7.7 - nutritional requirements of athletes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Why is nutrition crucial for athletes
to provide the energy needed for physical activity during training, competition, and recovery
plays a key role in optimizing sports performance
What are the key components of appropriate nutrition for athletes
Athletes need to consume appropriate quantities of:
carbohydrates
fats
proteins
vitamins
minerals
water
fibre
What factors are important when it comes to nutrition for athletes
The types of foods eaten, the quantity consumed
the timing of consumption
Why should athletes have hydration and nutrition plans
Athletes should have nutrition and hydration plans for before (pre), during, and after (post) training and competition
to optimize performance and recover
Why is optimal ingestion of carbohydrates essential for performance
they are the most preferred and readily available source of energy to fuel working muscles
What are the functions of carbohydrates in the human body
Major energy fuel source for physical activities
Regulate metabolism of fat and protein
Provide energy for nervous system functioning
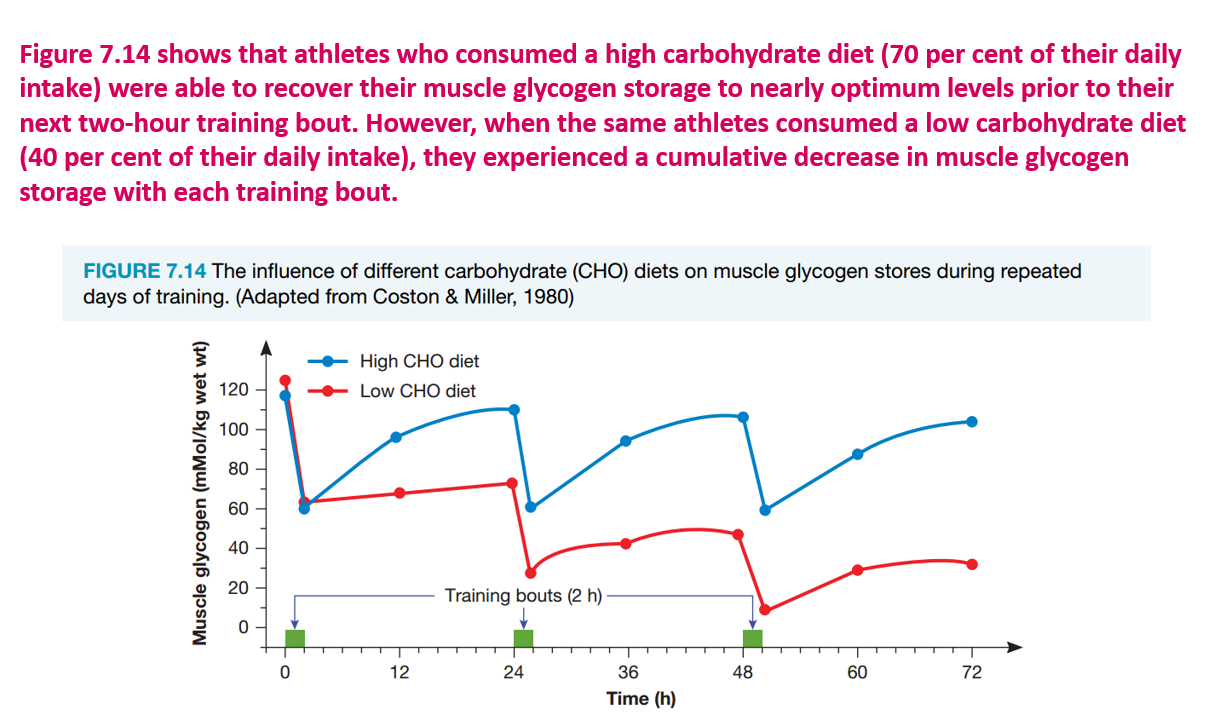
How can carbohydrates be classified
simple carbohydrates (sugars)
complex carbohydrates (starches)
What are simple carbohydrates, and how are they metabolized
metabolized quickly by the digestive system, providing an immediate release of energy
Examples include watermelon, jelly beans, sports drinks, and carbohydrate gels
What are complex carbohydrates, and how are they metabolized
metabolized slowly by the digestive system, providing a more gradual, sustained release of energy
Examples include pasta, wholegrain rice, yoghurt, and porridge
Why are pre-exercise meals important for athletes in longer duration events
provide an opportunity for athletes to increase fuel storage
carbohydrate loading maximizes muscle glycogen stores before endurance events
What is carbohydrate loading, and when should it be done
a nutritional strategy to maximize muscle glycogen stores before endurance events
particularly for events lasting longer than 90 minutes
Why should carbohydrates be consumed during exercise
enhances endurance and performance by providing an immediate energy source through rapid digestion and absorption
What is an example of a carbohydrate to consume during exercise
Sports gels, which are a highly concentrated source of carbohydrates with a honey- or syrup-like consistency, are often consumed during exercise
What should post-exercise meals consist of, and why
carbohydrates to promote muscle glycogen resynthesis
Examples include a banana or a peanut butter sandwich
What is the purpose of carbohydrate intake before training or competition
optimize muscle and liver glycogen stores, particularly for endurance events lasting 90 minutes or longer, where glycogen depletion can be a major cause of fatigue.
Carbohydrate loading is recommended for such events
What type of carbohydrates should athletes consume during training or competition
simple carbohydrates that are digested and absorbed quickly to maintain blood glucose levels as an immediate energy source.
This can also be beneficial for events as short as 30 minutes
What is the purpose of carbohydrate intake after training or competition
replenish energy stores to optimize recovery in preparation for the next session.
This should occur within the first 30-60 minutes post-exercise when the body is most receptive to converting glucose to glycogen
What is the recommended quantity of carbohydrates for athletes before training or competition
A daily intake of 7-10 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body mass for most athletes, with up to 10-12 grams for ultra-endurance events lasting 6 hours or longer
How many grams of carbohydrates should athletes consume per hour during training or competition
Athletes should consume 30-60 grams of carbohydrates per hour for events lasting 1 hour or longer, with practice during training to ensure palatability and gastric comfort
What is the recommended carbohydrate intake after training or competition
Athletes should consume 1-1.5 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body mass post-exercise
Why does protein gain more attention from athletes than other nutrients
protein is vital for muscle growth and repair
especially important for athletes participating in endurance and muscle-strengthening exercises
how do endurance and muscle-strengthening exercises impact protein needs
stimulate muscle protein synthesis
making protein essential for recovery and growth in athletes engaging in these activities
What are the two main types of proteins, and what are their functions
structural proteins, which provide support and shape to cells and tissues,
regulatory proteins, which help in controlling body processes such as enzyme activity and muscle contraction
Does increasing protein intake throughout the day lead to greater lean-muscle gains for athletes
Research suggests that simply increasing protein intake does not necessarily lead to more lean-muscle tissue.
Instead, the timing of protein intake is crucial for maximizing muscle protein synthesis
How should protein intake be spread across the day to benefit muscle protein synthesis
consumed throughout the day to create multiple spikes in muscle protein synthesis
maintaining a balance between protein breakdown and rebuilding in the muscles
What happens to excess protein that is consumed by the body
cannot be stored and are broken down and excreted by the bod
Why is protein consumption important post-exercise
After intense exercise, muscle protein is broken down due to micro-traumas, creating a negative protein balance.
Consuming protein within an hour post-exercise promotes muscle gain and minimizes muscle breakdown by enhancing amino acid uptake and retention
Why are protein and carbohydrates considered excellent partners for post-exercise nutrition
When consumed together, protein and carbohydrates stimulate a greater release of insulin, which promotes the absorption of nutrients and accelerates the recovery of muscle glycogen levels
Why is consuming protein with carbohydrates important for endurance athletes
endurance athletes use a significant amount of glycogen stores during training and competition.
Consuming protein with carbohydrates helps replenish muscle glycogen and promotes muscle growth and repair
What are the two main benefits of consuming protein with carbohydrates post-exercise
It increases the absorption of carbohydrates, speeding up the replenishment of muscle glycogen stores.
It promotes faster muscle growth and repair.
Can you provide examples of good post-exercise snacks that include both protein and carbohydrates
Good examples include yoghurt, milk drinks, fruit smoothies, lean meat, or cheese sandwiches
Why should athletes eat carbohydrates and protein together
Consuming carbohydrates and protein together helps repair muscle micro-tears sustained during activity and enhances carbohydrate absorption for glycogen refueling, allowing the athlete to return to optimal levels more quickly.
The combination, such as in chocolate milk, leads to faster replenishment of muscle glycogen stores and promotes faster recovery