicrobial susceptibility testing