current electricity
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
def electricity and electric current
The type of energy due to the flow of electric charges is called as electricity
the flow of charge through a conductor is called as electric current

direction of current

def EMF
Electromotive force of a source can be defined as the work done by the source in moving a unit positive charge from lower potential to the higher potential
EMF is maximum potential unit of a circuit
E=W/Q
Def OHM’S Law

def resistance
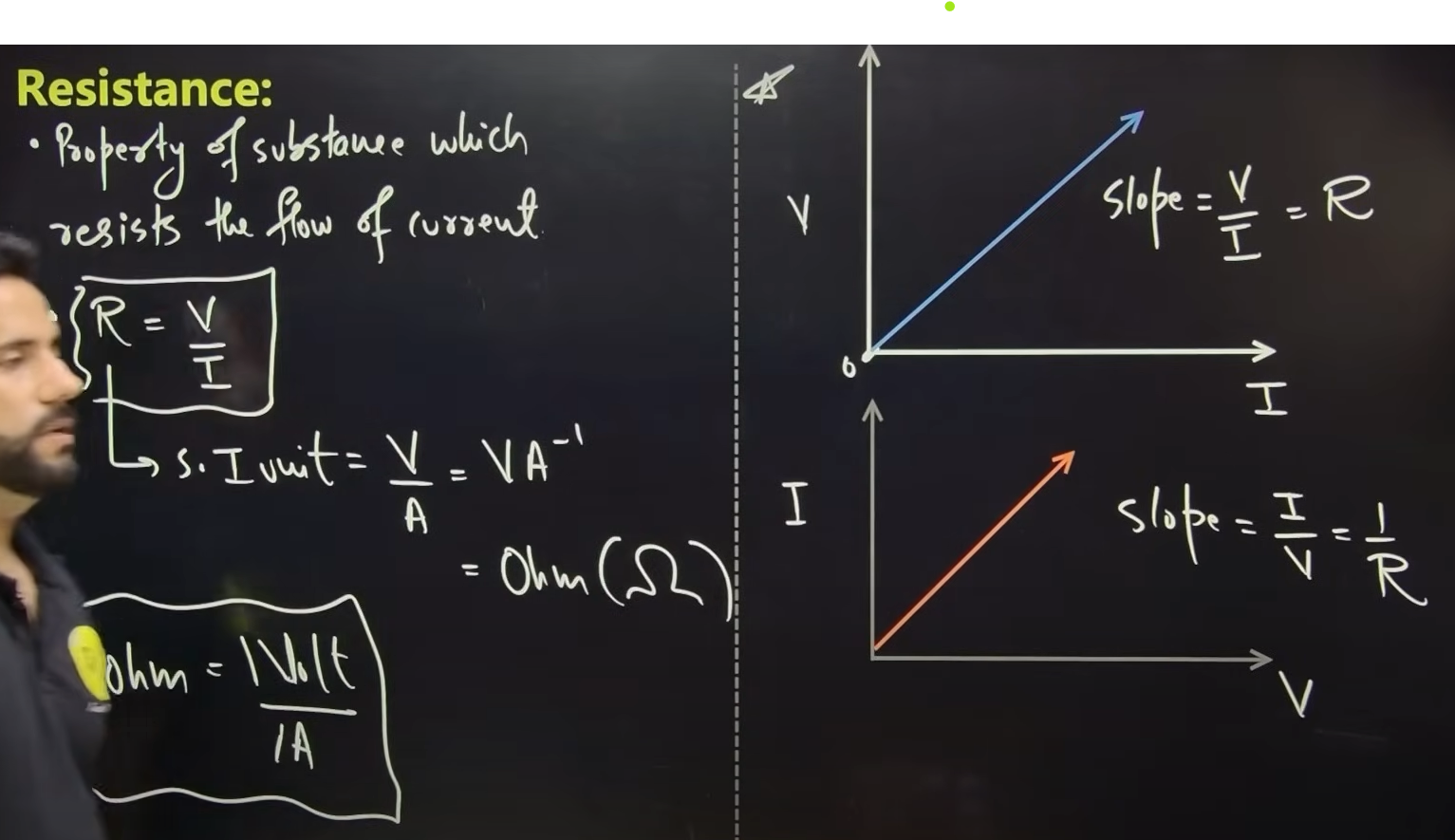
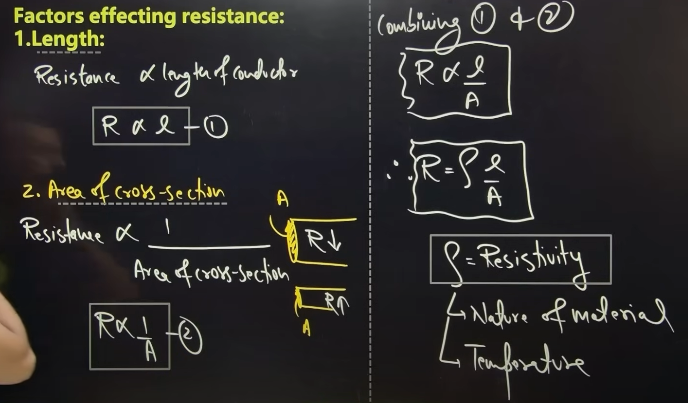
what are the factors affecting resistance
TEMPERATURE directly propotional
SI unit ohm for resistivity it is ohm metre
Classification of materials in terms of resistivity

temperature dependance of resistivity for conductors

def current density and SI unit
current density is the amount of current flowing per unit cross sectional area

current density when area not in direction to current

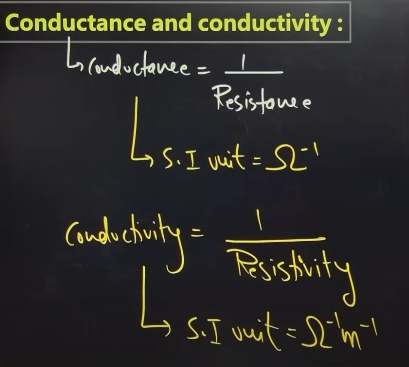
Conductance and conductivity
Conductance- inverse of resistance
conductivity- inverse of resistivity
mechanism of current flow in a conductor: DRIFT VELOCITY AND RELAXATION TIME
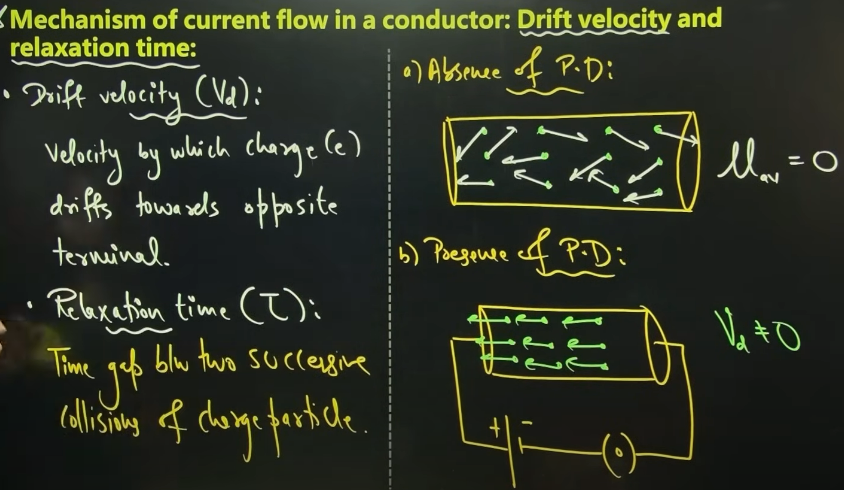
Drift velocity derivation
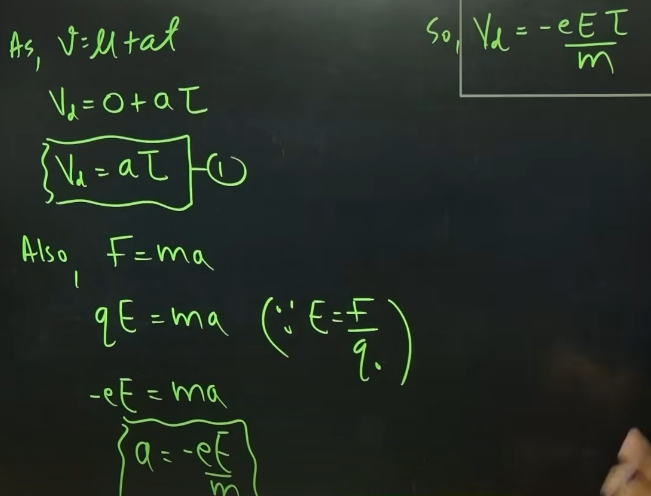
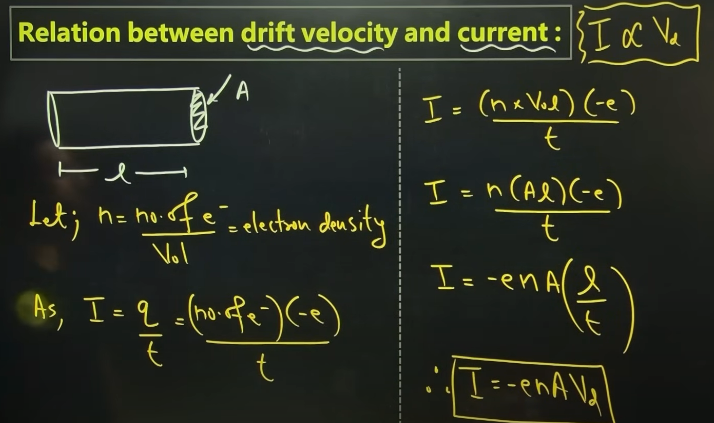
relation btw drift velocity and current
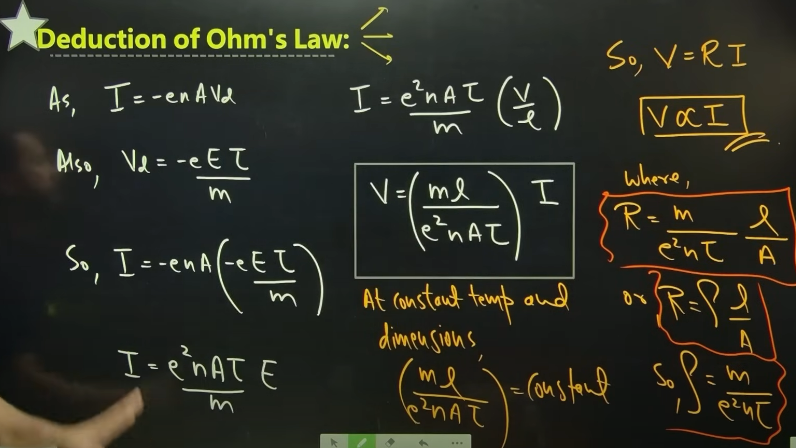
deduction of OHM’S law (V.IMP)
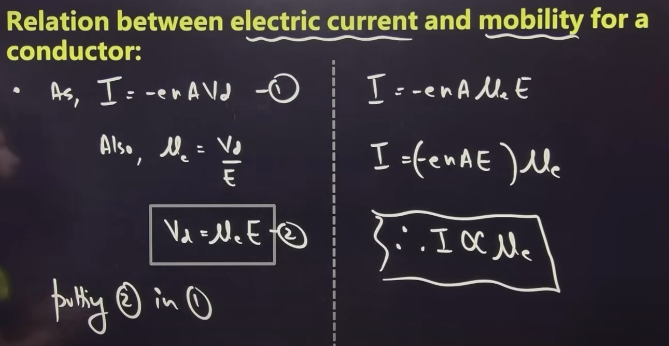
Mobility of charge carriers

relation between electric current and mobility for a conductor
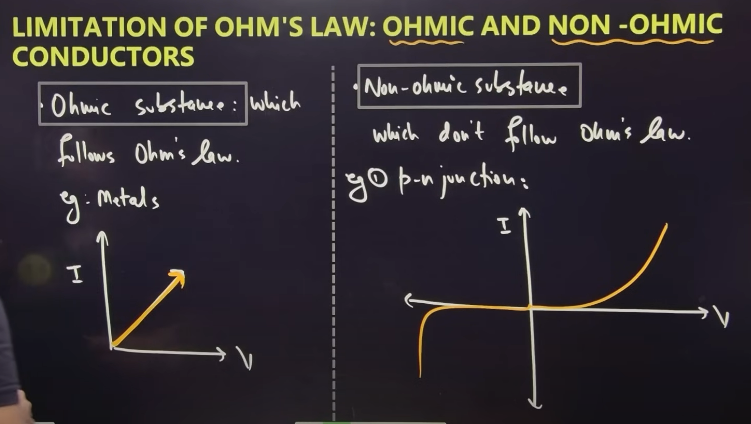
types of conductors OHM’s law holds true and not
Superconductivity

Meissener effect
TC-- Critical temp

Resistance in series

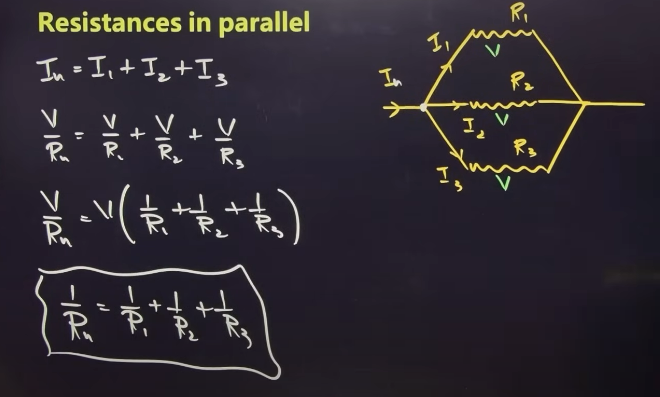
Resistance in parallel
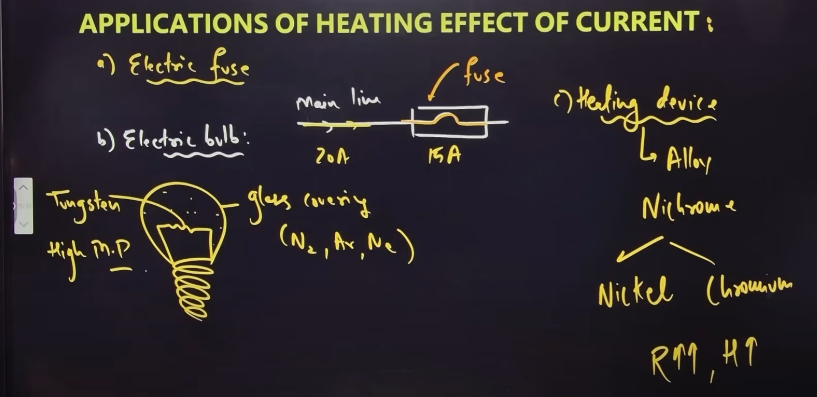
Heating effect of current

Applications of heating of current
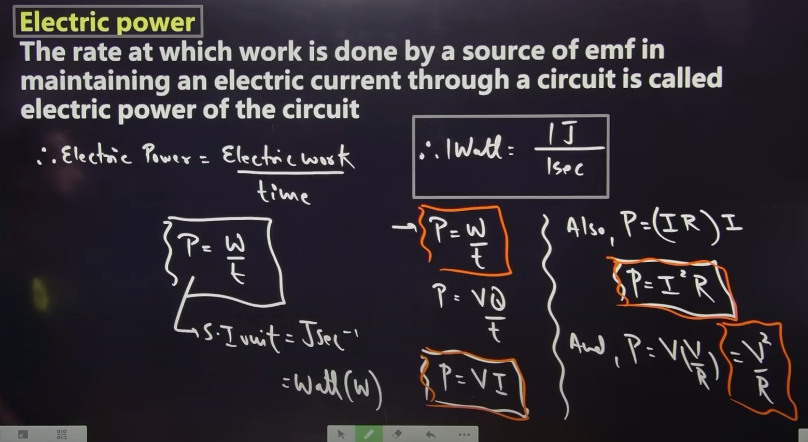
Electric power
proof of heating effect of current
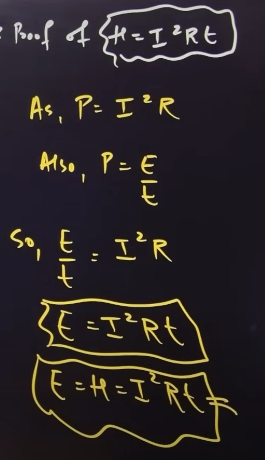
commercal unit of electric energy

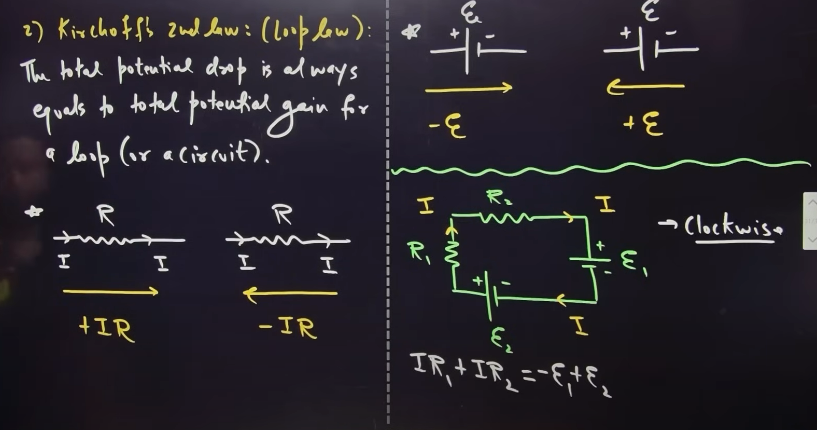
Kirchhoff’s 1st law
based on law of conservation of charge

Kirchhoff’s 2nd law
based on law of conservation of energy
Wheatstone bridge (imp derivation)
inbetween the current does not flow because both the junctions have the same potential
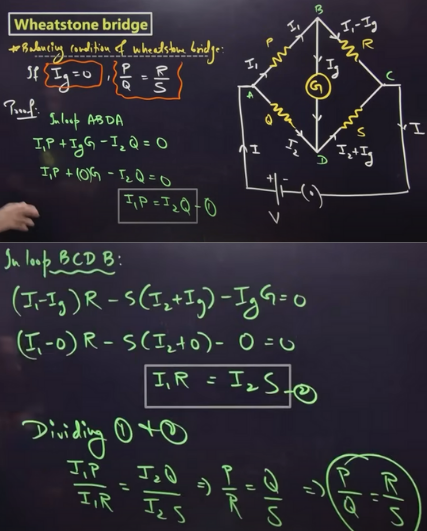
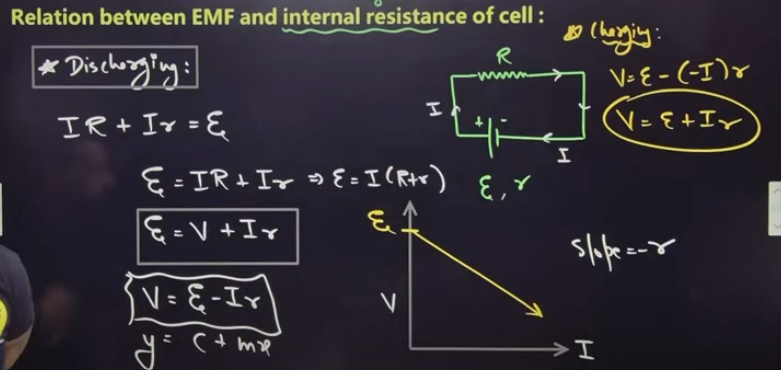
relation between EMF and internal resistance of a cell (imp)
cell in series
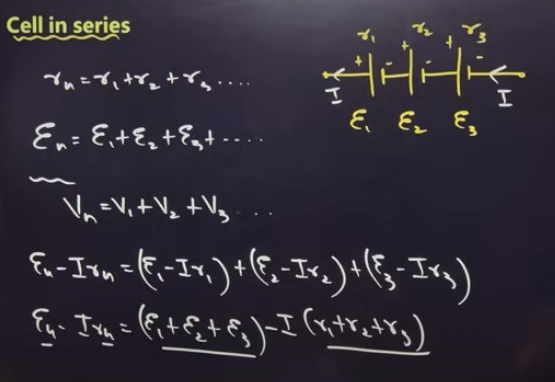
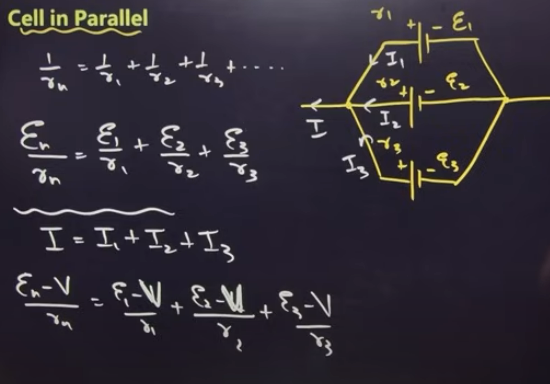
cell in parallel
define temperature coefficient of resistance of metal
it is the fractional change in resistance of a metal corresponding to a temperature change of 1degree
the ratio of current density and electric field is called
conductivity