Physics waves
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
wave motion
the transfer of energy from one point of the medium to another point of the medium without actual transport of matter between two points
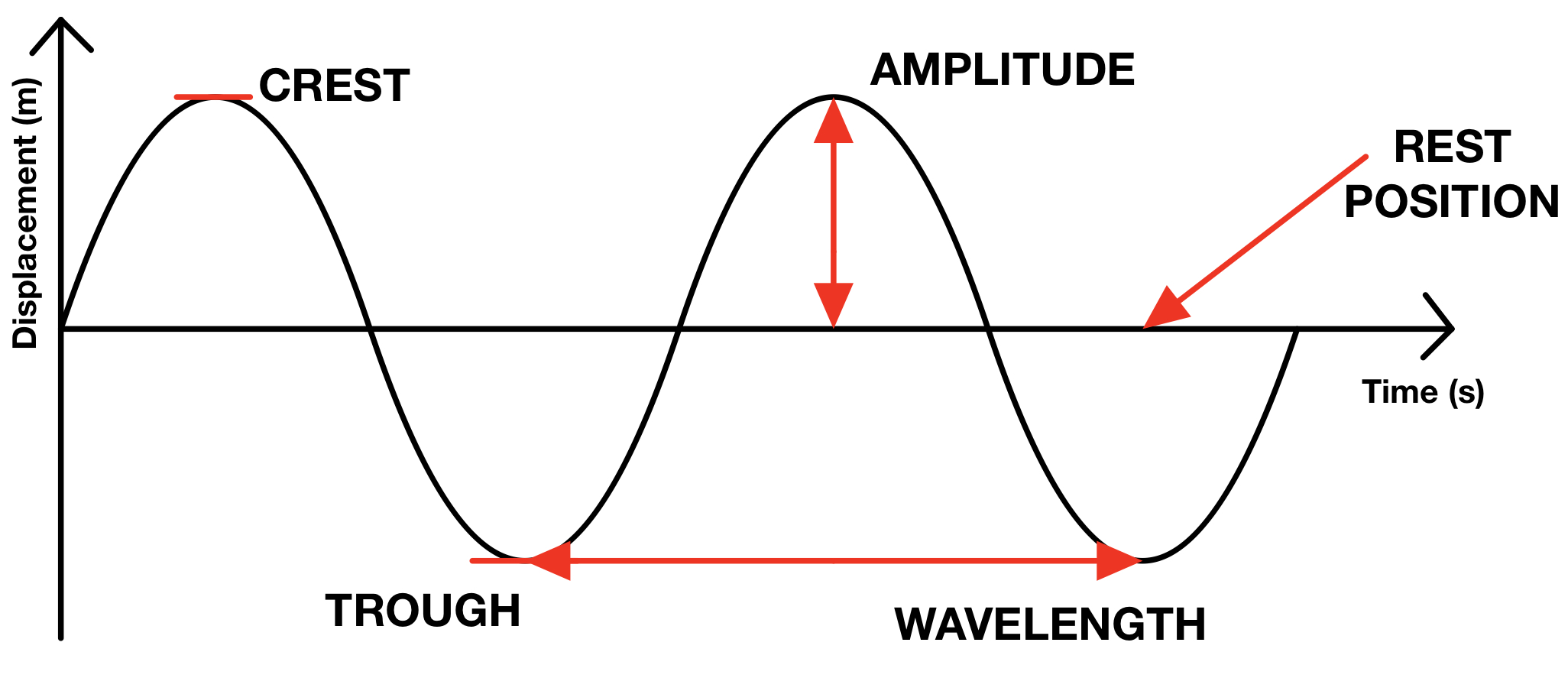
wavefront
the front of the wave, or the same point on each wave. Tends to be the peak or the crest. The distance between neighbouring wavefronts is equal to one wavelength.
frequency
the number of waves that pass a certain point each second. The unit of frequency is the hertz (Hz).
wavelength
the distance between a point on one wave and the same point on the next wave
amplitude
the maximum displacement of a point on a wave from its rest position
transverse
The direction of vibration is at right angles to the direction of travel and energy transfer. Eg light and any other electromagnetic wave, water waves and earthquake s-waves
longitudinal
The direction of vibration is parallel to the direction of wave travel and energy transfer. Eg sound waves, earthquake p-waves
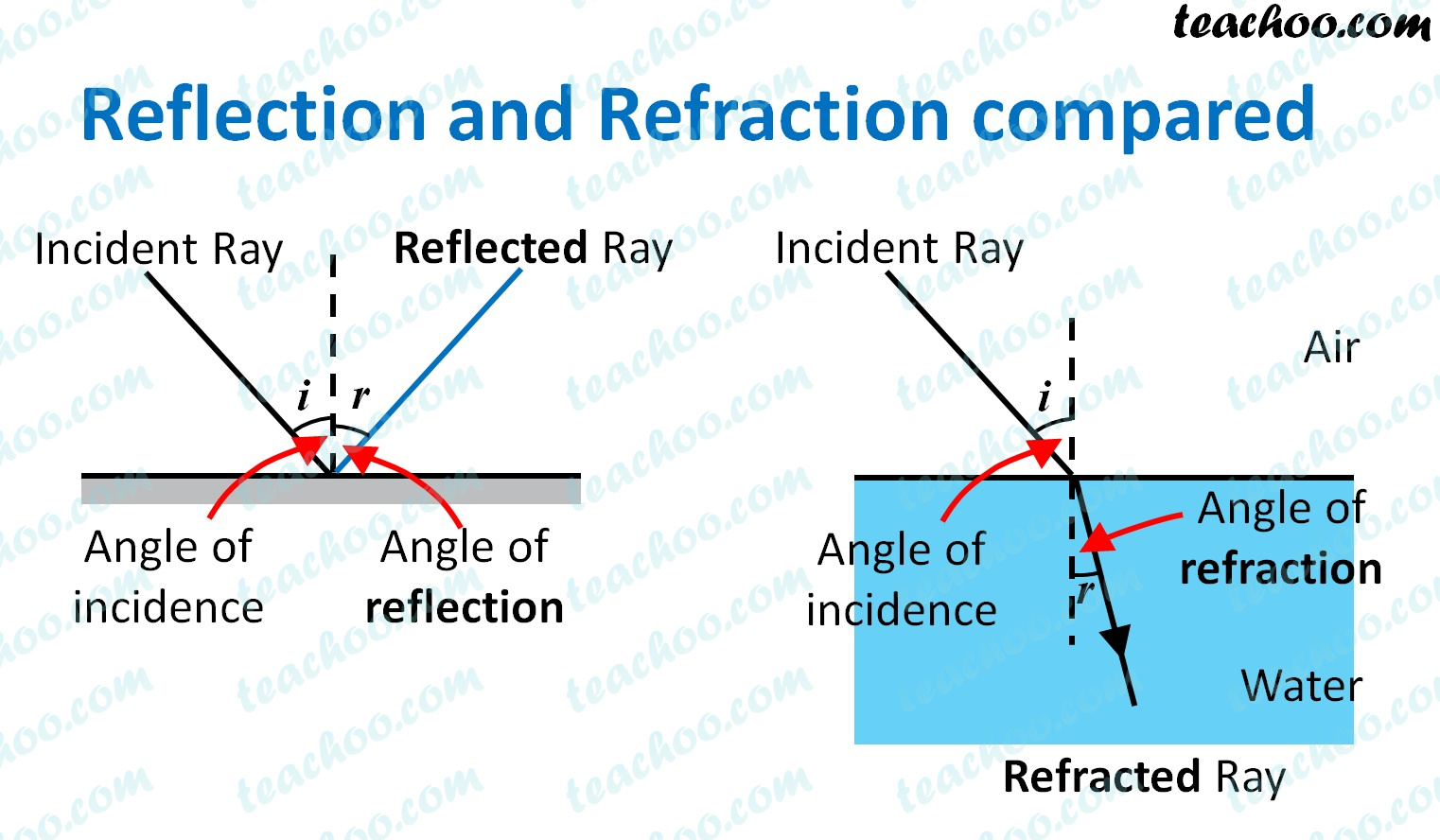
reflection
this involves a change in the direction of propagation of a wave when it travels back from a barrier or from the boundary between two different media.
Reflection occurs when a wave encounters a barrier or a boundary between different media, causing it to change direction and travel back into the original medium.
refraction
the change in direction of a wave at a boundary between two mediums due to a difference in wave speed between the two media.
diffraction
the spreading out of waves when they pass through a gap or around a barrier
angle of incidence
The angle of incidence is measured between the incoming light ray (the incident ray) and the normal.
normal
The normal is an imaginary line at 90° to the surface and is drawn as a dotted line.
angle of reflection
The angle of reflection is measured between the outgoing light ray (the reflected ray) and the normal.
angle of refraction
The angle of refraction is measured between the light ray in the second medium (the refracted ray) and the normal.
total internal reflection
When waves travel from a more dense medium (slower wave speed) to a less dense medium (faster wave speed) both reflection and refraction occur at the boundary.
At angles greater than a certain angle of incidence, called the critical angle, no refraction occurs. This means that only the reflected ray is produced at the boundary.
This reflected ray stays inside the first medium, with no refracted ray able to exit the medium. This process is called total internal reflection
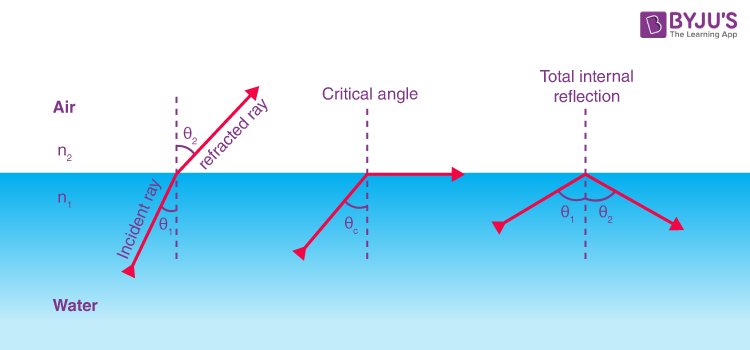
critical angle
The critical angle is the angle of incidence at which the angle of refraction is 90° and above which all light is totally internally reflected, when entering a less dense medium.
refractive index
Refractive index, n, is the ratio of the speeds of a wave in two different regions
principal focus
the point on the principal axis through which rays of light parallel to the principal axis converge after passing through the lens. This is also called the focal point.
focal length
the distance between the centre of a lens and its principle focus.
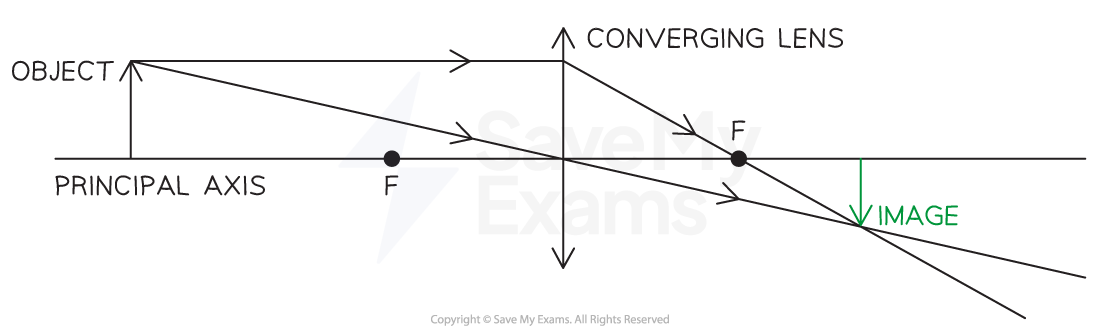
real image
A real image is formed when the rays pass through the image. This also means that a real image may be projected onto a distant screen.
virtual image
A virtual image is formed when `al image may be produced include reflections from a plane mirror and light passing through a converging lens with an object-lens distance lesser than the focal length.
upright
this is a property of an image. In an upright image the top of the image is the same way up as the top of the object.
inverted
In an inverted image the top of the image is the opposite way up to the object (i.e. up is down and vice versa)
enlarged
An enlarged image has a larger size than the size of the original object.
diminished
A diminished image is smaller than the size of the original object.
Compression
In a compression the particles in the medium are closest together. This is a region of high pressure in a sound wave. The distance between neighbouring compressions is equal to one wavelength.
Rarefaction
In a rarefaction the particles in the medium are furthest apart. This is a region of low pressure in a sound wave. The distance between neighbouring rarefactions is equal to one wavelength.
Pitch
The pitch of a sound depends on its frequency. A high pitch corresponds to a high frequency sound wave.
Loudness
The loudness of a sound depends on its amplitude. The higher the amplitude the louder the sound.
Echo
A reflected sound wave is called an echo.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with a frequency higher than 20 kHz
Wave speed equation
v = f λ.
v = speed
v = 3.0 × 108 m/s
f = frequency Hz
λ = wavelength m
Reflection law
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
i = r
Refractive Index (in terms of angles)
n= sin i/ sin r
n = refractive index (no units)
i = angle of incidence °
r = angle of refraction °
Refractive Index (in terms of speeds)
n = refractive index (no units)
c = speed of light in air or vacuum
= 3.0 × 108 m/s
vm = speed of light in the medium
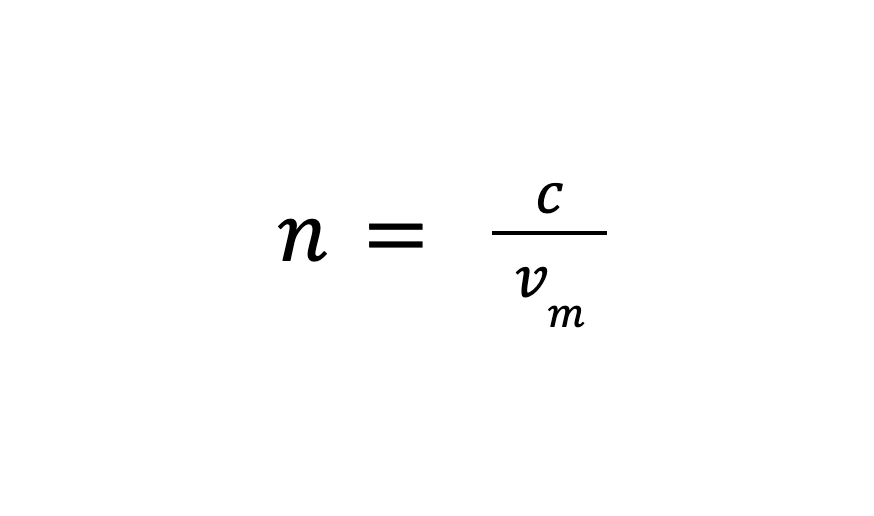
Distance (by echo method)
distance =speed of sound × time taken for echo/2
distance = m
speed of sound = m/s
time taken = s